Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Untitled Document - Google Docs
Untitled Document - Google Docs
Uploaded by
agastyarajchauhanCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Untitled Document - Google Docs
Untitled Document - Google Docs
Uploaded by
agastyarajchauhanCopyright:
Available Formats
Brain
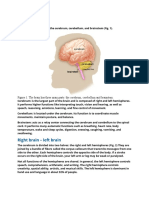
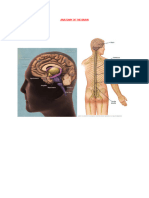
The brain is composed of the cerebrum, cerebellum, and brainstem (Fig. 1).
Figure 1. The brain has three main parts: the cerebrum, cerebellum and brainstem.
Cerebrum: is the largest part of the brain and is composed of right and left hemispheres.
It performs higher functions like interpreting touch, vision and hearing, as well as
speech, reasoning, emotions, learning, and fine control of movement.
Cerebellum: is located under the cerebrum. Its function is to coordinate muscle
movements, maintain posture, and balance.
Brainstem: acts as a relay center connecting the cerebrum and cerebellum to the spinal
cord. It performs many automatic functions such as breathing, heart rate, body
temperature, wake and sleep cycles, digestion, sneezing, coughing, vomiting, and
swallowing.
Right brain – left brain
The cerebrum is divided into two halves: the right and left hemispheres (Fig. 2) They are
joined by a bundle of fibers called the corpus callosum that transmits messages from
one side to the other. Each hemisphere controls the opposite side of the body. If a
stroke occurs on the right side of the brain, your left arm or leg may be weak or
paralyzed.
Not all functions of the hemispheres are shared. In general, the left hemisphere controls
speech, comprehension, arithmetic, and writing. The right hemisphere controls
creativity, spatial ability, artistic, and musical skills. The left hemisphere is dominant in
hand use and language in about 92% of people.
igure 2. The cerebrum is divided into left and right hemispheres. The two sides are
F
connected by the nerve fibers corpus callosum.
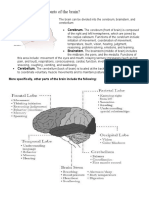
Lobes of the brain
The cerebral hemispheres have distinct fissures, which divide the brain into lobes. Each
hemisphere has 4 lobes: frontal, temporal, parietal, and occipital (Fig. 3). Each lobe may
be divided, once again, into areas that serve very specific functions. It’s important to
understand that each lobe of the brain does not function alone. There are very complex
relationships between the lobes of the brain and between the right and left
hemispheres.
Figure 3. The cerebrum is divided into four lobes: frontal, parietal, occipital and
temporal.
Frontal lobe
● Personality, behavior, emotions
● Judgment, planning, problem solving
● Speech: speaking and writing (Broca’s area)
● Body movement (motor strip)
● Intelligence, concentration, self awareness
Parietal lobe
● Interprets language, words
You might also like
- Muhammad Ali Roll No 53Document18 pagesMuhammad Ali Roll No 53Abu GNo ratings yet
- Neuroanatomy (Reading Topic 1)Document6 pagesNeuroanatomy (Reading Topic 1)Fernanda LópezNo ratings yet
- Brain Anatomy, Anatomy of The Human BrainDocument12 pagesBrain Anatomy, Anatomy of The Human BrainElmir ƏzimovNo ratings yet
- Brain: Figure 1. The Brain Has Three Main Parts: The Cerebrum, Cerebellum and BrainstemDocument7 pagesBrain: Figure 1. The Brain Has Three Main Parts: The Cerebrum, Cerebellum and BrainstemsukhleenNo ratings yet
