Professional Documents
Culture Documents
ACreative Exploration of_ISO 14971
ACreative Exploration of_ISO 14971
Uploaded by
hithamextrastep0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1 views22 pagesACreative Exploration of_ISO 14971
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentACreative Exploration of_ISO 14971
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1 views22 pagesACreative Exploration of_ISO 14971
ACreative Exploration of_ISO 14971
Uploaded by
hithamextrastepACreative Exploration of_ISO 14971
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 22
Swipe to see…
Risk Management Unveiled:
ACreative Exploration of
ISO 14971
Ch Mohammed Gamal
.
Introduction
Welcome to Risk Management
Unveiled: A Creative Exploration of
ISO 14971. In this presentation, we will
explore the fundamentals of risk
management and how it relates to ISO
14971. We will also discuss creative
approaches to risk management.
Documents may be used to guide the journey
· The Therapeutic Goods Administration’s risk management approach to
the regulation of therapeutic goods
· Draft international standard ISO/DIS 13022 ‘Medical products containing
viable human cells – application of risk management and requirements for
processing practices’
· ISO 14971 ‘Risk assessment for medical devices’
· ISO 22442 ‘Part 1 Medical devices utilizing animal tissues and their
derivatives - Part 1: Application of risk management’
· ICH Q9 “Quality Risk Management”
· EMEA ‘Guideline of Human cell-based medicinal products’
· EMEA ‘Guideline on safety and efficacy following-up-Risk management of
advance therapy medicinal products’
· AS/NZS ISO 31000:2009 Risk management, Principles and Guidelines.
What is Risk Management?
Risk management is the process of
identifying, assessing, and controlling
risks that could potentially impact a
project or product. It involves evaluating
the likelihood and severity of risks and
taking action to minimize or eliminate
them.
Risk Management Definitions You Need To Understand
risk management—systematic application of management policies,
procedures, and practices to the tasks of analyzing, evaluating,
controlling, and monitoring risk
risk—combination of the probability of occurrence of harm and the
severity of that harm
hazard—potential source of harm
hazardous situation—circumstance in which people, property, or
the environment are exposed to one or more hazard(s)
harm—physical injury or damage to the health of people, or
damage to property or the environment
severity—measure of the possible consequences of a hazard
risk analysis—systematic use of available information to identify
hazards and to estimate the risk
risk estimation—process used to assign values to the probability of
occurrence of harm and the severity of that harm
Risk Management Definitions You Need To Understand
risk evaluation—process of comparing the estimated risk against
given risk criteria to determine the acceptability of the risk
risk assessment—overall process comprising a risk analysis and a
risk evaluation
risk control—process in which decisions are made and measures
implemented by which risks are reduced to, or maintained within,
specified levels
residual risk—risk remaining after risk control measures have been
taken
Risk Assessment = Risk Analysis +Risk Evaluation
ISO 14971Overview
ISO 14971 is an international standard that
provides a framework for managing risks
associated with medical devices. It
outlines a process for identifying,
evaluating, and controlling risks
throughout the lifecycle of a device.
Design Controls & Risk Management
Design Controls are intended to demonstrate that a medical device has
been:
1. Designed to address the needs of users and patients.
2. Designed to meet inputs and requirements.
3. Proven to meet applicable standards.
4. Meets performance criteria.
• In fact, using Risk Management as a real tool will help you with Design
Verification and Design Validation planning.
Risk Management Plan
• A Risk Management Plan is a product-level document.
• The Risk Management Plan should identify the risk management activities
you anticipate and plan throughout the product’s life cycle.
• The Risk Management Plan is dynamic and should be revisited and
updated often.
• This is not a “one and done” activity.
Risk Management Plan criteria
• Scope of the Risk Management activities. Define the product included. It is possible to have
multiple products described within a single Risk Management Plan.
• •Describe the intended use of the product(s).
• Identify all Risk Management activities planned throughout the product life cycle.
• Define roles and responsibilities. Identify the Risk Management team that will be reviewing
and approving risk documentation.
• Criteria for the product’s risk acceptability. (Note, that oftentimes this is likely to be defined
within your Risk Management Procedure.)
• Specify methods to verify Risk Control measures are implemented and reduce risks to the
pre-established acceptable levels.
• Define how post-production information will be captured and fed into Risk Management
activities for the product.
Risk Identification
The first step in risk management is
identifying potential risks. This can be
done through brainstorming, analyzing
past experiences, and consulting with
experts. It's important to consider all
possible risks, including those that may
seem unlikely.
A good technique for identifying hazards is to go
through all the steps required for your product to be
used. At each step, identify if there are any potential
sources of harm.
