Professional Documents
Culture Documents
seminar on Haematuria PPT
seminar on Haematuria PPT
Uploaded by
Omar KhashashnehCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Roszak - The Making of A Counter Culture, Ausschn. (1969) PM PDFDocument23 pagesRoszak - The Making of A Counter Culture, Ausschn. (1969) PM PDFljunnamedNo ratings yet
- MSC Nursing QN PaperDocument9 pagesMSC Nursing QN Papersanthyakunjumon100% (1)
- Wild Yam Cream RecipeDocument2 pagesWild Yam Cream RecipeWayne Wiltshire67% (3)
- Medical Necessity Physician LetterDocument1 pageMedical Necessity Physician LetterMichael_Lee_RobertsNo ratings yet
- Hemodialysis PPTDocument1 pageHemodialysis PPTjasminemuammilNo ratings yet
- Public Health Questions and Answers For Students 5Document1 pagePublic Health Questions and Answers For Students 5Tharani SelvendranNo ratings yet
- Public Health Questions and Answers For Students 3Document1 pagePublic Health Questions and Answers For Students 3Tharani SelvendranNo ratings yet
- ShockDocument2 pagesShock2b4kj7xdchNo ratings yet
- Drug of Choice (1) 3Document2 pagesDrug of Choice (1) 3Muzammil HusainNo ratings yet
- Chronic Myeloid Leukemia (CML) 3Document1 pageChronic Myeloid Leukemia (CML) 3Augustine A. KollieNo ratings yet
- Gu trauma- urethra PPTDocument1 pageGu trauma- urethra PPTOmar KhashashnehNo ratings yet
- Dialysis Machines Key FeaturesDocument1 pageDialysis Machines Key FeaturessurainepNo ratings yet
- JaundiceDocument1 pageJaundiceAugustine A. KollieNo ratings yet
- Pediatrics History Taking PDF 2Document2 pagesPediatrics History Taking PDF 2Red DevilNo ratings yet
- Pediatrics History Taking PDF 4Document2 pagesPediatrics History Taking PDF 4Red DevilNo ratings yet
- AbortionDocument1 pageAbortionArjesa TakaNo ratings yet
- More Related Content: Turp TechniqueDocument1 pageMore Related Content: Turp TechniqueRavi PramudiaNo ratings yet
- Cushings Syndrome - PPTX 2Document1 pageCushings Syndrome - PPTX 2gjct2bxm6yNo ratings yet
- PAIN HISTORY TAKING PPT 2Document1 pagePAIN HISTORY TAKING PPT 2Omar KhashashnehNo ratings yet
- History taking PPTDocument1 pageHistory taking PPTOmar KhashashnehNo ratings yet
- Phimosis & Paraphimosis PDFDocument1 pagePhimosis & Paraphimosis PDFAdaeze DouglasNo ratings yet
- Sinusoidal Current PPTDocument1 pageSinusoidal Current PPTAyesha MunirNo ratings yet
- Pap SmearDocument1 pagePap SmearMaria Carmela CastilloNo ratings yet
- Anemia (Investigatory Project) Class 11 | PDFDocument16 pagesAnemia (Investigatory Project) Class 11 | PDFDivyanilamaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Pharmacognosy 2Document1 pageIntroduction To Pharmacognosy 2Idenyi Daniel EwaNo ratings yet
- Hiv Treatment Final PPT 3Document1 pageHiv Treatment Final PPT 3Umer IsmailNo ratings yet
- Pathogenesis Hiv Slide 2Document1 pagePathogenesis Hiv Slide 2Augustine A. KollieNo ratings yet
- Handout PrenatalDocument1 pageHandout PrenataljasminemuammilNo ratings yet
- Benign Lesions of LarynxDocument1 pageBenign Lesions of LarynxAnjana UNo ratings yet
- Bio Medical Waste ManagementDocument1 pageBio Medical Waste Managementkabeerkhan30013No ratings yet
- Gingivectomy (Oral Surgery)Document1 pageGingivectomy (Oral Surgery)Daraí Bárbara Sánchez MonteroNo ratings yet
- Screenshot 2023-02-24 at 10.42.04 AMDocument1 pageScreenshot 2023-02-24 at 10.42.04 AMMir DanishNo ratings yet
- Acute PancreatitisDocument6 pagesAcute PancreatitisFatema AlburiNo ratings yet
- Abortion - PPT For 2nd MSCDocument1 pageAbortion - PPT For 2nd MSCArjesa TakaNo ratings yet
- Anemia PPT 2Document1 pageAnemia PPT 2sana ahmedNo ratings yet
- Meningococcal InfectionsDocument1 pageMeningococcal Infectionsheng28369No ratings yet
- Cast and Immobilization Techniques in OrthopaedicDocument3 pagesCast and Immobilization Techniques in OrthopaedicandysgraphicssNo ratings yet
- Patient Education ProgramDocument4 pagesPatient Education ProgramBriane OmondiNo ratings yet
