Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Experiment-No.7
Experiment-No.7
Uploaded by
Kent RodriguezCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Physics Report - Simple PendulumDocument4 pagesPhysics Report - Simple PendulumMartine Gjermundsen Ræstad95% (61)
- Lab 6Document5 pagesLab 6Yisela Bolanos0% (1)
- General Instructions: Do The Activity at Home. This Must Be Submitted Online. Save It in PDFDocument2 pagesGeneral Instructions: Do The Activity at Home. This Must Be Submitted Online. Save It in PDFSean Ben KadusaleNo ratings yet
- A-level Physics Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandA-level Physics Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (10)
- AP LabDocument4 pagesAP LabShabbir AlamNo ratings yet
- 01 135241 027 117221112503 01032024 114312amDocument4 pages01 135241 027 117221112503 01032024 114312amShabbir AlamNo ratings yet
- فيزياء تجربة البندول البسيطDocument6 pagesفيزياء تجربة البندول البسيطنعمه الشمريNo ratings yet
- Exp - 2 Simple Pendulam G DeterminationDocument5 pagesExp - 2 Simple Pendulam G DeterminationNahid HasanNo ratings yet
- Physic Lab Report Exp.5 Simple Harmonic MotionDocument14 pagesPhysic Lab Report Exp.5 Simple Harmonic Motioniqmalaqish05No ratings yet
- Expt-4:: Period of Oscillation For A Simple PendulumDocument7 pagesExpt-4:: Period of Oscillation For A Simple PendulumIsmail H. SiddiqueeNo ratings yet
- Real Depth in PHYSICS Measurement: Solution 1Document3 pagesReal Depth in PHYSICS Measurement: Solution 1Bidisha DeyNo ratings yet
- Salud, Juan Vicente 2017131112 PHYS101L/A2 2/11/2021Document13 pagesSalud, Juan Vicente 2017131112 PHYS101L/A2 2/11/2021yyuan ssaludNo ratings yet
- AP - Lab 04 - Measuring Time Period of Second Simple PendulumDocument3 pagesAP - Lab 04 - Measuring Time Period of Second Simple PendulumsalihaNo ratings yet
- Experiment 1 Simple Pendulum: Learning OutcomesDocument9 pagesExperiment 1 Simple Pendulum: Learning Outcomes翁绍棠No ratings yet
- 1C PhysicsDocument9 pages1C Physicsheartmelt slimesNo ratings yet
- Lab Report. 09: HY - 1104 Hysics AboratoryDocument6 pagesLab Report. 09: HY - 1104 Hysics AboratoryZulfiqar SakibNo ratings yet
- Determination of The Acceleration Due To Gravity Through A Simple PendulumDocument3 pagesDetermination of The Acceleration Due To Gravity Through A Simple PendulumKateNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4 Acceleration of Falling Bodies PendulumDocument4 pagesLesson 4 Acceleration of Falling Bodies PendulumCharles CristobalNo ratings yet
- Simple Pendulum: Applied MechanicsDocument4 pagesSimple Pendulum: Applied MechanicsabdulazizNo ratings yet
- PhylabDocument13 pagesPhylabMatihas DerejeNo ratings yet
- Lab 5Document5 pagesLab 5Yisela BolanosNo ratings yet
- PHYS 121L Laboratory Exerccise 3Document7 pagesPHYS 121L Laboratory Exerccise 3Ronaldo MaañoNo ratings yet
- Lab Report Experiment 2: Equation of Motion of Compound PendulumDocument9 pagesLab Report Experiment 2: Equation of Motion of Compound PendulumIhsan SamohNo ratings yet
- مختبر الفيزياء الطبية - pendulumDocument6 pagesمختبر الفيزياء الطبية - pendulumm9ngmnsxp4No ratings yet
- Mechanical Prinicples J Simple Pendulum Lab ReportDocument4 pagesMechanical Prinicples J Simple Pendulum Lab ReportNimi Lawson0% (1)
- Lab 5Document7 pagesLab 5tanoli9596No ratings yet
- Simple Pendulum (Lab Report 2)Document7 pagesSimple Pendulum (Lab Report 2)Erwin Manongol YsugNo ratings yet
- Lab The Simple PendulumDocument3 pagesLab The Simple PendulumBryan VillalobosNo ratings yet
- 126 Gravitational Acceleration PDFDocument2 pages126 Gravitational Acceleration PDFappannusaNo ratings yet
- Centre of Foundation Studies: Foundation Physics I Laboratory ReportDocument17 pagesCentre of Foundation Studies: Foundation Physics I Laboratory ReportMUHAMMAD YUS SHAFIQ MOHD HAFIZNo ratings yet
