Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Introduction to AI notes
Introduction to AI notes
Uploaded by
mapetir317Copyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Ai & ML - PPTDocument38 pagesAi & ML - PPTPooja100% (4)
- Edpm SbaDocument16 pagesEdpm SbaROYAL GAMING100% (1)
- Module 3 Spitting Out The HookDocument3 pagesModule 3 Spitting Out The Hookapi-538740413No ratings yet
- Class X-BookDocument16 pagesClass X-BookPratyakshNo ratings yet
- AI Chapter1 NotesDocument9 pagesAI Chapter1 NotesAlwinaNo ratings yet
- AI - Notes (Introduction To AI& AI Project Cycle)Document11 pagesAI - Notes (Introduction To AI& AI Project Cycle)Aabida Rafik ChikteNo ratings yet
- GradeX Introduction To AIDocument5 pagesGradeX Introduction To AIshreyasgupta118No ratings yet
- Artificial Intelligence Class 10 Questions and AnswersDocument10 pagesArtificial Intelligence Class 10 Questions and AnswersPrathik Raj PNo ratings yet
- Ch-1 An Introduction To AI - Part2Document14 pagesCh-1 An Introduction To AI - Part2ritukakugandhiNo ratings yet
- UT 1 Intro To AI Class 10Document54 pagesUT 1 Intro To AI Class 10pratheeshNo ratings yet
- Unit 3-Basics of AIDocument7 pagesUnit 3-Basics of AIvanshika raiNo ratings yet
- Assignmet Pre Final Application Dev Emerging TechDocument2 pagesAssignmet Pre Final Application Dev Emerging Techpia espanilloNo ratings yet
- Artificial Intelligence and SecurityDocument12 pagesArtificial Intelligence and SecurityHiffsah NaikNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - Artificial Intelligence (AI)Document101 pagesChapter 3 - Artificial Intelligence (AI)Sam ContactNo ratings yet
- Artificial IntelligenceDocument13 pagesArtificial Intelligenceheyimchad28No ratings yet
- AI ImportantDocument20 pagesAI ImportantVikash Ku VickyNo ratings yet
- artificial-intelligence-questionsDocument12 pagesartificial-intelligence-questionsJeronimoNo ratings yet
- What Is Artificial IntelligenceDocument14 pagesWhat Is Artificial IntelligenceBeanka PaulNo ratings yet
- Introduction of Artificial IntelligenceDocument38 pagesIntroduction of Artificial IntelligenceKISHAN MALAVIYANo ratings yet
- Ict PresentationDocument22 pagesIct Presentationadilattique859No ratings yet
- Compte Rendu Partie 1Document19 pagesCompte Rendu Partie 1Soufyane AyanouzNo ratings yet
- Basics of Artificial Intelligence (AI)Document2 pagesBasics of Artificial Intelligence (AI)siddhg09No ratings yet
- Artificial Intelligence ArticleDocument6 pagesArtificial Intelligence Articlekhadija ait elimamNo ratings yet
- Artifical Intelligence (10. Gopika Rawte 8B)Document14 pagesArtifical Intelligence (10. Gopika Rawte 8B)Gopika RawteNo ratings yet
- Emerging To Technology Group 6 Assignment by DaniDocument5 pagesEmerging To Technology Group 6 Assignment by DaniDaniel KasayeNo ratings yet
- Introduction To AiDocument12 pagesIntroduction To Aivanshika rajNo ratings yet
- Unit 1aimlDocument21 pagesUnit 1aimlworriedaboutcarrierandfutureNo ratings yet
- Artificial Intelligence NotesDocument66 pagesArtificial Intelligence NotesfacebookdotcomNo ratings yet
- What Is Artificial Intelligence?: Last Updated: 19 Mar, 2024Document14 pagesWhat Is Artificial Intelligence?: Last Updated: 19 Mar, 2024workspace626100% (1)
- Ai MLDocument25 pagesAi MLOuis SãłNo ratings yet
- OFTW#2 - Emerging Technologies Artificial Intelligence (AI)Document8 pagesOFTW#2 - Emerging Technologies Artificial Intelligence (AI)depapcatNo ratings yet
- OFTW#2 - Emerging Technologies Artificial Intelligence (AI)Document8 pagesOFTW#2 - Emerging Technologies Artificial Intelligence (AI)depapcatNo ratings yet
