Professional Documents
Culture Documents
HW01Answer
HW01Answer
Uploaded by
kameshCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Cs456 Sample MidtermDocument10 pagesCs456 Sample MidtermTiasa MondolNo ratings yet
- Key Assignment 1Document14 pagesKey Assignment 1Karthik BalasubramanianNo ratings yet
- 20 ECE350 Final Exam 220914 141156Document20 pages20 ECE350 Final Exam 220914 141156LMAO KidUrBadNo ratings yet
- Home Work-3: CAP306: Computer NetworksDocument10 pagesHome Work-3: CAP306: Computer NetworksSurendra Singh ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Mob Net 2011 Exam SolutionDocument13 pagesMob Net 2011 Exam Solutionمحيي الدين الكميشىNo ratings yet
- ComputerNetworks ClassTest2 SolutionsDocument3 pagesComputerNetworks ClassTest2 Solutionshuyencttde180614No ratings yet
- Microcontroller: Alexander Kößler, Matthias Függer SS 2012 CourseDocument57 pagesMicrocontroller: Alexander Kößler, Matthias Függer SS 2012 Coursezzshi_200% (1)
- Introduction To Computer Networking (SSC 4) Exercise SeriesDocument27 pagesIntroduction To Computer Networking (SSC 4) Exercise SeriesMahmoud Handase35No ratings yet
- Chap 12Document6 pagesChap 12Varun AgarwalNo ratings yet
- 2013 Session 1: TELE3118: Network Technologies Week 2: Data Link LayerDocument28 pages2013 Session 1: TELE3118: Network Technologies Week 2: Data Link LayerXozanNo ratings yet
- Computer Communications & Networks Layer 2 Error ControlDocument23 pagesComputer Communications & Networks Layer 2 Error ControlKun NvtNo ratings yet
- Dnet Final 2022 To PrintDocument18 pagesDnet Final 2022 To PrintMevlüt YıldırımNo ratings yet
- Lte Mod 3 NTS EditdDocument27 pagesLte Mod 3 NTS EditdDavid DvoskineNo ratings yet
- Solutions OSI ExercisesDocument50 pagesSolutions OSI ExercisesHussam AlwareethNo ratings yet
- Solutions To EE555 Midterm, Summer 2003: Part 1: True/False Question (25 Points)Document4 pagesSolutions To EE555 Midterm, Summer 2003: Part 1: True/False Question (25 Points)MUHAMMAD AHSANNo ratings yet
- ComputernetwoektextDocument9 pagesComputernetwoektextVimal KumarNo ratings yet
- Faculty of Engineering, Sciences & Technology: Assignment # 03 - Spring Semester 2020Document8 pagesFaculty of Engineering, Sciences & Technology: Assignment # 03 - Spring Semester 2020Muhammad Usman AfaqNo ratings yet
- Computer Communication and NetworksDocument52 pagesComputer Communication and NetworksSaurabh JaiswalNo ratings yet
- Transport AnswersDocument5 pagesTransport AnswersPebo GreenNo ratings yet
- 2006 Exam PaperDocument2 pages2006 Exam PapernicholasiNo ratings yet
- d1 Multi AccessDocument14 pagesd1 Multi AccessgvgbabuNo ratings yet
- CCN NOTS Final Unit - 3Document39 pagesCCN NOTS Final Unit - 3Bruce Randall100% (3)
- SwitchDocument229 pagesSwitchABDELKARIM YOUSIFNo ratings yet
- Ee132b Hw3 SolDocument7 pagesEe132b Hw3 SolDylan Ler100% (1)
- Module3 ProblemsDocument11 pagesModule3 ProblemsGokul GokulNo ratings yet
- ACARSDocument42 pagesACARSanticlockwise180100% (3)
- Medium Access Control (MAC) Protocols For Ad Hoc Wireless Networks - IIIDocument47 pagesMedium Access Control (MAC) Protocols For Ad Hoc Wireless Networks - IIIfarhad_mfhNo ratings yet
