Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Worksheet Week 2 Respirasi_English
Worksheet Week 2 Respirasi_English
Uploaded by
Princes TelCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- RESPIRATORY SYSTEM WORKSHEET Answer KeyDocument5 pagesRESPIRATORY SYSTEM WORKSHEET Answer KeyIker AragonesNo ratings yet
- Respiratory Respiratory Physiology (MCQS)Document2 pagesRespiratory Respiratory Physiology (MCQS)atefmabood100% (11)
- Histology Question Bank-1Document55 pagesHistology Question Bank-1Abd El-Rahman Salah100% (5)
- Supercharging Quantum-Touch - Alan Herriott (Color Charts & Summary Only)Document12 pagesSupercharging Quantum-Touch - Alan Herriott (Color Charts & Summary Only)Dragorad Vitoriović100% (10)
- Shier - Hole's Human Anatomy & Physiology 13e-1Document30 pagesShier - Hole's Human Anatomy & Physiology 13e-1ptchiquynhNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Test Report: Test Name Result Biological Reference Interval Uric AcidDocument5 pagesLaboratory Test Report: Test Name Result Biological Reference Interval Uric AcidBalraj EnjamuriNo ratings yet
- 36 ch17 PDFDocument19 pages36 ch17 PDFShivamNo ratings yet
- Class11 Biology Chapter 17. BREATHING AND EXCHANGE OF GASESDocument5 pagesClass11 Biology Chapter 17. BREATHING AND EXCHANGE OF GASESrn0828027No ratings yet
- Introduction To Blood: PlasmaDocument7 pagesIntroduction To Blood: Plasmaعبدالحكيم النهديNo ratings yet
- Mind Booster 03 (10th)Document6 pagesMind Booster 03 (10th)bijaypdgupta30No ratings yet
- Biology Chapter 7Document18 pagesBiology Chapter 7edain84No ratings yet
- Breathing and Exchange of GasesDocument12 pagesBreathing and Exchange of Gasessneh882016No ratings yet
- Answer Discussion Share: (A) Inspiratory Reserve Volume (IRV) Expiratory Reserve Volume (ERV)Document8 pagesAnswer Discussion Share: (A) Inspiratory Reserve Volume (IRV) Expiratory Reserve Volume (ERV)gopeabhijit85No ratings yet
- Breathing and Exchange of GasesDocument5 pagesBreathing and Exchange of Gasessonu kumarNo ratings yet
- Breathing and Exchange of GasesDocument8 pagesBreathing and Exchange of GasesArnav DeshpandeNo ratings yet
- Part 1: Critical Thinking: A. Arterial Blood Gas Analysis Is Commonly Used Diagnostic Tool To Evaluate The PartialDocument4 pagesPart 1: Critical Thinking: A. Arterial Blood Gas Analysis Is Commonly Used Diagnostic Tool To Evaluate The PartialJewel BerbanoNo ratings yet
- 11.17 Breathing and Exchanges of GasesDocument7 pages11.17 Breathing and Exchanges of GasesMoonesh MKNo ratings yet
- Breathing and Exchange of GasesDocument384 pagesBreathing and Exchange of GasesM.Kishore KumarNo ratings yet
- 2.3 Transport: - The Metabolic Demands of Many OrganismsDocument8 pages2.3 Transport: - The Metabolic Demands of Many OrganismsAnonymous u7cQyr3QYNo ratings yet
- respiratory MCQs.pdfDocument8 pagesrespiratory MCQs.pdfnadakattan2004No ratings yet
- CHAPTER Respiration and CirculationDocument5 pagesCHAPTER Respiration and CirculationlatasabarikNo ratings yet
- Soalan Sains PMRDocument121 pagesSoalan Sains PMRFazil Jay100% (2)
- Breathing and RespirationDocument5 pagesBreathing and RespirationPriyansh PatelNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System Power PointDocument24 pagesRespiratory System Power PointammarNo ratings yet
- Q1: Explain Briefly The Mechanism of Ventilation? Ans: VentilationDocument5 pagesQ1: Explain Briefly The Mechanism of Ventilation? Ans: VentilationAsmaa KhanNo ratings yet
- Respiratory Physiology MCQ'SDocument5 pagesRespiratory Physiology MCQ'SayashanpNo ratings yet
- Module 6 AssessmentDocument6 pagesModule 6 Assessmentapi-98991203No ratings yet
- Chapter 23 ExcretionDocument3 pagesChapter 23 Excretionmmido1425No ratings yet
