Professional Documents
Culture Documents
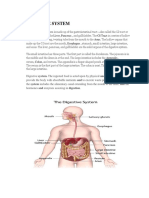
Nutrition and Diet Therapy PROCESS OF DIGESTION
Nutrition and Diet Therapy PROCESS OF DIGESTION
Uploaded by
ferrerjericho300Copyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Pass The MRCS PDFDocument533 pagesPass The MRCS PDFYahya Alborno100% (5)
- Anatomy and Physiology of Digestive SystemDocument3 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of Digestive SystemAngelica JavierNo ratings yet
- Digestive SystemDocument7 pagesDigestive SystemChristine Joyce S. CruzNo ratings yet
- Enhanced Science 8 Q4 Week 1Document1 pageEnhanced Science 8 Q4 Week 1chl03b4y09No ratings yet
- GASTROINTESTINAL SYSTEM 1 Ngan 2Document14 pagesGASTROINTESTINAL SYSTEM 1 Ngan 2Stephen Jil BocoNo ratings yet
- BIO 1133 Exercise 9 (Digestive Sytem of The Frog)Document6 pagesBIO 1133 Exercise 9 (Digestive Sytem of The Frog)Tonet LapeNo ratings yet
- Study Guide 1 Assessment of Digestive and Gastrointestinal Function and Treatment ModalitiesDocument10 pagesStudy Guide 1 Assessment of Digestive and Gastrointestinal Function and Treatment ModalitiesKc Cabanilla LizardoNo ratings yet
- Digestive System PowerPointDocument35 pagesDigestive System PowerPointcelineNo ratings yet
- Functions of The Digestive SystemDocument12 pagesFunctions of The Digestive SystemRomeo Penyihir ChrestomancyNo ratings yet
- Digestive System, Educational PlatformDocument77 pagesDigestive System, Educational Platformluckytraders0511No ratings yet
- Nutrition in HumansDocument82 pagesNutrition in HumansSyed Burhan UddinNo ratings yet
- Case Scenario Group 1Document12 pagesCase Scenario Group 1iluvmunicamuchNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument13 pagesAnatomy and Physiologydaculareyndel04No ratings yet
- Digestive System PresentationDocument20 pagesDigestive System Presentationrocky2219No ratings yet
- The Digestive System M.I.Document10 pagesThe Digestive System M.I.May KimNo ratings yet
- Digestive SystemDocument9 pagesDigestive SystemhlorenoNo ratings yet
- Digestive System (Autosaved)Document53 pagesDigestive System (Autosaved)Jeyger Borres BuadlartNo ratings yet
- Digestive System Grade 10-11Document7 pagesDigestive System Grade 10-11Nandana Nayana KumaraNo ratings yet
- Nutrition and Diet Therapy: Process of DigestionDocument3 pagesNutrition and Diet Therapy: Process of DigestionShun Reigh SumilangNo ratings yet
- Module 14 AbdomenDocument22 pagesModule 14 Abdomenjohn maikeilNo ratings yet
- NUTRITIONDocument11 pagesNUTRITIONRushana SadaqatNo ratings yet
- Unit IV - Digestive and Excretory SystemDocument54 pagesUnit IV - Digestive and Excretory SystemsahilNo ratings yet
- Digestive Sysytem: Basic Health CareDocument50 pagesDigestive Sysytem: Basic Health CareBecky GalanoNo ratings yet
- Digestive System: Liver Pancreas GI Tract Anus EsophagusDocument10 pagesDigestive System: Liver Pancreas GI Tract Anus EsophagusKyle NoolNo ratings yet
- Digestive SystemDocument26 pagesDigestive SystemFrancisco D. AndaquigNo ratings yet
- Digestive System DraftDocument39 pagesDigestive System DraftDiosa BakingNo ratings yet
- Digestive SystemDocument29 pagesDigestive Systemsugar kookie0% (1)
- The Digestive SystemDocument44 pagesThe Digestive SystemJoy NatividadNo ratings yet
- AbalalalalalalalalalDocument82 pagesAbalalalalalalalalalSyed Burhan UddinNo ratings yet
