Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 viewsOB-NURSING-INCO
OB-NURSING-INCO
Uploaded by
SJane FeriaCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Simple Nursing Medical Surgical - CompletoDocument157 pagesSimple Nursing Medical Surgical - CompletoRenato Bandeira100% (6)
- Lithium Carbonate Drug StudyDocument3 pagesLithium Carbonate Drug Studynot your medz duranNo ratings yet
- Abruptio Placenta and AbortionDocument10 pagesAbruptio Placenta and Abortiondanica grace gubaNo ratings yet
- 2 - Pre Gestational ConditionDocument11 pages2 - Pre Gestational ConditionAngelica Dalit MendozaNo ratings yet
- Gestational 1Document8 pagesGestational 1RoseAngelyne VicenteNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care of The High Risk Pregnant Client With Gestational ConditionDocument55 pagesNursing Care of The High Risk Pregnant Client With Gestational ConditionMarc FresNo ratings yet
- MCN ReviewerDocument4 pagesMCN ReviewerMaria Arabella LanacaNo ratings yet
- Case Study 29-APHDocument31 pagesCase Study 29-APHZarul Naim Mohd TamiziNo ratings yet
- Abruptio PlacentaDocument36 pagesAbruptio PlacentaBriandon CanlasNo ratings yet
- NCM 109 - Week 1Document6 pagesNCM 109 - Week 1Aly HannahNo ratings yet
- Module 2 - Maternal TransesDocument6 pagesModule 2 - Maternal TransesCarl UyNo ratings yet
- APH PresentationDocument42 pagesAPH Presentationestela aberaNo ratings yet
- Antepartum HaemorrhageDocument21 pagesAntepartum HaemorrhageDavina DakapNo ratings yet
- Module 2 - MCN TransesDocument6 pagesModule 2 - MCN TransesCarl UyNo ratings yet
- NCM 109 ReviewerDocument8 pagesNCM 109 ReviewerAlma Janella TOSINO100% (2)
- NCM 109 High Risk PregnancyDocument11 pagesNCM 109 High Risk PregnancyLea BorceNo ratings yet
- MCN NotesDocument20 pagesMCN NotesLiamLexus JavierNo ratings yet
- 2 Nursing Care of The Pregnant Client Gestational ConditionDocument120 pages2 Nursing Care of The Pregnant Client Gestational ConditionjustinjareddNo ratings yet
- Chapter 21 Reviewer TillesDocument16 pagesChapter 21 Reviewer Tillescutiepie creampieNo ratings yet
- Case Study 1Document8 pagesCase Study 1inspire.nacNo ratings yet
- Bleeding During PregnancyDocument4 pagesBleeding During PregnancyCarl Andre ReyesNo ratings yet
- GYN Module 3 Case 1: Gestational Trophoblastic NeoplasiaDocument21 pagesGYN Module 3 Case 1: Gestational Trophoblastic NeoplasiaElaine Marie Rendon PalmejarNo ratings yet
- Early Pregnancy ComplicationDocument31 pagesEarly Pregnancy ComplicationHizami NorddinNo ratings yet
- PIHDocument4 pagesPIHCatherine PradoNo ratings yet
- Post Partum ComplicationsDocument40 pagesPost Partum ComplicationsMahmoud Abu Al AmrainNo ratings yet
- GYN Module 3 Case 1: Gestational Trophoblastic NeoplasiaDocument21 pagesGYN Module 3 Case 1: Gestational Trophoblastic NeoplasiaElaine Marie Rendon PalmejarNo ratings yet
- High Risk PregnancyDocument12 pagesHigh Risk Pregnancyggrrk7100% (2)
- NCM 109 (PRELIMS) - Lesson 3Document17 pagesNCM 109 (PRELIMS) - Lesson 3nianNo ratings yet
- Pregnancy HypertensionDocument71 pagesPregnancy Hypertensionbazuu mbwegzeNo ratings yet
- Placenta PreviaDocument43 pagesPlacenta PreviaAngela Joy AmparadoNo ratings yet
- Placenta Abruptio: Maneja, Jan Michael B. BSN 223Document6 pagesPlacenta Abruptio: Maneja, Jan Michael B. BSN 223JiraGonzales100% (1)
- Obstetric Highlights, Elmar P. SakalaDocument47 pagesObstetric Highlights, Elmar P. Sakaladukelist5660% (1)
- Chapter 21Document69 pagesChapter 212082194No ratings yet
- Chapter 21 Sudden Pregnancy Complications YBOA 1Document6 pagesChapter 21 Sudden Pregnancy Complications YBOA 1syroise margauxNo ratings yet
- CA MaternalDocument156 pagesCA MaternalLovely Hope LugatimanNo ratings yet
- Maternal Reviewer FinalsDocument36 pagesMaternal Reviewer FinalsHannah QuindipanNo ratings yet
- Antepartum HaemorrhageDocument57 pagesAntepartum HaemorrhageLady350z100% (3)
- Complication of PregnancyDocument44 pagesComplication of PregnancyJharaNo ratings yet
- Gestational Conditions HandoutDocument17 pagesGestational Conditions HandoutFilamae Jayahr Caday100% (4)
