Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Class X Light
Class X Light
Uploaded by
uncool.vedant2009Copyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Introduction - Macro SkillsDocument14 pagesIntroduction - Macro SkillsChermie Sarmiento77% (75)
- Agile One Pager PDFDocument2 pagesAgile One Pager PDFEgeruoh Chigoziri CyrinusNo ratings yet
- Human Resource DevelopmentDocument137 pagesHuman Resource Developmenturfriendkrupa100% (1)
- Problems On Ray Optics and Optical Instruments For NEETDocument19 pagesProblems On Ray Optics and Optical Instruments For NEETRohit Gupta100% (1)
- 644d431abb6c94001859ad6d ## Light Reflation and Refraction DPPs PDFDocument5 pages644d431abb6c94001859ad6d ## Light Reflation and Refraction DPPs PDFDINANATH SINGHNo ratings yet
- Light Work SheetDocument3 pagesLight Work Sheetphysicsbooks.storeNo ratings yet
- Optics QuestionsDocument2 pagesOptics QuestionsUnidentified PersonNo ratings yet
- 1822-12 Phy P15 Ray Optics B 30Q (1) - 1Document3 pages1822-12 Phy P15 Ray Optics B 30Q (1) - 1JeevanNo ratings yet
- Physics Light Daily Home Assignment 04 Udaan 3 0 1Document4 pagesPhysics Light Daily Home Assignment 04 Udaan 3 0 1HARSHIT GUPTANo ratings yet
- Acids, Bases and Salts Light-Reflection and Refraction: Multiple Choice Questions (MCQS)Document12 pagesAcids, Bases and Salts Light-Reflection and Refraction: Multiple Choice Questions (MCQS)Bhanu PurushothamaNo ratings yet
- Physics Class XIIDocument177 pagesPhysics Class XIIManavendra PratapNo ratings yet
- MCQ REFR AND REFLDocument11 pagesMCQ REFR AND REFLsheikharmaanusmaniNo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan 05-Nov-2021Document13 pagesAdobe Scan 05-Nov-2021SIDDHANT BHATTNo ratings yet
- CH - 01 - Light - Only PDFDocument12 pagesCH - 01 - Light - Only PDFrohitdodamanib352No ratings yet
- DPP3Document2 pagesDPP3TrtyiiijhhNo ratings yet
- Go (Jee Main Online)Document19 pagesGo (Jee Main Online)balvantgk.hemant123No ratings yet
- Revision Sheet 2 Light Reflection and RefractionDocument4 pagesRevision Sheet 2 Light Reflection and RefractionRiyansh WarikooNo ratings yet
- 03 Light (Reflection of Spherical Surfaces) Elevate 1Document5 pages03 Light (Reflection of Spherical Surfaces) Elevate 1akshitwalia209No ratings yet
- PHYSICS-test Electric Potential, Current Electricity-A, Ray Optics-A 1mark Questions: (ANSWER ALL)Document4 pagesPHYSICS-test Electric Potential, Current Electricity-A, Ray Optics-A 1mark Questions: (ANSWER ALL)shylaNo ratings yet
- Class 10 Test - 1 1693184362Document6 pagesClass 10 Test - 1 1693184362samsuzzaman sahinNo ratings yet
- Light-Reflection & Refraction - Practice Sheet - 10th Board Booster 2.0 2024Document5 pagesLight-Reflection & Refraction - Practice Sheet - 10th Board Booster 2.0 2024yashasvisharma sharmaNo ratings yet
- Light - Reflection & Refraction - Practice Sheet - WARRIOR SERIES CLASS-10THDocument5 pagesLight - Reflection & Refraction - Practice Sheet - WARRIOR SERIES CLASS-10THhiranyakshivNo ratings yet
- AssignmentDocument2 pagesAssignmentNeeraj PuniaNo ratings yet
- Fisica 3Document1 pageFisica 3Andres Felipe HigueraNo ratings yet
- Sainik School Goalpara: Extra Homework Subject: Science (Physics) Class: XDocument4 pagesSainik School Goalpara: Extra Homework Subject: Science (Physics) Class: XBornil Bikash BhuyanNo ratings yet
- Spherical Mirror-Vsq1.1-QuesDocument1 pageSpherical Mirror-Vsq1.1-QuesRonit RoyNo ratings yet
- Reflection & Refraction PDFDocument5 pagesReflection & Refraction PDFSushri Sangeeta MohantyNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 24 Ray Optics and Optical InstrumentsDocument37 pagesChapter - 24 Ray Optics and Optical Instrumentsagoel0844No ratings yet
- Ray Optics & Optical Instruments, Home Work Sheet-1: Plane Mirror 1Document60 pagesRay Optics & Optical Instruments, Home Work Sheet-1: Plane Mirror 1venkat krishnanNo ratings yet
- Ray Optics DC Pandey MCQ With Detailed SolutionDocument30 pagesRay Optics DC Pandey MCQ With Detailed Solutionvivek100% (1)
- Light Assign MentDocument32 pagesLight Assign MentAyush ChouhanNo ratings yet
- Physics DPPDocument19 pagesPhysics DPPasgurudevNo ratings yet
- Tips The TempestDocument8 pagesTips The TempestGopal Kumar VermaNo ratings yet
