Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Computer MEMORY (1)
Computer MEMORY (1)
Uploaded by
dannycage254Copyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Cohesity Oracle RMAN Solution GuideDocument22 pagesCohesity Oracle RMAN Solution GuidejoneberNo ratings yet
- Company Profile Sample PDFDocument17 pagesCompany Profile Sample PDFSan Lizas Airen100% (2)
- F MemoryDocument17 pagesF MemoryMahrukh FidaNo ratings yet
- H MemoryDocument10 pagesH MemoryPooja Singh SolankiNo ratings yet
- H MemoryDocument10 pagesH MemoryjaybharathNo ratings yet
- H MemoryDocument12 pagesH MemoryRuchi SharmaNo ratings yet
- Ram Rom MemoryDocument8 pagesRam Rom MemorySohit ThapaNo ratings yet
- Computer Memory: Rovelito I. NavarraDocument26 pagesComputer Memory: Rovelito I. NavarraCelestial Manikan Cangayda-AndradaNo ratings yet
- Primary MemoryDocument20 pagesPrimary MemoryAayushmanNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4 Day 5 - Main Memory - PPSXDocument25 pagesLecture 4 Day 5 - Main Memory - PPSXBindu Devender MahajanNo ratings yet
- Sreememory 151216145054Document23 pagesSreememory 151216145054Herwin CapiñanesNo ratings yet
- Memory: Information System (3) Computer Maintenance and Technical SupportDocument48 pagesMemory: Information System (3) Computer Maintenance and Technical SupportChala BojaNo ratings yet
- Computers MemoryDocument26 pagesComputers MemoryRandyNo ratings yet
- MemoryDocument14 pagesMemoryDipesh SAPKOTANo ratings yet
- Memory HierarchyDocument20 pagesMemory HierarchySailash RanaNo ratings yet
- "Memory": College of Information Technology and Engineering Notre Dame of Midsayap CollegeDocument21 pages"Memory": College of Information Technology and Engineering Notre Dame of Midsayap CollegeLeo HiddenValleyNo ratings yet
- Internal Memory Ch1Document26 pagesInternal Memory Ch1shanbel ayayuNo ratings yet
- Ram and RomDocument13 pagesRam and RomJSD190No ratings yet
- Puter MemoryDocument28 pagesPuter MemoryMDSR AKRAMNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Memory OrganizationDocument23 pagesChapter 2 Memory OrganizationChe AisarNo ratings yet
- Lecture 6Document36 pagesLecture 6Anas SheikhNo ratings yet
- Puter MemoryDocument15 pagesPuter MemorySaima Binte IkramNo ratings yet
- CAODocument65 pagesCAOPriya SinghNo ratings yet
- ch01 2-Memory HierarchyDocument16 pagesch01 2-Memory Hierarchytabkhat.3alsari3No ratings yet
- Memory TypesDocument17 pagesMemory TypesMitul Modi100% (2)
- 04 - Cache Memoryfinal 04Document29 pages04 - Cache Memoryfinal 04vianneloroNo ratings yet
- Semiconductor MemoriesDocument63 pagesSemiconductor MemoriesNayanjyot SinghNo ratings yet
- Primary Memory FinalDocument24 pagesPrimary Memory FinalRavikiranSharmaSrkNo ratings yet
- Memor y and Storage DeviceDocument50 pagesMemor y and Storage DevicesolomongebreamanuelNo ratings yet
- Lecture 02 - Memory OrganizationDocument22 pagesLecture 02 - Memory OrganizationSandeep SahaNo ratings yet
- Computer MemoryDocument23 pagesComputer MemoryAleeza gondalNo ratings yet
- Rakesh Reddy K (CO)Document10 pagesRakesh Reddy K (CO)Rakesh ReddyNo ratings yet
- Types of Memory Their UsesDocument12 pagesTypes of Memory Their UsesAtul KashyapNo ratings yet
- Group Members: Karnail Katoch Vishal Mahant Archana Kahrinar Mohammad Pisavadi Kashyap BaradDocument55 pagesGroup Members: Karnail Katoch Vishal Mahant Archana Kahrinar Mohammad Pisavadi Kashyap BaradpRiNcE DuDhAtRaNo ratings yet
- Different Types of MemoryDocument26 pagesDifferent Types of MemorySayani Chandra100% (1)