- Perdarahan Antepartum - EmiliaDocument26 pagesPerdarahan Antepartum - EmiliaEmilia NazmaNo ratings yet
- 2 Pre Gestation and Gestational ConditionsDocument88 pages2 Pre Gestation and Gestational Conditionslermacornel61No ratings yet
- Ob Final ReviewDocument13 pagesOb Final Reviewraquel maniegoNo ratings yet
- Gestational ConditionsDocument4 pagesGestational ConditionsHyacinth Mae Virtudazo RaganasNo ratings yet
- #12 - NCM 109 (Rle) - TransesDocument4 pages#12 - NCM 109 (Rle) - TransesJaimie BanaagNo ratings yet
- Chapter21trans 1Document8 pagesChapter21trans 1syroise margauxNo ratings yet
- MANAGEMENT OF ABRUPTIO PLACENTAEDocument7 pagesMANAGEMENT OF ABRUPTIO PLACENTAEchdxemailNo ratings yet
- Abnormal Pregnancy1653 160118115626Document7 pagesAbnormal Pregnancy1653 160118115626sufian ahmadNo ratings yet
- Handout 4Document13 pagesHandout 4ApRil Anne BalanonNo ratings yet
- Placenta AbruptioDocument30 pagesPlacenta AbruptioArchana MaharjanNo ratings yet
- Seminar Gestational Trophoblastic DiseaseDocument27 pagesSeminar Gestational Trophoblastic DiseaseCourtney Dela FierraNo ratings yet
- Multiple PregnancesssssDocument29 pagesMultiple PregnancesssssNajjemba ShanitahNo ratings yet
- Thursday, February 11, 2021 8:04 PM: Chapter 21 Page 1Document29 pagesThursday, February 11, 2021 8:04 PM: Chapter 21 Page 1Christel Ann TianchonNo ratings yet
- A.1 AbortionDocument47 pagesA.1 AbortionRiza Mae Follero DanteNo ratings yet
- Multiple PregnancyDocument25 pagesMultiple PregnancyArya S BijuNo ratings yet
- Abnormalities of Amniotic FluidDocument32 pagesAbnormalities of Amniotic FluidMuhammad Abdillah100% (1)
- Hyperemesis, Hmole, Placenta PreviaDocument12 pagesHyperemesis, Hmole, Placenta Previadanica grace gubaNo ratings yet
- COURSE in The WARD Interhospital FinalDocument8 pagesCOURSE in The WARD Interhospital Finalkimadlo656No ratings yet
- PihDocument35 pagesPihmark100% (6)
- Ward Class - PCI, HPN DX in PregnancyDocument26 pagesWard Class - PCI, HPN DX in Pregnancyhrry stylesNo ratings yet
- Pregnancy ComplicationsDocument3 pagesPregnancy ComplicationsJeizel IgnacioNo ratings yet
- Pre-eclampsia, (Pregnancy with Hypertension And Proteinuria) A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandPre-eclampsia, (Pregnancy with Hypertension And Proteinuria) A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- It's Not Just a Heavy Period; The Miscarriage HandbookFrom EverandIt's Not Just a Heavy Period; The Miscarriage HandbookRating: 2 out of 5 stars2/5 (1)
- LAWS AND REGULATIONS DISASTER NURSING REVIEWERDocument2 pagesLAWS AND REGULATIONS DISASTER NURSING REVIEWERSJane FeriaNo ratings yet
- 3 Acid Base ImbalanceDocument5 pages3 Acid Base ImbalanceSJane FeriaNo ratings yet
- Head and NeckDocument41 pagesHead and NeckSJane FeriaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Module Therapeutic CommunicationDocument6 pagesChapter 3 Module Therapeutic CommunicationSJane FeriaNo ratings yet
- 1ST Term SummaryDocument5 pages1ST Term SummarySJane FeriaNo ratings yet
- 4 - CoparDocument4 pages4 - CoparSJane FeriaNo ratings yet
- ACE AND ARBs PRACTICE QUESTIONS HIghlightedDocument2 pagesACE AND ARBs PRACTICE QUESTIONS HIghlightedSJane FeriaNo ratings yet
- 4 Neurologic Nursing DisordersDocument4 pages4 Neurologic Nursing DisordersSJane FeriaNo ratings yet
- Disaster Preparedness 1Document10 pagesDisaster Preparedness 1SJane FeriaNo ratings yet
- Emergency Severity Index LEC MLT 2 10 24Document27 pagesEmergency Severity Index LEC MLT 2 10 24SJane FeriaNo ratings yet
- CD Cheat Sheet CompleteDocument6 pagesCD Cheat Sheet CompleteSJane FeriaNo ratings yet
- Endo SummarizedDocument8 pagesEndo SummarizedSJane FeriaNo ratings yet
- Chem and Hazmat MCI 2 13 24Document50 pagesChem and Hazmat MCI 2 13 24SJane FeriaNo ratings yet
- Urinary System1Document4 pagesUrinary System1SJane FeriaNo ratings yet
- TRANSCULTURALDocument5 pagesTRANSCULTURALSJane FeriaNo ratings yet
- Neurologic NursingDocument3 pagesNeurologic NursingSJane FeriaNo ratings yet
- MicroPara LabDocument2 pagesMicroPara LabSJane FeriaNo ratings yet