- Test Your KnowledgeDocument3 pagesTest Your KnowledgeSantosh Kumar MallickNo ratings yet
- General Instructions: Section (A) : (1 Marks)Document2 pagesGeneral Instructions: Section (A) : (1 Marks)exploreharyanaNo ratings yet
- Class X Science Multiple Choice Questions 1Document1 pageClass X Science Multiple Choice Questions 1rayi17198467% (12)
- CH Light AssignmentDocument6 pagesCH Light Assignmentaltxd1313No ratings yet
- Multiple Choice Questions Based On ExperimentDocument1 pageMultiple Choice Questions Based On ExperimentkapilNo ratings yet
- Reflection From Plane MirrorDocument4 pagesReflection From Plane Mirroryadavutpal1021No ratings yet
- 18 Geometrical OpticsDocument40 pages18 Geometrical OpticsSamsul BahriNo ratings yet
- Class 10 Test - 1 1693006894Document2 pagesClass 10 Test - 1 1693006894samsuzzaman sahinNo ratings yet
- 01 Ray Optics MMDocument71 pages01 Ray Optics MMmonikeshNo ratings yet
- G10 - Chapter Test 5 Ans - Ch.10 - 06 NOV 23Document10 pagesG10 - Chapter Test 5 Ans - Ch.10 - 06 NOV 23Urmila GNo ratings yet
- Ques Complete Ray OpticsDocument20 pagesQues Complete Ray OpticsAishani SaxenaNo ratings yet
- Light Revision Class 10Document34 pagesLight Revision Class 10karun.senthil.kumar.25No ratings yet
- LIGHTsDocument10 pagesLIGHTsjapneets764No ratings yet
- 2024-04-18-0.7264717555178133Document24 pages2024-04-18-0.7264717555178133Devansh DodaNo ratings yet
- X - Science - Physics - CH-9 Light - Assignment-1Document2 pagesX - Science - Physics - CH-9 Light - Assignment-1Shweta DuhanNo ratings yet
- 01 Ray Optics MMDocument71 pages01 Ray Optics MMMission NEET 2022No ratings yet
- 2nd Yr Phy-7CDocument48 pages2nd Yr Phy-7CRakshitha BSNo ratings yet
- Class X Science Multiple Choice Questions 1Document1 pageClass X Science Multiple Choice Questions 1Rohit GuptaNo ratings yet
- 10 - Light - Reflection and Refraction + The Colourful World - 15.sep.21 - 3 PMDocument2 pages10 - Light - Reflection and Refraction + The Colourful World - 15.sep.21 - 3 PMHarshNo ratings yet
- IIT FILEDocument3 pagesIIT FILEdhikiviyu666No ratings yet
- Light PDFDocument3 pagesLight PDFVasu GargNo ratings yet
- Assign IiDocument4 pagesAssign IiSangeeta ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- Ray Optics (Ques Bank)Document7 pagesRay Optics (Ques Bank)Om GoyalNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12Document16 pagesChapter 12api-3826695No ratings yet
- Xii Ray BoardDocument14 pagesXii Ray Boarddhruvpandey1612No ratings yet
- OPTICS-05 - Objective UnSolvedDocument6 pagesOPTICS-05 - Objective UnSolvedRaju SinghNo ratings yet
- X - Science - Physics - CH-9 Light - Assignment-4Document3 pagesX - Science - Physics - CH-9 Light - Assignment-4Shweta DuhanNo ratings yet
- X - PCBM, Mat & SSTDocument27 pagesX - PCBM, Mat & SSTRitesh SNo ratings yet
- Cylindrical Perspective: Cylindrical Perspective: Exploring Visual Perception in Computer VisionFrom EverandCylindrical Perspective: Cylindrical Perspective: Exploring Visual Perception in Computer VisionNo ratings yet
- Reverse Perspective: Reimagining Visual Perception in Computer VisionFrom EverandReverse Perspective: Reimagining Visual Perception in Computer VisionNo ratings yet
- Creative Non Fiction - 1STC - Q2Document2 pagesCreative Non Fiction - 1STC - Q2Cow Cow CowNo ratings yet
- TransisorsDocument6 pagesTransisorsZavdielNo ratings yet
- Masterthesis: Technische Universität München Lehrstuhl Für Netzarchitekturen Und Netzdienste Prof. Dr. Georg CarleDocument1 pageMasterthesis: Technische Universität München Lehrstuhl Für Netzarchitekturen Und Netzdienste Prof. Dr. Georg Carlenashwan mustafaNo ratings yet
- Mughal ArchitectureDocument9 pagesMughal ArchitectureLettisha LijuNo ratings yet
- Elster (1985) Morality, Rationality and Collective Action PDFDocument21 pagesElster (1985) Morality, Rationality and Collective Action PDFDenisse CejudoNo ratings yet
- Proximate Cause and Scope of Liability Chapters 11 & 12 - Geistfeld - Product LiabilityDocument93 pagesProximate Cause and Scope of Liability Chapters 11 & 12 - Geistfeld - Product LiabilityGeorge ConkNo ratings yet
- Gastroenterology Case Discussion: JANUARY 07, 2021 Dr. Stephen Wong Indigo and VioletDocument19 pagesGastroenterology Case Discussion: JANUARY 07, 2021 Dr. Stephen Wong Indigo and VioletJolaine ValloNo ratings yet
