Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 viewsUnit 12 hydrocarbon
Unit 12 hydrocarbon
Uploaded by
ShahzadCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Science Group 9424713991Document48 pagesScience Group 9424713991Shahzad50% (2)
- 11.1.26 AOAC of Fi Cial Method 974.27 Cad Mium, Chro Mium, Cop Per, Iron, Lead, Mag Ne Sium, Man Ga Nese, Sil Ver, and Zinc in Wa TerDocument2 pages11.1.26 AOAC of Fi Cial Method 974.27 Cad Mium, Chro Mium, Cop Per, Iron, Lead, Mag Ne Sium, Man Ga Nese, Sil Ver, and Zinc in Wa Termttla100% (1)
- Taller 1Document2 pagesTaller 1Andres ArmeroNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Ch7,8 Part IIDocument4 pagesChemistry Ch7,8 Part IIdania.siddiqui195No ratings yet
- XII CH#09 P.S#01 HareshDocument3 pagesXII CH#09 P.S#01 Hareshpapukhan67zkqNo ratings yet
- Alcohols, Phenols and EthersDocument2 pagesAlcohols, Phenols and EthersDr. Vijay Kumar SahNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry Questions2023Document11 pagesOrganic Chemistry Questions2023xqfs2cd44sNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Test # 8Document4 pagesChemistry Test # 8dania.siddiqui195No ratings yet
- Chemistry Ch11,12 Part IIDocument4 pagesChemistry Ch11,12 Part IIAbdul RehmanNo ratings yet
- 12 MCQDocument2 pages12 MCQSheraz ShahNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Ch9,10 Part IIDocument4 pagesChemistry Ch9,10 Part IIdania.siddiqui195No ratings yet
- Aldehydes, Ketons and Carboxylic Acid Unit 11 MCQDocument4 pagesAldehydes, Ketons and Carboxylic Acid Unit 11 MCQAbhinav TripathiNo ratings yet
- C12 - ALDEHYDES KETONES AND CARBOXYLIC ACIDS (1) .9cfd4beDocument4 pagesC12 - ALDEHYDES KETONES AND CARBOXYLIC ACIDS (1) .9cfd4beakashkishore363No ratings yet
- unit 11 organic chemistryDocument5 pagesunit 11 organic chemistryShahzadNo ratings yet
- Learnvel Recuritment Test Chemistry - PGTDocument8 pagesLearnvel Recuritment Test Chemistry - PGTUma KumaranNo ratings yet
- Tick The Correct Option.: Chemistry Entry Test MCAT By: Sagheer Ahmad Gudara M.Phill ChemistryDocument4 pagesTick The Correct Option.: Chemistry Entry Test MCAT By: Sagheer Ahmad Gudara M.Phill ChemistrykamranNo ratings yet
- Dicc Xii Chem 400 McqsDocument18 pagesDicc Xii Chem 400 Mcqsadilahmedfreelance213No ratings yet
- Unit 11 MCQDocument7 pagesUnit 11 MCQJay VermaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry-FUNGAT/ECAT: (Chapter 10+11+12 B-II)Document2 pagesChemistry-FUNGAT/ECAT: (Chapter 10+11+12 B-II)XXXNo ratings yet
- AldehydesDocument22 pagesAldehydesjksiddharth24No ratings yet
- Question BankDocument133 pagesQuestion BankBabar AliNo ratings yet
- SIET CHEM Mock 2 PDFDocument7 pagesSIET CHEM Mock 2 PDFVikashNo ratings yet
- CH# 11 XII (Chem 12 Exam Task)Document4 pagesCH# 11 XII (Chem 12 Exam Task)Zeeshan Haider ChemistNo ratings yet
- Kcet Mock Test Chemistry 1Document8 pagesKcet Mock Test Chemistry 1VikashNo ratings yet
- Benzene and Alkyl Halides PDFDocument4 pagesBenzene and Alkyl Halides PDFakshaydewat786No ratings yet
- 1000 Mcqs ChemistryDocument113 pages1000 Mcqs ChemistryMariam IshtiaqNo ratings yet
- AlcoholDocument11 pagesAlcoholmkhanmughal4No ratings yet
- CH 4Document11 pagesCH 4ojha.ramNo ratings yet
- Chem Test No. 4 (Alkyl Halides, Alcohol and Phenols)Document4 pagesChem Test No. 4 (Alkyl Halides, Alcohol and Phenols)fahadmustafa100% (1)
- ECAT II Key DecDocument4 pagesECAT II Key DecSamia SajidNo ratings yet
- ECAT II Q.P DecDocument4 pagesECAT II Q.P DecSamia SajidNo ratings yet
