Professional Documents
Culture Documents
DF_Syllabus (1)
DF_Syllabus (1)
Uploaded by
Andrea FernandesCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- M1516-1517 ManualDocument105 pagesM1516-1517 ManualGeovane BarbosaNo ratings yet
- HP Wifi Controller Configuration Guide PDFDocument635 pagesHP Wifi Controller Configuration Guide PDFEnis Byci100% (1)
- BCI4001 Cyber Forensics and Investigation: LTPJC 3 0 0 4 4Document4 pagesBCI4001 Cyber Forensics and Investigation: LTPJC 3 0 0 4 4raj anaNo ratings yet
- Bca Ctis Sem-5 Digital Forensic InvestigationDocument20 pagesBca Ctis Sem-5 Digital Forensic InvestigationVikas SharmaNo ratings yet
- FRM Course Syllabus IPDownloadDocument2 pagesFRM Course Syllabus IPDownloadutsav mandalNo ratings yet
- INT250Document2 pagesINT250Sambit Sagar PanigrahyNo ratings yet
- Digital Forensics: Unit No. 1 Computer ForensicsDocument2 pagesDigital Forensics: Unit No. 1 Computer ForensicskingraajaNo ratings yet
- CSE4004Document2 pagesCSE4004Ayush KarnNo ratings yet
- Computer Forensics FundamentalsDocument13 pagesComputer Forensics FundamentalsUtkarsh KumarNo ratings yet
- Acfrogbe 8qvtusc L2v40k9blceiv1jkdeobytypvmzsrr0k9pfe Zagtyxckpuhntgurnkkkmrivpjnx6yrefzxedzzvDocument2 pagesAcfrogbe 8qvtusc L2v40k9blceiv1jkdeobytypvmzsrr0k9pfe Zagtyxckpuhntgurnkkkmrivpjnx6yrefzxedzzvANANDHU KNo ratings yet
- Cyber Forensics 12-SeptDocument13 pagesCyber Forensics 12-SeptArun KrishnanNo ratings yet
- INT243Document2 pagesINT243Jatin wattsNo ratings yet
- INT243Document2 pagesINT243manvendraNo ratings yet
- System SecurityDocument4 pagesSystem SecurityTanishka MayekarNo ratings yet
- Module 5 - FinalDocument76 pagesModule 5 - Finalchethan140205No ratings yet
- Cyber ForensicDocument123 pagesCyber Forensicdinu89No ratings yet
- 1-Reference Material I Cse4004 Digital-Forensics Eth 1.1 47 Cse4004Document10 pages1-Reference Material I Cse4004 Digital-Forensics Eth 1.1 47 Cse4004Nigel JohnNo ratings yet
- CHFI (B) 5 daysDocument5 pagesCHFI (B) 5 daysnurul aisyahNo ratings yet
- Cyber Security and Digital ForensicDocument4 pagesCyber Security and Digital ForensicAmanpal Singh RayatNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Cyber ForensicDocument10 pagesIntroduction To Cyber ForensicRaj Vardhan SinhaNo ratings yet
- Qualitative Assessment of Digital ForensDocument8 pagesQualitative Assessment of Digital ForensLucas LeiteNo ratings yet
- Ch00-Course OutlineDocument11 pagesCh00-Course OutlinehaileNo ratings yet
- Cyber U-4 One Shot NotesDocument32 pagesCyber U-4 One Shot Notesv.c cNo ratings yet
- Digital: Cyber Security Training & Program Powered by Ignite TechnologiesDocument5 pagesDigital: Cyber Security Training & Program Powered by Ignite TechnologiesrberrospiNo ratings yet
- Kijito Cha Utakaso Ni Damu Ya YesuDocument3 pagesKijito Cha Utakaso Ni Damu Ya YesuGabriel KamauNo ratings yet
- What Is Digital Forensics - History, Process, Types, ChallengesDocument6 pagesWhat Is Digital Forensics - History, Process, Types, ChallengesTefe100% (1)
- Chfi Computer Hacking Forensic Investigator Ec ChfiDocument4 pagesChfi Computer Hacking Forensic Investigator Ec ChfiEng SaraNo ratings yet
