Professional Documents
Culture Documents
ALPS 2334 Maths Assignment Paper
ALPS 2334 Maths Assignment Paper
Uploaded by
Shivam yadavCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Question Bank 2nd Year Math CT - 3Document5 pagesQuestion Bank 2nd Year Math CT - 3awaisasghar935No ratings yet
- Live Quiz 11: Mathematics 1. (1 Min)Document3 pagesLive Quiz 11: Mathematics 1. (1 Min)sikkaNo ratings yet
- Live Quiz - IC-1 - (1-07-21) - QuestionDocument4 pagesLive Quiz - IC-1 - (1-07-21) - Questionlavya guptaNo ratings yet
- Assign-1 Integration by Use of Basic FormulaeDocument3 pagesAssign-1 Integration by Use of Basic FormulaeDhruv KuchhalNo ratings yet
- Maths Advanced Level Problem Solving (ALPS-4) - PaperDocument9 pagesMaths Advanced Level Problem Solving (ALPS-4) - PaperAnanmay ChauhanNo ratings yet
- ALPS 2332 Maths Assignment PaperDocument10 pagesALPS 2332 Maths Assignment PaperDhruv JainNo ratings yet
- Indefinite Integrals Assignment Maths NKMDocument24 pagesIndefinite Integrals Assignment Maths NKMDisha KatariaNo ratings yet
- Indefinite Integration - QuestionDocument4 pagesIndefinite Integration - Questionbest badmintonNo ratings yet
- Indefinite IntegrationDocument58 pagesIndefinite IntegrationSubrata KarmakarNo ratings yet
- Integration Fiitjee CPPDocument6 pagesIntegration Fiitjee CPPPratham Sharma50% (2)
- Assignment: Chapter # 4 DifferentiabilityDocument3 pagesAssignment: Chapter # 4 DifferentiabilityRamish AhmedNo ratings yet
- Before Allen Class 11 29 JuneDocument3 pagesBefore Allen Class 11 29 JuneYatharth KaranNo ratings yet
- Functions, Inverse Trigonometry (ALPS-1) PaperDocument14 pagesFunctions, Inverse Trigonometry (ALPS-1) PaperRajendra JatNo ratings yet
- I Integration-03 - Exercise 1Document20 pagesI Integration-03 - Exercise 1Raju SinghNo ratings yet
- 12th Maths Chapter 2 Test 1 MCQsDocument1 page12th Maths Chapter 2 Test 1 MCQsabdul majeedNo ratings yet
- limitsDocument26 pageslimitsShikamaru NaraNo ratings yet
- ALPS Mathematics 2201 - JEE 2022: SyllabusDocument14 pagesALPS Mathematics 2201 - JEE 2022: SyllabusYash Dhoke100% (1)
- IndefiniteDocument40 pagesIndefinitePritee Priyambada TripathyNo ratings yet
- Spotlight - Advanced - Day-1 - In-Class Assignment - Mathematics - (Que. & Answer Key)Document8 pagesSpotlight - Advanced - Day-1 - In-Class Assignment - Mathematics - (Que. & Answer Key)Jyothi BrothersNo ratings yet
- Indefinite Integration-CLIP-1: Log Sinx Cosx C Log - Sin X Cosx - CDocument5 pagesIndefinite Integration-CLIP-1: Log Sinx Cosx C Log - Sin X Cosx - CDishika MaityNo ratings yet
- Not To Be Taken AwayDocument3 pagesNot To Be Taken AwayTonyNo ratings yet
- basic maths calculus 2Document5 pagesbasic maths calculus 2SashankNo ratings yet
- DPP No.3 For Week (07-06-10 To 12-06-10) Total Marks: 33 Max. Time: 33 MinDocument2 pagesDPP No.3 For Week (07-06-10 To 12-06-10) Total Marks: 33 Max. Time: 33 MinDhruv SharmaNo ratings yet
- Black Board Problems For JEE Advanced Set-9Document8 pagesBlack Board Problems For JEE Advanced Set-9ASHISH NAIK100% (1)
- Differentiation Question FinalDocument19 pagesDifferentiation Question FinalAnubhav vaishNo ratings yet
- SM 025 - Integration SoalanDocument9 pagesSM 025 - Integration SoalansharuNo ratings yet
- 2011E.C Second Semester Mathematics Worksheet-Five For Grade 12Document10 pages2011E.C Second Semester Mathematics Worksheet-Five For Grade 12Firie SibihatNo ratings yet
- 10Document4 pages10sikkaNo ratings yet
- 2024 Maths 1st Final ExamDocument4 pages2024 Maths 1st Final ExamOsman AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Quiz-9: Vidyamandir Classes: Innovating For Your SuccessDocument4 pagesQuiz-9: Vidyamandir Classes: Innovating For Your SuccesssikkaNo ratings yet