- Screenshot 2023-08-23 at 5.06.03 PMDocument2 pagesScreenshot 2023-08-23 at 5.06.03 PMYashas V SureshNo ratings yet
- Medicolegal Aspects of DeathDocument1 pageMedicolegal Aspects of DeathGurdeep KaurNo ratings yet
- Community Mental HealthDocument1 pageCommunity Mental HealthSree LathaNo ratings yet
- Megaloblastic AnemiaDocument2 pagesMegaloblastic Anemiamoncalshareen3No ratings yet
- Ophthalmic PreparationsDocument2 pagesOphthalmic Preparations033 preya patelNo ratings yet
- Occupational Health & Occupational HazardsDocument1 pageOccupational Health & Occupational HazardsSree LathaNo ratings yet
- HypersensitivityDocument1 pageHypersensitivitySanjana ReddyNo ratings yet
- Bone Mineral Density (BMD) Test 2Document1 pageBone Mineral Density (BMD) Test 2Rica adriani SantikaNo ratings yet
- Bone Mineral Density (BMD) TestDocument1 pageBone Mineral Density (BMD) TestRica adriani SantikaNo ratings yet
- Medical Ethics Principles PDFDocument14 pagesMedical Ethics Principles PDFjtt8btwxhvNo ratings yet
- International Health Regulations (Ihr)Document1 pageInternational Health Regulations (Ihr)Sree LathaNo ratings yet
- Caisson's Disease PPT 2Document1 pageCaisson's Disease PPT 2Uzma TahseenNo ratings yet
- Newborn Care Oxygen Therapy PDFDocument1 pageNewborn Care Oxygen Therapy PDFAnjana UNo ratings yet
- Caisson's DiseaseDocument1 pageCaisson's DiseaseUzma TahseenNo ratings yet
- Nutrients Classification PPTDocument3 pagesNutrients Classification PPTmwqzdpztczNo ratings yet
- Emergency Nursing Questionnaires 2Document1 pageEmergency Nursing Questionnaires 2Mark Jayson TuazonNo ratings yet
- GAP - PPTX: RecommendedDocument10 pagesGAP - PPTX: RecommendedOm PawarNo ratings yet
- PROCESS OF ICH (International Council For HarmoniDocument3 pagesPROCESS OF ICH (International Council For Harmonilolipoppopcorn11111No ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Cavity PreparationDocument5 pagesFundamentals of Cavity PreparationAjay Praveen0% (1)
- Namaz PDFDocument14 pagesNamaz PDFnedimpolic16No ratings yet
- Nursing As A ProfessionDocument1 pageNursing As A ProfessionMaribel Diana YsulatNo ratings yet
- Artificial Reproductive TechnologyDocument12 pagesArtificial Reproductive Technologytokor40413No ratings yet
- Materi Sistem ImunDocument1 pageMateri Sistem ImunAbikNo ratings yet
- Reading ListDocument1 pageReading ListShaikh TahiraNo ratings yet
- Classical ConditioningDocument1 pageClassical Conditioninggerald almencionNo ratings yet
- Nutri 0713 SeDocument13 pagesNutri 0713 SeAileen BobadillaNo ratings yet
- Philips Titration Protocol 2017Document12 pagesPhilips Titration Protocol 2017Sam WhiteNo ratings yet
- Nootropic DrugsDocument13 pagesNootropic DrugsPetar DimkovNo ratings yet
- Occupational Safety and Health STDDocument65 pagesOccupational Safety and Health STDKirk Corales100% (4)
- Synonyms: Sreedhar's CCEDocument5 pagesSynonyms: Sreedhar's CCEOmaisNo ratings yet
- Solution Focused TechniquesDocument5 pagesSolution Focused TechniquesNazario Israel Narvaez ArzateNo ratings yet
- Risk Assessment and Analysis For Sliding Gates: Analysis of Gate Structure To Be MovedDocument6 pagesRisk Assessment and Analysis For Sliding Gates: Analysis of Gate Structure To Be Movedsmart_onyx17No ratings yet
- Lesson 4 Health PDFDocument25 pagesLesson 4 Health PDFRomeo BalingaoNo ratings yet
- List 13 HomeworkDocument2 pagesList 13 Homeworkapi-328692644No ratings yet
- Full PDFDocument9 pagesFull PDFAle TabaskoNo ratings yet
- Kenneth Jake T. BatiduanDocument1 pageKenneth Jake T. BatiduanKenneth Jake BatiduanNo ratings yet
- Ismenore: You Should Also DoDocument2 pagesIsmenore: You Should Also DoNurul Ilmi UtamiNo ratings yet
- BullyingDocument3 pagesBullyingdarwin wongNo ratings yet
- Mechanism of LaborDocument98 pagesMechanism of LaborLaarnee Sinsioco SantosNo ratings yet
- Class II Neurotic DisordersDocument37 pagesClass II Neurotic DisordersNarayan K Ghorapde100% (1)
