Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views13 Antiparkinsonian drug
13 Antiparkinsonian drug
Uploaded by
مشتاقة للجنةCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Parkinson's Disease NCPDocument1 pageParkinson's Disease NCPAlexa Lexington Rae Zagado67% (3)
- Chap 5 CNSDocument106 pagesChap 5 CNSKIDUS YAREDNo ratings yet
- Neurology Pharmacology - 20240517Document9 pagesNeurology Pharmacology - 20240517deidra1120No ratings yet
- Drug Therapy of ParkinsonismDocument28 pagesDrug Therapy of ParkinsonismZobayer AhmedNo ratings yet
- ParkinsonDocument13 pagesParkinsonKirti SinghNo ratings yet
- Anti Parkinsonism DrugsDocument8 pagesAnti Parkinsonism DrugsFaria Islam Juhi100% (1)
- CAS 3 Drug ChartDocument20 pagesCAS 3 Drug Chartnaazaninrahat76No ratings yet
- Drugs That Cause and Drugs That Alleviate Parkinsonism: BY Prof. Mbah A.UDocument24 pagesDrugs That Cause and Drugs That Alleviate Parkinsonism: BY Prof. Mbah A.UtemitopeNo ratings yet
- HNS50 - Drugs Used For Neurodegenerative DiseasesDocument55 pagesHNS50 - Drugs Used For Neurodegenerative DiseasesJinyoungNo ratings yet
- Drugs For Parkinson's DiseaseDocument52 pagesDrugs For Parkinson's DiseaseKAMALNo ratings yet
- Antiparkinsonian DrugsDocument35 pagesAntiparkinsonian DrugsvimalaNo ratings yet
- Block I Posting, Pharmacology Lectures: Antiparkisonian DrugsDocument41 pagesBlock I Posting, Pharmacology Lectures: Antiparkisonian DrugsOdiete EfeNo ratings yet
- Block I Posting, Pharmacology Lectures: Dr. Aduragbenro AdedapoDocument47 pagesBlock I Posting, Pharmacology Lectures: Dr. Aduragbenro AdedapoOdiete EfeNo ratings yet
- Antiparkinsons DrugsDocument19 pagesAntiparkinsons Drugs39 Nayan BhagatNo ratings yet
- Right-Hand Tremor at Rest, WhichDocument47 pagesRight-Hand Tremor at Rest, WhichsyarintaadeninaNo ratings yet
- Drugs For Parkinson's DiseaseDocument52 pagesDrugs For Parkinson's Diseasebhagyashri chaudhariNo ratings yet
- Movement Disorder TreatmentsDocument3 pagesMovement Disorder TreatmentsJustin HulinNo ratings yet
- K10 (A1) - 2015pharmacotherapy For ParkinsonDocument41 pagesK10 (A1) - 2015pharmacotherapy For Parkinsonali100% (1)
- PD (Sple Lec) 13.10.21Document48 pagesPD (Sple Lec) 13.10.21لوى كمالNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology of Drugs in Extrapyramidal Disorders: Prof - Aznan Lelo, DR, PHD, SPFK & DR Datten Bangun, MSC, SPFKDocument42 pagesPharmacology of Drugs in Extrapyramidal Disorders: Prof - Aznan Lelo, DR, PHD, SPFK & DR Datten Bangun, MSC, SPFKWinson ChitraNo ratings yet
- Parkinson's DiseaseDocument65 pagesParkinson's DiseaseGerald Resubal OriñaNo ratings yet
- Anti Parkinson Drugs FinallDocument36 pagesAnti Parkinson Drugs FinallandrapradeshsseNo ratings yet
- Parkinson's DiseaseDocument33 pagesParkinson's DiseasekapilNo ratings yet
- Anti-Parkinsonism DrugDocument15 pagesAnti-Parkinsonism Drugsaihjad pramaniNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology of Drugs Used in Movement Disorders: Christian WaeberDocument34 pagesPharmacology of Drugs Used in Movement Disorders: Christian WaeberciaranNo ratings yet