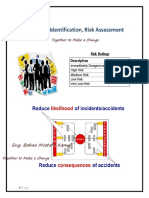
Risk Assessment
Once risks have been identified, they
must be assessed to determine their
likelihood and severity. This involves
analyzing the probability of a risk
occurring and the potential impact it
could have. Risks are typically
categorized as low, medium, or high.
Risk Control
After risks have been identified and assessed, measures
must be taken to control them. The goal is to reduce the
likelihood and severity of risks.
You should consider Risk Control options according to
the following priority:
• Inherent safety by design
• Protective measures in the actual medical device
and/or manufacturing process
• Information for safety, such as labeling and
instructions for use
Risk Acceptance
In some cases, it may not be possible to
completely eliminate a risk. In these
situations, the risk may be accepted if its
likelihood and severity are deemed
acceptable. This decision should be made
by a team of experts and documented in
a risk management plan.
Risk Communication
Effective communication is essential in
risk management. It's important to
communicate risks to stakeholders,
including users, regulatory agencies, and
internal teams. This can be done through
labeling, instructions for use, and other
forms of documentation.
Creative Risk Management
While risk management can be a complex
process, there are creative approaches that can
be taken to make it more effective. These
include involving users in the risk management
process, using storytelling to communicate
risks, and leveraging technology to automate
risk management tasks.
Risk Management and Compliance
Compliance with regulatory
requirements is an important aspect of
risk management. ISO 14971 provides a
framework for managing risks
associated with medical devices, and
compliance with this standard is
required by regulatory agencies in many
countries. It's important to understand
and comply with all relevant regulations.
Risk Management and Quality
Effective risk management is essential
for ensuring the quality of a product or
project. By identifying and controlling
risks, quality can be improved and
potential issues can be avoided. Risk
management should be integrated into
all aspects of a project or product's
lifecycle.
Case Studies
Case studies can provide valuable insights into effective
risk management practices. We will review several case
studies that illustrate the importance of risk
management and the creative approaches that can be
taken to manage risks.
Studies
Best Practices
In summary, effective risk management involves
identifying, assessing, and controlling risks associated
with a project or product. It's important to
communicate risks to stakeholders and comply with
relevant regulations.
Creative approaches can be taken to make risk
management more effective.
Thanks!
Do you have any
questions?
mohammed.alkhelaly@gmail.com
+201276079449
You might also like
- Full Download PDF of The Cell: A Molecular Approach 7th Edition (Ebook PDF) All ChapterDocument41 pagesFull Download PDF of The Cell: A Molecular Approach 7th Edition (Ebook PDF) All Chapterkutsisanouh100% (14)
- Risk and Opportunities ProcedureDocument4 pagesRisk and Opportunities ProcedureRotimi Shitta-Bey100% (1)
- Nature Care Products Risk Management PlanDocument7 pagesNature Care Products Risk Management PlanSyeda MaryamNo ratings yet
- Ioannis Tsiouras - The risk management according to the standard ISO 31000From EverandIoannis Tsiouras - The risk management according to the standard ISO 31000Rating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- Risk Assessment Report: ON Sun CaterersDocument14 pagesRisk Assessment Report: ON Sun CaterersRaichel SuseelNo ratings yet
- Hazard Identification & Risk Assessment GuidelineDocument81 pagesHazard Identification & Risk Assessment Guidelinebahaa mostafa100% (5)
- POI Procedure BSNLDocument21 pagesPOI Procedure BSNLRavi ShahNo ratings yet
- Quality Risk BVRDocument36 pagesQuality Risk BVRjaanhoneyNo ratings yet