- 5.2 CMOS Logic Gate Design: Serial or Parallel in Rs Transisto of NoDocument15 pages5.2 CMOS Logic Gate Design: Serial or Parallel in Rs Transisto of NoRaj AryanNo ratings yet
- For 15 MinDocument15 pagesFor 15 MinNaveen Kumar GummidalaNo ratings yet
- Midterm 1 Exam: Exercise 1 (5) Exercise 2 (5) Exercise 3 (4) Exercise 4 (6) TotalDocument4 pagesMidterm 1 Exam: Exercise 1 (5) Exercise 2 (5) Exercise 3 (4) Exercise 4 (6) TotalNada FSNo ratings yet
- 2012 Solutions PDFDocument17 pages2012 Solutions PDFYu Chen NgNo ratings yet
- Ee132b Homework 2Document3 pagesEe132b Homework 2YouRong YangNo ratings yet
- Hwk3 4 Su10 SolDocument11 pagesHwk3 4 Su10 SolKun LiNo ratings yet
- ch13 SolDocument4 pagesch13 SolSalekin MishuNo ratings yet
- Stop and Wait ProtocolDocument11 pagesStop and Wait ProtocolSanthoshSandyNo ratings yet
- Sample Solutions: TH TH THDocument6 pagesSample Solutions: TH TH THDivyankk VyasNo ratings yet
- Cs/ee 143 Communication Networks Chapter 4 Transport: Text: Walrand & Parakh, 2010 Steven Low CMS, EE, CaltechDocument34 pagesCs/ee 143 Communication Networks Chapter 4 Transport: Text: Walrand & Parakh, 2010 Steven Low CMS, EE, CaltechThinh Tran VanNo ratings yet
- Homework Assignment #3: EE122: Introduction To Communication Networks (Fall 2007)Document4 pagesHomework Assignment #3: EE122: Introduction To Communication Networks (Fall 2007)Jack Chen Su-LeeNo ratings yet
- NAME: - : Computer Networks I MID-TERM EXAM 2 - PART 2 (TOTAL: 5 Points) InstructionsDocument5 pagesNAME: - : Computer Networks I MID-TERM EXAM 2 - PART 2 (TOTAL: 5 Points) InstructionsikejimenesNo ratings yet
- LABORATORY MANUAL ON Digital COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUESDocument29 pagesLABORATORY MANUAL ON Digital COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUESChandra Mohanty0% (1)
- Final SolutionDocument3 pagesFinal SolutionJeanFrancoisAtemengueEbangaNo ratings yet
- 1C - Communication Networks - Circuit SwitchingDocument14 pages1C - Communication Networks - Circuit SwitchingDang KhueNo ratings yet
- Device Information: Investigating The CAMDocument4 pagesDevice Information: Investigating The CAMКирилл ГулякевичNo ratings yet
- Unmanaged Ethernet Redundant RingDocument12 pagesUnmanaged Ethernet Redundant RingForrest Heath IIINo ratings yet
- Exam #2 For Computer Networks (CIS 6930) SOLUTIONS : Problem #1Document4 pagesExam #2 For Computer Networks (CIS 6930) SOLUTIONS : Problem #1svahidsNo ratings yet
- Chap 05 PDFDocument21 pagesChap 05 PDFSidney100% (1)
- CIS 81 Fundamentals of Networking Chapter 5: Ethernet Part 2 of 2Document88 pagesCIS 81 Fundamentals of Networking Chapter 5: Ethernet Part 2 of 2amgstiNo ratings yet
- Space-Division Switch FabricsDocument18 pagesSpace-Division Switch FabricsHiteshwar GaurNo ratings yet
- Primbon RFDocument76 pagesPrimbon RFLutfi ArifNo ratings yet
- Nokia Double Data Rate For FDD Downlink Through Channel Code Puncturing in MIMO ChannelsDocument4 pagesNokia Double Data Rate For FDD Downlink Through Channel Code Puncturing in MIMO ChannelsPhebeNo ratings yet