- Health Lesson 2Document13 pagesHealth Lesson 2rosemarie guimbaolibotNo ratings yet
- RomsDocument106 pagesRomsitalo naelNo ratings yet
- Frank S. Waits v. Hon. Raymond McGowan A. J. S. C., Monmouth County, 516 F.2d 203, 3rd Cir. (1975)Document8 pagesFrank S. Waits v. Hon. Raymond McGowan A. J. S. C., Monmouth County, 516 F.2d 203, 3rd Cir. (1975)Scribd Government DocsNo ratings yet
- Journey To SelfDocument2 pagesJourney To SelfGuy HamiltonNo ratings yet
- How To Ace The Number One Question in Interviews - "Tell Me About Yourself"Document3 pagesHow To Ace The Number One Question in Interviews - "Tell Me About Yourself"Christine CaoNo ratings yet
- 11 Amazing Benefits of PineapplesDocument9 pages11 Amazing Benefits of PineapplesEirojram MarjorieNo ratings yet
- Ai Search StrategiesDocument14 pagesAi Search StrategiesAgni DevNo ratings yet
- Lea 4Document53 pagesLea 4Anna Marie Ventayen Miranda100% (1)
- A.Blikle - A Teal Doctrine of QualityDocument511 pagesA.Blikle - A Teal Doctrine of QualityMonikaNo ratings yet
- NewsletterDocument2 pagesNewsletterboonchuan20095886No ratings yet
- Grid Analysis: Making A Decision by Weighing Up Different FactorsDocument2 pagesGrid Analysis: Making A Decision by Weighing Up Different FactorsFebby LienNo ratings yet
- Evidencia 2 BUSINESSDocument6 pagesEvidencia 2 BUSINESSEscalante YesiddNo ratings yet
- Scheme of Work - Paper 1: Cambridge O Level Islamiyat 2058Document27 pagesScheme of Work - Paper 1: Cambridge O Level Islamiyat 2058Ayesha FarhanNo ratings yet
- Public Policy EvaluationDocument80 pagesPublic Policy EvaluationDayyanealosNo ratings yet
- The Rock Cut Temples of Ajanta PDFDocument77 pagesThe Rock Cut Temples of Ajanta PDFAmit BhagatNo ratings yet
- Database Security: Under Authorization of DR - SalwaDocument11 pagesDatabase Security: Under Authorization of DR - SalwaKhaled AdelNo ratings yet
- TAYAG v. CADocument1 pageTAYAG v. CAJessie Marie dela Peña100% (1)
- Surgical Site Infection: Dr. Maryam. Surgical Unit 3Document22 pagesSurgical Site Infection: Dr. Maryam. Surgical Unit 3med stuNo ratings yet
- Psychiatry LPDocument21 pagesPsychiatry LPKristine BoholstNo ratings yet
- What Is OrnithologyDocument6 pagesWhat Is OrnithologyMandeep BatraNo ratings yet
Class X Light
Class X Light
Uploaded by
uncool.vedant2009Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Class X Light
Class X Light
Uploaded by
uncool.vedant2009Copyright:
Available Formats
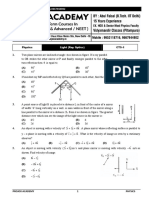
ltipleChoiceQuestions (1
(a) behind the mirror
(b) between the mirror and focus
ich ofthe allowing can make a parallel beam of light (c) at focus
Wh t from a point source is incident o n it?
when (d) centre ofcurvature of mirror
(Un) (NCERT Exemplar)
8. Light rays A and B fall on optical component X and come
Concave mirror as well as convex lens out as Cand D.
(Un)
a Convex mirror as well as concave lens
Two plane mirrors placed at 90° to cach other 4-
A Concave mirror as well as concave lens
ding in front of a magic mirror. She nds the
B-
Achila
image o)
head bigger, the middle portion of her body of D
and that of the legs smaller. The following is The optical component is a
the Saafcombinations
theorder ofcombina for the magic mirror from the top. (a) concave lens (c) convex mirror
(6) convex lens (d) prism
(Ap) (NCERT Exemplar)
(a) Plane, convex and concave 9. Ifa spherical mirror has negative focal length then it is (Re)
(6) Convex, Concave and plane (a) Concave mirror
c) Concave, plane and convex (6) Convex mirror
Convex, planc and concave (c) Plane mirror
Inwhich of the following, the image of an objcct placed at (d) Both plane and convex mirror
in r will be highly diminished andpointsized? 10. Light of velocity 3 x 108 m/sec, falls on a glass prism. The
frequency of light is 2 x 10° Hz. What will be its frequency
(Re) (NCERT Exemplar)
(a) Concave mirror only after passing through glass prism: (Ap)
(b) Convex mirror only
(a) ixI0'Hz (6) X10HZ
(c) Convex lens only 2
iÀ Concave mirror, convex mirror, concave lens and (c) 2 x 10° Hz (d) None of these
convex lens 11. A real and enlarged image can be formed by using a (Un)
Find theangle of incidence and angle of re ection from the (a) concave mirror
diagram.