- Module 2 Section 5 AIDocument9 pagesModule 2 Section 5 AIElla MontefalcoNo ratings yet
- Artificial Intelligence NotesDocument20 pagesArtificial Intelligence Notesvisheshjha112No ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document13 pagesChapter 3Jiru AlemayehuNo ratings yet
- Introduction to Artificial IntelligenceDocument4 pagesIntroduction to Artificial Intelligencesiddhg09No ratings yet
- PdfScanner 1664335281137Document52 pagesPdfScanner 1664335281137Sohel MullaNo ratings yet
- CLASS-9 ch-1Document3 pagesCLASS-9 ch-1Asdfgh HjklNo ratings yet
- AI (Artificial Intelligence) : Expert Systems Speech Recognition Machine VisionDocument9 pagesAI (Artificial Intelligence) : Expert Systems Speech Recognition Machine VisionRasel moreNo ratings yet
- Grade Ix Artificial Intelligence Chapter-1 Question BankDocument5 pagesGrade Ix Artificial Intelligence Chapter-1 Question BankFree FireNo ratings yet
- Resume About AIDocument2 pagesResume About AIDavi Lucas Lima SousaNo ratings yet
- Artificial IntelligenceDocument6 pagesArtificial IntelligenceEesha Mushtaq 1422-FMS/BBAIT/S20No ratings yet
- Ch-1 Introduction To Artificial IntelligenceDocument20 pagesCh-1 Introduction To Artificial IntelligenceManish SaraswatNo ratings yet
- Arjun Reds Assignment 2Document7 pagesArjun Reds Assignment 2Danny DanNo ratings yet
- Artifical Intelligence Class 10thDocument193 pagesArtifical Intelligence Class 10thrajbirsinghgill002No ratings yet
- Cbse - Department of Skill Education Artificial IntelligenceDocument9 pagesCbse - Department of Skill Education Artificial IntelligenceHaresh NathaniNo ratings yet
- AI StudyMaterialDocument52 pagesAI StudyMaterialsejalsonimishraNo ratings yet
- Unit 1Document21 pagesUnit 1shreya kharolaNo ratings yet
- CC 13 Unit 1Document12 pagesCC 13 Unit 1Priyaranjan SorenNo ratings yet
- Report 1Document5 pagesReport 1harith12342461No ratings yet
- Artificial IntelligenceDocument2 pagesArtificial IntelligenceDhenn Valmonte SindolNo ratings yet
- Ai 1Document35 pagesAi 1Sayantan MajhiNo ratings yet
- AI-ML EditedDocument12 pagesAI-ML Editedalum jacob100% (1)
- Introduction To Artificial IntelligenceDocument12 pagesIntroduction To Artificial IntelligenceNeha MakhijaNo ratings yet
- Emerged TechnologiesDocument6 pagesEmerged TechnologiesDarek HaileNo ratings yet
- cs8691-AI - 1st-UnitDocument38 pagescs8691-AI - 1st-Unit4011 DHANU SHREE RNo ratings yet
- Final AIDocument37 pagesFinal AIdarteerrNo ratings yet
- Artificial IntelligenceDocument49 pagesArtificial IntelligenceKristopher France PunioNo ratings yet
- Artificial IntelligenceDocument10 pagesArtificial IntelligenceRo TechnologiesNo ratings yet
- Artificial Intelligence: How Machine Learning, Robotics, and Automation Have Shaped Our SocietyFrom EverandArtificial Intelligence: How Machine Learning, Robotics, and Automation Have Shaped Our SocietyRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (4)
- Ks2 NC Reading Progress ReportDocument5 pagesKs2 NC Reading Progress ReportCyndee PamintuanNo ratings yet
- 2.7 2012 Influence of Implant Neck Design and Implant-Abutment Connection Type On Peri-Implant Health. Radiological StudyDocument9 pages2.7 2012 Influence of Implant Neck Design and Implant-Abutment Connection Type On Peri-Implant Health. Radiological StudyDuilioJrNo ratings yet
- Tomlinson - What Was The Third WorldDocument16 pagesTomlinson - What Was The Third WorldMaría Camila Valbuena LondoñoNo ratings yet
- Mod 11.9Document55 pagesMod 11.9trcabhijeet123No ratings yet
- Being Aware of Being AwareDocument12 pagesBeing Aware of Being AwareChanchal LNo ratings yet
