Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Wild pansy (flowering aerial parts)
Wild pansy (flowering aerial parts)
Uploaded by
aymenbiogalenicCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Wild pansy (flowering aerial parts)
Wild pansy (flowering aerial parts)
Uploaded by
aymenbiogalenicCopyright:
Available Formats
Wild pansy (flowering aerial parts) EUROPEAN PHARMACOPOEIA 11.
Calculate the percentage content of marrubiin from the arvensis) or 4 pores (Viola tricolor) ; occasional fragments
following expression : of spiral and reticulate vessels and groups of fibres from
the stem.
A1 ´ m 2 ´ p ´ 2.5
C. Thin-layer chromatography (2.2.27).
A 2 ´ m1
Test solution. Heat in a water-bath at 65 °C for 5 min, with
A1 = area of the peak due to marrubiin in the frequent stirring, 2.0 g of the powdered herbal drug (355)
chromatogram obtained with the test solution ; (2.9.12) in 10 mL of alcohol (70 per cent V/V) R. Cool and
filter.
A2 = area of the peak due to marrubiin in the
chromatogram obtained with the reference Reference solution. Dissolve 2.5 mg of rutoside trihydrate R,
solution ; 2.5 mg of hyperoside R and 1.0 mg of caffeic acid R in
methanol R and dilute to 10 mL with the same solvent.
m1 = mass of the herbal drug to be examined used to
Plate : TLC silica gel plate R.
prepare the test solution, in milligrams ;
m2 Mobile phase : anhydrous formic acid R, acetic acid R,
= mass of marrubiin CRS used to prepare the water R, ethyl acetate R (11:11:27:100 V/V/V/V).
reference solution, in milligrams ;
Application : 10 μL, as bands.
p = percentage content of marrubiin in marrubiin CRS. Development : over a path of 12 cm.
Drying : at 100-105 °C.
01/2008:1855 Detection : spray with a solution containing 10 g/L of
corrected 6.0 diphenylboric acid aminoethyl ester R and 50 g/L of
macrogol 400 R in methanol R. Allow the plate to dry in air
for 30 min. Examine in ultraviolet light at 365 nm.
Results : see below the sequence of the zones present in the
chromatograms obtained with the reference solution and
WILD PANSY the test solution. Furthermore, other zones may be present
in the chromatogram obtained with the test solution.
(FLOWERING AERIAL PARTS)
Top of the plate
Violae herba cum flore Caffeic acid : a greenish-blue to
light blue fluorescent zone
DEFINITION A blue fluorescent zone
Dried flowering aerial parts of Viola arvensis Murray and/or
Viola tricolor L.
_______ _______
Content : minimum 1.5 per cent of flavonoids, expressed as
violanthin (C27H30O14 ; Mr 578.5) (dried drug).
IDENTIFICATION Hyperoside : a yellowish-brown
fluorescent zone
A. The stem is angular and hollow. The leaves are oval, A yellowish-green fluorescent
petiolate, with a cordate base or elongated and obtuse, with zone
lyrate stipules, divided in the middle. The flowers, with a
long peduncle, are zygomorphic, with 5 oval, lanceolate
sepals, an appendage pointed outwards and 5 petals of _______ _______
which the lower one bears a spur ; in Viola arvensis, the Rutoside : a yellowish-brown An intense yellowish-brown
petals are shorter than the calyx, the lower petal is cream fluorescent zone fluorescent zone (rutoside)
coloured, with black lines, the 4 upper petals may be
cream coloured or violet blue ; in Viola tricolor, the petals A yellowish-green fluorescent
are longer than the calyx and violet coloured, more or zone
less tinged with yellow. The androecium consisting of A yellowish-green fluorescent
zone
5 stamens bears at the apex a membranous connective A yellowish-green fluorescent
appendage with 2 spurs. The trilocular ovary shows a zone
short style and globular stigmata. The fruit are navicular
capsules, three-lobed, yellowish brown, 5 mm to 10 mm
Reference solution Test solution
long. The pale yellow, pyriform seeds are about 1 mm long,
bearing a caruncle.
