Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Uv protection-004
Uv protection-004
Uploaded by
Muhammad Mushtaq AliCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Awwa M45Document6 pagesAwwa M45Rafael Ramirez0% (1)
- Nano Finishes For Uv Protection in TextilesDocument17 pagesNano Finishes For Uv Protection in Textilesmythilirani100% (2)
- Assignment II Fsa-Iii UV Protective FinishesDocument12 pagesAssignment II Fsa-Iii UV Protective FinishesUjwala JainNo ratings yet
- UVDocument5 pagesUVSifat RaihanNo ratings yet
- Nanonotechnology NoteDocument13 pagesNanonotechnology NoteProttoy DiptoNo ratings yet
- Blocking Ultraviolet and Anti-Staining For Cotton Fabric 100% Using Nano Titan DioxideDocument7 pagesBlocking Ultraviolet and Anti-Staining For Cotton Fabric 100% Using Nano Titan DioxideBOHR International Journal of Biocomputing and Nano TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Protective TextilesDocument6 pagesProtective TextilesKhubab ShakerNo ratings yet
- Term Paper On Reduction of Direct Sun Light Heat by Proper Selection of ClothingDocument20 pagesTerm Paper On Reduction of Direct Sun Light Heat by Proper Selection of ClothingMukesh TiwariNo ratings yet
- Proteccion UV: Grupo - Yaziel Brenda Jaime Torres - Rosa Aponte Hurtado - Luisa Aguilar GuzmanDocument11 pagesProteccion UV: Grupo - Yaziel Brenda Jaime Torres - Rosa Aponte Hurtado - Luisa Aguilar GuzmanYaziel Jaime TorresNo ratings yet
- Use of Nanotechnology in Technical TextilesDocument12 pagesUse of Nanotechnology in Technical TextilesNaimul HasanNo ratings yet
- UV Protection FinishDocument24 pagesUV Protection Finishmuhammadahmad75492No ratings yet
- Performance Textiles PDFDocument4 pagesPerformance Textiles PDFUtkay DönmezNo ratings yet
- PROTECH Protective TextilesDocument29 pagesPROTECH Protective TextilesAneesha Panda0% (1)
- Presentation On Uv Protection FinishingDocument43 pagesPresentation On Uv Protection FinishingimranNo ratings yet
- Ultraviolet Protection Factor (UPF)Document4 pagesUltraviolet Protection Factor (UPF)YashNo ratings yet
- Uvf Technic in TextileDocument7 pagesUvf Technic in TextileDurgesh TripathiNo ratings yet
- Protective TextilesDocument36 pagesProtective TextilesDewan Ajuad Hossain Rifat100% (1)
- Ultra Violet Protection FinishDocument16 pagesUltra Violet Protection Finishdona biswasNo ratings yet
- Prakash Khude UV ProtectionDocument29 pagesPrakash Khude UV ProtectionariefNo ratings yet
- Funtional textile define-002Document3 pagesFuntional textile define-002Muhammad Mushtaq AliNo ratings yet
- UV Svetlina Vlijanie Na OciDocument5 pagesUV Svetlina Vlijanie Na OciDoe BlackNo ratings yet
- U V Procted Textile PDFDocument15 pagesU V Procted Textile PDFMusa EltayebNo ratings yet
- Defense Textiles FINALDocument10 pagesDefense Textiles FINALSudhir JainNo ratings yet
- Photochem Photobiology - 2022 - Aguilera - Sun Protective Properties of Technical Sportswear Fabrics 100 Polyester TheDocument9 pagesPhotochem Photobiology - 2022 - Aguilera - Sun Protective Properties of Technical Sportswear Fabrics 100 Polyester Thethelazyllama444No ratings yet
- Factsheet Textile UV Protection enDocument4 pagesFactsheet Textile UV Protection enariefNo ratings yet
- Hand Skin ProtectionDocument2 pagesHand Skin ProtectionPatrascu CristinaNo ratings yet
- Nuclear Protective TextilesDocument34 pagesNuclear Protective TextilesVikas SinghNo ratings yet
- 12 - Chapter 2 PDFDocument106 pages12 - Chapter 2 PDFGizachew Zeleke100% (1)
- IAETSD-JARAS A Study On Uv Protection Activity of Selected Herbs On Bamboocotton Woven FabricDocument5 pagesIAETSD-JARAS A Study On Uv Protection Activity of Selected Herbs On Bamboocotton Woven Fabriciaetsdiaetsd100% (1)
- UV Protection Finishes On Textile Fabric PDFDocument8 pagesUV Protection Finishes On Textile Fabric PDFruchika prasadNo ratings yet
- Protective TextilesDocument22 pagesProtective Textilesbeskyraj100% (1)
- Nonotechnology in TextilesDocument45 pagesNonotechnology in TextilesjayantverNo ratings yet
