Professional Documents
Culture Documents
RealNumberSystemGuidedNotesandHomework-1
RealNumberSystemGuidedNotesandHomework-1
Uploaded by
Sneha MahapatraCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
RealNumberSystemGuidedNotesandHomework-1
RealNumberSystemGuidedNotesandHomework-1
Uploaded by
Sneha MahapatraCopyright:
Available Formats
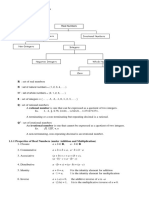
Lesson 1: The Real Number System
Key Vocabulary:
Rational Numbers: Irrational Numbers:
Natural numbers-
Whole numbers- Integers:
Integers-
Whole Numbers:
Rational numbers-
Natural Numbers:
Irrational numbers-
Example: Classifying Real Numbers
Determine which numbers are (a) natural numbers, (b) whole numbers, (c) integers, (d) rational numbers,
and (e) irrational numbers.
1 7
−10, − 3, −2, − , 0, , 5, 𝜋, 8
2 8
a. Natural numbers:
b. Whole Numbers:
c. Integers:
d. Rational Numbers:
e. Irrational Numbers:
Inequalities:
< > ≤ ≥
Example: Interpreting Inequalities
Describe the subset of real numbers that the inequality represents.
a. 𝑥 ≥ 4 b. −5 < 𝑥 ≤ 2
Copyright Krystal Kovisto- Math with a Mountain View
Sets and Intervals:
Key Vocabulary:
Interval notation-
Set-builder notation-
Bounded Intervals on the Real Number Line
Interval Notation Set Builder Notation Graph
Open Interval
(𝑎, 𝑏)
Closed Interval
[𝑎, 𝑏]
Half-Open Interval
(𝑎, 𝑏]
[𝑎, 𝑏)
Open-Infinite Interval
(𝑎, ∞)
(−∞, 𝑏)
Closed-Infinite Interval
[𝑎, ∞)
(−∞, 𝑏]
Example: Representing Intervals
Write each interval in set-builder notation and sketch the graph.
Interval Notation: Set-Builder Notation: Graph:
a. (−4,3]
b. − ,
c. [−2, ∞)
d. (−∞, 1)
Copyright Krystal Kovisto- Math with a Mountain View
Intersection and Union of Sets:
Key Vocabulary:
Intersection- Union-
Example: Intersection and Union of Sets
Let 𝐴 = −6, 0, , 10, 15 , 𝐵 = −6, −5,3,15 and 𝐶 = −3, 0,
a. Find 𝐴 ∪ 𝐵
b. Find 𝐴 ∩ 𝐵
c. Find 𝐵 ∩ 𝐶
Example: Intersection of Sets
Find the intersection of the following sets and graph the set on a number line
a. [0, ∞) ∩ (−∞, 5]
b. −∞, −2 ∪ −2, ∞ ∩ [−4, ∞)
Copyright Krystal Kovisto- Math with a Mountain View
Understanding Absolute Value:
Key Vocabulary:
Absolute value-
Properties of Absolute Values
𝑎 ≥0 −𝑎 = 𝑎 𝑎𝑏 = 𝑎 𝑏 𝑎 𝑎
= ,b ≠ 0
𝑏 𝑏
Example: Evaluate Absolute Value Expressions
Evaluate the following expressions involving absolute values.
a. − 3 b. − c. 3 − 6
Distance between Two Real Numbers on a Number Line
For any real numbers a and b, the distance between a and b on a number line is defined by …
Example: Evaluate Find the Distance between Two Real Numbers
Find the distance between the numbers -4 and 2 using absolute value.
Copyright Krystal Kovisto- Math with a Mountain View
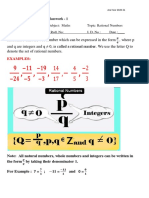
The Real Number System
Key Vocabulary:
Rational Numbers: Irrational Numbers:
Natural numbers-
The counting numbers starting with 1
Whole numbers- Integers:
Numbers starting with 0
Integers-
Whole Numbers:
The positive and negative whole numbers,
including 0
Rational numbers-
Numbers that can be written as the ratio Natural Numbers:
of integers i.e., fractions and decimals
Irrational numbers-
Real numbers that cannot be written as a
ratio of integers
Example: Classifying Real Numbers
Determine which numbers are (a) natural numbers, (b) whole numbers, (c) integers, (d) rational numbers,
and (e) irrational numbers.