- Alkyl HalideDocument8 pagesAlkyl HalideMegh Raj BhattNo ratings yet
- 12.Mcq - Aldehydes Ketones Carboxylic AcidsDocument23 pages12.Mcq - Aldehydes Ketones Carboxylic AcidsBedosi Bidita PandaNo ratings yet
- CC 13Document6 pagesCC 13Deepak SethyNo ratings yet
- 12th Chemistry CH-15MCQsDocument4 pages12th Chemistry CH-15MCQsRana DugNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Xii NAME: - : Alcohol, Phenol & EtherDocument1 pageChemistry Xii NAME: - : Alcohol, Phenol & EtherSahir Hemnani100% (1)
- Halogen Derivetives of Alkane MCQDocument11 pagesHalogen Derivetives of Alkane MCQParshantKumarBajaj93% (14)
- PPSC Lecture Chemisty Past PaperDocument5 pagesPPSC Lecture Chemisty Past PaperShahzadNo ratings yet
- Answer Key Assignment No. 6 Carboxylic Acid and DerivativesDocument5 pagesAnswer Key Assignment No. 6 Carboxylic Acid and DerivativesREGINE CUEVASNo ratings yet
- Haloalkanes and Haloarenes PDFDocument3 pagesHaloalkanes and Haloarenes PDFarya sonarNo ratings yet
- 12TH CBSE DPP 37. Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids MCQ ASSERTION REASON CS QDocument20 pages12TH CBSE DPP 37. Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids MCQ ASSERTION REASON CS Q123No ratings yet
- Haloalkanes and Haloarenes Q 5Document3 pagesHaloalkanes and Haloarenes Q 5jayjena007No ratings yet
- Alcohol Phenol and EtherDocument5 pagesAlcohol Phenol and EtherManthan JhaNo ratings yet
- Sample Question Paper 2021-22 Term 1 Subject: ChemistryDocument16 pagesSample Question Paper 2021-22 Term 1 Subject: Chemistrysarthak MongaNo ratings yet
- Sample Question Paper 2021-22 Term 1 Subject: ChemistryDocument10 pagesSample Question Paper 2021-22 Term 1 Subject: ChemistryNishi Kant MishraNo ratings yet
- (Xii) Alcohol, Phenol, EtherDocument10 pages(Xii) Alcohol, Phenol, EtherAbhishek SharmaNo ratings yet
- Lecturer Chemistry Mcqs PSC Past PaperDocument28 pagesLecturer Chemistry Mcqs PSC Past PaperNauman Khalid0% (1)
- Alcohols TestDocument2 pagesAlcohols TestAboahmed AliNo ratings yet
- 12th Chemistry CH-3MCQsDocument4 pages12th Chemistry CH-3MCQskirabankai5No ratings yet
- Organic Sub-Part 1Document16 pagesOrganic Sub-Part 1ahsaanahmadNo ratings yet
- 12th Chemistry CH-2MCQsDocument3 pages12th Chemistry CH-2MCQsadilahmedfreelance213No ratings yet
- Aldehydes Ketones and Carboxylic Acids YuvabrigadeDocument4 pagesAldehydes Ketones and Carboxylic Acids YuvabrigadeRavishankar H SNo ratings yet
- C11 - ALCOHOLS PHENOLS & ETHERS (1) .9c6f83eDocument4 pagesC11 - ALCOHOLS PHENOLS & ETHERS (1) .9c6f83eakashkishore363No ratings yet
- Unit 11 - Alcohols, Phenols & Ethers - MCQDocument5 pagesUnit 11 - Alcohols, Phenols & Ethers - MCQalisha iqbalNo ratings yet
- CH-12 - MCQS Ald, Ket & Car - AcidsDocument3 pagesCH-12 - MCQS Ald, Ket & Car - AcidsPranav ShankarNo ratings yet
- Nsec 1999Document12 pagesNsec 1999CorneliaNo ratings yet
- PRE BOARD Class XII 21-22Document6 pagesPRE BOARD Class XII 21-22Kavin SatyaNo ratings yet
- Organic SolveDocument6 pagesOrganic SolveKR KhanNo ratings yet
- KCet Chapter QuestionsDocument6 pagesKCet Chapter Questionslakashl14No ratings yet
- C10 - HALOALKANES & HALOARENES (1) .9bd6790Document4 pagesC10 - HALOALKANES & HALOARENES (1) .9bd6790akashkishore363No ratings yet
- XII CHEM CHAP 10 CHEMISTRY OF LIFEDocument4 pagesXII CHEM CHAP 10 CHEMISTRY OF LIFEShahzadNo ratings yet
- 19-100+ Everyday Science Solved Mcqs PDFDocument14 pages19-100+ Everyday Science Solved Mcqs PDFShahzadNo ratings yet
- Everyday Science MCQs For NTS FPSCDocument13 pagesEveryday Science MCQs For NTS FPSCShahzadNo ratings yet