- Final: Total 200 Points, Duration: 12:15pm-3:15pm: EE 359 - Wireless Communications - Autumn 2016Document3 pagesFinal: Total 200 Points, Duration: 12:15pm-3:15pm: EE 359 - Wireless Communications - Autumn 2016Debajyoti DattaNo ratings yet
- This Study Resource Was: Multiple Choice Questions ( × . )Document3 pagesThis Study Resource Was: Multiple Choice Questions ( × . )Đình NghĩaNo ratings yet
- 434 HW 3 SolDocument5 pages434 HW 3 SolSweet AliaNo ratings yet
- Data Link LayerDocument40 pagesData Link Layeronline support sr dream itNo ratings yet
- Solution Manual For Computer Networking A Top Down Approach 6 e 6th EditionDocument38 pagesSolution Manual For Computer Networking A Top Down Approach 6 e 6th Editionbrookemaxwellfhfpy100% (16)
- Analytical Modeling of Wireless Communication SystemsFrom EverandAnalytical Modeling of Wireless Communication SystemsNo ratings yet
- Digital Signal Processing Techniques and Applications in Radar Image ProcessingFrom EverandDigital Signal Processing Techniques and Applications in Radar Image ProcessingNo ratings yet
- SFP Modules UkDocument4 pagesSFP Modules UkcttopNo ratings yet
- HP Waranty ProductDocument34 pagesHP Waranty Productvno2000No ratings yet
- Cisco 2960g 8tcDocument5 pagesCisco 2960g 8tcZts MksNo ratings yet
- Fortinet Wireless Product MatrixDocument14 pagesFortinet Wireless Product MatrixAndrew WebbNo ratings yet
- IES-2060/IES-2042FX Series: Industrial 6-Port Lite-Managed Ethernet SwitchDocument4 pagesIES-2060/IES-2042FX Series: Industrial 6-Port Lite-Managed Ethernet Switchoring2012No ratings yet
- Formato Baja de Series 11sep23Document11 pagesFormato Baja de Series 11sep23ACEVEDO RIOS JOSE ANTONIONo ratings yet
- Midterm Exam - Attempt Review Data Com 3Document18 pagesMidterm Exam - Attempt Review Data Com 3dun lelNo ratings yet
- Qos SettingDocument21 pagesQos Settinglucky chandelNo ratings yet
- Technical Specification MEF 11Document33 pagesTechnical Specification MEF 11Nguyễn Văn PhụngNo ratings yet
- Network Security Issues of Data Link Layer An OverviewDocument6 pagesNetwork Security Issues of Data Link Layer An Overviewpuyish100% (1)
- OpenSAFETY Basic 2013 en PrintDocument45 pagesOpenSAFETY Basic 2013 en PrintAlexandru BourNo ratings yet
- IEEE 802.11 Architecture: Protocol - HTMLDocument8 pagesIEEE 802.11 Architecture: Protocol - HTMLThaddeus MooreNo ratings yet
- ACI 710 C.link Access Modem RevC 080110Document2 pagesACI 710 C.link Access Modem RevC 080110rbroussard2182No ratings yet
- ET GT 5ES Datasheet LDocument2 pagesET GT 5ES Datasheet LMuhammad Mubashir HassanNo ratings yet
- Cisco 4800 Access Point DatasheetDocument15 pagesCisco 4800 Access Point DatasheetBrandon BarreraNo ratings yet
- POE-151 / POE-152 / POE-161 User's ManualDocument52 pagesPOE-151 / POE-152 / POE-161 User's ManualgonzaloNo ratings yet
- LAN x64Document13 pagesLAN x64edgardo2No ratings yet
- Full Gigabit Ethernet Switch L2 Software 16 PortsDocument2 pagesFull Gigabit Ethernet Switch L2 Software 16 PortsMatijaDebogovićNo ratings yet