- B - Simple Pendulum2 Rev PDFDocument4 pagesB - Simple Pendulum2 Rev PDFAnagha SubashNo ratings yet
- PendulumDocument3 pagesPendulumvenkat krishnaNo ratings yet
- Pendulum Lab Report 3 (Final Rough Copy 1)Document15 pagesPendulum Lab Report 3 (Final Rough Copy 1)joe zouNo ratings yet
- F4 ExperimentsDocument52 pagesF4 ExperimentsKiTTy94% (16)
- Pendulum Lab Report 3 (Final Rough Copy 1)Document15 pagesPendulum Lab Report 3 (Final Rough Copy 1)joe zouNo ratings yet
- Physics Notes - 10 - 01 - MeasurementsDocument9 pagesPhysics Notes - 10 - 01 - MeasurementsNgosa MafotiNo ratings yet
- PHY 107 Experiment 5Document8 pagesPHY 107 Experiment 5Abdurrahman AdigunNo ratings yet
- Lab Manual E8 - Simple Harmonic MotionDocument3 pagesLab Manual E8 - Simple Harmonic MotionShu YeeNo ratings yet
- PHYSICS LAB MANUAL B Tech.Document44 pagesPHYSICS LAB MANUAL B Tech.mohammad.basitNo ratings yet
- Negative Mass and Negative Refractive Index in Atom Nuclei - Nuclear Wave Equation - Gravitational and Inertial Control: Part 3: Gravitational and Inertial Control, #3From EverandNegative Mass and Negative Refractive Index in Atom Nuclei - Nuclear Wave Equation - Gravitational and Inertial Control: Part 3: Gravitational and Inertial Control, #3No ratings yet
- Introduction to Non-Linear Mechanics. (AM-11), Volume 11From EverandIntroduction to Non-Linear Mechanics. (AM-11), Volume 11No ratings yet
- Applications of Derivatives Rate of Change (Calculus) Mathematics Question BankFrom EverandApplications of Derivatives Rate of Change (Calculus) Mathematics Question BankNo ratings yet
- The Spectral Theory of Toeplitz Operators. (AM-99), Volume 99From EverandThe Spectral Theory of Toeplitz Operators. (AM-99), Volume 99No ratings yet
- Navigation & Voyage Planning Companions: Navigation, Nautical Calculation & Passage Planning CompanionsFrom EverandNavigation & Voyage Planning Companions: Navigation, Nautical Calculation & Passage Planning CompanionsNo ratings yet
- Green's Function Estimates for Lattice Schrödinger Operators and Applications. (AM-158)From EverandGreen's Function Estimates for Lattice Schrödinger Operators and Applications. (AM-158)No ratings yet
- Standing on the Shoulder of Richard Feynman to Teach Physics BetterFrom EverandStanding on the Shoulder of Richard Feynman to Teach Physics BetterNo ratings yet
- O level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2From EverandO level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Mathematical Solution Unifying the Four Fundamental Forces in NatureFrom EverandMathematical Solution Unifying the Four Fundamental Forces in NatureNo ratings yet
Experiment-No.7
Experiment-No.7
Uploaded by
Kent RodriguezCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Experiment-No.7
Experiment-No.7
Uploaded by
Kent RodriguezCopyright:
Available Formats
Name: Student ID No.
: Course & Year:
Experiment No. 7
Measuring Acceleration Due to Gravity
Objectives
To determine the exact measurement of the acceleration due to gravity using
a simple pendulum
Theory and Analysis
The period of oscillation for 10 oscillations is measured and from the duration 𝜏 for
the oscillation determined.
Period of time for 10 oscillation -s
Duration T-s
From the formula of the period of oscillation
𝐿
T = 2𝜋
𝑔
Acceleration due to gravity
𝐿
g=4𝜋 2 𝑇2
T- Time period of simple pendulum (s)
g- Acceleration due to gravity (m/s2)
L-length of the pendulum (m)
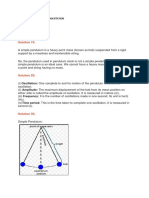
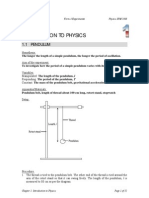
Figure 7 Simple Pendulum
Procedure:
1. Attach two (2) slotted weights at 50g.
2. The length of pendulum is about 70 to 90 cm.
3. Note the time (t) for oscillations using stop watch.
4. The period of oscillation T= t/10
5. Repeat the experiment for different lengths of the pendulum ‘L’. Find the
acceleration due to gravity (g) for the following lengths of pendulum: original length of
pendulum +5cm, original length of pendulum -5cm.