- Unit No 4Document20 pagesUnit No 4ShahzadNo ratings yet
- Unit 06Document35 pagesUnit 06ShahzadNo ratings yet
- Trends & IssuesDocument32 pagesTrends & IssuesShahzadNo ratings yet
- Joule Thomson Effect: Paper: Physical Chemistry (UNIT-I Thermodynamics)Document10 pagesJoule Thomson Effect: Paper: Physical Chemistry (UNIT-I Thermodynamics)Shahzad100% (1)
- C13 NMRDocument11 pagesC13 NMRShahzadNo ratings yet
- Chapter 24 - ChemoselectivityDocument8 pagesChapter 24 - ChemoselectivityShahzadNo ratings yet
- 20: Carbohydrates: PreviewDocument20 pages20: Carbohydrates: PreviewShahzadNo ratings yet
- Periodic Table of The Elements: Be B C LiDocument1 pagePeriodic Table of The Elements: Be B C LiShahzadNo ratings yet
- NMR BasicsDocument25 pagesNMR BasicsShahzadNo ratings yet
- Assignment:-Advance Organic Chemistry (B-2) Paper: - B-2 (1st/a-2014) Name:-Muhammad Shahzad Ayyaz Roll No:-16 Submitted To: - Dr. Saifullah JamiDocument6 pagesAssignment:-Advance Organic Chemistry (B-2) Paper: - B-2 (1st/a-2014) Name:-Muhammad Shahzad Ayyaz Roll No:-16 Submitted To: - Dr. Saifullah JamiShahzadNo ratings yet
- PPSC Lecture Chemisty Past PaperDocument5 pagesPPSC Lecture Chemisty Past PaperShahzadNo ratings yet
- Short Quwestions of Macro MoleculesDocument9 pagesShort Quwestions of Macro MoleculesShahzadNo ratings yet
- 2nd Year Chem (Dec. Test)Document3 pages2nd Year Chem (Dec. Test)ShahzadNo ratings yet
- Bio Data FormDocument1 pageBio Data FormShahzadNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding HandoutDocument6 pagesChemical Bonding HandoutApril Ann Encinas CanlasNo ratings yet
- Halogen Derivatives SheetDocument6 pagesHalogen Derivatives SheetRajeev GangwarNo ratings yet
- Acid and BasesDocument15 pagesAcid and Basesharssh adhhiyaNo ratings yet
- Plasticizer 130414225921 Phpapp02Document22 pagesPlasticizer 130414225921 Phpapp02sonchemenNo ratings yet
- NeomycinDocument7 pagesNeomycinPapaindoNo ratings yet
- Soal B. Ing Wajib Xi GenapDocument32 pagesSoal B. Ing Wajib Xi Genaphamami0% (1)
- Moradi 2011 EdDocument16 pagesMoradi 2011 EdhunNo ratings yet
- 0620 Y16 SM 6 PDFDocument4 pages0620 Y16 SM 6 PDFsookchinNo ratings yet
- Infinity For Cement Equipment: Quality & Composition of Cement ClinkerDocument48 pagesInfinity For Cement Equipment: Quality & Composition of Cement ClinkerYhaneNo ratings yet
- 6 CNE Coupling Reactions 2019-20 PDFDocument39 pages6 CNE Coupling Reactions 2019-20 PDFChisom AdaobiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 16 Macro Etching ExaminationDocument10 pagesChapter 16 Macro Etching ExaminationBARCELON, CHRISTOPHER JAMES100% (1)
- Sulphate AttackDocument9 pagesSulphate AttackDevinder ChawlaNo ratings yet
- Synthesis of Ruthenium Nitrosyl Complexes of Bipyridine and Phenanthroline.Document4 pagesSynthesis of Ruthenium Nitrosyl Complexes of Bipyridine and Phenanthroline.Benjamín Marc Ridgway de SassouNo ratings yet
- BELSIL 6502 - EN - CardsDocument28 pagesBELSIL 6502 - EN - Cardsquimico10012812No ratings yet
- Chemical Equilibria of Aqueous Solutions: Che 401: Analytical ChemistryDocument31 pagesChemical Equilibria of Aqueous Solutions: Che 401: Analytical ChemistryScrappy WellNo ratings yet
- LAB 3-Concentration-CHM01alDocument5 pagesLAB 3-Concentration-CHM01alNova Jane EdradNo ratings yet
- Cape Chemistry Unit II Worksheet 2Document3 pagesCape Chemistry Unit II Worksheet 2Helpful HandNo ratings yet
- Pamphlet 89 - Chlorine Scrubbing Systems PDFDocument36 pagesPamphlet 89 - Chlorine Scrubbing Systems PDFJacques BlueqNo ratings yet