- CMTS Handout 4Document6 pagesCMTS Handout 4Tolosa TafeseNo ratings yet
- Computer MemoryDocument16 pagesComputer MemoryAjay KumarNo ratings yet
- CSC113 AssignmentDocument3 pagesCSC113 AssignmentAlphus DavidNo ratings yet
- Performing Mensuration Q3Document10 pagesPerforming Mensuration Q3Janice Agbuya TamondongNo ratings yet
- Comuter Science Lec 1,2Document19 pagesComuter Science Lec 1,2Kareem AdelNo ratings yet
- Memory DevicesDocument20 pagesMemory DevicesMD AZIZUL HOQUENo ratings yet
- MemoryDocument10 pagesMemorynet_friend05No ratings yet
- organization_Unit 5 _CODocument62 pagesorganization_Unit 5 _COAkash RajNo ratings yet
- RANDOM ACCESS MemoryDocument13 pagesRANDOM ACCESS Memoryfraolhailu6No ratings yet
- Chapter 2 COM101Document5 pagesChapter 2 COM101Christean Val Bayani ValezaNo ratings yet
- Co2 Ppt-Part2Document38 pagesCo2 Ppt-Part2Pradeep TataNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 - Memory OrganizationDocument35 pagesChapter 4 - Memory OrganizationDawit TekesteNo ratings yet
- Computer PresentationDocument14 pagesComputer PresentationAayush Niroula OfficialNo ratings yet
- MemoryDocument42 pagesMemoryDINESH RAWATNo ratings yet
- Computer MemoryDocument28 pagesComputer MemoryAngelica BaborNo ratings yet
- Memory Organization 666-41-13Document23 pagesMemory Organization 666-41-13mr xyzNo ratings yet
- Computer MemoryDocument5 pagesComputer MemorySisbiNo ratings yet
- Memory UnitDocument11 pagesMemory Unitanuskar.sigdel.34No ratings yet
- Memory OrganizationDocument70 pagesMemory OrganizationrahqansayeedNo ratings yet
- Logical Memory OrganisationDocument20 pagesLogical Memory OrganisationArchana SonawaneNo ratings yet
- RAM ROM Cache Memory RegistersDocument32 pagesRAM ROM Cache Memory Registersnagara hyoukaNo ratings yet
- Ram RomDocument42 pagesRam Rommohit mishraNo ratings yet
- Co2 Ppt-Part2Document38 pagesCo2 Ppt-Part2SWAMI AYYAPPANo ratings yet
- Unit 2Document15 pagesUnit 2Smit AnjanaNo ratings yet
- Internal MemoryDocument22 pagesInternal MemoryAbdukadir AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 Memory OrganizationDocument104 pagesUnit 5 Memory OrganizationNarsingh Pal YadavNo ratings yet
- Computer Science: Learn about Algorithms, Cybersecurity, Databases, Operating Systems, and Web DesignFrom EverandComputer Science: Learn about Algorithms, Cybersecurity, Databases, Operating Systems, and Web DesignNo ratings yet
- Electionville-Online-Instructions A4 Eng Fa WebDocument20 pagesElectionville-Online-Instructions A4 Eng Fa Webplasticfish29No ratings yet
- Raspberry Pi Pico C SDKDocument301 pagesRaspberry Pi Pico C SDKesassu100% (1)
- Special MT103Document1 pageSpecial MT103Eller100% (1)
- ECON 141 Problem Set 4Document3 pagesECON 141 Problem Set 4dnlmsgnNo ratings yet
- Pet Et7000 Quickstart enDocument4 pagesPet Et7000 Quickstart enIlham NugrohoNo ratings yet
- What Is Big DataDocument3 pagesWhat Is Big DataBalkaran singhNo ratings yet
- 802.11 Wi-Fi Physical Layer and Transmitter MeasurementsDocument1 page802.11 Wi-Fi Physical Layer and Transmitter Measurementshitler1994No ratings yet
- 3 PDFDocument1 page3 PDFaritw541214No ratings yet
- 25 Run Commands in Windows You Should Memorize - ENDocument19 pages25 Run Commands in Windows You Should Memorize - ENStayNo ratings yet
- Control SpeedDocument4 pagesControl SpeedNghiep Hua CongNo ratings yet
- ML AlgorithmsDocument2 pagesML AlgorithmshemaNo ratings yet
- Nominal Risk Technique TemplateDocument2 pagesNominal Risk Technique Templatesubrato.malick7473No ratings yet