- And Other Movement DisordersDocument38 pagesAnd Other Movement DisordersshravaniNo ratings yet
- Pharmacotherapy of Parkinson's DiseaseDocument66 pagesPharmacotherapy of Parkinson's DiseaseKenneth NuñezNo ratings yet
- Drugs Used in Parkinsonism: Functional Circuitry Between The Cortex, Basal Ganglia, and ThalamusDocument5 pagesDrugs Used in Parkinsonism: Functional Circuitry Between The Cortex, Basal Ganglia, and ThalamusHamad AlshabiNo ratings yet
- Antiparkinson Pharma 2020Document26 pagesAntiparkinson Pharma 2020Ida Bagus Putu SwabawaNo ratings yet
- Pharm Step 2Document1 pagePharm Step 2srothschildNo ratings yet
- Anti Parkinson DrugsDocument33 pagesAnti Parkinson Drugsraina3546No ratings yet
- Anti ParkinsonDocument29 pagesAnti Parkinsonking_gold100% (1)
- Antiparkinsonian DrugsDocument5 pagesAntiparkinsonian Drugsluq9fifNo ratings yet
- Parkinson's Disease: Destruction of DA Neurons in The Substantia Nigra (Part of Extrapyramidal System)Document1 pageParkinson's Disease: Destruction of DA Neurons in The Substantia Nigra (Part of Extrapyramidal System)srothschildNo ratings yet
- Pharm STEP 2Document1 pagePharm STEP 2srothschildNo ratings yet
- Drugs For Parkinson's DiseaseDocument43 pagesDrugs For Parkinson's DiseasesabaNo ratings yet
- Pharm Step 2Document1 pagePharm Step 2srothschildNo ratings yet
- Parkinsons DiseaseDocument3 pagesParkinsons Diseasem3d1kNo ratings yet
- Anti ParkinsonDocument18 pagesAnti ParkinsonRitika DasNo ratings yet
- Mayra Pagan: Pharmacology-NursingDocument50 pagesMayra Pagan: Pharmacology-NursingmayraNo ratings yet
- Anti ParkinsonDocument43 pagesAnti ParkinsonSasya pashaNo ratings yet
- Anti Parkinsonian DrugsDocument23 pagesAnti Parkinsonian DrugsMinhal AsimNo ratings yet
- Parkinson's DieseaseDocument31 pagesParkinson's DieseaseAryaman MohapatraNo ratings yet
- Antiparkinson DrugsDocument19 pagesAntiparkinson DrugsSV SagarNo ratings yet
- 5-Drugs Used in Parkinsonism Summary and QuestionsDocument7 pages5-Drugs Used in Parkinsonism Summary and QuestionsmugtabaNo ratings yet
- Parkinson's Disease Therapeutic Strategies: Surat Tanprawate, MD Division of Neurology University of Chiang MaiDocument42 pagesParkinson's Disease Therapeutic Strategies: Surat Tanprawate, MD Division of Neurology University of Chiang MaiNEuRoLoGisT CoFFeeCuP100% (1)
- By Agus Soedomo Department of Neurology Medicine Faculty, Sebelas Maret University/Moewardi General Hospital SurakartaDocument51 pagesBy Agus Soedomo Department of Neurology Medicine Faculty, Sebelas Maret University/Moewardi General Hospital SurakartaRina Dwi PurnamasariNo ratings yet
- Nursing - 1 AntiParkinsonian Drug - MehreenDocument35 pagesNursing - 1 AntiParkinsonian Drug - MehreenKhubaib KhanNo ratings yet
- Parkinson Disease: Devyani Diah WulansariDocument28 pagesParkinson Disease: Devyani Diah WulansariDYANA DWI HARTATINo ratings yet
