Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Arts & Crafts
Arts & Crafts
Uploaded by
swarada phatakCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Arts & Crafts
Arts & Crafts
Uploaded by
swarada phatakCopyright:
Available Formats
ARTS & CRAFTS MOVEMENT
PERIOD : 1834 AD – 1896 AD
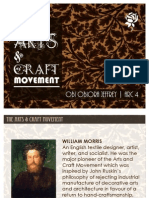
PIONEERS OF THE MOVEMENT: JOHN RUSKIN, WILLIAM MORRIS
CENTERS: ENGLAND, Architects: Philip Webb, Charles F. Voysey, Edwin Lutyens
: USA, Architect: F.L.Wright
The Arts and Crafts Movement began in England primarily as a search for authentic and meaningful styles for
the 19th century and as a reaction to the eclectic historicism of the Victorian era and to 'soulless' machine-
made production aided by the Industrial Revolution
A prelude to Modernism, with pure forms rejecting superficial, false “revivalism”
A celebration of individual design and craftsmanship where the personality of the designer became more central
than the historical "style" of a design
Enormously influenced by the progressive and rational writings and the legendary book “Seven Lamps of
Architecture” of John Ruskin, the English writer, thinker, painter, moralist. He advocated for:
return of the medieval craft tradition
rejection of machine
a socialistic theory to improve towns, buildings, design of products, & the lives of the common men
best known practitioners was William Morris who implemented it
The Philosophy:
turned away from the use of machines and advocated handcraft
simplicity and honest use of materials negating historicism
Socialist undertones, as the goal was to create design “for the people and by the people, and a source of pleasure
to the maker and the user."
rectilinear and angular forms with stylized decorative motifs reminiscent of medieval (Gothic) and Islamic
design
Arts & Crafts Movement in Architecture:
An aesthetic reformist Movement influenced British decorative arts, architecture, furniture, crafts, 'cottage' and
garden designs and also town planning.
The principles:
Free Planning- asymmetrical, non-formal, functional planning in non- urban setting.
Honesty of use of materials – use of vernacular materials with traditional medieval craftsmanship.
Gothic influence – in the roof profile & the non-picturesqueness.
Rejection of superficial, false ornamentation of Neo-Classic or Neo-Gothic.
Influence of Arts & Crafts Movement
USA: F.L.Wright was inspired by the Movement & manifested in “organic Architecture” of “Prairie
Houses” in search of a national identity in Architecture
Germany: initiated the national obsession for values for honesty in use of materials, simplicity and rationality in
design approach, ultimately manifested in “Bauhaus”
Spain: Antonio Gaudi was inspired: embraced naturalism, medievalism
India: “Indo-Saracenic” Colonial Architecture Style became official style for New Delhi
Town Planning – revival of English medieval, vernacular, cottage architecture initiated “Garden City”
movement
Art Nouveau - “new style” manifested the ideologies of the Arts & Crafts Movement
EXAMPLE: Red House, Bexleyheath, London
IN USA: The
movement often is referred as the style of interior design known as Mission style served middle class consumers
with affordable, decent looking furniture. Furniture were designed to take advantage of machines to produce mass
quantity low-cost, sturdy, serviceable furniture. The style was a blending of the arts and crafts rectilinear forms with
traditional Spanish colonial architecture and Native American artifacts.
PRAIRIE HOUSES
F.L. Wright was inspired by the Arts & Crafts Movement & traditional Japanese architecture and in search of a
national style he formulated the concept of his “Organic Architecture” for designing suburban domestic architecture
called as “Prairie houses” in Illinois.
The principles of the Prairie Houses:
Harmony with the nature – building should appear to grow from the ground and merge with nature
Spatial continuity – Hearth ( fire place ) at the center and spaces arranged around the hearth with minimum
internal walls.
Honesty in the use of materials and structure – use of vernacular materials in its original colour & textures.
Horizontality
Integrity in design – each element including furnitures were designed in integrity with the planning.
Identity of each house –Each house should express the identity according to the users.
