Professional Documents
Culture Documents
4.5 3D
4.5 3D
Uploaded by
unknownartist9256Copyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- (Rykken) Geometry The Line and The CircleDocument502 pages(Rykken) Geometry The Line and The CircleBrenda Denise Schaffhauser MermozNo ratings yet
- Triangle Theorems Key PDFDocument14 pagesTriangle Theorems Key PDFAiden ChristensenNo ratings yet
- IGCSEFM TrigonometryII ExercisesDocument4 pagesIGCSEFM TrigonometryII ExercisessreelakshmiNo ratings yet
- Mathematics D - 5Document4 pagesMathematics D - 5Aditya GhoseNo ratings yet
- Three Dimensional Geometry QDocument4 pagesThree Dimensional Geometry Qhildahjones123No ratings yet
- GCSE 3DTrigAndPythagorasDocument3 pagesGCSE 3DTrigAndPythagorasJean AlmiraNo ratings yet
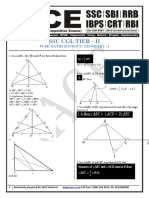
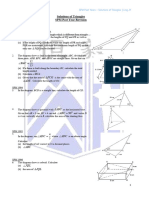
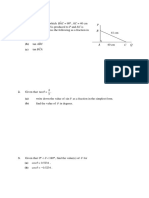
- SSC CGL Tier - II: Pure Maths Handout: Geometry - IDocument4 pagesSSC CGL Tier - II: Pure Maths Handout: Geometry - IKenny CharlesNo ratings yet
- SPM 1993-2021 PAST YEARS Solutions of TrianglesDocument8 pagesSPM 1993-2021 PAST YEARS Solutions of TrianglesTIME DIDA滴答No ratings yet
- Sohcahtoa Worksheet 1Document6 pagesSohcahtoa Worksheet 1Daffa Guevara RaushanfikriNo ratings yet
- Exercise: and 乙ABC=Document5 pagesExercise: and 乙ABC=5D-11-李嘉豪 stu-LI KA HONo ratings yet
- 2.12 Intersecting CirclesDocument9 pages2.12 Intersecting CirclesNehemiah kipchumbaNo ratings yet
- Review Trig GRD 9Document6 pagesReview Trig GRD 9JanvierNo ratings yet
- 3D Pythagoras & Trigonometry: (AQA FM Mock Set 4 Paper 2) ADocument3 pages3D Pythagoras & Trigonometry: (AQA FM Mock Set 4 Paper 2) Askchatterjee2012No ratings yet
- WS Quadrilateral IX QuestionsDocument3 pagesWS Quadrilateral IX Questionsaks252625No ratings yet
- Three Dimensional GeometryDocument3 pagesThree Dimensional GeometrycalebNo ratings yet
- Loci QDocument2 pagesLoci QMy fluffy MochiNo ratings yet
- VIII-Arithmetic-Revision Worksheet-1Document2 pagesVIII-Arithmetic-Revision Worksheet-1anousha1488No ratings yet
- AQA Maths M2 Topic Questions From Papers Centre of MassDocument10 pagesAQA Maths M2 Topic Questions From Papers Centre of MassJing XieNo ratings yet
- Problem Set 4.1Document3 pagesProblem Set 4.1james.ebardolazaNo ratings yet
- 28-Trigonometry Paper 2Document6 pages28-Trigonometry Paper 2iyaad MubarakNo ratings yet
- Ijaz O&A-Level NotesDocument6 pagesIjaz O&A-Level Notesijazkhan22yahooNo ratings yet
- 1 TriangleDocument24 pages1 Triangleavijit ghoshNo ratings yet
- GCSE Trigonometry1RightAngledDocument3 pagesGCSE Trigonometry1RightAngledĐặng Minh TuấnNo ratings yet
- Chapter Iii: Similar Triangles: Two Line Segments AB and CD Are Propotional To ADocument14 pagesChapter Iii: Similar Triangles: Two Line Segments AB and CD Are Propotional To ADuong QuangNo ratings yet
- 278316geometry Practice Sheet - 10 - CrwillDocument6 pages278316geometry Practice Sheet - 10 - Crwillsivejad276No ratings yet
- Trigonometry (1) WorkshtDocument2 pagesTrigonometry (1) WorkshtHugh IngramNo ratings yet
- HIS-IG - OL-P-MathB Exam Question (2hr)Document5 pagesHIS-IG - OL-P-MathB Exam Question (2hr)cinna morollNo ratings yet
- W s-6 Thales TheoremDocument3 pagesW s-6 Thales Theoremapi-253679034No ratings yet
- (S3) Test-Midterm 20230315Document10 pages(S3) Test-Midterm 20230315gurnoorkaur sandhuNo ratings yet