- Introduction To NeuropsychologyDocument15 pagesIntroduction To NeuropsychologyPsychology Department Ilahia Arts CollegeNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of The Brain and FunctionsDocument4 pagesAnatomy of The Brain and FunctionsGopinadh GanjiNo ratings yet
- The Human BrainDocument9 pagesThe Human BrainelenibacousiNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of The BrainDocument9 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of The BrainAbdelmar SusulanNo ratings yet
- โท the BrainDocument39 pagesโท the BrainFadil Wanna-mart100% (1)
- Biology Notes 2Document5 pagesBiology Notes 2Vanessa SantosNo ratings yet
- Brain Anatomy, Anatomy of The Human Brain - Mayfield Brain & Spine Cincinnati, Ohio 2 PDFDocument20 pagesBrain Anatomy, Anatomy of The Human Brain - Mayfield Brain & Spine Cincinnati, Ohio 2 PDFRitika Kishore100% (1)
- 0301a AllDocument3 pages0301a AllWiendha LiendriasariNo ratings yet
- Parts of The Brain Anatomy Structure Amp FunctionsDocument23 pagesParts of The Brain Anatomy Structure Amp FunctionsWasana FernandoNo ratings yet
- What's The Control Center of Your Body?Document3 pagesWhat's The Control Center of Your Body?caoimhin54No ratings yet
- PDF 2Document1 pagePDF 2Nassim HamadehNo ratings yet
- About BrainDocument4 pagesAbout Brainanand sahuNo ratings yet
- Lateralization. Language Functions, For Instance, Are More Concentrated in The Left Hemisphere in MostDocument2 pagesLateralization. Language Functions, For Instance, Are More Concentrated in The Left Hemisphere in MostVinvieleen Francesca TalaveraNo ratings yet
- Science ReportDocument3 pagesScience ReportAna Miadel Mojica MartalNo ratings yet
- General Psychology-Module 8Document3 pagesGeneral Psychology-Module 8Ralph Kevin CorboNo ratings yet
- The BrainDocument50 pagesThe BrainJana khatibNo ratings yet
- Trixie - Anatomy and Physiology (Brain Tumor)Document4 pagesTrixie - Anatomy and Physiology (Brain Tumor)Trixie Marie Sabile AbdullaNo ratings yet
- Case Study: Yoga Teachers TrainingDocument17 pagesCase Study: Yoga Teachers TrainingKaran PatelNo ratings yet
- Why The Brain Like Some Word Fonts More Than OthersDocument17 pagesWhy The Brain Like Some Word Fonts More Than OthersameliaNo ratings yet
- What Are The Different Parts of The Brain?: CerebrumDocument4 pagesWhat Are The Different Parts of The Brain?: CerebrumDhez Bertudaso-Morales ManansalaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of Human BrainDocument2 pagesAnatomy of Human BrainIan Rhadel RaganasNo ratings yet
- OUR BODY Chapter - I (Science Class IV)Document4 pagesOUR BODY Chapter - I (Science Class IV)doultaniskNo ratings yet
- t2 S 1398 Ks2 Parts of The Brain Powerpoint Ver 4Document14 pagest2 S 1398 Ks2 Parts of The Brain Powerpoint Ver 4fandomstwentyoneNo ratings yet
- What Comprises A Brain?Document2 pagesWhat Comprises A Brain?NataliaLizcanoNo ratings yet
- Health Psychology - The BrainDocument3 pagesHealth Psychology - The BrainSaerah ParkNo ratings yet
- Human BrainDocument12 pagesHuman BrainJashwanthNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument4 pagesAnatomy and PhysiologyMaquirang Cris JaisonNo ratings yet
- How The Brain WorksDocument12 pagesHow The Brain WorksAbdullah B.No ratings yet
- Control and Coordination, PPT, Module-1.3Document22 pagesControl and Coordination, PPT, Module-1.3Khushi GuptaNo ratings yet
- Brain or Neural NetworkDocument37 pagesBrain or Neural NetworkAmirh AfunayNo ratings yet
- Nervous System NotesDocument5 pagesNervous System Notesveena3diwakarNo ratings yet