- Ehs UvDocument3 pagesEhs UvAdesh GurjarNo ratings yet
- Fabric and Garment Finishing Protective Fabric Finishes: By: Ankesh Dev Bhavyaa GuptaDocument31 pagesFabric and Garment Finishing Protective Fabric Finishes: By: Ankesh Dev Bhavyaa GuptaBhavyaa Gupta100% (1)
- Agro-Textiles: Textile Departmenf, Jayo Engineering College, ChennaiDocument6 pagesAgro-Textiles: Textile Departmenf, Jayo Engineering College, Chennaiمصطفى عبدالرحيمNo ratings yet
- Cotton Fabric and Uv-ProtectionDocument2 pagesCotton Fabric and Uv-Protectionstylish eagleNo ratings yet
- Advance Protective TextilesDocument28 pagesAdvance Protective Textilesimrans1100% (1)
- Nano Technology in Textiles A ReviewDocument6 pagesNano Technology in Textiles A ReviewMohammed Atiqul Hoque Chowdhury100% (1)
- Defence TextilesDocument28 pagesDefence TextilesAzl10471% (7)
- Fabric and Garment Finishing Protective Fabric Finishes: By: Ankesh Dev Bhavyaa GuptaDocument29 pagesFabric and Garment Finishing Protective Fabric Finishes: By: Ankesh Dev Bhavyaa GuptaBhavyaa GuptaNo ratings yet
- Evaluating The Ultraviolet Protection Factor (UPF) of Various Knit Fabric StructuresDocument15 pagesEvaluating The Ultraviolet Protection Factor (UPF) of Various Knit Fabric StructuresTas Kanken IndonesiaNo ratings yet
- IADVL CHAPTER 24 Photodermatology and Photodermatoses - SunscreenDocument7 pagesIADVL CHAPTER 24 Photodermatology and Photodermatoses - SunscreenNahas NazarNo ratings yet
- NullDocument4 pagesNullMaliha MazharNo ratings yet
- Application of Nanotechnology in TextileDocument34 pagesApplication of Nanotechnology in Textileparthjoshi91No ratings yet
- Assignment On: Textiles in Agriculture (Agrotech)Document6 pagesAssignment On: Textiles in Agriculture (Agrotech)AmirParvezNo ratings yet
- TECHNICAL TEXTILESDocument32 pagesTECHNICAL TEXTILESdivya.kvNo ratings yet
- Agro TextileDocument14 pagesAgro TextileASEEM SUPANNo ratings yet
- moisture wicking-003Document2 pagesmoisture wicking-003Muhammad Mushtaq AliNo ratings yet
- Medical TextileDocument22 pagesMedical TextileknjinnNo ratings yet
- Describe The Perspective Clothing That Should Be Worn For The Lab Staff Working in A Lab With Radioactive ElementsDocument9 pagesDescribe The Perspective Clothing That Should Be Worn For The Lab Staff Working in A Lab With Radioactive ElementsexjupiterNo ratings yet
- Ultravioletprotectionoftextiles 120526004725 Phpapp02Document24 pagesUltravioletprotectionoftextiles 120526004725 Phpapp02rajasajjadNo ratings yet
- Technical Textiles by AARDocument37 pagesTechnical Textiles by AARAtaur RahmanNo ratings yet
- Antimicrobial Finish of Textiles by Chitosan UV-Curing: Journal of Nanoscience and Nanotechnology June 2012Document9 pagesAntimicrobial Finish of Textiles by Chitosan UV-Curing: Journal of Nanoscience and Nanotechnology June 2012Federico SandroniNo ratings yet
- Syntheticand Natural UVProtectiveDocument25 pagesSyntheticand Natural UVProtectivefivudesignNo ratings yet
- Assignment On Special Fabrics: Properties and Quality ControlDocument30 pagesAssignment On Special Fabrics: Properties and Quality ControlNakib Ibna BasharNo ratings yet
- Technical TextilesDocument23 pagesTechnical TextilesNintha Jalan80% (5)
- OverviewDocument16 pagesOverviewAmal El-ebissyNo ratings yet
- UV STANDARD 801 Brochure Textile Uv Protection ENDocument12 pagesUV STANDARD 801 Brochure Textile Uv Protection ENAmir ShahzadNo ratings yet
- Personal Protective Equipment for Chemical, Biological, and Radiological Hazards: Design, Evaluation, and SelectionFrom EverandPersonal Protective Equipment for Chemical, Biological, and Radiological Hazards: Design, Evaluation, and SelectionNo ratings yet
- Occupational Radiation Protection in the Uranium Mining and Processing IndustryFrom EverandOccupational Radiation Protection in the Uranium Mining and Processing IndustryNo ratings yet
- 9Document2 pages9Muhammad Mushtaq AliNo ratings yet
- 6Document2 pages6Muhammad Mushtaq AliNo ratings yet
- moisture wicking-003Document2 pagesmoisture wicking-003Muhammad Mushtaq AliNo ratings yet