- Module 4 Digestive SystemDocument9 pagesModule 4 Digestive SystemupadhiNo ratings yet
- Digestive System Kaikiyi Sykay Pacheco BEED1Document3 pagesDigestive System Kaikiyi Sykay Pacheco BEED1Kaikiyi Sykay PachecoNo ratings yet
- DigestiveDocument11 pagesDigestiveSuahniNo ratings yet
- Git HandoutsDocument49 pagesGit HandoutsCharlz Zipagan100% (1)
- 1 Digestive SystemDocument1 page1 Digestive SystemRussel GuratNo ratings yet
- Life Processes (Part-2) (1)Document24 pagesLife Processes (Part-2) (1)TANMAYA DASHNo ratings yet
- SCIENCE DIgestive SystemDocument7 pagesSCIENCE DIgestive SystemRichard MerkNo ratings yet
- The Digestive System: Reporeted By: Jabel, Honeylyn Lou Wong, Leah Castro, Shiela MaeDocument42 pagesThe Digestive System: Reporeted By: Jabel, Honeylyn Lou Wong, Leah Castro, Shiela MaeRaisa GravadorNo ratings yet
- Digestive System PowerpointDocument33 pagesDigestive System PowerpointThomas41767% (6)
- SCI G8 Q4 Week 1 DIGESTIVE SYSTEMDocument114 pagesSCI G8 Q4 Week 1 DIGESTIVE SYSTEM• S h ı m m y •No ratings yet
- Lab Exercise Digestive System Bautista Maria LuisaDocument9 pagesLab Exercise Digestive System Bautista Maria LuisaEricka ElloNo ratings yet
- Digestive SystemDocument6 pagesDigestive SystemAiman AfzalNo ratings yet
- Project Free Digestive SystemDocument24 pagesProject Free Digestive Systemfelina.duran001No ratings yet
- The Human Digestive SystemDocument14 pagesThe Human Digestive Systemsushmits040808No ratings yet
- Science 8 Module Final QuarterDocument28 pagesScience 8 Module Final QuarterSJBLCMary OrpillaNo ratings yet
- AN01200.PDF PigDocument4 pagesAN01200.PDF PigGabu FiguracionNo ratings yet
- Digestive SystemDocument20 pagesDigestive SystemJean AlbertoNo ratings yet
- Jawaban Tugas Biology Digestive SystemDocument3 pagesJawaban Tugas Biology Digestive Systemaulia nurfadillahNo ratings yet
- Human Body Digestive SystemDocument6 pagesHuman Body Digestive SystemMaria SibauNo ratings yet
- The Digestive System Handouts GENBIO2 STEM12Document4 pagesThe Digestive System Handouts GENBIO2 STEM12April Joy T. GrijaldoNo ratings yet
- Animal Science 42 Laboratory22Document7 pagesAnimal Science 42 Laboratory22PEARL ALPHA MAE MATURANNo ratings yet
- Structure and Functions of The Gastro Intestinal SystemDocument13 pagesStructure and Functions of The Gastro Intestinal SystemhahahahaaaaaaaNo ratings yet
- Digestive System: Five Basic ActivitiesDocument5 pagesDigestive System: Five Basic ActivitiesCrystal MaidenNo ratings yet
- Metabolism (Ncm-216)Document10 pagesMetabolism (Ncm-216)Sofronio OmboyNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of The GDocument18 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of The Gbryan leguiabNo ratings yet
- Running Head - (Assignment)Document7 pagesRunning Head - (Assignment)Anousha AamirNo ratings yet
- دمج شباتر البالغين .....Document511 pagesدمج شباتر البالغين .....Abdallah AlasalNo ratings yet
- The Human Digestive SystemDocument34 pagesThe Human Digestive SystemKayla Denize GerardinoNo ratings yet
- Esophagus Is About 8 Inches Long, and Is Lined by Moist Pink Tissue CalledDocument6 pagesEsophagus Is About 8 Inches Long, and Is Lined by Moist Pink Tissue CalledMJ Caysip100% (1)
- He Module 2 Learning TheoriesDocument6 pagesHe Module 2 Learning Theoriesferrerjericho300No ratings yet
- ProtozoaDocument11 pagesProtozoaferrerjericho300No ratings yet
- MHE para Module 2Document12 pagesMHE para Module 2ferrerjericho300No ratings yet