- Cttplus HandbookDocument36 pagesCttplus HandbookgcarreongNo ratings yet
- Jabem Bible Papua New GuineaDocument1,848 pagesJabem Bible Papua New GuineaAsia BiblesNo ratings yet
- Oyster Mushroom Cultivation - Ralph H. Kurtzman, JRDocument86 pagesOyster Mushroom Cultivation - Ralph H. Kurtzman, JRCaptn100% (2)
- RectiDocument7 pagesRectiaskj78100% (1)
- Instrumentation and Control of Heat ExchangerDocument29 pagesInstrumentation and Control of Heat Exchangerpra578No ratings yet
- CDA ResumewithFolioDocument25 pagesCDA ResumewithFoliocdabandoNo ratings yet
- 4 Process - Analysis - Practice - Problem - SolutionsDocument7 pages4 Process - Analysis - Practice - Problem - SolutionsHEMANT KUMARNo ratings yet
- 1st Year Exam (Re-Exam) 1. Årsprøve (Reeksamen) : August 2021Document14 pages1st Year Exam (Re-Exam) 1. Årsprøve (Reeksamen) : August 2021SafridNo ratings yet
- Preventing Maintaince Procedure Froklift HanlerDocument2 pagesPreventing Maintaince Procedure Froklift HanlerAli AlahmaNo ratings yet
- Scissor - Platform - Hidral - Tech SpecificationsDocument10 pagesScissor - Platform - Hidral - Tech SpecificationsSajidNo ratings yet
- Otis Software Basic DataDocument23 pagesOtis Software Basic Datanr1wolf_co_6952990682% (17)
- J4500 Basic Electrical Schematics (Epa2017, Gen V) W/Parker VMM, Effective With Unit 68229Document91 pagesJ4500 Basic Electrical Schematics (Epa2017, Gen V) W/Parker VMM, Effective With Unit 68229HamiltonNo ratings yet
- SMK Bandaraya Kota Kinabalu English Language Lesson Plan: MondayDocument6 pagesSMK Bandaraya Kota Kinabalu English Language Lesson Plan: MondaySITI NORZUANI BINTI BAHARUDDIN MoeNo ratings yet
- Chafi2009Document7 pagesChafi2009radhakrishnanNo ratings yet
- Suitcase X-Treme 12Vs: Ce and Non-Ce ModelsDocument44 pagesSuitcase X-Treme 12Vs: Ce and Non-Ce ModelsBaskoro PMCKNo ratings yet
- TPHA Conference Paper - Kasongi 2022Document15 pagesTPHA Conference Paper - Kasongi 2022Donald KasongiNo ratings yet
- The Effects of Fuel Dilution With Biodiesel On Lubricant Acidity, Oxidation and Corrosion - A Study With CJ-4 and CI-4 PLUS LubricantsDocument21 pagesThe Effects of Fuel Dilution With Biodiesel On Lubricant Acidity, Oxidation and Corrosion - A Study With CJ-4 and CI-4 PLUS Lubricantsgilar herliana putraNo ratings yet
- The Physical Layer of The IEEE 802.11p WAVEDocument8 pagesThe Physical Layer of The IEEE 802.11p WAVEZeeshan ShafiqNo ratings yet
- Ansys Fluent Brings CFD Performance With Intel Processors and FabricsDocument8 pagesAnsys Fluent Brings CFD Performance With Intel Processors and FabricsSaid FerdjallahNo ratings yet
- Preguntas Itil v3Document91 pagesPreguntas Itil v3Leo Duran TNo ratings yet
- The Importance of Reading To Expand KnowledgeDocument8 pagesThe Importance of Reading To Expand KnowledgeAnindhita NabilahNo ratings yet
- Indotech Power Transformers BrochureDocument2 pagesIndotech Power Transformers BrochurenmanjNo ratings yet
- The Genesis Project PDFDocument19 pagesThe Genesis Project PDFvikas kansalNo ratings yet
- 4robbins Mgmt15 PPT 02-Updated3Document46 pages4robbins Mgmt15 PPT 02-Updated3SanaaAbdelganyNo ratings yet
Introduction to AI notes
Introduction to AI notes
Uploaded by
mapetir317Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Introduction to AI notes
Introduction to AI notes
Uploaded by
mapetir317Copyright:
Available Formats
Introduction to AI: Foundational Concepts
01. What is Intelligence?
Ans: Intelligence is the ‘ability to perceive or infer information, and to retain it as knowledge to be applied towards
adaptive behaviors within an environment or context.’