- System Forensics, Investigation, and Response (Information Systems Security & Assurance) 3rd Edition – Ebook PDF Version full chapter instant downloadDocument45 pagesSystem Forensics, Investigation, and Response (Information Systems Security & Assurance) 3rd Edition – Ebook PDF Version full chapter instant downloadchebrihiasat85No ratings yet
- Exam One Kar2Document3 pagesExam One Kar2shahebgoudahalladamaniNo ratings yet
- cs4Cyber security unit 4Document18 pagescs4Cyber security unit 4kimetsunoyaiba2503No ratings yet
- Certified Digital Forensic Examiner v8Document5 pagesCertified Digital Forensic Examiner v8Chris BuenaventuraNo ratings yet
- Using Neural Network Techniques To Detect Malicious URL For Preventing RansomwaresDocument9 pagesUsing Neural Network Techniques To Detect Malicious URL For Preventing RansomwaresIJRASETPublicationsNo ratings yet
- Co6i-Eti-Unit 4 NotesDocument23 pagesCo6i-Eti-Unit 4 NotesMSBTE ObserverNo ratings yet
- Ceh V10Document97 pagesCeh V10Sachjith MNo ratings yet
- Chapter FourDocument27 pagesChapter FourJONAS J JONASNo ratings yet
- Interviewing in Forensic InvestigationDocument5 pagesInterviewing in Forensic InvestigationNereah DebrahNo ratings yet
- Assignment 9 - Grazelyn RabeDocument1 pageAssignment 9 - Grazelyn RabeGrazelyn RabeNo ratings yet
- Sec535 PR PDFDocument23 pagesSec535 PR PDFFREDDY ALLAN PALACIOS GONZÁLEZNo ratings yet
- Criminalitate InformaticaDocument56 pagesCriminalitate InformaticaLoredana TomaNo ratings yet
- Module 5Document14 pagesModule 5Swathi. N.No ratings yet
- Digital Forensic-Introduction 1Document29 pagesDigital Forensic-Introduction 1Shu Bham100% (1)
- Jaipur Engineering College and Research CenterDocument24 pagesJaipur Engineering College and Research CenterSrishti HasijaniNo ratings yet
- Computer ForensicsDocument2 pagesComputer ForensicsKevin NeshNo ratings yet
- 3 - Investigating Cyber Crimes - Introduction To Cyber Forensic - 1Document5 pages3 - Investigating Cyber Crimes - Introduction To Cyber Forensic - 1SINGE JUDENo ratings yet
- 1.introduction To CFDocument22 pages1.introduction To CFRekha V RNo ratings yet
- Digital Forensics, Investigation, and ResponseDocument804 pagesDigital Forensics, Investigation, and ResponseMorgan HollingsNo ratings yet
- Cyber ForensicsDocument3 pagesCyber ForensicspranaysohamprabhaNo ratings yet
- (Paras - 19EARCS737) Cyber ForensicsDocument9 pages(Paras - 19EARCS737) Cyber ForensicsMahesh SharmaNo ratings yet
- SEM 6 - CS Cyber ForensicsDocument43 pagesSEM 6 - CS Cyber ForensicsPUBG NoobNo ratings yet
- Forensics ExamDocument5 pagesForensics ExamzaphneathpeneahNo ratings yet
- What Is Computer Forensics?Document16 pagesWhat Is Computer Forensics?Pragyanshu ParadkarNo ratings yet
- Digital ForensicsDocument103 pagesDigital ForensicsRohith VavaNo ratings yet
- Comprehensive Study of Digital Forensics Branches and ToolsDocument7 pagesComprehensive Study of Digital Forensics Branches and ToolsDwiki MaulanaNo ratings yet
- Gujarat Technological University: W.E.F. AY 2018-19Document2 pagesGujarat Technological University: W.E.F. AY 2018-19Mit PhanaseNo ratings yet