- Arens Aud16 Inppt09Document33 pagesArens Aud16 Inppt09euncieNo ratings yet
- Job Description: Cardiff and Vale University Health Board Job DetailsDocument9 pagesJob Description: Cardiff and Vale University Health Board Job DetailsmustakNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular and Respiratory Systems - Unit TestDocument7 pagesCardiovascular and Respiratory Systems - Unit Testapi-305647618No ratings yet
- CCM 3225 Community DiagnosisDocument7 pagesCCM 3225 Community DiagnosisLulano MbasuNo ratings yet
- Malaria PreventionDocument3 pagesMalaria PreventionRohit_Patkar_2942No ratings yet
- NCP Tissue PerfusionDocument2 pagesNCP Tissue PerfusionNiña Montejo Ealdama100% (1)
- Scratch AssayDocument2 pagesScratch AssayElsya Veranza100% (1)
- Key To Being A Good ParentDocument15 pagesKey To Being A Good ParentJelena Preradovic100% (1)
- Clinical Teaching MethodsDocument29 pagesClinical Teaching MethodsDr. Jayesh Patidar100% (7)
- Iqvia Launch Excellence For Multi Indication Assets 02 23 ForwebDocument20 pagesIqvia Launch Excellence For Multi Indication Assets 02 23 ForwebsethirohinNo ratings yet
- Hair Loss Help ForumsDocument18 pagesHair Loss Help Forumshabitualnurture69No ratings yet
seminar on Haematuria PPT
seminar on Haematuria PPT
Uploaded by
Omar KhashashnehCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
seminar on Haematuria PPT
seminar on Haematuria PPT
Uploaded by
Omar KhashashnehCopyright:
Available Formats
Search Upload Login Signup
seminar on Haematuria
Dr. Habibur Rahim
Apr 28, 2021 • 3 likes • 720 views
14 of 52
Health & Medicine
seminar on Haematuria
Recommended
Evaluation of the patient with hematuria.
Meshari Alzahrani
21.1K views • 67 slides
Approach to hematuria
Krishna Bharadwaj
12.2K views • 19 slides
Approach to splenomegaly
Sarath Menon
59.8K views • 37 slides
Haematuria causes and evaluation
dr vipin Drvipinsharma3
6.7K views • 33 slides
Hematuria
Mohamed Mustafa
42K views • 35 slides
Approach to Hematuria
Dr Sushil Gyawali
1.6K views • 50 slides
Hematuria
Salwa Ibrahim
13K views • 80 slides
Acute glomerulonephritis
Soumya Ranjan Parida
7.2K views • 22 slides
More Related Content
What's hot (20)
Approach to nephrotic A 33-year old man with Management of lupus
syndrome polyuria and polydipsia nephritis
Abhay Mange • 8.1K views Usama Ragab • 3.1K views Arnab Nandy • 924 views
Similar to seminar on Haematuria (20)
Haematuria & Renal Failure Acute Glomerulonephritis Approach to a child with
(AGN) by Dr. Dilip hematuria
mimios • 4.5K views DrDilip86 • 14.4K views Nehal Shah • 155 views
Slideshows for you (20)
Ulcer Swelling - Examination General examination
Dr KAMBLE • 135.9K views Uthamalingam … • 138.8K views Chiranjeevi JIP… • 219.6K views
More from Dr. Habibur Rahim (20)
neuromonitoring of a basics of mechanical approach to Rh
newborn from common … ventilator Dr … Isoimmunization Materna…
nervous
Dr. Habibursystem
Rah… • disease
4 views Asaduzzaman.pptx
Dr. Habibur Rah… • 48 views and neonatal
Dr. Habibur Rah…aspects | Dr
• 47 views
perspectives ... Habibur Rahim
Recently uploaded (20)
Impact of Public Health Atrial fibrillation (1).pptx Adverse Drug Reactions
Postnatal Home Visiting i…
NB on Breastfeeding
DataNB • 20 views among MohamadAlhes • 24 views NAKUL DHORE • 33 views
...
Related Books
Free with a 30 day trial from Everand View All
Ebook Ebook Ebook Ebook
Nursing: Lab Hematology Notes Liver Cirrhosis, A Nephrology,
Values: a… for Medical… Simple Guide To… eTextbook: Clinic…
Henry
QuickStudy J.R. Phillip, MD, PhD
Students Kenneth Kee
The Condition, Menna
CasesClatworthy
Uncovered
Laminated 6-Page Treatment And
0Reference
/5 Guide 0/5 0Related
/5 Diseases 0/5
Related Audiobooks
Free with a 30 day trial from Everand View All
Audiobook Audiobook Audiobook Audiobook
The Checklist Eat Right for Your Dr Sebi Cure for The GutSMART
Manifesto: How t… Type Diabetes: The… Protocol: Revitali…
Atul
GetGawande
Things Right Peter D'Adamo Thomas Smith
Revolutionary Dr.