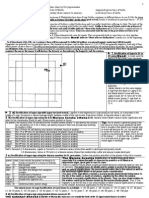
02. Types of Intelligence
Ans:
03. What is Artificial Intelligence?
Ans: When a machine possesses the ability to mimic human traits, i.e., make decisions, predict the future, learn and
improve on its own, it is said to have artificial intelligence. machines also become intelligent once they are trained with
some information which helps them achieve their tasks. AI machines also keep updating their knowledge to optimize
their output.
04. Applications of Artificial Intelligence around us
Ans: 01. Google 02. Hey Siri 03. Google Maps 04. FIFA 05. Amazon 06. Social
Websites (Facebook and Instagram) 07. Chatbots
05. What is not AI?
Ans: 01. A fully automatic washing machine can work on its own, but it requires human intervention
02. An air conditioner can be turned on and off remotely with the help of internet but still needs a human touch. This is
an example of Internet of Things (IoT).
03. A TV does not become AI-enabled if it is a smart one, it gets the power of AI when it is able to think and process on
its own.
Basics of AI
AI, ML & DL
01. Artificial Intelligence (AI): Refers to any technique that enables computers to mimic human intelligence. It gives the
ability to machines to recognize a human’s face; to move and manipulate objects; to understand the voice commands by
humans, and also do other tasks. The AI-enabled machines think algorithmically and execute what they have been asked
for intelligently.
02. Machine Learning (ML)
It is a subset of Artificial Intelligence which enables machines to improve at tasks with experience (data). The intention
of Machine Learning is to enable machines to learn by themselves using the provided data and make accurate
Predictions/ Decisions
03. Deep Learning (DL)
It enables software to train itself to perform tasks with vast amounts of data. In Deep Learning, the machine is trained
with huge amounts of data which helps it in training itself around the data. Such machines are intelligent enough to
develop algorithms for themselves. Deep Learning is the most advanced form of Artificial Intelligence out of these three.
Introduction to AI Domains
AI models can be broadly categorized into three domains:
Data Sciences :
Data sciences is a domain of AI related to data systems and processes, in which the system collects numerous data,
maintains data sets and derives meaning/sense out of them. The information extracted through data science can be
used to make a decision about it.
Example of Data Science: Price Comparison Websites
Computer Vision :
Computer Vision, abbreviated as CV, is a domain of AI that depicts the capability of a machine to get and analyze visual
information and afterwards predict some decisions about it. The entire process involves image acquiring, screening,
analyzing, identifying and extracting information.
Examples of Computer Vision:
01. Self-Driving cars/ Automatic Cars
02. Face Lock in Smartphones
Natural Language Processing:
Natural Language Processing, abbreviated as NLP, is a branch of artificial intelligence that deals with the interaction
between computers and humans using the natural language. Natural language refers to language that is spoken and
written by people, and natural language processing (NLP) attempts to extract information from the spoken and written
word using algorithms.
Examples of Natural Language Processing:
01. Email filters
02. Smart assistants
AI Ethics
we need to keep aspects relating to ethical practices in mind while developing solutions using AI.
Data Privacy: The world of Artificial Intelligence revolves around Data. Every company whether small or big is mining
data from as many sources as possible. Data is the new gold. One of the major sources of data for many major
companies is the device which all of us have in our hands all the time: Smartphones.
AI Bias : Another aspect to AI Ethics is bias. Everyone has a bias of their own no matter how much one tries to be
unbiased, we in some way or the other have our own biases even towards smaller things. Biases are not negative all the
time. Sometimes, it is required to have a bias to control a situation and keep things working.
Examples: 01. virtual assistants came into practice, female voices are always preferred for them over any other voice.
02. If you search on Google for salons, the first few searches are mostly for female salons. This is based on the
assumption that if a person is searching for a salon, in all probability it would be a female.
AI Access: Since Artificial Intelligence is still a budding technology, not everyone has the opportunity to access it. The
people who can afford AI enabled devices make the most of it while others who cannot are left behind. Because of this,
a gap has emerged between these two classes of people and it gets widened with the rapid advancement of technology.
AI creates unemployment : AI is making people’s lives easier. Most of the things nowadays are done in just a few clicks.
In no time AI will manage to be able to do all the laborious tasks which we humans have been doing since long.