- Components Version Information in Recent SAP HANA Cockpit Releases PatchesDocument2 pagesComponents Version Information in Recent SAP HANA Cockpit Releases PatchesankurbamelNo ratings yet
- SAFe Implementation Roadmap 6.0 Partner 11.7x8.5Document1 pageSAFe Implementation Roadmap 6.0 Partner 11.7x8.5deartoreadbookNo ratings yet
- AAF Animation Pack Guide - BasicDocument5 pagesAAF Animation Pack Guide - BasicOscar PMNo ratings yet
- UNIT 2 Basic Operations Lesson Plans: These Are Based On 45/50 Minute Lessons. Lesson No. Suggested Plan ReferencesDocument5 pagesUNIT 2 Basic Operations Lesson Plans: These Are Based On 45/50 Minute Lessons. Lesson No. Suggested Plan ReferencesChet Jerry AckNo ratings yet
- Las Ict Csa 9 Q3 Week 1Document10 pagesLas Ict Csa 9 Q3 Week 1Karell AnnNo ratings yet
- Dynon EFIS D10A EFIS D100 Install GuideDocument34 pagesDynon EFIS D10A EFIS D100 Install Guidedkc1967No ratings yet
- Pandas - Series - Short - NotesDocument7 pagesPandas - Series - Short - NotesSantosh KumarNo ratings yet
- File Manager ProDocument8 pagesFile Manager ProFile Manager ProNo ratings yet
- Introduction To NLP 2021Document13 pagesIntroduction To NLP 2021Vũ ĐinhNo ratings yet
- High-Accuracy Real Absolute Sealed Linear Encoder For High-Speed Motion!Document2 pagesHigh-Accuracy Real Absolute Sealed Linear Encoder For High-Speed Motion!Nathan ChenNo ratings yet
- ECMAScript 6Document6 pagesECMAScript 6Albano FuttaNo ratings yet
- Lab 04Document6 pagesLab 04Muskaan ZarrinNo ratings yet
- Exploring Microsoft PowerPoint AI, Using PythonDocument16 pagesExploring Microsoft PowerPoint AI, Using Pythonferdad4realNo ratings yet
- End of Session Result SlipDocument1 pageEnd of Session Result SlipBasiru AbubakarNo ratings yet
- JBL KX180 UserManual en 092017Document16 pagesJBL KX180 UserManual en 092017loc nguyenNo ratings yet
- Powerschool Parent Portal Login InstructionsDocument1 pagePowerschool Parent Portal Login Instructionsapi-321072730No ratings yet
Computer MEMORY (1)
Computer MEMORY (1)
Uploaded by
dannycage254Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Computer MEMORY (1)
Computer MEMORY (1)
Uploaded by
dannycage254Copyright:
Available Formats
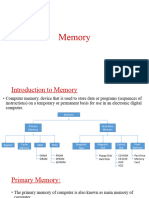
MEMORY
Refers to electronic components of the PC that store data and instructions either temporarily or in
various degrees of permanently.
Technically memory is the storage device on the computer, including the hard disk, floppy disks,
ROM, RAM and cache.
However in its more common usage, memory is the part of the computer’s hardware that is used
to hold data and instructions before and after they are passed to the CPU for analysis and
execution.
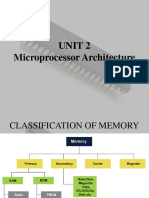
Types of main memory
There are two types of main memory, Random Access Memory (RAM) and Read Only
Memory (ROM)
Random Access Memory (RAM)
holds its data as long as the computer is switched on
All data in RAM is lost when the computer is switched off
Described as being volatile
It is direct access as it can be both written to or read from in any order
Its purpose is to temporarily hold programs and data for processing. In modern computers it also
holds the operating system.
Read only Memory ( ROM)
ROM (Read Only Memory) is used to store the instructions provided by the
manufacturer, which holds the instructions to check basic hardware
interconnecter and to load operating system from appropriate storage device
TYPES OF RAM
1. Dynamic Random Access Memory (DRAM)
• Contents are constantly refreshed 1000 times per second
• Access time 60 – 70 nanoseconds
Note: a nanosecond is one billionth of a second!