- Parkinsons Disease 2021Document30 pagesParkinsons Disease 2021Steph StephanieNo ratings yet
- Anti ParkinsonDocument37 pagesAnti ParkinsonAkmal SafwanNo ratings yet
- Parkinson's Disease IIDocument53 pagesParkinson's Disease IIalishba100% (6)
- CNS Pharmacology - 20231120 - 233736 - 0000Document10 pagesCNS Pharmacology - 20231120 - 233736 - 0000Meghana MaddaliNo ratings yet
- Dementia and ParkinsonDocument70 pagesDementia and ParkinsonCharles YiuNo ratings yet
- ParkinsonismDocument18 pagesParkinsonismShivsharanNo ratings yet
- Idiopathic Means The Cause Is UnknownDocument1 pageIdiopathic Means The Cause Is UnknownMichael MabiniNo ratings yet
- Drugs For Neurodegenarative DiseaesesDocument14 pagesDrugs For Neurodegenarative Diseaesesالطاهر زروقNo ratings yet
- Anti PD DrugsDocument41 pagesAnti PD Drugshassentullo430No ratings yet
- Parkinson'sDisease DrugsDocument54 pagesParkinson'sDisease DrugstheintrovNo ratings yet
- Antiparkinson Agents: Art Hupka, Ph.D. 2009Document52 pagesAntiparkinson Agents: Art Hupka, Ph.D. 2009Gurjot KaurNo ratings yet
- Fast Facts: Optimización del tratamiento de las fluctuaciones motoras en la enfermedad de Parkinson: Adaptando el tratamiento al pacienteFrom EverandFast Facts: Optimización del tratamiento de las fluctuaciones motoras en la enfermedad de Parkinson: Adaptando el tratamiento al pacienteNo ratings yet
- Lecture 8 Central Nervous System CnsDocument35 pagesLecture 8 Central Nervous System CnsakramuddaulaNo ratings yet
- Early Diagnosis of Parkinson's Disease: A Combined Method Using Deep Learning and Neuro-Fuzzy TechniquesDocument14 pagesEarly Diagnosis of Parkinson's Disease: A Combined Method Using Deep Learning and Neuro-Fuzzy TechniquesSally AbdulazizNo ratings yet
- Pharmacotherapy of Parkinson's DiseaseDocument66 pagesPharmacotherapy of Parkinson's DiseaseKenneth NuñezNo ratings yet
- 25274Document93 pages25274prnjanNo ratings yet
- Essay On Importance of ReligionDocument7 pagesEssay On Importance of Religiond3gn731z100% (2)
- Hoehn and Yahr Staging of ParkinsonDocument8 pagesHoehn and Yahr Staging of ParkinsonMuresan CalinNo ratings yet
- Zigmond MJ, Burke RE - Pathophysiology of Parkinson's DiseaseDocument14 pagesZigmond MJ, Burke RE - Pathophysiology of Parkinson's Diseaseursula_ursula100% (1)
- NEJMoa2312323 1Document10 pagesNEJMoa2312323 1lakshminivas PingaliNo ratings yet
- Degenerative Diseases of The Brain 2Document66 pagesDegenerative Diseases of The Brain 2Janie-Vi Villamor Ismael-GorospeNo ratings yet
- Neurology Work BookDocument73 pagesNeurology Work BookCastleKGNo ratings yet
- FS38 Drug Induced Parkinsonism - 0Document8 pagesFS38 Drug Induced Parkinsonism - 0Harnoor SinghNo ratings yet
- 05 Degenerative - Demyelinating DiseasesDocument26 pages05 Degenerative - Demyelinating DiseasesMalinda KarunaratneNo ratings yet
- Abstractbook Si-Pmse 13Document80 pagesAbstractbook Si-Pmse 13Leslie Wilson50% (2)
- Ms CompreDocument19 pagesMs ComprenokolipNo ratings yet