1 7
−10, − 3, −2, − , 0, , 5, 𝜋, 8
2 8
a. Natural numbers: 8
b. Whole Numbers: 0, 8
c. Integers: −10, −2, 0, 8
1 7
d. Rational Numbers: −10, −2, − , 0, , 8
2 8
e. Irrational Numbers: − 3, 5, 𝜋
Inequalities:
< > ≤ ≥
Less than Greater than Less than or equal Greater than or equal
Example: Interpreting Inequalities
Describe the subset of real numbers that the inequality represents.
a. 𝑥 ≥ 4 b. −5 < 𝑥 ≤ 2
The subset of all real numbers that are The subset of all real numbers that are greater than
greater than or equal to 4. -5 but less than or equal to 2.
Copyright Krystal Kovisto- Math with a Mountain View
Sets and Intervals:
Key Vocabulary:
Interval notation-
A way to write a subset of real numbers by using the endpoints of the interval contained by inclusive
brackets [ ] or exclusive parenthesis ( ).
Set-builder notation-
A way to describe a set that uses inequality notation to describe the properties of the elements of the set
contained within set brackets {x| description of elements }.
Bounded Intervals on the Real Number Line
Interval Notation Set Builder Notation Graph
Open Interval 𝑥 𝑎 < 𝑥 < 𝑏}
(𝑎, 𝑏)
Closed Interval 𝑥 𝑎 ≤ 𝑥 ≤ 𝑏}
[𝑎, 𝑏]
Half-Open Interval
(𝑎, 𝑏] 𝑥 𝑎 < 𝑥 ≤ 𝑏}
[𝑎, 𝑏) 𝑥 𝑎 ≤ 𝑥 < 𝑏}
Open-Infinite Interval
(𝑎, ∞) 𝑥 𝑥 > 𝑎}
(−∞, 𝑏) 𝑥 𝑥 < 𝑏}
Closed-Infinite Interval
[𝑎, ∞) 𝑥 𝑥 ≥ 𝑎}
(−∞, 𝑏] 𝑥 𝑥 ≤ 𝑏}
Example: Representing Intervals
Write each interval in set-builder notation and sketch the graph.
Interval Notation: Set-Builder Notation: Graph:
a. (−4,3]
b. − ,
c. [−2, ∞)
d. (−∞, 1)
Copyright Krystal Kovisto- Math with a Mountain View
Intersection and Union of Sets:
Key Vocabulary:
Intersection- Union-
The intersection of two sets The union of two sets is made by
contains the elements common combining the elements of the
to both sets. two sets.
Example: Intersection and Union of Sets
Let 𝐴 = −6, 0, , 10, 15 , 𝐵 = −6, −5,3,15 and 𝐶 = −3, 0,
a. Find 𝐴 ∪ 𝐵 1
−6, −5, 1, , 3, 10, 15
2
b. Find 𝐴 ∩ 𝐵 −6, 15
c. Find 𝐵 ∩ 𝐶 ∅
Example: Intersection of Sets
Find the intersection of the following sets and graph the set on a number line
a. [0, ∞) ∩ (−∞, 5] [0,5]
b. −∞, −2 ∪ −2, ∞ ∩ [−4, ∞)
[−4, −2) ∪ (−2, ∞)
Copyright Krystal Kovisto- Math with a Mountain View
Understanding Absolute Value:
Key Vocabulary:
Absolute value-
The distance a value is from zero.