- Lecture 7 (Gasses & Pressure)Document9 pagesLecture 7 (Gasses & Pressure)Άγγελος ΧαβέλαςNo ratings yet
- PHYSIO MCQsDocument10 pagesPHYSIO MCQsarwa fawzy100% (1)
- ExerciseDocument16 pagesExercisePriyanshu PalNo ratings yet
- Modul 1Document28 pagesModul 1Irrinna Shakinah100% (1)
- Oxygen and Carbon Dioxide Transport - PPTX JONELTADocument32 pagesOxygen and Carbon Dioxide Transport - PPTX JONELTArithikaNo ratings yet
- Section-I Mcqs and SeqsDocument3 pagesSection-I Mcqs and SeqsSadia NasirNo ratings yet
- Lec-18 - Respiratory & Excretory SystemDocument23 pagesLec-18 - Respiratory & Excretory Systemfahadkhanbd911No ratings yet
- Ncert Solutions Feb2021 For Class 11 Biology Chapter 17Document8 pagesNcert Solutions Feb2021 For Class 11 Biology Chapter 17TheLost GuyNo ratings yet
- Breathing & Exchange of Gases 90 QuestionsDocument92 pagesBreathing & Exchange of Gases 90 Questionsa0762580No ratings yet
- Transport of Respiratory GasesDocument27 pagesTransport of Respiratory GasesSyahmi Ieskandar100% (1)
- Question Bank: Gaseous ExchangeDocument3 pagesQuestion Bank: Gaseous Exchangewallace120No ratings yet
- Points To Remember: Biology Class - 11Document8 pagesPoints To Remember: Biology Class - 11AnitaNo ratings yet
- First Step To ModDocument41 pagesFirst Step To Modcarlos ali issaNo ratings yet
- Carboxytherapy 2018 Final EditDocument19 pagesCarboxytherapy 2018 Final Editd.miramontesNo ratings yet
- Gas Exchange - Respirasi Blok 2.1.maret.15Document29 pagesGas Exchange - Respirasi Blok 2.1.maret.15Fatiha TamadNo ratings yet
- Latih Tubi Topikal Form 3Document9 pagesLatih Tubi Topikal Form 3Mona MohtarNo ratings yet
- MV FAsjn 50 Jeq F0 HBKQFVDocument12 pagesMV FAsjn 50 Jeq F0 HBKQFVaanyapandey102No ratings yet
- Chapter: Breathing and Exchange of Gases: BIOLOGY - AssignmentDocument9 pagesChapter: Breathing and Exchange of Gases: BIOLOGY - Assignmentyogesh ahireNo ratings yet
- Self Quizzes Chapter 2-3: See This Figure Then Answer (1-2)Document3 pagesSelf Quizzes Chapter 2-3: See This Figure Then Answer (1-2)Dr DolittleNo ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument10 pagesRespiratory SystemSudip NeupaneNo ratings yet
- Gaseous Exchange NotesDocument8 pagesGaseous Exchange NotesMonique RobinsonNo ratings yet
- 8.DAY-8 ZOO - Breathing and Exchange of Gases - 25-05-2020Document11 pages8.DAY-8 ZOO - Breathing and Exchange of Gases - 25-05-2020Ramakrishna ReddyNo ratings yet
- Crash DPT Zoo 29.03.24Document3 pagesCrash DPT Zoo 29.03.24Deena chemistNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 14 The Respiratory System PDFDocument7 pagesChapter - 14 The Respiratory System PDFben martin100% (1)
- Breathing and Exchange of GasesDocument8 pagesBreathing and Exchange of GasessuryababaNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 17 Breathing &exchange of Gases-NotesDocument9 pagesCHAPTER 17 Breathing &exchange of Gases-Notessukaina mumtazNo ratings yet
- Chapter 17 - BREATHING AND EXCHANGE OF GASESDocument7 pagesChapter 17 - BREATHING AND EXCHANGE OF GASESprernatiwary508No ratings yet
- List Major Muscles Involved in Respiration (Inspiration and Expiration) at Rest and During ExerciseDocument5 pagesList Major Muscles Involved in Respiration (Inspiration and Expiration) at Rest and During ExerciseEmMa DHieyahNo ratings yet
- Blood Circulation QuestionsDocument3 pagesBlood Circulation QuestionsMo GamerNo ratings yet
- Class XI Breathing and Exchange of Gases Biology (MCQ'S) (21 - 07 - 2023)Document5 pagesClass XI Breathing and Exchange of Gases Biology (MCQ'S) (21 - 07 - 2023)soda pdfNo ratings yet
- Ncert Solution Breathing and Exchange of GasesDocument10 pagesNcert Solution Breathing and Exchange of GasesAyush DuttaNo ratings yet