(Un) (6) place mirror
(c) convex mirror
(d) Both concave and a plane mirror
12. For an incident ray directed towards centre of curvature of
a spherical mirror the re ected ray (Un)
Mirror
surface (a) retraces its path
35
(6) passes through focus
(a) 45°,40° (b) 55°, 55° (c) passes through the pole
(c) 60°, 60° (d) 30°, 30° (d) becomes parallel to the principal axis
5. Velocity of light in air is 3 x 10 m/s. While its velocity in 13. Two mirors M, and M, are placed at right angle to each
a medium is 1.5 x 108 m/s. Then, refractive index of this other as shown in the gure. The total number of images of
medium is (Ap) an object 0' that can be seenare (Ap)
M.
(a) 3 (c) 0.5
(6) (d) 2
0. An object is situatcd at a distance of fI2 from a convex lens
of focal length f. Distance of image will be (Ap)
(a) + (f/2) (c) + (f14)
(b) +(/3) (d) -f M,
(a) Two
An object is placed 20 cm from theconcavemirror offocal (6) Three
length 10 cm, then image is formed at (Ap) (c) Four
(d) In nite
Created with Scanner Pro
fi
fi
fi
fi
fl
fl
14. Consider the statements given below (Un) Reason (R): The speed of light decreases when it passes
(a) The speed of light is more in a rarer medium than in a from a denser medium to a rarer medium. (Re + Un)
denser medium.
(b) When a ray of light travels from air to water, its speed
Subjective Questions
inccreases
Which of these statement(s) is/are correct? Very Short Answer Type Questions (2 M)
(a) (a) only (b) (b) only
1. Sarah is presented with a challenge. She needs to explain
(c) Both (a) and (b) (d) Neither (a) nor (b) how to identify the three types of mirrors (plane, convex,
15. A convex lens has a focal length of 0.5 m. It is combined and concave) without physically touching them. (Un)
with a second lens, so that the combination has a power of
2. Sunlight enters the water at an angle of 30 degrees from the
1.5 diopter. Then the second lens is (Ap) normal. Ifthe water has a refractive index of 1.33, then nd
(a) A concave lens of focal length 2 m. the angle of refraction of the sunlight inside water. (Ev)
(b) A convex lens of focal length 0.5 m.
3. A light ray is incident on a concave mirror with a radius of
(c) A concave lens of focal length 0.5 m. curvature of 20 cm. If the object distance is 15 cm,calculate
(d) A convex lens of focal length 2m. the image distance. (Ev)
16. A convex lens A of focal length 20 cm and a concave lens 4. A converging lens has a focal length of 20 cm. An object is.
B of focal length S cm are kept along the same axis with a placed 30 cm away from the lens. Calculate the position of
distance d between them. If a parallel beam of light falling the image formed by the lens. Is the image larger or smaller
on A leaves B as a parallel beam, then the distance d in cm
than the object? Justify your response. (Ev)
will be (Ap)
5. What is the nature of image formed when object is placed
(a) 25 (c) 30 at the centre of curvature of a concave mirror? Draw the ray
(b) 15 (d) 50
diagram for the mentioned position. (Re)
6. A student is using a magnifying glass to examine a small
Assertion and Reason object. They noticed that when they moved the magnifying
(1 M)
glass closer to the object, the magni cation increases.
Direction: The following questions consist of two statements. Explain why this happens and discuss the relationship
Assertion (A) and Reason (R). Answer these questions by between the distance of the magnifying glass from the object
selecting the appropriate option given below: and the magni cation. (Ap)
(a) BothA and R are true, andR is the correct explanation of A. 7. A diverging lens with a focal length of -15 cm is used
(b) BothA and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of A. to form an image of an object. If the object is placed at a
(c) A is true, but R is false distance of-20 cm from the lens, calculate the position and
(d) A is false, butR is true. characteristics of the image formed. Is the image virtual or
1. Assertion (A):A concave mirror can forma real and inverted real? Provide a reason for your answer. (E)
image of an object. 8. Imagine that you are observing an object placed in front of
Reason (R): A concave mirror always converges the incident a concave mirror. The object is at a distance greater than the
light rays towards a focal point (Re + Un) focal length of the mirror. Describe the nature(real/virtual),
position, and size of the image formed by the miror. (Un)
2. Assertion (A): The refractive index of a medium is always
greater than or equal to one. 9. When a light ray moves obliquely from air into water,does
Reason (R): The refractive index of a medium is de ned it shift closer to the normal line or farther from it?Explain.
(Un)
as the ratio of the speed of light in a vacuum to the speed of
light in that medium. (Re) 10. A dentist usesa mirror to examinea tooth that is l cm in front
of the mirror. If the mirror has a focal length of-5 cm,describe:
3. Assertion (A): From a smooth surface incident light is
re ected in only one direction. () Thetypeofmirrorandthereasonforitsuse.
Reason (R): As the angle of incidence is always equal to the (ii) The nature of the image formed of the tooth. (Ap)
angle of re ection, therefore a parallel beam of rays falling
Short AnswerType Questions (3 M)
on a smooth surface is re ected as a parallel beam of rays
in one direction only. (Re + Un) i. (a) Describe the relationship between the focal length and
4. Assertion (A): The word AMBULANCE written on the the power of a lens.
hospital vans is in the form of its mirror image. (b) Imagine you are designing a magnifying glass, andyou
Reason (R): The image formed by a plane mirror is not have two lenses to choose from: onc with a focal length
(Un) of 20 cm and another with a shorter focal length. How
laterally inverted.
would you calculate the power of cach lens?