- d10 - 2022 EM Year 3 EOY - Congruency and Similarity - Revision PDFDocument13 pagesd10 - 2022 EM Year 3 EOY - Congruency and Similarity - Revision PDFWilliamNo ratings yet
- 6.triangles MCQsDocument7 pages6.triangles MCQsAnubhav KattnaNo ratings yet
- Math ChapterDocument6 pagesMath ChapterRavi AutiNo ratings yet
- Adv Ex 07 Trigonometry II (Application)Document12 pagesAdv Ex 07 Trigonometry II (Application)Leroy ChengNo ratings yet
- GCSE H3 02g4 02 3D TrigonometryDocument2 pagesGCSE H3 02g4 02 3D TrigonometryAndrei StanescuNo ratings yet
- Construction Past PapersDocument2 pagesConstruction Past PapersTaniel JallaiNo ratings yet
- Complete Geometry Class 3 Circle and Quadrilateral SSC Special BatchDocument15 pagesComplete Geometry Class 3 Circle and Quadrilateral SSC Special BatchMohit1 Mj1No ratings yet
- Geometrical Construction 9Document6 pagesGeometrical Construction 9Darwin ManoNo ratings yet
- Angle Properties of Circles QDocument7 pagesAngle Properties of Circles Qjulius muiruriNo ratings yet
- Centers of Triangle (Printable)Document14 pagesCenters of Triangle (Printable)sudhansu singhNo ratings yet
- F.iv Home Package DecemberDocument3 pagesF.iv Home Package Decemberelvingodfrey8No ratings yet
- ملزمة اسئلة شاملة على Geometry للصف الاول الثانوى اللغات الترم الاول-الامتحان التعليمىDocument6 pagesملزمة اسئلة شاملة على Geometry للصف الاول الثانوى اللغات الترم الاول-الامتحان التعليمىMaths And Technology Aladdin FathiNo ratings yet
- TriangleDocument36 pagesTrianglewisdomacademyapp1No ratings yet
- Sec3 TrigonometryDocument10 pagesSec3 TrigonometryCharles PeterNo ratings yet
- Topic - 9 Similarity and CongruencyDocument9 pagesTopic - 9 Similarity and CongruencyJorifNo ratings yet
- Allen: Pre-Nurture CourseDocument2 pagesAllen: Pre-Nurture CourseAshrithNo ratings yet
- Right Angled Triangle Trigonometry 2 IB Math SLDocument4 pagesRight Angled Triangle Trigonometry 2 IB Math SLFransiska KNo ratings yet
- KS Papers 2010 - Maths BDocument4 pagesKS Papers 2010 - Maths BakashNo ratings yet
- Tareas Sec G5 S3Document2 pagesTareas Sec G5 S3JoEl Perez0% (1)
- Similarity and Congruence Summary : AB PQ PR QRDocument9 pagesSimilarity and Congruence Summary : AB PQ PR QRkaziba stephenNo ratings yet
- RS Aggarwal Class 9 Solutions Chapter-13 Geometrical ConstructionsDocument6 pagesRS Aggarwal Class 9 Solutions Chapter-13 Geometrical Constructionsrahulkashyapr9999No ratings yet
- AMATH Solution of TriangleDocument12 pagesAMATH Solution of TriangleLeneNo ratings yet
- 3 DimensionsDocument12 pages3 DimensionsFauziah SallehNo ratings yet
- C-9 Math PNCF Race CbseDocument66 pagesC-9 Math PNCF Race CbsePranoy MazumdarNo ratings yet
- Prmo Daily Practice Problems: Sub.: Mathematics DPP: 14Document19 pagesPrmo Daily Practice Problems: Sub.: Mathematics DPP: 14sudhir singh100% (3)
- MATHS - 12th MAY TRIANGLES - AssignmentDocument4 pagesMATHS - 12th MAY TRIANGLES - AssignmentSai KrithikNo ratings yet
- Geometry 123Document4 pagesGeometry 123vinayhedaoo28No ratings yet
- Jeep 206Document18 pagesJeep 206Arun KumarvermaNo ratings yet
- Semana 2 Tema: Congruencia de Triángulos: GeometríaDocument5 pagesSemana 2 Tema: Congruencia de Triángulos: GeometríaAntonny GonzalesNo ratings yet
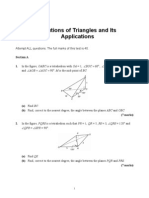
- Solutions of Triangles and Its Applications: Section ADocument3 pagesSolutions of Triangles and Its Applications: Section AkkakilaiNo ratings yet
- Math P2 N2000Document10 pagesMath P2 N2000ntandosithole923No ratings yet