- Function-04 - Exercise - 1Document20 pagesFunction-04 - Exercise - 1Raju SinghNo ratings yet
- MAC2233 2010 Summer T3ADocument5 pagesMAC2233 2010 Summer T3AlllloNo ratings yet
- Quiz - Basic MathsDocument3 pagesQuiz - Basic MathsShashwat MishraNo ratings yet
- 2Document2 pages2sikkaNo ratings yet
- (Only Single Correct Answer Type Questions) : Part-ADocument4 pages(Only Single Correct Answer Type Questions) : Part-AAdrielly LopesNo ratings yet
- Master Sheet Indef e Nite Integration by Om SirDocument16 pagesMaster Sheet Indef e Nite Integration by Om SirRajvardhan singh SisodiyaNo ratings yet
- 129 Class TestDocument4 pages129 Class Testjaiswal23456No ratings yet
- Ii 3 8 2020Document6 pagesIi 3 8 2020ROBIN GUPTANo ratings yet
- I Integration-04 - ExerciseDocument13 pagesI Integration-04 - ExerciseRaju SinghNo ratings yet
- JEE Main Integral Calculus Important QuestionsDocument21 pagesJEE Main Integral Calculus Important QuestionsZombie Gamer100% (1)
- Differentiation: Dy DX Dy DX Dy DXDocument3 pagesDifferentiation: Dy DX Dy DX Dy DXcharan dheepNo ratings yet
- Allen Adv PapersDocument152 pagesAllen Adv PapersAbdullapoor RamReddy0% (2)
- Tutorial 9 (Baru06)Document6 pagesTutorial 9 (Baru06)nabilahNo ratings yet
- Student Copy. CAPS-1Document4 pagesStudent Copy. CAPS-1Vanshika LudhaniNo ratings yet
- M1 Bit Bank PDFDocument10 pagesM1 Bit Bank PDFK Sushmanth ReddyNo ratings yet
- Differentiation: FIIT-JEE LTD., 48, Gurukripa Complex, M.P. Nagar, Zone-II, Bhopal (M.P.), PH.: 4253355, 4253455Document2 pagesDifferentiation: FIIT-JEE LTD., 48, Gurukripa Complex, M.P. Nagar, Zone-II, Bhopal (M.P.), PH.: 4253355, 4253455Anonymous UserNo ratings yet
- LCD RKTDocument12 pagesLCD RKTTamanna SahuNo ratings yet
- M A T H e M A T I C SDocument5 pagesM A T H e M A T I C SAtharva GanjuNo ratings yet
- 11 Indefinite Integration DPP 11Document16 pages11 Indefinite Integration DPP 11tikam chandNo ratings yet
- Vibrant Academy: (India) Private LimitedDocument2 pagesVibrant Academy: (India) Private LimitedShadhasanNo ratings yet
- MathematicsDocument3 pagesMathematicsChinil Kumar ABNo ratings yet
- Errorless MoDDocument23 pagesErrorless MoDashmitaramoliya123No ratings yet
- Xercise: Multiple Correct (Objective Questions)Document1 pageXercise: Multiple Correct (Objective Questions)Vishu vevoNo ratings yet
- Definite Indefinite Integration (Area) (12th Pass)Document131 pagesDefinite Indefinite Integration (Area) (12th Pass)inventing new100% (1)
- PracticePaper - D06 Jul 2023Document8 pagesPracticePaper - D06 Jul 2023kadianvikhyatNo ratings yet
- Manoj Chauhan Sir: Maths byDocument15 pagesManoj Chauhan Sir: Maths byAbhiyanshu KumarNo ratings yet
- LCDDocument2 pagesLCDKumar AtthiNo ratings yet
- Function_NOS_ModerateDocument3 pagesFunction_NOS_Moderatearijeet141556No ratings yet
- Factoring and Algebra - A Selection of Classic Mathematical Articles Containing Examples and Exercises on the Subject of Algebra (Mathematics Series)From EverandFactoring and Algebra - A Selection of Classic Mathematical Articles Containing Examples and Exercises on the Subject of Algebra (Mathematics Series)No ratings yet
- MA1511 Chapter 4Document18 pagesMA1511 Chapter 4Kang Le LimNo ratings yet
- Maths Revision DPP No 4Document8 pagesMaths Revision DPP No 4Praphul Pulkit GiriNo ratings yet
- Sydney Grammar 2017 Year 10 Maths Yearly & SolutionsDocument18 pagesSydney Grammar 2017 Year 10 Maths Yearly & Solutionschloe.paleoNo ratings yet
- Myp 4 Extended Mathematics Holiday Assignment 2Document1 pageMyp 4 Extended Mathematics Holiday Assignment 2Joel LogboNo ratings yet
- Finite Difference Method: ME710 Mathematical Methods For Engineers Mechanical Engineering NITK SurathkalDocument20 pagesFinite Difference Method: ME710 Mathematical Methods For Engineers Mechanical Engineering NITK SurathkalSantosh Kumar AgastiNo ratings yet
