Professional Documents
Culture Documents
4-3
4-3
Uploaded by
umar272Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
4-3
4-3
Uploaded by
umar272Copyright:
Available Formats
9-48
9-77 A stationary gas-turbine power plant operates on a simple ideal Brayton cycle with air as the working
fluid. The power delivered by this plant is to be determined assuming constant and variable specific heats.
Assumptions 1 Steady operating conditions exist. 2 The air-standard assumptions are applicable. 3 Kinetic
and potential energy changes are negligible. 4 Air is an ideal gas.
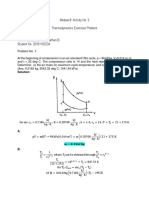
T
Analysis (a) Assuming constant specific heats,
(k −1) / k 1100 K 3
P
T2 s = T1 2 = (290 K )(8)0.4/1.4 = 525.3 K qin
P1
2
(k −1) / k 0.4/1.4
P 1 4
T4 s = T3 4
= (1100 K ) = 607.2 K 290 K 1 qout
P3 8 s
q out c p (T4 − T1 )
T −T 607.2 − 290
η th = 1 − = 1− = 1− 4 1 = 1− = 0.448
q in c p (T3 − T2 ) T3 − T2 1100 − 525.3
W& net,out = η th Q& in = (0.448)(35,000 kW ) = 15,680 kW
(b) Assuming variable specific heats (Table A-17),
h1 = 290.16 kJ/kg
T1 = 290 K
→
Pr1 = 1.2311
P2
Pr 2 = Pr = (8)(1.2311) = 9.8488
→ h2 = 526.12 kJ/kg
P1 1
h3 = 1161.07 kJ/kg
T3 = 1100 K
→
Pr3 = 167.1
P4 1
Pr 4 = Pr = (167.1) = 20.89 → h4 = 651.37 kJ/kg
P3 3 8
q h −h 651.37 − 290.16
η th = 1 − out == 1 − 4 1 = 1 − = 0.431
q in h3 − h2 1161.07 − 526.11
W& net,out = η T Q& in = (0.431)(35,000 kW ) = 15,085 kW
PROPRIETARY MATERIAL. © 2006 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Limited distribution permitted only to teachers and
educators for course preparation. If you are a student using this Manual, you are using it without permission.
You might also like
- Calculated Fields in WorkdayDocument203 pagesCalculated Fields in Workdaysudeep chowdary100% (4)
- ch08 41 85Document52 pagesch08 41 85Giuseppe TestarossaNo ratings yet
- Crystallization Material BalanceDocument5 pagesCrystallization Material BalanceAron BalinesNo ratings yet
- Imprimir PDFDocument20 pagesImprimir PDFBoris Yeltsin Ramos BautistaNo ratings yet
- Additional ProblemsDocument5 pagesAdditional ProblemsPJ PerezNo ratings yet
- O Level Computer Studies Notes - ZIMSEC Syllabus PDFDocument98 pagesO Level Computer Studies Notes - ZIMSEC Syllabus PDFkeith magaka71% (89)
- Solutions 3 F14Document2 pagesSolutions 3 F14Leul AchawNo ratings yet
- A Stationary GasDocument10 pagesA Stationary GassugiantobarusNo ratings yet
- A Stationary GasDocument9 pagesA Stationary GassugiantobarusNo ratings yet
- 4-2Document1 page4-2umar272No ratings yet
- Termodinamica Roario GayDocument3 pagesTermodinamica Roario GayJose Omar Ramos GutierrezNo ratings yet
- T Q P P T T: AssumptionsDocument3 pagesT Q P P T T: AssumptionsJose Omar Ramos GutierrezNo ratings yet
- Sheet (1&2) ThermoDocument17 pagesSheet (1&2) ThermoAhmed A. TaimaNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 4sol PDFDocument4 pagesTutorial 4sol PDFSohayb GattousNo ratings yet
- Siklus Brayton Contoh:: P P T TDocument7 pagesSiklus Brayton Contoh:: P P T TDicky PasaribuNo ratings yet
- Ideal Gas Processes ExampleDocument14 pagesIdeal Gas Processes ExampleMary Joy AlmerenoNo ratings yet
- Thermo 5th Chap10 P001Document29 pagesThermo 5th Chap10 P001Rodrigo Andre Zuniga JuarezNo ratings yet
- Problem Sheet No. 1 Submitted By: Mukhamad Zaman Chatkha Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics-II (CHE-332)Document6 pagesProblem Sheet No. 1 Submitted By: Mukhamad Zaman Chatkha Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics-II (CHE-332)Izza AfaqNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics An Engineering Approach 6Th Edition Cengel Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFDocument67 pagesThermodynamics An Engineering Approach 6Th Edition Cengel Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFphelimletitiaioxb0100% (9)
- Solutions ProblemSet8 Sem22007Document7 pagesSolutions ProblemSet8 Sem22007clearcastingNo ratings yet
- Activity 1 in PpeDocument4 pagesActivity 1 in PpeJenny Mae Pomeda100% (1)
