Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Willow bark
Willow bark
Uploaded by
aymenbiogalenicCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Willow bark
Willow bark
Uploaded by
aymenbiogalenicCopyright:
Available Formats
Willow bark EUROPEAN PHARMACOPOEIA 11.
Plate : TLC silica gel F254 plate R (5-40 μm) [or TLC silica 01/2013:1583
gel F254 plate R (2-10 μm)].
Mobile phase : anhydrous formic acid R, water R, ethyl
acetate R (1:1:15 V/V/V).
Application : 20 μL [or 5 μL] as bands of 20 mm [or 8 mm]. WILLOW BARK
Development : over a path of 15 cm [or 6 cm]. Salicis cortex
Drying : in air. DEFINITION
Whole or fragmented dried bark of young branches or
Detection : heat at 100 °C for 3 min ; treat the still-hot plate whole dried pieces of current-year twigs of various species of
with a 5 g/L solution of diphenylboric acid aminoethyl genus Salix including S. purpurea L., S. daphnoides Vill. and
ester R in ethyl acetate R, then treat with a 50 g/L solution S. fragilis L.
of macrogol 400 R in methylene chloride R ; examine in
Content : minimum 1.5 per cent of total salicylic derivatives,
ultraviolet light at 365 nm.
expressed as salicin (C13H18O7 ; Mr 286.3) (dried drug).
Results : see below the sequence of zones present in the IDENTIFICATION
chromatograms obtained with the reference solution and
A. The bark is 1-2 mm thick and occurs in flexible, elongated,
the test solution. Furthermore, other faint fluorescent
quilled or curved pieces. The outer surface is smooth
zones may be present in the chromatogram obtained with
or slightly wrinkled longitudinally and greenish-yellow
the test solution.
or brownish-grey. The inner surface is smooth or
finely striated longitudinally and white, pale yellow or
Top of the plate reddish-brown, depending on the species. The fracture is
A red fluorescent zone short in the outer part and coarsely fibrous in the inner
region. The diameter of current-year twigs is not greater
than 10 mm. The wood is white or pale yellow.
Rosmarinic acid : a blue A blue fluorescent zone
fluorescent zone (rosmarinic acid)
_______ _______
1 or 2 blue fluorescent zones
_______ _______
A yellow or orange fluorescent
zone
A green or blue fluorescent zone
may be present
Rutoside : an orange-yellow
fluorescent zone
Reference solution Test solution
TESTS
Foreign matter (2.8.2) : maximum 3 per cent, determined on
30 g.
Thymus vulgaris L. or Thymus zygis L. Adulteration with
T. vulgaris L. or T. zygis L. is indicated by the presence of
acicular to linear-lanceolate leaves with a strongly bent margin,
the adaxial surface showing covering trichomes shaped as
pointed teeth with warty walls, the abaxial surface showing
many types of warty covering trichomes : unicellular, straight
or slightly curved, bicellular or tricellular, often elbow-shaped,
and bicellular or tricellular, more or less straight.
Loss on drying (2.2.32) : maximum 10.0 per cent, determined
on 1.000 g of the powdered herbal drug (355) (2.9.12) by
drying in an oven at 105 °C for 2 h.
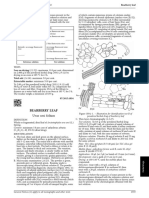
Figure 1583.-1. – Illustration for identification test B of
Total ash (2.4.16) : maximum 10.0 per cent. powdered herbal drug of willow bark
Ash insoluble in hydrochloric acid (2.8.1): maximum 3.0 per B. Microscopic examination (2.8.23). The powder is pale
cent. yellow, greenish-yellow or light brown. Examine under a
microscope using chloral hydrate solution R. The powder
shows the following diagnostic characters (Figure 1583.-1) :
bundles [B, C] of narrow fibres [Ba, Ca], up to about 600 μm
ASSAY
long, with very thick walls and surrounded by a crystal
Essential oil (2.8.12). Use 50.0 g of the cut herbal drug, a sheath containing prisms of calcium oxalate [Bb, Cb] ;
1000 mL round-bottomed flask and 500 mL of water R as parenchymatous cells of the cortex [D, J], with thick, pitted
the distillation liquid. Distil at a rate of 2-3 mL/min for 2 h and deeply beaded walls [Da], and containing large cluster
without xylene R in the graduated tube. crystals of calcium oxalate [Ga, Ja] ; some parenchyma
1778 See the information section on general monographs (cover pages)
www.webofpharma.com
EUROPEAN PHARMACOPOEIA 11.0 Willow bark dry extract
cells are collenchymatous [G] ; uniseriate medullary rays volumetric flask, wash and dilute to 100.0 mL with a mixture
(tangential section [Db]) ; thickened cork cells (surface of equal volumes of methanol R and water R. Filter through a
view [F]) ; numerous scattered prism crystals [E] and membrane filter (nominal pore size 0.45 μm).