5 =5
−5 = 5 5 units 5 units
Properties of Absolute Values
𝑎 ≥0 −𝑎 = 𝑎 𝑎𝑏 = 𝑎 𝑏 𝑎 𝑎
= ,b ≠ 0
𝑏 𝑏
Example: Evaluate Absolute Value Expressions
Evaluate the following expressions involving absolute values.
a. − 3 b. − c. 3 − 6
− 3 = 3 5 5 1 3 − 6 = −3 = 3
− = =
20 20 4
Distance between Two Real Numbers on a Number Line
For any real numbers a and b, the distance between a and b on a number line is defined by …
𝑑 = 𝑎 − 𝑏 and 𝑑 = 𝑏 − 𝑎
Example: Evaluate Find the Distance between Two Real Numbers
Find the distance between the numbers -4 and 2 using absolute value.
𝑑 = 𝑎−𝑏 𝑑 = 𝑏−𝑎
𝑑 = −4 − 2 𝑑 = 2 − (−4)
𝑑 = −6 𝑑= 6
𝑑=6 𝑑=6
Copyright Krystal Kovisto- Math with a Mountain View
The Real Number System-Homework
Name: ____________________________________________ Date: ____________________ Class: ________________
Determine which numbers in the set are (a) natural numbers, (b) whole numbers, (c) integers, (d) rational
numbers and (e) irrational numbers.
1. −9, − , 5, , 3, 0, 8, −4, 2, −11 2. 25, −17, − , 9, 3.12, 𝜋, 18, −11.1, 13
a. Natural Numbers: a. Natural Numbers:
b. Whole Numbers: b. Whole Numbers:
c. Integers: c. Integers:
d. Rational Numbers: d. Rational Numbers:
e. Irrational Numbers: e. Irrational Numbers:
Describe the subset of real numbers that the inequality represents.
3. 𝑥 ≤ 5 4. 𝑥 < 0
5. −2 < 𝑥 < 2 6. 0 < 𝑥 ≤ 6
Write each interval in set-builder notation and sketch the graph.
7. [4, ∞) 8. (−∞, 2)
Set Builder: Set Builder:
Graph: Graph:
9. [−5,2) 10. (−1,2]
Set Builder: Set Builder:
Graph: Graph:
Copyright Krystal Kovisto- Math with a Mountain View
Sets A and B are given. Find (a) 𝑨 ∩ 𝑩 and (b) 𝑨 ∪ 𝑩.
11. A = −1, 0, 1, 2 and 𝐵 = {0, 2, 4} 12. A = 1, 2, 3, 4 and 𝐵 = {0, 5, 6}
a. 𝐴 ∩ 𝐵 = a. 𝐴 ∩ 𝐵 =
b. 𝐴 ∪ 𝐵 = b. 𝐴 ∪ 𝐵 =
Find the intersection of the given intervals and graph the set on a number line.
13. (−∞, ∞) ∩ (−∞, 3) 14. (−8,5] ∩ (−12,3)
15. [0, ∞) ∩ (−∞, 4] 16. ( −∞, 1 ∪ 1, ∞ ) ∩ (−∞, ∞)
17. −∞, 0 ∪ 0, ∞ ∩ [−3, ∞) 18. (−∞, 10) ∩ (−5, ∞) ∩ (−∞, 1]
Evaluate the absolute value expression.
19. −2.2 20. −2 3
21. − 22. 2 − 𝜋
Find the distance between the two real numbers using absolute value.
23. 3 and 14 24. -5 and 7
Copyright Krystal Kovisto- Math with a Mountain View
The Real Number System-Homework
Answer Key
Name: ____________________________________________ Date: ____________________ Class: ________________
Determine which numbers in the set are (a) natural numbers, (b) whole numbers, (c) integers, (d) rational
numbers and (e) irrational numbers.
1. −9, − , 5, , 3, 0, 8, −4, 2, −11 2. 25, −17, − , 9, 3.12, 𝜋, 18, −11.1, 13
a. Natural Numbers: 2, 5, 8 a. Natural Numbers: 9, 13, 18, 25
b. Whole Numbers: 0, 2, 5, 8 b. Whole Numbers: 9, 13, 18, 25
c. Integers: −11, −9, −4, 0, 2, 5, 8 c. Integers: −17, 9, 13, 18, 25
7 2 12
d. Rational Numbers: −11, −9, −4, − , 0, , 2, 5, 8 d. Rational Numbers:−17, −11.1, − , 9, 3.12, 13, 18, 25
2 3 3
e. Irrational Numbers: 3 e. Irrational Numbers: 1
𝜋
2
Describe the subset of real numbers that the inequality represents.