- Zinc GluconateDocument2 pagesZinc GluconateAlexi Del Castillo MustaineNo ratings yet
- Et Iso 18609 2012Document13 pagesEt Iso 18609 2012JyShe_laNo ratings yet
- Baxenden Trixene ASF TDSDocument2 pagesBaxenden Trixene ASF TDSmanojNo ratings yet
- 0620 s03 Ms 1+2+3+5+6 PDFDocument18 pages0620 s03 Ms 1+2+3+5+6 PDFSumaira AliNo ratings yet
- Improved Etherification Procedure For The Preparation of Dibenz (B, F) (1,4) OxazepineDocument3 pagesImproved Etherification Procedure For The Preparation of Dibenz (B, F) (1,4) Oxazepineebi1364No ratings yet
- Coordination Compounds 12thDocument34 pagesCoordination Compounds 12thShahidNo ratings yet
- 4.4, 4.5 Exam Questions MsDocument9 pages4.4, 4.5 Exam Questions MsswanderfeildNo ratings yet
- Risk Assessment of ChemicalsDocument3 pagesRisk Assessment of ChemicalsKingsley WongNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Viva QuestionsDocument3 pagesChemistry Viva QuestionsAnonymous vNiXkNxf8No ratings yet
- BondingDocument45 pagesBondingRalph Rezin MooreNo ratings yet
Unit 12 hydrocarbon
Unit 12 hydrocarbon
Uploaded by
Shahzad0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views6 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views6 pagesUnit 12 hydrocarbon
Unit 12 hydrocarbon
Uploaded by
ShahzadCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 6
10th chemistry
Unit # 12 Hydrocarbon
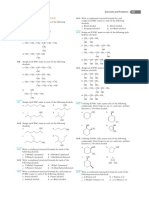
1) Alkane in the form of ring is called
a) Cycloalkane
b) Cycloalkyne
c) Cycloalkene
d) None
2) General formula of Cycloalkane is
a) CnH2n
b) CnH2n-2
c) CnH2n+2
d) None
3) Old name of alkane is
a) Olefins
b) Paraffin
c) Oleum
d) None
4) The catalyst used for the hydrogenation of alkene is
a) Co
b) Fe2O3
c) Ni
d) ZnCl2
5) Temperature range for the hydrogenation of alkene is
a) 250-300 C
b) 150-450 C
c) 20-200 C
d) None
6) Alkyl halide is reduced by
a) H2
b) [H]
c) CO+H2
d) ZnCl2
7) Which reaction is conducted by the presence of zinc dust and hydrochloric acid?
a) Hydrogenation of alkene
b) Combustion of alkane
c) Reduction of Alkyl halide
d) None
8) Ethane is ......... in water
a) Partially soluble
b) Soluble
c) Insoluble
d) None
9) Pentane is
a) Colourless gas
b) Colourless liquid
c) Black solid
d) Yellowish green gas
10) Melting point and boiling point of alkane ........... with increase in molecular mass
a) Increase
b) Decrease
c) Remains same
d) Irregular pattern
11) Hexane is less viscous than
a) Pentane
b) Butane
c) Decane
d) Propane
12) Density of octane is greater than
a) Methane
b) Nonane
c) Decane
d) Undecane
13) Halogenation is ......... reaction
a) Addition
b) Substitution
c) Elimination
d) Reduction
14) Condition for Halogenation reaction is
a) UV light
b) Zn/HCl
c) Ni, pt
d) Ether solvent
15) Reactants of Halogenation reaction are
a) Alkane + chlorine
b) Alkyl halide + hydrochloric acid
c) Alkane only
d) Chlorine only
16) Molecular formula of Butene is
a) C4H10
b) C4H8
c) C4H6
d) C4H9
17) Alkene is .......... Hydrocarbons
a) Saturated
b) Unsaturated
c) Single bonded compounds
d) Triple bonded compounds
18) Propene is
a) Colourless gas
b) Colourless liquid
c) Dark solid
d) None
19) Product of dehydration of alcohol are
a) Alkene + water
b) Alkane + water
c) Alkyne + water
d) Aldehyde + Methanol
20) For the dehydration of alcohol ........ catalyst is used
a) Nitric acid
b) Sulphuric acid
c) Accetic acid
d) Carbolic acid
21) Dehydrohalogenation means removal of
a) Hydrogen
b) Halogen
c) Hydrogen and halogen
d) Halogen and halogen