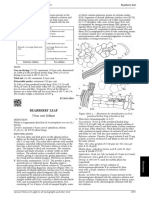
B. Microscopic examination (2.8.23). The powder is greenish. TESTS
Examine under a microscope using chloral hydrate Foreign matter (2.8.2) : maximum 3 per cent.
solution R. The powder shows the following diagnostic Swelling index (2.8.4) : minimum 9, determined on the
characters : fragments of the epidermis of the leaves in powdered herbal drug (355) (2.9.12).
surface view with wavy-walled cells and anomocytic
stomata (2.8.3) ; conical unicellular covering trichomes, Loss on drying (2.2.32) : maximum 12.0 per cent, determined
widened at the base and sharply pointed at the apex, with on 1.000 g of the powdered herbal drug (355) (2.9.12) by
a striated cuticle ; glandular trichomes with a multicellular drying in an oven at 105 °C for 2 h.
head, and a short, multicellular stalk in the indentations Total ash (2.4.16) : maximum 15.0 per cent.
of the leaf margins ; cluster crystals of calcium oxalate,
sometimes included in parenchyma ; fragments of the ASSAY
corolla with wavy-walled epidermal cells, those from the Stock solution. In a 200 mL flask, introduce 0.300 g of the
mid-region papillose and with some extended to form flask powdered herbal drug (250) (2.9.12) and 40 mL of alcohol
or bottle-shaped projections, those from the base of the (60 per cent V/V) R. Heat in a water-bath at 60 °C for 10 min,
petals with covering trichomes up to about 300 μm long shaking frequently. Allow to cool and filter through a plug of
with characteristic hump-like swellings along their length ; absorbent cotton into a 100 mL volumetric flask. Transfer the
spherical or polyhedral pollen grains, 60 μm to 80 μm absorbent cotton with the drug residue back into the 200 mL
in diameter, with finely pitted exines and 5 pores (Viola flask, add 40 mL of alcohol (60 per cent V/V) R and heat again
1776 See the information section on general monographs (cover pages)
www.webofpharma.com
EUROPEAN PHARMACOPOEIA 11.0 Wild thyme
in a water-bath at 60 °C for 10 min, shaking frequently. Allow B. Microscopic examination (2.8.23). The powder is
to cool and filter into the same 100 mL volumetric flask as greyish-green or greenish-brown. Examine under a
used previously. Rinse the 200 mL flask with a further quantity microscope using chloral hydrate solution R. The powder
of alcohol (60 per cent V/V) R, filter and transfer to the same shows the following diagnostic characters (Figure 1891.-1) :
100 mL volumetric flask. Dilute to volume with alcohol (60 per fragments of the leaf epidermises [A, B, F] covered by a
cent V/V) R and filter. finely striated cuticle and consisting of cells with sinuous
Test solution. Introduce 5.0 mL of the stock solution into anticlinal walls [Aa, Ba, Fa] and diacytic stomata (2.8.3)
a round-bottomed flask and evaporate to dryness under [Ab, Bb, Fb] ; cells of the adaxial leaf epidermis [B] with
reduced pressure. Take up the residue with 8 mL of a mixture wavy, irregularly thickened anticlinal walls [Ba] ; numerous
of 10 volumes of methanol R and 100 volumes of glacial acetic covering trichomes on both epidermises and the leaf
acid R and transfer into a 25 mL volumetric flask. Rinse the margins, with some of the cells containing very small
round-bottomed flask with 3 mL of a mixture of 10 volumes crystals of calcium oxalate [Af, Ca, Fd], the majority are
of methanol R and 100 volumes of glacial acetic acid R short, conical, unicellular, with thickened and warty walls
and transfer into the same 25 mL volumetric flask as used (surface view [Bc], side view [Fc]) ; fewer multicellular