- Presentation RMDocument7 pagesPresentation RMMuhammad Mushtaq AliNo ratings yet
- Montmorillonite Bio-Nanocomposite FilmsDocument23 pagesMontmorillonite Bio-Nanocomposite FilmsMuhammad Mushtaq AliNo ratings yet
- the art of cinematographyDocument10 pagesthe art of cinematographyMuhammad Mushtaq AliNo ratings yet
- Page Proof Instructions and Queries: Journal of Industrial Textiles (JIT) 831083Document12 pagesPage Proof Instructions and Queries: Journal of Industrial Textiles (JIT) 831083Muhammad Mushtaq AliNo ratings yet
- Electrospun Poly Lactic Acid (PLA) Fibreseffect of Different Solvent Systems On Fibre Morphology and DiameterDocument10 pagesElectrospun Poly Lactic Acid (PLA) Fibreseffect of Different Solvent Systems On Fibre Morphology and DiameterMuhammad Mushtaq AliNo ratings yet
- Functional Copolymer Organo MMT Nanoarchitectures XXVI Fa1-Brication and Characterization of Electrospun Nanofibers From PCL ODA MMT and Copolymer GDocument13 pagesFunctional Copolymer Organo MMT Nanoarchitectures XXVI Fa1-Brication and Characterization of Electrospun Nanofibers From PCL ODA MMT and Copolymer GMuhammad Mushtaq AliNo ratings yet
- Biomedical MaterialsDocument29 pagesBiomedical MaterialsMuhammad Mushtaq AliNo ratings yet
- Characterization of Antimicrobial Polylactic Acid Based FilmsDocument9 pagesCharacterization of Antimicrobial Polylactic Acid Based FilmsMuhammad Mushtaq AliNo ratings yet
- Biomedical MaterialsDocument32 pagesBiomedical MaterialsMuhammad Mushtaq AliNo ratings yet
- 1 Teaching As A ProfessionDocument63 pages1 Teaching As A ProfessionMuhammad Mushtaq AliNo ratings yet
- Biomedical MaterialsDocument36 pagesBiomedical MaterialsMuhammad Mushtaq AliNo ratings yet
- Sound Absorbing Properties of Roller Blind Curtain Fabrics: Og Uz Demiryu Rek and Hu Snu AydemirDocument17 pagesSound Absorbing Properties of Roller Blind Curtain Fabrics: Og Uz Demiryu Rek and Hu Snu AydemirMuhammad Mushtaq AliNo ratings yet
- Message: Secretary Ministry of Textile IndustryDocument38 pagesMessage: Secretary Ministry of Textile IndustryMuhammad Mushtaq AliNo ratings yet
- 3 Curriculum Development, Assesment and EvaluationDocument119 pages3 Curriculum Development, Assesment and EvaluationMuhammad Mushtaq AliNo ratings yet
- App-Form For FacultyDocument5 pagesApp-Form For FacultyMuhammad Mushtaq AliNo ratings yet
- 2-Electrospinning Fabrication and Characterization ofDocument8 pages2-Electrospinning Fabrication and Characterization ofMuhammad Mushtaq AliNo ratings yet
- 100906-2323 Ijbas-IjensDocument9 pages100906-2323 Ijbas-IjensMuhammad Mushtaq AliNo ratings yet
- Unit Rate AnalysisDocument341 pagesUnit Rate AnalysisAshebirNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Civil Engg Objective Type RAgor - pdf.XP0gDbpt84gkO1dc85Cbz6jAcACPldCqDocument69 pagesChapter 1 Civil Engg Objective Type RAgor - pdf.XP0gDbpt84gkO1dc85Cbz6jAcACPldCqSurya PatanNo ratings yet
- Cement IndustryDocument22 pagesCement IndustryChaudary Usman GondalNo ratings yet
- BCP 503Document28 pagesBCP 503Vineet JhambNo ratings yet
- Co-Ordination Compound (Question Paper)Document4 pagesCo-Ordination Compound (Question Paper)Param shahNo ratings yet
- MKIII and NO96 Procedure For General Approval of Materials and ComponentDocument6 pagesMKIII and NO96 Procedure For General Approval of Materials and ComponentYongkoo HanNo ratings yet
- An Experimental Evaluation of Fiber Reinforced PolypropyleneDocument6 pagesAn Experimental Evaluation of Fiber Reinforced PolypropyleneRafael ZanettiNo ratings yet
- Acoustic Energy Absorption Properties of Fibrous Materials A Review PDFDocument47 pagesAcoustic Energy Absorption Properties of Fibrous Materials A Review PDFFloreaNo ratings yet
- Tekapur Super Flex enDocument2 pagesTekapur Super Flex enEzeval GráficaNo ratings yet
- Treatment of Soap and Detergent Industry WastesDocument76 pagesTreatment of Soap and Detergent Industry Wastessumit kumar0% (1)
- Important Question ICSE 2010 Class 10th Hydrogen ChlorideDocument5 pagesImportant Question ICSE 2010 Class 10th Hydrogen ChlorideYash KapoorNo ratings yet