- Datasheet Titanium2122A CeDocument2 pagesDatasheet Titanium2122A CemmopNo ratings yet
- DrayTek Vigor AP 810Document2 pagesDrayTek Vigor AP 810pdelgadoNo ratings yet
- PCS-9882n+ìETHERNET SWITCH 2010catalog-15Document2 pagesPCS-9882n+ìETHERNET SWITCH 2010catalog-15Rinda_RaynaNo ratings yet
- CRS112 8P PDFDocument3 pagesCRS112 8P PDFLeonardo PachillaNo ratings yet
- Integra X DS v1.06Document6 pagesIntegra X DS v1.06Stefan HartungNo ratings yet
- Dynamic Adaption of DCF and PCF Mode of IEEE 802.11 WLAN: Abhishek GoliyaDocument57 pagesDynamic Adaption of DCF and PCF Mode of IEEE 802.11 WLAN: Abhishek GoliyaGaurav PathakNo ratings yet
- Albis Datasheet ACCEED 1416Document4 pagesAlbis Datasheet ACCEED 1416Gilberto GuzmánNo ratings yet
- iDRAC-G8PM9W2 - iDRAC9 - Sy1stem PDFDocument2 pagesiDRAC-G8PM9W2 - iDRAC9 - Sy1stem PDFSureSh FreemanNo ratings yet
- Allied Telesyn AT-MC10 - InstallDocument50 pagesAllied Telesyn AT-MC10 - InstallDBRSMedicalNo ratings yet
- TMGCMPDFDocument1 pageTMGCMPDFHakim Moi-memeNo ratings yet
- V1600G Series GPON OLT Datasheet V1.0Document13 pagesV1600G Series GPON OLT Datasheet V1.0nildo137 SANTOSNo ratings yet
- Network AssignmentDocument8 pagesNetwork AssignmentMohammed KhaleelullahNo ratings yet
HW01Answer
HW01Answer
Uploaded by
kameshCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
HW01Answer
HW01Answer
Uploaded by
kameshCopyright:
Available Formats
IT377 Homework #1 Answer Sheet
Name: ANSWER
Part I. Multiple choice - 40%, 1. MC 28%
1. _A__ 10. _C__
2. _B__ 11. _B__
3. _A__ 12. _D__
4. _C__ 13. -D—
5. _C__ 14. -C---
6. _C__
7. _B__
8. _A__ .
9. _A__
2. T/F (12%)
1. T
2. F
3. T
4. T
5. F
6. F
Part II. Questions - 36%
1. When multiple stations use the shared medium to send the data at the same time.
A collision will occur. The collision itself is a signal with evidently increased
amplitude (almost doubled). When a collision is detected, the sender will stop
sending data immediately and send a jam signal. The jam signal is designed to be
placed in the field of CRC (or FCS) of an Ethernet frame to prevent a receiver
from receiving a corrupted data frame (jam signal uses a fixed signal pattern,
which has only 1/(2^32) chance to be a correct CRC for the received frame).
2. A collision domain is a section of network that allows (layer-1) signal to be sent
across it. A consequence is if two stations on the same collision domain send
signals at the same time, a collision will occur.
- Each port on a hub is in the same collision domain.
- By contrast, each port on a bridge, a switch or a router is in a separate
collision domain.
IT377-HW#1 Answer Page 1 of 3
A broadcast domain is a network that allows (layer-2) broadcast messages to be
sent across it. A consequence is if a station A wants to talk to another station B
(knowing B’s IP address) on the same broadcast domain, station A can broadcast
a query (using ARP) to all stations on the same broadcast domain and find B’s
MAC address, then station A can send data (Ethernet frames) to B via layer-1 or
layer-2 devices.
- All ports on a hub or a switch are by default in the same broadcast
domain.