cluster crystals [A] of calcium oxalate ; fragments of Reference solution. Dissolve 5.0 mg of picein R in 25.0 mL
brownish collenchyma from the buds may also be present. of a mixture of 20 volumes of water R and 80 volumes of
Twigs show, additionally, wood fragments [H] composed methanol R (solution A). Dissolve 15.0 mg of salicin CRS in
of lignified fibres [Ha] and vessels [Hb], sometimes 25 mL of a mixture of 20 volumes of water R and 80 volumes
accompanied by medullary rays [Hc]. of methanol R ; add 5.0 mL of solution A and dilute to 50.0 mL
C. Thin-layer chromatography (2.2.27). with water R.
Test solution (a). To 1.0 g of the powdered herbal drug Column :
(355) (2.9.12) add 10 mL of methanol R. Heat on a – size : l = 0.10 m, Ø = 4.6 mm ;
water-bath at about 50 °C, with frequent shaking, for – stationary phase : octadecylsilyl silica gel for
10 min. Cool and filter. chromatography R (3 μm).
Test solution (b). To 5.0 mL of test solution (a) add 1.0 mL Mobile phase :
of a 50 g/L solution of anhydrous sodium carbonate R and
heat in a water-bath at about 60 °C for 10 min. Cool and – mobile phase A : tetrahydrofuran R, 0.5 per cent V/V
filter if necessary. solution of phosphoric acid R (1.8:98.2 V/V) ;
Reference solution. Dissolve 2 mg of salicin R and 2 mg of – mobile phase B : tetrahydrofuran R ;
chlorogenic acid R in 1.0 mL of methanol R. Time Mobile phase A Mobile phase B
Plate : TLC silica gel plate R (5-40 μm) [or TLC silica gel (min) (per cent V/V) (per cent V/V)
plate R (2-10 μm)].
Mobile phase : water R, methanol R, ethyl acetate R 0 - 15 100 0
(8:15:77 V/V/V). 15 - 17 100 → 90 0 → 10
Application : 10 μL [or 2 μL] as bands.
17 - 23 90 10
Development : over a path of 15 cm [or 6 cm].
Drying : in a current of warm air. Flow rate : 1.0 mL/min.
Detection : treat with a mixture of 5 volumes of sulfuric Detection : spectrophotometer at 270 nm.
acid R and 95 volumes of methanol R. Heat at 100-105 °C Injection : 10 μL.
for 5 min and examine in daylight.
Retention time : salicin = about 6.4 min ; pi-
Results : see below the sequence of zones present in the cein = about 7.7 min.
chromatograms obtained with the reference solution
and test solutions (a) and (b). Furthermore, other zones System suitability : reference solution :
may be present in the chromatograms obtained with test – resolution : minimum 1.5 between the peaks due to salicin
solutions (a) and (b). and picein.
Calculate the percentage content of total salicylic derivatives,
Top of the plate expressed as salicin, using the following expression :
_______ _______ A1 ´ m 2 ´ p ´ 2
Several reddish- A 2 ´ m1
violet zones may be
present
A1 = area of the peak due to salicin in the chromatogram
Salicin : a reddish- A weak reddish- A reddish-violet zone obtained with the test solution ;
violet zone violet zone (salicin) (salicin)
A2 = area of the peak due to salicin in the chromatogram
_______ _______ obtained with the reference solution ;
Chlorogenic acid : a m1
brown zone = mass of the herbal drug to be examined used to
prepare the test solution, in grams ;
Reference solution Test solution (a) Test solution (b)
m2 = mass of salicin CRS used to prepare the reference
TESTS solution, in grams ;
Foreign matter (2.8.2) : maximum 3 per cent of twigs with p = percentage content of salicin in salicin CRS.
a diameter greater than 10 mm and maximum 2 per cent of
other foreign matter.