- Worksheet 12 Analytical Geometry Grade 10 MathematicsDocument2 pagesWorksheet 12 Analytical Geometry Grade 10 Mathematicsreyneke.monyaNo ratings yet
- 2016-2019 Paper 2 Revision PDFDocument140 pages2016-2019 Paper 2 Revision PDFslap bwoy100% (1)
- Midpoint of A Line PDFDocument3 pagesMidpoint of A Line PDFR NovNo ratings yet
- Sim 3D TRANSFORMATIONS FinalDocument22 pagesSim 3D TRANSFORMATIONS FinalVaishakh SasikumarNo ratings yet
- 1.9. Composition of TransformationsDocument10 pages1.9. Composition of TransformationsAngus TeeNo ratings yet
- GeometryDocument9 pagesGeometryleolong34No ratings yet
- Module-2 Fill Area Primitives, 2D Geometric Transformations and 2D ViewingDocument54 pagesModule-2 Fill Area Primitives, 2D Geometric Transformations and 2D ViewingShain SethiNo ratings yet
- 7.1 Polygon Formulas: Mental Floss: Mon, Jan 8Document4 pages7.1 Polygon Formulas: Mental Floss: Mon, Jan 8Jhon Lou Raña ManuelNo ratings yet
- 3D Geometric Transformation: CGVR - Korea.ac - KRDocument26 pages3D Geometric Transformation: CGVR - Korea.ac - KRPraveen SharmaNo ratings yet
- 2D TransformationsDocument56 pages2D Transformationsguptatulsi31No ratings yet
- 16 6 Solving Sss TrianglesDocument5 pages16 6 Solving Sss Trianglesapi-299265916No ratings yet
- Activity 32 - Omitted Measurement For Adjoining Courses (Case 1)Document13 pagesActivity 32 - Omitted Measurement For Adjoining Courses (Case 1)John Angelo CompetenteNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10: Solution of TrianglesDocument4 pagesChapter 10: Solution of TrianglesHayati Aini AhmadNo ratings yet
- Intro To TrigonometryDocument4 pagesIntro To TrigonometrySanjayNo ratings yet
- Ramon Teves Pastor Memorial - Dumaguete Science High School: Prepared By: Miss Kassandra VenzueloDocument11 pagesRamon Teves Pastor Memorial - Dumaguete Science High School: Prepared By: Miss Kassandra Venzuelomarjun catanNo ratings yet
- Law of Sines and CosinesDocument21 pagesLaw of Sines and CosinesAnthony CaputolNo ratings yet
- Affine TransformationDocument4 pagesAffine Transformationcircleteam123No ratings yet
- Determining Angle VisuallyDocument2 pagesDetermining Angle Visuallyapi-263867215No ratings yet
- Naming of PolygonsDocument46 pagesNaming of PolygonsCharlie RiveraNo ratings yet
- Corbett Maths Angles PolygonsDocument4 pagesCorbett Maths Angles PolygonskdebipershadNo ratings yet
- PolygonsDocument46 pagesPolygonsERIC VALLENo ratings yet
- CAT 2009 Quant QuestionsDocument3 pagesCAT 2009 Quant QuestionscomploreNo ratings yet
- 8M03 Understanding Quadrilaterals (v1)Document3 pages8M03 Understanding Quadrilaterals (v1)neomatrix70No ratings yet
- Topic 3 Regular and Semi-Regular SolidsDocument12 pagesTopic 3 Regular and Semi-Regular SolidsAngieLeeNo ratings yet
- Finding Angles by Degrees StudentDocument1 pageFinding Angles by Degrees StudentDarwin Vasquez OrocioNo ratings yet
- Homogeneous TransformDocument12 pagesHomogeneous TransformAnonymous G9t3IVfL4JNo ratings yet
- hw3 SolDocument4 pageshw3 Solkalaputra100% (1)
- 3rd Quarter Exam - MATH 7Document3 pages3rd Quarter Exam - MATH 7Carlz BrianNo ratings yet
- Quadrilateral - Angles: A) Find The Measure of The Indicated Angle in Each QuadrilateralDocument2 pagesQuadrilateral - Angles: A) Find The Measure of The Indicated Angle in Each QuadrilateralAngel AngiaNo ratings yet
4.5 3D
4.5 3D
Uploaded by
unknownartist9256Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
4.5 3D
4.5 3D
Uploaded by
unknownartist9256Copyright:
Available Formats
Mr Ogana
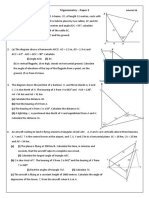
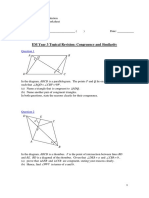
FORM 4 THREE DIMENSIONONAL GEOMETRY MR STEPHEN OGANA
1. The figure below PQRST is a right pyramid with base PQ = 8cm, QR = 6cm and PT = QT = RT = ST = 13cm.
J and K are mid points of QT and RT respectively,
Determine;
(a) The height of the pyramid (2mks)
T
K
J
S
R
6cm
P
8cm Q
(b) The angle the length TS makes with SJ (3mks)
(c) The angle PTS makes with the base PQRS. (2mks)
(d) The angle between the plane PTS and the plane PJKS. (3mks)
Page 1 of 16 Ngere High School
Mr Ogana
2. The figure below is a rectangular base pyramid with the base ABCD and vertex V. VC=VB=VA=VD = 39
AB̳̳̳̳̳̳̳̳̳ 24 and BC = 18 EF =8cm FG = 6cm
V
H G
E 8cm F 6 cm
D C
O•
18 cm
A 24cm B
(a) Calculate the height VO of the Pyramid. (2mks)
(a) The Pyramid is cut along a plane EFGH parallel to ABCD as shown.
(i) Calculate the angle between VHE and VBC (3mks)
(ii) Calculate the angle between ABGH and ABCD (5mks)
Page 2 of 16 Ngere High School
Mr Ogana
3. The figure below is a cuboid ABCDFFGH such that AB 8cm, BC = 6cm and CF 4cm.
F
E
H G
D C
A B
Determine:
a) the length
(i) AC (2mks)
(ii) AF (2mks)
b) The angle AF makes with plane ABCD. (2mks)
c) The angle plane AEFB makes with the plane ABCD (2mks)
d) Find the angle between line EG and line DC (2mks)
Page 3 of 16 Ngere High School
Mr Ogana
4. The figure below shows a cuboid ABCDEFGH. (Given that AB 12cm, BC=8cm and BE=4cm)
(a) State the projection of AG on the plane EFGH. (2mk)
(b) Determine the angle between the line AG and the plane EFGH. (3mks)
(c) Given that M is the mid-point of FG, determine the angle between the planes AMD and ABCD.
(3mks)
Page 4 of 16 Ngere High School
Mr Ogana
5. The triangular base ABC of the pyramid OABC is right angled at C and lies in a horizontal plane. The edge OC is
vertical. AC = 5cm, OC = 8cm and angle CAB = 47 o.
8cm
C
5cm
A 47o
B
Calculate;
a) The length AB. (2 Marks)
b) The inclination of the edge OB to the horizontal. (2 Marks)
c) The inclination of the face OAB to the horizontal. (4 Marks)
Page 5 of 16 Ngere High School
Mr Ogana
6. The figure below shows a frustrum PQRSTUVW of a right pyramid. PQ = 20cm, QR = 15cm, UV = 10cm,
UT = 7.5cm and PU = QV = RW = ST = 12cm.
T W
7.5 cm
U 10 cm
V 12 cm
R
15 cm
P 20 cm Q
Leave all your answer to 4 s.f.