- My Draft Partial PressuresDocument4 pagesMy Draft Partial Pressureslovelyc95No ratings yet
- Mechanism of Respiration, Fermentation and ChemoheterothropDocument59 pagesMechanism of Respiration, Fermentation and Chemoheterothropd25No ratings yet
- BEG3Document4 pagesBEG3iks.ikshvaku.2829No ratings yet
- 15 Respiratory AcidosisDocument40 pages15 Respiratory AcidosisJoel Topf100% (8)
- O Level Biology Practice For Structured Questions RespirationFrom EverandO Level Biology Practice For Structured Questions RespirationRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2)
- Business ConceptDocument22 pagesBusiness ConceptJossi AbuleNo ratings yet
- CHN QUESTIONSDocument19 pagesCHN QUESTIONSChamCham Aquino100% (3)
- Tuberculosis (TB) Blood Test (IGRA)Document4 pagesTuberculosis (TB) Blood Test (IGRA)Denada Florencia LeonaNo ratings yet
- Dengue Hemorrhagic Fever: Supervised By: Dr. Pulung M. Silalahi, Sp.A Created: Siti Zulfah (1102014255)Document37 pagesDengue Hemorrhagic Fever: Supervised By: Dr. Pulung M. Silalahi, Sp.A Created: Siti Zulfah (1102014255)sitizulfahhNo ratings yet
- ஆடுDocument5 pagesஆடுMuthu SamyNo ratings yet
- Body PartsDocument4 pagesBody PartsMatthias Dos SantosNo ratings yet
- 1323101710area 10Document16 pages1323101710area 10CoolerAdsNo ratings yet
- The Reproductive System: Powerpoint Lecture SlidesDocument175 pagesThe Reproductive System: Powerpoint Lecture SlidesMartin R. GarciaNo ratings yet
- Radiology and HoneyCombDocument12 pagesRadiology and HoneyCombmuhhasanalbolkiah saidNo ratings yet
- Clinical QigongDocument5 pagesClinical QigongFlorin Iacob100% (1)
- NatokinaseDocument6 pagesNatokinasefabadioNo ratings yet
- Mock ExamsDocument3 pagesMock ExamsRon DanyNo ratings yet
- Wool and Worsted YarnDocument10 pagesWool and Worsted Yarnraghavbindal100% (1)
- Communicable Diseases: Presentation SubtitleDocument25 pagesCommunicable Diseases: Presentation Subtitlesarahsealey100% (1)
- Urinary SystemDocument66 pagesUrinary SystemJustine Vens G. AgustinNo ratings yet
- Worm Infestation and HomoeopathyDocument15 pagesWorm Infestation and HomoeopathyDr. Rajneesh Kumar Sharma MD Hom100% (2)
- Common Reproductive Issues Instructor VersionDocument13 pagesCommon Reproductive Issues Instructor VersionDanielle DiorioNo ratings yet
- Procedure Rabbit Blood CollectionDocument4 pagesProcedure Rabbit Blood CollectionryzeepotNo ratings yet
- Ecc and Rampant CariesDocument39 pagesEcc and Rampant CariesAnkita Arora100% (1)
- Blood Pressure Measurement in Children: A Pocket Guide ToDocument4 pagesBlood Pressure Measurement in Children: A Pocket Guide TostevetkwongNo ratings yet
- Background To Pig Production in FijiDocument58 pagesBackground To Pig Production in FijiManoa Nagatalevu Tupou91% (11)
- Fisher 2009Document6 pagesFisher 2009Maryanne CunhaNo ratings yet
- Mandibular Movements Up L of DDocument79 pagesMandibular Movements Up L of DkrondanNo ratings yet
- Pig Farming 3 LakDocument9 pagesPig Farming 3 Lakkartik Debnath100% (1)
- Basic Cardiac Life Support 2011Document6 pagesBasic Cardiac Life Support 2011Tashfeen Bin NazeerNo ratings yet
- Tema PediDocument9 pagesTema PediClaudiu Andrei MunteanuNo ratings yet
Worksheet Week 2 Respirasi_English
Worksheet Week 2 Respirasi_English
Uploaded by
Princes TelCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Worksheet Week 2 Respirasi_English
Worksheet Week 2 Respirasi_English
Uploaded by
Princes TelCopyright:
Available Formats
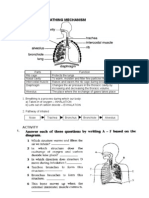
WORKSHEET WEEK 2
Physiology of Respiratory System
PRINCES ARDE LINES
MONICA
Name: TELAUMBANUA NIM:01501220035 Group: IT
1. What does it mean by (total 2 points):
a. Tidal volume (TV) adalah pernapasan normal 500 ml udara dalam setiap nafas.