2. Synchronous Dynamic Random Access Memory (SDRAM)
• Quicker than DRAM
• Access time less than 60 nanoseconds
3. Direct Ram bus Dynamic Random Access Memory (DRDRAM)
• New type of RAM architecture
• Access time 20 times faster than DRAM
• More expensive
4. Static Random Access Memory (SRAM)
• Doesn’t need refreshing
• Retains contents as long as power applied to the chip
• Access time around 10 nanoseconds
• Used for cache memory
• Also for date and time settings as powered by small battery
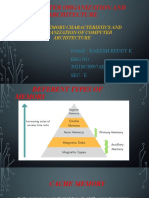
5. Cache memory
• Small amount of memory typically 256 or 512 kilobytes
• Temporary store for often used instructions
• Level 1 cache is built within the CPU (internal)
• Level 2 cache may be on chip or nearby (external)
• Faster for CPU to access than main memory
The operation of Cache memory
6. Video Random Access Memory
• Holds data to be displayed on computer screen
• Has two data paths allowing READ and WRITE to occur at the same time
• A system’s amount of VRAM relates to the no. of colors and resolution
7.Virtual Memory.
• Uses backing storage e.g. harddisk as a temporary location for programs and data where
insufficient RAM available.
• Swaps programs and data between the hard-disk and RAM as the CPU requires them for
processing
• Virtual memory is much slower than RAM
Types of Rom
• PROM ( programmable Read Only Memory) –type of ROM that can be written to by the user.
Data is held permanently once it is written.
• EPROM – (Erasable programmable Read Only Memory) – can be programmed by the user but it
can be erased. Its removed from the computer to be erased by use of EPROM erasers.
• EAPROM (Electrically Alterable Programmable Read Only Memory) – it can be read, erased
and deleted. It is erased without removing it from the computer . however the erasing and writing
is very slow which limits the use of these memory.
• EEPROM (Electrically erasable Programmable Read Only Memory) – similar to EAPROM
Memory configurations
• The elementary unit of memory is a bit. A group of 4 bits is called a nibble and a group of
8 bits is called a byte. One byte is the minimum space required to store one character.
Other units of memory are:
• 1 KB (Kilo Byte) = 210 bytes = 1024 bytes
• 1 MB (Mega Byte) = 210 KB = 1024 KB
• 1 GB (Giga Byte) = 210 MB = 1024 MB
• 1 TB (Tera Byte) = 210 GB = 1024 GB
• 1 PB (Peta Byte) = 210 TB = 1024 TB
You might also like
- Cohesity Oracle RMAN Solution GuideDocument22 pagesCohesity Oracle RMAN Solution GuidejoneberNo ratings yet
- Company Profile Sample PDFDocument17 pagesCompany Profile Sample PDFSan Lizas Airen100% (2)
- F MemoryDocument17 pagesF MemoryMahrukh FidaNo ratings yet
- H MemoryDocument10 pagesH MemoryPooja Singh SolankiNo ratings yet
- H MemoryDocument10 pagesH MemoryjaybharathNo ratings yet
- H MemoryDocument12 pagesH MemoryRuchi SharmaNo ratings yet
- Ram Rom MemoryDocument8 pagesRam Rom MemorySohit ThapaNo ratings yet
- Computer Memory: Rovelito I. NavarraDocument26 pagesComputer Memory: Rovelito I. NavarraCelestial Manikan Cangayda-AndradaNo ratings yet
- Primary MemoryDocument20 pagesPrimary MemoryAayushmanNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4 Day 5 - Main Memory - PPSXDocument25 pagesLecture 4 Day 5 - Main Memory - PPSXBindu Devender MahajanNo ratings yet
- Sreememory 151216145054Document23 pagesSreememory 151216145054Herwin CapiñanesNo ratings yet
- Memory: Information System (3) Computer Maintenance and Technical SupportDocument48 pagesMemory: Information System (3) Computer Maintenance and Technical SupportChala BojaNo ratings yet
- Computers MemoryDocument26 pagesComputers MemoryRandyNo ratings yet
- MemoryDocument14 pagesMemoryDipesh SAPKOTANo ratings yet
- Memory HierarchyDocument20 pagesMemory HierarchySailash RanaNo ratings yet