(a) Find the altitude of the pyramid from which the frustrum was cut. (3mks)
(b) Find the angle between
(i) PW and base PQRS (4mks)
(ii) PQVU and the base PQRS (3mks)
Page 6 of 16 Ngere High School
Mr Ogana
7. The figure below is a square based pyramid ABCDV with AD=DC=6cm, and height VO=10cm.
D
C
6cm
O
A
6cm B
(a) State the projection of VA on the base ABCD. (1mk)
(b) Find:
(i) The length of VA (3mks)
(ii) The angle between VA and ABCD (2mks)
(iii) The angle between VDC and ABCD. (2mks)
(iv) Volume of the pyramid. (2mks)
Page 7 of 16 Ngere High School
Mr Ogana
8. A pyramid with a vertex O and edge OA, OB, OC and OD each of 17cm long stands on a square base ABCD of
side 8cm as shown below.
A P B
8c
M
D 8cm C
Calculate;
a) The height OP of the pyramid. (3 Marks)
b) The angle between an edge and the base. (3 Marks)
c) The angle between a sloping face and the base. (4 Marks)
Page 8 of 16 Ngere High School
Mr Ogana
9. The figure below shows a right pyramid with a rectangular base ABCD. O is the centre of the base.
VA =VB=VC=VD=14cm. AB= 12cm and BC=9cm
14cm
D
C
O
9cm
A 12cm B
M
Calculate:
(a) The angle between the line VA and the plane ABCD (3marks)
(b) The angle between the planes VAD and VBC (4marks)
(c) The surface area of the pyramid (3marks)
Page 9 of 16 Ngere High School
Mr Ogana
10. The figure below shows a cube of side 10cm. M is the midpoint of AF.
E H
D C
A B
Find
(i) length HM (2mks)
(ii) the angle HM and ABCD. (4mks)
(iii) angle between HM and MC ( 4mks)
Page 10 of 16 Ngere High School
Mr Ogana
11. The figure below is a frustum of a rectangular pyramid with AB=12cm, EF=8cm,BC=9cm and height of
6 cm
H G
6cm
E 9cm F
D C
9cm
A 12cm B
Calculate:
a) the full height of the pyramid (2 marks)
b) angle that the plane ABFE makes with the base ABCD (2marks)
c) angle that AG makes with the base ABCD (3marks)
d) angle that AC makes with line AE (1mark)
e) angle that plane BCGF makes with the base ABCD (2marks)
Page 11 of 16 Ngere High School
Mr Ogana
12. The figure shows a right pyramid mounted onto a rectangular block. The length AB=8cm, BC = 6cm, CH =3cm
and VC = 15cm
V
D C
A B
E H
F G
1
Given that M is the centre of the plane ABCD and P is a point on MV such that MP = MV, Calculate: -
5
(a) The length of EG. (1 mark)
(b) The height MV of the pyramidal section to 2 decimal places. (2 marks)
(c) The angle between the plane BPC and the pyramidal base ABCD. (3 marks)
(d) The angle between the line GV and the plane EFGH. (2 marks)
(e) The volume of the solid to four significant figures. (2 marks)
Page 12 of 16 Ngere High School
Mr Ogana
13. The figure below represents a right pyramid on a rectangular base. AV=13cm, AB=8cm, BC=6cm
Calculate, correct to 1 decimal place.
(a) the length AC (2mks)
(b) the length VN (2mks)
(c) the angle between line AV and the bale ABCD (3mks)
(d) the angle between plane VAD and the base ABCD (3mks)
Page 13 of 16 Ngere High School
Mr Ogana
14. The figure below shows a regular tetrahedron VABC of sides 6cm. P and Q are the midpoints of AB and BC
respectively
Calculate
(a) The length VP (2 marks)
(b) The angle between the planes VAB and ABC (4 marks)
(c) The perpendicular height of the tetrahedron (2 marks)
(d) The angle between the line VP and the plane VAQ (2 marks)
Page 14 of 16 Ngere High School
Mr Ogana
15. The diagram below shows a right pyramid with a square base ABCD and vertex V. O is the centre of the
base. AB = 14m, VA = 20m and N is the midpoint of BC.
Find;
a) The lengths of BO, VO and VN (3 marks)
b) The angle between VO and plane VBC (3 marks)
c) The angle between VB and base ABCD (2 marks)
d) The angle between VDC and VBC (2 marks)
Page 15 of 16 Ngere High School
Mr Ogana
16. The figure below shows a frustum ABCDEFGH of a right pyramid. AB = 24cm, BC = 10cm, FG = 18cm,
GH = 7.5cm and AF = BG = CH = DE = 15cm.
