Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Atomic Structure IGCSE Revision Notes
Atomic Structure IGCSE Revision Notes
Uploaded by
DarkGamerMaazCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Atomic Structure IGCSE Revision Notes
Atomic Structure IGCSE Revision Notes
Uploaded by
DarkGamerMaazCopyright:
Available Formats
CIE IGCSE Chemistry
Revision Notes
IGCSE
Chemistry
CIE
Revision Notes
Atomic Structure
● All substances are made of tiny particles of matter called atoms which are the
building blocks of all matter
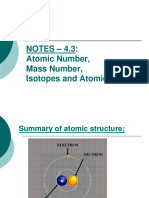
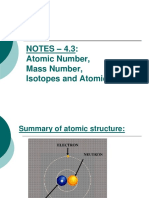
● Each atom is made of subatomic particles called protons, neutrons, and electrons
● The protons and neutrons are located at the centre of the atom, which is called the
nucleus
● The electrons move very fast around the nucleus in orbital paths called shells
● The mass of the electron is negligible, hence the mass of an atom is contained within
the nucleus where the protons and neutrons are located
Protons, Neutrons & Electrons
● The size of atoms is so tiny that we can't really compare their masses in conventional
units such as kilograms or grams, so a unit called the relative atomic mass is used
● One relative atomic mass unit is equal to 1/12th the mass of a carbon-12 atom.
● All other elements are measured relative to the mass of a carbon-12 atom, so relative
atomic mass has no units
● Hydrogen for example has a relative atomic mass of 1, meaning that 12 atoms of
hydrogen would have exactly the same mass as 1 atom of carbon
Defining Proton Number
● The atomic number (or proton number) is the number of protons in the nucleus of an
atom
● The symbol for atomic number is Z
● It is also the number of electrons present in a neutral atom and determines the
position of the element on the Periodic Table
Defining Mass Number
● The Nucleon number (or mass number) is the total number of protons and neutrons
in the nucleus of an atom
● The symbol for nucleon number is A
● The nucleon number minus the proton number gives you the number of neutrons of
an atom
● Note that protons and neutrons can collectively be called nucleons.
Deducing protons, neutrons & electrons
Finding the protons
● The atomic number of an atom and ion determines which element it is
● Therefore, all atoms and ions of the same element have the same number of protons
(atomic number) in the nucleus
● E.g. lithium has an atomic number of 3 (three protons) whereas beryllium has atomic
number of 4 (four protons)
● The number of protons equals the atomic (proton) number
● The number of protons of an unknown element can be calculated by using its mass
number and number of neutrons:
● Mass number = number of protons + number of neutrons
● Number of protons = mass number – number of neutrons
Finding the electrons
● An atom is neutral and therefore has the same number of protons and electrons
Finding the neutrons
● The mass and atomic numbers can be used to find the number of neutrons in ions
and atoms:
● Number of neutrons = mass number – number of protons
You might also like
- 1995 Drummond Maher Determination of PhosphorusDocument6 pages1995 Drummond Maher Determination of PhosphorusFederico LeonNo ratings yet
- 1C Atomic StructureDocument24 pages1C Atomic Structurejustme.azma.meNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure CRGDocument14 pagesAtomic Structure CRGCharlotte GoodeNo ratings yet
- Atoms, Isotopes, Ions, and Molecules: Key PointsDocument28 pagesAtoms, Isotopes, Ions, and Molecules: Key PointsCandyAnonymousNo ratings yet
- CIE Chemistry Chapter 2 - Atoms, Elements and CompoundsDocument38 pagesCIE Chemistry Chapter 2 - Atoms, Elements and CompoundsIt's futfutiNo ratings yet
- Atomic StructureDocument5 pagesAtomic StructureAyesha AhmedNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document27 pagesChapter 1Imperial PlayzNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Notes-1Document3 pagesChapter 2 Notes-1ARISHA REHMANNo ratings yet
- Chem ModuleDocument20 pagesChem Modulekeeno manzanoNo ratings yet
- Atomic StructureDocument11 pagesAtomic Structurevihaan.kharbandaNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Topical Past Papers Biology P4 C1 - C7Document1 pageIGCSE Topical Past Papers Biology P4 C1 - C7Muhammad AsgharNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure: Subatomic Particles and Descriptions of The AtomDocument16 pagesAtomic Structure: Subatomic Particles and Descriptions of The AtomShyam BudhwarNo ratings yet