- Basic Numeracy SimplificationDocument6 pagesBasic Numeracy SimplificationIAS EXAM PORTALNo ratings yet
- Integrals Yielding Inverse Hyperbolic Functions PDFDocument2 pagesIntegrals Yielding Inverse Hyperbolic Functions PDFStevenzel Eala EstellaNo ratings yet
- Operations Research: OxfordDocument7 pagesOperations Research: OxfordmadhavNo ratings yet
- Ma210 Course OutlineDocument1 pageMa210 Course OutlineVitu Verctor ViyuyiNo ratings yet
- 4 The General Term of A SequenceDocument10 pages4 The General Term of A SequenceSandra Nicole FernandezNo ratings yet
- ALGEBRADocument73 pagesALGEBRALorena Espeso JayawardenaNo ratings yet
- Turbulence: MIE1207 September, 2012Document128 pagesTurbulence: MIE1207 September, 2012Sepehr SaNo ratings yet
- Na - 2Document314 pagesNa - 2Himanshu YadavNo ratings yet
- Ex 4 7 FSC Part1Document2 pagesEx 4 7 FSC Part1usamalatif8941No ratings yet
- Lesson 4.A: Defining of Logarithmic Function, Equations and InequalitiesDocument9 pagesLesson 4.A: Defining of Logarithmic Function, Equations and InequalitiesAniqah Mardi Macuja EscarianNo ratings yet
- Field ProbsDocument19 pagesField Probsvanaj123No ratings yet
- IBHL Best 5Document4 pagesIBHL Best 5JennyNo ratings yet
- 9th Maths Chap 56Document2 pages9th Maths Chap 56Rana Hassan TariqNo ratings yet
- Ztransform AppDocument5 pagesZtransform AppSyed Ali RazaNo ratings yet
- Reaserch On PDE of Addis Abeba UniversityDocument31 pagesReaserch On PDE of Addis Abeba UniversityAman BetsoNo ratings yet
- InverseDocument31 pagesInverseShashank KumarNo ratings yet
- Prologue: 0.1 Books and AlgorithmsDocument9 pagesPrologue: 0.1 Books and AlgorithmsSivapremjiNo ratings yet
- Functional Analysis ChidumiDocument209 pagesFunctional Analysis ChidumiTaffohouo Nwaffeu Yves ValdezNo ratings yet
- On The Shortest Spanning Subtree of A Graph and The Traveling Salesman Problem - Joseph KruskalDocument3 pagesOn The Shortest Spanning Subtree of A Graph and The Traveling Salesman Problem - Joseph KruskalMauricioNo ratings yet
- Vector Mechanics by JohnsonDocument34 pagesVector Mechanics by JohnsonSushil AryanNo ratings yet
- Joint DensityDocument28 pagesJoint Densitylordbuzz123No ratings yet
- Ma 2211Document11 pagesMa 2211Saravanan MJNo ratings yet
- Laplace Table PDFDocument2 pagesLaplace Table PDFrobertNo ratings yet
- Jaypee University of Information Technology WAKNAGHAT, DISTT. SOLAN (H.P.) - 173215Document4 pagesJaypee University of Information Technology WAKNAGHAT, DISTT. SOLAN (H.P.) - 173215Shivam MauryaNo ratings yet
- The Limit Process (An Intuitive Introduction) : Calculus Is A Limit in One Sense or Another. For ExampleDocument1 pageThe Limit Process (An Intuitive Introduction) : Calculus Is A Limit in One Sense or Another. For ExampleagegnehutamiratNo ratings yet
ALPS 2334 Maths Assignment Paper
ALPS 2334 Maths Assignment Paper
Uploaded by
Shivam yadavCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
ALPS 2334 Maths Assignment Paper
ALPS 2334 Maths Assignment Paper
Uploaded by
Shivam yadavCopyright:
Available Formats
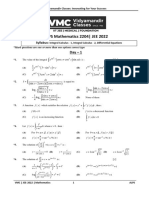
Vidyamandir Classes: Innovating for Your Success
Advanced Level Problem Solving-2334
JEE 2023 | Mathematics
Syllabus: Integral Calculus-1
*Mark questions are more than one options correct type
xm 1 f ( x)
1. xm1 1 2 x mx
m 2m
dx
mx m
c where f ( x ) is equal to: []
(A) 1 2 x m mx 2 m (B) 1 x m x 2m
1 1
(C) xm (D) x 2m
xm x 2m
2. log x
x 2 1 dx []
(A)
x log e x x 2 1 x 2 1 c (B)
x log e x x 2 1 x 2 1 c
(C)
x x2 1
2
log e x x 2 1 c (D)
x2 1
2
loge x x 2 1 c
a b sin x
3. (b a sin x)2 dx equals: [ ]
a cos x sin x
(A) c (B) c
b a sin x a b cos x
cos x sin x
(C) c (D) c
b a sin x a b cos x
*4.