- Supplemental Readings On ProtozoansDocument18 pagesSupplemental Readings On Protozoansferrerjericho300No ratings yet
- Pancreatita Acuta. Cancerul PancreaticDocument60 pagesPancreatita Acuta. Cancerul PancreaticElena CNo ratings yet
- InteGRATED SCIENCE - ExcretionDocument2 pagesInteGRATED SCIENCE - Excretionnehru09No ratings yet
- Murphy SignDocument3 pagesMurphy SignRobert HarijantoNo ratings yet
- E01723 Yogic Asanas For Health and Vigour TextDocument138 pagesE01723 Yogic Asanas For Health and Vigour TextAnonymous nKVk2VC2VENo ratings yet
- Assessing The Abdomen Basic Concept: Abdominal Assessment Is A Valuation of The Abdomen, Liver and BladderDocument6 pagesAssessing The Abdomen Basic Concept: Abdominal Assessment Is A Valuation of The Abdomen, Liver and BladderMay Chelle ErazoNo ratings yet
- Pemeriksaan Laboratorium HatiDocument67 pagesPemeriksaan Laboratorium HatiTutde SedanaNo ratings yet
- Article: ZootaxaDocument17 pagesArticle: ZootaxaJulian LeonardoNo ratings yet
- Abdomen-Clinicals - PDF Version 1Document11 pagesAbdomen-Clinicals - PDF Version 1hamzabhayatNo ratings yet
- Polariswushu NetDocument19 pagesPolariswushu NetspiraldaoNo ratings yet
- Excretory QuizDocument4 pagesExcretory QuizIris Podolsky SchreyNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Values: UrinalysisDocument4 pagesLaboratory Values: Urinalysissakura1717No ratings yet
- Topic 9.2 Graded QuizDocument8 pagesTopic 9.2 Graded QuizTran WinnerNo ratings yet
- Excretion and KidneysDocument39 pagesExcretion and KidneyselizabethNo ratings yet
- Unit 6 JadiDocument3 pagesUnit 6 JadiALIFIANo ratings yet
- Pathology of The Exocrine PancreasDocument5 pagesPathology of The Exocrine PancreassatriayanuwardaniNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology Basic LecturesDocument64 pagesAnatomy and Physiology Basic LecturesRamil Ephrem L. SanchezNo ratings yet
- Althazar Score: Grading of PancreatitisDocument1 pageAlthazar Score: Grading of PancreatitisJuan GomezNo ratings yet
- Chapter 26 Urinary SystemDocument17 pagesChapter 26 Urinary SystemAmy Lalringhluani100% (1)
- Sunday Bodyweight SquatsDocument3 pagesSunday Bodyweight Squatstomorrow x togetherNo ratings yet
- LaparotomyDocument36 pagesLaparotomydenekeNo ratings yet
- Jurnal CKDDocument5 pagesJurnal CKDramadhaniDLNo ratings yet
- Belly Fat in MenDocument4 pagesBelly Fat in MensatfasNo ratings yet
- Abdominal MassDocument7 pagesAbdominal MassRoseben SomidoNo ratings yet
- Complete Vocal Technique in Four Pages PDFDocument5 pagesComplete Vocal Technique in Four Pages PDFcairo861No ratings yet
- Whipple Procedure: Procedure at A GlanceDocument4 pagesWhipple Procedure: Procedure at A GlanceAze Andrea PutraNo ratings yet
- Incision Access UrologyDocument47 pagesIncision Access UrologyHafizur RashidNo ratings yet
- Swami Profile March 2023Document5 pagesSwami Profile March 2023Chomotkar 10No ratings yet
- Histology KUBDocument31 pagesHistology KUBkhiks34No ratings yet
- Anatomy ProstateDocument2 pagesAnatomy ProstatenavjavNo ratings yet
Nutrition and Diet Therapy PROCESS OF DIGESTION
Nutrition and Diet Therapy PROCESS OF DIGESTION
Uploaded by
ferrerjericho300Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Nutrition and Diet Therapy PROCESS OF DIGESTION
Nutrition and Diet Therapy PROCESS OF DIGESTION
Uploaded by
ferrerjericho300Copyright:
Available Formats
UNIVERSITY OF LA SALETTE, INC.