- DBD English-1Document7 pagesDBD English-1Risky Rahma Sari PutriNo ratings yet
- México Hígado GrasoDocument9 pagesMéxico Hígado GrasoAlan josue Hernandez lopezNo ratings yet
- Lebel1991 PDFDocument15 pagesLebel1991 PDFRamon CharlestienNo ratings yet
- OET Writing Case Notes Nursing 16 35Document38 pagesOET Writing Case Notes Nursing 16 35adnanshakeelm1No ratings yet
- Pet TherapyDocument2 pagesPet Therapyapi-543519166No ratings yet
- Scrutinizing The Fat Mass, Fat Free Mass, Fat Mass Index, Fat Free Mass Index Amidst Rural and Urban School Boys of PunjabDocument5 pagesScrutinizing The Fat Mass, Fat Free Mass, Fat Mass Index, Fat Free Mass Index Amidst Rural and Urban School Boys of Punjabnapinder singhNo ratings yet
- COT 2023 (First)Document6 pagesCOT 2023 (First)Rosalie dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Related Teenshealth Links: Health Problems SeriesDocument13 pagesRelated Teenshealth Links: Health Problems SeriesMario BadayosNo ratings yet
- RadioimmunassayDocument23 pagesRadioimmunassayVinayak Chura100% (1)
- Inguinal Hernia Case FileDocument2 pagesInguinal Hernia Case Filehttps://medical-phd.blogspot.comNo ratings yet
- Who Guideline On Use of Ferritin Concentrations To Assess Iron Status in Individuals and PopulationsDocument82 pagesWho Guideline On Use of Ferritin Concentrations To Assess Iron Status in Individuals and PopulationsLima NetNo ratings yet
- RealStar CCHFV RT-PCR Kit 1.0 - WEB - CE - EN-S02Document15 pagesRealStar CCHFV RT-PCR Kit 1.0 - WEB - CE - EN-S02saadNo ratings yet
- High Yield Pediatrics: Shelf Exam Review Emma Holliday RamahiDocument78 pagesHigh Yield Pediatrics: Shelf Exam Review Emma Holliday Ramahiskeebs230% (1)
- Pharma - SkinDocument8 pagesPharma - Skinreference books100% (1)
- 9D-NLS Features and Warranty (2021)Document10 pages9D-NLS Features and Warranty (2021)Danutz ChirilaNo ratings yet
- Registration Timings: OPD Schedule - Dr. Ram Manohar Lohia Institute of Medical Sciences (RMLIMS)Document8 pagesRegistration Timings: OPD Schedule - Dr. Ram Manohar Lohia Institute of Medical Sciences (RMLIMS)vivekNo ratings yet
- Donning Doffing Spotter Check List v1Document1 pageDonning Doffing Spotter Check List v1Rudyard Paul AmistadNo ratings yet
- Nature Review, Complete RevascularizationDocument14 pagesNature Review, Complete RevascularizationIván De LeónNo ratings yet
- Mapeh 10 Q3 M5Document27 pagesMapeh 10 Q3 M5Faye Anne Coy-omNo ratings yet
- Leaky Gut Solutions Guide - Peter OsborneDocument54 pagesLeaky Gut Solutions Guide - Peter OsborneFITPSNo ratings yet
- How To Store Vitafen: 1. What Vitafen Is and What It Is Used ForDocument7 pagesHow To Store Vitafen: 1. What Vitafen Is and What It Is Used FornurfaaaNo ratings yet
- CD HeightsDocument3 pagesCD HeightsTotal Pest ControlNo ratings yet
- National Programme For Prevention and Control of CancerDocument18 pagesNational Programme For Prevention and Control of CancerPrabhakaran AranganathanNo ratings yet
- ID Perbandingan Pemeriksaan ToksigenisitasDocument9 pagesID Perbandingan Pemeriksaan ToksigenisitasindahdwirahNo ratings yet
- Waterborne DiseasesDocument28 pagesWaterborne Diseasesm142106013 TMUNo ratings yet
- Review On Enterocutaneous FistulaDocument31 pagesReview On Enterocutaneous FistulaAbu ZidaneNo ratings yet
- Children Hypertension ChartDocument4 pagesChildren Hypertension ChartHo Yoke MeiNo ratings yet
- Health Sector in Ghana ReviewDocument17 pagesHealth Sector in Ghana ReviewBriant BlantonNo ratings yet
OB-NURSING-INCO
OB-NURSING-INCO
Uploaded by
SJane Feria0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views4 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views4 pagesOB-NURSING-INCO
OB-NURSING-INCO
Uploaded by
SJane FeriaCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 4
OB NURSING
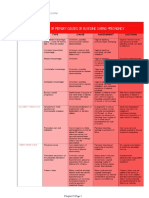
FEATURE ABRUPTIO PLACENTA PLACENTA PREVIA
Definition Premature separation of the Placenta partially or completely covers
placenta from the uterine wall. The the cervical opening.
blood may pool in the cul-de-sac of
Douglas. If blood cannot escape,
there is pain.