EXAMPLES : The Robie House
You might also like
- Math Lesson Plan - 5e Instructional ModelDocument7 pagesMath Lesson Plan - 5e Instructional Modelapi-33767788475% (4)
- A Vision of Mexico - B. TravenDocument447 pagesA Vision of Mexico - B. Travenw24ny100% (2)
- I. Objectives: SRF in EnglishDocument3 pagesI. Objectives: SRF in EnglishYami Kawaii50% (8)
- Art NouveauDocument4 pagesArt NouveauIrchalina FaNo ratings yet
- Adams, J. L. (1948) - Hitler in Our Selves. Max Picard, Heinrich Hauser.Document2 pagesAdams, J. L. (1948) - Hitler in Our Selves. Max Picard, Heinrich Hauser.Sta PapNo ratings yet
- Arts and Crafts MovementDocument48 pagesArts and Crafts Movementjaantam100% (1)
- ARTS AND CRAFTS MOVEMENT - ArchitectureDocument12 pagesARTS AND CRAFTS MOVEMENT - ArchitecturePradeepa PriyadharsiniNo ratings yet
- HOA III - Unit 2Document108 pagesHOA III - Unit 2Sangesh RajNo ratings yet
- Hoa - Arts and Crafts MovementDocument11 pagesHoa - Arts and Crafts Movement003. M.priyankaNo ratings yet
- Arts and Crafts Movement, Red HouseDocument9 pagesArts and Crafts Movement, Red HouseKavyaNo ratings yet
- Unit Iii Arts and Crafts MovementDocument12 pagesUnit Iii Arts and Crafts MovementManoj KumarNo ratings yet
- Modern Architecture TheoriesDocument5 pagesModern Architecture TheoriesChania Bhatia100% (1)
- Blank 7Document2 pagesBlank 7dv5sfntnz7No ratings yet
- Arts and Crafts Movement, de Stijl and CubismDocument8 pagesArts and Crafts Movement, de Stijl and CubismSamridhi SharmaNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 - Reactions To IndustrialisationDocument97 pagesUnit 2 - Reactions To IndustrialisationpriyaNo ratings yet
- History of DesignDocument8 pagesHistory of Designmuhammaddanish120gbNo ratings yet
- Arts and Crafts MovementDocument15 pagesArts and Crafts MovementArkitekNo ratings yet
- Progressive Trend in The 19 CenturyDocument50 pagesProgressive Trend in The 19 CenturyHanan AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Arts Crafts MovementDocument20 pagesArts Crafts MovementKurianPaulNo ratings yet
- Art and Craft - Art NoveauDocument42 pagesArt and Craft - Art NoveauShivram VJNo ratings yet
- Architectural Styles, Movements and IdeologiesDocument103 pagesArchitectural Styles, Movements and IdeologiesNancy Tess100% (4)
- Art and Craft MovementDocument23 pagesArt and Craft MovementNivedhaNo ratings yet
- Term Paper - Vedika Agrawal PDFDocument9 pagesTerm Paper - Vedika Agrawal PDFVedika AgrawalNo ratings yet
- The Arts and Crafts Movement in America - Essay - Heilbrunn Timeline of Art History - The Metropolitan Museum of ArtDocument5 pagesThe Arts and Crafts Movement in America - Essay - Heilbrunn Timeline of Art History - The Metropolitan Museum of ArtAmanda MonteiroNo ratings yet
- Soofiya His CAT03Document11 pagesSoofiya His CAT03SOOFIYA SAMAR barch2020No ratings yet
- A Review On Arts and Crafts MovementDocument10 pagesA Review On Arts and Crafts MovementShahrzad MaghazehNo ratings yet
- 5 Domestic RevivalDocument10 pages5 Domestic RevivalManishaDhimanNo ratings yet
- Man and His Individual Creativity Architecture at The Beginning of The 20th CenturyDocument68 pagesMan and His Individual Creativity Architecture at The Beginning of The 20th CenturyLester TanNo ratings yet