- Astm A692 PDFDocument2 pagesAstm A692 PDFgaminNo ratings yet
- Dokumen Tips - Ektraksi-Alumina-Dari-Lumpur Id enDocument8 pagesDokumen Tips - Ektraksi-Alumina-Dari-Lumpur Id enFatmawati KadirNo ratings yet
- Field Guide To Concrete Repair Application Procedures: Structural Crack Repair by Epoxy Injection ACI RAP Bulletin 1Document3 pagesField Guide To Concrete Repair Application Procedures: Structural Crack Repair by Epoxy Injection ACI RAP Bulletin 1jamjam75No ratings yet
- Fibre Reinforced ConcreteDocument16 pagesFibre Reinforced ConcreteSîdDhàñt SätYãmNo ratings yet
- Sustainable Biomaterials and Their Applications - A Short ReviewDocument9 pagesSustainable Biomaterials and Their Applications - A Short ReviewvalentinaNo ratings yet
- A Study and Analysis of Manifacturing Process of Thiokol Rubber Swapna V, K. MounikaDocument8 pagesA Study and Analysis of Manifacturing Process of Thiokol Rubber Swapna V, K. Mounikamuhammad sameer ansariNo ratings yet
- My FinaleDocument36 pagesMy Finaleyohanis ashineNo ratings yet
- Sotrafer-Quality Observation Complaince Tracking Record.Document63 pagesSotrafer-Quality Observation Complaince Tracking Record.mitendra singhNo ratings yet
- Form 2 Chapter 6 Acid and AlkaliDocument28 pagesForm 2 Chapter 6 Acid and AlkaliammyNo ratings yet
- 2021 Master CatalogDocument330 pages2021 Master Cataloggeetha raniNo ratings yet
- 125E-5 SEN00697-03 Disassembly & AssemblyDocument112 pages125E-5 SEN00697-03 Disassembly & AssemblydatphuongNo ratings yet
- Ds - Concrete Mix DesignDocument51 pagesDs - Concrete Mix DesignDarshan ShahNo ratings yet
- Gmaw Fcaw Mcaw WeldingDocument4 pagesGmaw Fcaw Mcaw Weldingsajeed76743031No ratings yet
- Kps LPG Installation Manual 1 2 1 English PDFDocument36 pagesKps LPG Installation Manual 1 2 1 English PDFgheorghe garduNo ratings yet
- Highwaymaintenance M KennyDocument28 pagesHighwaymaintenance M KennyEbsa KelifaNo ratings yet
- ABC Gasket KitDocument97 pagesABC Gasket KitBenjamin romeroNo ratings yet
- Analysis and Design of SlabsDocument6 pagesAnalysis and Design of SlabsricardoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 15 Acids and Bases PDFDocument28 pagesChapter 15 Acids and Bases PDFJoshua NaemonNo ratings yet
Uv protection-004
Uv protection-004
Uploaded by
Muhammad Mushtaq AliCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Uv protection-004
Uv protection-004
Uploaded by
Muhammad Mushtaq AliCopyright:
Available Formats
2.
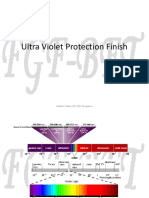
UV-Protection Textiles
Description: UV-protection textiles are designed to block or absorb harmful ultraviolet (UV)
radiation from the sun, reducing the risk of skin damage and related health issues. UV
radiation, comprising UVA and UVB rays, can cause sunburn, premature aging, and skin
cancer. These textiles are crucial for outdoor activities and work environments where
prolonged sun exposure is a concern.
Applications:
1. Outdoor Clothing:
o Hats and Caps: Provide essential protection for the face and neck.
o Shirts and Pants: Long-sleeved shirts and full-length pants offer maximum
coverage, reducing skin exposure to UV rays.
2. Swimwear:
o Rash Guards and Swimsuits: Designed for water activities, these garments
provide UV protection even when wet.
3. Protective Gear:
o Uniforms for Outdoor Workers: Essential for construction workers,
landscapers, and other outdoor professionals to prevent occupational sun
exposure.
4. Children’s Wear:
o Kids’ Clothing: Ensures that children, who have more sensitive skin, are
protected during outdoor play.
Key Technologies and Materials:
1. UV-Absorbing Chemicals:
o Titanium Dioxide and Zinc Oxide: Commonly used minerals that absorb
and scatter UV radiation. These are often used in sunscreen and can be applied
to textiles.
o UV-Absorbing Dyes: Chemical dyes that absorb UV light and prevent it from
reaching the skin.
2. Reflective Coatings:
o Metallic Coatings: Reflect UV radiation away from the fabric surface,
providing a barrier against UV penetration.