AI for kids : kids nowadays are smart enough to understand technology from a very early age. As their thinking
capabilities increase, they start becoming techno-savvy and eventually they learn everything more easily than an adult.
But should technology be given to children so young?
A young boy in class 3 has got some Maths homework to finish. He is sitting at a table which has the Google chat bot -
Alexa on it, and he is struggling with his homework. Soon, he starts asking Alexa to answer all his questions. Alexa replies
with answers and the boy simply writes them down in his notebook.
You might also like
- Ai & ML - PPTDocument38 pagesAi & ML - PPTPooja100% (4)
- Edpm SbaDocument16 pagesEdpm SbaROYAL GAMING100% (1)
- Module 3 Spitting Out The HookDocument3 pagesModule 3 Spitting Out The Hookapi-538740413No ratings yet
- Class X-BookDocument16 pagesClass X-BookPratyakshNo ratings yet
- AI Chapter1 NotesDocument9 pagesAI Chapter1 NotesAlwinaNo ratings yet
- AI - Notes (Introduction To AI& AI Project Cycle)Document11 pagesAI - Notes (Introduction To AI& AI Project Cycle)Aabida Rafik ChikteNo ratings yet
- GradeX Introduction To AIDocument5 pagesGradeX Introduction To AIshreyasgupta118No ratings yet
- Artificial Intelligence Class 10 Questions and AnswersDocument10 pagesArtificial Intelligence Class 10 Questions and AnswersPrathik Raj PNo ratings yet
- Ch-1 An Introduction To AI - Part2Document14 pagesCh-1 An Introduction To AI - Part2ritukakugandhiNo ratings yet
- UT 1 Intro To AI Class 10Document54 pagesUT 1 Intro To AI Class 10pratheeshNo ratings yet
- Unit 3-Basics of AIDocument7 pagesUnit 3-Basics of AIvanshika raiNo ratings yet
- Assignmet Pre Final Application Dev Emerging TechDocument2 pagesAssignmet Pre Final Application Dev Emerging Techpia espanilloNo ratings yet
- Artificial Intelligence and SecurityDocument12 pagesArtificial Intelligence and SecurityHiffsah NaikNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - Artificial Intelligence (AI)Document101 pagesChapter 3 - Artificial Intelligence (AI)Sam ContactNo ratings yet
- Artificial IntelligenceDocument13 pagesArtificial Intelligenceheyimchad28No ratings yet
- AI ImportantDocument20 pagesAI ImportantVikash Ku VickyNo ratings yet
- artificial-intelligence-questionsDocument12 pagesartificial-intelligence-questionsJeronimoNo ratings yet
- What Is Artificial IntelligenceDocument14 pagesWhat Is Artificial IntelligenceBeanka PaulNo ratings yet
- Introduction of Artificial IntelligenceDocument38 pagesIntroduction of Artificial IntelligenceKISHAN MALAVIYANo ratings yet
- Ict PresentationDocument22 pagesIct Presentationadilattique859No ratings yet
- Compte Rendu Partie 1Document19 pagesCompte Rendu Partie 1Soufyane AyanouzNo ratings yet
- Basics of Artificial Intelligence (AI)Document2 pagesBasics of Artificial Intelligence (AI)siddhg09No ratings yet
- Artificial Intelligence ArticleDocument6 pagesArtificial Intelligence Articlekhadija ait elimamNo ratings yet
- Artifical Intelligence (10. Gopika Rawte 8B)Document14 pagesArtifical Intelligence (10. Gopika Rawte 8B)Gopika RawteNo ratings yet
- Emerging To Technology Group 6 Assignment by DaniDocument5 pagesEmerging To Technology Group 6 Assignment by DaniDaniel KasayeNo ratings yet
- Introduction To AiDocument12 pagesIntroduction To Aivanshika rajNo ratings yet
- Unit 1aimlDocument21 pagesUnit 1aimlworriedaboutcarrierandfutureNo ratings yet
- Artificial Intelligence NotesDocument66 pagesArtificial Intelligence NotesfacebookdotcomNo ratings yet