- BARC505 - 01 - A19 - Tanvi SalunkeDocument8 pagesBARC505 - 01 - A19 - Tanvi SalunkeTanviNo ratings yet
- Key Movements in DesignDocument40 pagesKey Movements in DesignNirmal HembramNo ratings yet
- Document 2Document9 pagesDocument 2anas tariqNo ratings yet
- History of ArchDocument11 pagesHistory of ArchDawit TesfayNo ratings yet
- Truth in Design: The Origin of Wright's Organic ArchitectureDocument10 pagesTruth in Design: The Origin of Wright's Organic Architectureapi-402980391No ratings yet
- Arts and Crafts BlogDocument5 pagesArts and Crafts BlogStephen DobsonNo ratings yet
- 20th Century ArchitectureDocument8 pages20th Century ArchitectureNATNAEL ZEWDUNo ratings yet
- Arts and Crafts MovementDocument11 pagesArts and Crafts MovementChania BhatiaNo ratings yet
- WEEK 4 Arts Crafts MovementDocument23 pagesWEEK 4 Arts Crafts MovementJeuxNo ratings yet
- Arts and Crafts Movement - 19th CenturyDocument20 pagesArts and Crafts Movement - 19th CenturyKushagra ChawlaNo ratings yet
- Project Famous ArchitectsDocument7 pagesProject Famous ArchitectsCristianNo ratings yet
- Theory of Design: Design Principles and Philosophies of F.L.WrightDocument18 pagesTheory of Design: Design Principles and Philosophies of F.L.WrightPreethi HannahNo ratings yet
- History of Architecture2Document41 pagesHistory of Architecture2praveenhansraj100% (1)
- 7-Architectural Design and Allied ArtsDocument46 pages7-Architectural Design and Allied ArtsAngeline CuriosoNo ratings yet
- UNIT III - Arts and CraftDocument11 pagesUNIT III - Arts and Craftmayeelah usmaniNo ratings yet
- CH 1 NoteDocument9 pagesCH 1 NoteSara MengistuNo ratings yet
- Arts N Crafts ReportDocument10 pagesArts N Crafts ReportReleyNo ratings yet
- Arts Architects WorksDocument17 pagesArts Architects WorksAr Parth JainNo ratings yet
- The Arts and Craft MovementDocument21 pagesThe Arts and Craft MovementObi Obiora Jeffrey100% (2)
- Scandinavian Interior Design HistoryDocument19 pagesScandinavian Interior Design Historygetu0% (1)
- HOA-Art & Craft MovementDocument21 pagesHOA-Art & Craft MovementfrajoNo ratings yet
- Interior DesignDocument11 pagesInterior Designapran arfanNo ratings yet
- Reviewing IndustrialisationDocument89 pagesReviewing IndustrialisationVeeraNo ratings yet
- Design Movement Post IndustializationDocument4 pagesDesign Movement Post IndustializationakuuNo ratings yet
- Hoa ModulDocument107 pagesHoa ModulJan WickNo ratings yet
- Arts & CratfsDocument11 pagesArts & CratfsLizzieLoveLustoNo ratings yet
- Art and CraftDocument42 pagesArt and CraftShatha AlawnehNo ratings yet
- Shruti Vinod Kale Third Year - ADocument45 pagesShruti Vinod Kale Third Year - AbhushanNo ratings yet
- Old English Chintzes - Chintz in Relation to Antique FurnitureFrom EverandOld English Chintzes - Chintz in Relation to Antique FurnitureNo ratings yet
- Hoa - Hoa Module 2 P3Document103 pagesHoa - Hoa Module 2 P3andreaNo ratings yet
- LECTURE - 3 - Modern Architecture TheoriesDocument74 pagesLECTURE - 3 - Modern Architecture TheoriesYeshiwas MelkamuNo ratings yet
- History Pattern BooksDocument7 pagesHistory Pattern BookslauradipasqualeNo ratings yet