b. Vital Capacity: jumlah total udara yang dapat bertukar. Rumursnya vc= tv+irv+erv
c. Residual volume: udara yang tetap ada dalam paru paru dari udara setelah
mengeluarkan nafas. Jumlah udara 1200 ml.
d. Dead space volume:udara yang tetap ada dalam zona penghantaran dan tidak pernah
mencapai alveoi ,sekitar 150 ml.
2. Write the meaning of the term below (1 point):
Perfusion (Q) is:
Ventilation (V) is:
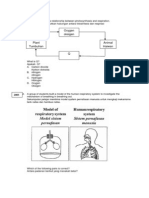
3. State what is included in the respiratory zone (1 point):
4. Name the two main areas of the brain involved in the control of breathing (1 point):
Complete the following paragraphs with the answers below. Keywords can be used
more than one time.
Total 12 points
Alveoli Red blood cells Hemoglobin Carbonic acid Oxyhemoglobin
Carbon dioxide Plasma Bicarbonate ions Water
External respiration is gas exchange between (5) _alveoli_____ and blood. Oxygen is
transported in two ways. Most oxygen binds to (6) __hemoglobin____ molecules in red
blood cells to form (7) ____oxyhemoglobin___ (HbO2).
Oxygen in small amounts is dissolved and carried in (8) ______. Most carbon dioxide is
transported in the plasma as (9) ___bikarbonats ions___ (HCO3-), which plays a vital role
in the blood buffer system. The conversion of carbon dioxide to bicarbonate ions occurs
in (10) ______, and the newly formed bicarbonate ions diffuse into plasma. A smaller
amount, between 20 and 30 percent of the carbon dioxide transported, is carried in (11)
______ to bind to hemoglobin.
Carbon dioxide carried in red blood cells binds to (12) ________ at a different
location from the oxygen bond in hemoglobin, so it does not affect oxygen transport.
Before carbon dioxide can diffuse from the blood into the alveoli, it must be released
from the bicarbonate ion form. For this process to occur, bicarbonate ions must enter the
red blood cells, where the bicarbonate ions combine with hydrogen ions (H +) to form
(13) __________ (H2CO3). Carbonic acid is rapidly broken down to form (14) ______
and (15) ____________ and carbon dioxide then diffuses from the blood and enters the
(16) _______.
Match the statements below correctly! Total 4 points.
17 The process of transporting oxygen from the lungs A External respiration
to the body’s tissue cells, and carbon dioxide to the
lungs through the cardiovascular system. D.
Gas transport
18 Movement of oxygen from the blood to the cell of B Pulmonary
tissues and carbon dioxide from the tissue cells to ventilation
the blood.C.
internal respiration
19 Air movement in and out lungs .B. C Internal respiration
Pulmonary ventilation
20 Movement of the oxygen from the blood to the D Gas transport
lungs and from the lungs to the blood.A.
external respiration
Complete the following paragraphs with the answer below. Keywords can be used more
than one time.
Total 4 POINTS
Tissue cells Red blood cells Oxygen
Internal respiration is the exchange of gases that occurs between the blood and (21) _______.
Carbon dioxide diffuses from the tissue cells into the blood. Carbon dioxide combines with
water in the blood to form carbonic acid, which quickly releases bicarbonate ions. Most of
the conversion of carbon dioxide to bicarbonate ions occurs in (22) __________. The
bicarbonate ions then diffuse into plasma, where they are transported . At the same time,
(23) _______ is released from hemoglobin, and oxygen rapidly diffuses out of the blood
and into (24) ________. Consequently, the blood in the veins of the systemic circulation
is poorer in oxygen and richer in carbon dioxide than in the veins leaving the lungs.