5. Assertion (A): When a ray of light passes Irom a denser (c) Explain how a shorter focal length affects the
medium to a rarer medium, it bends away from the normal. (CBSE 2023)
magni cation it provides.
Created with Scanner Pro
fi
fl
fl
fl
fi
fi
fi
fi
. Sialelaws ofre ection of light. List fourcharacteristicsof mirror. Use these two rays to nd the nature and position of
the image tormed by a plane mirror. (Re) the image of an object placed at a distance of 15 cm from a
, Satethe laws of refraction o ight. Explain the ten absolute
concave mirror of focal length 10 cm. (Un)
efactive index and write an expression to relate it with the 4. To construct a ray diagram we use two rays of light which
speedof light in vacuum. (CBSE 2018) are so chosen that it is easy to determine their directions
after re ection from the mirror. Choose these two rays and
I Draw a ray diagram to show the refraction through a
state the path of these rays after re ection from a concave
rectangular glass slab. How is the emergent ray related to
mirror. Use these two rays to nd the nature and position of
the incident ray? (CBSE 2019)
the image of an object placed at a distance of 15 cm from a
6 Writetwo different uses of a concave mirror. (CBSE 2017) concave mirror of focal length 10 cm. (Un + Ap)
6 State two positions in which a concave mirror produces a (a) What is the minimum number of rays required for
magni ed image. (Re) locating the image formed by a concave mirror for an
1. Absolute refractive indices of two media P and are object? Draw a ray diagram to show the formation of a
1.33 (a,) and 2.52 (n,) respectively. The speed of light in virtual image by a concave mirror.
medium P is 2 x 10 m/s. (6) The linear magni cation produced by a spherical mirror
() What would be the speed of light in medium (V? is+3. Analyse this value and state the () type ofmirror
() lf theangleofincidencefor a ray o ight travelling from and (ii) position of the object with respect to the pole of
medium P to Q is 0°, then what will be the path of light the mirror. Draw ray diagram to show the formation of
in the medium 0?
image in this cased
(Un) (CBSE APQ, 2023)
8. Explain how the focal length of a mirror is related to its
(c) An object is placed at a distance of 30 cm in front of a
convex mirror of focal length 15 cm.
curvature. Find the focal length of a convex mirror whose
radius of curvaturę is 32 cm. (NCERT Intext) Write four characteristics of the image formed by the
miror.
9. ldentify the device used as a spherical mirror or lens in
following cases, when the image formed is virtual and erect
in each case. Case Based Questions
() Object is placed between the device and its focus, the
image formed is enlarged and behind it. Case Based-I: The focal length is a crucial parameter in
(i) Object is placed between the focus and device, the image determining the characteristics of an optical system, such as the
formed is enlarged and on the same side as that of the magni cation, image formation, and the ability to focus light at a
object. speci c distance. The radius of curvature of a convex mirror of a
moving automobile is 2.0 m. A truck is coming behind and is at a
(ii) Object is placed between in nity and device, image
formed is diminished and between focus and optical
distance of 3.5 m. (Ap)
centre on the same side as that of the object. () What is the image distance behind the miror? (2 M)
(i) Object is placed between in nity and device, image (i) What is the nature of the image? (I M)
formed is diminished and between pole and focus,
behind it.
(ii) What is the size of the image relative to the size of the truck?
(Un) (NCERT Exemplar)
10. A convex lens forms a real and inverted image of a needle
(1 M)
at a distance of 50 cm from it. Where is the needle placed Case Based-II: Aconverging mirror forms a real image of height
in front of the convex lens if the image is equal to the size 4 cm, of an object of height 1 cm placed 20 cm away from the
of the object? Also, nd the power of the lens.
mirror. (Ev)
(Ap)
() The image distance is (1 M)
Long Answer Type Questions (5 M)
(a) -80 cm (b) -90 cm
1. An object, 4.0 cm in size, is placed at 25.0 cm in front of a
(c) -100 cm (d) -110 cm
concave mirror of focal length 15.0 cm. At what distance
from the mirror should a screen be placed in order to obtain (i) Magnitude of the focal length of the mirror is (1 M)
a sharp image? Find the nature and the size of the image. (a) 15 cm (b) 16 cm
(Ap) (c) 17 cm (d) 18 cm
. A convex mirror used for rear-view on an automobile has (iii) The mirror used here is a mirror.
a radius of curvature of 3.00 m. If a bus is located at 5.00
m from this mirror, nd the position, nature and size of the (a) concave (b) convex
image. (Ap) (c) plano convex (d) plano concave
3. To construct a ray diagram we use two rays of light which Case Based-IlI: When the rays of light travel from one
are so chosen that it is easy to determine their directions ransparent medium to another, the path of light is deviate (d).