Onset Sudden Gradual or sudden
Bleeding Painful vaginal bleeding Painless vaginal bleeding
Hematoma The accumulated blood can form a No apparent hematoma.
retroplacental hematoma, which
exerts pressure on the surrounding
tissues. This will eventually
manifest Cullen’s sign.
Timing Usually occurs after 20 weeks of Typically identified in the second or
gestation third trimester
Pain Abdominal pain and uterine Usually no pain
tenderness
Uterine Tone Increased uterine tone (rigid, hard Normal uterine tone
abdomen)
Fetal Heart Rate May show signs of distress or Usually normal unless severe
abnormalities hemorrhage
Risk Factors Hypertension, trauma, smoking, Previous placenta previa, multiple
multiple gestations, advanced pregnancies, advanced maternal age,
maternal age uterine surgery
Diagnosis Clinical assessment, ultrasound, and Ultrasound
fetal monitoring
Complications Shock, coagulation disorders, fetal Preterm birth, hemorrhage, placental
distress or death, maternal abruption, fetal growth restriction
morbidity
Management Immediate medical intervention, Depends on gestational age and severity,
possible delivery, monitoring and may include bed rest, cesarean delivery
stabilization if necessary
Nursing 1. Monitor vital signs and 1. Monitor vital signs and fetal
Management fetal heart rate heart rate Assess and quantify
2. Assess and quantify vaginal vaginal bleeding
bleeding 2. Avoid vaginal examinations
3. Administer IV fluids and 3. Prepare for possible cesarean
blood products as needed delivery
4. Prepare for possible 4. Provide emotional support and
emergency delivery education to the patient and
5. Provide emotional support family
and education to the patient
and family
GESTATIONAL TROPHOBLASTIC DSE HYPERTENSIVE DISORDERS IN
PREGNANCY
(HYDATIDIFORM MOLE)
is a condition which vasospasm occurs during
• It is an abnormal proliferation and pregnancy in both small and large arteries.
degeneration of the trophoblastic villi,
they become filled with fluid and appear Pre Eclampsia
as graped-like vesicles.
▪ a pregnancy related disease process
Incidence: is 1 for every 1,500 pregnancy evidence by hpn and proteinuria
Risk factors: ▪ Also termed as Toxemia of pregnancy
1. Women older that 35 yrs old
2. Woman with low intake of protein Cause:
3. Hx of H mole ▪ Unknown
▪ Common in women younger than 20 and
Types: above 40 y/o
1. Complete ▪ Underlying diseases DM, heart disease
• All trophoblastic villi swell and becomes
cystic TYPES
• If embryo forms, it dies immediately
a. Gestational Hypertension
Chromosomes was only contributed by
▪ elevated blood pressure of 140/90 but has
the father or an empty ovum
no proteinuria or edema
2. Partial
▪ BP returns to normal after birth
• Some villi normally grow
▪ No drug therapy is necessary
• Fetal may grow about 9 weeks then
macerates b. Preeclampsia without severe features or PE
• mother’s chromosomes remain but there c mild feature
are 2 sets from the father, placenta and ▪ Blood pressure of 140/90 taken on 2
fetus are formed but failed to develop occasion with 6 hrs apart
• Rarely leads to chorio carcinoma ▪ or systolic elevated 30mmhg
▪ or diastolic pressure elevated 15 mmhg
Treatment: above pre pregnancy level,
▪ Suction curettage ▪ proteinuria of 1-2+, wt gain over 2 lbs per
▪ Test for HCG week in the 2nd tri and 1 lb per week in
o Analyzed every 2 wks until level 3rd tri
are normal, then every 4 wks for ▪ mild edema on the upper extremities or
6-12 mos (some have still (+) @ face
3 weeks/ ¼ @ 40 days)
▪ Declining result suggest no complication Management: usually managed at home
▪ While, 3x increase suggest malignancy 1. Promote bed rest
▪ Woman should use oral contraceptive for 2. Monitor anti platelet therapy
12 mos 3. Promote good nutrition
▪ After 6 months and HCG is negative, the 4. Provide emotional support
woman is free of malignancy
▪ METHOTREXATE is given as c. Preeclampsia with severe features
prophylactic o Early screening for next ➢ Blood pressure of 160/110;