22) Condition for dehydrohalogenation of Alkyl halide are
a) Sulphuric acid
b) Hot alcoholic KOH
c) CCl4
d) Ni/Pt
23) Dehydrohalogenation is ........ reaction
a) Addition
b) Substitution
c) Elimination
d) Reduction
24) Melting point of octene is greater than
a) Pentene
b) Nonene
c) Decene
d) Undecene
25) Most common reactions of alkene are
a) Addition
b) Substitution
c) Elimination
d) Oxidation
26) Halogenation is ........ reaction
a) Addition
b) Substitution
c) Elimination
d) Oxidation
27) Halogenation is done in the presence of
a) Sulphuric acid
b) Hot alcoholic KOH
c) CCl4
d) Ni/Pt
28) Decolourizing of bromine is a test for the presence of
a) Single bond
b) Double bond
c) Alcohol
d) Acid group
29) Hydrohalogenation is
a) Addition
b) Substitution
c) Elimination
d) Oxidation
30) Order of reactivity of Hydrogen halide is
a) HF>HCl>HBr>HI
b) HI>HBr>HCl>HF
c) HCl>HBr>HI>HF
d) None
31) Hydrogenation is
a) Addition
b) Substitution
c) Elimination
d) Oxidation
32) Hydrogenation is ......... process
a) Endothermic
b) Exothermic
c) Both a and b
d) None
33) Process of conversion of vegetable oil into ghee is called
a) Oxidation
b) Hydrogenation
c) Dehydrohalogenation
d) Dehydratio
34) When alkene is oxidised by potassium permanganate the major product is
a) Alkane
b) Alkyne
c) Alcohol
d) Ethylene glycol
35) Baeyer’s test is used for the detection of
a) Single bond
b) Double bond
c) Alcohol
d) Acid group
36) Baeyer’s test is done in ........ medium
a) Acidic
b) Basic
c) Neutral
d) None
37) Glycerol are alcohols with two .......... on adjacent carbons
a) OH
b) H
c) Br
d) N
38) Ethene is a plant hormone that triggers
a) Growth of root
b) Growth of shoot
c) Production of gum
d) Ripening of fruit
39) Alkyne are Unsaturated compounds with
a) Single bonds
b) Double bond
c) Triple bond
d) None
40) General formula of alkyne is
a) CnH2n
b) CnH2n-2
c) CnH2n+2
d) CnH2n-4
41) ........ gas is used for cutting and welding purposes
a) Methane
b) Ethane
c) Ethene
d) Ethyne
42) Other name for propyne is
a) Dimethyl acetylene
b) Methyl acetylene
c) Ethyl acetylene
d) None
43) Alkyne are mainly prepared by
a) Addition
b) Substitution
c) Elimination
d) Oxidation
44) Vicinal di halide is
a) Alkane
b) Alkene
c) Alkyl halide
d) Aldehyde
45) Dehalogenation of vicinal dihalide is done in the presence of
a) Sulphuric acid
b) Hot alcoholic KOH
c) CCl4
d) Ni/Pt
46) Halogenation is done in the presence of
a) Sulphuric acid
b) Hot alcoholic KOH
c) PCl3
d) Ni/Pt
47) Oxidation of acetylene in the presence of potassium permanganate gives
a) Oxalic acid
b) Ethylene glycol
c) Vic-dibromo Ethane
d) Accetic acid
You might also like
- Science Group 9424713991Document48 pagesScience Group 9424713991Shahzad50% (2)
- 11.1.26 AOAC of Fi Cial Method 974.27 Cad Mium, Chro Mium, Cop Per, Iron, Lead, Mag Ne Sium, Man Ga Nese, Sil Ver, and Zinc in Wa TerDocument2 pages11.1.26 AOAC of Fi Cial Method 974.27 Cad Mium, Chro Mium, Cop Per, Iron, Lead, Mag Ne Sium, Man Ga Nese, Sil Ver, and Zinc in Wa Termttla100% (1)
- Taller 1Document2 pagesTaller 1Andres ArmeroNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Ch7,8 Part IIDocument4 pagesChemistry Ch7,8 Part IIdania.siddiqui195No ratings yet
- XII CH#09 P.S#01 HareshDocument3 pagesXII CH#09 P.S#01 Hareshpapukhan67zkqNo ratings yet
- Alcohols, Phenols and EthersDocument2 pagesAlcohols, Phenols and EthersDr. Vijay Kumar SahNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry Questions2023Document11 pagesOrganic Chemistry Questions2023xqfs2cd44sNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Test # 8Document4 pagesChemistry Test # 8dania.siddiqui195No ratings yet