- Gnipst 4 30 5694 2.3Document4 pagesGnipst 4 30 5694 2.3Antar GayenNo ratings yet
- Quality Risk Management ISO 9001-2015Document9 pagesQuality Risk Management ISO 9001-2015dhir.ankurNo ratings yet
- Pharma Risk MGMTDocument2 pagesPharma Risk MGMTSaravanan JothiNo ratings yet
- DEM 609 Module-2 Risk Management-IntroductionDocument29 pagesDEM 609 Module-2 Risk Management-IntroductionJoseph Berlin JuanzonNo ratings yet
- Risk Management For Medical DevicesDocument3 pagesRisk Management For Medical DevicesAyman HassanNo ratings yet
- Construction Quality and Risk ManagementDocument65 pagesConstruction Quality and Risk ManagementAyesha Amie G. De LeonNo ratings yet
- Risk Assessment Policy and Procedures PDFDocument9 pagesRisk Assessment Policy and Procedures PDFErnest KyereNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 Risk Management Concepts and PrinciplesDocument24 pagesLesson 1 Risk Management Concepts and PrinciplesShaina Tancio Abanid100% (1)
- FDA Seeks Comment On ICH Q9Document11 pagesFDA Seeks Comment On ICH Q9qac gmpNo ratings yet
- A Guide On Quality Risk ManagementDocument10 pagesA Guide On Quality Risk Managementisrael afolayan mayomiNo ratings yet
- HTTPWWW BG Utp Edu Plartpe42009pe42009019032Document14 pagesHTTPWWW BG Utp Edu Plartpe42009pe42009019032Krishna Kumar AlagarNo ratings yet
- Risk Assessment DocumentDocument10 pagesRisk Assessment DocumentSukanta BrahmaNo ratings yet
- Comprehensive Guide To Risk Management in Medical Device ProjectsDocument4 pagesComprehensive Guide To Risk Management in Medical Device Projectsjicet67288No ratings yet
- Risk Assesment in Microbiology: Presented by K. Santosh KumarDocument23 pagesRisk Assesment in Microbiology: Presented by K. Santosh KumarsanthoshkurvaNo ratings yet
- Risk Management in Tunneling ProjectsDocument2 pagesRisk Management in Tunneling ProjectsWai Yan SoeNo ratings yet
- Monitoring and Quality Control SystemsDocument5 pagesMonitoring and Quality Control SystemsSalah KhaledNo ratings yet
- 4.2 Risk Treatment ProcessDocument4 pages4.2 Risk Treatment ProcessRizky Hardiana de Toulouse-LautrecNo ratings yet
- Group 4 Written ReportDocument15 pagesGroup 4 Written ReportKezNo ratings yet
- Section1. (3.3) Risk Management Policy and ProceduresDocument10 pagesSection1. (3.3) Risk Management Policy and ProceduresanalistaxxNo ratings yet
- Quality Risk ManagementDocument56 pagesQuality Risk ManagementTatiana Rilo100% (3)
- Unit Ii: Pharmaceutical Quality System Pharmaceutical Quality System (PQS)Document11 pagesUnit Ii: Pharmaceutical Quality System Pharmaceutical Quality System (PQS)Sitti Rayna RickyNo ratings yet
- 1 PurposeDocument4 pages1 PurposeBryan DyNo ratings yet
- Risk Management Chapter 2Document33 pagesRisk Management Chapter 2Mercado jomerNo ratings yet
- 2004-4052S1 03 RazzaghiDocument29 pages2004-4052S1 03 RazzaghiSarat KumarNo ratings yet
- Appendix 1 NatureCares Risk Management Policy ProcedureDocument4 pagesAppendix 1 NatureCares Risk Management Policy ProcedureErsan ResurreccionNo ratings yet
- Approaching Risk Assessment: Tools and Methods by DR - Tim SandleDocument23 pagesApproaching Risk Assessment: Tools and Methods by DR - Tim SandlePiruzi MaghlakelidzeNo ratings yet
- RA Level ThreeDocument18 pagesRA Level ThreeAbra AbraNo ratings yet
- Risk Register-GuidelineDocument2 pagesRisk Register-GuidelineMasbooksNo ratings yet
- Risk Assessment ProcessDocument18 pagesRisk Assessment Processre2phukanNo ratings yet
- IUM-Safety Risk Management Concept (1635)Document2 pagesIUM-Safety Risk Management Concept (1635)Risad ChoudhuryNo ratings yet
- Bkai3043 Topic 3Document25 pagesBkai3043 Topic 3Amr FahmiNo ratings yet
- 15JF Brady PDFDocument8 pages15JF Brady PDFitung23No ratings yet
- MONITORINGDocument6 pagesMONITORINGSalah KhaledNo ratings yet
- This Document Is Risk Management Policy and Procedures.Document6 pagesThis Document Is Risk Management Policy and Procedures.enxing ZhouNo ratings yet