Dubinan East, Santiago City, Philippines, 3311
COLLEGE OF NURSING, PUBLIC HEALTH AND MIDWIFERY
Nutrition and Diet Therapy
Review Notes
Topic: Process of Digestion
Digestion- It is defined as process of breaking down food into substance like carbohydrates,
proteins, fats, and vitamins that aid body in its different functions.
• The digestive system is made up of gastrointestinal tract, the liver, pancreas, and gall
bladder.
• The GI tract is a chain of hollow organs connected in a long, twisting tube from the
mount to the anus.
• The Hollow organs that make up the GI tract are the mouth, esophagus, stomach, small
intestines, large intestines, and anus.
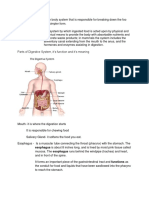
Parts of Human Digestive System
1. Mouth- Digestion begins in the mouth where food is broken into pieces by chewing or
mastication. Amylase is the enzymes that aids in faster breaking down of foods.
2. Throat- Also known as the Pharynx, transfers food from the mouth to the esophagus
3. Esophagus- Through a series of contractions known as peristalsis, food goes to the
stomach. A “Zone of high pressure” known as the lower esophageal sphincter, prevents
food from passing backwards into the esophagus.
4. Stomach- Secretes stomach acid or Hydrochloric Acid to carry on the process of breaking
down the food
5. Small Intestine
- 20 Feet Long
- Made of three parts: 1. Duodenum, 2. Jejunum, and 3. Ileum.
- Duodenum continues the process of breaking down of food
- Jejunum and Ileum responsible for nutrients absorption into the blood stream
Three supporting organs in digestion
Prepared by: Jericho G. Ferrer, MSPH-Candidate
UNIVERSITY OF LA SALETTE, INC.
Dubinan East, Santiago City, Philippines, 3311
COLLEGE OF NURSING, PUBLIC HEALTH AND MIDWIFERY
1. Pancreas- Breaks down protein, fats, and carbohydrates from the food
2. Liver- Produces and secretes bile aiding in absorption of fats, and fat-soluble
vitamins. Also cleansed and purifies the blood comes from the small intestines
3. Gall Bladder- Pear-shaped reservoir. Storage section of Bile.
- During meals, gallbladder contracts and sends bile to
the small intestines
6. Large Intestine
The colon is a long muscular tube 5-6 foot that connects the Cecum
Cecum is the first part of the large intestine
Five Parts of Large Intestine
Cecum
Ascending right colon
Transverse colon
Descending colon
Sigmoid Colon
Note: Stools are kept in the sigmoid colon Until a “Mass movement”. It normally takes about 36
hours for the stool to get through the colon.
7. Rectum- 8-inch Chamber. It receives stool from the colon and holds the stool until
defecation.
8. Anus- Consist of pelvic floor muscles and 2 anal sphincters
Lining of Upper anus- Specialized to detect rectal concerns
Pelvic floor muscles- Creates an angle between the rectum and the anus that stops
stool.
Anal Sphincters- Provides control in elimination of stool.