- ChemistryDocument20 pagesChemistryrida ikramNo ratings yet
- ElementsDocument6 pagesElementsAbdullah SalmanNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure BDocument21 pagesAtomic Structure Babd rahmanNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure and Atomic Mass - NCUKDocument27 pagesAtomic Structure and Atomic Mass - NCUKphonepyaehtut2006No ratings yet
- Atomic Number and Atomic MassDocument9 pagesAtomic Number and Atomic MassAnonymous DKxeQVEevNo ratings yet
- 5th Grade CurriculumDocument12 pages5th Grade Curriculumapi-256256410No ratings yet
- Atomic Structure and Isotopes NotesDocument5 pagesAtomic Structure and Isotopes Notesyanny280906No ratings yet
- Atomic Structure & The Periodic TableDocument56 pagesAtomic Structure & The Periodic TableAnas DarwishNo ratings yet
- Inside Atoms, The Proton NumbersDocument3 pagesInside Atoms, The Proton NumbersFatafut ShoppingNo ratings yet
- Atomic Number, Mass Number, Atomic Mass and IsotopesDocument21 pagesAtomic Number, Mass Number, Atomic Mass and IsotopesKenny James CuberoNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure: Unit II-Part 3Document14 pagesAtomic Structure: Unit II-Part 3道友謙No ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Atomic StructureDocument12 pagesChapter 1 - Atomic StructureFelix LiandaNo ratings yet
- SSC Mts Ex: Studymaterialfor GenralawarenessDocument8 pagesSSC Mts Ex: Studymaterialfor GenralawarenessAmrit SinghNo ratings yet
- ISOTOPO BOM 2 C Atomic Number, Mass Number, Atomic Mass and Isotopes-1Document21 pagesISOTOPO BOM 2 C Atomic Number, Mass Number, Atomic Mass and Isotopes-1idalia helenaNo ratings yet
- Atoms & ElementsDocument14 pagesAtoms & ElementsMy Cambridge IGCSENo ratings yet
- Properties of MaterialsDocument9 pagesProperties of MaterialsSailas Khulumani TshabanguNo ratings yet
- 2.atoms, Elements & CompoundDocument6 pages2.atoms, Elements & CompoundhenryNo ratings yet
- 5th Grade CurriculumDocument12 pages5th Grade Curriculumapi-244991152No ratings yet
- Session 2-Description of An AtomDocument32 pagesSession 2-Description of An Atomvalerianphotunatus2002No ratings yet
- Chemistry Strand Notes 3Document1 pageChemistry Strand Notes 3Mazuba ChibbelaNo ratings yet
- IsotopesDocument15 pagesIsotopesapi-276003030No ratings yet
- Structure of The Atom and The Periodic TableDocument8 pagesStructure of The Atom and The Periodic TableClive NyabutiNo ratings yet
- Structure of Atoms and IonsDocument34 pagesStructure of Atoms and IonsChristineNo ratings yet
- Structure of Substance - Lesson - 2Document10 pagesStructure of Substance - Lesson - 2samsonNo ratings yet
- Module As Level ChemistryDocument407 pagesModule As Level ChemistryBank Yossy WoluslaweNo ratings yet
- Folio Physics Form 5Document3 pagesFolio Physics Form 5Siti Nur NabilahNo ratings yet
- 1.1. A Simple Model of The Atom, Symbols, Relative Atomic Mass, Electronic Charge and Isotopes PDFDocument4 pages1.1. A Simple Model of The Atom, Symbols, Relative Atomic Mass, Electronic Charge and Isotopes PDFUloko ChristopherNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure: Presented By: Syed ArhamDocument32 pagesAtomic Structure: Presented By: Syed ArhamSyed ArhamNo ratings yet
- Atomic Theory: A Modern Model of The AtomDocument8 pagesAtomic Theory: A Modern Model of The AtomSophia MartinezNo ratings yet
- Atomic History/Structure: Unit 3Document23 pagesAtomic History/Structure: Unit 3lancerfootballNo ratings yet
- Atomic StructureDocument19 pagesAtomic Structuregoh benNo ratings yet
- 1.3 Atomic Mass Atomic Number and Isotopes PDFDocument23 pages1.3 Atomic Mass Atomic Number and Isotopes PDFMARVIN DELA CRUZNo ratings yet
- A Level Chemistry Notes Physical ChemDocument47 pagesA Level Chemistry Notes Physical ChemSolomon MuwandiNo ratings yet
- Atomic Mass and NumberDocument15 pagesAtomic Mass and NumberKalaisan KalaichelvanNo ratings yet
- 001 Atomic StructureDocument33 pages001 Atomic Structurekays MNo ratings yet
- Atoms and Atomic Strucure NoteDocument2 pagesAtoms and Atomic Strucure NoteMy Cambridge IGCSENo ratings yet
- 1.physical ChemistryDocument411 pages1.physical ChemistryTendaiNo ratings yet
- Dalton's Atomic TheoryDocument19 pagesDalton's Atomic TheoryKatherine CampillosNo ratings yet
- Atomic IsotopesDocument16 pagesAtomic Isotopesbrenda.mboghoNo ratings yet