after re ection from the mirror. Choose these two rays and This phenomenon is called the refraction of light. The bending of
light depends on the optical density of the mediumthrough which
state the path of these rays after re ection from a concave
the light nasses
Created with Scanner Pro
fi
fi
fi
fi
fl
fl
fi
fi
fl
fl
fl
fl
fl
fi
fi
fi
fi
A concave mirror always forms a real and inverted image for
Rarer Denser
different positions of the object. But if the object is placedbetween
the focus and pole. The image formed is virtual and erect. A convex
mirror always forms a virtual, erect, and diminished image. A
.. concave mirror is used as a doctor's head mirror to focus light on
body parts like eyes, cars, nose, etc., to be examined because it
Rarer
Denser can form an erect and magni ed image of the object. The convex
The speed of light varies from medium to medium. A medium mirror is used as a rear view mirror in automobiles because it can
in which the speed of light is more is an optically rarer medium form a small and erect image of an object. (Un)
whereas in which the speed of light is less is an optically denser () When an object is placed at the centre of curvature of a
medium. Whenever light goes from one medium to another,
concave mirror, the image formed is (1 M)
the frequency of light does not change; however, speed and
wavelength change. It concluded that change in the speed of light (a) larger than the object
is the basic cause of refraction. (Un) (6) smaller than the object
() When light travels from air to glass, the ray of light bends (c) same size as that of the object
( M) (d) highly enlarged
(a) towards the nomal (6) away from normal
(i) No matter how far you stand from a mirror, your image
(c) anywhere (d) none of these
appears erect. The mirror is likely to be (1 M)
(ü) A ray of light passes from medium A to another medium
(a) plane (b) concave
B. No bending of light occurs if the ray of light hits the
boundary of medium B at an angle of (1 M) (c) convex (d) either plane or convex.
(a) 0° (b) 45° (iüi) Which of the following characteristics is true for a concave
(c) 90° (d) 120o mirror? (I M)
(iti) When light passes from one medium to another, the (a) Always forms a virtual image
frequency of light (1 M)
(b) Can form both real and virtual images
(a) increases (b) decreases
(c) remains samne (d) none of these (c) Always forms a real image
(iv) When light passes from glass to water, the speed of light (d) Only forms an inverted image
(1 M) (iv) To get an image larger than the object, one can use (1 M)
(a) increases (b) decreases (a) convex mirrOr but not a concave mirror
(C) remains same (d) rst increases then decrease
(6) a concave mirror but not a convex mirror
(v) The bottom of a pool lled with water appears to be
(c) either a convex mirror or a concave mirror
due to the refraction of light (1 M)
(d) a plane mirror.
(a) shallower (b) deeper
(c) at same depth (d) empty
(v) A convex mirror has wider eld of view because ( M)
Case Based-IV: The spherical mirror forms different types of (a) the image formed is much smaller than the object and a
images when the object is placed at different locations. When the large number of images can beseen.
image is formed on the screen, the image is real and when the
(b) the image formed is much closer to the mirror
image does not form on the screen, the image is virtual. When the
two re ected rays meet actually, the image is real and when they (c) both (a) and (b)
appear to meet, the image is virtual. (d) none of these
Created with Scanner Pro
fi
fi
fi
fl
fi
You might also like
- Introduction - Macro SkillsDocument14 pagesIntroduction - Macro SkillsChermie Sarmiento77% (75)
- Agile One Pager PDFDocument2 pagesAgile One Pager PDFEgeruoh Chigoziri CyrinusNo ratings yet
- Human Resource DevelopmentDocument137 pagesHuman Resource Developmenturfriendkrupa100% (1)
- Problems On Ray Optics and Optical Instruments For NEETDocument19 pagesProblems On Ray Optics and Optical Instruments For NEETRohit Gupta100% (1)
- 644d431abb6c94001859ad6d ## Light Reflation and Refraction DPPs PDFDocument5 pages644d431abb6c94001859ad6d ## Light Reflation and Refraction DPPs PDFDINANATH SINGHNo ratings yet
- Light Work SheetDocument3 pagesLight Work Sheetphysicsbooks.storeNo ratings yet
- Optics QuestionsDocument2 pagesOptics QuestionsUnidentified PersonNo ratings yet
- 1822-12 Phy P15 Ray Optics B 30Q (1) - 1Document3 pages1822-12 Phy P15 Ray Optics B 30Q (1) - 1JeevanNo ratings yet
- Physics Light Daily Home Assignment 04 Udaan 3 0 1Document4 pagesPhysics Light Daily Home Assignment 04 Udaan 3 0 1HARSHIT GUPTANo ratings yet