Determine:
(a) the altitude of the pyramid. (2 marks)
(b) the angle between
(i) AF and the base ABCD (3 marks)
(ii) the planes ABCF and ABCD (3 marks)
(iii) FE and GB (2 marks)
Page 16 of 16 Ngere High School
You might also like
- (Rykken) Geometry The Line and The CircleDocument502 pages(Rykken) Geometry The Line and The CircleBrenda Denise Schaffhauser MermozNo ratings yet
- Triangle Theorems Key PDFDocument14 pagesTriangle Theorems Key PDFAiden ChristensenNo ratings yet
- IGCSEFM TrigonometryII ExercisesDocument4 pagesIGCSEFM TrigonometryII ExercisessreelakshmiNo ratings yet
- Mathematics D - 5Document4 pagesMathematics D - 5Aditya GhoseNo ratings yet
- Three Dimensional Geometry QDocument4 pagesThree Dimensional Geometry Qhildahjones123No ratings yet
- GCSE 3DTrigAndPythagorasDocument3 pagesGCSE 3DTrigAndPythagorasJean AlmiraNo ratings yet
- SSC CGL Tier - II: Pure Maths Handout: Geometry - IDocument4 pagesSSC CGL Tier - II: Pure Maths Handout: Geometry - IKenny CharlesNo ratings yet
- SPM 1993-2021 PAST YEARS Solutions of TrianglesDocument8 pagesSPM 1993-2021 PAST YEARS Solutions of TrianglesTIME DIDA滴答No ratings yet
- Sohcahtoa Worksheet 1Document6 pagesSohcahtoa Worksheet 1Daffa Guevara RaushanfikriNo ratings yet
- Exercise: and 乙ABC=Document5 pagesExercise: and 乙ABC=5D-11-李嘉豪 stu-LI KA HONo ratings yet
- 2.12 Intersecting CirclesDocument9 pages2.12 Intersecting CirclesNehemiah kipchumbaNo ratings yet
- Review Trig GRD 9Document6 pagesReview Trig GRD 9JanvierNo ratings yet
- 3D Pythagoras & Trigonometry: (AQA FM Mock Set 4 Paper 2) ADocument3 pages3D Pythagoras & Trigonometry: (AQA FM Mock Set 4 Paper 2) Askchatterjee2012No ratings yet
- WS Quadrilateral IX QuestionsDocument3 pagesWS Quadrilateral IX Questionsaks252625No ratings yet
- Three Dimensional GeometryDocument3 pagesThree Dimensional GeometrycalebNo ratings yet
- Loci QDocument2 pagesLoci QMy fluffy MochiNo ratings yet
- VIII-Arithmetic-Revision Worksheet-1Document2 pagesVIII-Arithmetic-Revision Worksheet-1anousha1488No ratings yet
- AQA Maths M2 Topic Questions From Papers Centre of MassDocument10 pagesAQA Maths M2 Topic Questions From Papers Centre of MassJing XieNo ratings yet
- Problem Set 4.1Document3 pagesProblem Set 4.1james.ebardolazaNo ratings yet
- 28-Trigonometry Paper 2Document6 pages28-Trigonometry Paper 2iyaad MubarakNo ratings yet
- Ijaz O&A-Level NotesDocument6 pagesIjaz O&A-Level Notesijazkhan22yahooNo ratings yet
- 1 TriangleDocument24 pages1 Triangleavijit ghoshNo ratings yet
- GCSE Trigonometry1RightAngledDocument3 pagesGCSE Trigonometry1RightAngledĐặng Minh TuấnNo ratings yet
- Chapter Iii: Similar Triangles: Two Line Segments AB and CD Are Propotional To ADocument14 pagesChapter Iii: Similar Triangles: Two Line Segments AB and CD Are Propotional To ADuong QuangNo ratings yet
- 278316geometry Practice Sheet - 10 - CrwillDocument6 pages278316geometry Practice Sheet - 10 - Crwillsivejad276No ratings yet
- Trigonometry (1) WorkshtDocument2 pagesTrigonometry (1) WorkshtHugh IngramNo ratings yet
- HIS-IG - OL-P-MathB Exam Question (2hr)Document5 pagesHIS-IG - OL-P-MathB Exam Question (2hr)cinna morollNo ratings yet
- W s-6 Thales TheoremDocument3 pagesW s-6 Thales Theoremapi-253679034No ratings yet
- (S3) Test-Midterm 20230315Document10 pages(S3) Test-Midterm 20230315gurnoorkaur sandhuNo ratings yet