3. Dense Fabric Construction:
o Tightly Woven Fabrics: Fabrics with high thread counts and dense weaves
naturally block more UV radiation due to their reduced pore size.
4. Synthetic Fibers:
o Polyester and Nylon: These fibers inherently offer better UV protection
compared to natural fibers like cotton and linen due to their tighter structures
and ability to incorporate UV-absorbing chemicals during production.
Performance Measurement:
1. Ultraviolet Protection Factor (UPF):
o UPF Rating: Indicates the effectiveness of the fabric in blocking UV
radiation. A UPF rating of 50 means that only 1/50th of UV radiation
penetrates the fabric, providing excellent protection.
o Standards and Testing: UPF testing involves exposing the fabric to UV
radiation and measuring the amount that passes through. Standards like
AS/NZS 4399 and ASTM D6603 are commonly used.
Manufacturing Techniques:
1. Chemical Treatments:
o Dyeing and Finishing: Textiles are treated with UV-absorbing dyes or
finishes during or after the dyeing process.
2. Fiber Modification:
o Incorporation During Spinning: UV-absorbing agents can be embedded into
synthetic fibers during the spinning process, ensuring durable protection.
3. Coating and Laminating:
o Surface Application: Applying UV-protective coatings on the fabric surface
through processes like padding, spraying, or laminating.
Challenges and Future Directions:
1. Durability: Ensuring that UV protection remains effective after multiple washes and
prolonged use.
2. Comfort: Balancing UV protection with breathability and comfort, especially in hot
climates.
3. Aesthetic Considerations: Developing UV-protective textiles that are fashionable
and appealing to consumers.
4. Environmental Impact: Addressing the sustainability of UV-protective treatments
and materials.
Conclusion: UV-protection textiles are essential for safeguarding skin health during outdoor
activities. Advances in materials and technologies continue to improve their effectiveness,
durability, and comfort, making them an integral part of outdoor wear and protective
clothing. Future developments aim to enhance their sustainability and integration into
everyday fashion
You might also like
- Awwa M45Document6 pagesAwwa M45Rafael Ramirez0% (1)
- Nano Finishes For Uv Protection in TextilesDocument17 pagesNano Finishes For Uv Protection in Textilesmythilirani100% (2)
- Assignment II Fsa-Iii UV Protective FinishesDocument12 pagesAssignment II Fsa-Iii UV Protective FinishesUjwala JainNo ratings yet
- UVDocument5 pagesUVSifat RaihanNo ratings yet
- Nanonotechnology NoteDocument13 pagesNanonotechnology NoteProttoy DiptoNo ratings yet
- Blocking Ultraviolet and Anti-Staining For Cotton Fabric 100% Using Nano Titan DioxideDocument7 pagesBlocking Ultraviolet and Anti-Staining For Cotton Fabric 100% Using Nano Titan DioxideBOHR International Journal of Biocomputing and Nano TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Protective TextilesDocument6 pagesProtective TextilesKhubab ShakerNo ratings yet
- Term Paper On Reduction of Direct Sun Light Heat by Proper Selection of ClothingDocument20 pagesTerm Paper On Reduction of Direct Sun Light Heat by Proper Selection of ClothingMukesh TiwariNo ratings yet
- Proteccion UV: Grupo - Yaziel Brenda Jaime Torres - Rosa Aponte Hurtado - Luisa Aguilar GuzmanDocument11 pagesProteccion UV: Grupo - Yaziel Brenda Jaime Torres - Rosa Aponte Hurtado - Luisa Aguilar GuzmanYaziel Jaime TorresNo ratings yet
- Use of Nanotechnology in Technical TextilesDocument12 pagesUse of Nanotechnology in Technical TextilesNaimul HasanNo ratings yet
- UV Protection FinishDocument24 pagesUV Protection Finishmuhammadahmad75492No ratings yet
- Performance Textiles PDFDocument4 pagesPerformance Textiles PDFUtkay DönmezNo ratings yet
- PROTECH Protective TextilesDocument29 pagesPROTECH Protective TextilesAneesha Panda0% (1)
- Presentation On Uv Protection FinishingDocument43 pagesPresentation On Uv Protection FinishingimranNo ratings yet
- Ultraviolet Protection Factor (UPF)Document4 pagesUltraviolet Protection Factor (UPF)YashNo ratings yet