- "Memory": College of Information Technology and Engineering Notre Dame of Midsayap CollegeDocument21 pages"Memory": College of Information Technology and Engineering Notre Dame of Midsayap CollegeLeo HiddenValleyNo ratings yet
- Internal Memory Ch1Document26 pagesInternal Memory Ch1shanbel ayayuNo ratings yet
- Ram and RomDocument13 pagesRam and RomJSD190No ratings yet
- Puter MemoryDocument28 pagesPuter MemoryMDSR AKRAMNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Memory OrganizationDocument23 pagesChapter 2 Memory OrganizationChe AisarNo ratings yet
- Lecture 6Document36 pagesLecture 6Anas SheikhNo ratings yet
- Puter MemoryDocument15 pagesPuter MemorySaima Binte IkramNo ratings yet
- CAODocument65 pagesCAOPriya SinghNo ratings yet
- ch01 2-Memory HierarchyDocument16 pagesch01 2-Memory Hierarchytabkhat.3alsari3No ratings yet
- Memory TypesDocument17 pagesMemory TypesMitul Modi100% (2)
- 04 - Cache Memoryfinal 04Document29 pages04 - Cache Memoryfinal 04vianneloroNo ratings yet
- Semiconductor MemoriesDocument63 pagesSemiconductor MemoriesNayanjyot SinghNo ratings yet
- Primary Memory FinalDocument24 pagesPrimary Memory FinalRavikiranSharmaSrkNo ratings yet
- Memor y and Storage DeviceDocument50 pagesMemor y and Storage DevicesolomongebreamanuelNo ratings yet
- Lecture 02 - Memory OrganizationDocument22 pagesLecture 02 - Memory OrganizationSandeep SahaNo ratings yet
- Computer MemoryDocument23 pagesComputer MemoryAleeza gondalNo ratings yet
- Rakesh Reddy K (CO)Document10 pagesRakesh Reddy K (CO)Rakesh ReddyNo ratings yet
- Types of Memory Their UsesDocument12 pagesTypes of Memory Their UsesAtul KashyapNo ratings yet
- Group Members: Karnail Katoch Vishal Mahant Archana Kahrinar Mohammad Pisavadi Kashyap BaradDocument55 pagesGroup Members: Karnail Katoch Vishal Mahant Archana Kahrinar Mohammad Pisavadi Kashyap BaradpRiNcE DuDhAtRaNo ratings yet
- Different Types of MemoryDocument26 pagesDifferent Types of MemorySayani Chandra100% (1)
- CMTS Handout 4Document6 pagesCMTS Handout 4Tolosa TafeseNo ratings yet
- Computer MemoryDocument16 pagesComputer MemoryAjay KumarNo ratings yet
- CSC113 AssignmentDocument3 pagesCSC113 AssignmentAlphus DavidNo ratings yet
- Performing Mensuration Q3Document10 pagesPerforming Mensuration Q3Janice Agbuya TamondongNo ratings yet
- Comuter Science Lec 1,2Document19 pagesComuter Science Lec 1,2Kareem AdelNo ratings yet
- Memory DevicesDocument20 pagesMemory DevicesMD AZIZUL HOQUENo ratings yet
- MemoryDocument10 pagesMemorynet_friend05No ratings yet
- organization_Unit 5 _CODocument62 pagesorganization_Unit 5 _COAkash RajNo ratings yet
- RANDOM ACCESS MemoryDocument13 pagesRANDOM ACCESS Memoryfraolhailu6No ratings yet
- Chapter 2 COM101Document5 pagesChapter 2 COM101Christean Val Bayani ValezaNo ratings yet
- Co2 Ppt-Part2Document38 pagesCo2 Ppt-Part2Pradeep TataNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 - Memory OrganizationDocument35 pagesChapter 4 - Memory OrganizationDawit TekesteNo ratings yet
- Computer PresentationDocument14 pagesComputer PresentationAayush Niroula OfficialNo ratings yet
- MemoryDocument42 pagesMemoryDINESH RAWATNo ratings yet
- Computer MemoryDocument28 pagesComputer MemoryAngelica BaborNo ratings yet
- Memory Organization 666-41-13Document23 pagesMemory Organization 666-41-13mr xyzNo ratings yet
- Computer MemoryDocument5 pagesComputer MemorySisbiNo ratings yet
- Memory UnitDocument11 pagesMemory Unitanuskar.sigdel.34No ratings yet
- Memory OrganizationDocument70 pagesMemory OrganizationrahqansayeedNo ratings yet
- Logical Memory OrganisationDocument20 pagesLogical Memory OrganisationArchana SonawaneNo ratings yet
- RAM ROM Cache Memory RegistersDocument32 pagesRAM ROM Cache Memory Registersnagara hyoukaNo ratings yet