Maximum Total Points = 25 POINTS
Student Point = _____ POINTS
SCORE = (Student Point / 25) x 100%
You might also like
- RESPIRATORY SYSTEM WORKSHEET Answer KeyDocument5 pagesRESPIRATORY SYSTEM WORKSHEET Answer KeyIker AragonesNo ratings yet
- Respiratory Respiratory Physiology (MCQS)Document2 pagesRespiratory Respiratory Physiology (MCQS)atefmabood100% (11)
- Histology Question Bank-1Document55 pagesHistology Question Bank-1Abd El-Rahman Salah100% (5)
- Supercharging Quantum-Touch - Alan Herriott (Color Charts & Summary Only)Document12 pagesSupercharging Quantum-Touch - Alan Herriott (Color Charts & Summary Only)Dragorad Vitoriović100% (10)
- Shier - Hole's Human Anatomy & Physiology 13e-1Document30 pagesShier - Hole's Human Anatomy & Physiology 13e-1ptchiquynhNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Test Report: Test Name Result Biological Reference Interval Uric AcidDocument5 pagesLaboratory Test Report: Test Name Result Biological Reference Interval Uric AcidBalraj EnjamuriNo ratings yet
- 36 ch17 PDFDocument19 pages36 ch17 PDFShivamNo ratings yet
- Class11 Biology Chapter 17. BREATHING AND EXCHANGE OF GASESDocument5 pagesClass11 Biology Chapter 17. BREATHING AND EXCHANGE OF GASESrn0828027No ratings yet
- Introduction To Blood: PlasmaDocument7 pagesIntroduction To Blood: Plasmaعبدالحكيم النهديNo ratings yet
- Mind Booster 03 (10th)Document6 pagesMind Booster 03 (10th)bijaypdgupta30No ratings yet
- Biology Chapter 7Document18 pagesBiology Chapter 7edain84No ratings yet
- Breathing and Exchange of GasesDocument12 pagesBreathing and Exchange of Gasessneh882016No ratings yet
- Answer Discussion Share: (A) Inspiratory Reserve Volume (IRV) Expiratory Reserve Volume (ERV)Document8 pagesAnswer Discussion Share: (A) Inspiratory Reserve Volume (IRV) Expiratory Reserve Volume (ERV)gopeabhijit85No ratings yet
- Breathing and Exchange of GasesDocument5 pagesBreathing and Exchange of Gasessonu kumarNo ratings yet
- Breathing and Exchange of GasesDocument8 pagesBreathing and Exchange of GasesArnav DeshpandeNo ratings yet
- Part 1: Critical Thinking: A. Arterial Blood Gas Analysis Is Commonly Used Diagnostic Tool To Evaluate The PartialDocument4 pagesPart 1: Critical Thinking: A. Arterial Blood Gas Analysis Is Commonly Used Diagnostic Tool To Evaluate The PartialJewel BerbanoNo ratings yet
- 11.17 Breathing and Exchanges of GasesDocument7 pages11.17 Breathing and Exchanges of GasesMoonesh MKNo ratings yet
- Breathing and Exchange of GasesDocument384 pagesBreathing and Exchange of GasesM.Kishore KumarNo ratings yet
- 2.3 Transport: - The Metabolic Demands of Many OrganismsDocument8 pages2.3 Transport: - The Metabolic Demands of Many OrganismsAnonymous u7cQyr3QYNo ratings yet
- respiratory MCQs.pdfDocument8 pagesrespiratory MCQs.pdfnadakattan2004No ratings yet
- CHAPTER Respiration and CirculationDocument5 pagesCHAPTER Respiration and CirculationlatasabarikNo ratings yet
- Soalan Sains PMRDocument121 pagesSoalan Sains PMRFazil Jay100% (2)
- Breathing and RespirationDocument5 pagesBreathing and RespirationPriyansh PatelNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System Power PointDocument24 pagesRespiratory System Power PointammarNo ratings yet
- Q1: Explain Briefly The Mechanism of Ventilation? Ans: VentilationDocument5 pagesQ1: Explain Briefly The Mechanism of Ventilation? Ans: VentilationAsmaa KhanNo ratings yet
- Respiratory Physiology MCQ'SDocument5 pagesRespiratory Physiology MCQ'SayashanpNo ratings yet