- ChfiDocument9 pagesChfikgeorgisNo ratings yet
- ETI U-III NotesDocument13 pagesETI U-III Notesshraddha_mundadada100% (1)
- Prde Noes Part - 1Document16 pagesPrde Noes Part - 1sravansibisNo ratings yet
- Sejal ReserchDocument5 pagesSejal ReserchUmashankar GhugarNo ratings yet
- Important Two MarksDocument6 pagesImportant Two MarksTHARUN MIRUDANNo ratings yet
- Int242 Cyber Security EssentialsDocument2 pagesInt242 Cyber Security EssentialsJenish ButaniNo ratings yet
- Digital Forensics Basics: A Practical Guide Using Windows OSFrom EverandDigital Forensics Basics: A Practical Guide Using Windows OSNo ratings yet
- Literature Survey: 2.1 Review On Machine Learning Techniques For Stock Price PredictionDocument15 pagesLiterature Survey: 2.1 Review On Machine Learning Techniques For Stock Price Predictionritesh sinhaNo ratings yet
- Essay Contest Rules On West Philippine Sea: 115 East 57th Street, Suite 1430 New York, NY 10022Document5 pagesEssay Contest Rules On West Philippine Sea: 115 East 57th Street, Suite 1430 New York, NY 10022ramszlaiNo ratings yet
- Cyber Pornography - ArticlesDocument20 pagesCyber Pornography - ArticlesJasleen SoinNo ratings yet
- Class A Output Stage - RecapDocument18 pagesClass A Output Stage - RecaplvsaruNo ratings yet
- 3GPP TS 23.038Document56 pages3GPP TS 23.038Eddie CarpenterNo ratings yet
- Stand Alone PV SystemsDocument244 pagesStand Alone PV SystemsKits KittuNo ratings yet
- LTE TDD B2268HS Quick Start GuideDocument28 pagesLTE TDD B2268HS Quick Start GuideNour El HoudaNo ratings yet
- Wipro Company Profile: Corporate ViewDocument43 pagesWipro Company Profile: Corporate ViewmecitfuturedreamsNo ratings yet
- Schmidt 2019 NetflixDocument5 pagesSchmidt 2019 Netflixdani habibiNo ratings yet
- (John E Grayson PH.D.) Python and Tkinter ProgrammDocument83 pages(John E Grayson PH.D.) Python and Tkinter ProgrammCorcodel PopescuNo ratings yet
- Exercise RustDocument2 pagesExercise RustjppoujadeNo ratings yet
- "Internship": Presentation ONDocument13 pages"Internship": Presentation ONChethanNo ratings yet
- Queuing ModelsDocument32 pagesQueuing Modelscamille malonzoNo ratings yet
- Cavitation and Pipe DetailsDocument34 pagesCavitation and Pipe DetailsSANDIP ROYNo ratings yet
- MCOM 402 - Online Journalism: The Digital Journalist's Handbook, 2012, by Mark S. Luckie. ISBN-13: 978-1450565608Document5 pagesMCOM 402 - Online Journalism: The Digital Journalist's Handbook, 2012, by Mark S. Luckie. ISBN-13: 978-1450565608Stan DielNo ratings yet
- Forensics FJDocument28 pagesForensics FJFaizan Javed (Faizi)No ratings yet
- Semiconductor 101Document79 pagesSemiconductor 101jamalur.lNo ratings yet
- Reset Alarm E On Duplomatic TMC Unit-0617Document3 pagesReset Alarm E On Duplomatic TMC Unit-0617Vladimir100% (2)
- Bryon K. Randle - Servicenow AdminDocument4 pagesBryon K. Randle - Servicenow AdminNarvada Shankar SinghNo ratings yet
- P Tel LST 970 30002 3 Rlmu F - SDocument8 pagesP Tel LST 970 30002 3 Rlmu F - SBenkhira HoucineNo ratings yet
- How To Install Firebird DDEX Provider For .NET Into Visual Studio 2010 ProfessionalDocument2 pagesHow To Install Firebird DDEX Provider For .NET Into Visual Studio 2010 Professionaleupintea2057No ratings yet