- Acids, Bases and Salts Light-Reflection and Refraction: Multiple Choice Questions (MCQS)Document12 pagesAcids, Bases and Salts Light-Reflection and Refraction: Multiple Choice Questions (MCQS)Bhanu PurushothamaNo ratings yet
- Physics Class XIIDocument177 pagesPhysics Class XIIManavendra PratapNo ratings yet
- MCQ REFR AND REFLDocument11 pagesMCQ REFR AND REFLsheikharmaanusmaniNo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan 05-Nov-2021Document13 pagesAdobe Scan 05-Nov-2021SIDDHANT BHATTNo ratings yet
- CH - 01 - Light - Only PDFDocument12 pagesCH - 01 - Light - Only PDFrohitdodamanib352No ratings yet
- DPP3Document2 pagesDPP3TrtyiiijhhNo ratings yet
- Go (Jee Main Online)Document19 pagesGo (Jee Main Online)balvantgk.hemant123No ratings yet
- Revision Sheet 2 Light Reflection and RefractionDocument4 pagesRevision Sheet 2 Light Reflection and RefractionRiyansh WarikooNo ratings yet
- 03 Light (Reflection of Spherical Surfaces) Elevate 1Document5 pages03 Light (Reflection of Spherical Surfaces) Elevate 1akshitwalia209No ratings yet
- PHYSICS-test Electric Potential, Current Electricity-A, Ray Optics-A 1mark Questions: (ANSWER ALL)Document4 pagesPHYSICS-test Electric Potential, Current Electricity-A, Ray Optics-A 1mark Questions: (ANSWER ALL)shylaNo ratings yet
- Class 10 Test - 1 1693184362Document6 pagesClass 10 Test - 1 1693184362samsuzzaman sahinNo ratings yet
- Light-Reflection & Refraction - Practice Sheet - 10th Board Booster 2.0 2024Document5 pagesLight-Reflection & Refraction - Practice Sheet - 10th Board Booster 2.0 2024yashasvisharma sharmaNo ratings yet
- Light - Reflection & Refraction - Practice Sheet - WARRIOR SERIES CLASS-10THDocument5 pagesLight - Reflection & Refraction - Practice Sheet - WARRIOR SERIES CLASS-10THhiranyakshivNo ratings yet
- AssignmentDocument2 pagesAssignmentNeeraj PuniaNo ratings yet
- Fisica 3Document1 pageFisica 3Andres Felipe HigueraNo ratings yet
- Sainik School Goalpara: Extra Homework Subject: Science (Physics) Class: XDocument4 pagesSainik School Goalpara: Extra Homework Subject: Science (Physics) Class: XBornil Bikash BhuyanNo ratings yet
- Spherical Mirror-Vsq1.1-QuesDocument1 pageSpherical Mirror-Vsq1.1-QuesRonit RoyNo ratings yet
- Reflection & Refraction PDFDocument5 pagesReflection & Refraction PDFSushri Sangeeta MohantyNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 24 Ray Optics and Optical InstrumentsDocument37 pagesChapter - 24 Ray Optics and Optical Instrumentsagoel0844No ratings yet
- Ray Optics & Optical Instruments, Home Work Sheet-1: Plane Mirror 1Document60 pagesRay Optics & Optical Instruments, Home Work Sheet-1: Plane Mirror 1venkat krishnanNo ratings yet
- Ray Optics DC Pandey MCQ With Detailed SolutionDocument30 pagesRay Optics DC Pandey MCQ With Detailed Solutionvivek100% (1)
- Light Assign MentDocument32 pagesLight Assign MentAyush ChouhanNo ratings yet
- Physics DPPDocument19 pagesPhysics DPPasgurudevNo ratings yet
- Tips The TempestDocument8 pagesTips The TempestGopal Kumar VermaNo ratings yet
- Test Your KnowledgeDocument3 pagesTest Your KnowledgeSantosh Kumar MallickNo ratings yet
- General Instructions: Section (A) : (1 Marks)Document2 pagesGeneral Instructions: Section (A) : (1 Marks)exploreharyanaNo ratings yet
- Class X Science Multiple Choice Questions 1Document1 pageClass X Science Multiple Choice Questions 1rayi17198467% (12)
- CH Light AssignmentDocument6 pagesCH Light Assignmentaltxd1313No ratings yet
- Multiple Choice Questions Based On ExperimentDocument1 pageMultiple Choice Questions Based On ExperimentkapilNo ratings yet
- Reflection From Plane MirrorDocument4 pagesReflection From Plane Mirroryadavutpal1021No ratings yet
- 18 Geometrical OpticsDocument40 pages18 Geometrical OpticsSamsul BahriNo ratings yet
- Class 10 Test - 1 1693006894Document2 pagesClass 10 Test - 1 1693006894samsuzzaman sahinNo ratings yet
- 01 Ray Optics MMDocument71 pages01 Ray Optics MMmonikeshNo ratings yet
- G10 - Chapter Test 5 Ans - Ch.10 - 06 NOV 23Document10 pagesG10 - Chapter Test 5 Ans - Ch.10 - 06 NOV 23Urmila GNo ratings yet
- Ques Complete Ray OpticsDocument20 pagesQues Complete Ray OpticsAishani SaxenaNo ratings yet
- Light Revision Class 10Document34 pagesLight Revision Class 10karun.senthil.kumar.25No ratings yet
- LIGHTsDocument10 pagesLIGHTsjapneets764No ratings yet
- 2024-04-18-0.7264717555178133Document24 pages2024-04-18-0.7264717555178133Devansh DodaNo ratings yet
- X - Science - Physics - CH-9 Light - Assignment-1Document2 pagesX - Science - Physics - CH-9 Light - Assignment-1Shweta DuhanNo ratings yet
- 01 Ray Optics MMDocument71 pages01 Ray Optics MMMission NEET 2022No ratings yet
- 2nd Yr Phy-7CDocument48 pages2nd Yr Phy-7CRakshitha BSNo ratings yet
- Class X Science Multiple Choice Questions 1Document1 pageClass X Science Multiple Choice Questions 1Rohit GuptaNo ratings yet