- Module 6 AssessmentDocument6 pagesModule 6 Assessmentapi-98991203No ratings yet
- Chapter 23 ExcretionDocument3 pagesChapter 23 Excretionmmido1425No ratings yet
- Lecture 7 (Gasses & Pressure)Document9 pagesLecture 7 (Gasses & Pressure)Άγγελος ΧαβέλαςNo ratings yet
- PHYSIO MCQsDocument10 pagesPHYSIO MCQsarwa fawzy100% (1)
- ExerciseDocument16 pagesExercisePriyanshu PalNo ratings yet
- Modul 1Document28 pagesModul 1Irrinna Shakinah100% (1)
- Oxygen and Carbon Dioxide Transport - PPTX JONELTADocument32 pagesOxygen and Carbon Dioxide Transport - PPTX JONELTArithikaNo ratings yet
- Section-I Mcqs and SeqsDocument3 pagesSection-I Mcqs and SeqsSadia NasirNo ratings yet
- Lec-18 - Respiratory & Excretory SystemDocument23 pagesLec-18 - Respiratory & Excretory Systemfahadkhanbd911No ratings yet
- Ncert Solutions Feb2021 For Class 11 Biology Chapter 17Document8 pagesNcert Solutions Feb2021 For Class 11 Biology Chapter 17TheLost GuyNo ratings yet
- Breathing & Exchange of Gases 90 QuestionsDocument92 pagesBreathing & Exchange of Gases 90 Questionsa0762580No ratings yet
- Transport of Respiratory GasesDocument27 pagesTransport of Respiratory GasesSyahmi Ieskandar100% (1)
- Question Bank: Gaseous ExchangeDocument3 pagesQuestion Bank: Gaseous Exchangewallace120No ratings yet
- Points To Remember: Biology Class - 11Document8 pagesPoints To Remember: Biology Class - 11AnitaNo ratings yet
- First Step To ModDocument41 pagesFirst Step To Modcarlos ali issaNo ratings yet
- Carboxytherapy 2018 Final EditDocument19 pagesCarboxytherapy 2018 Final Editd.miramontesNo ratings yet
- Gas Exchange - Respirasi Blok 2.1.maret.15Document29 pagesGas Exchange - Respirasi Blok 2.1.maret.15Fatiha TamadNo ratings yet
- Latih Tubi Topikal Form 3Document9 pagesLatih Tubi Topikal Form 3Mona MohtarNo ratings yet
- MV FAsjn 50 Jeq F0 HBKQFVDocument12 pagesMV FAsjn 50 Jeq F0 HBKQFVaanyapandey102No ratings yet
- Chapter: Breathing and Exchange of Gases: BIOLOGY - AssignmentDocument9 pagesChapter: Breathing and Exchange of Gases: BIOLOGY - Assignmentyogesh ahireNo ratings yet
- Self Quizzes Chapter 2-3: See This Figure Then Answer (1-2)Document3 pagesSelf Quizzes Chapter 2-3: See This Figure Then Answer (1-2)Dr DolittleNo ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument10 pagesRespiratory SystemSudip NeupaneNo ratings yet
- Gaseous Exchange NotesDocument8 pagesGaseous Exchange NotesMonique RobinsonNo ratings yet
- 8.DAY-8 ZOO - Breathing and Exchange of Gases - 25-05-2020Document11 pages8.DAY-8 ZOO - Breathing and Exchange of Gases - 25-05-2020Ramakrishna ReddyNo ratings yet
- Crash DPT Zoo 29.03.24Document3 pagesCrash DPT Zoo 29.03.24Deena chemistNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 14 The Respiratory System PDFDocument7 pagesChapter - 14 The Respiratory System PDFben martin100% (1)
- Breathing and Exchange of GasesDocument8 pagesBreathing and Exchange of GasessuryababaNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 17 Breathing &exchange of Gases-NotesDocument9 pagesCHAPTER 17 Breathing &exchange of Gases-Notessukaina mumtazNo ratings yet
- Chapter 17 - BREATHING AND EXCHANGE OF GASESDocument7 pagesChapter 17 - BREATHING AND EXCHANGE OF GASESprernatiwary508No ratings yet
- List Major Muscles Involved in Respiration (Inspiration and Expiration) at Rest and During ExerciseDocument5 pagesList Major Muscles Involved in Respiration (Inspiration and Expiration) at Rest and During ExerciseEmMa DHieyahNo ratings yet
- Blood Circulation QuestionsDocument3 pagesBlood Circulation QuestionsMo GamerNo ratings yet