- Anti ParkinsonDocument38 pagesAnti Parkinsonarif khalidNo ratings yet
- Parkinsonism Caused by Adverse Drug Reactions: A Case SeriesDocument3 pagesParkinsonism Caused by Adverse Drug Reactions: A Case SeriesFendi ManopeNo ratings yet
- Neuropsychiatric Disorders - Miyoshi, Koho (2010)Document339 pagesNeuropsychiatric Disorders - Miyoshi, Koho (2010)Ramon MagsaysayNo ratings yet
- ParkinsonDocument54 pagesParkinsonAngel YapNo ratings yet
- MedSurg NeuroDocument8 pagesMedSurg NeuroZachary T Hall100% (1)
- MS Neurologic Conditions J2018 Ans KeyDocument13 pagesMS Neurologic Conditions J2018 Ans KeyPaul Lexus Gomez LorenzoNo ratings yet
- Sifrol® ER: What Is in This LeafletDocument3 pagesSifrol® ER: What Is in This LeafletDenaraAshaPutriNo ratings yet
- Neurohealth Properties of Hericium Erinaceus MycelDocument11 pagesNeurohealth Properties of Hericium Erinaceus Myceldokan42No ratings yet
- Norris Claire White Paper Liftware PDFDocument14 pagesNorris Claire White Paper Liftware PDFmeysam NaaNo ratings yet
- Antiparkinsonian Drugs PDFDocument47 pagesAntiparkinsonian Drugs PDFUmair AhmedNo ratings yet
- DiPiro's Pharmacotherapy Handbook 12E 2023 ALGrawany-658-667Document10 pagesDiPiro's Pharmacotherapy Handbook 12E 2023 ALGrawany-658-667azimahakimNo ratings yet
- Ccare Pro Les Waye FeatureDocument10 pagesCcare Pro Les Waye Featureapi-604638740No ratings yet
- KGH Together Issue 26Document15 pagesKGH Together Issue 26Irina Gheorghies ZosimNo ratings yet
- Course Objectives 3313Document11 pagesCourse Objectives 3313Hugh JacobsNo ratings yet
- Michael J. Fox: Get To Know The Amazing Story BehindDocument5 pagesMichael J. Fox: Get To Know The Amazing Story BehindTRIXIA MAY ELEVADONo ratings yet
13 Antiparkinsonian drug
13 Antiparkinsonian drug
Uploaded by
مشتاقة للجنة0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views4 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views4 pages13 Antiparkinsonian drug
13 Antiparkinsonian drug
Uploaded by
مشتاقة للجنةCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 4
Antiparkinsonian Drugs
Dr. maged bin hariz
• Definition
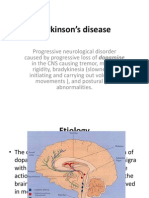
Parkinson's disease is a slowly progressive neurological disease →Degeneration of
nigrostriatal DA (Dopamine) neurons → ↓striatal DA & dominance of cholinergic
system
Symptom of Parkinson's disease :
Bradykinesia or akinesia (failure to initiate movement)- Tremors at reset- Rigidity-
postural instability.
Causes of Parkinsonism (most common in the elderly)
Idiopathic - Viral encephalitis
Drug-Induced Parkinsonism:
o Antipsychotics → block D2 receptors.
o Reserpine → depletes DA stores.
o Methyldopa → inhibits DA synthesis.
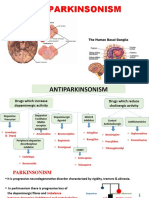
Antiparkinsonian Drugs
Antiparkinsonian Drugs aim to restore DA/Ach balance
↑ Dopaminergic Activity ↓ Cholinergic Activity
Dopaminergic Drugs Anticholinergics.
• Levodopa/carbidopa. • Benztropine
• Bromocriptine (ergot) • Trihcxphcnidyl
• Pramipexole- ropinirol
(non-ergots)
• Amantadine.
• Entacapone.