YourVincent PedreBoost
Health,
Method to Prevent Your Energy, and
4.5 / 5 3.5 / 5 5and
/ 5 Quickly 5Lose
/ 5 Weight in Jus
Reverse Type 1 and 14 Days with Your
seminar on Haematuria
1. WELCOME To Seminar Dr Mehadi Hasan Rimon Resident, Year-1(neonatology) Dr. Ishrat Zahan Nigar Resident, Year-2( Pediatric
Neurology) Dr. Zannatul Ferdous Resident, Year-2 (Pediatric Neurology)
2. Case Scenerio Redwan , 6 years old boy, 3rd issue of his non consanguineous parents, got admitted with the complaints of
generalized swelling of body for 7days along with scanty micturition and passage of red colored urine for same duration. O/E, he had
pu!y face with generalized oedema . He was mildly pale, anicteric, BP: 130/80mm of Hg (> 99th centile) & BSUA ++. Genitourinary
system examination revealed abdomen was distended; ascites present. Provisional Diagnosis Acute Glomerulonephritis
3. Approach to a child with Hematuria
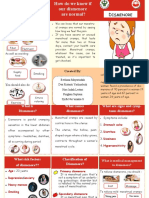
4. Definition Presence of red blood cell (RBC) in the urine, >10 RBC per cubic mm of freshly voided, uncentrifuged urine or >5 RBC per
high power field of 10 ml of freshly voided centrifuged urine.
5. Physiological Pathological Gross Microscopic glomerular non glomerular non glomerular glomerular • Heavy proteinuria • Fever
• menstruation Classification painless Painful
6. Classification Painful Hematuria Painless Hematuria UTI Calculi Hypercalciuria IgA nephropathy Renal tumor Renal TB
Coagulation disorder Alport syndrome Post traumatic
7. Classification Gross hematuria Microscopic hematuria UTI Infection related GN Renal calculi IgA nephropathy Hypercalciuria
alport syndrome TBMD Coagulation disorder Thrombocytopenia malignancy Vasculitis membranous nephropathy IgA nephropathy
TBMD alport syndrome idiopathic hypercalciuria renal vesical calculi urinary tract anomalies UTI PKD tuberous sclerosis wilms
tumour sickle cell disease Penicilium lithium recurrent
8. Classification Glomerular Nonglomerular PSGN RPGN IgA nephropathy Vasculitis HSP nephritis Lupus nephritis Alport
syndrome Membranous nephropathy TBMD HUS Hypercalciuria Renal calculi UTI Hemorrhagic cystitis Coagulation disorder
Thrombocytopenia Malignancy Urinary tract anomalies Vascular malformation Trauma Exercise Drugs
9. Conditions mimicking hematuria Drugs: Rifampicin Phenothiazines Nitrofurantoin Desferoxamine Chloroquine Ibuprofen
Levodopa
10. Foods: beet root, fruit containing anthocyanins (eg. black berries, plums, cherries) and food dyes (cake coloring). Pigments:
hemoglobinuria (intravascular hemolysis) myglobinuria (rhabdomyolysis) Bilirubin urate crystal (pink).
11. Approach to a child with Hematuria
12. History + symptom analysis Physical findings Lab investigations
13. History • Age: 5-12 yrs: PSGN 2-8 yrs: HSP <4 yrs: HUS 2-5 yrs: Wilms tumor 2nd decade: IgA nephropathy • Sex: F>>M in >1-2 yrs:
UTI F>>M: SLE nephritis M>F : X-linked form of Alport syndrome • Race: whites: Idiopathic hypercalciuria blacks: Sickle cell disease
14. History contd… • Amount of urine: Reduced in AGN, AKI • Clots in urine: Extraglomerular • Frequency, Dysuria, recent enuresis :
UTI • Frothy urine: Suggests Proteinuria seen in Glomerular diseases • Hematuria in relation to time of micturition: Initial stream –
from urethra (Urethrorrhagia – spotting In underwear) Terminal – from bladder (with suprapubic pain, disturbance of micturition)
Throughout the urinary stream - glomerular
15. Associated Symptoms Fever Infection SLE AGN Facial pu!iness Oedema of legs weight gain Shortness of breath Acute
Glomerulonephritis
16. Abdominal pain Urolithiasis (Loin to groin) Cystitis (lower abdominal) Pyelonephritis (loin pain) Abdominal mass
Hydronephrosis PKD Wilm’s tumour Joint pain Rashes HSP SLE Neurologic (seizures, irritability) SLE HUS
17. Jaundice Hemolysis, Obstructive jaundice APSGN HUS IgA nephropathy HSP nephritis Recent upper respiratory tract, skin
infection, GI infection Bleeding disorders, Hemoptysis in Good Pasture syndrome H/o bleeding from other sites
18. H/o Vision or hearing defects Alport syndrome Family h/o hematuria Hereditary glomerular diseases (Alport syndrome, Thin
glomerular Basement Membrane Disease, IgA Nephropathy), Urolithiasis, Hypercalciuria, Sickle cell disease/trait H/o consanguinity or
a!ected siblings ARPKD, Metabolic disorders