- The Frontal Lobe Is The MostDocument6 pagesThe Frontal Lobe Is The MostJingky MarzanPurisima Lumauig SallicopNo ratings yet
- Right Brain - Left Brain: Frontal LobeDocument6 pagesRight Brain - Left Brain: Frontal LobeI Gusti Ayu Agung YuliantiNo ratings yet
- BrainDocument35 pagesBrainRonaleen mislang100% (1)
- The Powers of The MindDocument2 pagesThe Powers of The MindErron Francisco NicolNo ratings yet
- Brain - Effects of Stroke: E-Mail Story Print StoryDocument4 pagesBrain - Effects of Stroke: E-Mail Story Print StoryAlexandru VeliciNo ratings yet
- Brain Basics - Know Your Brain - National Institute of Neurological Disorders and StrokeDocument4 pagesBrain Basics - Know Your Brain - National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Strokesurajit halderNo ratings yet
- NeuropsychologyDocument28 pagesNeuropsychologyFarhan AkhtarNo ratings yet
- 1.7 What Does The Brain DoDocument3 pages1.7 What Does The Brain DoStella StaryNo ratings yet
- Function of The BrainDocument16 pagesFunction of The BrainJohn Matthew CrisostomoNo ratings yet
- Sci 10 Week 3 Nervous SystemDocument17 pagesSci 10 Week 3 Nervous SystemNikkha elle Teleron100% (1)
- Personal Development Lesson 6Document30 pagesPersonal Development Lesson 6Nikka Irah CamaristaNo ratings yet
- Biological Bases of BehaviorDocument74 pagesBiological Bases of BehaviorKylie AnneNo ratings yet
- Anfis Sistem NeuroBehaviourDocument37 pagesAnfis Sistem NeuroBehaviourDediSunartoNo ratings yet
- The BrainDocument28 pagesThe BrainAnania EmmanuelNo ratings yet
- Structure of BrainDocument24 pagesStructure of Brainhajiwaheed0604No ratings yet
- BrainDocument11 pagesBrainShridhar malagi malagiNo ratings yet
- 3rd Week 9 BioDocument6 pages3rd Week 9 BioTaze UtoroNo ratings yet
- Anaphy PPT - Nervous SystemDocument36 pagesAnaphy PPT - Nervous SystemJamaica TuellaNo ratings yet
- 3B The Brain: Unit Questions: Mia Ramos Block-2Document2 pages3B The Brain: Unit Questions: Mia Ramos Block-2api-296059071No ratings yet
- Brain and StructuteDocument10 pagesBrain and Structutedhatreyi.g.gubbalaNo ratings yet
- Brain PP 5Document18 pagesBrain PP 5Ain lorraine BacaniNo ratings yet
- The Central Nervous SystemDocument24 pagesThe Central Nervous SystemBlanche Mascarinas LaborteNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of The Brain - GeeksforGeeksDocument11 pagesAnatomy of The Brain - GeeksforGeeksopheokani2000No ratings yet
- Brain: A Closer Look at YourDocument1 pageBrain: A Closer Look at YourJuan Carlos Solís RiveraNo ratings yet
- Super Brain: Strategies to Upgrade Your Brain, Unlock Your Potential, Perform at Your Peak, and Achieve AnythingFrom EverandSuper Brain: Strategies to Upgrade Your Brain, Unlock Your Potential, Perform at Your Peak, and Achieve AnythingNo ratings yet
- Astm A194Document11 pagesAstm A194Jarek CieslakNo ratings yet
- Curiculum Vitae JurnalisDocument1 pageCuriculum Vitae JurnalisEh Ada UjankNo ratings yet
- Month + Teaching Days Unit Total Teaching Periods: Vibgyor High Grade - 2 English Literature Year Plan (AY 2020 - 2021)Document65 pagesMonth + Teaching Days Unit Total Teaching Periods: Vibgyor High Grade - 2 English Literature Year Plan (AY 2020 - 2021)TAPASsenguptaNo ratings yet
- On Arushi Murder CaseDocument8 pagesOn Arushi Murder Case0000No ratings yet
- Listen To The Following Words Carefully and Write Them. (Any Three)Document9 pagesListen To The Following Words Carefully and Write Them. (Any Three)Anonymous wfZ9qDMNNo ratings yet
- Topic 4-Bv2Document77 pagesTopic 4-Bv2hooranghooraeNo ratings yet