Antiparkinsonian Drugs
Dopaminergic Drugs
Levodopa (L-dopa) : (Mainstay of Therapy)
L- dopa is a DA precursor that crosses BBB &is decarboxylated to DA in the CNS.
It is given with the peripheral decarboxylase inhibitor, carbidopa, as Ldopa/
carbidopa (sinemet).
Carbidopa : prevents peripheral decarboxylation of L-dopa to DA →↓ dose of
Ldopa by 75%.
benefits of L-dopa decrease in a few years due to gradual neuronal degeneration
• Adverse Effects of L-dopa:
A. Peripheral (due to↑ DA peripherally;↓ DA with carbidopa)
GIT: Nausea - vomiting .
CVS: postural hypotension & arrhythmias
B. Central (due to ↑ DA centrally; ↓ DA with carbidopa)
Dyskinesia.
Confusion, hallucinations; psychosis.
C. Fluctuations in Response
On-off effect (sudden swings from mobility to bradykinesia).
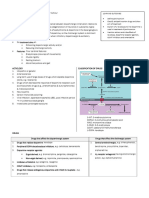
Other Dopaminergic Drugs Used in Parkinsonism
Drug Mechanism of Action
Pramipexole - Ropinirole Direct D2 agonists.
Bromocriptine- Apomorphine Similar to L-dopa
Amantadine ↑ DA release (mild effect)
↓ DA reuptake
Selegiline Selective inhibitor of MAO-B (brain)
Entacapone COMT inhibitor(GIT , liver)
Anticholinergics (Benztropine – Trihexphenidyl)
Block central cholinergic activity
restore DA/Ach balance.
Improve tremors (mainly)& rigidity, but less effective on bradykinesia.
Used in:
Drug induced Parkinsonism:
Parkinson disease (especially in the young)
Side Effects:
Similar to atropine but less severe (dry mouth, constipation, confusion ).
You might also like
- Parkinson's Disease NCPDocument1 pageParkinson's Disease NCPAlexa Lexington Rae Zagado67% (3)
- Chap 5 CNSDocument106 pagesChap 5 CNSKIDUS YAREDNo ratings yet
- Neurology Pharmacology - 20240517Document9 pagesNeurology Pharmacology - 20240517deidra1120No ratings yet
- Drug Therapy of ParkinsonismDocument28 pagesDrug Therapy of ParkinsonismZobayer AhmedNo ratings yet
- ParkinsonDocument13 pagesParkinsonKirti SinghNo ratings yet
- Anti Parkinsonism DrugsDocument8 pagesAnti Parkinsonism DrugsFaria Islam Juhi100% (1)
- CAS 3 Drug ChartDocument20 pagesCAS 3 Drug Chartnaazaninrahat76No ratings yet
- Drugs That Cause and Drugs That Alleviate Parkinsonism: BY Prof. Mbah A.UDocument24 pagesDrugs That Cause and Drugs That Alleviate Parkinsonism: BY Prof. Mbah A.UtemitopeNo ratings yet
- HNS50 - Drugs Used For Neurodegenerative DiseasesDocument55 pagesHNS50 - Drugs Used For Neurodegenerative DiseasesJinyoungNo ratings yet
- Drugs For Parkinson's DiseaseDocument52 pagesDrugs For Parkinson's DiseaseKAMALNo ratings yet
- Antiparkinsonian DrugsDocument35 pagesAntiparkinsonian DrugsvimalaNo ratings yet
- Block I Posting, Pharmacology Lectures: Antiparkisonian DrugsDocument41 pagesBlock I Posting, Pharmacology Lectures: Antiparkisonian DrugsOdiete EfeNo ratings yet
- Block I Posting, Pharmacology Lectures: Dr. Aduragbenro AdedapoDocument47 pagesBlock I Posting, Pharmacology Lectures: Dr. Aduragbenro AdedapoOdiete EfeNo ratings yet
- Antiparkinsons DrugsDocument19 pagesAntiparkinsons Drugs39 Nayan BhagatNo ratings yet
