Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Ijaz O&A-Level Notes
Ijaz O&A-Level Notes
Uploaded by
ijazkhan22yahooCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Ijaz O&A-Level Notes
Ijaz O&A-Level Notes
Uploaded by
ijazkhan22yahooCopyright:
Available Formats
1
Cambridge International Examination
Ordinary Level
Beaconhouse School System
Boys Campus, Canal Side
Symmetry
Notes, examples, hints & practice sums from Cambridge Exams for (O1, O2 & O3)
Cambridge International Syllabus
Cambridge O Level Mathematics (4024 & 0580) syllabus for 2025, 2026 and 2027
Symmetry Notes and examples
1 Recognize line symmetry and order of rotational Includes properties of triangles, quadrilaterals and
symmetry in two dimensions. polygons directly related to their symmetries. e.g.
identify planes and axes of symmetry.
2 Recognise symmetry properties of prisms,
cylinders, pyramids and cones.
A plane of symmetry is an imaginary plane that bisects a solid into halves that are mirror
images of each other.
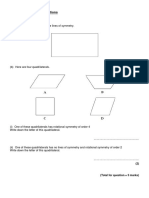
1 (a) The diagram shows a rhombus.
On the diagram, draw all the lines of symmetry.
(b)
Shade two squares so that the diagram has rotational symmetry of
order 2.
BSS-BCCS Math/4024/0580/O-Level # (92) 302-4018320
2
(c) Write down the order of rotational symmetry of the followings.
(i) (ii) (iii)
An Octagon
____________ _______ __________
(iv) (v) (vi)
Equilateral triangle
____________ __________________ _______________
(a) Write down the order of rotational symmetry of this diagram
(b) On the diagram, draw all the lines of symmetry.
3 (a) Complete this statement.
The diagram has rotational symmetry of order ...................
(b) On the diagram, draw all the lines of symmetry.
BSS-BCCS Math/4024/0580/O-Level # (92) 302-4018320
3
4 (a)
Shade two more small squares to give a pattern
with exactly one line of symmetry
(b) Complete the description of this pattern.
The pattern has .............................. lines of symmetry
and order of rotational symmetry ..........................
(a) Shade one more small triangle in the shape to make a pattern with one
line of symmetry
(b) Shade two more small triangles in the shape below to make a pattern
with rotational symmetry of order 2.
6 (a)
(a) The diagram shows part of a figure that has AB as its line of
Symmetry, Complete the figure.
Answer
BSS-BCCS Math/4024/0580/O-Level # (92) 302-4018320
4
(b) In the diagram, six small squares are shaded.
Shade two more small squares so that the completed diagram
has rotational symmetry of order 4.
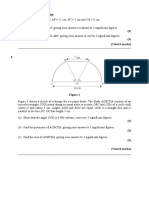
7 (a) The diagram shows a circle, its centre and two chords of equal length.
The diagram has one line of symmetry.
Draw this line of symmetry
(b)
In the diagram, two small triangles are shaded
Shade one more small triangle to give a diagram that has rotational symmetry of order 3.
BSS-BCCS Math/4024/0580/O-Level # (92) 302-4018320
5
(c)
From the word above, write down
(a) all the letters which have line symmetry ___________________________________
(b) all the letters which have rotational symmetry. _______________________________
(a) Write down the order of rotational symmetry of this shape.
(b) Samuel describes a special quadrilateral.
It has only one line of symmetry.
Its diagonals cross at right angles.
Write down the name of this special quadrilateral.
___________________________________________________
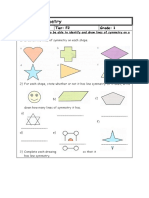
9 Complete the description of the symmetry for each shape.
BSS-BCCS Math/4024/0580/O-Level # (92) 302-4018320
6
10
(a) Shade one more small square so the (b) Shade two more small squares so the
diagram has rotational symmetry of order 4. diagram has 2 lines of symmetry
11 (a) Complete the pattern so that AB is the only line of symmetry
(b) A hexagon has rotational symmetry of order 6.
The perimeter of the hexagon is 30 cm.
Draw a sketch of the hexagon labelling the lengths of the sides.