previously. Add 10.0 mL of a solution containing 25.0 g/L of covering trichomes, long, tapering to a point, composed
boric acid R and 20.0 g/L of oxalic acid R in anhydrous formic of up to 8 cells, slightly swollen at the joints, with finely
acid R and dilute to 25.0 mL with anhydrous acetic acid R. pitted walls, on an epidermis [Ae] or fragmented [C] ;
Compensation liquid. Introduce 5.0 mL of the stock solution abundant glandular trichomes, mostly multicellular of
into a round-bottomed flask and evaporate to dryness under the lamiaceous type [Ac] with a unicellular stalk and a
reduced pressure. Take up the residue with 8 mL of a mixture glandular head consisting of 12 inconspicuous cells, others
of 10 volumes of methanol R and 100 volumes of glacial with a unicellular stalk and a unicellular globular or ovoid
acetic acid R and transfer into a 25 mL volumetric flask. head [Ad] ; purplish-violet fragments of the corolla whose
Rinse the round-bottomed flask with 3 mL of a mixture of inner epidermis consists of cells with rounded papillae [D]
10 volumes of methanol R and 100 volumes of glacial acetic and whose outer epidermis [E], with a striated cuticle,
acid R and transfer into the same 25 mL volumetric flask as consists of cells with lobed walls [Ea], unicellular [Eb] or
used previously. Add 10.0 mL of anhydrous formic acid R and multicellular [Ec] uniseriate covering trichomes, glandular
dilute to 25.0 mL with anhydrous acetic acid R. trichomes with a unicellular head and a unicellular stalk
[Ed] and glandular trichomes of the lamiaceous type ;
Measure the absorbance (2.2.25) of the test solution at 405 nm relatively rare pollen grains, spherical, about 30 μm in
after 30 min. diameter, with a finely pitted exine and 6 germinal pores
Calculate the percentage content of total flavonoids, expressed [G].
as violanthin from the expression :
A ´ 1.25
m
taking the specific absorbance of violanthin to be 400.
A = measured absorbance at 405 nm,
m = mass of the herbal drug to be examined, in grams.
07/2014:1891
WILD THYME
Serpylli herba
DEFINITION
Whole or cut, dried, flowering aerial parts of Thymus
serpyllum L.
Content : minimum 3.0 mL/kg of essential oil (dried drug).
IDENTIFICATION
A. The stem is much branched, up to about 1.5 mm in
diameter, cylindrical or indistinctly quadrangular, green,
reddish or purplish, the older stems brown and woody, the
younger stems pubescent. The leaves are opposite, 3-12 mm
long and up to 4 mm wide, elliptical to ovate-lanceolate
with an obtuse apex, cuneate and shortly petiolate at the
base ; the margin is entire and markedly ciliate, especially
near the base ; both surfaces are more or less glabrous but
distinctly punctate. The inflorescence is composed of about Figure 1891.-1.– Illustration for identification test B of
6-12 flowers in rounded to ovoid, terminal heads. The calyx powdered herbal drug of wild thyme
is tubular, 2-lipped with the upper lip dividing to form
3 teeth, the lower lip with 2 teeth, edged with long hairs ; C. Thin-layer chromatography (2.2.27).
the inner surfaces are strongly pubescent, the hairs forming Test solution. To 0.5 g of the powdered herbal drug (355)
a closed tube after flowering. The corolla is purplish-violet (2.9.12) add 5 mL of methanol R. Sonicate for 10 min.
or red, 2-lipped, the lower lip with 3 lobes and the upper Centrifuge or filter ; use the supernatant or the filtrate.
lip notched, the inner surface is strongly pubescent ; 4 Reference solution. Dissolve 1 mg of rutoside trihydrate R
epipetalous stamens project from the corolla tube. and 1 mg of rosmarinic acid R in 5 mL of methanol R.