- Final Requirement Hoa, Gonzalez 2aDocument22 pagesFinal Requirement Hoa, Gonzalez 2aZachary Yassir GonzalezNo ratings yet
- Louis I KhanDocument8 pagesLouis I KhanDurgesh Prãtäp SïñghNo ratings yet
- Arts and Crafts MovementDocument10 pagesArts and Crafts MovementKavyaNo ratings yet
- The Rise of Competitive AuthoritarianismDocument16 pagesThe Rise of Competitive AuthoritarianismDavid Sforza100% (1)
- Alison - Race Gender and ColonialismDocument367 pagesAlison - Race Gender and ColonialismsamcoltrinNo ratings yet
- Repeated Addition Math LessonDocument13 pagesRepeated Addition Math LessonAshley McMenamy100% (1)
- Micro TeachingDocument20 pagesMicro TeachingArti NigamNo ratings yet
- Frame SemanticsDocument60 pagesFrame Semanticseraserhead7100% (1)
- Introduction To Hospitality and Tourism IndustryDocument4 pagesIntroduction To Hospitality and Tourism IndustrySujay Vikram Singh100% (1)
- Ernest GellnerDocument19 pagesErnest GellnerAlexandru ȚîrdeaNo ratings yet
- New Era University: "Architects vs. Engineers"Document3 pagesNew Era University: "Architects vs. Engineers"Khryz AbadNo ratings yet
- Training and Development Program of Askari BankDocument30 pagesTraining and Development Program of Askari BankShumaila Khan100% (1)
- Ge 20 Reading Visual Arts SyllabusDocument13 pagesGe 20 Reading Visual Arts SyllabusJanNo ratings yet
- RPH CefrDocument4 pagesRPH CefrtuhcytazziNo ratings yet
- Limits of Global Civil SocietyDocument20 pagesLimits of Global Civil SocietyWilfred OnuosahNo ratings yet
- UN Declaration of Victims' RightsDocument7 pagesUN Declaration of Victims' RightsMuhammad A. A. MamunNo ratings yet
- Influence of Korean Drama Series in Grade 9 Continuatio Pt.2 1Document38 pagesInfluence of Korean Drama Series in Grade 9 Continuatio Pt.2 1jana80% (5)
- PPT-REPORT in Teaching ProfessionDocument11 pagesPPT-REPORT in Teaching ProfessionJommer Ramosa PajanustanNo ratings yet
- Reluctant FundamentalistDocument20 pagesReluctant FundamentalistM Shakeel Anjum JuttNo ratings yet
- Rodrigues JoaoDocument6 pagesRodrigues JoaoWilliam FergusonNo ratings yet
- PGDM - MBA - Syllabus PDFDocument5 pagesPGDM - MBA - Syllabus PDFSreenath Reddy0% (1)
- NUR Hazwani Binte Mohammad Hisham: Areer BjectiveDocument2 pagesNUR Hazwani Binte Mohammad Hisham: Areer Bjectiveapi-446178702No ratings yet
- Quiz On PunctuationDocument64 pagesQuiz On PunctuationSvijayakanthan SelvarajNo ratings yet
- NGO Profile-AKDF MombasaDocument2 pagesNGO Profile-AKDF MombasaTeachers Without BordersNo ratings yet
- Past Perfect ProgressiveDocument8 pagesPast Perfect ProgressiveAndrei HurdubeiNo ratings yet
- Commencement Speech by Rajat M. Nag Managing Director General, AsianDocument5 pagesCommencement Speech by Rajat M. Nag Managing Director General, Asianapi-15403391100% (2)
- UntitledDocument477 pagesUntitledAlp ÇelikNo ratings yet
- Faith Comes by Hearing. A Response To Inclusivism (Christopher W. Morgan, Robert A. Peterson) (Z-Lib - Org) - 2Document519 pagesFaith Comes by Hearing. A Response To Inclusivism (Christopher W. Morgan, Robert A. Peterson) (Z-Lib - Org) - 2drnkwochailNo ratings yet
- Sample Emcee ScriptDocument7 pagesSample Emcee ScriptMehedi Hasan83% (6)