- 5-Risk Management ProcessDocument3 pages5-Risk Management ProcessHenry dragoNo ratings yet
- Risk Management PolicyDocument4 pagesRisk Management Policyoleksandr.jobNo ratings yet
- Risk ManagementDocument20 pagesRisk ManagementAnna Lyssa BatasNo ratings yet
- Approaching Risk Assessment: Tools and MethodsDocument23 pagesApproaching Risk Assessment: Tools and MethodsTim Sandle100% (1)
- Arvind Sharma (QRM)Document35 pagesArvind Sharma (QRM)Arvind Kumar SharmaNo ratings yet
- Project Risk Management - PM0007 SET-1Document5 pagesProject Risk Management - PM0007 SET-1mbaguideNo ratings yet
- HSE for NDDocument84 pagesHSE for NDanjolabagbenroNo ratings yet
- Module in Risk ManagementDocument76 pagesModule in Risk Managementelle gutierrezNo ratings yet
- Risk ManagementDocument12 pagesRisk ManagementSubodh Kumar0% (1)
- Risk ManagementDocument14 pagesRisk Managementbradsean1350No ratings yet
- As Per Ich Guideline Q9 Introduction, Risk Asseessment, Risk Contol, Risk ReviewDocument14 pagesAs Per Ich Guideline Q9 Introduction, Risk Asseessment, Risk Contol, Risk ReviewDevang GondaliyaNo ratings yet
- Risk Management Fundamental Tools and StrategiesDocument20 pagesRisk Management Fundamental Tools and Strategiesf.alferez.145722.tcNo ratings yet
- Risk AssessmentDocument10 pagesRisk AssessmentLee Taeyong, Kim Taehyung & exoNo ratings yet
- Entrep Module 3Document2 pagesEntrep Module 3JM NavarretteNo ratings yet
- Procurement 3 PDFDocument33 pagesProcurement 3 PDFShabnam ShahNo ratings yet
- حسين عامر -RISK MANAGEMENTDocument8 pagesحسين عامر -RISK MANAGEMENTaker asdNo ratings yet
- Adventurer's Guide to Risk Management: Fictional Tales about Risk ManagementFrom EverandAdventurer's Guide to Risk Management: Fictional Tales about Risk ManagementNo ratings yet
- Mastering Safety Risk Management for Medical and In Vitro DevicesFrom EverandMastering Safety Risk Management for Medical and In Vitro DevicesNo ratings yet
- BSI Medical Devices _ Microbiology whitepaperDocument11 pagesBSI Medical Devices _ Microbiology whitepaperhithamextrastepNo ratings yet
- 2014 GMP and PRP's training material--Document72 pages2014 GMP and PRP's training material--hithamextrastepNo ratings yet
- A summary of the guidance on slecting a predicate deviceDocument10 pagesA summary of the guidance on slecting a predicate devicehithamextrastepNo ratings yet
- Cactus-Life-Sciences-Periodic-Safety-Update-Report-PSUR-WhitepaperDocument13 pagesCactus-Life-Sciences-Periodic-Safety-Update-Report-PSUR-WhitepaperhithamextrastepNo ratings yet
- Process Validation for Medical DeviceDocument69 pagesProcess Validation for Medical DevicehithamextrastepNo ratings yet
- Template-MDCG-2022-21-ANNEX-IDocument8 pagesTemplate-MDCG-2022-21-ANNEX-IhithamextrastepNo ratings yet
- STABILITY-PACKAGING-ANDREUSABLES-final-1Document59 pagesSTABILITY-PACKAGING-ANDREUSABLES-final-1hithamextrastepNo ratings yet
- IMDRF Standard Operating Procedures 2024Document42 pagesIMDRF Standard Operating Procedures 2024hithamextrastepNo ratings yet
- Process for Fulfillment of PRRC Obligations Under EU MDRDocument3 pagesProcess for Fulfillment of PRRC Obligations Under EU MDRhithamextrastepNo ratings yet
- Post Market SurveillanceDocument39 pagesPost Market SurveillancehithamextrastepNo ratings yet
- IEC 60601-1 2020 Medical Electrical Equipment - Part 1 General Requirements For Basic Safety and Essential PerformanceDocument45 pagesIEC 60601-1 2020 Medical Electrical Equipment - Part 1 General Requirements For Basic Safety and Essential PerformancehithamextrastepNo ratings yet
- PMS Overview under MDRDocument46 pagesPMS Overview under MDRhithamextrastepNo ratings yet
- ISO 11607-1 2019 Packaging For Terminally Sterilized Medical devices-Part1Requirements For Materials, Sterile Barrier SystemsDocument43 pagesISO 11607-1 2019 Packaging For Terminally Sterilized Medical devices-Part1Requirements For Materials, Sterile Barrier SystemshithamextrastepNo ratings yet