pregnancy ➢ Proteinuria 3- 4+, on a random sample
and 5g on a 24 hr sample,
➢ Oliguria,
➢ Altered creatinine,
➢ Cerebral and visual disturbances,
➢ Epigastric pain, ▪ Vaginal birth with minimum anesthesia
➢ Extensive peripheral edema is ideal
▪ CS if fetal distress is imminent
Management:
▪ Bed rest
▪ Monitor maternal and fetal well being HELLP SYNDROME
▪ Provide nutritious diet
▪ Administer Medication to prevent Is a variation of the gestational hypertensive
eclampsia process named for symptoms that occur:
a. Hemolysis that leads to anemia
Magnesium Sulfate b. Elevated liver enzymes that lead to
Action: prevent convulsion epigastric pain
c. Low platelets lead to abnormal bleeding
Intervention before the administration:
▪ + deep tendon reflex o RR= above Incidence:
12bpm Occurs 4%-12% of patients who have elevated
▪ Urine output of 30 ml per hr blood pressure during pregnancy
▪ Therapeutic range: 5-8 mg/ml Occurs primigravida and multi
▪ Antidote: Calcium Gluconate
▪ Induced labor/CS if pregnancy is 36 wks Cause: unknown
and there is evidence of fetal lung
maturity Signs and Symptoms:
1. Proteinuria
d. Eclampsia 2. Edema
▪ seizure accompanied by S/Sx of pre 3. Hypertension
eclampsia 4. Nausea
▪ Usually happens at late pregnancy up to 5. Epigastric pain
48 hrs after childbirth 6. Right upper quadrant pain and tenderness
7. Bleeding
Signs and Symptoms before seizure
1. Increase in BP Complications:
2. Increase in Temp ▪ hyponatremia, renal failure,
3. Blurring of vision hypoglycemia, renal failure, cerebral
4. Decrease urinary output hemorrhage
5. Severe epigastric pain ▪ FETUS: IUGR & Preterm Labor
During Seizure: Treatment:
▪ Cyanosis ▪ Transfusion of Fresh plasma or Platelets
▪ Incontinence of urine and feces ▪ Intravenous glucose
▪ Mother delivers either vaginal or CS
Treatment/ Management:
▪ Tonic -Clonic seizure
▪ Maintain airway
▪ Prevent aspiration
▪ Monitor FHT
▪ Administer MgSO4 or Valium
▪ Monitor for Vaginal bleeding and uterine
contraction
▪ Pt is NPO BIRTH
▪ Decision about birth will be made soon
after seizure ( 12hrs-24 hrs)
CAESAREAN SECTION ▪ Estimated fetal size of over 9lbs(4.1kg).
A maternal disease or
It is a surgical delivery of an infant through an ▪ Condition that may be worsened by the
incision in the mother’s abdomen and uterus stress of labor, such as diabetes.
▪ A placenta that is blocking the cervix
Indications:
placenta previa
▪ CPD
▪ Open sores from active genital herpes
▪ Severe pre-eclampsia
near the due the date
▪ Placental accidents
▪ Fetal distress
PRE-OPERATIVE CARE:
▪ Previous classic CS and elective CS=
1. Check vital signs, uterine contractions
done prior to onset of labor
and FHR
2. Physical examination; routine lab tests,
TYPES
blood typing and cross matching
a. LOW-SEGMENT 3. Abdomino-perineal preparation
▪ “bikini” type, low transverse 4. Retention catheter is inserted to
▪ the best method of choice constantly drain the urine
▪ the incision is made in the lower uterine 5. Administer ATROPINE SULFATE. No
segment which is the thinnest and most narcotics are given bec. This can lead to
passive part during labor respiratory depression to the newborn
Advantages: POSTOPERATIVE CARE:
▪ Minimal blood loss ▪ Deep breathing, coughing exercises,
▪ Incision is easier to repair turning from side to side
▪ Lower incidence of postpartum infection ▪ Encourage ambulation after 12 hours as
▪ No possibility of uterine rupture tolerated
▪ Monitor vital signs
B. CLASSIC ▪ Watch for signs of hemorrhage
▪ vertical incision, recommended in a. Inspect lochia
bladder or lower uterine segment b. Check for involution
adhesions c. inspect operative site
Resulting from previous operations ▪ Encourage breastfeeding – 24 hours after
Low-lying/marginal placenta previa delivery
Fetal transverse lie
DISORDER OF PLACENTA NORMAL:
RISKS: ▪ Weight: 500 g
▪ Infection ▪ Diameter: 15-20cm
▪ Heavy blood loss >500 ml ▪ Thickness: 1.5-3cm