General Notices (1) apply to all monographs and other texts 1777
www.webofpharma.com
You might also like
- Plant Structure Lab Report 3 PDFDocument4 pagesPlant Structure Lab Report 3 PDFVermilah Ann Despi67% (6)
- Wild thymeDocument2 pagesWild thymeaymenbiogalenicNo ratings yet
- Centellae Asiaticae Herba: CentellaDocument2 pagesCentellae Asiaticae Herba: Centella0039Phùng Ngân LộcNo ratings yet
- Thymi HerbaDocument3 pagesThymi HerbaArtem KulikovNo ratings yet
- Thymi HerbaDocument3 pagesThymi HerbaartemNo ratings yet
- Origani HerbaDocument3 pagesOrigani HerbaArtem KulikovNo ratings yet
- Menthae Piperitae FoliumDocument2 pagesMenthae Piperitae FoliumartemNo ratings yet
- Willow barkDocument2 pagesWillow barkaymenbiogalenicNo ratings yet
- Lupuli FlosDocument2 pagesLupuli FlosArtem KulikovNo ratings yet
- Alfalfa For Homoeopathic Preparations Alfalfa For Homoeopathic PreparationsDocument3 pagesAlfalfa For Homoeopathic Preparations Alfalfa For Homoeopathic PreparationsmuhammadNo ratings yet
- Millefolii HerbaDocument2 pagesMillefolii HerbaArtem KulikovNo ratings yet
- Angelicae Archangelicae RadixDocument2 pagesAngelicae Archangelicae RadixArtem KulikovNo ratings yet
- Rosmarinus - Farmakope MonografıDocument3 pagesRosmarinus - Farmakope Monografıeylul.irmak.tNo ratings yet
- YarrowDocument2 pagesYarrowaymenbiogalenicNo ratings yet
- Bitter-Orange-epicarp and Mesocarp TinctureDocument2 pagesBitter-Orange-epicarp and Mesocarp TinctureNikotiano TobacumNo ratings yet
- Equiseti HerbaDocument3 pagesEquiseti HerbaArtem KulikovNo ratings yet
- Flos and Fruit PowderDocument46 pagesFlos and Fruit PowderAÏCHA GnosisteNo ratings yet
- White Horehound: Marrubii HerbaDocument2 pagesWhite Horehound: Marrubii HerbaArtem KulikovNo ratings yet
- Uvae Ursi FoliumDocument2 pagesUvae Ursi FoliumartemNo ratings yet
- Angelicae Pubescentis RadixDocument3 pagesAngelicae Pubescentis RadixartemNo ratings yet
- Agaricus Phalloides For Homoeopathic PreparationDocument7 pagesAgaricus Phalloides For Homoeopathic PreparationMTG_1234No ratings yet
- Yarrow For Homoeopathic Preparations Millefolium For Homoeopathic PreparationsDocument4 pagesYarrow For Homoeopathic Preparations Millefolium For Homoeopathic PreparationsHasan Abu AlhabNo ratings yet
- Agrimoniae HerbaDocument2 pagesAgrimoniae HerbaartemNo ratings yet
- Sambuci FlosDocument3 pagesSambuci FlosartemNo ratings yet
- Matricaria Flower: Matricariae OsDocument2 pagesMatricaria Flower: Matricariae OsArtem KulikovNo ratings yet
- Angelicae Sinensis RadixDocument2 pagesAngelicae Sinensis RadixArtem KulikovNo ratings yet
- 6 1 200 Ipecacuanha-Root - (Ipecacuanhae-Radix)Document2 pages6 1 200 Ipecacuanha-Root - (Ipecacuanhae-Radix)Fitry Ana UtamNo ratings yet
- Ipecacuanha Tincture, StandardisedDocument2 pagesIpecacuanha Tincture, StandardisedJjangyiNo ratings yet
- Allium Sativum For Homoeopathic PreparationsDocument2 pagesAllium Sativum For Homoeopathic PreparationsMTG_1234No ratings yet
- Pharmacopee Francaise - Field Horsetail FHP - Equisetum Arvense PPHDocument4 pagesPharmacopee Francaise - Field Horsetail FHP - Equisetum Arvense PPHValentina MolinaNo ratings yet
- Foeniculi FructusDocument3 pagesFoeniculi FructusHaitao GuanNo ratings yet
- Zanthoxylum bungeanum pericarpDocument2 pagesZanthoxylum bungeanum pericarpaymenbiogalenicNo ratings yet