- PACKAGING TEST REPORTDocument13 pagesPACKAGING TEST REPORThithamextrastepNo ratings yet
- Technical Documentation File ChecklistDocument11 pagesTechnical Documentation File ChecklisthithamextrastepNo ratings yet
- USP 797 Ensuring A State of ControlDocument68 pagesUSP 797 Ensuring A State of ControlhithamextrastepNo ratings yet
- Analisis Jarak Dilatasi Struktur Bangunan Menggunakan Sistem Dilatasi Dua KolomDocument11 pagesAnalisis Jarak Dilatasi Struktur Bangunan Menggunakan Sistem Dilatasi Dua KolomVvvg JNo ratings yet
- Five Year Development Plan (2003-2008)Document190 pagesFive Year Development Plan (2003-2008)Saurav SenNo ratings yet
- The Odyssey of Homer PDFDocument370 pagesThe Odyssey of Homer PDFNeha VarshneyNo ratings yet
- LacanDocument21 pagesLacannatitvzandtNo ratings yet
- Cuento en InglesDocument5 pagesCuento en InglesFcm Felicidad YhamelNo ratings yet
- Preparation and Characterization of Membranes Formed by NIPS A REVIEWDocument20 pagesPreparation and Characterization of Membranes Formed by NIPS A REVIEW이주신No ratings yet
- Thermetco-Thermocouple Welder TW9Document10 pagesThermetco-Thermocouple Welder TW9ghostinshellNo ratings yet
- Ergonomic Analysis of Train Driver Workplace of Train Pendolino Ics - ReferatDocument8 pagesErgonomic Analysis of Train Driver Workplace of Train Pendolino Ics - ReferathitfromNo ratings yet
- Knowledge, Attitude and Practice Towards Needle Stick Injury Among Health Care Workers in A Private Hospital-Questionnaire Based StudyDocument7 pagesKnowledge, Attitude and Practice Towards Needle Stick Injury Among Health Care Workers in A Private Hospital-Questionnaire Based StudyIJAR JOURNALNo ratings yet
- Agricultural Fertilizers and Pesticides Sprayers PDFDocument4 pagesAgricultural Fertilizers and Pesticides Sprayers PDFIrving Ruiz Espinoza0% (1)
- Cybe Mortar DatasheetDocument3 pagesCybe Mortar DatasheetElisa Pavez A.No ratings yet
- WAH - Working On Roofs - 0Document13 pagesWAH - Working On Roofs - 0Rizki DarmawanNo ratings yet
- Podar International School Practice Sheet STD: X Topic: 12.2: Electricity Subject: PhysicsDocument6 pagesPodar International School Practice Sheet STD: X Topic: 12.2: Electricity Subject: PhysicsHemant PadalkarNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry Quarter 2 Week 1 3Document7 pagesGeneral Chemistry Quarter 2 Week 1 3Istian VlogsNo ratings yet
- The Dowser's Handbook - Pendulums, Muscle Testing, Applied Kinesiology by Jimmy MackDocument44 pagesThe Dowser's Handbook - Pendulums, Muscle Testing, Applied Kinesiology by Jimmy MackZach90% (10)
- đề 5Document8 pagesđề 5Thư NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Analysis of The Main Characters in Little Women by AlcottDocument6 pagesAnalysis of The Main Characters in Little Women by AlcottMiguel VizcainoNo ratings yet
- Raw Mix DesignDocument8 pagesRaw Mix DesignkazamNo ratings yet
- Assignment 3 BSE5Document7 pagesAssignment 3 BSE5Sania ShehzadNo ratings yet
- QC Case StudyDocument77 pagesQC Case StudyBibhudutta mishraNo ratings yet
- SRS Medical ManagementDocument7 pagesSRS Medical ManagementAtharv KatkarNo ratings yet
- D 6730 - 01 AstmDocument55 pagesD 6730 - 01 AstmSebastian GonzalezNo ratings yet
- Cardiomyopathy: Restrictive Heart DiseaseDocument18 pagesCardiomyopathy: Restrictive Heart DiseaseMitch GabuyaNo ratings yet
- Filter MiliporeDocument8 pagesFilter Miliporemotasa mojosarilabNo ratings yet
- Beginning Trumpet PP - Lesson 1Document12 pagesBeginning Trumpet PP - Lesson 1api-233367985No ratings yet
- Xenon 21-22 Sheet Without Answer (EUDIOMETRY)Document3 pagesXenon 21-22 Sheet Without Answer (EUDIOMETRY)Krishna GoyalNo ratings yet
- 17-03-10 Inductive Conductivity Transmitter CIT-8920Document30 pages17-03-10 Inductive Conductivity Transmitter CIT-8920Juan CarvajalNo ratings yet
- Fluidisation: Stages in Fluidisation or Fluidisation CharacterisationDocument6 pagesFluidisation: Stages in Fluidisation or Fluidisation Characterisationdevilturn70No ratings yet