- Class XI Breathing and Exchange of Gases Biology (MCQ'S) (21 - 07 - 2023)Document5 pagesClass XI Breathing and Exchange of Gases Biology (MCQ'S) (21 - 07 - 2023)soda pdfNo ratings yet
- Ncert Solution Breathing and Exchange of GasesDocument10 pagesNcert Solution Breathing and Exchange of GasesAyush DuttaNo ratings yet
- My Draft Partial PressuresDocument4 pagesMy Draft Partial Pressureslovelyc95No ratings yet
- Mechanism of Respiration, Fermentation and ChemoheterothropDocument59 pagesMechanism of Respiration, Fermentation and Chemoheterothropd25No ratings yet
- BEG3Document4 pagesBEG3iks.ikshvaku.2829No ratings yet
- 15 Respiratory AcidosisDocument40 pages15 Respiratory AcidosisJoel Topf100% (8)
- O Level Biology Practice For Structured Questions RespirationFrom EverandO Level Biology Practice For Structured Questions RespirationRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2)
- Business ConceptDocument22 pagesBusiness ConceptJossi AbuleNo ratings yet
- CHN QUESTIONSDocument19 pagesCHN QUESTIONSChamCham Aquino100% (3)
- Tuberculosis (TB) Blood Test (IGRA)Document4 pagesTuberculosis (TB) Blood Test (IGRA)Denada Florencia LeonaNo ratings yet
- Dengue Hemorrhagic Fever: Supervised By: Dr. Pulung M. Silalahi, Sp.A Created: Siti Zulfah (1102014255)Document37 pagesDengue Hemorrhagic Fever: Supervised By: Dr. Pulung M. Silalahi, Sp.A Created: Siti Zulfah (1102014255)sitizulfahhNo ratings yet
- ஆடுDocument5 pagesஆடுMuthu SamyNo ratings yet
- Body PartsDocument4 pagesBody PartsMatthias Dos SantosNo ratings yet
- 1323101710area 10Document16 pages1323101710area 10CoolerAdsNo ratings yet
- The Reproductive System: Powerpoint Lecture SlidesDocument175 pagesThe Reproductive System: Powerpoint Lecture SlidesMartin R. GarciaNo ratings yet
- Radiology and HoneyCombDocument12 pagesRadiology and HoneyCombmuhhasanalbolkiah saidNo ratings yet
- Clinical QigongDocument5 pagesClinical QigongFlorin Iacob100% (1)
- NatokinaseDocument6 pagesNatokinasefabadioNo ratings yet
- Mock ExamsDocument3 pagesMock ExamsRon DanyNo ratings yet
- Wool and Worsted YarnDocument10 pagesWool and Worsted Yarnraghavbindal100% (1)
- Communicable Diseases: Presentation SubtitleDocument25 pagesCommunicable Diseases: Presentation Subtitlesarahsealey100% (1)
- Urinary SystemDocument66 pagesUrinary SystemJustine Vens G. AgustinNo ratings yet
- Worm Infestation and HomoeopathyDocument15 pagesWorm Infestation and HomoeopathyDr. Rajneesh Kumar Sharma MD Hom100% (2)
- Common Reproductive Issues Instructor VersionDocument13 pagesCommon Reproductive Issues Instructor VersionDanielle DiorioNo ratings yet
- Procedure Rabbit Blood CollectionDocument4 pagesProcedure Rabbit Blood CollectionryzeepotNo ratings yet
- Ecc and Rampant CariesDocument39 pagesEcc and Rampant CariesAnkita Arora100% (1)
- Blood Pressure Measurement in Children: A Pocket Guide ToDocument4 pagesBlood Pressure Measurement in Children: A Pocket Guide TostevetkwongNo ratings yet
- Background To Pig Production in FijiDocument58 pagesBackground To Pig Production in FijiManoa Nagatalevu Tupou91% (11)
- Fisher 2009Document6 pagesFisher 2009Maryanne CunhaNo ratings yet
- Mandibular Movements Up L of DDocument79 pagesMandibular Movements Up L of DkrondanNo ratings yet
- Pig Farming 3 LakDocument9 pagesPig Farming 3 Lakkartik Debnath100% (1)
- Basic Cardiac Life Support 2011Document6 pagesBasic Cardiac Life Support 2011Tashfeen Bin NazeerNo ratings yet
- Tema PediDocument9 pagesTema PediClaudiu Andrei MunteanuNo ratings yet