Table 7-1
Length of the Time taken for 10 oscillations t Period of T² 4𝜋 2 𝐿
pendulum L (s) oscillation 𝑔=
𝑇2
(meter) Trial 1 Trial 2 Trial 3 𝑡 (s²)
𝑇=
10 (m/s²)
(s)
0.15
0.25
0.35
0.45
0.55
Observations:
Questions:
1. How is pendulum affected by gravity?
2. How does the time period of a pendulum depend on gravity?
3. The period of simple pendulum at a given place with acceleration due to gravity depends
on?
4. Describe the experiment simple pendulum to find the value of acceleration due to gravity.
You might also like
- Physics Report - Simple PendulumDocument4 pagesPhysics Report - Simple PendulumMartine Gjermundsen Ræstad95% (61)
- Lab 6Document5 pagesLab 6Yisela Bolanos0% (1)
- General Instructions: Do The Activity at Home. This Must Be Submitted Online. Save It in PDFDocument2 pagesGeneral Instructions: Do The Activity at Home. This Must Be Submitted Online. Save It in PDFSean Ben KadusaleNo ratings yet
- A-level Physics Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandA-level Physics Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (10)
- AP LabDocument4 pagesAP LabShabbir AlamNo ratings yet
- 01 135241 027 117221112503 01032024 114312amDocument4 pages01 135241 027 117221112503 01032024 114312amShabbir AlamNo ratings yet
- فيزياء تجربة البندول البسيطDocument6 pagesفيزياء تجربة البندول البسيطنعمه الشمريNo ratings yet
- Exp - 2 Simple Pendulam G DeterminationDocument5 pagesExp - 2 Simple Pendulam G DeterminationNahid HasanNo ratings yet
- Physic Lab Report Exp.5 Simple Harmonic MotionDocument14 pagesPhysic Lab Report Exp.5 Simple Harmonic Motioniqmalaqish05No ratings yet
- Expt-4:: Period of Oscillation For A Simple PendulumDocument7 pagesExpt-4:: Period of Oscillation For A Simple PendulumIsmail H. SiddiqueeNo ratings yet
- Real Depth in PHYSICS Measurement: Solution 1Document3 pagesReal Depth in PHYSICS Measurement: Solution 1Bidisha DeyNo ratings yet
- Salud, Juan Vicente 2017131112 PHYS101L/A2 2/11/2021Document13 pagesSalud, Juan Vicente 2017131112 PHYS101L/A2 2/11/2021yyuan ssaludNo ratings yet
- AP - Lab 04 - Measuring Time Period of Second Simple PendulumDocument3 pagesAP - Lab 04 - Measuring Time Period of Second Simple PendulumsalihaNo ratings yet
- Experiment 1 Simple Pendulum: Learning OutcomesDocument9 pagesExperiment 1 Simple Pendulum: Learning Outcomes翁绍棠No ratings yet
- 1C PhysicsDocument9 pages1C Physicsheartmelt slimesNo ratings yet
- Lab Report. 09: HY - 1104 Hysics AboratoryDocument6 pagesLab Report. 09: HY - 1104 Hysics AboratoryZulfiqar SakibNo ratings yet
- Determination of The Acceleration Due To Gravity Through A Simple PendulumDocument3 pagesDetermination of The Acceleration Due To Gravity Through A Simple PendulumKateNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4 Acceleration of Falling Bodies PendulumDocument4 pagesLesson 4 Acceleration of Falling Bodies PendulumCharles CristobalNo ratings yet
- Simple Pendulum: Applied MechanicsDocument4 pagesSimple Pendulum: Applied MechanicsabdulazizNo ratings yet
- PhylabDocument13 pagesPhylabMatihas DerejeNo ratings yet
- Lab 5Document5 pagesLab 5Yisela BolanosNo ratings yet
- PHYS 121L Laboratory Exerccise 3Document7 pagesPHYS 121L Laboratory Exerccise 3Ronaldo MaañoNo ratings yet
- Lab Report Experiment 2: Equation of Motion of Compound PendulumDocument9 pagesLab Report Experiment 2: Equation of Motion of Compound PendulumIhsan SamohNo ratings yet