- AI Term-II Periodic TestDocument3 pagesAI Term-II Periodic TestSmriti RoutNo ratings yet
- Cisco Model Epc3940 and Epc3940L Eurodocsis 3.0 16X4 W Ireless Residential Gateway With Embedded Digital Voice Adapter User GuideDocument54 pagesCisco Model Epc3940 and Epc3940L Eurodocsis 3.0 16X4 W Ireless Residential Gateway With Embedded Digital Voice Adapter User Guidemanuolo27No ratings yet
- Putty HelpDocument6 pagesPutty Helpatul.jha2545No ratings yet
- React 4 Week Mastery NotesDocument9 pagesReact 4 Week Mastery NotesHaa haNo ratings yet
- BAED-MEIL2122 Media and Information LiteracyDocument53 pagesBAED-MEIL2122 Media and Information LiteracyGlen joseph SerranoNo ratings yet
- Aes Algorithm CBC Mode Source Code:: Roll No:17Mci0021 Name: Bhanu TejayadaDocument24 pagesAes Algorithm CBC Mode Source Code:: Roll No:17Mci0021 Name: Bhanu TejayadaAkhil VenkataNo ratings yet
- Sales Daily Report KeerthiRDocument57 pagesSales Daily Report KeerthiRKeerthi Bagare RaoNo ratings yet
DF_Syllabus (1)
DF_Syllabus (1)
Uploaded by
Andrea FernandesCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
DF_Syllabus (1)
DF_Syllabus (1)
Uploaded by
Andrea FernandesCopyright:
Available Formats
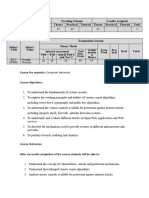
Course Code: Course Title Credit
CSDC8012 Digital Forensics 3
Prerequisite: Computer Network, Cryptography and System Security
Course Objectives:
1 To discuss the need and process of digital forensics and Incident Response Methodology.
2 To explore the procedures for identification, preservation, and acquisition of digital
evidence.
3 To explore techniques and tools used in digital forensics for Operating system and malware
investigation .
4 To explore techniques and tools used for Mobile forensics and browser, email forensics
Course Outcomes:
1 Discuss the phases of Digital Forensics and methodology to handle the computer security
incident.
2 Describe the process of collection, analysis and recovery of the digital evidence.
3 Explore various tools to analyze malwares and acquired images of RAM/hard drive.
4 Acquire adequate perspectives of digital forensic investigation in mobile devices
5 Analyze the source and content authentication of emails and browsers.
6 Produce unambiguous investigation reports which offer valid conclusions.
Module Content Hrs
1 Introduction to Digital Forensics 6
1.1 Digital ForensicsDefination, Digital Forensics Goals, Digital
Forensics Categories - Computer Forensics, Mobile Forensics,
Network Forensics, Database Forensics
1.2 Introduction to Incident - Computer Security Incident, Goals of
Incident Response, CSIRT, Incident Response Methodology, Phase
after detection of an incident
2 Digital Evidence, Forensics Duplication and Digital Evidence 9
Acquisition
2.1 Digital evidence, Types of Digital Evidence, Challenges in acquiring
Digital evidence, Admissibility of evidence, Challenges in evidence
handling, Chain of Custody
2.2 Digital Forensics Examination Process - Seizure, Acquisition,
Analysis, Reporting. Necessity of forensic duplication, Forensic
image formats, Forensic duplication techniques,.