BSS-BCCS Math/4024/0580/O-Level # (92) 302-4018320
7
12 The diagram shows a triangular prism. The cross-section is a right-angled isosceles triangle.
(a) Write down the number of planes of symmetry of the prism.
(b) Work out the volume of the prism.
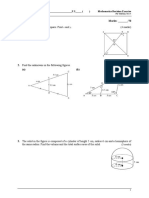
13 (a)Write down the number of lines of symmetry of this diagram.
(b) Write down the order of rotational symmetry of this diagram given below.
BSS-BCCS Math/4024/0580/O-Level # (92) 302-4018320
8
14 Sam has six square tiles labelled A, B, C, D, E and F.
When Sam places tiles E and F side by side the resulting rectangle has no lines of symmetry and no
rotational symmetry.
Write down the two tiles that Sam should place side by side to make a rectangle that has
(a) one line of symmetry only,
(b) rotational symmetry of order 2.
15
(a) The diagram shows part of a shape which is (b) The diagram shows part of a shape which has
symmetrical about the line L. rotational symmetry of order 2 about the point O.
Complete the shape. Complete the shape.
BSS-BCCS Math/4024/0580/O-Level # (92) 302-4018320
9
15 Plane Symmetry: A plane of symmetry divides a three dimensional shape in to two congruent halves that
are mirror image of each other.
A cuboid has three planes of symmetry.
A square based prism has 5 plane of symmetry.
BSS-BCCS Math/4024/0580/O-Level # (92) 302-4018320
10
A cube has 9 plane of symmetry.
An isosceles triangular based prism has 2 plane of symmetry.
An equilateral triangular based prism has four planes of symmetry.
BSS-BCCS Math/4024/0580/O-Level # (92) 302-4018320
11
A rectangular bases pyramid has two planes of symmetry.
A square based pyramid has 4 planes of symmetry.
A regular tetrahedron has 6 planes of symmetry.
BSS-BCCS Math/4024/0580/O-Level # (92) 302-4018320
12
Planes of symmetry of different shapes.
BSS-BCCS Math/4024/0580/O-Level # (92) 302-4018320
You might also like
- ST7Document4 pagesST7marcelonieto761No ratings yet
- Classification of AttachmentsDocument6 pagesClassification of AttachmentsAniket PotnisNo ratings yet
- Weber Carburarori. Tuning ManualDocument66 pagesWeber Carburarori. Tuning ManualOlga Petrovna100% (1)
- SymmetryDocument13 pagesSymmetryngunangawinnieNo ratings yet
- Mastery Test Order of Rotational & Symmetry Line - Cs2Document4 pagesMastery Test Order of Rotational & Symmetry Line - Cs2MCHNo ratings yet
- Symmetry (FH)Document15 pagesSymmetry (FH)Zunaira KamranNo ratings yet
- Symmetry Question'sDocument12 pagesSymmetry Question'sAira HabibNo ratings yet
- 44 Symmetry2Document8 pages44 Symmetry2sadiaaziz838No ratings yet
- 44 Symmetry2 PDFDocument8 pages44 Symmetry2 PDFRAMAN KUMARNo ratings yet
- A Level Mathematics - Practice Paper - 50 - Trigonometry (Part 1)Document8 pagesA Level Mathematics - Practice Paper - 50 - Trigonometry (Part 1)Veselina KaraslavovaNo ratings yet
- P1P2 Revision Worksheet Month-06 (December 2023)Document3 pagesP1P2 Revision Worksheet Month-06 (December 2023)Kana MatabborNo ratings yet
- Cad Assignment #3Document3 pagesCad Assignment #3Johnson123_45670% (2)
- Sample Paper IX Mathematics Annual Exams 2022-23Document4 pagesSample Paper IX Mathematics Annual Exams 2022-23Kriday MisriNo ratings yet