Cadmium (2.4.27): maximum 2.0 ppm.
04/2008:2312
Loss on drying (2.2.32): maximum 11 per cent, determined
on 1.000 g of the powdered herbal drug (355) (2.9.12) by
drying in an oven at 105 °C for 2 h.
Total ash (2.4.16) : maximum 10 per cent.
ASSAY WILLOW BARK DRY EXTRACT
Liquid chromatography (2.2.29).
Test solution. To 1.000 g of the powdered herbal drug (355) Salicis corticis extractum siccum
(2.9.12) add 40 mL of methanol R and 40.0 mL of a 4.2 g/L DEFINITION
solution of sodium hydroxide R. Heat in a water-bath at about
60 °C under a reflux condenser, with frequent shaking, for Dry extract produced from Willow bark (1583).
about 1 h. After cooling, add 4.0 mL of a 103.0 g/L solution Content : minimum 5.0 per cent of total salicylic derivatives,
of hydrochloric acid R. Filter the suspension into a 100 mL expressed as salicin (C13H18O7 ; Mr 286.3) (dried extract).
General Notices (1) apply to all monographs and other texts 1779
www.webofpharma.com
You might also like
- Cae Writing GuideDocument60 pagesCae Writing Guideelisadp95% (20)
- Special Quadrilaterals: Honors GeometryDocument38 pagesSpecial Quadrilaterals: Honors GeometryMuhammad MirzaNo ratings yet
- Ballet Arts Young Children: Classwork & Teaching Helps For The Ballet Teacher of Children Ages 4 & 5Document39 pagesBallet Arts Young Children: Classwork & Teaching Helps For The Ballet Teacher of Children Ages 4 & 5L100% (1)
- Wild thymeDocument2 pagesWild thymeaymenbiogalenicNo ratings yet
- Rosmarinus - Farmakope MonografıDocument3 pagesRosmarinus - Farmakope Monografıeylul.irmak.tNo ratings yet
- Lupuli FlosDocument2 pagesLupuli FlosArtem KulikovNo ratings yet
- Angelicae Sinensis RadixDocument2 pagesAngelicae Sinensis RadixArtem KulikovNo ratings yet
- Centellae Asiaticae Herba: CentellaDocument2 pagesCentellae Asiaticae Herba: Centella0039Phùng Ngân LộcNo ratings yet
- YarrowDocument2 pagesYarrowaymenbiogalenicNo ratings yet
- Angelicae Archangelicae RadixDocument2 pagesAngelicae Archangelicae RadixArtem KulikovNo ratings yet
- Menthae Piperitae FoliumDocument2 pagesMenthae Piperitae FoliumartemNo ratings yet
- Thymi HerbaDocument3 pagesThymi HerbaartemNo ratings yet
- Thymi HerbaDocument3 pagesThymi HerbaArtem KulikovNo ratings yet
- Willow Bark 1583eDocument2 pagesWillow Bark 1583eBogdan CioroiuNo ratings yet
- Betulae FoliumDocument3 pagesBetulae FoliumartemNo ratings yet
- Millefolii HerbaDocument2 pagesMillefolii HerbaArtem KulikovNo ratings yet
- Wild pansy (flowering aerial parts)Document2 pagesWild pansy (flowering aerial parts)aymenbiogalenicNo ratings yet
- Sambuci FlosDocument3 pagesSambuci FlosartemNo ratings yet
- Angelicae Pubescentis RadixDocument3 pagesAngelicae Pubescentis RadixartemNo ratings yet
- Origani HerbaDocument3 pagesOrigani HerbaArtem KulikovNo ratings yet
- 1847 eDocument3 pages1847 eMiroslav IlicNo ratings yet
- Ipecacuanha Tincture, StandardisedDocument2 pagesIpecacuanha Tincture, StandardisedRhosuna AinaNo ratings yet
- Matricaria Flower: Matricariae OsDocument2 pagesMatricaria Flower: Matricariae OsArtem KulikovNo ratings yet
- Cotton, Absorbent: Lanugo Gossypii AbsorbensDocument2 pagesCotton, Absorbent: Lanugo Gossypii AbsorbensHamed GholamiNo ratings yet
- Uvae Ursi FoliumDocument2 pagesUvae Ursi FoliumartemNo ratings yet
- Melissa LeafDocument2 pagesMelissa LeafArtem KulikovNo ratings yet