- Right-Hand Tremor at Rest, WhichDocument47 pagesRight-Hand Tremor at Rest, WhichsyarintaadeninaNo ratings yet
- Drugs For Parkinson's DiseaseDocument52 pagesDrugs For Parkinson's Diseasebhagyashri chaudhariNo ratings yet
- Movement Disorder TreatmentsDocument3 pagesMovement Disorder TreatmentsJustin HulinNo ratings yet
- K10 (A1) - 2015pharmacotherapy For ParkinsonDocument41 pagesK10 (A1) - 2015pharmacotherapy For Parkinsonali100% (1)
- PD (Sple Lec) 13.10.21Document48 pagesPD (Sple Lec) 13.10.21لوى كمالNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology of Drugs in Extrapyramidal Disorders: Prof - Aznan Lelo, DR, PHD, SPFK & DR Datten Bangun, MSC, SPFKDocument42 pagesPharmacology of Drugs in Extrapyramidal Disorders: Prof - Aznan Lelo, DR, PHD, SPFK & DR Datten Bangun, MSC, SPFKWinson ChitraNo ratings yet
- Parkinson's DiseaseDocument65 pagesParkinson's DiseaseGerald Resubal OriñaNo ratings yet
- Anti Parkinson Drugs FinallDocument36 pagesAnti Parkinson Drugs FinallandrapradeshsseNo ratings yet
- Parkinson's DiseaseDocument33 pagesParkinson's DiseasekapilNo ratings yet
- Anti-Parkinsonism DrugDocument15 pagesAnti-Parkinsonism Drugsaihjad pramaniNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology of Drugs Used in Movement Disorders: Christian WaeberDocument34 pagesPharmacology of Drugs Used in Movement Disorders: Christian WaeberciaranNo ratings yet
- And Other Movement DisordersDocument38 pagesAnd Other Movement DisordersshravaniNo ratings yet
- Pharmacotherapy of Parkinson's DiseaseDocument66 pagesPharmacotherapy of Parkinson's DiseaseKenneth NuñezNo ratings yet
- Drugs Used in Parkinsonism: Functional Circuitry Between The Cortex, Basal Ganglia, and ThalamusDocument5 pagesDrugs Used in Parkinsonism: Functional Circuitry Between The Cortex, Basal Ganglia, and ThalamusHamad AlshabiNo ratings yet
- Antiparkinson Pharma 2020Document26 pagesAntiparkinson Pharma 2020Ida Bagus Putu SwabawaNo ratings yet
- Pharm Step 2Document1 pagePharm Step 2srothschildNo ratings yet
- Anti Parkinson DrugsDocument33 pagesAnti Parkinson Drugsraina3546No ratings yet
- Anti ParkinsonDocument29 pagesAnti Parkinsonking_gold100% (1)
- Antiparkinsonian DrugsDocument5 pagesAntiparkinsonian Drugsluq9fifNo ratings yet
- Parkinson's Disease: Destruction of DA Neurons in The Substantia Nigra (Part of Extrapyramidal System)Document1 pageParkinson's Disease: Destruction of DA Neurons in The Substantia Nigra (Part of Extrapyramidal System)srothschildNo ratings yet
- Pharm STEP 2Document1 pagePharm STEP 2srothschildNo ratings yet
- Drugs For Parkinson's DiseaseDocument43 pagesDrugs For Parkinson's DiseasesabaNo ratings yet
- Pharm Step 2Document1 pagePharm Step 2srothschildNo ratings yet
- Parkinsons DiseaseDocument3 pagesParkinsons Diseasem3d1kNo ratings yet
- Anti ParkinsonDocument18 pagesAnti ParkinsonRitika DasNo ratings yet
- Mayra Pagan: Pharmacology-NursingDocument50 pagesMayra Pagan: Pharmacology-NursingmayraNo ratings yet