19. Others • H/o exercise, trauma, menstruation, recent bladder catheterization or passage of a calculus • H/o ingestion of drugs (ATT
– Rifampicin, Ibuprofen, Chloroquine, Metronidazole, Iron), i.v. contrast agents (Toxic nephropathy, RVT)
20. Examination HTN AGN PKD Raised temp. Infection SLE AGN Oedema AGN Pallor HUS SLE CKD Bleeding disorders Raised JVP
CHF
21. Palpable flank mass Hydronephrosis (Urinary tract obstruction) Wilms tumour ARPKD, hydronephrosis (B/L) Bladder palpable
Skin lesions Abnormal external genitalia, hypospadias, cryptorchidism, Genital trauma Distal obstruction Palpable Purpura(HSP)
Butterfly rash (SLE) Bruises (Trauma, Child abuse) WAGR syndrome Wilms tumour
22. Signs of Congestive cardiac failure, Hypertensive encephalopathy Joint swelling, tenderness Ophthalmologic (Anterior
lenticonus, macular flecks, recurrent corneal erosions) AGN HSP, SLE Alport syndrome Hearing assessment (B/L SNHL) Alport
syndrome
23. NEXT
25. Glomerular VS Non glomerular Features Glomerular hematuria Non-glomerular hematuria Pattern of hematuria: Hematuria
throughout urinary stream. Initial, terminal. Urinary symptoms: Painless. Dysuria, urgency, frequency Associated feature: Sore throat,
hypertension, edema. Fever, colicky pain. Family history: Deafness, renal failure. Renal stone, urinary infection. Clinical HTN, edema:
Usually present Less common
26. Features Glomerular hematuria Non-glomerular hematuria color Tea colored. Bright red, blood clots. Proteinuria 2+ or more on
dipstick; protein creatinine ratio>1. Trace to 1+; protein creatinine ratio<1. Dysmorphic RBC >20%. <15%, eumorphic. Cellular cast RBC
cast, leukocyte or tubular cast may be present Absent Crystal absent May be present Glomerular VS Non glomerular Urinalysis
27. No No How to investigate a case of Hematuria Physiological cause like viral illness, exercise, trauma, menstruation Take History &
do physical examination Do Urine R/E including phase contrast microscopy Do a dipstick test & exclude ABCDE ( ABCDE are Dipstick –
ve) A=Alkaptonuria B=billirubinuria C=Carotinemia D=Drugs E= Endocrine/Metabolic-Porphyria+
28. Role of Urine examination A. Urinanalysis 1. Urine dipstick test Based on the peroxidase- like activity of hemoglobin. • Positive in
presence of- Hb, Myoglobin & RBC • False +ve: Urine pH >9, H2O2 • False –ve: High ascorbic acid, formalin 2. Urine R/M/E RBC, protein,
RBC cast Pus cells, WBC cast Crystalluria Eosinophil Glomerular disease UTI Urolithiasis, Nephrocalcinosis Interstitial nephritis 3.
Urine C/S Number & type of bacteria UTI RBC: False negative in case of low specific gravity or alkaline pH as it causes hemolysis. Phase
Contrast microscopy >90-95% isomorphic >20% dysmorphic
29. No RBC Hemoglobinuria/ Myoglobinuria RBC/+- Hb Hb only, no RBC Search other cause of red urine Nonglomerular Glomerular
Check RBC Morphology
30. Urea, Creatinine, Electrolyte, ABG, ASO, C3, Spot urinary PCR, S Albumin, Cholesterol , Glomerular Hematuria No Consistent with
PSGN HTN, Azotemia Supportive Treatment USG, ANA, anti ds DNA, Family history of blurring & visual examination, Renal biopsy
31. Positive Renal US +/- VCUG Non glomerular Hematuria Negative Pyelonephritis, Cystitis Hydronephrosis, PUJ, PUV, MCKD, Tumor,
PKD,VUR, Lithiasis, RVT Abnormal Urine Culture Urinary Ca/Cr Normal Hypercalciuria Check 24-h Urine Bleeding disorder Meatitis
Idiopathic Abnormal Normal
32. Isolated microscopic hematuria Follow up Urine R/E with examination For asymptomatic, isolated microscopic hematuria
Repeat urinalysisis weekly × 2 No exercise × 48 hr F/H/O calculi Test parents for hematuria Benign familial hematuria ± hematuria, ±
USG, ± X ray KUB region Urinary Ca/Cr ratio Urine R/E, examination, BP
34. Role of Imaging 1. Structure: USG of KUB X-Ray KUB Doppler study of renal vessels and IVC Intravenous urography Spiral CT scan
Micturating cystourethrograms Renal cystic disease Hydronephrosis, Hydroureter, nephrocalcinosis, tumor, urolithiasis, Renal
parenchymal disease calculi Renal vein thrombosis Nutcracker syndrome Urolithiasis, Wilms tumor and polycystic kidney disease,
Renal trauma Urethral and bladder abnormalities (eg, cystitis), in recurrent UTI to r/o VUR, anomalies 2. Function DTPA DMSA
Functional excretory function. To see renal scar.