2.3 Acquiring Digital Evidence - Forensic Image File Format, Acquiring
Volatile Memory (Live Acquisition), Acquiring Nonvolatile Memory
(Static Acquisition), Hard Drive Imaging Risks and Challenges,
Network Acquisition
3 Forensics Investigation 4
3.1 Analyzing Hard Drive Forensic Images, Analyzing RAM Forensic
Image, Investigating Routers
3.2 Malware Analysis - Malware, Viruses, Worms, Essential skills and
tools for Malware Analysis, List of Malware Analysis Tools and
Techniques
4 Windows and Unix Forensics Investigation 8
4.1 Investigating Windows Systems - File Recovery, Windows Recycle
Bin Forensics, Data Carving, Windows Registry Analysis, USB
Device Forensics, File Format Identification, Windows Features
Forensics Analysis, Windows 10 Forensics, Cortana Forensics
4.2 Investigating Unix Systems - Reviewing Pertinent Logs, Performing
Keyword Searches, Reviewing Relevant Files, Identifying
Unauthorized User Accounts or Groups, Identifying Rogue
Processes, Checking for Unauthorized Access Points, Analyzing
Trust Relationships
5 Mobile Forensics 8
5.1 Android Forensics, Mobile Device Forensic Investigation - Storage
location, Acquisition methods, Data Analysis
5.2 GPS forensics - GPS Evidentiary data, GPS Exchange Format
(GPX), GPX Files, Extraction of Waypoints and TrackPoints,
Display the Tracks on a Map.
5.3 SIM Cards Forensics - The Subscriber Identification Module (SIM),
SIM Architecture, Security, Evidence Extraction.
6 Browser, Email Forensic & Forensic Investigation Reporting 4
6.1 Web Browser Forensics, Google chrome, Other web browser
investigation
Email forensics - Sender Policy Framework (SPF), Domain Key
Identified Mail (DKIM), Domain based Message Authentication
Reporting and Confirmation (DMARC)
6.2 Investigative Report Template, Layout of an Investigative Report,
Guidelines for Writing a Report
Textbooks:
1 Kevin Mandia, Chris Prosise, ―Incident Response and computer forensics‖, Tata
McGrawHill, 2006
2 Digital Forensics Basics A Practical Guide Using Windows OS — Nihad A. Hassan,
APress Publication, 2019
3 Xiaodong Lin, ―Introductory Computer Forensics: A Hands-on Practical Approach‖,
Springer Nature, 2018
Suggested MOOC Course Links
1 Course on ―Ethical Hacking‖
https://nptel.ac.in/courses/106/105/106105217/
2 Course on ―Digital Forensics‖
https://onlinecourses.swayam2.ac.in/cec20_lb06/preview
3 Course on Cyber Incident Response
https://www.coursera.org/learn/incident-response
4 Course on ―Penetration Testing, Incident Responses and Forensics‖
https://www.coursera.org/learn/ibm-penetration-testing-incident-response-forensics
Assessment:
Internal Assessment:
Assessment consists of two class tests of 20 marks each. The first class test is to be conducted
when approx. 40% syllabus is completed and second class test when additional 40% syllabus is
completed. Duration of each test shall be one hour.
End Semester Theory Examination:
1 Question paper will comprise a total of six questions.
2 All question carries equal marks
3 Questions will be mixed in nature (for example supposed Q.2 has part (a) from module 3
then part (b) will be from any module other than module 3)
4 Only Four questions need to be solved.
5 In question paper weightage of each module will be proportional to the number of
respective lecture hours as mention in the syllabus.