- Chemistry Ch11,12 Part IIDocument4 pagesChemistry Ch11,12 Part IIAbdul RehmanNo ratings yet
- 12 MCQDocument2 pages12 MCQSheraz ShahNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Ch9,10 Part IIDocument4 pagesChemistry Ch9,10 Part IIdania.siddiqui195No ratings yet
- Aldehydes, Ketons and Carboxylic Acid Unit 11 MCQDocument4 pagesAldehydes, Ketons and Carboxylic Acid Unit 11 MCQAbhinav TripathiNo ratings yet
- C12 - ALDEHYDES KETONES AND CARBOXYLIC ACIDS (1) .9cfd4beDocument4 pagesC12 - ALDEHYDES KETONES AND CARBOXYLIC ACIDS (1) .9cfd4beakashkishore363No ratings yet
- unit 11 organic chemistryDocument5 pagesunit 11 organic chemistryShahzadNo ratings yet
- Learnvel Recuritment Test Chemistry - PGTDocument8 pagesLearnvel Recuritment Test Chemistry - PGTUma KumaranNo ratings yet
- Tick The Correct Option.: Chemistry Entry Test MCAT By: Sagheer Ahmad Gudara M.Phill ChemistryDocument4 pagesTick The Correct Option.: Chemistry Entry Test MCAT By: Sagheer Ahmad Gudara M.Phill ChemistrykamranNo ratings yet
- Dicc Xii Chem 400 McqsDocument18 pagesDicc Xii Chem 400 Mcqsadilahmedfreelance213No ratings yet
- Unit 11 MCQDocument7 pagesUnit 11 MCQJay VermaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry-FUNGAT/ECAT: (Chapter 10+11+12 B-II)Document2 pagesChemistry-FUNGAT/ECAT: (Chapter 10+11+12 B-II)XXXNo ratings yet
- AldehydesDocument22 pagesAldehydesjksiddharth24No ratings yet
- Question BankDocument133 pagesQuestion BankBabar AliNo ratings yet
- SIET CHEM Mock 2 PDFDocument7 pagesSIET CHEM Mock 2 PDFVikashNo ratings yet
- CH# 11 XII (Chem 12 Exam Task)Document4 pagesCH# 11 XII (Chem 12 Exam Task)Zeeshan Haider ChemistNo ratings yet
- Kcet Mock Test Chemistry 1Document8 pagesKcet Mock Test Chemistry 1VikashNo ratings yet
- Benzene and Alkyl Halides PDFDocument4 pagesBenzene and Alkyl Halides PDFakshaydewat786No ratings yet
- 1000 Mcqs ChemistryDocument113 pages1000 Mcqs ChemistryMariam IshtiaqNo ratings yet
- AlcoholDocument11 pagesAlcoholmkhanmughal4No ratings yet
- CH 4Document11 pagesCH 4ojha.ramNo ratings yet
- Chem Test No. 4 (Alkyl Halides, Alcohol and Phenols)Document4 pagesChem Test No. 4 (Alkyl Halides, Alcohol and Phenols)fahadmustafa100% (1)
- ECAT II Key DecDocument4 pagesECAT II Key DecSamia SajidNo ratings yet
- ECAT II Q.P DecDocument4 pagesECAT II Q.P DecSamia SajidNo ratings yet
- Alkyl HalideDocument8 pagesAlkyl HalideMegh Raj BhattNo ratings yet
- 12.Mcq - Aldehydes Ketones Carboxylic AcidsDocument23 pages12.Mcq - Aldehydes Ketones Carboxylic AcidsBedosi Bidita PandaNo ratings yet
- CC 13Document6 pagesCC 13Deepak SethyNo ratings yet
- 12th Chemistry CH-15MCQsDocument4 pages12th Chemistry CH-15MCQsRana DugNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Xii NAME: - : Alcohol, Phenol & EtherDocument1 pageChemistry Xii NAME: - : Alcohol, Phenol & EtherSahir Hemnani100% (1)
- Halogen Derivetives of Alkane MCQDocument11 pagesHalogen Derivetives of Alkane MCQParshantKumarBajaj93% (14)
- PPSC Lecture Chemisty Past PaperDocument5 pagesPPSC Lecture Chemisty Past PaperShahzadNo ratings yet
- Answer Key Assignment No. 6 Carboxylic Acid and DerivativesDocument5 pagesAnswer Key Assignment No. 6 Carboxylic Acid and DerivativesREGINE CUEVASNo ratings yet
- Haloalkanes and Haloarenes PDFDocument3 pagesHaloalkanes and Haloarenes PDFarya sonarNo ratings yet