tan x cot x dx is equal to: []
tan x cot x tan x cot x
(A) 2 tan 1 c (B) 2 tan 1 c
2 2
(C) 2 sin 1(sin x cos x) c (D) 2 tan 1(sin x cos x) c
*5. If sin x(sec x tan x) dx f ( x) g( x) c, then: []
(A) f ( x) tan x (B) f ( x) sec x (C) g ( x ) 2 x (D) g ( x) x
VMC | Mathematics 1 ALPS-2334 | JEE-2023
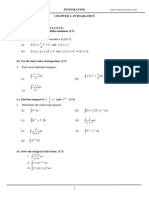
Vidyamandir Classes: Innovating for Your Success
*6. Let f ( x) x3 ax 2 bx c where a , b, c are real numbers. If f ( x ) has local minimum at x 1 and
a local maximum at x 1/ 3 and f (2) 0 , then: []
(A) f ( x) x3 x 2 x 2
(B) f ( x) x3 x 2 x 2
(C) f ( x) x3 x 2 x 2
14
(D) If F ( x) f ( x) dx, then F (1) F (1) 3
Paragraph for Q-7 to 9 []
Using the formula udv uv vdu, answer the following questions
sec
3
7. xdx is equal to:
1
(A) (sec x tan x log e | sec x tan x |) c
2
1
(B) (sec x log e | sec x tan x |) c
2
1
(C) (sec x tan x log e | sec x tan x |) c
2
(D) sec x tan x 2log e | sec x tan x |) c
x
8. loge (1 cos x)dx x tan 2 dx equals:
(A) x loge (1 cos x) c (B) x loge (1 cos x) c
(C) x log e (1 tan x) c (D) x log e (1 sin x) c
e
x
9. sin xdx is equal to:
ex e x
(A) (sin x cos x) c (B) (sin x cos x) c
2 2
ex ex
(C) (sin x cos x) c (D) (cos x sin x) c
4 4
dx 1 x 1 3 1
10. If ( x2 4) log e tan 1 x 1 c then 12 3 k equals _____. []
x 1 k x 1 3 2
VMC | Mathematics 2 ALPS-2334 | JEE-2023
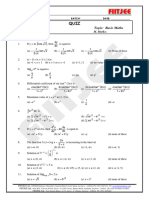
Vidyamandir Classes: Innovating for Your Success
11.
If I n (sin x cos x) n dx( n 2), then nI n 2(n 1) I n 2 is equal to: []
(A) (sin x cos x)n (sin x cos x) (B) (sin x cos x)n 1 (sin x cos x)
(C) (sin x cos x)n 1 (cos x sin x) (D) (sin x cos x)n (cos x sin x)
x 2 n(n 1)
12. ( x sin x n cos x) dx is equal to: [ ]
x cos x sec x
(A) tan x c (B) tan x c
x sin x n cos x x sin x n cos x
x sec x x n sec x
(C) cot x c (D) tan x c
x sin x n cos x x n sin x nx n 1 cos x
dx
13. cos6 x sin 6 x equals: []
1 (tan x cot x)
(A) tan 1(tan x cot x) c (B) tan 1 c
3 3
1 1 (sin x cos x)
(C) tan 1 (sin x cos x) c (D) tan 1 c
3 3 3
ax
*14. ax
dx equals: []
x a2 x2 x
(A) a sin 1
c (B) a sin 1 a2 x2 c
a 2 a
x x
(C) a sin 1 a2 x2 c (D) a cos 1 a2 x2 c
a a
x3
*15. x8 1
dx can be evaluated by using one (or more) substitutions. [ ]
(A) x4 t (B) x 4t 2 1 x8
(C) t 2 x8 1 x8 (D) t 4 x8 1 x8
x
*16. Which of the following methods are handy to evaluate the indefinite integral 9 8x x 2
dx ?
(A) The substitution x 4 t (B) Writing x (8 2 x )
(C) Substitution 9 8x x 2 t 2 (D) Both (A) and (B) [ ]
VMC | Mathematics 3 ALPS-2334 | JEE-2023
Vidyamandir Classes: Innovating for Your Success
Paragraph for Q-17 to 18 [ ]
x (a bx n ) p dx can be evaluated in the following
m
If m, n, p are rational numbers, then the indefinite integral
cases with the help of the substitution suggested.
m 1
Case-I : If is an integer, put a bx n t , where is the denominator of p.
n
m 1
Case-II : If p is an integer, put a bx n t x n , where is the denominator of p.
n
Answer the following questions
2 12
17. If x
1/3
(2 x 2/3 )1/ 4 dx (2 x 2/3 )1 (2 x 2/3 ) 2 c then 1 2 is equal to
3 5
(A) 4 (B) 3 (C) 2 (D) 1
dx 5 1 5 1
18. If x3 5 1 (1 / x) 4 1 x 9 1 x c then equals
(A) 1 (B) 2 (C) -1 (D) 3
dx 8 9
19. If a 1 4 x b 1 4 x then 9b( a b) is _______. []
10
x 1 x 4
c,
1/7 8
then 64( 1 ) is __________.