- Ipecacuanha Tincture, StandardisedDocument2 pagesIpecacuanha Tincture, StandardisedJjangyiNo ratings yet
- WormwoodDocument2 pagesWormwoodaymenbiogalenicNo ratings yet
- Senna Lea Et: Time (Min) Mobile Phase A (Per Cent Mobile Phase B (Per CentDocument3 pagesSenna Lea Et: Time (Min) Mobile Phase A (Per Cent Mobile Phase B (Per CentartemNo ratings yet
- Agrimoniae HerbaDocument2 pagesAgrimoniae HerbaartemNo ratings yet
- GoldenrodDocument3 pagesGoldenrodnguyentuanson167No ratings yet
- Solidaginis HerbaDocument2 pagesSolidaginis HerbaartemNo ratings yet
- 6 1 200 Ipecacuanha-Root - (Ipecacuanhae-Radix)Document2 pages6 1 200 Ipecacuanha-Root - (Ipecacuanhae-Radix)Fitry Ana UtamNo ratings yet
- Equiseti HerbaDocument3 pagesEquiseti HerbaArtem KulikovNo ratings yet
- kiểm nghiệm theo European pharmacopeiaDocument3 pageskiểm nghiệm theo European pharmacopeiaktrang.vt2001No ratings yet
- Viscose wadding, absorbentDocument3 pagesViscose wadding, absorbentaymenbiogalenicNo ratings yet
- Yarrow For Homoeopathic Preparations Millefolium For Homoeopathic PreparationsDocument4 pagesYarrow For Homoeopathic Preparations Millefolium For Homoeopathic PreparationsHasan Abu AlhabNo ratings yet
- Tormentillae RhizomaDocument1 pageTormentillae RhizomaartemNo ratings yet
- Willow bark dry extractDocument2 pagesWillow bark dry extractaymenbiogalenicNo ratings yet
- Fenugreek Droga PE1323EDocument2 pagesFenugreek Droga PE1323Eisabelle.pradoNo ratings yet
- White Horehound: Marrubii HerbaDocument2 pagesWhite Horehound: Marrubii HerbaArtem KulikovNo ratings yet
- Chapter A: New Text of The German PharmacopoeiaDocument9 pagesChapter A: New Text of The German PharmacopoeiaAlessandra SeverinoNo ratings yet
- Flos and Fruit PowderDocument46 pagesFlos and Fruit PowderAÏCHA GnosisteNo ratings yet
- Bitter-Orange-epicarp and Mesocarp TinctureDocument2 pagesBitter-Orange-epicarp and Mesocarp TinctureNikotiano TobacumNo ratings yet
- Aniseed - British Pharmacopoeia 2012 UpdatedDocument3 pagesAniseed - British Pharmacopoeia 2012 UpdatedRoger (Sisfarma)No ratings yet
- Zanthoxylum bungeanum pericarpDocument2 pagesZanthoxylum bungeanum pericarpaymenbiogalenicNo ratings yet
- Hawthorn Berries: Crataegi FructusDocument2 pagesHawthorn Berries: Crataegi FructusartemNo ratings yet
- Glucosum Liquidum: Glucose, LiquidDocument2 pagesGlucosum Liquidum: Glucose, LiquidCosmina GeorgianaNo ratings yet
- Agaricus Phalloides For Homoeopathic PreparationDocument7 pagesAgaricus Phalloides For Homoeopathic PreparationMTG_1234No ratings yet
- Scutellaria Root 1764Document2 pagesScutellaria Root 1764NDung NDungNo ratings yet
- Turmeric RhizomeDocument2 pagesTurmeric RhizomeGrenfell VPKNo ratings yet
- Cetirizine DihydrochlorideDocument3 pagesCetirizine DihydrochloridePRADIKA HANDIWIANTANo ratings yet
- Belladonna Leaf Tincture, StandardisedDocument2 pagesBelladonna Leaf Tincture, StandardisedJjangyiNo ratings yet
- Foeniculi FructusDocument3 pagesFoeniculi FructusHaitao GuanNo ratings yet
- IPECACUANHADocument3 pagesIPECACUANHALeonardo Henrique SiqueiraNo ratings yet
- Pharmacopee Francaise - Field Horsetail FHP - Equisetum Arvense PPHDocument4 pagesPharmacopee Francaise - Field Horsetail FHP - Equisetum Arvense PPHValentina MolinaNo ratings yet