You might also like
- M1516-1517 ManualDocument105 pagesM1516-1517 ManualGeovane BarbosaNo ratings yet
- HP Wifi Controller Configuration Guide PDFDocument635 pagesHP Wifi Controller Configuration Guide PDFEnis Byci100% (1)
- BCI4001 Cyber Forensics and Investigation: LTPJC 3 0 0 4 4Document4 pagesBCI4001 Cyber Forensics and Investigation: LTPJC 3 0 0 4 4raj anaNo ratings yet
- Bca Ctis Sem-5 Digital Forensic InvestigationDocument20 pagesBca Ctis Sem-5 Digital Forensic InvestigationVikas SharmaNo ratings yet
- FRM Course Syllabus IPDownloadDocument2 pagesFRM Course Syllabus IPDownloadutsav mandalNo ratings yet
- INT250Document2 pagesINT250Sambit Sagar PanigrahyNo ratings yet
- Digital Forensics: Unit No. 1 Computer ForensicsDocument2 pagesDigital Forensics: Unit No. 1 Computer ForensicskingraajaNo ratings yet
- CSE4004Document2 pagesCSE4004Ayush KarnNo ratings yet
- Computer Forensics FundamentalsDocument13 pagesComputer Forensics FundamentalsUtkarsh KumarNo ratings yet
- Acfrogbe 8qvtusc L2v40k9blceiv1jkdeobytypvmzsrr0k9pfe Zagtyxckpuhntgurnkkkmrivpjnx6yrefzxedzzvDocument2 pagesAcfrogbe 8qvtusc L2v40k9blceiv1jkdeobytypvmzsrr0k9pfe Zagtyxckpuhntgurnkkkmrivpjnx6yrefzxedzzvANANDHU KNo ratings yet
- Cyber Forensics 12-SeptDocument13 pagesCyber Forensics 12-SeptArun KrishnanNo ratings yet
- INT243Document2 pagesINT243Jatin wattsNo ratings yet
- INT243Document2 pagesINT243manvendraNo ratings yet
- System SecurityDocument4 pagesSystem SecurityTanishka MayekarNo ratings yet
- Module 5 - FinalDocument76 pagesModule 5 - Finalchethan140205No ratings yet
- Cyber ForensicDocument123 pagesCyber Forensicdinu89No ratings yet
- 1-Reference Material I Cse4004 Digital-Forensics Eth 1.1 47 Cse4004Document10 pages1-Reference Material I Cse4004 Digital-Forensics Eth 1.1 47 Cse4004Nigel JohnNo ratings yet
- CHFI (B) 5 daysDocument5 pagesCHFI (B) 5 daysnurul aisyahNo ratings yet
- Cyber Security and Digital ForensicDocument4 pagesCyber Security and Digital ForensicAmanpal Singh RayatNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Cyber ForensicDocument10 pagesIntroduction To Cyber ForensicRaj Vardhan SinhaNo ratings yet
- Qualitative Assessment of Digital ForensDocument8 pagesQualitative Assessment of Digital ForensLucas LeiteNo ratings yet
- Ch00-Course OutlineDocument11 pagesCh00-Course OutlinehaileNo ratings yet
- Cyber U-4 One Shot NotesDocument32 pagesCyber U-4 One Shot Notesv.c cNo ratings yet
- Digital: Cyber Security Training & Program Powered by Ignite TechnologiesDocument5 pagesDigital: Cyber Security Training & Program Powered by Ignite TechnologiesrberrospiNo ratings yet
- Kijito Cha Utakaso Ni Damu Ya YesuDocument3 pagesKijito Cha Utakaso Ni Damu Ya YesuGabriel KamauNo ratings yet
- What Is Digital Forensics - History, Process, Types, ChallengesDocument6 pagesWhat Is Digital Forensics - History, Process, Types, ChallengesTefe100% (1)
- Chfi Computer Hacking Forensic Investigator Ec ChfiDocument4 pagesChfi Computer Hacking Forensic Investigator Ec ChfiEng SaraNo ratings yet
- System Forensics, Investigation, and Response (Information Systems Security & Assurance) 3rd Edition – Ebook PDF Version full chapter instant downloadDocument45 pagesSystem Forensics, Investigation, and Response (Information Systems Security & Assurance) 3rd Edition – Ebook PDF Version full chapter instant downloadchebrihiasat85No ratings yet
- Exam One Kar2Document3 pagesExam One Kar2shahebgoudahalladamaniNo ratings yet