35. • Significant proteinuria (>1g/1.73m2/day) except Post- infectious GN. • Recurrent persistent hematuria (Microscopic >2yrs) •
Recurrent gross hematuria • Abnormal renal function, Persistent HTN • Hematuria, Proteinuria, diminished renal function, low C3 level
persist beyond 2 mo of onset of AGN • Serologic abnormalities (abnormal ANA or dsDNA levels) • A family history of end stage renal
disease. Indication of Renal biopsy
36. • Urinanalysis of siblings & parents: Thin glomerular basement membrane disease • Urine Ca/Creatinine ratio: > 0.2 in Idiopathic
hypercalciuria. • 24hrs urine for Calcium, uric acid, oxalate: Urolithiasis & Nephrocalcinosis • Cystogram & renal scan. • Slit lamp
examination of eye & audiometry.-Alport How to screen families in a case of Hematuria Hereditary causes of hematuria: •Benign
familial Hematuria(Thin basement membrane disease) •Alport Syndrome(Hereditary Nephritis) •Idiopathic hypercalciuria •Polycystic
kidney disease •Fabry’s disease •Nail patella syndrome •Sickle cell trait/disease
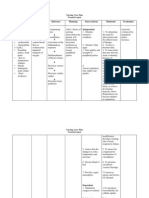
37. Management
38. • Hematuria is a clinical (or laboratory) sign, not a diagnosis. • Treatment is according to cause. • Reassurance and F/U: isolated
microscopic hematuria, familial microscopic haematuria. • Antibiotics : To treat cystitis, pyelonephritis • Supportive treatment: Proper
nutrition Diuretics Fluid and salt restriction Antihypertensives General Management
39. • Treatment of complication: Electrolyte abnormality, AKI, HF, acidosis, fluid overload, HTN. • Monitoring: Vitals, I/O, weight, urine
RME.
40. Management of some specific diseases
41. • Adequate fluid intake • Appropriate antibiotic • Prophylactic antibiotic when indicated. UTI
42. • Salt, fruit & fluid restriction • Diuretics • Antihypertensive • Antibiotics • Treatment of complication Prognosis • 98% complete
recovery within 1-2 weeks • 1% immediate mortality • 1% may proceed to chronic GN/CKD • 0.7-7% recurrence PSGN
43. • Prednisolone • MMF, cyclosporine, azathioprim • IV methylprednisolone, IV/oral cyclophosphamide • Immunosuppressive in
di!erent combination Prognosis • Not good • 50% turn into CKD within 10 years • 90% turn into CKD within 20 years Rx: RRT
Membranoproliferative Glomerulonephritis
44. • Treatment according to staging • Immunosuppressive therapy Prednisolone Cyclophosphamide MMF Prognosis • Relapse: 33% •
Childhood onset: worse prognosis SLE Nephritis
45. • Mild disease: no specific therapy • Persistent proteinuria: ACEi, corticosteroid • Severe nephritis/ Nephrotic syndrome:
corticosteroids & cytotoxic drugs. • Crescentic glomerulonephritis: IV corticosteroids, cyclophosphamide, plasma exchange in
nonresponsive cases. Prognosis • 15-40% at least 1 recurrence • <1% ESRD HSP Nephritis
46. • ACE inhibitor • Immune suppressive: prednisolone, azathioprime • Omega 3 fatty acid, fish oil Prognosis • Good in children •
RPGN: bad prognosis • ESRD: 30-40% cases in 3rd to 4th decade Ig A nephropathy
47. • ACE inhibitor • Renal replacement Prognosis • 60% ESRD by 60 years • 40% ESRD by 40 years Alport Syndrome
48. • Avoid dehydration • High liquid intake • Moderate salt restriction • Avoidance of high protein(animal protein) diet • Avoid excess
dietary calcium • Citrate supplementation • Thiazide diuretics Idiopathic hypercalciuria
49. • Usually benign. • Episodic gross hematuria in association with acute infection. • Prognosis: favorable. • Follow up: annually for
proteinuria & hypertension. Thin Basement Membrane Disease
50. • Increased fluid intake • Appropriate antibiotics Renal Stone • Increased fluid intake • Urological consultation Pyelonephritis
51. • Every case of hematuria should be properly evaluated. • Isolated asymptomatic microscopic hematuria can be an incidental
finding. Most of the cases it possess no threat to health, only reassurance & F/U is needed. • Gross & microscopic hematuria with family
history/additional findings are usually pathological. Proper evaluation & family screening can elicit a diagnosis. • With early diagnosis
and proper treatment of most of the disease related to hematuria can be well managed. Take home message
About Support Terms Privacy Copyright Cookie Preferences
English
Do not sell or share my personal information Everand
© 2023 SlideShare from Scribd
You might also like