- GoldenrodDocument3 pagesGoldenrodnguyentuanson167No ratings yet
- Solidaginis HerbaDocument2 pagesSolidaginis HerbaartemNo ratings yet
- Anacardium For Homoeopathic PreparationsDocument4 pagesAnacardium For Homoeopathic PreparationsMTG_1234No ratings yet
- Lavandulae Flos PH Eur PDFDocument2 pagesLavandulae Flos PH Eur PDFCeangoNo ratings yet
- Senna Lea Et: Time (Min) Mobile Phase A (Per Cent Mobile Phase B (Per CentDocument3 pagesSenna Lea Et: Time (Min) Mobile Phase A (Per Cent Mobile Phase B (Per CentartemNo ratings yet
- Ipecacuanha Tincture, StandardisedDocument2 pagesIpecacuanha Tincture, StandardisedRhosuna AinaNo ratings yet
- Melissa LeafDocument2 pagesMelissa LeafArtem KulikovNo ratings yet
- Turmeric RhizomeDocument2 pagesTurmeric RhizomeGrenfell VPKNo ratings yet
- MONOGRAPHIE Purple Cone FlowerDocument3 pagesMONOGRAPHIE Purple Cone Flowerasmae.labindusNo ratings yet
- Betulae FoliumDocument3 pagesBetulae FoliumartemNo ratings yet
- White horehoundDocument3 pagesWhite horehoundaymenbiogalenicNo ratings yet
- Fenugreek Droga PE1323EDocument2 pagesFenugreek Droga PE1323Eisabelle.pradoNo ratings yet
- WormwoodDocument2 pagesWormwoodaymenbiogalenicNo ratings yet
- Chapter A: New Text of The German PharmacopoeiaDocument9 pagesChapter A: New Text of The German PharmacopoeiaAlessandra SeverinoNo ratings yet
- Eucalyptus OilDocument2 pagesEucalyptus Oilsheenali0% (1)
- IPECACUANHADocument3 pagesIPECACUANHALeonardo Henrique SiqueiraNo ratings yet
- 7 - Flavonoid Drugs Incl Ginkgo Biloba and Echinaceae SpeciesDocument51 pages7 - Flavonoid Drugs Incl Ginkgo Biloba and Echinaceae SpeciesAmmy Joana Gallegos GarcíaNo ratings yet
- Hawthorn Berries: Crataegi FructusDocument2 pagesHawthorn Berries: Crataegi FructusartemNo ratings yet
- Crataegus Oxycanthalinné (Fam - Rosaceae) .It Contains Not Less Than 0.6percent of C-GlycosylatedDocument3 pagesCrataegus Oxycanthalinné (Fam - Rosaceae) .It Contains Not Less Than 0.6percent of C-GlycosylatedcarbouNo ratings yet
- Aniseed - British Pharmacopoeia 2012 UpdatedDocument3 pagesAniseed - British Pharmacopoeia 2012 UpdatedRoger (Sisfarma)No ratings yet
- Antimicrobial Activity of Terpenoids From Sphaeranthus Indicus. LDocument6 pagesAntimicrobial Activity of Terpenoids From Sphaeranthus Indicus. LAgus HendraNo ratings yet
- Bitter Drugs: Preparation of ExtractsDocument25 pagesBitter Drugs: Preparation of ExtractsAmmy Joana Gallegos GarcíaNo ratings yet
- Tormentillae RhizomaDocument1 pageTormentillae RhizomaartemNo ratings yet
- AssignmentFile 867 13092023121819Document13 pagesAssignmentFile 867 13092023121819Prince DograNo ratings yet
- Papain: ThevohimeofacetoniirlleDocument2 pagesPapain: ThevohimeofacetoniirlleLTV TM DVNo ratings yet
- 6.1.323.senna-Leaf - (Sennae-Folium) Monograph by IP 9ed, 2019 From WHODocument2 pages6.1.323.senna-Leaf - (Sennae-Folium) Monograph by IP 9ed, 2019 From WHOMaikel Perez NavarroNo ratings yet
- Identification of Plant Pigments (Carotenoids) by Thin LayeDocument7 pagesIdentification of Plant Pigments (Carotenoids) by Thin LayeRegina PramuditaNo ratings yet
- Growing Succulents: A Pictorial Guide (Over 1,500 photos and 700 plants)From EverandGrowing Succulents: A Pictorial Guide (Over 1,500 photos and 700 plants)No ratings yet