- All ports on a router are in the different broadcast domains
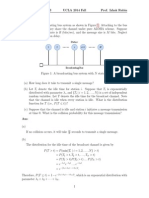
3. Compute the probability of collision at 2nd try.
2nd try: K = 1, using k=k+1
2nd try: K = 1 + 1 = 2
Random back-off window = P= 2k – 1 = 3
=> R= [0, P] = [0, 1, 2, 3]
A 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 1 2 2 2 2 3 3 3 3
B 0 1 2 3 0 1 2 3 0 1 2 3 0 1 2 3
The chance that two stations choose Window 0 at the same time is: 1/4 x 1/4; the
same chance if two stations choose Window 1, 2 or 3.
Thus, the probability of choosing the same back-off window = 4 x (1/4) x (1/4 )=25%
4. What is the mechanism in CSMA/CD to guarantee a sender can always detection
any potential collision? Please explain your answer.
- One condition needs be satisfied: slot time (frame size) >= round trip delay for
collision signal
- Min Ethernet frame size is used to meet this requirement which is 64 Bytes.
Part III Populate the MAC Forwarding Table (24%)
Ethernet Switch 1 (SW1) Ethernet Switch 2 (SW2)
Port Mac Address Port MAC Address
P11 99-88-77-01-01-01 P21 99-88-77-02-02-02
P12 33-22-11-11-11-11 P22 33-22-11-44-44-44
P12 33-22-11-22-22-22 P23 33-22-11-55-55-55
P13 33-22-11-33-33-33 P23 33-22-11-66-66-66
IT377-HW#1 Answer Page 2 of 3
Ethernet Switch 1 (SW3)
Port Mac Address
P31 99-88-77-02-02-02
P31 33-22-11-44-44-44
P32 33-22-11-55-55-55
P33 33-22-11-66-66-66
The MAC address of the switch is not needed on the MAC forwarding table. However,
one may argue about the bridge control protocol (such as STP). In this case, the MAC
address of Ethernet switch will also be seen on the MAC forwarding table of neighboring
switches.
- There are 2 broadcast domains; 8 collision domains.
IT377-HW#1 Answer Page 3 of 3
You might also like
- Cs456 Sample MidtermDocument10 pagesCs456 Sample MidtermTiasa MondolNo ratings yet
- Key Assignment 1Document14 pagesKey Assignment 1Karthik BalasubramanianNo ratings yet
- 20 ECE350 Final Exam 220914 141156Document20 pages20 ECE350 Final Exam 220914 141156LMAO KidUrBadNo ratings yet
- Home Work-3: CAP306: Computer NetworksDocument10 pagesHome Work-3: CAP306: Computer NetworksSurendra Singh ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Mob Net 2011 Exam SolutionDocument13 pagesMob Net 2011 Exam Solutionمحيي الدين الكميشىNo ratings yet
- ComputerNetworks ClassTest2 SolutionsDocument3 pagesComputerNetworks ClassTest2 Solutionshuyencttde180614No ratings yet
- Microcontroller: Alexander Kößler, Matthias Függer SS 2012 CourseDocument57 pagesMicrocontroller: Alexander Kößler, Matthias Függer SS 2012 Coursezzshi_200% (1)
- Introduction To Computer Networking (SSC 4) Exercise SeriesDocument27 pagesIntroduction To Computer Networking (SSC 4) Exercise SeriesMahmoud Handase35No ratings yet
- Chap 12Document6 pagesChap 12Varun AgarwalNo ratings yet
- 2013 Session 1: TELE3118: Network Technologies Week 2: Data Link LayerDocument28 pages2013 Session 1: TELE3118: Network Technologies Week 2: Data Link LayerXozanNo ratings yet