- Gujarat Technological UniversityDocument3 pagesGujarat Technological UniversityNIRAV GOHELNo ratings yet
- SymmetryDocument34 pagesSymmetryAftab AhmadNo ratings yet
- Topic:Geometry Time-2 Hrs. Date: 8/02/2024 Set A Marks - 40 STD - XDocument2 pagesTopic:Geometry Time-2 Hrs. Date: 8/02/2024 Set A Marks - 40 STD - XXoxxoNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Revision (Coordinate Geometry)Document8 pagesIGCSE Revision (Coordinate Geometry)He WhcsNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 12 Analytical GeometryDocument3 pagesWorksheet 12 Analytical GeometryOlerato NtsimaneNo ratings yet
- Symmetry and Shapes Class 7Document4 pagesSymmetry and Shapes Class 7jellybeanvscanman18No ratings yet
- S.3 Holiday Work (Technical Drawing) Attempt All QuestionsDocument3 pagesS.3 Holiday Work (Technical Drawing) Attempt All QuestionsAthiyo MartinNo ratings yet
- Derivation of Formulas in Spherical Trigonometry BDocument6 pagesDerivation of Formulas in Spherical Trigonometry BSannyBombeoJomocNo ratings yet
- 4 - SymmetryDocument10 pages4 - SymmetryMichelleNo ratings yet
- Maths F2Document8 pagesMaths F2arisya amranNo ratings yet
- S.4 Maths Seminar Questions-2022Document11 pagesS.4 Maths Seminar Questions-2022MASEDE JOBNo ratings yet
- 42 Circle Geometry With Answers Apr2020Document17 pages42 Circle Geometry With Answers Apr2020Kyle kNo ratings yet
- Year 12 Test 7Document8 pagesYear 12 Test 7Candy ENo ratings yet
- Coordinate Geometry (Done)Document14 pagesCoordinate Geometry (Done)Vedika SeepersadNo ratings yet
- P1 Practice - Trigonometry 1Document7 pagesP1 Practice - Trigonometry 1mishita khiaraNo ratings yet
- Shape and SpaceDocument32 pagesShape and SpaceJoshuaUntungNo ratings yet
- Y7 Math RevisionDocument6 pagesY7 Math RevisionAskiitians Education CentreNo ratings yet
- 6 7. Trig and Radian MeasuresDocument15 pages6 7. Trig and Radian MeasuresMl SurakshaNo ratings yet
- Computer Graphics PYQDocument6 pagesComputer Graphics PYQnitob90303No ratings yet
- f4 2022 MidDocument15 pagesf4 2022 MidHafiza rozikNo ratings yet
- Review For Unit Test Week 23Document4 pagesReview For Unit Test Week 23anas_tiyamaulaniNo ratings yet
- Maths pp1 Set 5 EditedDocument12 pagesMaths pp1 Set 5 EditedNicholas NyongesaNo ratings yet
- Section A: 456/1 Mathematics 2hrs 30 MinutesDocument4 pagesSection A: 456/1 Mathematics 2hrs 30 MinutesAthiyo Martin100% (1)
- Maths DaisDocument9 pagesMaths DaisIshaanNo ratings yet
- Coordinate Geometry WorksheetDocument10 pagesCoordinate Geometry WorksheetChido DzirutweNo ratings yet
- Study Material Term Ii: Class - Ix Subject: MathematicsDocument49 pagesStudy Material Term Ii: Class - Ix Subject: MathematicsCHIRAG MATTANo ratings yet
- GTU DOM Paper 2Document2 pagesGTU DOM Paper 2ManavNo ratings yet
- Use and Interpret Geometrical Terms P4Document11 pagesUse and Interpret Geometrical Terms P4Ucok PandapotanNo ratings yet
- vt59.2708 21381269991 - 711359507478687 - 785660292262764965 - N.pdftransformation and Matrices Math B.PDF - NDocument40 pagesvt59.2708 21381269991 - 711359507478687 - 785660292262764965 - N.pdftransformation and Matrices Math B.PDF - NdekuNo ratings yet
- Answer All Questions.: True or FalseDocument7 pagesAnswer All Questions.: True or FalseAteef HatifaNo ratings yet