- Roszak - The Making of A Counter Culture, Ausschn. (1969) PM PDFDocument23 pagesRoszak - The Making of A Counter Culture, Ausschn. (1969) PM PDFljunnamedNo ratings yet
- MSC Nursing QN PaperDocument9 pagesMSC Nursing QN Papersanthyakunjumon100% (1)
- Wild Yam Cream RecipeDocument2 pagesWild Yam Cream RecipeWayne Wiltshire67% (3)
- Medical Necessity Physician LetterDocument1 pageMedical Necessity Physician LetterMichael_Lee_RobertsNo ratings yet
- Hemodialysis PPTDocument1 pageHemodialysis PPTjasminemuammilNo ratings yet
- Public Health Questions and Answers For Students 5Document1 pagePublic Health Questions and Answers For Students 5Tharani SelvendranNo ratings yet
- Public Health Questions and Answers For Students 3Document1 pagePublic Health Questions and Answers For Students 3Tharani SelvendranNo ratings yet
- ShockDocument2 pagesShock2b4kj7xdchNo ratings yet
- Drug of Choice (1) 3Document2 pagesDrug of Choice (1) 3Muzammil HusainNo ratings yet
- Chronic Myeloid Leukemia (CML) 3Document1 pageChronic Myeloid Leukemia (CML) 3Augustine A. KollieNo ratings yet
- Gu trauma- urethra PPTDocument1 pageGu trauma- urethra PPTOmar KhashashnehNo ratings yet
- Dialysis Machines Key FeaturesDocument1 pageDialysis Machines Key FeaturessurainepNo ratings yet
- JaundiceDocument1 pageJaundiceAugustine A. KollieNo ratings yet
- Pediatrics History Taking PDF 2Document2 pagesPediatrics History Taking PDF 2Red DevilNo ratings yet
- Pediatrics History Taking PDF 4Document2 pagesPediatrics History Taking PDF 4Red DevilNo ratings yet
- AbortionDocument1 pageAbortionArjesa TakaNo ratings yet
- More Related Content: Turp TechniqueDocument1 pageMore Related Content: Turp TechniqueRavi PramudiaNo ratings yet
- Cushings Syndrome - PPTX 2Document1 pageCushings Syndrome - PPTX 2gjct2bxm6yNo ratings yet
- PAIN HISTORY TAKING PPT 2Document1 pagePAIN HISTORY TAKING PPT 2Omar KhashashnehNo ratings yet
- History taking PPTDocument1 pageHistory taking PPTOmar KhashashnehNo ratings yet
- Phimosis & Paraphimosis PDFDocument1 pagePhimosis & Paraphimosis PDFAdaeze DouglasNo ratings yet
- Sinusoidal Current PPTDocument1 pageSinusoidal Current PPTAyesha MunirNo ratings yet
- Pap SmearDocument1 pagePap SmearMaria Carmela CastilloNo ratings yet
- Anemia (Investigatory Project) Class 11 | PDFDocument16 pagesAnemia (Investigatory Project) Class 11 | PDFDivyanilamaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Pharmacognosy 2Document1 pageIntroduction To Pharmacognosy 2Idenyi Daniel EwaNo ratings yet
- Hiv Treatment Final PPT 3Document1 pageHiv Treatment Final PPT 3Umer IsmailNo ratings yet
- Pathogenesis Hiv Slide 2Document1 pagePathogenesis Hiv Slide 2Augustine A. KollieNo ratings yet
- Handout PrenatalDocument1 pageHandout PrenataljasminemuammilNo ratings yet
- Benign Lesions of LarynxDocument1 pageBenign Lesions of LarynxAnjana UNo ratings yet
- Bio Medical Waste ManagementDocument1 pageBio Medical Waste Managementkabeerkhan30013No ratings yet
- Gingivectomy (Oral Surgery)Document1 pageGingivectomy (Oral Surgery)Daraí Bárbara Sánchez MonteroNo ratings yet
- Screenshot 2023-02-24 at 10.42.04 AMDocument1 pageScreenshot 2023-02-24 at 10.42.04 AMMir DanishNo ratings yet
- Acute PancreatitisDocument6 pagesAcute PancreatitisFatema AlburiNo ratings yet
- Abortion - PPT For 2nd MSCDocument1 pageAbortion - PPT For 2nd MSCArjesa TakaNo ratings yet
- Anemia PPT 2Document1 pageAnemia PPT 2sana ahmedNo ratings yet
- Meningococcal InfectionsDocument1 pageMeningococcal Infectionsheng28369No ratings yet
- Cast and Immobilization Techniques in OrthopaedicDocument3 pagesCast and Immobilization Techniques in OrthopaedicandysgraphicssNo ratings yet
- Patient Education ProgramDocument4 pagesPatient Education ProgramBriane OmondiNo ratings yet
- Screenshot 2023-08-23 at 5.06.03 PMDocument2 pagesScreenshot 2023-08-23 at 5.06.03 PMYashas V SureshNo ratings yet
- Medicolegal Aspects of DeathDocument1 pageMedicolegal Aspects of DeathGurdeep KaurNo ratings yet
- Community Mental HealthDocument1 pageCommunity Mental HealthSree LathaNo ratings yet
- Megaloblastic AnemiaDocument2 pagesMegaloblastic Anemiamoncalshareen3No ratings yet
- Ophthalmic PreparationsDocument2 pagesOphthalmic Preparations033 preya patelNo ratings yet
- Occupational Health & Occupational HazardsDocument1 pageOccupational Health & Occupational HazardsSree LathaNo ratings yet
- HypersensitivityDocument1 pageHypersensitivitySanjana ReddyNo ratings yet