3. 𝑥 ≤ 5 4. 𝑥 < 0
All real numbers less than or equal to 5. All real numbers less than 0.
5. −2 < 𝑥 < 2 6. 0 < 𝑥 ≤ 6
All real numbers greater than -1 but less than 2. All real numbers greater than 0 but less than or
equal to 6.
Write each interval in set-builder notation and sketch the graph.
7. [4, ∞) 8. (−∞, 2)
Set Builder: {𝑥|𝑥 ≥ 4} Set Builder: {𝑥|𝑥 < 2}
Graph: Graph:
9. [−5,2) 10. (−1,2]
Set Builder: {𝑥| − 5 ≤ 𝑥 < 2} Set Builder: {𝑥| − 1 < 𝑥 ≤ 2}
Graph: Graph:
Copyright Krystal Kovisto- Math with a Mountain View
Sets A and B are given. Find (a) 𝑨 ∩ 𝑩 and (b) 𝑨 ∪ 𝑩.
11. A = −1, 0, 1, 2 and 𝐵 = {0, 2, 4} 12. A = 1, 2, 3, 4 and 𝐵 = {0, 5, 6}
a. 𝐴 ∩ 𝐵 = {0, 2} a. 𝐴 ∩ 𝐵 = {∅}
b. 𝐴 ∪ 𝐵 = −1, 0, 1, 2, 4 b. 𝐴 ∪ 𝐵 = {0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6}
Find the intersection of the given intervals and graph the set on a number line.
13. (−∞, ∞) ∩ (−∞, 3) 14. (−8,5] ∩ (−12,3)
(−∞, 3) (−8,3)
15. [0, ∞) ∩ (−∞, 4] 16. ( −∞, 1 ∪ 1, ∞ ) ∩ (−∞, ∞)
[0,4] (−∞, 1) ∪ (1, ∞)
17. −∞, 0 ∪ 0, ∞ ∩ [−3, ∞) 18. (−∞, 10) ∩ (−5, ∞) ∩ (−∞, 1]
[−3, 0) ∪ (0, ∞) (−5,1]
Evaluate the absolute value expression.
19. −2.2 2.2 20. −2 3 6
21. − 22. 2 − 𝜋
−3 −2 + 𝜋
Find the distance between the two real numbers using absolute value.
23. 3 and 14 11 24. -5 and 7 12
Copyright Krystal Kovisto- Math with a Mountain View
Thank You!
Thank you for your purchase! By purchasing this resource, you are agreeing that the contents are
the property of Krystal Kovisto-Math with a Mountain View and licensed to you only for classroom /
personal use as a single user. I retain the copyright, and reserve all rights to this product. Please
remember to leave feedback so you will earn TpT Credits, which may be applied to your future
purchases.
YOU MAY:
Use free and purchased items for your own classroom students, or your own personal
use.
Reference this product in blog posts, at seminars, professional development, workshops,
or other such venues, ONLY if both credit is given to myself as the author, and a link
back to my TpT store is included in the presentation.
Purchase licenses at a great discount for other teachers to use this resource.
YOU MAY NOT:
Claim this work as your own, alter the files in any way, or remove copyright /
watermarks.
Sell the files or combine them into another unit for sale / free.
Post this document for sale / free elsewhere on the internet (this includes Google Doc
links on blogs).
Making copies of purchased items to share with others is strictly forbidden and is a
violation of the TOU / law.
Thank you for abiding by universally accepted codes of professional ethics while using this
product. If you encounter an issue with your file, notice an error, or are in any way
experiencing a problem, please contact me and I will be more than happy to help sort it
out. You can send me an email at mathwithamountainview@gmail.com.
THANK YOU!