- 12TH CBSE DPP 37. Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids MCQ ASSERTION REASON CS QDocument20 pages12TH CBSE DPP 37. Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids MCQ ASSERTION REASON CS Q123No ratings yet
- Haloalkanes and Haloarenes Q 5Document3 pagesHaloalkanes and Haloarenes Q 5jayjena007No ratings yet
- Alcohol Phenol and EtherDocument5 pagesAlcohol Phenol and EtherManthan JhaNo ratings yet
- Sample Question Paper 2021-22 Term 1 Subject: ChemistryDocument16 pagesSample Question Paper 2021-22 Term 1 Subject: Chemistrysarthak MongaNo ratings yet
- Sample Question Paper 2021-22 Term 1 Subject: ChemistryDocument10 pagesSample Question Paper 2021-22 Term 1 Subject: ChemistryNishi Kant MishraNo ratings yet
- (Xii) Alcohol, Phenol, EtherDocument10 pages(Xii) Alcohol, Phenol, EtherAbhishek SharmaNo ratings yet
- Lecturer Chemistry Mcqs PSC Past PaperDocument28 pagesLecturer Chemistry Mcqs PSC Past PaperNauman Khalid0% (1)
- Alcohols TestDocument2 pagesAlcohols TestAboahmed AliNo ratings yet
- 12th Chemistry CH-3MCQsDocument4 pages12th Chemistry CH-3MCQskirabankai5No ratings yet
- Organic Sub-Part 1Document16 pagesOrganic Sub-Part 1ahsaanahmadNo ratings yet
- 12th Chemistry CH-2MCQsDocument3 pages12th Chemistry CH-2MCQsadilahmedfreelance213No ratings yet
- Aldehydes Ketones and Carboxylic Acids YuvabrigadeDocument4 pagesAldehydes Ketones and Carboxylic Acids YuvabrigadeRavishankar H SNo ratings yet
- C11 - ALCOHOLS PHENOLS & ETHERS (1) .9c6f83eDocument4 pagesC11 - ALCOHOLS PHENOLS & ETHERS (1) .9c6f83eakashkishore363No ratings yet
- Unit 11 - Alcohols, Phenols & Ethers - MCQDocument5 pagesUnit 11 - Alcohols, Phenols & Ethers - MCQalisha iqbalNo ratings yet
- CH-12 - MCQS Ald, Ket & Car - AcidsDocument3 pagesCH-12 - MCQS Ald, Ket & Car - AcidsPranav ShankarNo ratings yet
- Nsec 1999Document12 pagesNsec 1999CorneliaNo ratings yet
- PRE BOARD Class XII 21-22Document6 pagesPRE BOARD Class XII 21-22Kavin SatyaNo ratings yet
- Organic SolveDocument6 pagesOrganic SolveKR KhanNo ratings yet
- KCet Chapter QuestionsDocument6 pagesKCet Chapter Questionslakashl14No ratings yet
- C10 - HALOALKANES & HALOARENES (1) .9bd6790Document4 pagesC10 - HALOALKANES & HALOARENES (1) .9bd6790akashkishore363No ratings yet
- XII CHEM CHAP 10 CHEMISTRY OF LIFEDocument4 pagesXII CHEM CHAP 10 CHEMISTRY OF LIFEShahzadNo ratings yet
- 19-100+ Everyday Science Solved Mcqs PDFDocument14 pages19-100+ Everyday Science Solved Mcqs PDFShahzadNo ratings yet
- Everyday Science MCQs For NTS FPSCDocument13 pagesEveryday Science MCQs For NTS FPSCShahzadNo ratings yet
- Unit No 4Document20 pagesUnit No 4ShahzadNo ratings yet
- Unit 06Document35 pagesUnit 06ShahzadNo ratings yet
- Trends & IssuesDocument32 pagesTrends & IssuesShahzadNo ratings yet
- Joule Thomson Effect: Paper: Physical Chemistry (UNIT-I Thermodynamics)Document10 pagesJoule Thomson Effect: Paper: Physical Chemistry (UNIT-I Thermodynamics)Shahzad100% (1)
- C13 NMRDocument11 pagesC13 NMRShahzadNo ratings yet
- Chapter 24 - ChemoselectivityDocument8 pagesChapter 24 - ChemoselectivityShahzadNo ratings yet
- 20: Carbohydrates: PreviewDocument20 pages20: Carbohydrates: PreviewShahzadNo ratings yet
- Periodic Table of The Elements: Be B C LiDocument1 pagePeriodic Table of The Elements: Be B C LiShahzadNo ratings yet
- NMR BasicsDocument25 pagesNMR BasicsShahzadNo ratings yet
- Assignment:-Advance Organic Chemistry (B-2) Paper: - B-2 (1st/a-2014) Name:-Muhammad Shahzad Ayyaz Roll No:-16 Submitted To: - Dr. Saifullah JamiDocument6 pagesAssignment:-Advance Organic Chemistry (B-2) Paper: - B-2 (1st/a-2014) Name:-Muhammad Shahzad Ayyaz Roll No:-16 Submitted To: - Dr. Saifullah JamiShahzadNo ratings yet