▪ A woman with previous CS has a lesser ▪ Extra large for DM, syphilis,
chance of delivering her next baby erythroblastosis
vaginally
PLANNED CAESARIAN
Medical reasons for planned caesarian section:
▪ A fetus in any position that is not head
down
▪ Decreased blood supply to the placenta
before birth
▪ The medical need to deliver and no
success with inducing labor
You might also like
- Simple Nursing Medical Surgical - CompletoDocument157 pagesSimple Nursing Medical Surgical - CompletoRenato Bandeira100% (6)
- Lithium Carbonate Drug StudyDocument3 pagesLithium Carbonate Drug Studynot your medz duranNo ratings yet
- Abruptio Placenta and AbortionDocument10 pagesAbruptio Placenta and Abortiondanica grace gubaNo ratings yet
- 2 - Pre Gestational ConditionDocument11 pages2 - Pre Gestational ConditionAngelica Dalit MendozaNo ratings yet
- Gestational 1Document8 pagesGestational 1RoseAngelyne VicenteNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care of The High Risk Pregnant Client With Gestational ConditionDocument55 pagesNursing Care of The High Risk Pregnant Client With Gestational ConditionMarc FresNo ratings yet
- MCN ReviewerDocument4 pagesMCN ReviewerMaria Arabella LanacaNo ratings yet
- Case Study 29-APHDocument31 pagesCase Study 29-APHZarul Naim Mohd TamiziNo ratings yet
- Abruptio PlacentaDocument36 pagesAbruptio PlacentaBriandon CanlasNo ratings yet
- NCM 109 - Week 1Document6 pagesNCM 109 - Week 1Aly HannahNo ratings yet
- Module 2 - Maternal TransesDocument6 pagesModule 2 - Maternal TransesCarl UyNo ratings yet
- APH PresentationDocument42 pagesAPH Presentationestela aberaNo ratings yet
- Antepartum HaemorrhageDocument21 pagesAntepartum HaemorrhageDavina DakapNo ratings yet
- Module 2 - MCN TransesDocument6 pagesModule 2 - MCN TransesCarl UyNo ratings yet
- NCM 109 ReviewerDocument8 pagesNCM 109 ReviewerAlma Janella TOSINO100% (2)
- NCM 109 High Risk PregnancyDocument11 pagesNCM 109 High Risk PregnancyLea BorceNo ratings yet
- MCN NotesDocument20 pagesMCN NotesLiamLexus JavierNo ratings yet
- 2 Nursing Care of The Pregnant Client Gestational ConditionDocument120 pages2 Nursing Care of The Pregnant Client Gestational ConditionjustinjareddNo ratings yet
- Chapter 21 Reviewer TillesDocument16 pagesChapter 21 Reviewer Tillescutiepie creampieNo ratings yet
- Case Study 1Document8 pagesCase Study 1inspire.nacNo ratings yet
- Bleeding During PregnancyDocument4 pagesBleeding During PregnancyCarl Andre ReyesNo ratings yet
- GYN Module 3 Case 1: Gestational Trophoblastic NeoplasiaDocument21 pagesGYN Module 3 Case 1: Gestational Trophoblastic NeoplasiaElaine Marie Rendon PalmejarNo ratings yet
- Early Pregnancy ComplicationDocument31 pagesEarly Pregnancy ComplicationHizami NorddinNo ratings yet
- PIHDocument4 pagesPIHCatherine PradoNo ratings yet
- Post Partum ComplicationsDocument40 pagesPost Partum ComplicationsMahmoud Abu Al AmrainNo ratings yet
- GYN Module 3 Case 1: Gestational Trophoblastic NeoplasiaDocument21 pagesGYN Module 3 Case 1: Gestational Trophoblastic NeoplasiaElaine Marie Rendon PalmejarNo ratings yet
- High Risk PregnancyDocument12 pagesHigh Risk Pregnancyggrrk7100% (2)
- NCM 109 (PRELIMS) - Lesson 3Document17 pagesNCM 109 (PRELIMS) - Lesson 3nianNo ratings yet
- Pregnancy HypertensionDocument71 pagesPregnancy Hypertensionbazuu mbwegzeNo ratings yet
- Placenta PreviaDocument43 pagesPlacenta PreviaAngela Joy AmparadoNo ratings yet
- Placenta Abruptio: Maneja, Jan Michael B. BSN 223Document6 pagesPlacenta Abruptio: Maneja, Jan Michael B. BSN 223JiraGonzales100% (1)
- Obstetric Highlights, Elmar P. SakalaDocument47 pagesObstetric Highlights, Elmar P. Sakaladukelist5660% (1)
- Chapter 21Document69 pagesChapter 212082194No ratings yet
- Chapter 21 Sudden Pregnancy Complications YBOA 1Document6 pagesChapter 21 Sudden Pregnancy Complications YBOA 1syroise margauxNo ratings yet
- CA MaternalDocument156 pagesCA MaternalLovely Hope LugatimanNo ratings yet