- Uvf Technic in TextileDocument7 pagesUvf Technic in TextileDurgesh TripathiNo ratings yet
- Protective TextilesDocument36 pagesProtective TextilesDewan Ajuad Hossain Rifat100% (1)
- Ultra Violet Protection FinishDocument16 pagesUltra Violet Protection Finishdona biswasNo ratings yet
- Prakash Khude UV ProtectionDocument29 pagesPrakash Khude UV ProtectionariefNo ratings yet
- Funtional textile define-002Document3 pagesFuntional textile define-002Muhammad Mushtaq AliNo ratings yet
- UV Svetlina Vlijanie Na OciDocument5 pagesUV Svetlina Vlijanie Na OciDoe BlackNo ratings yet
- U V Procted Textile PDFDocument15 pagesU V Procted Textile PDFMusa EltayebNo ratings yet
- Defense Textiles FINALDocument10 pagesDefense Textiles FINALSudhir JainNo ratings yet
- Photochem Photobiology - 2022 - Aguilera - Sun Protective Properties of Technical Sportswear Fabrics 100 Polyester TheDocument9 pagesPhotochem Photobiology - 2022 - Aguilera - Sun Protective Properties of Technical Sportswear Fabrics 100 Polyester Thethelazyllama444No ratings yet
- Factsheet Textile UV Protection enDocument4 pagesFactsheet Textile UV Protection enariefNo ratings yet
- Hand Skin ProtectionDocument2 pagesHand Skin ProtectionPatrascu CristinaNo ratings yet
- Nuclear Protective TextilesDocument34 pagesNuclear Protective TextilesVikas SinghNo ratings yet
- 12 - Chapter 2 PDFDocument106 pages12 - Chapter 2 PDFGizachew Zeleke100% (1)
- IAETSD-JARAS A Study On Uv Protection Activity of Selected Herbs On Bamboocotton Woven FabricDocument5 pagesIAETSD-JARAS A Study On Uv Protection Activity of Selected Herbs On Bamboocotton Woven Fabriciaetsdiaetsd100% (1)
- UV Protection Finishes On Textile Fabric PDFDocument8 pagesUV Protection Finishes On Textile Fabric PDFruchika prasadNo ratings yet
- Protective TextilesDocument22 pagesProtective Textilesbeskyraj100% (1)
- Nonotechnology in TextilesDocument45 pagesNonotechnology in TextilesjayantverNo ratings yet
- Ehs UvDocument3 pagesEhs UvAdesh GurjarNo ratings yet
- Fabric and Garment Finishing Protective Fabric Finishes: By: Ankesh Dev Bhavyaa GuptaDocument31 pagesFabric and Garment Finishing Protective Fabric Finishes: By: Ankesh Dev Bhavyaa GuptaBhavyaa Gupta100% (1)
- Agro-Textiles: Textile Departmenf, Jayo Engineering College, ChennaiDocument6 pagesAgro-Textiles: Textile Departmenf, Jayo Engineering College, Chennaiمصطفى عبدالرحيمNo ratings yet
- Cotton Fabric and Uv-ProtectionDocument2 pagesCotton Fabric and Uv-Protectionstylish eagleNo ratings yet
- Advance Protective TextilesDocument28 pagesAdvance Protective Textilesimrans1100% (1)
- Nano Technology in Textiles A ReviewDocument6 pagesNano Technology in Textiles A ReviewMohammed Atiqul Hoque Chowdhury100% (1)
- Defence TextilesDocument28 pagesDefence TextilesAzl10471% (7)
- Fabric and Garment Finishing Protective Fabric Finishes: By: Ankesh Dev Bhavyaa GuptaDocument29 pagesFabric and Garment Finishing Protective Fabric Finishes: By: Ankesh Dev Bhavyaa GuptaBhavyaa GuptaNo ratings yet
- Evaluating The Ultraviolet Protection Factor (UPF) of Various Knit Fabric StructuresDocument15 pagesEvaluating The Ultraviolet Protection Factor (UPF) of Various Knit Fabric StructuresTas Kanken IndonesiaNo ratings yet
- IADVL CHAPTER 24 Photodermatology and Photodermatoses - SunscreenDocument7 pagesIADVL CHAPTER 24 Photodermatology and Photodermatoses - SunscreenNahas NazarNo ratings yet
- NullDocument4 pagesNullMaliha MazharNo ratings yet
- Application of Nanotechnology in TextileDocument34 pagesApplication of Nanotechnology in Textileparthjoshi91No ratings yet
- Assignment On: Textiles in Agriculture (Agrotech)Document6 pagesAssignment On: Textiles in Agriculture (Agrotech)AmirParvezNo ratings yet
- TECHNICAL TEXTILESDocument32 pagesTECHNICAL TEXTILESdivya.kvNo ratings yet
- Agro TextileDocument14 pagesAgro TextileASEEM SUPANNo ratings yet
- moisture wicking-003Document2 pagesmoisture wicking-003Muhammad Mushtaq AliNo ratings yet
- Medical TextileDocument22 pagesMedical TextileknjinnNo ratings yet