- مختبر الفيزياء الطبية - pendulumDocument6 pagesمختبر الفيزياء الطبية - pendulumm9ngmnsxp4No ratings yet
- Mechanical Prinicples J Simple Pendulum Lab ReportDocument4 pagesMechanical Prinicples J Simple Pendulum Lab ReportNimi Lawson0% (1)
- Lab 5Document7 pagesLab 5tanoli9596No ratings yet
- Simple Pendulum (Lab Report 2)Document7 pagesSimple Pendulum (Lab Report 2)Erwin Manongol YsugNo ratings yet
- Lab The Simple PendulumDocument3 pagesLab The Simple PendulumBryan VillalobosNo ratings yet
- 126 Gravitational Acceleration PDFDocument2 pages126 Gravitational Acceleration PDFappannusaNo ratings yet
- Centre of Foundation Studies: Foundation Physics I Laboratory ReportDocument17 pagesCentre of Foundation Studies: Foundation Physics I Laboratory ReportMUHAMMAD YUS SHAFIQ MOHD HAFIZNo ratings yet
- B - Simple Pendulum2 Rev PDFDocument4 pagesB - Simple Pendulum2 Rev PDFAnagha SubashNo ratings yet
- PendulumDocument3 pagesPendulumvenkat krishnaNo ratings yet
- Pendulum Lab Report 3 (Final Rough Copy 1)Document15 pagesPendulum Lab Report 3 (Final Rough Copy 1)joe zouNo ratings yet
- F4 ExperimentsDocument52 pagesF4 ExperimentsKiTTy94% (16)
- Pendulum Lab Report 3 (Final Rough Copy 1)Document15 pagesPendulum Lab Report 3 (Final Rough Copy 1)joe zouNo ratings yet
- Physics Notes - 10 - 01 - MeasurementsDocument9 pagesPhysics Notes - 10 - 01 - MeasurementsNgosa MafotiNo ratings yet
- PHY 107 Experiment 5Document8 pagesPHY 107 Experiment 5Abdurrahman AdigunNo ratings yet
- Lab Manual E8 - Simple Harmonic MotionDocument3 pagesLab Manual E8 - Simple Harmonic MotionShu YeeNo ratings yet
- PHYSICS LAB MANUAL B Tech.Document44 pagesPHYSICS LAB MANUAL B Tech.mohammad.basitNo ratings yet
- Negative Mass and Negative Refractive Index in Atom Nuclei - Nuclear Wave Equation - Gravitational and Inertial Control: Part 3: Gravitational and Inertial Control, #3From EverandNegative Mass and Negative Refractive Index in Atom Nuclei - Nuclear Wave Equation - Gravitational and Inertial Control: Part 3: Gravitational and Inertial Control, #3No ratings yet
- Introduction to Non-Linear Mechanics. (AM-11), Volume 11From EverandIntroduction to Non-Linear Mechanics. (AM-11), Volume 11No ratings yet
- Applications of Derivatives Rate of Change (Calculus) Mathematics Question BankFrom EverandApplications of Derivatives Rate of Change (Calculus) Mathematics Question BankNo ratings yet
- The Spectral Theory of Toeplitz Operators. (AM-99), Volume 99From EverandThe Spectral Theory of Toeplitz Operators. (AM-99), Volume 99No ratings yet
- Navigation & Voyage Planning Companions: Navigation, Nautical Calculation & Passage Planning CompanionsFrom EverandNavigation & Voyage Planning Companions: Navigation, Nautical Calculation & Passage Planning CompanionsNo ratings yet
- Green's Function Estimates for Lattice Schrödinger Operators and Applications. (AM-158)From EverandGreen's Function Estimates for Lattice Schrödinger Operators and Applications. (AM-158)No ratings yet
- Standing on the Shoulder of Richard Feynman to Teach Physics BetterFrom EverandStanding on the Shoulder of Richard Feynman to Teach Physics BetterNo ratings yet
- O level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2From EverandO level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Mathematical Solution Unifying the Four Fundamental Forces in NatureFrom EverandMathematical Solution Unifying the Four Fundamental Forces in NatureNo ratings yet