- Maternal Reviewer FinalsDocument36 pagesMaternal Reviewer FinalsHannah QuindipanNo ratings yet
- Antepartum HaemorrhageDocument57 pagesAntepartum HaemorrhageLady350z100% (3)
- Complication of PregnancyDocument44 pagesComplication of PregnancyJharaNo ratings yet
- Gestational Conditions HandoutDocument17 pagesGestational Conditions HandoutFilamae Jayahr Caday100% (4)
- Perdarahan Antepartum - EmiliaDocument26 pagesPerdarahan Antepartum - EmiliaEmilia NazmaNo ratings yet
- 2 Pre Gestation and Gestational ConditionsDocument88 pages2 Pre Gestation and Gestational Conditionslermacornel61No ratings yet
- Ob Final ReviewDocument13 pagesOb Final Reviewraquel maniegoNo ratings yet
- Gestational ConditionsDocument4 pagesGestational ConditionsHyacinth Mae Virtudazo RaganasNo ratings yet
- #12 - NCM 109 (Rle) - TransesDocument4 pages#12 - NCM 109 (Rle) - TransesJaimie BanaagNo ratings yet
- Chapter21trans 1Document8 pagesChapter21trans 1syroise margauxNo ratings yet
- MANAGEMENT OF ABRUPTIO PLACENTAEDocument7 pagesMANAGEMENT OF ABRUPTIO PLACENTAEchdxemailNo ratings yet
- Abnormal Pregnancy1653 160118115626Document7 pagesAbnormal Pregnancy1653 160118115626sufian ahmadNo ratings yet
- Handout 4Document13 pagesHandout 4ApRil Anne BalanonNo ratings yet
- Placenta AbruptioDocument30 pagesPlacenta AbruptioArchana MaharjanNo ratings yet
- Seminar Gestational Trophoblastic DiseaseDocument27 pagesSeminar Gestational Trophoblastic DiseaseCourtney Dela FierraNo ratings yet
- Multiple PregnancesssssDocument29 pagesMultiple PregnancesssssNajjemba ShanitahNo ratings yet
- Thursday, February 11, 2021 8:04 PM: Chapter 21 Page 1Document29 pagesThursday, February 11, 2021 8:04 PM: Chapter 21 Page 1Christel Ann TianchonNo ratings yet
- A.1 AbortionDocument47 pagesA.1 AbortionRiza Mae Follero DanteNo ratings yet
- Multiple PregnancyDocument25 pagesMultiple PregnancyArya S BijuNo ratings yet
- Abnormalities of Amniotic FluidDocument32 pagesAbnormalities of Amniotic FluidMuhammad Abdillah100% (1)
- Hyperemesis, Hmole, Placenta PreviaDocument12 pagesHyperemesis, Hmole, Placenta Previadanica grace gubaNo ratings yet
- COURSE in The WARD Interhospital FinalDocument8 pagesCOURSE in The WARD Interhospital Finalkimadlo656No ratings yet
- PihDocument35 pagesPihmark100% (6)
- Ward Class - PCI, HPN DX in PregnancyDocument26 pagesWard Class - PCI, HPN DX in Pregnancyhrry stylesNo ratings yet
- Pregnancy ComplicationsDocument3 pagesPregnancy ComplicationsJeizel IgnacioNo ratings yet
- Pre-eclampsia, (Pregnancy with Hypertension And Proteinuria) A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandPre-eclampsia, (Pregnancy with Hypertension And Proteinuria) A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- It's Not Just a Heavy Period; The Miscarriage HandbookFrom EverandIt's Not Just a Heavy Period; The Miscarriage HandbookRating: 2 out of 5 stars2/5 (1)
- LAWS AND REGULATIONS DISASTER NURSING REVIEWERDocument2 pagesLAWS AND REGULATIONS DISASTER NURSING REVIEWERSJane FeriaNo ratings yet
- 3 Acid Base ImbalanceDocument5 pages3 Acid Base ImbalanceSJane FeriaNo ratings yet
- Head and NeckDocument41 pagesHead and NeckSJane FeriaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Module Therapeutic CommunicationDocument6 pagesChapter 3 Module Therapeutic CommunicationSJane FeriaNo ratings yet
- 1ST Term SummaryDocument5 pages1ST Term SummarySJane FeriaNo ratings yet
- 4 - CoparDocument4 pages4 - CoparSJane FeriaNo ratings yet
- ACE AND ARBs PRACTICE QUESTIONS HIghlightedDocument2 pagesACE AND ARBs PRACTICE QUESTIONS HIghlightedSJane FeriaNo ratings yet
- 4 Neurologic Nursing DisordersDocument4 pages4 Neurologic Nursing DisordersSJane FeriaNo ratings yet
- Disaster Preparedness 1Document10 pagesDisaster Preparedness 1SJane FeriaNo ratings yet
- Emergency Severity Index LEC MLT 2 10 24Document27 pagesEmergency Severity Index LEC MLT 2 10 24SJane FeriaNo ratings yet
- CD Cheat Sheet CompleteDocument6 pagesCD Cheat Sheet CompleteSJane FeriaNo ratings yet