- Bone Mineral Density (BMD) Test 2Document1 pageBone Mineral Density (BMD) Test 2Rica adriani SantikaNo ratings yet
- Bone Mineral Density (BMD) TestDocument1 pageBone Mineral Density (BMD) TestRica adriani SantikaNo ratings yet
- Medical Ethics Principles PDFDocument14 pagesMedical Ethics Principles PDFjtt8btwxhvNo ratings yet
- International Health Regulations (Ihr)Document1 pageInternational Health Regulations (Ihr)Sree LathaNo ratings yet
- Caisson's Disease PPT 2Document1 pageCaisson's Disease PPT 2Uzma TahseenNo ratings yet
- Newborn Care Oxygen Therapy PDFDocument1 pageNewborn Care Oxygen Therapy PDFAnjana UNo ratings yet
- Caisson's DiseaseDocument1 pageCaisson's DiseaseUzma TahseenNo ratings yet
- Nutrients Classification PPTDocument3 pagesNutrients Classification PPTmwqzdpztczNo ratings yet
- Emergency Nursing Questionnaires 2Document1 pageEmergency Nursing Questionnaires 2Mark Jayson TuazonNo ratings yet
- GAP - PPTX: RecommendedDocument10 pagesGAP - PPTX: RecommendedOm PawarNo ratings yet
- PROCESS OF ICH (International Council For HarmoniDocument3 pagesPROCESS OF ICH (International Council For Harmonilolipoppopcorn11111No ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Cavity PreparationDocument5 pagesFundamentals of Cavity PreparationAjay Praveen0% (1)
- Namaz PDFDocument14 pagesNamaz PDFnedimpolic16No ratings yet
- Nursing As A ProfessionDocument1 pageNursing As A ProfessionMaribel Diana YsulatNo ratings yet
- Artificial Reproductive TechnologyDocument12 pagesArtificial Reproductive Technologytokor40413No ratings yet
- Materi Sistem ImunDocument1 pageMateri Sistem ImunAbikNo ratings yet
- Reading ListDocument1 pageReading ListShaikh TahiraNo ratings yet
- Classical ConditioningDocument1 pageClassical Conditioninggerald almencionNo ratings yet
- Nutri 0713 SeDocument13 pagesNutri 0713 SeAileen BobadillaNo ratings yet
- Philips Titration Protocol 2017Document12 pagesPhilips Titration Protocol 2017Sam WhiteNo ratings yet
- Nootropic DrugsDocument13 pagesNootropic DrugsPetar DimkovNo ratings yet
- Occupational Safety and Health STDDocument65 pagesOccupational Safety and Health STDKirk Corales100% (4)
- Synonyms: Sreedhar's CCEDocument5 pagesSynonyms: Sreedhar's CCEOmaisNo ratings yet
- Solution Focused TechniquesDocument5 pagesSolution Focused TechniquesNazario Israel Narvaez ArzateNo ratings yet
- Risk Assessment and Analysis For Sliding Gates: Analysis of Gate Structure To Be MovedDocument6 pagesRisk Assessment and Analysis For Sliding Gates: Analysis of Gate Structure To Be Movedsmart_onyx17No ratings yet
- Lesson 4 Health PDFDocument25 pagesLesson 4 Health PDFRomeo BalingaoNo ratings yet
- List 13 HomeworkDocument2 pagesList 13 Homeworkapi-328692644No ratings yet
- Full PDFDocument9 pagesFull PDFAle TabaskoNo ratings yet
- Kenneth Jake T. BatiduanDocument1 pageKenneth Jake T. BatiduanKenneth Jake BatiduanNo ratings yet
- Ismenore: You Should Also DoDocument2 pagesIsmenore: You Should Also DoNurul Ilmi UtamiNo ratings yet
- BullyingDocument3 pagesBullyingdarwin wongNo ratings yet
- Mechanism of LaborDocument98 pagesMechanism of LaborLaarnee Sinsioco SantosNo ratings yet
- Class II Neurotic DisordersDocument37 pagesClass II Neurotic DisordersNarayan K Ghorapde100% (1)
- Arens Aud16 Inppt09Document33 pagesArens Aud16 Inppt09euncieNo ratings yet
- Job Description: Cardiff and Vale University Health Board Job DetailsDocument9 pagesJob Description: Cardiff and Vale University Health Board Job DetailsmustakNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular and Respiratory Systems - Unit TestDocument7 pagesCardiovascular and Respiratory Systems - Unit Testapi-305647618No ratings yet
- CCM 3225 Community DiagnosisDocument7 pagesCCM 3225 Community DiagnosisLulano MbasuNo ratings yet
- Malaria PreventionDocument3 pagesMalaria PreventionRohit_Patkar_2942No ratings yet
- NCP Tissue PerfusionDocument2 pagesNCP Tissue PerfusionNiña Montejo Ealdama100% (1)
- Scratch AssayDocument2 pagesScratch AssayElsya Veranza100% (1)
- Key To Being A Good ParentDocument15 pagesKey To Being A Good ParentJelena Preradovic100% (1)
- Clinical Teaching MethodsDocument29 pagesClinical Teaching MethodsDr. Jayesh Patidar100% (7)
- Iqvia Launch Excellence For Multi Indication Assets 02 23 ForwebDocument20 pagesIqvia Launch Excellence For Multi Indication Assets 02 23 ForwebsethirohinNo ratings yet
- Hair Loss Help ForumsDocument18 pagesHair Loss Help Forumshabitualnurture69No ratings yet