- Flora Zambesiaca Volume 12 Part 1: Araceae (Including Lemnaceae)From EverandFlora Zambesiaca Volume 12 Part 1: Araceae (Including Lemnaceae)No ratings yet
- Wheat-germ oil, virginDocument1 pageWheat-germ oil, virginaymenbiogalenicNo ratings yet
- Vinorelbine tartrateDocument3 pagesVinorelbine tartrateaymenbiogalenicNo ratings yet
- VinpocetineDocument2 pagesVinpocetineaymenbiogalenicNo ratings yet
- Vibriosis vaccine (inactivated) for salmonidsDocument2 pagesVibriosis vaccine (inactivated) for salmonidsaymenbiogalenicNo ratings yet
- VigabatrinDocument2 pagesVigabatrinaymenbiogalenicNo ratings yet
- White horehoundDocument3 pagesWhite horehoundaymenbiogalenicNo ratings yet
- Zuclopenthixol decanoateDocument2 pagesZuclopenthixol decanoateaymenbiogalenicNo ratings yet
- Zinc sulfate heptahydrateDocument1 pageZinc sulfate heptahydrateaymenbiogalenicNo ratings yet
- Vibriosis vaccine (inactivated) for sea bassDocument2 pagesVibriosis vaccine (inactivated) for sea bassaymenbiogalenicNo ratings yet
- 2.2.40. Near-infrared spectroscopyDocument6 pages2.2.40. Near-infrared spectroscopyaymenbiogalenicNo ratings yet
- 1C18060-AC-9102-01 - P&ID CTA 01 - RoomsDocument1 page1C18060-AC-9102-01 - P&ID CTA 01 - RoomsaymenbiogalenicNo ratings yet
- 2.2.4. Approximate pH of solutionsDocument1 page2.2.4. Approximate pH of solutionsaymenbiogalenicNo ratings yet
- 1c18060-Ac-9301-00 - P&id Cta 03 - AhDocument1 page1c18060-Ac-9301-00 - P&id Cta 03 - AhaymenbiogalenicNo ratings yet
- 2.2.6. Refractive indexDocument1 page2.2.6. Refractive indexaymenbiogalenicNo ratings yet
- 2.2.2. Degree of coloration of liquidsDocument4 pages2.2.2. Degree of coloration of liquidsaymenbiogalenicNo ratings yet
- 1c18060-Ac-9201-01 - P&id Cta 02 - AhDocument1 page1c18060-Ac-9201-01 - P&id Cta 02 - AhaymenbiogalenicNo ratings yet
- 1C18060-AC-9302-00 - P&ID CTA 03 - RoomsDocument1 page1C18060-AC-9302-00 - P&ID CTA 03 - RoomsaymenbiogalenicNo ratings yet
- Zoledronic acid monohydrateDocument2 pagesZoledronic acid monohydrateaymenbiogalenicNo ratings yet
- 1c18060-Ac-9801-00 - P&id Cta 08 - AhDocument1 page1c18060-Ac-9801-00 - P&id Cta 08 - AhaymenbiogalenicNo ratings yet
- 1C18060-AC-9202-01 - P&ID CTA 02 - RoomsDocument1 page1C18060-AC-9202-01 - P&ID CTA 02 - RoomsaymenbiogalenicNo ratings yet
- 1C18060-AC-9702-01 - P&ID CTA 07 - RoomsDocument1 page1C18060-AC-9702-01 - P&ID CTA 07 - RoomsaymenbiogalenicNo ratings yet
- 1c18060-Ac-9901-00 - P&id Cta Fresh AirDocument1 page1c18060-Ac-9901-00 - P&id Cta Fresh AiraymenbiogalenicNo ratings yet
- Tax Morfo Ast Cardueae Susanna2019Document11 pagesTax Morfo Ast Cardueae Susanna2019J CamiloNo ratings yet
- Pharmacognostic Standardization of The Leaves and Root Bark of Caesalpinia BenthamianaDocument4 pagesPharmacognostic Standardization of The Leaves and Root Bark of Caesalpinia BenthamianaMegi LimbaNo ratings yet
- Vol. 33. Pilocarpinae. Kaastra, R. 1982 PDFDocument200 pagesVol. 33. Pilocarpinae. Kaastra, R. 1982 PDFbioandreyNo ratings yet
- Morphological Studies On Three Amaranthus Species: Svetoslava Terzieva, Neli Grozeva, Katya VelichkovaDocument5 pagesMorphological Studies On Three Amaranthus Species: Svetoslava Terzieva, Neli Grozeva, Katya Velichkovaolajummy675No ratings yet