Prepared by: Jericho G. Ferrer, MSPH-Candidate
You might also like
- Pass The MRCS PDFDocument533 pagesPass The MRCS PDFYahya Alborno100% (5)
- Anatomy and Physiology of Digestive SystemDocument3 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of Digestive SystemAngelica JavierNo ratings yet
- Digestive SystemDocument7 pagesDigestive SystemChristine Joyce S. CruzNo ratings yet
- Enhanced Science 8 Q4 Week 1Document1 pageEnhanced Science 8 Q4 Week 1chl03b4y09No ratings yet
- GASTROINTESTINAL SYSTEM 1 Ngan 2Document14 pagesGASTROINTESTINAL SYSTEM 1 Ngan 2Stephen Jil BocoNo ratings yet
- BIO 1133 Exercise 9 (Digestive Sytem of The Frog)Document6 pagesBIO 1133 Exercise 9 (Digestive Sytem of The Frog)Tonet LapeNo ratings yet
- Study Guide 1 Assessment of Digestive and Gastrointestinal Function and Treatment ModalitiesDocument10 pagesStudy Guide 1 Assessment of Digestive and Gastrointestinal Function and Treatment ModalitiesKc Cabanilla LizardoNo ratings yet
- Digestive System PowerPointDocument35 pagesDigestive System PowerPointcelineNo ratings yet
- Functions of The Digestive SystemDocument12 pagesFunctions of The Digestive SystemRomeo Penyihir ChrestomancyNo ratings yet
- Digestive System, Educational PlatformDocument77 pagesDigestive System, Educational Platformluckytraders0511No ratings yet
- Nutrition in HumansDocument82 pagesNutrition in HumansSyed Burhan UddinNo ratings yet
- Case Scenario Group 1Document12 pagesCase Scenario Group 1iluvmunicamuchNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument13 pagesAnatomy and Physiologydaculareyndel04No ratings yet
- Digestive System PresentationDocument20 pagesDigestive System Presentationrocky2219No ratings yet
- The Digestive System M.I.Document10 pagesThe Digestive System M.I.May KimNo ratings yet
- Digestive SystemDocument9 pagesDigestive SystemhlorenoNo ratings yet
- Digestive System (Autosaved)Document53 pagesDigestive System (Autosaved)Jeyger Borres BuadlartNo ratings yet
- Digestive System Grade 10-11Document7 pagesDigestive System Grade 10-11Nandana Nayana KumaraNo ratings yet
- Nutrition and Diet Therapy: Process of DigestionDocument3 pagesNutrition and Diet Therapy: Process of DigestionShun Reigh SumilangNo ratings yet
- Module 14 AbdomenDocument22 pagesModule 14 Abdomenjohn maikeilNo ratings yet
- NUTRITIONDocument11 pagesNUTRITIONRushana SadaqatNo ratings yet
- Unit IV - Digestive and Excretory SystemDocument54 pagesUnit IV - Digestive and Excretory SystemsahilNo ratings yet
- Digestive Sysytem: Basic Health CareDocument50 pagesDigestive Sysytem: Basic Health CareBecky GalanoNo ratings yet
- Digestive System: Liver Pancreas GI Tract Anus EsophagusDocument10 pagesDigestive System: Liver Pancreas GI Tract Anus EsophagusKyle NoolNo ratings yet
- Digestive SystemDocument26 pagesDigestive SystemFrancisco D. AndaquigNo ratings yet
- Digestive System DraftDocument39 pagesDigestive System DraftDiosa BakingNo ratings yet
- Digestive SystemDocument29 pagesDigestive Systemsugar kookie0% (1)
- The Digestive SystemDocument44 pagesThe Digestive SystemJoy NatividadNo ratings yet
- AbalalalalalalalalalDocument82 pagesAbalalalalalalalalalSyed Burhan UddinNo ratings yet
- Module 4 Digestive SystemDocument9 pagesModule 4 Digestive SystemupadhiNo ratings yet