- What Is Artificial Intelligence?: Last Updated: 19 Mar, 2024Document14 pagesWhat Is Artificial Intelligence?: Last Updated: 19 Mar, 2024workspace626100% (1)
- Ai MLDocument25 pagesAi MLOuis SãłNo ratings yet
- OFTW#2 - Emerging Technologies Artificial Intelligence (AI)Document8 pagesOFTW#2 - Emerging Technologies Artificial Intelligence (AI)depapcatNo ratings yet
- OFTW#2 - Emerging Technologies Artificial Intelligence (AI)Document8 pagesOFTW#2 - Emerging Technologies Artificial Intelligence (AI)depapcatNo ratings yet
- Module 2 Section 5 AIDocument9 pagesModule 2 Section 5 AIElla MontefalcoNo ratings yet
- Artificial Intelligence NotesDocument20 pagesArtificial Intelligence Notesvisheshjha112No ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document13 pagesChapter 3Jiru AlemayehuNo ratings yet
- Introduction to Artificial IntelligenceDocument4 pagesIntroduction to Artificial Intelligencesiddhg09No ratings yet
- PdfScanner 1664335281137Document52 pagesPdfScanner 1664335281137Sohel MullaNo ratings yet
- CLASS-9 ch-1Document3 pagesCLASS-9 ch-1Asdfgh HjklNo ratings yet
- AI (Artificial Intelligence) : Expert Systems Speech Recognition Machine VisionDocument9 pagesAI (Artificial Intelligence) : Expert Systems Speech Recognition Machine VisionRasel moreNo ratings yet
- Grade Ix Artificial Intelligence Chapter-1 Question BankDocument5 pagesGrade Ix Artificial Intelligence Chapter-1 Question BankFree FireNo ratings yet
- Resume About AIDocument2 pagesResume About AIDavi Lucas Lima SousaNo ratings yet
- Artificial IntelligenceDocument6 pagesArtificial IntelligenceEesha Mushtaq 1422-FMS/BBAIT/S20No ratings yet
- Ch-1 Introduction To Artificial IntelligenceDocument20 pagesCh-1 Introduction To Artificial IntelligenceManish SaraswatNo ratings yet
- Arjun Reds Assignment 2Document7 pagesArjun Reds Assignment 2Danny DanNo ratings yet
- Artifical Intelligence Class 10thDocument193 pagesArtifical Intelligence Class 10thrajbirsinghgill002No ratings yet
- Cbse - Department of Skill Education Artificial IntelligenceDocument9 pagesCbse - Department of Skill Education Artificial IntelligenceHaresh NathaniNo ratings yet
- AI StudyMaterialDocument52 pagesAI StudyMaterialsejalsonimishraNo ratings yet
- Unit 1Document21 pagesUnit 1shreya kharolaNo ratings yet
- CC 13 Unit 1Document12 pagesCC 13 Unit 1Priyaranjan SorenNo ratings yet
- Report 1Document5 pagesReport 1harith12342461No ratings yet
- Artificial IntelligenceDocument2 pagesArtificial IntelligenceDhenn Valmonte SindolNo ratings yet
- Ai 1Document35 pagesAi 1Sayantan MajhiNo ratings yet
- AI-ML EditedDocument12 pagesAI-ML Editedalum jacob100% (1)
- Introduction To Artificial IntelligenceDocument12 pagesIntroduction To Artificial IntelligenceNeha MakhijaNo ratings yet
- Emerged TechnologiesDocument6 pagesEmerged TechnologiesDarek HaileNo ratings yet
- cs8691-AI - 1st-UnitDocument38 pagescs8691-AI - 1st-Unit4011 DHANU SHREE RNo ratings yet
- Final AIDocument37 pagesFinal AIdarteerrNo ratings yet
- Artificial IntelligenceDocument49 pagesArtificial IntelligenceKristopher France PunioNo ratings yet
- Artificial IntelligenceDocument10 pagesArtificial IntelligenceRo TechnologiesNo ratings yet
- Artificial Intelligence: How Machine Learning, Robotics, and Automation Have Shaped Our SocietyFrom EverandArtificial Intelligence: How Machine Learning, Robotics, and Automation Have Shaped Our SocietyRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (4)
- Ks2 NC Reading Progress ReportDocument5 pagesKs2 NC Reading Progress ReportCyndee PamintuanNo ratings yet