- 10 - Light - Reflection and Refraction + The Colourful World - 15.sep.21 - 3 PMDocument2 pages10 - Light - Reflection and Refraction + The Colourful World - 15.sep.21 - 3 PMHarshNo ratings yet
- IIT FILEDocument3 pagesIIT FILEdhikiviyu666No ratings yet
- Light PDFDocument3 pagesLight PDFVasu GargNo ratings yet
- Assign IiDocument4 pagesAssign IiSangeeta ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- Ray Optics (Ques Bank)Document7 pagesRay Optics (Ques Bank)Om GoyalNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12Document16 pagesChapter 12api-3826695No ratings yet
- Xii Ray BoardDocument14 pagesXii Ray Boarddhruvpandey1612No ratings yet
- OPTICS-05 - Objective UnSolvedDocument6 pagesOPTICS-05 - Objective UnSolvedRaju SinghNo ratings yet
- X - Science - Physics - CH-9 Light - Assignment-4Document3 pagesX - Science - Physics - CH-9 Light - Assignment-4Shweta DuhanNo ratings yet
- X - PCBM, Mat & SSTDocument27 pagesX - PCBM, Mat & SSTRitesh SNo ratings yet
- Cylindrical Perspective: Cylindrical Perspective: Exploring Visual Perception in Computer VisionFrom EverandCylindrical Perspective: Cylindrical Perspective: Exploring Visual Perception in Computer VisionNo ratings yet
- Reverse Perspective: Reimagining Visual Perception in Computer VisionFrom EverandReverse Perspective: Reimagining Visual Perception in Computer VisionNo ratings yet
- Creative Non Fiction - 1STC - Q2Document2 pagesCreative Non Fiction - 1STC - Q2Cow Cow CowNo ratings yet
- TransisorsDocument6 pagesTransisorsZavdielNo ratings yet
- Masterthesis: Technische Universität München Lehrstuhl Für Netzarchitekturen Und Netzdienste Prof. Dr. Georg CarleDocument1 pageMasterthesis: Technische Universität München Lehrstuhl Für Netzarchitekturen Und Netzdienste Prof. Dr. Georg Carlenashwan mustafaNo ratings yet
- Mughal ArchitectureDocument9 pagesMughal ArchitectureLettisha LijuNo ratings yet
- Elster (1985) Morality, Rationality and Collective Action PDFDocument21 pagesElster (1985) Morality, Rationality and Collective Action PDFDenisse CejudoNo ratings yet
- Proximate Cause and Scope of Liability Chapters 11 & 12 - Geistfeld - Product LiabilityDocument93 pagesProximate Cause and Scope of Liability Chapters 11 & 12 - Geistfeld - Product LiabilityGeorge ConkNo ratings yet
- Gastroenterology Case Discussion: JANUARY 07, 2021 Dr. Stephen Wong Indigo and VioletDocument19 pagesGastroenterology Case Discussion: JANUARY 07, 2021 Dr. Stephen Wong Indigo and VioletJolaine ValloNo ratings yet
- Health Lesson 2Document13 pagesHealth Lesson 2rosemarie guimbaolibotNo ratings yet
- RomsDocument106 pagesRomsitalo naelNo ratings yet
- Frank S. Waits v. Hon. Raymond McGowan A. J. S. C., Monmouth County, 516 F.2d 203, 3rd Cir. (1975)Document8 pagesFrank S. Waits v. Hon. Raymond McGowan A. J. S. C., Monmouth County, 516 F.2d 203, 3rd Cir. (1975)Scribd Government DocsNo ratings yet
- Journey To SelfDocument2 pagesJourney To SelfGuy HamiltonNo ratings yet
- How To Ace The Number One Question in Interviews - "Tell Me About Yourself"Document3 pagesHow To Ace The Number One Question in Interviews - "Tell Me About Yourself"Christine CaoNo ratings yet
- 11 Amazing Benefits of PineapplesDocument9 pages11 Amazing Benefits of PineapplesEirojram MarjorieNo ratings yet
- Ai Search StrategiesDocument14 pagesAi Search StrategiesAgni DevNo ratings yet
- Lea 4Document53 pagesLea 4Anna Marie Ventayen Miranda100% (1)
- A.Blikle - A Teal Doctrine of QualityDocument511 pagesA.Blikle - A Teal Doctrine of QualityMonikaNo ratings yet
- NewsletterDocument2 pagesNewsletterboonchuan20095886No ratings yet
- Grid Analysis: Making A Decision by Weighing Up Different FactorsDocument2 pagesGrid Analysis: Making A Decision by Weighing Up Different FactorsFebby LienNo ratings yet
- Evidencia 2 BUSINESSDocument6 pagesEvidencia 2 BUSINESSEscalante YesiddNo ratings yet
- Scheme of Work - Paper 1: Cambridge O Level Islamiyat 2058Document27 pagesScheme of Work - Paper 1: Cambridge O Level Islamiyat 2058Ayesha FarhanNo ratings yet
- Public Policy EvaluationDocument80 pagesPublic Policy EvaluationDayyanealosNo ratings yet
- The Rock Cut Temples of Ajanta PDFDocument77 pagesThe Rock Cut Temples of Ajanta PDFAmit BhagatNo ratings yet
- Database Security: Under Authorization of DR - SalwaDocument11 pagesDatabase Security: Under Authorization of DR - SalwaKhaled AdelNo ratings yet
- TAYAG v. CADocument1 pageTAYAG v. CAJessie Marie dela Peña100% (1)
- Surgical Site Infection: Dr. Maryam. Surgical Unit 3Document22 pagesSurgical Site Infection: Dr. Maryam. Surgical Unit 3med stuNo ratings yet
- Psychiatry LPDocument21 pagesPsychiatry LPKristine BoholstNo ratings yet
- What Is OrnithologyDocument6 pagesWhat Is OrnithologyMandeep BatraNo ratings yet