3 3
20. If 3
x 1 x 4
dx a 1 x 4
[]
VMC | Mathematics 4 ALPS-2334 | JEE-2023
Vidyamandir Classes: Innovating for Your Success
x2 2
21. x4 4 dx equals: []
1 1 x 2 2 1 1 x 2 2
tan c c
2 x
tan
x
(A) (B)
2 2
1 x2 2 1 x2 2
tan 1 c tan 1 c
2 x x
(C) (D)
2 2
x2 2
22. x4 4 dx is equal to: []
1 x2 2 x 2 1 x2 2
log e 2 c tan 1 c
x 2 x 2 2 x
(A) (B)
4 16
1 x2 2 x 2 1 x2 2 x 2
log e 2 c c
x 2 x 2
log e 2
x 2 x 2
(C) (D)
4 16
x 2 1 dx
23. x2 1 1 x4 is equal to: []
x 1 x
(A) cos 1 c (B) cos 1 2 c
x 1
2
2 x 1
1 x 2 1 x 2
(C) tan 1 2 c (D) cos1 2 c
2 x 1 2 x 1
dx 1 2
*24. (1 x)8
3(1 x ) k1
7(1 x ) k2
C , then: []
(A) k1 5 (B) k1 6 (C) k2 7 (D) k2 8
cos 4 x 1
If dx ( B cot 5 x) m / n c, then: []
sin 3 x[sin 5 x cos5 x]3/5
*25.
A
(A) A B 3 (B) mn 7 (C) mn 8 (D) A B 4
1 x
3/2
x
*26. For a 0, if I dx A sin C , where C is any arbitrary constant, then :
a3 x3 B
2 1
(A) A (B) B a3/2 (C) A (D) B a1/ 2 []
3 3
VMC | Mathematics 5 ALPS-2334 | JEE-2023
Vidyamandir Classes: Innovating for Your Success
Paragraph for Q-27 & 28
a sin x b cos x
To evaluate c sin x d cos x dx
where c 2 d 2 0 express the numerator as a sin x b cos x (Denominator) (Derivative of the
denominator)
Answer the following questions
2sin x 3cos x
27. 3sin x 4cos x dx equals: []
18 1 18 1
(A) x log e | 3sin x 4cos x | c (B) x log e | 3sin x 4cos x | c
25 25 25 25
x 18 x 18
(C) log e | 2sin x 3cos x | c (D) log e | 3sin x 4cos x | c
25 25 25 25
sin x 2cos x
28. If 2sin x cos x dx is equal to px q log e | 2sin x cos x | c, then p q equals: []
8 6 7
(A) (B) (C) (D) 1
5 5 5
11 1 6 1 1 c
29. If x (1 x 4 ) 1/2 dx x (1 x4 )5/2 x b (1 x4 )3/2 x (1 x4 )1/2 k then
10 3 2
a b c equals_________. [ ]
2x 5
30. If 9x 6x 2
2
dx a 9 x 2 6 x 2 b loge (3x 1 9 x 2 6 x 2) c then 9(a b) is
equal to ____________. []
VMC | Mathematics 6 ALPS-2334 | JEE-2023
Vidyamandir Classes: Innovating for Your Success
x tan x sec xdx []
2
31.
x sec2 x x tan x x sec2 x 1
(A) c (B) tan x c
2 2 2 2
x sec x tan x x sec2 x tan x
(C) c (D) c
2 2 2 2
x4 1
32. x2 x x 1
4 2
dx equals: []
x4 x2 1 x4 x2 1
(A) c (B) c
x x
1 x2 2 x 2
tan 1 x 2 2 c log e 2 c
x 2 x 2
(C) (D)
x
x2 1
33. x x 3x 1
4 2
dx loge ( f ( x)) c where f ( x ) is given by: []
x2 1 1 4
(A) (B) x 3x 2 1
x x
x 4 3x 2 1 1 2
(C) (D) ( x 1 x 4 3 x 2 1)
x2 x
sin
*34. If (sin 3 sin )cos e d ( Asin 3 Bcos 2 Csin Dcos E) esin F,
then : []
(A) A 4 (B) B 12 (C) C 20 (D) None of these
1
x sin x sec xdx ( x f ( x) g ( x )) k , then : []
3
*35. Let
2
(A) f ( x) (1, 1) (B) g ( x) sin x has 6 solution for x [ , 2]
(C) g '( x) f ( x), x R (D) f ( x) g ( x) has no solution
n
dx 1
*36. If 2 4 A 1 4 c, then: []
x ( x 1)3/4
x
(A) A 1 (B) B 1/ 4 (C) A 1/ 2 (D) B 1/ 3
VMC | Mathematics 7 ALPS-2334 | JEE-2023
Vidyamandir Classes: Innovating for Your Success
Paragraph for Q-37 & 39
1 1
To evaluate (Linear) Linear
and
(Quadratic) Linear
Put Linear t .