- 2.7 2012 Influence of Implant Neck Design and Implant-Abutment Connection Type On Peri-Implant Health. Radiological StudyDocument9 pages2.7 2012 Influence of Implant Neck Design and Implant-Abutment Connection Type On Peri-Implant Health. Radiological StudyDuilioJrNo ratings yet
- Tomlinson - What Was The Third WorldDocument16 pagesTomlinson - What Was The Third WorldMaría Camila Valbuena LondoñoNo ratings yet
- Mod 11.9Document55 pagesMod 11.9trcabhijeet123No ratings yet
- Being Aware of Being AwareDocument12 pagesBeing Aware of Being AwareChanchal LNo ratings yet
- Cttplus HandbookDocument36 pagesCttplus HandbookgcarreongNo ratings yet
- Jabem Bible Papua New GuineaDocument1,848 pagesJabem Bible Papua New GuineaAsia BiblesNo ratings yet
- Oyster Mushroom Cultivation - Ralph H. Kurtzman, JRDocument86 pagesOyster Mushroom Cultivation - Ralph H. Kurtzman, JRCaptn100% (2)
- RectiDocument7 pagesRectiaskj78100% (1)
- Instrumentation and Control of Heat ExchangerDocument29 pagesInstrumentation and Control of Heat Exchangerpra578No ratings yet
- CDA ResumewithFolioDocument25 pagesCDA ResumewithFoliocdabandoNo ratings yet
- 4 Process - Analysis - Practice - Problem - SolutionsDocument7 pages4 Process - Analysis - Practice - Problem - SolutionsHEMANT KUMARNo ratings yet
- 1st Year Exam (Re-Exam) 1. Årsprøve (Reeksamen) : August 2021Document14 pages1st Year Exam (Re-Exam) 1. Årsprøve (Reeksamen) : August 2021SafridNo ratings yet
- Preventing Maintaince Procedure Froklift HanlerDocument2 pagesPreventing Maintaince Procedure Froklift HanlerAli AlahmaNo ratings yet
- Scissor - Platform - Hidral - Tech SpecificationsDocument10 pagesScissor - Platform - Hidral - Tech SpecificationsSajidNo ratings yet
- Otis Software Basic DataDocument23 pagesOtis Software Basic Datanr1wolf_co_6952990682% (17)
- J4500 Basic Electrical Schematics (Epa2017, Gen V) W/Parker VMM, Effective With Unit 68229Document91 pagesJ4500 Basic Electrical Schematics (Epa2017, Gen V) W/Parker VMM, Effective With Unit 68229HamiltonNo ratings yet
- SMK Bandaraya Kota Kinabalu English Language Lesson Plan: MondayDocument6 pagesSMK Bandaraya Kota Kinabalu English Language Lesson Plan: MondaySITI NORZUANI BINTI BAHARUDDIN MoeNo ratings yet
- Chafi2009Document7 pagesChafi2009radhakrishnanNo ratings yet
- Suitcase X-Treme 12Vs: Ce and Non-Ce ModelsDocument44 pagesSuitcase X-Treme 12Vs: Ce and Non-Ce ModelsBaskoro PMCKNo ratings yet
- TPHA Conference Paper - Kasongi 2022Document15 pagesTPHA Conference Paper - Kasongi 2022Donald KasongiNo ratings yet
- The Effects of Fuel Dilution With Biodiesel On Lubricant Acidity, Oxidation and Corrosion - A Study With CJ-4 and CI-4 PLUS LubricantsDocument21 pagesThe Effects of Fuel Dilution With Biodiesel On Lubricant Acidity, Oxidation and Corrosion - A Study With CJ-4 and CI-4 PLUS Lubricantsgilar herliana putraNo ratings yet
- The Physical Layer of The IEEE 802.11p WAVEDocument8 pagesThe Physical Layer of The IEEE 802.11p WAVEZeeshan ShafiqNo ratings yet
- Ansys Fluent Brings CFD Performance With Intel Processors and FabricsDocument8 pagesAnsys Fluent Brings CFD Performance With Intel Processors and FabricsSaid FerdjallahNo ratings yet
- Preguntas Itil v3Document91 pagesPreguntas Itil v3Leo Duran TNo ratings yet
- The Importance of Reading To Expand KnowledgeDocument8 pagesThe Importance of Reading To Expand KnowledgeAnindhita NabilahNo ratings yet
- Indotech Power Transformers BrochureDocument2 pagesIndotech Power Transformers BrochurenmanjNo ratings yet
- The Genesis Project PDFDocument19 pagesThe Genesis Project PDFvikas kansalNo ratings yet
- 4robbins Mgmt15 PPT 02-Updated3Document46 pages4robbins Mgmt15 PPT 02-Updated3SanaaAbdelganyNo ratings yet