- Plant and Animal Bio-Chemistry - Including Information on Amino Acids, Proteins, Pigments and Other Chemical Constituents of Organic MatterFrom EverandPlant and Animal Bio-Chemistry - Including Information on Amino Acids, Proteins, Pigments and Other Chemical Constituents of Organic MatterNo ratings yet
- The Chemistry of Fertilisers and Manure - Including Information on the Chemical Constituents and Types of Fertilisers and ManuresFrom EverandThe Chemistry of Fertilisers and Manure - Including Information on the Chemical Constituents and Types of Fertilisers and ManuresRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Images from Lichenes Australasici Exsiccati and of other characteristic Australasian Lichens. Volume OneFrom EverandImages from Lichenes Australasici Exsiccati and of other characteristic Australasian Lichens. Volume OneNo ratings yet
- Advanced Pharmaceutical analysisFrom EverandAdvanced Pharmaceutical analysisRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- O Level Biology Practice For Structured Questions Movement Of SubstancesFrom EverandO Level Biology Practice For Structured Questions Movement Of SubstancesNo ratings yet
- Wheat-germ oil, virginDocument1 pageWheat-germ oil, virginaymenbiogalenicNo ratings yet
- Vinorelbine tartrateDocument3 pagesVinorelbine tartrateaymenbiogalenicNo ratings yet
- VinpocetineDocument2 pagesVinpocetineaymenbiogalenicNo ratings yet
- Vibriosis vaccine (inactivated) for salmonidsDocument2 pagesVibriosis vaccine (inactivated) for salmonidsaymenbiogalenicNo ratings yet
- VigabatrinDocument2 pagesVigabatrinaymenbiogalenicNo ratings yet
- White horehoundDocument3 pagesWhite horehoundaymenbiogalenicNo ratings yet
- Zuclopenthixol decanoateDocument2 pagesZuclopenthixol decanoateaymenbiogalenicNo ratings yet
- Zinc sulfate heptahydrateDocument1 pageZinc sulfate heptahydrateaymenbiogalenicNo ratings yet
- Vibriosis vaccine (inactivated) for sea bassDocument2 pagesVibriosis vaccine (inactivated) for sea bassaymenbiogalenicNo ratings yet
- 2.2.40. Near-infrared spectroscopyDocument6 pages2.2.40. Near-infrared spectroscopyaymenbiogalenicNo ratings yet
- 1C18060-AC-9102-01 - P&ID CTA 01 - RoomsDocument1 page1C18060-AC-9102-01 - P&ID CTA 01 - RoomsaymenbiogalenicNo ratings yet
- 2.2.4. Approximate pH of solutionsDocument1 page2.2.4. Approximate pH of solutionsaymenbiogalenicNo ratings yet
- 1c18060-Ac-9301-00 - P&id Cta 03 - AhDocument1 page1c18060-Ac-9301-00 - P&id Cta 03 - AhaymenbiogalenicNo ratings yet
- 2.2.6. Refractive indexDocument1 page2.2.6. Refractive indexaymenbiogalenicNo ratings yet
- 2.2.2. Degree of coloration of liquidsDocument4 pages2.2.2. Degree of coloration of liquidsaymenbiogalenicNo ratings yet
- 1c18060-Ac-9201-01 - P&id Cta 02 - AhDocument1 page1c18060-Ac-9201-01 - P&id Cta 02 - AhaymenbiogalenicNo ratings yet
- 1C18060-AC-9302-00 - P&ID CTA 03 - RoomsDocument1 page1C18060-AC-9302-00 - P&ID CTA 03 - RoomsaymenbiogalenicNo ratings yet
- Zoledronic acid monohydrateDocument2 pagesZoledronic acid monohydrateaymenbiogalenicNo ratings yet
- 1c18060-Ac-9801-00 - P&id Cta 08 - AhDocument1 page1c18060-Ac-9801-00 - P&id Cta 08 - AhaymenbiogalenicNo ratings yet
- 1C18060-AC-9202-01 - P&ID CTA 02 - RoomsDocument1 page1C18060-AC-9202-01 - P&ID CTA 02 - RoomsaymenbiogalenicNo ratings yet
- 1C18060-AC-9702-01 - P&ID CTA 07 - RoomsDocument1 page1C18060-AC-9702-01 - P&ID CTA 07 - RoomsaymenbiogalenicNo ratings yet