- cs4Cyber security unit 4Document18 pagescs4Cyber security unit 4kimetsunoyaiba2503No ratings yet
- Certified Digital Forensic Examiner v8Document5 pagesCertified Digital Forensic Examiner v8Chris BuenaventuraNo ratings yet
- Using Neural Network Techniques To Detect Malicious URL For Preventing RansomwaresDocument9 pagesUsing Neural Network Techniques To Detect Malicious URL For Preventing RansomwaresIJRASETPublicationsNo ratings yet
- Co6i-Eti-Unit 4 NotesDocument23 pagesCo6i-Eti-Unit 4 NotesMSBTE ObserverNo ratings yet
- Ceh V10Document97 pagesCeh V10Sachjith MNo ratings yet
- Chapter FourDocument27 pagesChapter FourJONAS J JONASNo ratings yet
- Interviewing in Forensic InvestigationDocument5 pagesInterviewing in Forensic InvestigationNereah DebrahNo ratings yet
- Assignment 9 - Grazelyn RabeDocument1 pageAssignment 9 - Grazelyn RabeGrazelyn RabeNo ratings yet
- Sec535 PR PDFDocument23 pagesSec535 PR PDFFREDDY ALLAN PALACIOS GONZÁLEZNo ratings yet
- Criminalitate InformaticaDocument56 pagesCriminalitate InformaticaLoredana TomaNo ratings yet
- Module 5Document14 pagesModule 5Swathi. N.No ratings yet
- Digital Forensic-Introduction 1Document29 pagesDigital Forensic-Introduction 1Shu Bham100% (1)
- Jaipur Engineering College and Research CenterDocument24 pagesJaipur Engineering College and Research CenterSrishti HasijaniNo ratings yet
- Computer ForensicsDocument2 pagesComputer ForensicsKevin NeshNo ratings yet
- 3 - Investigating Cyber Crimes - Introduction To Cyber Forensic - 1Document5 pages3 - Investigating Cyber Crimes - Introduction To Cyber Forensic - 1SINGE JUDENo ratings yet
- 1.introduction To CFDocument22 pages1.introduction To CFRekha V RNo ratings yet
- Digital Forensics, Investigation, and ResponseDocument804 pagesDigital Forensics, Investigation, and ResponseMorgan HollingsNo ratings yet
- Cyber ForensicsDocument3 pagesCyber ForensicspranaysohamprabhaNo ratings yet
- (Paras - 19EARCS737) Cyber ForensicsDocument9 pages(Paras - 19EARCS737) Cyber ForensicsMahesh SharmaNo ratings yet
- SEM 6 - CS Cyber ForensicsDocument43 pagesSEM 6 - CS Cyber ForensicsPUBG NoobNo ratings yet
- Forensics ExamDocument5 pagesForensics ExamzaphneathpeneahNo ratings yet
- What Is Computer Forensics?Document16 pagesWhat Is Computer Forensics?Pragyanshu ParadkarNo ratings yet
- Digital ForensicsDocument103 pagesDigital ForensicsRohith VavaNo ratings yet
- Comprehensive Study of Digital Forensics Branches and ToolsDocument7 pagesComprehensive Study of Digital Forensics Branches and ToolsDwiki MaulanaNo ratings yet
- Gujarat Technological University: W.E.F. AY 2018-19Document2 pagesGujarat Technological University: W.E.F. AY 2018-19Mit PhanaseNo ratings yet
- ChfiDocument9 pagesChfikgeorgisNo ratings yet
- ETI U-III NotesDocument13 pagesETI U-III Notesshraddha_mundadada100% (1)
- Prde Noes Part - 1Document16 pagesPrde Noes Part - 1sravansibisNo ratings yet
- Sejal ReserchDocument5 pagesSejal ReserchUmashankar GhugarNo ratings yet
- Important Two MarksDocument6 pagesImportant Two MarksTHARUN MIRUDANNo ratings yet
- Int242 Cyber Security EssentialsDocument2 pagesInt242 Cyber Security EssentialsJenish ButaniNo ratings yet
- Digital Forensics Basics: A Practical Guide Using Windows OSFrom EverandDigital Forensics Basics: A Practical Guide Using Windows OSNo ratings yet
- Literature Survey: 2.1 Review On Machine Learning Techniques For Stock Price PredictionDocument15 pagesLiterature Survey: 2.1 Review On Machine Learning Techniques For Stock Price Predictionritesh sinhaNo ratings yet