- North Point Maths PrelimDocument4 pagesNorth Point Maths PrelimcrimsonleafwindNo ratings yet
- Part I: Circle The Choice That Best Answers Each of The Following Questions Below. Show All Necessary WorkDocument9 pagesPart I: Circle The Choice That Best Answers Each of The Following Questions Below. Show All Necessary WorkLuca ParadisiNo ratings yet
- C1 Coordinate Geometry - Straight LinesDocument47 pagesC1 Coordinate Geometry - Straight LinesmanikNo ratings yet
- Value of (256) X (256) Is (A) 4 (B) 16 (C) 64 (D) 256.25 2. Form of 0.1 Is (A) (B) (C) (D) None of TheseDocument11 pagesValue of (256) X (256) Is (A) 4 (B) 16 (C) 64 (D) 256.25 2. Form of 0.1 Is (A) (B) (C) (D) None of TheseAkshita KambojNo ratings yet
- UPLOADDocument1 pageUPLOADDEBJYOTI SARKARNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 7 Maths Worksheet - SymmetryDocument7 pagesCBSE Class 7 Maths Worksheet - SymmetryDebojyoti Das ThakurNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 7 Maths Worksheet - SymmetryDocument7 pagesCBSE Class 7 Maths Worksheet - SymmetrymayurNo ratings yet
- (4 Marks) : Conventional Questions Marks: - /70 1. in The Figure, PQRS Is A Square. Find X and yDocument6 pages(4 Marks) : Conventional Questions Marks: - /70 1. in The Figure, PQRS Is A Square. Find X and y(4C27) Wong Ching Tung, Zoey 20181D043spss.hkNo ratings yet
- W36 Sun AM TunazDocument2 pagesW36 Sun AM TunazBiid HassanNo ratings yet
- CONSTRUCTIONDocument17 pagesCONSTRUCTIONwisdomacademyapp1No ratings yet
- Rotation (F)Document10 pagesRotation (F)Zunaira KamranNo ratings yet
- Final 9th SetB (22-23)Document5 pagesFinal 9th SetB (22-23)SAIDA KHATOONNo ratings yet
- Easy ReflectDocument16 pagesEasy Reflectali kundiNo ratings yet
- UNITS 1-17 Diagnostic Test 8E (Standard) : You Have ONE HOUR To Complete This TestDocument21 pagesUNITS 1-17 Diagnostic Test 8E (Standard) : You Have ONE HOUR To Complete This TestNayem Hossain HemuNo ratings yet
- Extra Exercises - Express and SpecialDocument26 pagesExtra Exercises - Express and Specialdmal88No ratings yet
- Sample QuestionsDocument17 pagesSample Questionsaditya devNo ratings yet
- 3673 Tut 01Document1 page3673 Tut 01Kuroko BasukeNNo ratings yet
- C1 Coordinate Geometry - Straight LinesDocument47 pagesC1 Coordinate Geometry - Straight LinesEricka AlvarezNo ratings yet
- Attainable Region Theory: An Introduction to Choosing an Optimal ReactorFrom EverandAttainable Region Theory: An Introduction to Choosing an Optimal ReactorNo ratings yet
- Ijaz O&A-Level NotesDocument1 pageIjaz O&A-Level Notesijazkhan22yahooNo ratings yet
- Ijaz O&A-Level NotesDocument15 pagesIjaz O&A-Level Notesijazkhan22yahooNo ratings yet
- Ijaz O&A-Level NotesDocument6 pagesIjaz O&A-Level Notesijazkhan22yahooNo ratings yet
- Ijaz O&A-Level NotesDocument5 pagesIjaz O&A-Level Notesijazkhan22yahooNo ratings yet
- Ijaz O&A-Level NotesDocument6 pagesIjaz O&A-Level Notesijazkhan22yahooNo ratings yet
- Ijaz O&A-Level NotesDocument9 pagesIjaz O&A-Level Notesijazkhan22yahooNo ratings yet
- Ijaz O&A-Level NotesDocument5 pagesIjaz O&A-Level Notesijazkhan22yahooNo ratings yet
- Ijaz O&A-Level NotesDocument8 pagesIjaz O&A-Level Notesijazkhan22yahooNo ratings yet
- Ijaz O&A-Level NotesDocument6 pagesIjaz O&A-Level Notesijazkhan22yahooNo ratings yet