- Computer Communications & Networks Layer 2 Error ControlDocument23 pagesComputer Communications & Networks Layer 2 Error ControlKun NvtNo ratings yet
- Dnet Final 2022 To PrintDocument18 pagesDnet Final 2022 To PrintMevlüt YıldırımNo ratings yet
- Lte Mod 3 NTS EditdDocument27 pagesLte Mod 3 NTS EditdDavid DvoskineNo ratings yet
- Solutions OSI ExercisesDocument50 pagesSolutions OSI ExercisesHussam AlwareethNo ratings yet
- Solutions To EE555 Midterm, Summer 2003: Part 1: True/False Question (25 Points)Document4 pagesSolutions To EE555 Midterm, Summer 2003: Part 1: True/False Question (25 Points)MUHAMMAD AHSANNo ratings yet
- ComputernetwoektextDocument9 pagesComputernetwoektextVimal KumarNo ratings yet
- Faculty of Engineering, Sciences & Technology: Assignment # 03 - Spring Semester 2020Document8 pagesFaculty of Engineering, Sciences & Technology: Assignment # 03 - Spring Semester 2020Muhammad Usman AfaqNo ratings yet
- Computer Communication and NetworksDocument52 pagesComputer Communication and NetworksSaurabh JaiswalNo ratings yet
- Transport AnswersDocument5 pagesTransport AnswersPebo GreenNo ratings yet
- 2006 Exam PaperDocument2 pages2006 Exam PapernicholasiNo ratings yet
- d1 Multi AccessDocument14 pagesd1 Multi AccessgvgbabuNo ratings yet
- CCN NOTS Final Unit - 3Document39 pagesCCN NOTS Final Unit - 3Bruce Randall100% (3)
- SwitchDocument229 pagesSwitchABDELKARIM YOUSIFNo ratings yet
- Ee132b Hw3 SolDocument7 pagesEe132b Hw3 SolDylan Ler100% (1)
- Module3 ProblemsDocument11 pagesModule3 ProblemsGokul GokulNo ratings yet
- ACARSDocument42 pagesACARSanticlockwise180100% (3)
- Medium Access Control (MAC) Protocols For Ad Hoc Wireless Networks - IIIDocument47 pagesMedium Access Control (MAC) Protocols For Ad Hoc Wireless Networks - IIIfarhad_mfhNo ratings yet
- 5.2 CMOS Logic Gate Design: Serial or Parallel in Rs Transisto of NoDocument15 pages5.2 CMOS Logic Gate Design: Serial or Parallel in Rs Transisto of NoRaj AryanNo ratings yet
- For 15 MinDocument15 pagesFor 15 MinNaveen Kumar GummidalaNo ratings yet
- Midterm 1 Exam: Exercise 1 (5) Exercise 2 (5) Exercise 3 (4) Exercise 4 (6) TotalDocument4 pagesMidterm 1 Exam: Exercise 1 (5) Exercise 2 (5) Exercise 3 (4) Exercise 4 (6) TotalNada FSNo ratings yet
- 2012 Solutions PDFDocument17 pages2012 Solutions PDFYu Chen NgNo ratings yet
- Ee132b Homework 2Document3 pagesEe132b Homework 2YouRong YangNo ratings yet
- Hwk3 4 Su10 SolDocument11 pagesHwk3 4 Su10 SolKun LiNo ratings yet
- ch13 SolDocument4 pagesch13 SolSalekin MishuNo ratings yet
- Stop and Wait ProtocolDocument11 pagesStop and Wait ProtocolSanthoshSandyNo ratings yet
- Sample Solutions: TH TH THDocument6 pagesSample Solutions: TH TH THDivyankk VyasNo ratings yet
- Cs/ee 143 Communication Networks Chapter 4 Transport: Text: Walrand & Parakh, 2010 Steven Low CMS, EE, CaltechDocument34 pagesCs/ee 143 Communication Networks Chapter 4 Transport: Text: Walrand & Parakh, 2010 Steven Low CMS, EE, CaltechThinh Tran VanNo ratings yet