- Os Past Papers' Solutions 2017Document4 pagesOs Past Papers' Solutions 2017zainab tehreemNo ratings yet
- Catalog Stationary Screw Compressors F en V 1 3 WebDocument28 pagesCatalog Stationary Screw Compressors F en V 1 3 WebcristiNo ratings yet
- 13.4.2 WBS 6.6 Cerberus Corperation Case Study Managing Stakeholder ConflictDocument7 pages13.4.2 WBS 6.6 Cerberus Corperation Case Study Managing Stakeholder ConflictJorge Alejandro Betancur JaramilloNo ratings yet
- Chechk List Fokker 50Document1 pageChechk List Fokker 50Felipe PinillaNo ratings yet
- Assignment Activity On Expenditure Cycles - To Be ContinuedDocument3 pagesAssignment Activity On Expenditure Cycles - To Be ContinuedRico, Jalaica B.No ratings yet
- Start With Why SummaryDocument6 pagesStart With Why SummaryAnurag100% (1)
- TPP Steel PlantDocument25 pagesTPP Steel PlantPRASANTHNo ratings yet
- Front Wheel Assy. DrumDocument2 pagesFront Wheel Assy. DrumSoroj BiswasNo ratings yet
- Barreramora Fernando Linear Algebra A Minimal Polynomial AppDocument313 pagesBarreramora Fernando Linear Algebra A Minimal Polynomial AppStrahinja DonicNo ratings yet
- 2127 - Mahatma Gandhi Missions College of Engineering, Hingoli RD, NandedDocument8 pages2127 - Mahatma Gandhi Missions College of Engineering, Hingoli RD, NandedAjit DeshmukhNo ratings yet
- Mathematics: Quarter 1 - Module 8: Division of Whole Numbers by Decimals Up To 2 Decimal PlacesDocument34 pagesMathematics: Quarter 1 - Module 8: Division of Whole Numbers by Decimals Up To 2 Decimal PlacesJohn Thomas Satimbre100% (1)
- Lab6 Phase Locked LoopsDocument20 pagesLab6 Phase Locked Loopsuitce2011No ratings yet
- SafeGrid Tutorial How To Perform A Simple Earthing DesignDocument10 pagesSafeGrid Tutorial How To Perform A Simple Earthing DesignAnwesh Kumar MaddikuntaNo ratings yet
- Renewable Energy Sources and MethodsDocument225 pagesRenewable Energy Sources and MethodsSemir Đedović100% (1)
- The Spirit of Jugaad / Bricolage For Enhanced Corporate EntrepreneurshipDocument20 pagesThe Spirit of Jugaad / Bricolage For Enhanced Corporate EntrepreneurshippanditpreachesNo ratings yet
- Job Posting Groups ListDocument3 pagesJob Posting Groups ListShrutika singhNo ratings yet
- Risk Assessment On Temperature and Relative Humidity Deviation During On-Going Stability StudiesDocument2 pagesRisk Assessment On Temperature and Relative Humidity Deviation During On-Going Stability StudiesAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAA ANo ratings yet
- Elements Cmpds Mix Ws-AnswersDocument2 pagesElements Cmpds Mix Ws-Answerseric sivaneshNo ratings yet
- Jeanette Novakovich Formal ResumeDocument4 pagesJeanette Novakovich Formal ResumeJ'etté NovakovichNo ratings yet
- TL Files Struktol Content Maerkte-Produkte Kautschuk-Additive en Technische-Merkblaetter 01032 WB16FLAKES GB TECHDocument2 pagesTL Files Struktol Content Maerkte-Produkte Kautschuk-Additive en Technische-Merkblaetter 01032 WB16FLAKES GB TECHJoban AroraNo ratings yet
- Quest Test 6 Wave Phenomena KEYDocument7 pagesQuest Test 6 Wave Phenomena KEYHa ViNo ratings yet
- Item Part No Location No - Available No. Used Remaining Min No. Required Reordered No Cost Per Item Total CostDocument1 pageItem Part No Location No - Available No. Used Remaining Min No. Required Reordered No Cost Per Item Total CostRockyNo ratings yet
- Worksheet in Deloittes System Design DocumentDocument32 pagesWorksheet in Deloittes System Design Documentascentcommerce100% (1)
- Lab ReportpdfDocument7 pagesLab ReportpdfStefano FochesattoNo ratings yet