Krystal Kovisto– Math with a Mountain View
THANK YOU TO THESE CLIPART & FONT ARTISTS:
Background by Mrs. M School Counseling
Fonts by Cori and Company
Copyright Krystal Kovisto- Math with a Mountain View
You might also like
- 1.1 - Real Numbers (S)Document25 pages1.1 - Real Numbers (S)sureintharaan100% (1)
- Chapter 1-2-Dela Cruz, Mina, JoshuaDocument29 pagesChapter 1-2-Dela Cruz, Mina, JoshuaJerryme Dela Cruz xx100% (1)
- 10 REAL NUMBERS Semi-Detailed LPDocument2 pages10 REAL NUMBERS Semi-Detailed LPDawn Razonable100% (2)
- Handout w01Document8 pagesHandout w01Ghifary ArrasyidNo ratings yet
- Intro Sets and The Real Nos (01-14-2015) PDFDocument7 pagesIntro Sets and The Real Nos (01-14-2015) PDFRiza Mae BayoNo ratings yet
- Math Chapter 1Document38 pagesMath Chapter 1Abu Huzaifah100% (1)
- Chapter 1 PDFDocument109 pagesChapter 1 PDFDeniell Joyce MarquezNo ratings yet
- 1.basic MathematicsDocument53 pages1.basic MathematicsJaysha GamingNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 Real NumbersDocument30 pagesLesson 1 Real NumbersLiendon Joey ParreñoNo ratings yet
- Real Numbers - 1hourDocument23 pagesReal Numbers - 1houralia syuhadaNo ratings yet
- Class Ix Subject: Mathematics: Gists of The LessonsDocument8 pagesClass Ix Subject: Mathematics: Gists of The LessonsMadhusudan BanerjeeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Number System STUDENTS' VERSION 2022Document37 pagesChapter 1 Number System STUDENTS' VERSION 2022Haziq NuqmanNo ratings yet
- Basic Mathematics TheoryDocument18 pagesBasic Mathematics TheoryAyan Khan100% (1)
- LectureNotes MAT111Document93 pagesLectureNotes MAT111Morena NtshaboNo ratings yet
- Calculus Week 1Document77 pagesCalculus Week 1shaheer ahmedNo ratings yet
- Basic Maths PDFDocument39 pagesBasic Maths PDFvineetthesupermanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 RealnumberDocument21 pagesChapter 1 RealnumberjamaludinizzadNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Number System and EquationsDocument36 pagesChapter 1 - Number System and EquationsNur Ashiqin NajmuddinNo ratings yet
- Math 7 Week 4 Q1Document14 pagesMath 7 Week 4 Q1Carl Joshua FranciscoNo ratings yet
- Intervention For CalculusDocument4 pagesIntervention For CalculusJustin JaranillaNo ratings yet
- Real Number SystemDocument19 pagesReal Number SystemAnupama NiroulaNo ratings yet
- 15 Function 01 TheoryDocument30 pages15 Function 01 TheoryRaju Singh100% (1)
- Introduction To Set Theory and Subsets and Set OperationsDocument11 pagesIntroduction To Set Theory and Subsets and Set OperationsNeville Faith MiculobNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1: Relations and Functions: 1.1 Sets of Real Numbers and The Cartesian Coordinate PlaneDocument10 pagesChapter 1: Relations and Functions: 1.1 Sets of Real Numbers and The Cartesian Coordinate Planerachel4uclaNo ratings yet
- FOM BasicsDocument40 pagesFOM Basicslol.mishra.121No ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Algebra PDFDocument33 pagesChapter 1 Algebra PDFpannNo ratings yet
- Final Module 4 The Language of SetsDocument12 pagesFinal Module 4 The Language of SetsLuccine ShinNo ratings yet
- Module 1 Lesson 5Document30 pagesModule 1 Lesson 5derp perdNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document73 pagesChapter 2Abdi MosisaNo ratings yet
- FunctionsDocument12 pagesFunctions김현주No ratings yet