- Homework Assignment #3: EE122: Introduction To Communication Networks (Fall 2007)Document4 pagesHomework Assignment #3: EE122: Introduction To Communication Networks (Fall 2007)Jack Chen Su-LeeNo ratings yet
- NAME: - : Computer Networks I MID-TERM EXAM 2 - PART 2 (TOTAL: 5 Points) InstructionsDocument5 pagesNAME: - : Computer Networks I MID-TERM EXAM 2 - PART 2 (TOTAL: 5 Points) InstructionsikejimenesNo ratings yet
- LABORATORY MANUAL ON Digital COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUESDocument29 pagesLABORATORY MANUAL ON Digital COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUESChandra Mohanty0% (1)
- Final SolutionDocument3 pagesFinal SolutionJeanFrancoisAtemengueEbangaNo ratings yet
- 1C - Communication Networks - Circuit SwitchingDocument14 pages1C - Communication Networks - Circuit SwitchingDang KhueNo ratings yet
- Device Information: Investigating The CAMDocument4 pagesDevice Information: Investigating The CAMКирилл ГулякевичNo ratings yet
- Unmanaged Ethernet Redundant RingDocument12 pagesUnmanaged Ethernet Redundant RingForrest Heath IIINo ratings yet
- Exam #2 For Computer Networks (CIS 6930) SOLUTIONS : Problem #1Document4 pagesExam #2 For Computer Networks (CIS 6930) SOLUTIONS : Problem #1svahidsNo ratings yet
- Chap 05 PDFDocument21 pagesChap 05 PDFSidney100% (1)
- CIS 81 Fundamentals of Networking Chapter 5: Ethernet Part 2 of 2Document88 pagesCIS 81 Fundamentals of Networking Chapter 5: Ethernet Part 2 of 2amgstiNo ratings yet
- Space-Division Switch FabricsDocument18 pagesSpace-Division Switch FabricsHiteshwar GaurNo ratings yet
- Primbon RFDocument76 pagesPrimbon RFLutfi ArifNo ratings yet
- Nokia Double Data Rate For FDD Downlink Through Channel Code Puncturing in MIMO ChannelsDocument4 pagesNokia Double Data Rate For FDD Downlink Through Channel Code Puncturing in MIMO ChannelsPhebeNo ratings yet
- Final: Total 200 Points, Duration: 12:15pm-3:15pm: EE 359 - Wireless Communications - Autumn 2016Document3 pagesFinal: Total 200 Points, Duration: 12:15pm-3:15pm: EE 359 - Wireless Communications - Autumn 2016Debajyoti DattaNo ratings yet
- This Study Resource Was: Multiple Choice Questions ( × . )Document3 pagesThis Study Resource Was: Multiple Choice Questions ( × . )Đình NghĩaNo ratings yet
- 434 HW 3 SolDocument5 pages434 HW 3 SolSweet AliaNo ratings yet
- Data Link LayerDocument40 pagesData Link Layeronline support sr dream itNo ratings yet
- Solution Manual For Computer Networking A Top Down Approach 6 e 6th EditionDocument38 pagesSolution Manual For Computer Networking A Top Down Approach 6 e 6th Editionbrookemaxwellfhfpy100% (16)
- Analytical Modeling of Wireless Communication SystemsFrom EverandAnalytical Modeling of Wireless Communication SystemsNo ratings yet
- Digital Signal Processing Techniques and Applications in Radar Image ProcessingFrom EverandDigital Signal Processing Techniques and Applications in Radar Image ProcessingNo ratings yet
- SFP Modules UkDocument4 pagesSFP Modules UkcttopNo ratings yet
- HP Waranty ProductDocument34 pagesHP Waranty Productvno2000No ratings yet