Answer the following questions
dx
37. If ( x 2) 3x 4
2 f ( x) c, then f ( x ) equals: []
1 3x 4
3x 4 1/2
1
tan tan
2
(A) (B)
2
x2 x2
(C) tan 1 (D) tan 1
2 2
dx x 1 3
38. If ( x2 4) p log e q tan 1 x 1 c , then pq is equal to: []
x 1 x 1 3
1 1 1 1
(A) (B) (C) (D)
4 3 8 3 3 8 3
dx
39. If ( x 3) x2
is equal to: []
1 x2 5 1 x2 5
(A) log e c (B) log e c
5 x2 5 5 x2 5
1 x2 5 1 x2 5
(C) log e c (D) log e c
5 x2 5 5 x2 5
n (e) n (1)
If Fn ( x) (log x) dx & n Fn nFn 1, then n (e) n (1) then
n
40. is equal to
e
___________. []
VMC | Mathematics 8 ALPS-2334 | JEE-2023
Vidyamandir Classes: Innovating for Your Success
dx 1
41. If 1 sin 4 x 2 tan x f ( x) c then f ( x ) is: []
(A) tan 1 2 tan x (B)
1
2
tan 1 2 tan x
(C)
2 2
1
tan 1 2 tan x (D)
1
4 2
tan 1 2 tan x
cos 2 x sin 4 x
cos4 x(1 cos2 2 x) dx 2loge (1 cos 2 x) loge (1 cos 2 x) f ( x) c then f ( x ) is:
2
42. If
(A) sec 2 x (B) tan x (C) cosec2 x (D) cot x [ ]
ex 2
(1 x 2 )
43. dx is equal to: []
1 x 2 1 2 x2
1 2 1 x 2 1 2 1 x 2
(A) ex c (B) ex c
2 2 1 x 2 2 2 1 x 2
1 1 x 2 1 1 x 2
(C) ex 2
c (D) ex 2
c
2 2 1 x 2 2 2 1 x 2
log x e logex e loge2 x e
*44. If x
dx A(log(loge x)) B loge (1 loge x) []
C log(2 log e x) K , then
(A) A B 2 (B) AC 0 (C) A B 0 (D) A B C 3
dx 1
*45. If 1 sin 4 x x a tan x b tan ( c tan x) D, then : []
1 1
(A) a (B) b 2 (C) c 2 (D) b
2 2 2
tan x
sin x cos x dx A( f ( x)) c, then: []
1/ m
*46. If
(A) A=2 (B) m=2 (C) f ( x) tan x (D) A m 5
dx x 4a
47. If 1 sin x tan 2 a c, then
is equal to ______. []
3sin x 2cos x
2sin x 3cos x dx lx m log e | 2sin x 3cos x | c then l m2 is equal to ______. []
2
48. If
dx
49. If 1 tan x px q log e | cos x sin x | c then p q equals __________. []
11/3 1/3 3(1 4 tan 2 x)
50. (sin x) (cos x) dx
8 H ( x)
c, then H ( / 4) is _________. []
VMC | Mathematics 9 ALPS-2334 | JEE-2023
You might also like
- Question Bank 2nd Year Math CT - 3Document5 pagesQuestion Bank 2nd Year Math CT - 3awaisasghar935No ratings yet
- Live Quiz 11: Mathematics 1. (1 Min)Document3 pagesLive Quiz 11: Mathematics 1. (1 Min)sikkaNo ratings yet
- Live Quiz - IC-1 - (1-07-21) - QuestionDocument4 pagesLive Quiz - IC-1 - (1-07-21) - Questionlavya guptaNo ratings yet
- Assign-1 Integration by Use of Basic FormulaeDocument3 pagesAssign-1 Integration by Use of Basic FormulaeDhruv KuchhalNo ratings yet
- Maths Advanced Level Problem Solving (ALPS-4) - PaperDocument9 pagesMaths Advanced Level Problem Solving (ALPS-4) - PaperAnanmay ChauhanNo ratings yet
- ALPS 2332 Maths Assignment PaperDocument10 pagesALPS 2332 Maths Assignment PaperDhruv JainNo ratings yet
- Indefinite Integrals Assignment Maths NKMDocument24 pagesIndefinite Integrals Assignment Maths NKMDisha KatariaNo ratings yet
- Indefinite Integration - QuestionDocument4 pagesIndefinite Integration - Questionbest badmintonNo ratings yet
- Indefinite IntegrationDocument58 pagesIndefinite IntegrationSubrata KarmakarNo ratings yet
- Integration Fiitjee CPPDocument6 pagesIntegration Fiitjee CPPPratham Sharma50% (2)
- Assignment: Chapter # 4 DifferentiabilityDocument3 pagesAssignment: Chapter # 4 DifferentiabilityRamish AhmedNo ratings yet
- Before Allen Class 11 29 JuneDocument3 pagesBefore Allen Class 11 29 JuneYatharth KaranNo ratings yet
- Functions, Inverse Trigonometry (ALPS-1) PaperDocument14 pagesFunctions, Inverse Trigonometry (ALPS-1) PaperRajendra JatNo ratings yet
- I Integration-03 - Exercise 1Document20 pagesI Integration-03 - Exercise 1Raju SinghNo ratings yet
- 12th Maths Chapter 2 Test 1 MCQsDocument1 page12th Maths Chapter 2 Test 1 MCQsabdul majeedNo ratings yet
- limitsDocument26 pageslimitsShikamaru NaraNo ratings yet
- ALPS Mathematics 2201 - JEE 2022: SyllabusDocument14 pagesALPS Mathematics 2201 - JEE 2022: SyllabusYash Dhoke100% (1)
- IndefiniteDocument40 pagesIndefinitePritee Priyambada TripathyNo ratings yet
- Spotlight - Advanced - Day-1 - In-Class Assignment - Mathematics - (Que. & Answer Key)Document8 pagesSpotlight - Advanced - Day-1 - In-Class Assignment - Mathematics - (Que. & Answer Key)Jyothi BrothersNo ratings yet