- PPSC Lecture Chemisty Past PaperDocument5 pagesPPSC Lecture Chemisty Past PaperShahzadNo ratings yet
- Short Quwestions of Macro MoleculesDocument9 pagesShort Quwestions of Macro MoleculesShahzadNo ratings yet
- 2nd Year Chem (Dec. Test)Document3 pages2nd Year Chem (Dec. Test)ShahzadNo ratings yet
- Bio Data FormDocument1 pageBio Data FormShahzadNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding HandoutDocument6 pagesChemical Bonding HandoutApril Ann Encinas CanlasNo ratings yet
- Halogen Derivatives SheetDocument6 pagesHalogen Derivatives SheetRajeev GangwarNo ratings yet
- Acid and BasesDocument15 pagesAcid and Basesharssh adhhiyaNo ratings yet
- Plasticizer 130414225921 Phpapp02Document22 pagesPlasticizer 130414225921 Phpapp02sonchemenNo ratings yet
- NeomycinDocument7 pagesNeomycinPapaindoNo ratings yet
- Soal B. Ing Wajib Xi GenapDocument32 pagesSoal B. Ing Wajib Xi Genaphamami0% (1)
- Moradi 2011 EdDocument16 pagesMoradi 2011 EdhunNo ratings yet
- 0620 Y16 SM 6 PDFDocument4 pages0620 Y16 SM 6 PDFsookchinNo ratings yet
- Infinity For Cement Equipment: Quality & Composition of Cement ClinkerDocument48 pagesInfinity For Cement Equipment: Quality & Composition of Cement ClinkerYhaneNo ratings yet
- 6 CNE Coupling Reactions 2019-20 PDFDocument39 pages6 CNE Coupling Reactions 2019-20 PDFChisom AdaobiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 16 Macro Etching ExaminationDocument10 pagesChapter 16 Macro Etching ExaminationBARCELON, CHRISTOPHER JAMES100% (1)
- Sulphate AttackDocument9 pagesSulphate AttackDevinder ChawlaNo ratings yet
- Synthesis of Ruthenium Nitrosyl Complexes of Bipyridine and Phenanthroline.Document4 pagesSynthesis of Ruthenium Nitrosyl Complexes of Bipyridine and Phenanthroline.Benjamín Marc Ridgway de SassouNo ratings yet
- BELSIL 6502 - EN - CardsDocument28 pagesBELSIL 6502 - EN - Cardsquimico10012812No ratings yet
- Chemical Equilibria of Aqueous Solutions: Che 401: Analytical ChemistryDocument31 pagesChemical Equilibria of Aqueous Solutions: Che 401: Analytical ChemistryScrappy WellNo ratings yet
- LAB 3-Concentration-CHM01alDocument5 pagesLAB 3-Concentration-CHM01alNova Jane EdradNo ratings yet
- Cape Chemistry Unit II Worksheet 2Document3 pagesCape Chemistry Unit II Worksheet 2Helpful HandNo ratings yet
- Pamphlet 89 - Chlorine Scrubbing Systems PDFDocument36 pagesPamphlet 89 - Chlorine Scrubbing Systems PDFJacques BlueqNo ratings yet
- Zinc GluconateDocument2 pagesZinc GluconateAlexi Del Castillo MustaineNo ratings yet
- Et Iso 18609 2012Document13 pagesEt Iso 18609 2012JyShe_laNo ratings yet
- Baxenden Trixene ASF TDSDocument2 pagesBaxenden Trixene ASF TDSmanojNo ratings yet
- 0620 s03 Ms 1+2+3+5+6 PDFDocument18 pages0620 s03 Ms 1+2+3+5+6 PDFSumaira AliNo ratings yet
- Improved Etherification Procedure For The Preparation of Dibenz (B, F) (1,4) OxazepineDocument3 pagesImproved Etherification Procedure For The Preparation of Dibenz (B, F) (1,4) Oxazepineebi1364No ratings yet
- Coordination Compounds 12thDocument34 pagesCoordination Compounds 12thShahidNo ratings yet
- 4.4, 4.5 Exam Questions MsDocument9 pages4.4, 4.5 Exam Questions MsswanderfeildNo ratings yet
- Risk Assessment of ChemicalsDocument3 pagesRisk Assessment of ChemicalsKingsley WongNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Viva QuestionsDocument3 pagesChemistry Viva QuestionsAnonymous vNiXkNxf8No ratings yet
- BondingDocument45 pagesBondingRalph Rezin MooreNo ratings yet