- Digestive System Kaikiyi Sykay Pacheco BEED1Document3 pagesDigestive System Kaikiyi Sykay Pacheco BEED1Kaikiyi Sykay PachecoNo ratings yet
- DigestiveDocument11 pagesDigestiveSuahniNo ratings yet
- Git HandoutsDocument49 pagesGit HandoutsCharlz Zipagan100% (1)
- 1 Digestive SystemDocument1 page1 Digestive SystemRussel GuratNo ratings yet
- Life Processes (Part-2) (1)Document24 pagesLife Processes (Part-2) (1)TANMAYA DASHNo ratings yet
- SCIENCE DIgestive SystemDocument7 pagesSCIENCE DIgestive SystemRichard MerkNo ratings yet
- The Digestive System: Reporeted By: Jabel, Honeylyn Lou Wong, Leah Castro, Shiela MaeDocument42 pagesThe Digestive System: Reporeted By: Jabel, Honeylyn Lou Wong, Leah Castro, Shiela MaeRaisa GravadorNo ratings yet
- Digestive System PowerpointDocument33 pagesDigestive System PowerpointThomas41767% (6)
- SCI G8 Q4 Week 1 DIGESTIVE SYSTEMDocument114 pagesSCI G8 Q4 Week 1 DIGESTIVE SYSTEM• S h ı m m y •No ratings yet
- Lab Exercise Digestive System Bautista Maria LuisaDocument9 pagesLab Exercise Digestive System Bautista Maria LuisaEricka ElloNo ratings yet
- Digestive SystemDocument6 pagesDigestive SystemAiman AfzalNo ratings yet
- Project Free Digestive SystemDocument24 pagesProject Free Digestive Systemfelina.duran001No ratings yet
- The Human Digestive SystemDocument14 pagesThe Human Digestive Systemsushmits040808No ratings yet
- Science 8 Module Final QuarterDocument28 pagesScience 8 Module Final QuarterSJBLCMary OrpillaNo ratings yet
- AN01200.PDF PigDocument4 pagesAN01200.PDF PigGabu FiguracionNo ratings yet
- Digestive SystemDocument20 pagesDigestive SystemJean AlbertoNo ratings yet
- Jawaban Tugas Biology Digestive SystemDocument3 pagesJawaban Tugas Biology Digestive Systemaulia nurfadillahNo ratings yet
- Human Body Digestive SystemDocument6 pagesHuman Body Digestive SystemMaria SibauNo ratings yet
- The Digestive System Handouts GENBIO2 STEM12Document4 pagesThe Digestive System Handouts GENBIO2 STEM12April Joy T. GrijaldoNo ratings yet
- Animal Science 42 Laboratory22Document7 pagesAnimal Science 42 Laboratory22PEARL ALPHA MAE MATURANNo ratings yet
- Structure and Functions of The Gastro Intestinal SystemDocument13 pagesStructure and Functions of The Gastro Intestinal SystemhahahahaaaaaaaNo ratings yet
- Digestive System: Five Basic ActivitiesDocument5 pagesDigestive System: Five Basic ActivitiesCrystal MaidenNo ratings yet
- Metabolism (Ncm-216)Document10 pagesMetabolism (Ncm-216)Sofronio OmboyNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of The GDocument18 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of The Gbryan leguiabNo ratings yet
- Running Head - (Assignment)Document7 pagesRunning Head - (Assignment)Anousha AamirNo ratings yet
- دمج شباتر البالغين .....Document511 pagesدمج شباتر البالغين .....Abdallah AlasalNo ratings yet
- The Human Digestive SystemDocument34 pagesThe Human Digestive SystemKayla Denize GerardinoNo ratings yet
- Esophagus Is About 8 Inches Long, and Is Lined by Moist Pink Tissue CalledDocument6 pagesEsophagus Is About 8 Inches Long, and Is Lined by Moist Pink Tissue CalledMJ Caysip100% (1)
- He Module 2 Learning TheoriesDocument6 pagesHe Module 2 Learning Theoriesferrerjericho300No ratings yet