- Thermo 5th Chap17 P096Document19 pagesThermo 5th Chap17 P096UTA - Std - Elvin ChantreNo ratings yet
- Brayton Cycle: The Ideal Cycle For Gas-Turbine EnginesDocument21 pagesBrayton Cycle: The Ideal Cycle For Gas-Turbine EnginesBilly JhunNo ratings yet
- Integrated Course 1 - Module 8 - Activity No. 3Document3 pagesIntegrated Course 1 - Module 8 - Activity No. 3aljon gonzalesNo ratings yet
- 2300 HW 13 SolDocument4 pages2300 HW 13 SolFrederick DugayNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics 2 Quiz #3 - T01: Name: ID #: Problem:: 1 Mark 1 MarkDocument2 pagesThermodynamics 2 Quiz #3 - T01: Name: ID #: Problem:: 1 Mark 1 MarkPratulya KolheNo ratings yet
- ch05 PDFDocument8 pagesch05 PDFAkash ThummarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 Vapor and Combined Power CyclesDocument29 pagesChapter 10 Vapor and Combined Power Cyclesnamsun100% (1)
- Cycles Revision SolutionsDocument11 pagesCycles Revision SolutionsLayla JhNo ratings yet
- 5Document4 pages5umar272No ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics Cengel (Solutions Manual) Chap12-001Document34 pagesFluid Mechanics Cengel (Solutions Manual) Chap12-001NURUL SYUHADA BT ISMAIL HAJAR50% (2)
- FM Sol Chap12-131Document41 pagesFM Sol Chap12-131CEMONo ratings yet
- Otto CycleDocument9 pagesOtto CycleMohammed Al-Odat100% (1)
- Assignment No. 1 in PpeDocument3 pagesAssignment No. 1 in PpeJenny Mae PomedaNo ratings yet
- HomeworkDocument7 pagesHomeworkTlhologeloNo ratings yet
- At 2.5 Mpa 2803.1 6.2575 at 50 Kpa 340.49 1.0910 2305.4 6.2575 0.000103 Sol'N: 280.31Kj /KG Solving For H: + 6.2575 1.0910+X (6.5029)Document22 pagesAt 2.5 Mpa 2803.1 6.2575 at 50 Kpa 340.49 1.0910 2305.4 6.2575 0.000103 Sol'N: 280.31Kj /KG Solving For H: + 6.2575 1.0910+X (6.5029)Ariel Gamboa100% (1)
- Steam Turbinedocx PDF FreeDocument13 pagesSteam Turbinedocx PDF Freeben richNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics ProbDocument7 pagesThermodynamics ProbJan Mae Beja AdolfoNo ratings yet
- De GUZMAN Module 4 Activity No. 6Document5 pagesDe GUZMAN Module 4 Activity No. 6John Mark AlvesNo ratings yet
- Thermo 5th Chap09 p060Document1 pageThermo 5th Chap09 p060superaluddinNo ratings yet
- Exercises Problem 3 Refrigeration - PascualDocument4 pagesExercises Problem 3 Refrigeration - PascualJef PascualNo ratings yet
- CalculationsDocument2 pagesCalculationsLeoNo ratings yet
- CH 10Document38 pagesCH 10정민교No ratings yet
- Evaporator 2 Effect Final EXPORTDocument2 pagesEvaporator 2 Effect Final EXPORTRitik ChaturvediNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Gas Dynamics (NOC16 - ME05) Assignment - 3: SolutionsDocument4 pagesFundamentals of Gas Dynamics (NOC16 - ME05) Assignment - 3: SolutionsOyewole EmmanuelNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 PDFDocument3 pagesChapter 4 PDFMarvin LabajoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 PDFDocument3 pagesChapter 4 PDFSusana PérezNo ratings yet
- 01 Positive Displacement Machines Part 1 and 2 Class ExampleDocument13 pages01 Positive Displacement Machines Part 1 and 2 Class ExamplemohamedNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document3 pagesChapter 4nick thompsonNo ratings yet
- Ps Gs PDFDocument10 pagesPs Gs PDFVivek MauryaNo ratings yet
- Ciclo BraytonDocument17 pagesCiclo BraytonNubia Bergamini100% (2)
- ASEN3113 HW4 SolutionsDocument6 pagesASEN3113 HW4 Solutionsandres179No ratings yet
- 04 - Thermodynamic - Cycles - (Joule - B) PDFDocument8 pages04 - Thermodynamic - Cycles - (Joule - B) PDFAntonio Di FioreNo ratings yet
- 4-4Document1 page4-4umar272No ratings yet
- Lectures in Thermodynamics Claus BorgnakkeDocument38 pagesLectures in Thermodynamics Claus BorgnakkeJkun gamingNo ratings yet
- Example CH 2 PDFDocument6 pagesExample CH 2 PDFRojan PradhanNo ratings yet
- Example 2.1: DP DP P P or P PDocument6 pagesExample 2.1: DP DP P P or P PEzanaLordNo ratings yet
- Module 5 Activity No. 2Document4 pagesModule 5 Activity No. 2Seb TayagNo ratings yet