- Essay Contest Rules On West Philippine Sea: 115 East 57th Street, Suite 1430 New York, NY 10022Document5 pagesEssay Contest Rules On West Philippine Sea: 115 East 57th Street, Suite 1430 New York, NY 10022ramszlaiNo ratings yet
- Cyber Pornography - ArticlesDocument20 pagesCyber Pornography - ArticlesJasleen SoinNo ratings yet
- Class A Output Stage - RecapDocument18 pagesClass A Output Stage - RecaplvsaruNo ratings yet
- 3GPP TS 23.038Document56 pages3GPP TS 23.038Eddie CarpenterNo ratings yet
- Stand Alone PV SystemsDocument244 pagesStand Alone PV SystemsKits KittuNo ratings yet
- LTE TDD B2268HS Quick Start GuideDocument28 pagesLTE TDD B2268HS Quick Start GuideNour El HoudaNo ratings yet
- Wipro Company Profile: Corporate ViewDocument43 pagesWipro Company Profile: Corporate ViewmecitfuturedreamsNo ratings yet
- Schmidt 2019 NetflixDocument5 pagesSchmidt 2019 Netflixdani habibiNo ratings yet
- (John E Grayson PH.D.) Python and Tkinter ProgrammDocument83 pages(John E Grayson PH.D.) Python and Tkinter ProgrammCorcodel PopescuNo ratings yet
- Exercise RustDocument2 pagesExercise RustjppoujadeNo ratings yet
- "Internship": Presentation ONDocument13 pages"Internship": Presentation ONChethanNo ratings yet
- Queuing ModelsDocument32 pagesQueuing Modelscamille malonzoNo ratings yet
- Cavitation and Pipe DetailsDocument34 pagesCavitation and Pipe DetailsSANDIP ROYNo ratings yet
- MCOM 402 - Online Journalism: The Digital Journalist's Handbook, 2012, by Mark S. Luckie. ISBN-13: 978-1450565608Document5 pagesMCOM 402 - Online Journalism: The Digital Journalist's Handbook, 2012, by Mark S. Luckie. ISBN-13: 978-1450565608Stan DielNo ratings yet
- Forensics FJDocument28 pagesForensics FJFaizan Javed (Faizi)No ratings yet
- Semiconductor 101Document79 pagesSemiconductor 101jamalur.lNo ratings yet
- Reset Alarm E On Duplomatic TMC Unit-0617Document3 pagesReset Alarm E On Duplomatic TMC Unit-0617Vladimir100% (2)
- Bryon K. Randle - Servicenow AdminDocument4 pagesBryon K. Randle - Servicenow AdminNarvada Shankar SinghNo ratings yet
- P Tel LST 970 30002 3 Rlmu F - SDocument8 pagesP Tel LST 970 30002 3 Rlmu F - SBenkhira HoucineNo ratings yet
- How To Install Firebird DDEX Provider For .NET Into Visual Studio 2010 ProfessionalDocument2 pagesHow To Install Firebird DDEX Provider For .NET Into Visual Studio 2010 Professionaleupintea2057No ratings yet
- AI Term-II Periodic TestDocument3 pagesAI Term-II Periodic TestSmriti RoutNo ratings yet
- Cisco Model Epc3940 and Epc3940L Eurodocsis 3.0 16X4 W Ireless Residential Gateway With Embedded Digital Voice Adapter User GuideDocument54 pagesCisco Model Epc3940 and Epc3940L Eurodocsis 3.0 16X4 W Ireless Residential Gateway With Embedded Digital Voice Adapter User Guidemanuolo27No ratings yet
- Putty HelpDocument6 pagesPutty Helpatul.jha2545No ratings yet
- React 4 Week Mastery NotesDocument9 pagesReact 4 Week Mastery NotesHaa haNo ratings yet
- BAED-MEIL2122 Media and Information LiteracyDocument53 pagesBAED-MEIL2122 Media and Information LiteracyGlen joseph SerranoNo ratings yet
- Aes Algorithm CBC Mode Source Code:: Roll No:17Mci0021 Name: Bhanu TejayadaDocument24 pagesAes Algorithm CBC Mode Source Code:: Roll No:17Mci0021 Name: Bhanu TejayadaAkhil VenkataNo ratings yet
- Sales Daily Report KeerthiRDocument57 pagesSales Daily Report KeerthiRKeerthi Bagare RaoNo ratings yet