- Indefinite Integration-CLIP-1: Log Sinx Cosx C Log - Sin X Cosx - CDocument5 pagesIndefinite Integration-CLIP-1: Log Sinx Cosx C Log - Sin X Cosx - CDishika MaityNo ratings yet
- Not To Be Taken AwayDocument3 pagesNot To Be Taken AwayTonyNo ratings yet
- basic maths calculus 2Document5 pagesbasic maths calculus 2SashankNo ratings yet
- DPP No.3 For Week (07-06-10 To 12-06-10) Total Marks: 33 Max. Time: 33 MinDocument2 pagesDPP No.3 For Week (07-06-10 To 12-06-10) Total Marks: 33 Max. Time: 33 MinDhruv SharmaNo ratings yet
- Black Board Problems For JEE Advanced Set-9Document8 pagesBlack Board Problems For JEE Advanced Set-9ASHISH NAIK100% (1)
- Differentiation Question FinalDocument19 pagesDifferentiation Question FinalAnubhav vaishNo ratings yet
- SM 025 - Integration SoalanDocument9 pagesSM 025 - Integration SoalansharuNo ratings yet
- 2011E.C Second Semester Mathematics Worksheet-Five For Grade 12Document10 pages2011E.C Second Semester Mathematics Worksheet-Five For Grade 12Firie SibihatNo ratings yet
- 10Document4 pages10sikkaNo ratings yet
- 2024 Maths 1st Final ExamDocument4 pages2024 Maths 1st Final ExamOsman AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Quiz-9: Vidyamandir Classes: Innovating For Your SuccessDocument4 pagesQuiz-9: Vidyamandir Classes: Innovating For Your SuccesssikkaNo ratings yet
- Function-04 - Exercise - 1Document20 pagesFunction-04 - Exercise - 1Raju SinghNo ratings yet
- MAC2233 2010 Summer T3ADocument5 pagesMAC2233 2010 Summer T3AlllloNo ratings yet
- Quiz - Basic MathsDocument3 pagesQuiz - Basic MathsShashwat MishraNo ratings yet
- 2Document2 pages2sikkaNo ratings yet
- (Only Single Correct Answer Type Questions) : Part-ADocument4 pages(Only Single Correct Answer Type Questions) : Part-AAdrielly LopesNo ratings yet
- Master Sheet Indef e Nite Integration by Om SirDocument16 pagesMaster Sheet Indef e Nite Integration by Om SirRajvardhan singh SisodiyaNo ratings yet
- 129 Class TestDocument4 pages129 Class Testjaiswal23456No ratings yet
- Ii 3 8 2020Document6 pagesIi 3 8 2020ROBIN GUPTANo ratings yet
- I Integration-04 - ExerciseDocument13 pagesI Integration-04 - ExerciseRaju SinghNo ratings yet
- JEE Main Integral Calculus Important QuestionsDocument21 pagesJEE Main Integral Calculus Important QuestionsZombie Gamer100% (1)
- Differentiation: Dy DX Dy DX Dy DXDocument3 pagesDifferentiation: Dy DX Dy DX Dy DXcharan dheepNo ratings yet
- Allen Adv PapersDocument152 pagesAllen Adv PapersAbdullapoor RamReddy0% (2)
- Tutorial 9 (Baru06)Document6 pagesTutorial 9 (Baru06)nabilahNo ratings yet
- Student Copy. CAPS-1Document4 pagesStudent Copy. CAPS-1Vanshika LudhaniNo ratings yet
- M1 Bit Bank PDFDocument10 pagesM1 Bit Bank PDFK Sushmanth ReddyNo ratings yet
- Differentiation: FIIT-JEE LTD., 48, Gurukripa Complex, M.P. Nagar, Zone-II, Bhopal (M.P.), PH.: 4253355, 4253455Document2 pagesDifferentiation: FIIT-JEE LTD., 48, Gurukripa Complex, M.P. Nagar, Zone-II, Bhopal (M.P.), PH.: 4253355, 4253455Anonymous UserNo ratings yet
- LCD RKTDocument12 pagesLCD RKTTamanna SahuNo ratings yet
- M A T H e M A T I C SDocument5 pagesM A T H e M A T I C SAtharva GanjuNo ratings yet
- 11 Indefinite Integration DPP 11Document16 pages11 Indefinite Integration DPP 11tikam chandNo ratings yet
- Vibrant Academy: (India) Private LimitedDocument2 pagesVibrant Academy: (India) Private LimitedShadhasanNo ratings yet
- MathematicsDocument3 pagesMathematicsChinil Kumar ABNo ratings yet
- Errorless MoDDocument23 pagesErrorless MoDashmitaramoliya123No ratings yet
- Xercise: Multiple Correct (Objective Questions)Document1 pageXercise: Multiple Correct (Objective Questions)Vishu vevoNo ratings yet
- Definite Indefinite Integration (Area) (12th Pass)Document131 pagesDefinite Indefinite Integration (Area) (12th Pass)inventing new100% (1)
- PracticePaper - D06 Jul 2023Document8 pagesPracticePaper - D06 Jul 2023kadianvikhyatNo ratings yet
- Manoj Chauhan Sir: Maths byDocument15 pagesManoj Chauhan Sir: Maths byAbhiyanshu KumarNo ratings yet