- 1c18060-Ac-9901-00 - P&id Cta Fresh AirDocument1 page1c18060-Ac-9901-00 - P&id Cta Fresh AiraymenbiogalenicNo ratings yet
- Powerful Computing and Dynamic Scheduling: Digital EngineDocument2 pagesPowerful Computing and Dynamic Scheduling: Digital EngineLeomark RespondeNo ratings yet
- 3Rd Floor Plan: Schedule of Floor FinishesDocument1 page3Rd Floor Plan: Schedule of Floor FinishespolislimuelsundyNo ratings yet
- Aeotec DSD37-ZWUS by Aeon Labs - Installation ManualDocument2 pagesAeotec DSD37-ZWUS by Aeon Labs - Installation ManualAlarm Grid Home Security and Alarm MonitoringNo ratings yet
- Get Best Long Coat Green Apple ShampooDocument1 pageGet Best Long Coat Green Apple ShampooBhawna SinghNo ratings yet
- Antiragging Committee - Jan-20Document1 pageAntiragging Committee - Jan-20TRH RECRUITMENTNo ratings yet
- 6-9 Summer Happy LearningDocument8 pages6-9 Summer Happy Learningjairohith9711No ratings yet
- Merc (Partnership) March 14Document27 pagesMerc (Partnership) March 14kristian datinguinooNo ratings yet
- DISS Worksheet Week 5Document7 pagesDISS Worksheet Week 5Joanna Marie Mariscotes PalacioNo ratings yet
- Sapiens A Brief History of HumankindDocument8 pagesSapiens A Brief History of HumankindAli GoharNo ratings yet
- The Right of Privacy in The Digital AgeDocument16 pagesThe Right of Privacy in The Digital AgeGrace KPATINVONo ratings yet
- November 2019 (v3) QP - Paper 4 CIE Chemistry IGCSEDocument16 pagesNovember 2019 (v3) QP - Paper 4 CIE Chemistry IGCSEJeevith Soumya SuhasNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Irregular Multistorey Buildings With and Without Floating Columns Under Seismic LoadingDocument8 pagesAnalysis of Irregular Multistorey Buildings With and Without Floating Columns Under Seismic Loadingnxdpm6td5gNo ratings yet
- Succession Cause 846 of 2011Document6 pagesSuccession Cause 846 of 2011kbaisa7No ratings yet
- Inorganic Chemistry 1 - Alkali Metals RevisioDocument7 pagesInorganic Chemistry 1 - Alkali Metals RevisioAshleyn Mary SandersNo ratings yet
- Project Management A Systems Approach To Planning Scheduling and Controlling 10Th Edition Kerzner Test Bank Full Chapter PDFDocument24 pagesProject Management A Systems Approach To Planning Scheduling and Controlling 10Th Edition Kerzner Test Bank Full Chapter PDFGeorgeAndersonkqmr100% (13)
- KMPDocument2 pagesKMPPrajeesh KrishnanNo ratings yet
- Sixth Meeting MinutesDocument4 pagesSixth Meeting MinutesTanvi BakshiNo ratings yet
- NutriSmart - Food Products Recommendation SystemDocument3 pagesNutriSmart - Food Products Recommendation SystemAnonymous izrFWiQNo ratings yet
- ReleaseDocument168 pagesReleaseNabil HarizNo ratings yet
- Corporate QA-QC ManagerDocument7 pagesCorporate QA-QC ManagerDeo MNo ratings yet
- Simple Past Full ExercisesDocument6 pagesSimple Past Full Exercisespablo1130No ratings yet
- Unit 4-2-NonferrousDocument32 pagesUnit 4-2-NonferrousNisha JaiswalNo ratings yet
- Notes On TennysonDocument2 pagesNotes On TennysonDonatella Di LelloNo ratings yet
- Neet Code C Question Paper PDFDocument41 pagesNeet Code C Question Paper PDFMagnifestoNo ratings yet
- LCM105 LCM115 PDFDocument3 pagesLCM105 LCM115 PDFCABean1No ratings yet
- Case 1Document2 pagesCase 1Wanda Marie SingletaryNo ratings yet
- BusEthSocResp Weeks 3-4Document6 pagesBusEthSocResp Weeks 3-4Christopher Nanz Lagura CustanNo ratings yet