- Describe The Perspective Clothing That Should Be Worn For The Lab Staff Working in A Lab With Radioactive ElementsDocument9 pagesDescribe The Perspective Clothing That Should Be Worn For The Lab Staff Working in A Lab With Radioactive ElementsexjupiterNo ratings yet
- Ultravioletprotectionoftextiles 120526004725 Phpapp02Document24 pagesUltravioletprotectionoftextiles 120526004725 Phpapp02rajasajjadNo ratings yet
- Technical Textiles by AARDocument37 pagesTechnical Textiles by AARAtaur RahmanNo ratings yet
- Antimicrobial Finish of Textiles by Chitosan UV-Curing: Journal of Nanoscience and Nanotechnology June 2012Document9 pagesAntimicrobial Finish of Textiles by Chitosan UV-Curing: Journal of Nanoscience and Nanotechnology June 2012Federico SandroniNo ratings yet
- Syntheticand Natural UVProtectiveDocument25 pagesSyntheticand Natural UVProtectivefivudesignNo ratings yet
- Assignment On Special Fabrics: Properties and Quality ControlDocument30 pagesAssignment On Special Fabrics: Properties and Quality ControlNakib Ibna BasharNo ratings yet
- Technical TextilesDocument23 pagesTechnical TextilesNintha Jalan80% (5)
- OverviewDocument16 pagesOverviewAmal El-ebissyNo ratings yet
- UV STANDARD 801 Brochure Textile Uv Protection ENDocument12 pagesUV STANDARD 801 Brochure Textile Uv Protection ENAmir ShahzadNo ratings yet
- Personal Protective Equipment for Chemical, Biological, and Radiological Hazards: Design, Evaluation, and SelectionFrom EverandPersonal Protective Equipment for Chemical, Biological, and Radiological Hazards: Design, Evaluation, and SelectionNo ratings yet
- Occupational Radiation Protection in the Uranium Mining and Processing IndustryFrom EverandOccupational Radiation Protection in the Uranium Mining and Processing IndustryNo ratings yet
- 9Document2 pages9Muhammad Mushtaq AliNo ratings yet
- 6Document2 pages6Muhammad Mushtaq AliNo ratings yet
- moisture wicking-003Document2 pagesmoisture wicking-003Muhammad Mushtaq AliNo ratings yet
- Presentation RMDocument7 pagesPresentation RMMuhammad Mushtaq AliNo ratings yet
- Montmorillonite Bio-Nanocomposite FilmsDocument23 pagesMontmorillonite Bio-Nanocomposite FilmsMuhammad Mushtaq AliNo ratings yet
- the art of cinematographyDocument10 pagesthe art of cinematographyMuhammad Mushtaq AliNo ratings yet
- Page Proof Instructions and Queries: Journal of Industrial Textiles (JIT) 831083Document12 pagesPage Proof Instructions and Queries: Journal of Industrial Textiles (JIT) 831083Muhammad Mushtaq AliNo ratings yet
- Electrospun Poly Lactic Acid (PLA) Fibreseffect of Different Solvent Systems On Fibre Morphology and DiameterDocument10 pagesElectrospun Poly Lactic Acid (PLA) Fibreseffect of Different Solvent Systems On Fibre Morphology and DiameterMuhammad Mushtaq AliNo ratings yet
- Functional Copolymer Organo MMT Nanoarchitectures XXVI Fa1-Brication and Characterization of Electrospun Nanofibers From PCL ODA MMT and Copolymer GDocument13 pagesFunctional Copolymer Organo MMT Nanoarchitectures XXVI Fa1-Brication and Characterization of Electrospun Nanofibers From PCL ODA MMT and Copolymer GMuhammad Mushtaq AliNo ratings yet
- Biomedical MaterialsDocument29 pagesBiomedical MaterialsMuhammad Mushtaq AliNo ratings yet
- Characterization of Antimicrobial Polylactic Acid Based FilmsDocument9 pagesCharacterization of Antimicrobial Polylactic Acid Based FilmsMuhammad Mushtaq AliNo ratings yet
- Biomedical MaterialsDocument32 pagesBiomedical MaterialsMuhammad Mushtaq AliNo ratings yet
- 1 Teaching As A ProfessionDocument63 pages1 Teaching As A ProfessionMuhammad Mushtaq AliNo ratings yet
- Biomedical MaterialsDocument36 pagesBiomedical MaterialsMuhammad Mushtaq AliNo ratings yet
- Sound Absorbing Properties of Roller Blind Curtain Fabrics: Og Uz Demiryu Rek and Hu Snu AydemirDocument17 pagesSound Absorbing Properties of Roller Blind Curtain Fabrics: Og Uz Demiryu Rek and Hu Snu AydemirMuhammad Mushtaq AliNo ratings yet
- Message: Secretary Ministry of Textile IndustryDocument38 pagesMessage: Secretary Ministry of Textile IndustryMuhammad Mushtaq AliNo ratings yet
- 3 Curriculum Development, Assesment and EvaluationDocument119 pages3 Curriculum Development, Assesment and EvaluationMuhammad Mushtaq AliNo ratings yet