- (World Crops_ Production, Utilization, And Description 7) a. M. Bosabalidis, I. Tsekos (Auth.), Nikos Margaris, Arthur Koedam, Despina Vokou (Eds.)-Aromatic Plants_ Basic and Applied Aspects-SpringerDocument280 pages(World Crops_ Production, Utilization, And Description 7) a. M. Bosabalidis, I. Tsekos (Auth.), Nikos Margaris, Arthur Koedam, Despina Vokou (Eds.)-Aromatic Plants_ Basic and Applied Aspects-SpringerquininogroNo ratings yet
- Kistamma Singanaboina and Venkateshwar Chinna PDFDocument10 pagesKistamma Singanaboina and Venkateshwar Chinna PDFDeependra Yadav0% (1)
- ZIZKA Bromeliaceae ChileDocument22 pagesZIZKA Bromeliaceae ChileJoaquín Eduardo Sepúlveda AstudilloNo ratings yet
- Surgical DressingsDocument14 pagesSurgical DressingsFaisal Rana100% (1)
- PolygonumDocument40 pagesPolygonum167 AmmarNo ratings yet
- Morfologi TumbuhanDocument8 pagesMorfologi TumbuhanEryNo ratings yet
- IJCRT2106647Document10 pagesIJCRT2106647Darshan RNo ratings yet
- Module On LeavesDocument28 pagesModule On LeavesCharles Linelle MendozaNo ratings yet
- Conneely (2020) Characterization of The Cannabis Sativa Glandular Trichome ProteomeDocument209 pagesConneely (2020) Characterization of The Cannabis Sativa Glandular Trichome ProteomeJ. Joaquin Varela-RestrepoNo ratings yet
- Ijnpr 6 (4) 261-267Document7 pagesIjnpr 6 (4) 261-267pamely peseNo ratings yet
- Analysis and Review of Trichomes in PlantsDocument11 pagesAnalysis and Review of Trichomes in Plantsjose juanNo ratings yet
- 1926-Article Text-7798-3-10-20191117 PDFDocument11 pages1926-Article Text-7798-3-10-20191117 PDFJan Angela BaylonNo ratings yet
- Morphological Basis of Resistance in Plants To InsectsDocument12 pagesMorphological Basis of Resistance in Plants To Insectshasu9749No ratings yet
- Geranium Andina-Chilensia (Reviction) GeraniaceaeDocument68 pagesGeranium Andina-Chilensia (Reviction) GeraniaceaeJorge Hernán Macaya BertiNo ratings yet
- Insect ResistanceDocument14 pagesInsect ResistanceSuneel SharmaNo ratings yet
- A Method For Microclonal Propagation of Staurogyne Repens in Tissue CultureDocument53 pagesA Method For Microclonal Propagation of Staurogyne Repens in Tissue CulturecatalinNo ratings yet
- Abunance Biofertilizer CyanobactDocument4 pagesAbunance Biofertilizer CyanobactkuldeepdeepikaNo ratings yet
- Trichomes As Models For Studying Plant Cell Differentiation: Cellular and Molecular Life SciencesDocument12 pagesTrichomes As Models For Studying Plant Cell Differentiation: Cellular and Molecular Life Sciencesjose juanNo ratings yet
- Preliminary Phytochemical and Pharmacognostical Screening of The Ayurvedic Drug Hygrophila Auriculata (K. Schum) HeineDocument13 pagesPreliminary Phytochemical and Pharmacognostical Screening of The Ayurvedic Drug Hygrophila Auriculata (K. Schum) HeineKicky Chaca100% (1)
- Potter Thesis 2009Document255 pagesPotter Thesis 2009projectcbd100% (1)
- Anatomy of Vegetative Organs of Scutellaria AgrestDocument13 pagesAnatomy of Vegetative Organs of Scutellaria AgrestValeria CasiqueNo ratings yet
- Coleus LeavesDocument23 pagesColeus Leaves존 셔윈No ratings yet
- Olympic 2018Document303 pagesOlympic 2018Tiến KhangNo ratings yet
- Dheeraj BishtDocument38 pagesDheeraj Bishtdheeraj bishtNo ratings yet
- Analytical PharmacognosyDocument16 pagesAnalytical PharmacognosySAIDALAVI KMNo ratings yet