- The Language of Sets Discrete MathematicsDocument34 pagesThe Language of Sets Discrete MathematicschatgptbeybeNo ratings yet
- Real Number SystemDocument10 pagesReal Number System10 Paat, King EdmarNo ratings yet
- Tools of Algebra PacketDocument17 pagesTools of Algebra PacketA.BensonNo ratings yet
- The Set of Real Numbers: Ms. Jiecel Maedeen Aquino SantosDocument70 pagesThe Set of Real Numbers: Ms. Jiecel Maedeen Aquino SantosJiecel Maedeen SantosNo ratings yet
- 1 Speaking MathematicallyDocument33 pages1 Speaking MathematicallyJessaNo ratings yet
- Enrichment Course (Maths)Document52 pagesEnrichment Course (Maths)Srinivas VakaNo ratings yet
- Real Number SystemDocument32 pagesReal Number SystemJoy MendozaNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 NotesDocument15 pagesUnit 1 Notesanon-605611No ratings yet
- Chapter PDocument11 pagesChapter PSamira MinNo ratings yet
- Afrin Sadia Rumana Lecturer Bangladesh University of ProfessionalsDocument37 pagesAfrin Sadia Rumana Lecturer Bangladesh University of ProfessionalsJHNo ratings yet
- MA1200 Chapter 2 Sets and FunctionsDocument15 pagesMA1200 Chapter 2 Sets and FunctionsWai Ho ChoiNo ratings yet
- Basic MathematicsDocument55 pagesBasic MathematicsRaas Venkata Santosh SteelNo ratings yet
- Mte 101 C 1 PDFDocument11 pagesMte 101 C 1 PDFKenias NdunaNo ratings yet
- Math 123 Lesson 1.1Document10 pagesMath 123 Lesson 1.1Supitran Reygie BamanNo ratings yet
- Module 1 Unit 1A PreCalc ConceptsDocument9 pagesModule 1 Unit 1A PreCalc Conceptskorleon gNo ratings yet
- Calculus 1 Notes 1 1Document99 pagesCalculus 1 Notes 1 1Iradukunda GirukwishakaNo ratings yet
- Numbers 6Document22 pagesNumbers 6marypipNo ratings yet
- Gujarat Technological UniversityDocument2 pagesGujarat Technological Universityfeyayel988No ratings yet
- National Academy Dharmapuri 97876 60996, 7010865319Document11 pagesNational Academy Dharmapuri 97876 60996, 7010865319Muralidharan KrishnamoorthyNo ratings yet
- Math 9 - Q1 - WK 2 - Module 2 - The Nature Sum and Product of The Roots of Quadratic EquationDocument20 pagesMath 9 - Q1 - WK 2 - Module 2 - The Nature Sum and Product of The Roots of Quadratic EquationTerrence RicafrancaNo ratings yet
- Remesh's Maths Coaching: A XNN NNDocument6 pagesRemesh's Maths Coaching: A XNN NNrajlagwalNo ratings yet
- AMA1110 Lecture - 1-Written-In-2-Gp103Document35 pagesAMA1110 Lecture - 1-Written-In-2-Gp103Brian LiNo ratings yet
- AMA1110 Lecture - 1-Written-Gp103-MonDocument33 pagesAMA1110 Lecture - 1-Written-Gp103-MonBrian LiNo ratings yet
- First Year CH 1Document7 pagesFirst Year CH 1Faheem HayyatNo ratings yet
- MAAHL12 Mockp2Document13 pagesMAAHL12 Mockp2Nadia VellaNo ratings yet
- Module 1-Mathematics As A Language: Maribel D. Cariñ0Document4 pagesModule 1-Mathematics As A Language: Maribel D. Cariñ0KhalidNo ratings yet
- Module 3: The Language of Mathematics: Unit 1: SetsDocument24 pagesModule 3: The Language of Mathematics: Unit 1: SetsKiwiTiwiTVNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Functions and Relations: 1 1 Number TheoryDocument37 pagesUnit 1 Functions and Relations: 1 1 Number TheorySandra MillerNo ratings yet
- A. Equation: Input OutputDocument2 pagesA. Equation: Input OutputMystic lifeNo ratings yet
- B.ed Full OriginalDocument12 pagesB.ed Full OriginalMELVE FRANCIS100% (1)
- AafmtDocument228 pagesAafmtShailanie Valle RiveraNo ratings yet