- App-Form For FacultyDocument5 pagesApp-Form For FacultyMuhammad Mushtaq AliNo ratings yet
- 2-Electrospinning Fabrication and Characterization ofDocument8 pages2-Electrospinning Fabrication and Characterization ofMuhammad Mushtaq AliNo ratings yet
- 100906-2323 Ijbas-IjensDocument9 pages100906-2323 Ijbas-IjensMuhammad Mushtaq AliNo ratings yet
- Unit Rate AnalysisDocument341 pagesUnit Rate AnalysisAshebirNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Civil Engg Objective Type RAgor - pdf.XP0gDbpt84gkO1dc85Cbz6jAcACPldCqDocument69 pagesChapter 1 Civil Engg Objective Type RAgor - pdf.XP0gDbpt84gkO1dc85Cbz6jAcACPldCqSurya PatanNo ratings yet
- Cement IndustryDocument22 pagesCement IndustryChaudary Usman GondalNo ratings yet
- BCP 503Document28 pagesBCP 503Vineet JhambNo ratings yet
- Co-Ordination Compound (Question Paper)Document4 pagesCo-Ordination Compound (Question Paper)Param shahNo ratings yet
- MKIII and NO96 Procedure For General Approval of Materials and ComponentDocument6 pagesMKIII and NO96 Procedure For General Approval of Materials and ComponentYongkoo HanNo ratings yet
- An Experimental Evaluation of Fiber Reinforced PolypropyleneDocument6 pagesAn Experimental Evaluation of Fiber Reinforced PolypropyleneRafael ZanettiNo ratings yet
- Acoustic Energy Absorption Properties of Fibrous Materials A Review PDFDocument47 pagesAcoustic Energy Absorption Properties of Fibrous Materials A Review PDFFloreaNo ratings yet
- Tekapur Super Flex enDocument2 pagesTekapur Super Flex enEzeval GráficaNo ratings yet
- Treatment of Soap and Detergent Industry WastesDocument76 pagesTreatment of Soap and Detergent Industry Wastessumit kumar0% (1)
- Important Question ICSE 2010 Class 10th Hydrogen ChlorideDocument5 pagesImportant Question ICSE 2010 Class 10th Hydrogen ChlorideYash KapoorNo ratings yet
- Astm A692 PDFDocument2 pagesAstm A692 PDFgaminNo ratings yet
- Dokumen Tips - Ektraksi-Alumina-Dari-Lumpur Id enDocument8 pagesDokumen Tips - Ektraksi-Alumina-Dari-Lumpur Id enFatmawati KadirNo ratings yet
- Field Guide To Concrete Repair Application Procedures: Structural Crack Repair by Epoxy Injection ACI RAP Bulletin 1Document3 pagesField Guide To Concrete Repair Application Procedures: Structural Crack Repair by Epoxy Injection ACI RAP Bulletin 1jamjam75No ratings yet
- Fibre Reinforced ConcreteDocument16 pagesFibre Reinforced ConcreteSîdDhàñt SätYãmNo ratings yet
- Sustainable Biomaterials and Their Applications - A Short ReviewDocument9 pagesSustainable Biomaterials and Their Applications - A Short ReviewvalentinaNo ratings yet
- A Study and Analysis of Manifacturing Process of Thiokol Rubber Swapna V, K. MounikaDocument8 pagesA Study and Analysis of Manifacturing Process of Thiokol Rubber Swapna V, K. Mounikamuhammad sameer ansariNo ratings yet
- My FinaleDocument36 pagesMy Finaleyohanis ashineNo ratings yet
- Sotrafer-Quality Observation Complaince Tracking Record.Document63 pagesSotrafer-Quality Observation Complaince Tracking Record.mitendra singhNo ratings yet
- Form 2 Chapter 6 Acid and AlkaliDocument28 pagesForm 2 Chapter 6 Acid and AlkaliammyNo ratings yet
- 2021 Master CatalogDocument330 pages2021 Master Cataloggeetha raniNo ratings yet
- 125E-5 SEN00697-03 Disassembly & AssemblyDocument112 pages125E-5 SEN00697-03 Disassembly & AssemblydatphuongNo ratings yet
- Ds - Concrete Mix DesignDocument51 pagesDs - Concrete Mix DesignDarshan ShahNo ratings yet
- Gmaw Fcaw Mcaw WeldingDocument4 pagesGmaw Fcaw Mcaw Weldingsajeed76743031No ratings yet
- Kps LPG Installation Manual 1 2 1 English PDFDocument36 pagesKps LPG Installation Manual 1 2 1 English PDFgheorghe garduNo ratings yet
- Highwaymaintenance M KennyDocument28 pagesHighwaymaintenance M KennyEbsa KelifaNo ratings yet
- ABC Gasket KitDocument97 pagesABC Gasket KitBenjamin romeroNo ratings yet
- Analysis and Design of SlabsDocument6 pagesAnalysis and Design of SlabsricardoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 15 Acids and Bases PDFDocument28 pagesChapter 15 Acids and Bases PDFJoshua NaemonNo ratings yet