- d10 - 2022 EM Year 3 EOY - Congruency and Similarity - Revision PDFDocument13 pagesd10 - 2022 EM Year 3 EOY - Congruency and Similarity - Revision PDFWilliamNo ratings yet
- 6.triangles MCQsDocument7 pages6.triangles MCQsAnubhav KattnaNo ratings yet
- Math ChapterDocument6 pagesMath ChapterRavi AutiNo ratings yet
- Adv Ex 07 Trigonometry II (Application)Document12 pagesAdv Ex 07 Trigonometry II (Application)Leroy ChengNo ratings yet
- GCSE H3 02g4 02 3D TrigonometryDocument2 pagesGCSE H3 02g4 02 3D TrigonometryAndrei StanescuNo ratings yet
- Construction Past PapersDocument2 pagesConstruction Past PapersTaniel JallaiNo ratings yet
- Complete Geometry Class 3 Circle and Quadrilateral SSC Special BatchDocument15 pagesComplete Geometry Class 3 Circle and Quadrilateral SSC Special BatchMohit1 Mj1No ratings yet
- Geometrical Construction 9Document6 pagesGeometrical Construction 9Darwin ManoNo ratings yet
- Angle Properties of Circles QDocument7 pagesAngle Properties of Circles Qjulius muiruriNo ratings yet
- Centers of Triangle (Printable)Document14 pagesCenters of Triangle (Printable)sudhansu singhNo ratings yet
- F.iv Home Package DecemberDocument3 pagesF.iv Home Package Decemberelvingodfrey8No ratings yet
- ملزمة اسئلة شاملة على Geometry للصف الاول الثانوى اللغات الترم الاول-الامتحان التعليمىDocument6 pagesملزمة اسئلة شاملة على Geometry للصف الاول الثانوى اللغات الترم الاول-الامتحان التعليمىMaths And Technology Aladdin FathiNo ratings yet
- TriangleDocument36 pagesTrianglewisdomacademyapp1No ratings yet
- Sec3 TrigonometryDocument10 pagesSec3 TrigonometryCharles PeterNo ratings yet
- Topic - 9 Similarity and CongruencyDocument9 pagesTopic - 9 Similarity and CongruencyJorifNo ratings yet
- Allen: Pre-Nurture CourseDocument2 pagesAllen: Pre-Nurture CourseAshrithNo ratings yet
- Right Angled Triangle Trigonometry 2 IB Math SLDocument4 pagesRight Angled Triangle Trigonometry 2 IB Math SLFransiska KNo ratings yet
- KS Papers 2010 - Maths BDocument4 pagesKS Papers 2010 - Maths BakashNo ratings yet
- Tareas Sec G5 S3Document2 pagesTareas Sec G5 S3JoEl Perez0% (1)
- Similarity and Congruence Summary : AB PQ PR QRDocument9 pagesSimilarity and Congruence Summary : AB PQ PR QRkaziba stephenNo ratings yet
- RS Aggarwal Class 9 Solutions Chapter-13 Geometrical ConstructionsDocument6 pagesRS Aggarwal Class 9 Solutions Chapter-13 Geometrical Constructionsrahulkashyapr9999No ratings yet
- AMATH Solution of TriangleDocument12 pagesAMATH Solution of TriangleLeneNo ratings yet
- 3 DimensionsDocument12 pages3 DimensionsFauziah SallehNo ratings yet
- C-9 Math PNCF Race CbseDocument66 pagesC-9 Math PNCF Race CbsePranoy MazumdarNo ratings yet
- Prmo Daily Practice Problems: Sub.: Mathematics DPP: 14Document19 pagesPrmo Daily Practice Problems: Sub.: Mathematics DPP: 14sudhir singh100% (3)
- MATHS - 12th MAY TRIANGLES - AssignmentDocument4 pagesMATHS - 12th MAY TRIANGLES - AssignmentSai KrithikNo ratings yet
- Geometry 123Document4 pagesGeometry 123vinayhedaoo28No ratings yet
- Jeep 206Document18 pagesJeep 206Arun KumarvermaNo ratings yet
- Semana 2 Tema: Congruencia de Triángulos: GeometríaDocument5 pagesSemana 2 Tema: Congruencia de Triángulos: GeometríaAntonny GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Solutions of Triangles and Its Applications: Section ADocument3 pagesSolutions of Triangles and Its Applications: Section AkkakilaiNo ratings yet