- Cisco 2960g 8tcDocument5 pagesCisco 2960g 8tcZts MksNo ratings yet
- Fortinet Wireless Product MatrixDocument14 pagesFortinet Wireless Product MatrixAndrew WebbNo ratings yet
- IES-2060/IES-2042FX Series: Industrial 6-Port Lite-Managed Ethernet SwitchDocument4 pagesIES-2060/IES-2042FX Series: Industrial 6-Port Lite-Managed Ethernet Switchoring2012No ratings yet
- Formato Baja de Series 11sep23Document11 pagesFormato Baja de Series 11sep23ACEVEDO RIOS JOSE ANTONIONo ratings yet
- Midterm Exam - Attempt Review Data Com 3Document18 pagesMidterm Exam - Attempt Review Data Com 3dun lelNo ratings yet
- Qos SettingDocument21 pagesQos Settinglucky chandelNo ratings yet
- Technical Specification MEF 11Document33 pagesTechnical Specification MEF 11Nguyễn Văn PhụngNo ratings yet
- Network Security Issues of Data Link Layer An OverviewDocument6 pagesNetwork Security Issues of Data Link Layer An Overviewpuyish100% (1)
- OpenSAFETY Basic 2013 en PrintDocument45 pagesOpenSAFETY Basic 2013 en PrintAlexandru BourNo ratings yet
- IEEE 802.11 Architecture: Protocol - HTMLDocument8 pagesIEEE 802.11 Architecture: Protocol - HTMLThaddeus MooreNo ratings yet
- ACI 710 C.link Access Modem RevC 080110Document2 pagesACI 710 C.link Access Modem RevC 080110rbroussard2182No ratings yet
- ET GT 5ES Datasheet LDocument2 pagesET GT 5ES Datasheet LMuhammad Mubashir HassanNo ratings yet
- Cisco 4800 Access Point DatasheetDocument15 pagesCisco 4800 Access Point DatasheetBrandon BarreraNo ratings yet
- POE-151 / POE-152 / POE-161 User's ManualDocument52 pagesPOE-151 / POE-152 / POE-161 User's ManualgonzaloNo ratings yet
- LAN x64Document13 pagesLAN x64edgardo2No ratings yet
- Full Gigabit Ethernet Switch L2 Software 16 PortsDocument2 pagesFull Gigabit Ethernet Switch L2 Software 16 PortsMatijaDebogovićNo ratings yet
- Datasheet Titanium2122A CeDocument2 pagesDatasheet Titanium2122A CemmopNo ratings yet
- DrayTek Vigor AP 810Document2 pagesDrayTek Vigor AP 810pdelgadoNo ratings yet
- PCS-9882n+ìETHERNET SWITCH 2010catalog-15Document2 pagesPCS-9882n+ìETHERNET SWITCH 2010catalog-15Rinda_RaynaNo ratings yet
- CRS112 8P PDFDocument3 pagesCRS112 8P PDFLeonardo PachillaNo ratings yet
- Integra X DS v1.06Document6 pagesIntegra X DS v1.06Stefan HartungNo ratings yet
- Dynamic Adaption of DCF and PCF Mode of IEEE 802.11 WLAN: Abhishek GoliyaDocument57 pagesDynamic Adaption of DCF and PCF Mode of IEEE 802.11 WLAN: Abhishek GoliyaGaurav PathakNo ratings yet
- Albis Datasheet ACCEED 1416Document4 pagesAlbis Datasheet ACCEED 1416Gilberto GuzmánNo ratings yet
- iDRAC-G8PM9W2 - iDRAC9 - Sy1stem PDFDocument2 pagesiDRAC-G8PM9W2 - iDRAC9 - Sy1stem PDFSureSh FreemanNo ratings yet
- Allied Telesyn AT-MC10 - InstallDocument50 pagesAllied Telesyn AT-MC10 - InstallDBRSMedicalNo ratings yet
- TMGCMPDFDocument1 pageTMGCMPDFHakim Moi-memeNo ratings yet
- V1600G Series GPON OLT Datasheet V1.0Document13 pagesV1600G Series GPON OLT Datasheet V1.0nildo137 SANTOSNo ratings yet
- Network AssignmentDocument8 pagesNetwork AssignmentMohammed KhaleelullahNo ratings yet