- Significant FiguresDocument10 pagesSignificant FiguresamirNo ratings yet
- Chapter# 02 Complex Number: (I) +1 0 1 (Ii) +a 0 ADocument10 pagesChapter# 02 Complex Number: (I) +1 0 1 (Ii) +a 0 AMehtab Ahmed ChannaNo ratings yet
- Number System ConversionsDocument24 pagesNumber System ConversionssujathaNo ratings yet
- Coding System in ComputerDocument4 pagesCoding System in ComputerOdia Etinosa JuliusNo ratings yet
- Grade 5 Mixed Numbers To Decimals FDocument2 pagesGrade 5 Mixed Numbers To Decimals FTanja LazovaNo ratings yet
- Data RepresentationDocument20 pagesData RepresentationKapil YadavNo ratings yet
- TOFAS検定システムDocument1 pageTOFAS検定システムRichard GalangNo ratings yet
- Perfect NumbersDocument25 pagesPerfect NumbersCarlos LopezNo ratings yet
- Grade 7 - MATH - RATIONAL NUMBERS - Notes - 1Document8 pagesGrade 7 - MATH - RATIONAL NUMBERS - Notes - 1Kandavel KandyNo ratings yet
- Lunes Martes Miyerkules Huwebes Biyernes: Grade OneDocument3 pagesLunes Martes Miyerkules Huwebes Biyernes: Grade OneCharisse Pizarro DionisioNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12 PercentageDocument11 pagesChapter 12 PercentageAhsysgsggssgNo ratings yet
- ArithmeticDocument187 pagesArithmetic4anahat100% (1)
- Indian Standard: Rules For Rounding Off Numerical ValuesDocument14 pagesIndian Standard: Rules For Rounding Off Numerical ValuesPradip Tapan BanerjeeNo ratings yet
- Place Value Chart (20 Places) PDFDocument1 pagePlace Value Chart (20 Places) PDFKim ReevesNo ratings yet
- Boe-Ii Tutorial Sheet Ece/Eee/CseDocument3 pagesBoe-Ii Tutorial Sheet Ece/Eee/CseramNo ratings yet
- Peta Penggunaan Kawasan Hutan 28-DesDocument1 pagePeta Penggunaan Kawasan Hutan 28-Desagus erwantoNo ratings yet
- Math Worksheet-1 Place Value Name: - Grade V Sec: - Date: 18-04-16 - Basic Level I. Fill in The BlanksDocument3 pagesMath Worksheet-1 Place Value Name: - Grade V Sec: - Date: 18-04-16 - Basic Level I. Fill in The BlanksShri NeeruNo ratings yet
- M1 Mathematics Cat B1 & B2 V4.3Document136 pagesM1 Mathematics Cat B1 & B2 V4.3Abhijith KaushikNo ratings yet
- 5c2ca00904e56bbc2161da31 5ba3e5f4e4b061908b47bc7a 1540202978735Document50 pages5c2ca00904e56bbc2161da31 5ba3e5f4e4b061908b47bc7a 1540202978735Abhishek SahuNo ratings yet
- Nama: Andi Ihzan Iznain NIM: 1926042013 Prodi: Pendidikan Vokasional MekatronikaDocument9 pagesNama: Andi Ihzan Iznain NIM: 1926042013 Prodi: Pendidikan Vokasional MekatronikaAndi Ihzan IznainNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 5 Mathematics Worksheet - Place ValueDocument3 pagesCBSE Class 5 Mathematics Worksheet - Place ValueDrishtiNo ratings yet
- Hojoo Lee & Peter Vandendriessche - Problems in Elementary Number TheoryDocument88 pagesHojoo Lee & Peter Vandendriessche - Problems in Elementary Number TheoryDijkschneier100% (1)
- Adding and Subtracting BinaryDocument7 pagesAdding and Subtracting BinaryGeve PacultadNo ratings yet
- Number SystemsDocument24 pagesNumber SystemsShishupal SinghNo ratings yet
- Numbers 04Document29 pagesNumbers 04deepak SunalNo ratings yet
- QuantMasters TextbookDocument100 pagesQuantMasters TextbookRavi Teja AJNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Number SystemDocument15 pagesIntroduction To Number SystemRaja AubaidNo ratings yet
- Math Quest 9 Chapter 1Document42 pagesMath Quest 9 Chapter 1Joshua TellvikNo ratings yet