- ProtozoaDocument11 pagesProtozoaferrerjericho300No ratings yet
- MHE para Module 2Document12 pagesMHE para Module 2ferrerjericho300No ratings yet
- Supplemental Readings On ProtozoansDocument18 pagesSupplemental Readings On Protozoansferrerjericho300No ratings yet
- Pancreatita Acuta. Cancerul PancreaticDocument60 pagesPancreatita Acuta. Cancerul PancreaticElena CNo ratings yet
- InteGRATED SCIENCE - ExcretionDocument2 pagesInteGRATED SCIENCE - Excretionnehru09No ratings yet
- Murphy SignDocument3 pagesMurphy SignRobert HarijantoNo ratings yet
- E01723 Yogic Asanas For Health and Vigour TextDocument138 pagesE01723 Yogic Asanas For Health and Vigour TextAnonymous nKVk2VC2VENo ratings yet
- Assessing The Abdomen Basic Concept: Abdominal Assessment Is A Valuation of The Abdomen, Liver and BladderDocument6 pagesAssessing The Abdomen Basic Concept: Abdominal Assessment Is A Valuation of The Abdomen, Liver and BladderMay Chelle ErazoNo ratings yet
- Pemeriksaan Laboratorium HatiDocument67 pagesPemeriksaan Laboratorium HatiTutde SedanaNo ratings yet
- Article: ZootaxaDocument17 pagesArticle: ZootaxaJulian LeonardoNo ratings yet
- Abdomen-Clinicals - PDF Version 1Document11 pagesAbdomen-Clinicals - PDF Version 1hamzabhayatNo ratings yet
- Polariswushu NetDocument19 pagesPolariswushu NetspiraldaoNo ratings yet
- Excretory QuizDocument4 pagesExcretory QuizIris Podolsky SchreyNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Values: UrinalysisDocument4 pagesLaboratory Values: Urinalysissakura1717No ratings yet
- Topic 9.2 Graded QuizDocument8 pagesTopic 9.2 Graded QuizTran WinnerNo ratings yet
- Excretion and KidneysDocument39 pagesExcretion and KidneyselizabethNo ratings yet
- Unit 6 JadiDocument3 pagesUnit 6 JadiALIFIANo ratings yet
- Pathology of The Exocrine PancreasDocument5 pagesPathology of The Exocrine PancreassatriayanuwardaniNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology Basic LecturesDocument64 pagesAnatomy and Physiology Basic LecturesRamil Ephrem L. SanchezNo ratings yet
- Althazar Score: Grading of PancreatitisDocument1 pageAlthazar Score: Grading of PancreatitisJuan GomezNo ratings yet
- Chapter 26 Urinary SystemDocument17 pagesChapter 26 Urinary SystemAmy Lalringhluani100% (1)
- Sunday Bodyweight SquatsDocument3 pagesSunday Bodyweight Squatstomorrow x togetherNo ratings yet
- LaparotomyDocument36 pagesLaparotomydenekeNo ratings yet
- Jurnal CKDDocument5 pagesJurnal CKDramadhaniDLNo ratings yet
- Belly Fat in MenDocument4 pagesBelly Fat in MensatfasNo ratings yet
- Abdominal MassDocument7 pagesAbdominal MassRoseben SomidoNo ratings yet
- Complete Vocal Technique in Four Pages PDFDocument5 pagesComplete Vocal Technique in Four Pages PDFcairo861No ratings yet
- Whipple Procedure: Procedure at A GlanceDocument4 pagesWhipple Procedure: Procedure at A GlanceAze Andrea PutraNo ratings yet
- Incision Access UrologyDocument47 pagesIncision Access UrologyHafizur RashidNo ratings yet
- Swami Profile March 2023Document5 pagesSwami Profile March 2023Chomotkar 10No ratings yet
- Histology KUBDocument31 pagesHistology KUBkhiks34No ratings yet
- Anatomy ProstateDocument2 pagesAnatomy ProstatenavjavNo ratings yet