- Anti ParkinsonDocument43 pagesAnti ParkinsonSasya pashaNo ratings yet
- Anti Parkinsonian DrugsDocument23 pagesAnti Parkinsonian DrugsMinhal AsimNo ratings yet
- Parkinson's DieseaseDocument31 pagesParkinson's DieseaseAryaman MohapatraNo ratings yet
- Antiparkinson DrugsDocument19 pagesAntiparkinson DrugsSV SagarNo ratings yet
- 5-Drugs Used in Parkinsonism Summary and QuestionsDocument7 pages5-Drugs Used in Parkinsonism Summary and QuestionsmugtabaNo ratings yet
- Parkinson's Disease Therapeutic Strategies: Surat Tanprawate, MD Division of Neurology University of Chiang MaiDocument42 pagesParkinson's Disease Therapeutic Strategies: Surat Tanprawate, MD Division of Neurology University of Chiang MaiNEuRoLoGisT CoFFeeCuP100% (1)
- By Agus Soedomo Department of Neurology Medicine Faculty, Sebelas Maret University/Moewardi General Hospital SurakartaDocument51 pagesBy Agus Soedomo Department of Neurology Medicine Faculty, Sebelas Maret University/Moewardi General Hospital SurakartaRina Dwi PurnamasariNo ratings yet
- Nursing - 1 AntiParkinsonian Drug - MehreenDocument35 pagesNursing - 1 AntiParkinsonian Drug - MehreenKhubaib KhanNo ratings yet
- Parkinson Disease: Devyani Diah WulansariDocument28 pagesParkinson Disease: Devyani Diah WulansariDYANA DWI HARTATINo ratings yet
- Parkinsons Disease 2021Document30 pagesParkinsons Disease 2021Steph StephanieNo ratings yet
- Anti ParkinsonDocument37 pagesAnti ParkinsonAkmal SafwanNo ratings yet
- Parkinson's Disease IIDocument53 pagesParkinson's Disease IIalishba100% (6)
- CNS Pharmacology - 20231120 - 233736 - 0000Document10 pagesCNS Pharmacology - 20231120 - 233736 - 0000Meghana MaddaliNo ratings yet
- Dementia and ParkinsonDocument70 pagesDementia and ParkinsonCharles YiuNo ratings yet
- ParkinsonismDocument18 pagesParkinsonismShivsharanNo ratings yet
- Idiopathic Means The Cause Is UnknownDocument1 pageIdiopathic Means The Cause Is UnknownMichael MabiniNo ratings yet
- Drugs For Neurodegenarative DiseaesesDocument14 pagesDrugs For Neurodegenarative Diseaesesالطاهر زروقNo ratings yet
- Anti PD DrugsDocument41 pagesAnti PD Drugshassentullo430No ratings yet
- Parkinson'sDisease DrugsDocument54 pagesParkinson'sDisease DrugstheintrovNo ratings yet
- Antiparkinson Agents: Art Hupka, Ph.D. 2009Document52 pagesAntiparkinson Agents: Art Hupka, Ph.D. 2009Gurjot KaurNo ratings yet
- Fast Facts: Optimización del tratamiento de las fluctuaciones motoras en la enfermedad de Parkinson: Adaptando el tratamiento al pacienteFrom EverandFast Facts: Optimización del tratamiento de las fluctuaciones motoras en la enfermedad de Parkinson: Adaptando el tratamiento al pacienteNo ratings yet
- Lecture 8 Central Nervous System CnsDocument35 pagesLecture 8 Central Nervous System CnsakramuddaulaNo ratings yet
- Early Diagnosis of Parkinson's Disease: A Combined Method Using Deep Learning and Neuro-Fuzzy TechniquesDocument14 pagesEarly Diagnosis of Parkinson's Disease: A Combined Method Using Deep Learning and Neuro-Fuzzy TechniquesSally AbdulazizNo ratings yet