- LCDDocument2 pagesLCDKumar AtthiNo ratings yet
- Function_NOS_ModerateDocument3 pagesFunction_NOS_Moderatearijeet141556No ratings yet
- Factoring and Algebra - A Selection of Classic Mathematical Articles Containing Examples and Exercises on the Subject of Algebra (Mathematics Series)From EverandFactoring and Algebra - A Selection of Classic Mathematical Articles Containing Examples and Exercises on the Subject of Algebra (Mathematics Series)No ratings yet
- MA1511 Chapter 4Document18 pagesMA1511 Chapter 4Kang Le LimNo ratings yet
- Maths Revision DPP No 4Document8 pagesMaths Revision DPP No 4Praphul Pulkit GiriNo ratings yet
- Sydney Grammar 2017 Year 10 Maths Yearly & SolutionsDocument18 pagesSydney Grammar 2017 Year 10 Maths Yearly & Solutionschloe.paleoNo ratings yet
- Myp 4 Extended Mathematics Holiday Assignment 2Document1 pageMyp 4 Extended Mathematics Holiday Assignment 2Joel LogboNo ratings yet
- Finite Difference Method: ME710 Mathematical Methods For Engineers Mechanical Engineering NITK SurathkalDocument20 pagesFinite Difference Method: ME710 Mathematical Methods For Engineers Mechanical Engineering NITK SurathkalSantosh Kumar AgastiNo ratings yet
- Basic Numeracy SimplificationDocument6 pagesBasic Numeracy SimplificationIAS EXAM PORTALNo ratings yet
- Integrals Yielding Inverse Hyperbolic Functions PDFDocument2 pagesIntegrals Yielding Inverse Hyperbolic Functions PDFStevenzel Eala EstellaNo ratings yet
- Operations Research: OxfordDocument7 pagesOperations Research: OxfordmadhavNo ratings yet
- Ma210 Course OutlineDocument1 pageMa210 Course OutlineVitu Verctor ViyuyiNo ratings yet
- 4 The General Term of A SequenceDocument10 pages4 The General Term of A SequenceSandra Nicole FernandezNo ratings yet
- ALGEBRADocument73 pagesALGEBRALorena Espeso JayawardenaNo ratings yet
- Turbulence: MIE1207 September, 2012Document128 pagesTurbulence: MIE1207 September, 2012Sepehr SaNo ratings yet
- Na - 2Document314 pagesNa - 2Himanshu YadavNo ratings yet
- Ex 4 7 FSC Part1Document2 pagesEx 4 7 FSC Part1usamalatif8941No ratings yet
- Lesson 4.A: Defining of Logarithmic Function, Equations and InequalitiesDocument9 pagesLesson 4.A: Defining of Logarithmic Function, Equations and InequalitiesAniqah Mardi Macuja EscarianNo ratings yet
- Field ProbsDocument19 pagesField Probsvanaj123No ratings yet
- IBHL Best 5Document4 pagesIBHL Best 5JennyNo ratings yet
- 9th Maths Chap 56Document2 pages9th Maths Chap 56Rana Hassan TariqNo ratings yet
- Ztransform AppDocument5 pagesZtransform AppSyed Ali RazaNo ratings yet
- Reaserch On PDE of Addis Abeba UniversityDocument31 pagesReaserch On PDE of Addis Abeba UniversityAman BetsoNo ratings yet
- InverseDocument31 pagesInverseShashank KumarNo ratings yet
- Prologue: 0.1 Books and AlgorithmsDocument9 pagesPrologue: 0.1 Books and AlgorithmsSivapremjiNo ratings yet
- Functional Analysis ChidumiDocument209 pagesFunctional Analysis ChidumiTaffohouo Nwaffeu Yves ValdezNo ratings yet
- On The Shortest Spanning Subtree of A Graph and The Traveling Salesman Problem - Joseph KruskalDocument3 pagesOn The Shortest Spanning Subtree of A Graph and The Traveling Salesman Problem - Joseph KruskalMauricioNo ratings yet
- Vector Mechanics by JohnsonDocument34 pagesVector Mechanics by JohnsonSushil AryanNo ratings yet
- Joint DensityDocument28 pagesJoint Densitylordbuzz123No ratings yet
- Ma 2211Document11 pagesMa 2211Saravanan MJNo ratings yet
- Laplace Table PDFDocument2 pagesLaplace Table PDFrobertNo ratings yet
- Jaypee University of Information Technology WAKNAGHAT, DISTT. SOLAN (H.P.) - 173215Document4 pagesJaypee University of Information Technology WAKNAGHAT, DISTT. SOLAN (H.P.) - 173215Shivam MauryaNo ratings yet
- The Limit Process (An Intuitive Introduction) : Calculus Is A Limit in One Sense or Another. For ExampleDocument1 pageThe Limit Process (An Intuitive Introduction) : Calculus Is A Limit in One Sense or Another. For ExampleagegnehutamiratNo ratings yet