- Ram RomDocument42 pagesRam Rommohit mishraNo ratings yet
- Co2 Ppt-Part2Document38 pagesCo2 Ppt-Part2SWAMI AYYAPPANo ratings yet
- Unit 2Document15 pagesUnit 2Smit AnjanaNo ratings yet
- Internal MemoryDocument22 pagesInternal MemoryAbdukadir AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 Memory OrganizationDocument104 pagesUnit 5 Memory OrganizationNarsingh Pal YadavNo ratings yet
- Computer Science: Learn about Algorithms, Cybersecurity, Databases, Operating Systems, and Web DesignFrom EverandComputer Science: Learn about Algorithms, Cybersecurity, Databases, Operating Systems, and Web DesignNo ratings yet
- Electionville-Online-Instructions A4 Eng Fa WebDocument20 pagesElectionville-Online-Instructions A4 Eng Fa Webplasticfish29No ratings yet
- Raspberry Pi Pico C SDKDocument301 pagesRaspberry Pi Pico C SDKesassu100% (1)
- Special MT103Document1 pageSpecial MT103Eller100% (1)
- ECON 141 Problem Set 4Document3 pagesECON 141 Problem Set 4dnlmsgnNo ratings yet
- Pet Et7000 Quickstart enDocument4 pagesPet Et7000 Quickstart enIlham NugrohoNo ratings yet
- What Is Big DataDocument3 pagesWhat Is Big DataBalkaran singhNo ratings yet
- 802.11 Wi-Fi Physical Layer and Transmitter MeasurementsDocument1 page802.11 Wi-Fi Physical Layer and Transmitter Measurementshitler1994No ratings yet
- 3 PDFDocument1 page3 PDFaritw541214No ratings yet
- 25 Run Commands in Windows You Should Memorize - ENDocument19 pages25 Run Commands in Windows You Should Memorize - ENStayNo ratings yet
- Control SpeedDocument4 pagesControl SpeedNghiep Hua CongNo ratings yet
- ML AlgorithmsDocument2 pagesML AlgorithmshemaNo ratings yet
- Nominal Risk Technique TemplateDocument2 pagesNominal Risk Technique Templatesubrato.malick7473No ratings yet
- Components Version Information in Recent SAP HANA Cockpit Releases PatchesDocument2 pagesComponents Version Information in Recent SAP HANA Cockpit Releases PatchesankurbamelNo ratings yet
- SAFe Implementation Roadmap 6.0 Partner 11.7x8.5Document1 pageSAFe Implementation Roadmap 6.0 Partner 11.7x8.5deartoreadbookNo ratings yet
- AAF Animation Pack Guide - BasicDocument5 pagesAAF Animation Pack Guide - BasicOscar PMNo ratings yet
- UNIT 2 Basic Operations Lesson Plans: These Are Based On 45/50 Minute Lessons. Lesson No. Suggested Plan ReferencesDocument5 pagesUNIT 2 Basic Operations Lesson Plans: These Are Based On 45/50 Minute Lessons. Lesson No. Suggested Plan ReferencesChet Jerry AckNo ratings yet
- Las Ict Csa 9 Q3 Week 1Document10 pagesLas Ict Csa 9 Q3 Week 1Karell AnnNo ratings yet
- Dynon EFIS D10A EFIS D100 Install GuideDocument34 pagesDynon EFIS D10A EFIS D100 Install Guidedkc1967No ratings yet
- Pandas - Series - Short - NotesDocument7 pagesPandas - Series - Short - NotesSantosh KumarNo ratings yet
- File Manager ProDocument8 pagesFile Manager ProFile Manager ProNo ratings yet
- Introduction To NLP 2021Document13 pagesIntroduction To NLP 2021Vũ ĐinhNo ratings yet
- High-Accuracy Real Absolute Sealed Linear Encoder For High-Speed Motion!Document2 pagesHigh-Accuracy Real Absolute Sealed Linear Encoder For High-Speed Motion!Nathan ChenNo ratings yet
- ECMAScript 6Document6 pagesECMAScript 6Albano FuttaNo ratings yet
- Lab 04Document6 pagesLab 04Muskaan ZarrinNo ratings yet
- Exploring Microsoft PowerPoint AI, Using PythonDocument16 pagesExploring Microsoft PowerPoint AI, Using Pythonferdad4realNo ratings yet
- End of Session Result SlipDocument1 pageEnd of Session Result SlipBasiru AbubakarNo ratings yet
- JBL KX180 UserManual en 092017Document16 pagesJBL KX180 UserManual en 092017loc nguyenNo ratings yet
- Powerschool Parent Portal Login InstructionsDocument1 pagePowerschool Parent Portal Login Instructionsapi-321072730No ratings yet