- Endo SummarizedDocument8 pagesEndo SummarizedSJane FeriaNo ratings yet
- Chem and Hazmat MCI 2 13 24Document50 pagesChem and Hazmat MCI 2 13 24SJane FeriaNo ratings yet
- Urinary System1Document4 pagesUrinary System1SJane FeriaNo ratings yet
- TRANSCULTURALDocument5 pagesTRANSCULTURALSJane FeriaNo ratings yet
- Neurologic NursingDocument3 pagesNeurologic NursingSJane FeriaNo ratings yet
- MicroPara LabDocument2 pagesMicroPara LabSJane FeriaNo ratings yet
- DBD English-1Document7 pagesDBD English-1Risky Rahma Sari PutriNo ratings yet
- México Hígado GrasoDocument9 pagesMéxico Hígado GrasoAlan josue Hernandez lopezNo ratings yet
- Lebel1991 PDFDocument15 pagesLebel1991 PDFRamon CharlestienNo ratings yet
- OET Writing Case Notes Nursing 16 35Document38 pagesOET Writing Case Notes Nursing 16 35adnanshakeelm1No ratings yet
- Pet TherapyDocument2 pagesPet Therapyapi-543519166No ratings yet
- Scrutinizing The Fat Mass, Fat Free Mass, Fat Mass Index, Fat Free Mass Index Amidst Rural and Urban School Boys of PunjabDocument5 pagesScrutinizing The Fat Mass, Fat Free Mass, Fat Mass Index, Fat Free Mass Index Amidst Rural and Urban School Boys of Punjabnapinder singhNo ratings yet
- COT 2023 (First)Document6 pagesCOT 2023 (First)Rosalie dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Related Teenshealth Links: Health Problems SeriesDocument13 pagesRelated Teenshealth Links: Health Problems SeriesMario BadayosNo ratings yet
- RadioimmunassayDocument23 pagesRadioimmunassayVinayak Chura100% (1)
- Inguinal Hernia Case FileDocument2 pagesInguinal Hernia Case Filehttps://medical-phd.blogspot.comNo ratings yet
- Who Guideline On Use of Ferritin Concentrations To Assess Iron Status in Individuals and PopulationsDocument82 pagesWho Guideline On Use of Ferritin Concentrations To Assess Iron Status in Individuals and PopulationsLima NetNo ratings yet
- RealStar CCHFV RT-PCR Kit 1.0 - WEB - CE - EN-S02Document15 pagesRealStar CCHFV RT-PCR Kit 1.0 - WEB - CE - EN-S02saadNo ratings yet
- High Yield Pediatrics: Shelf Exam Review Emma Holliday RamahiDocument78 pagesHigh Yield Pediatrics: Shelf Exam Review Emma Holliday Ramahiskeebs230% (1)
- Pharma - SkinDocument8 pagesPharma - Skinreference books100% (1)
- 9D-NLS Features and Warranty (2021)Document10 pages9D-NLS Features and Warranty (2021)Danutz ChirilaNo ratings yet
- Registration Timings: OPD Schedule - Dr. Ram Manohar Lohia Institute of Medical Sciences (RMLIMS)Document8 pagesRegistration Timings: OPD Schedule - Dr. Ram Manohar Lohia Institute of Medical Sciences (RMLIMS)vivekNo ratings yet
- Donning Doffing Spotter Check List v1Document1 pageDonning Doffing Spotter Check List v1Rudyard Paul AmistadNo ratings yet
- Nature Review, Complete RevascularizationDocument14 pagesNature Review, Complete RevascularizationIván De LeónNo ratings yet
- Mapeh 10 Q3 M5Document27 pagesMapeh 10 Q3 M5Faye Anne Coy-omNo ratings yet
- Leaky Gut Solutions Guide - Peter OsborneDocument54 pagesLeaky Gut Solutions Guide - Peter OsborneFITPSNo ratings yet
- How To Store Vitafen: 1. What Vitafen Is and What It Is Used ForDocument7 pagesHow To Store Vitafen: 1. What Vitafen Is and What It Is Used FornurfaaaNo ratings yet
- CD HeightsDocument3 pagesCD HeightsTotal Pest ControlNo ratings yet
- National Programme For Prevention and Control of CancerDocument18 pagesNational Programme For Prevention and Control of CancerPrabhakaran AranganathanNo ratings yet
- ID Perbandingan Pemeriksaan ToksigenisitasDocument9 pagesID Perbandingan Pemeriksaan ToksigenisitasindahdwirahNo ratings yet
- Waterborne DiseasesDocument28 pagesWaterborne Diseasesm142106013 TMUNo ratings yet
- Review On Enterocutaneous FistulaDocument31 pagesReview On Enterocutaneous FistulaAbu ZidaneNo ratings yet
- Children Hypertension ChartDocument4 pagesChildren Hypertension ChartHo Yoke MeiNo ratings yet
- Health Sector in Ghana ReviewDocument17 pagesHealth Sector in Ghana ReviewBriant BlantonNo ratings yet