- NOTES - 4.3 Atomic Mass Isotopes 2017 SlideshowDocument16 pagesNOTES - 4.3 Atomic Mass Isotopes 2017 SlideshowFatma MohamedNo ratings yet
- NOTES - 4.3 - Atomic - Mass - Isotopes - 2017 - SlideshowDocument16 pagesNOTES - 4.3 - Atomic - Mass - Isotopes - 2017 - SlideshowJoseph MusabukaNo ratings yet
- 2 AtomsDocument22 pages2 Atomsmrcornis18No ratings yet
- Atomic Structure: Unit III-Part 1Document13 pagesAtomic Structure: Unit III-Part 1nidelgadoNo ratings yet
- Inside The AtomDocument13 pagesInside The AtomAnita VardhanNo ratings yet
- Atomic StructureDocument225 pagesAtomic StructuresitajanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Atomic Structure Snr1Document50 pagesChapter 5 Atomic Structure Snr1Abdul HaseebNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure - NOTESDocument9 pagesAtomic Structure - NOTESMarshell JonesNo ratings yet
- Nuclear Physics NotesDocument55 pagesNuclear Physics Notesmsukwa.cheyoNo ratings yet
- Concepts of Nuclear Medicine Volume I: Concepts of Nuclear Medicine, #1From EverandConcepts of Nuclear Medicine Volume I: Concepts of Nuclear Medicine, #1No ratings yet
- ISSA Technical Bulleyin TB-145Document2 pagesISSA Technical Bulleyin TB-145anjana100% (1)
- BASF Effka FA 4663 Msds İngDocument16 pagesBASF Effka FA 4663 Msds İngphysengNo ratings yet
- 9907X0071 - 2 Operating InstructionsDocument12 pages9907X0071 - 2 Operating InstructionsabelardoNo ratings yet
- 17 Carbonyls Notes1 PDFDocument21 pages17 Carbonyls Notes1 PDFMary Joy BejeranoNo ratings yet
- Clinical MicrosDocument30 pagesClinical MicrosRyan PedregosaNo ratings yet
- Fosroc Conplast SP472: Constructive SolutionsDocument2 pagesFosroc Conplast SP472: Constructive SolutionsVincent JavateNo ratings yet
- Ghoubali Et Al. 2017Document15 pagesGhoubali Et Al. 2017Francisco OppsNo ratings yet
- Energy Balance For A MultiDocument12 pagesEnergy Balance For A MultiAwoluyi TolaNo ratings yet
- Is17127 2019Document14 pagesIs17127 2019GaneshBuilder .BatalalabNo ratings yet
- Classic 5 LD - W - D Calculations For Sprayed-On Fireproofing From The SCHUNDLER COMPANYDocument2 pagesClassic 5 LD - W - D Calculations For Sprayed-On Fireproofing From The SCHUNDLER COMPANYSalman ShaikhNo ratings yet
- VTP-VTPF - Ols 97891918Document30 pagesVTP-VTPF - Ols 97891918Hitesh Gajera100% (1)
- MC20190539 AS Product Catalog Digital-6-7 PDFDocument2 pagesMC20190539 AS Product Catalog Digital-6-7 PDFMiguelNo ratings yet
- Acid Base WebquestDocument3 pagesAcid Base WebquestJocelyn PoorNo ratings yet
- 150123006-1501 Multi Sera CalibratorDocument4 pages150123006-1501 Multi Sera CalibratorOjie SarojieNo ratings yet
- Starch Fatty EsteresDocument6 pagesStarch Fatty EsteresRobertaSouzaNo ratings yet
- Research Proposal For The Proton BatteryDocument4 pagesResearch Proposal For The Proton BatteryStacey SkibaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 25: Lipid Metabolism: Multiple ChoiceDocument7 pagesChapter 25: Lipid Metabolism: Multiple ChoiceMaxinefgc Baculo100% (1)
- The Mechanisms of Alloxan-And Streptozotocin-Induced DiabetesDocument11 pagesThe Mechanisms of Alloxan-And Streptozotocin-Induced DiabetesOktaviani Fitria Susanti SusantiNo ratings yet
- Amber Lisi-Pom Ifu enDocument2 pagesAmber Lisi-Pom Ifu enAnas AbassiNo ratings yet
- Green Chem Week 8-9-10 Solvents Student 2023-10-23Document76 pagesGreen Chem Week 8-9-10 Solvents Student 2023-10-23Phương TrangNo ratings yet
- Data 1-Clinoptilolite-00-025-1349Document3 pagesData 1-Clinoptilolite-00-025-1349BUSTANUL RIZKY RIZKYNo ratings yet
- Gómez Et Al (2018) Physicochemical Evaluation of Low-Fat YoghurtDocument7 pagesGómez Et Al (2018) Physicochemical Evaluation of Low-Fat YoghurtTahir AliNo ratings yet
- Chapter 03-Wall and Cladding Systems-RSCDocument21 pagesChapter 03-Wall and Cladding Systems-RSCWylieNo ratings yet
- Transformation of Sentences (Part-4)Document4 pagesTransformation of Sentences (Part-4)Nishinath Chondro GainNo ratings yet
- Solvay CoaDocument2 pagesSolvay Coavidur 17No ratings yet
- 2-Eha PRCS1Document45 pages2-Eha PRCS1MARISSE LYN DORADONo ratings yet
- Tutorial 4Document4 pagesTutorial 4iviyyyhNo ratings yet
- Aluminum Anodization: 1.1 HistoryDocument12 pagesAluminum Anodization: 1.1 Historymktg pNo ratings yet
- A Comparative Study Between Propane Dehydrogenation (PDH) Technologies and Plants in Saudi ArabiaDocument16 pagesA Comparative Study Between Propane Dehydrogenation (PDH) Technologies and Plants in Saudi ArabiaBihina HamanNo ratings yet