- Math P2 N2000Document10 pagesMath P2 N2000ntandosithole923No ratings yet
- Worksheet 12 Analytical Geometry Grade 10 MathematicsDocument2 pagesWorksheet 12 Analytical Geometry Grade 10 Mathematicsreyneke.monyaNo ratings yet
- 2016-2019 Paper 2 Revision PDFDocument140 pages2016-2019 Paper 2 Revision PDFslap bwoy100% (1)
- Midpoint of A Line PDFDocument3 pagesMidpoint of A Line PDFR NovNo ratings yet
- Sim 3D TRANSFORMATIONS FinalDocument22 pagesSim 3D TRANSFORMATIONS FinalVaishakh SasikumarNo ratings yet
- 1.9. Composition of TransformationsDocument10 pages1.9. Composition of TransformationsAngus TeeNo ratings yet
- GeometryDocument9 pagesGeometryleolong34No ratings yet
- Module-2 Fill Area Primitives, 2D Geometric Transformations and 2D ViewingDocument54 pagesModule-2 Fill Area Primitives, 2D Geometric Transformations and 2D ViewingShain SethiNo ratings yet
- 7.1 Polygon Formulas: Mental Floss: Mon, Jan 8Document4 pages7.1 Polygon Formulas: Mental Floss: Mon, Jan 8Jhon Lou Raña ManuelNo ratings yet
- 3D Geometric Transformation: CGVR - Korea.ac - KRDocument26 pages3D Geometric Transformation: CGVR - Korea.ac - KRPraveen SharmaNo ratings yet
- 2D TransformationsDocument56 pages2D Transformationsguptatulsi31No ratings yet
- 16 6 Solving Sss TrianglesDocument5 pages16 6 Solving Sss Trianglesapi-299265916No ratings yet
- Activity 32 - Omitted Measurement For Adjoining Courses (Case 1)Document13 pagesActivity 32 - Omitted Measurement For Adjoining Courses (Case 1)John Angelo CompetenteNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10: Solution of TrianglesDocument4 pagesChapter 10: Solution of TrianglesHayati Aini AhmadNo ratings yet
- Intro To TrigonometryDocument4 pagesIntro To TrigonometrySanjayNo ratings yet
- Ramon Teves Pastor Memorial - Dumaguete Science High School: Prepared By: Miss Kassandra VenzueloDocument11 pagesRamon Teves Pastor Memorial - Dumaguete Science High School: Prepared By: Miss Kassandra Venzuelomarjun catanNo ratings yet
- Law of Sines and CosinesDocument21 pagesLaw of Sines and CosinesAnthony CaputolNo ratings yet
- Affine TransformationDocument4 pagesAffine Transformationcircleteam123No ratings yet
- Determining Angle VisuallyDocument2 pagesDetermining Angle Visuallyapi-263867215No ratings yet
- Naming of PolygonsDocument46 pagesNaming of PolygonsCharlie RiveraNo ratings yet
- Corbett Maths Angles PolygonsDocument4 pagesCorbett Maths Angles PolygonskdebipershadNo ratings yet
- PolygonsDocument46 pagesPolygonsERIC VALLENo ratings yet
- CAT 2009 Quant QuestionsDocument3 pagesCAT 2009 Quant QuestionscomploreNo ratings yet
- 8M03 Understanding Quadrilaterals (v1)Document3 pages8M03 Understanding Quadrilaterals (v1)neomatrix70No ratings yet
- Topic 3 Regular and Semi-Regular SolidsDocument12 pagesTopic 3 Regular and Semi-Regular SolidsAngieLeeNo ratings yet
- Finding Angles by Degrees StudentDocument1 pageFinding Angles by Degrees StudentDarwin Vasquez OrocioNo ratings yet
- Homogeneous TransformDocument12 pagesHomogeneous TransformAnonymous G9t3IVfL4JNo ratings yet
- hw3 SolDocument4 pageshw3 Solkalaputra100% (1)
- 3rd Quarter Exam - MATH 7Document3 pages3rd Quarter Exam - MATH 7Carlz BrianNo ratings yet
- Quadrilateral - Angles: A) Find The Measure of The Indicated Angle in Each QuadrilateralDocument2 pagesQuadrilateral - Angles: A) Find The Measure of The Indicated Angle in Each QuadrilateralAngel AngiaNo ratings yet