- Pharmacotherapy of Parkinson's DiseaseDocument66 pagesPharmacotherapy of Parkinson's DiseaseKenneth NuñezNo ratings yet
- 25274Document93 pages25274prnjanNo ratings yet
- Essay On Importance of ReligionDocument7 pagesEssay On Importance of Religiond3gn731z100% (2)
- Hoehn and Yahr Staging of ParkinsonDocument8 pagesHoehn and Yahr Staging of ParkinsonMuresan CalinNo ratings yet
- Zigmond MJ, Burke RE - Pathophysiology of Parkinson's DiseaseDocument14 pagesZigmond MJ, Burke RE - Pathophysiology of Parkinson's Diseaseursula_ursula100% (1)
- NEJMoa2312323 1Document10 pagesNEJMoa2312323 1lakshminivas PingaliNo ratings yet
- Degenerative Diseases of The Brain 2Document66 pagesDegenerative Diseases of The Brain 2Janie-Vi Villamor Ismael-GorospeNo ratings yet
- Neurology Work BookDocument73 pagesNeurology Work BookCastleKGNo ratings yet
- FS38 Drug Induced Parkinsonism - 0Document8 pagesFS38 Drug Induced Parkinsonism - 0Harnoor SinghNo ratings yet
- 05 Degenerative - Demyelinating DiseasesDocument26 pages05 Degenerative - Demyelinating DiseasesMalinda KarunaratneNo ratings yet
- Abstractbook Si-Pmse 13Document80 pagesAbstractbook Si-Pmse 13Leslie Wilson50% (2)
- Ms CompreDocument19 pagesMs ComprenokolipNo ratings yet
- Anti ParkinsonDocument38 pagesAnti Parkinsonarif khalidNo ratings yet
- Parkinsonism Caused by Adverse Drug Reactions: A Case SeriesDocument3 pagesParkinsonism Caused by Adverse Drug Reactions: A Case SeriesFendi ManopeNo ratings yet
- Neuropsychiatric Disorders - Miyoshi, Koho (2010)Document339 pagesNeuropsychiatric Disorders - Miyoshi, Koho (2010)Ramon MagsaysayNo ratings yet
- ParkinsonDocument54 pagesParkinsonAngel YapNo ratings yet
- MedSurg NeuroDocument8 pagesMedSurg NeuroZachary T Hall100% (1)
- MS Neurologic Conditions J2018 Ans KeyDocument13 pagesMS Neurologic Conditions J2018 Ans KeyPaul Lexus Gomez LorenzoNo ratings yet
- Sifrol® ER: What Is in This LeafletDocument3 pagesSifrol® ER: What Is in This LeafletDenaraAshaPutriNo ratings yet
- Neurohealth Properties of Hericium Erinaceus MycelDocument11 pagesNeurohealth Properties of Hericium Erinaceus Myceldokan42No ratings yet
- Norris Claire White Paper Liftware PDFDocument14 pagesNorris Claire White Paper Liftware PDFmeysam NaaNo ratings yet
- Antiparkinsonian Drugs PDFDocument47 pagesAntiparkinsonian Drugs PDFUmair AhmedNo ratings yet
- DiPiro's Pharmacotherapy Handbook 12E 2023 ALGrawany-658-667Document10 pagesDiPiro's Pharmacotherapy Handbook 12E 2023 ALGrawany-658-667azimahakimNo ratings yet
- Ccare Pro Les Waye FeatureDocument10 pagesCcare Pro Les Waye Featureapi-604638740No ratings yet
- KGH Together Issue 26Document15 pagesKGH Together Issue 26Irina Gheorghies ZosimNo ratings yet
- Course Objectives 3313Document11 pagesCourse Objectives 3313Hugh JacobsNo ratings yet
- Michael J. Fox: Get To Know The Amazing Story BehindDocument5 pagesMichael J. Fox: Get To Know The Amazing Story BehindTRIXIA MAY ELEVADONo ratings yet