- ME 24-221 Thermodynamics I Solutions To Extra Problems in Chapter 9: November 17, 2000 J. MurthyDocument6 pagesME 24-221 Thermodynamics I Solutions To Extra Problems in Chapter 9: November 17, 2000 J. MurthyKen Joshua ValenciaNo ratings yet
- A Modern Course in Statistical PhysicsFrom EverandA Modern Course in Statistical PhysicsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- Mechanical 799202Document1 pageMechanical 799202umar272No ratings yet
- Technology Work Progress June 12 - June 15Document1 pageTechnology Work Progress June 12 - June 15umar272No ratings yet
- Experiment 4Document9 pagesExperiment 4umar272No ratings yet
- Vocabulary TechniqueDocument2 pagesVocabulary Techniqueumar272No ratings yet
- Serrano - Probability Distribution Test ProblemDocument6 pagesSerrano - Probability Distribution Test ProblemJosheyne Marzialli SerranoNo ratings yet
- Science A Chemistry: Foundation Tier Unit Chemistry C1Document20 pagesScience A Chemistry: Foundation Tier Unit Chemistry C1CamilleNo ratings yet
- Petroleum Engineering Programme HandbookDocument79 pagesPetroleum Engineering Programme HandbookMohammed Shoaib50% (2)
- Bachelor of Technology in Electrical Engineering: Programme Level Year of Commencement Minimum Duration Maximum DurationDocument6 pagesBachelor of Technology in Electrical Engineering: Programme Level Year of Commencement Minimum Duration Maximum Durationmayank kakkarNo ratings yet
- Exchanger DesignDocument17 pagesExchanger DesignRamesh mudunuriNo ratings yet
- Phased Array Radars: J. L. Chau, C. J. Heinselman, M. J. NicollsDocument52 pagesPhased Array Radars: J. L. Chau, C. J. Heinselman, M. J. NicollsNguyễn Hoàng Giang100% (1)
- Regression Analysis: Model Building: Learning ObjectivesDocument38 pagesRegression Analysis: Model Building: Learning ObjectivesAnh DoNo ratings yet
- BIDM RegDocument2 pagesBIDM RegSagar DamaniNo ratings yet
- Mmse and MseDocument3 pagesMmse and Mse황춘히No ratings yet
- Java 1Document99 pagesJava 1kaviarasu100% (1)
- PIC16F145x PDFDocument404 pagesPIC16F145x PDFArsalan88No ratings yet
- Dzexams 1am Anglais 2161233Document2 pagesDzexams 1am Anglais 2161233أبو إياد بوزيدNo ratings yet
- RFI Radiographic Film Interpretation 30 - October - 2020Document7 pagesRFI Radiographic Film Interpretation 30 - October - 2020SUNIL BABURAO GAVADENo ratings yet
- IECEx Za Namur Davač ImpulsaDocument12 pagesIECEx Za Namur Davač Impulsajosip miskovicNo ratings yet
- Annealing PDFDocument5 pagesAnnealing PDFKamran ShakeelNo ratings yet
- Scratch Test Methodology For Leadframe PlatingDocument5 pagesScratch Test Methodology For Leadframe PlatingMohamad Adli AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Acer Aspire m1900Document6 pagesAcer Aspire m1900Ali MashduqiNo ratings yet
- Abaqus Tunnel LiningDocument7 pagesAbaqus Tunnel LiningAhsan SattarNo ratings yet
- EC8751 Optical CommunicationDocument21 pagesEC8751 Optical CommunicationSrj SNo ratings yet
- Ionic EquilibriumDocument14 pagesIonic Equilibrium8842 AnuragNo ratings yet
- AMA46 3sum TarlBerry GeometricdesignoffruitpackaginginRSA PublishedDocument10 pagesAMA46 3sum TarlBerry GeometricdesignoffruitpackaginginRSA PublishedKosin HachaweeNo ratings yet
- Using Skellam's Distribution To Assess Soccer Team PerformanceDocument9 pagesUsing Skellam's Distribution To Assess Soccer Team PerformanceBartoszSowulNo ratings yet
- Research TerminologiesDocument42 pagesResearch TerminologiesPriya bhattiNo ratings yet
- Atoms and NucleiDocument12 pagesAtoms and NucleiBablu ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- Daytona 675R BrochureDocument8 pagesDaytona 675R BrochureKatreddi Chandu SaiNo ratings yet
- GTSTRUDL 32 - Student Edition 13: Quick-Start InstructionsDocument3 pagesGTSTRUDL 32 - Student Edition 13: Quick-Start InstructionsVimalan KannanNo ratings yet
- (Aviation Maintenance Technician Certification Series) - Module 15 For B1 Certification. Gas Turbine Engine-Aircraft Technical Book Company (2019)Document293 pages(Aviation Maintenance Technician Certification Series) - Module 15 For B1 Certification. Gas Turbine Engine-Aircraft Technical Book Company (2019)belinda koyaiye100% (1)