- Ijaz O&A-Level NotesDocument1 pageIjaz O&A-Level Notesijazkhan22yahooNo ratings yet
- Ijaz O&A-Level NotesDocument1 pageIjaz O&A-Level Notesijazkhan22yahooNo ratings yet
- Ijaz O&A-Level NotesDocument3 pagesIjaz O&A-Level Notesijazkhan22yahooNo ratings yet
- Ultratech Cement: Particulars Test Results Requirements ofDocument1 pageUltratech Cement: Particulars Test Results Requirements ofAshish SontakkeNo ratings yet
- 5 Thermodinamika II Siklus Daya Ideal OttoDocument20 pages5 Thermodinamika II Siklus Daya Ideal OttoEwing FadiansyahNo ratings yet
- Sliding Mode Control Strategy For A 6 DOF Quadrotor HelicopterDocument7 pagesSliding Mode Control Strategy For A 6 DOF Quadrotor HelicopternaderjsaNo ratings yet
- Building BlocksDocument3 pagesBuilding BlocksivoryspudNo ratings yet
- 304 Chromic Acid AnodizingDocument6 pages304 Chromic Acid AnodizingPuguh Cahpordjo BaeNo ratings yet
- TM 9 6625 474 14 and P 2Document89 pagesTM 9 6625 474 14 and P 2vonsaNo ratings yet
- Soal Uts Akm2 (2020-2021)Document2 pagesSoal Uts Akm2 (2020-2021)Fania AmbarwantiNo ratings yet
- Statista Digital Market Outlook: Product & MethodologyDocument42 pagesStatista Digital Market Outlook: Product & MethodologyKim Yến VũNo ratings yet
- Time Series QuestionsDocument1 pageTime Series QuestionsAdityNo ratings yet
- Airavata DasaDocument67 pagesAiravata DasayogalinkNo ratings yet
- Configure A Storage SpaceDocument4 pagesConfigure A Storage Spacelorien86No ratings yet
- 1.2m Type 123 Ku Ext RT Class II SpecDocument2 pages1.2m Type 123 Ku Ext RT Class II SpecPrithish DevadigaNo ratings yet
- CH 17 SolutionsDocument63 pagesCH 17 Solutions전민욱No ratings yet
- EE213 Topic00 IntroDocument84 pagesEE213 Topic00 Introapplebao1022No ratings yet
- ASSIGNMENT 10 WITH SOLUTION - FinalDocument12 pagesASSIGNMENT 10 WITH SOLUTION - FinalashoknrNo ratings yet
- Circle CPPDocument7 pagesCircle CPPAnugrah AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Fibers: Porosity Prediction of Plain Weft Knitted FabricsDocument11 pagesFibers: Porosity Prediction of Plain Weft Knitted FabricsAnonymous Pt7NHkat9No ratings yet
- IT Free PDF Sept - Dec 21Document267 pagesIT Free PDF Sept - Dec 21Saif Ur RehmanNo ratings yet
- QB WTDocument66 pagesQB WTSiddhi GavhaneNo ratings yet
- Nadia Karima Izzaty 1306369466 Dept. Teknik Sipil: Time (H) Rate (In/h) Direct Runoff (CFS) RM (In.)Document7 pagesNadia Karima Izzaty 1306369466 Dept. Teknik Sipil: Time (H) Rate (In/h) Direct Runoff (CFS) RM (In.)Nadia KarimaNo ratings yet
- Datasheet EE800Document3 pagesDatasheet EE800AdyMichaelNo ratings yet
- C748938 PDFDocument24 pagesC748938 PDFAkhmad SebehNo ratings yet
- Cognos Report Development Tips and Tricks Ver3Document24 pagesCognos Report Development Tips and Tricks Ver3Angshusmita Baruah SegraNo ratings yet
- Week 5 HomeworkDocument5 pagesWeek 5 Homeworkscribdpdfs50% (2)
- Intel® Ethernet Converged Network Adapter XL710: Product BriefDocument4 pagesIntel® Ethernet Converged Network Adapter XL710: Product Briefmatthew_mk_au2271No ratings yet
- Control Valve Specification For Steam Turbine BypassDocument5 pagesControl Valve Specification For Steam Turbine Bypassamer_arauf100% (3)
- FutureDocument37 pagesFutureBT20EEE052 KhushalNo ratings yet