Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Important unidentate and multidentate ligand
Important unidentate and multidentate ligand
Uploaded by
Abhilasha SharmaCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- BS en ISO 11114-2 - Compatibility of MaterialsDocument26 pagesBS en ISO 11114-2 - Compatibility of MaterialsAndy HowlettNo ratings yet
- Preparation of P-Nitroacetanilide, Hydrolysis of P-Nitroacetanilide, Preparation of P-Nitroaniline (Student's Handout)Document6 pagesPreparation of P-Nitroacetanilide, Hydrolysis of P-Nitroacetanilide, Preparation of P-Nitroaniline (Student's Handout)Dotsha Raheem100% (4)
- Coordination Chemistry - Handout 1Document3 pagesCoordination Chemistry - Handout 1Thisali RathnayakaNo ratings yet
- Coordination Compounds 2022Document16 pagesCoordination Compounds 2022SIDHARTH SINHNo ratings yet
- 02-Nomenclature of LigandsDocument2 pages02-Nomenclature of LigandsAshmit SinhaNo ratings yet
- 1group and 2 Group Disconnections 04-Mar-2021Document10 pages1group and 2 Group Disconnections 04-Mar-2021Sowmya N DNo ratings yet
- chemical reactions of cyanide and isocyanide summaryDocument1 pagechemical reactions of cyanide and isocyanide summaryAbhilasha SharmaNo ratings yet
- Diazonium Salts, Azo DyesDocument8 pagesDiazonium Salts, Azo DyesDotsha Raheem100% (4)
- Diazonium Salts Azo DyesDocument8 pagesDiazonium Salts Azo DyesAnthony Basanta100% (1)
- Chemistry: S.No Negative LigandDocument1 pageChemistry: S.No Negative Ligandvedang agarwalNo ratings yet
- Halogen Derivative 3Document11 pagesHalogen Derivative 3atharva kadgiNo ratings yet
- Asset-V1 HKVU+COSAS+2021 Q4 R1+type@asset+block@metal-SeminarDocument37 pagesAsset-V1 HKVU+COSAS+2021 Q4 R1+type@asset+block@metal-Seminar1126playpubgNo ratings yet
- ShortNotes-6. Aldehyde and Ketone - 22128886Document6 pagesShortNotes-6. Aldehyde and Ketone - 22128886PranavNo ratings yet
- Unit-13 Onc - SPL TPDocument14 pagesUnit-13 Onc - SPL TPjagannathanNo ratings yet
- DGT Organic Compounds C NitrogenDocument15 pagesDGT Organic Compounds C Nitrogensc5753972No ratings yet
- Coordination 1Document59 pagesCoordination 1akbar azamNo ratings yet
- Coordination CompoundDocument16 pagesCoordination CompoundRahul PrajapatiNo ratings yet
- 01-Classification OfligandsDocument2 pages01-Classification OfligandsAshmit SinhaNo ratings yet
- Amines, Reactions: Basic NucleophilicDocument37 pagesAmines, Reactions: Basic NucleophilicM. MoizNo ratings yet
- CH 17 PDFDocument15 pagesCH 17 PDFkrishnaNo ratings yet
- Zadaci Za Vezbanje - 02Document14 pagesZadaci Za Vezbanje - 02leontina.goncacalvesNo ratings yet
- Molecular Rearrangement (Electron Deficient Nitrogen), AsynchronousDocument45 pagesMolecular Rearrangement (Electron Deficient Nitrogen), AsynchronousAzka AmandaNo ratings yet
- Vitamin PDFDocument19 pagesVitamin PDFSrivikashini KNo ratings yet
- بحث د.ابتهال كاظمDocument11 pagesبحث د.ابتهال كاظمالباحثة عن الحقNo ratings yet
- Chem-353-Lecture 2Document10 pagesChem-353-Lecture 2Caleb AsharleyNo ratings yet
- Nitrogen CompoundsDocument20 pagesNitrogen Compoundsapi-3734333No ratings yet
- CCN MHT CET Synopsis PDFDocument7 pagesCCN MHT CET Synopsis PDFAbhishek Mandlik100% (1)
- 65bc787665022d00198279d3 - ## - Amines Short NotesDocument7 pages65bc787665022d00198279d3 - ## - Amines Short NotesImdadullah AkbarNo ratings yet
- Polynuclear Aromatics: Anthracene NaphthaleneDocument26 pagesPolynuclear Aromatics: Anthracene NaphthaleneRonak Modi0% (1)
- Iupac Nomenclature of Cod CompoundsDocument11 pagesIupac Nomenclature of Cod CompoundsVenkatesh VNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13 Compound Contaning NitrogenDocument27 pagesChapter 13 Compound Contaning NitrogenTanvi ShahNo ratings yet
- 01 Nitrogen Containging Compound Part 1 Theory Final EDocument8 pages01 Nitrogen Containging Compound Part 1 Theory Final EImtiaz AliNo ratings yet
- Lect. 7 Nitro CompoundsDocument13 pagesLect. 7 Nitro CompoundsAbdo HaiderNo ratings yet
- The Sandmeyer Reaction: Replacement of The Diazonium Group by CL, BR, or CNDocument2 pagesThe Sandmeyer Reaction: Replacement of The Diazonium Group by CL, BR, or CNUsman GhaniNo ratings yet
- Table of Common LigandsDocument1 pageTable of Common LigandsLet's work today For better tomorrow100% (2)
- AnilineDocument21 pagesAnilineDr M K GuptaNo ratings yet
- Phosphate Group (Double-Ringed: DeoxyriboseDocument6 pagesPhosphate Group (Double-Ringed: Deoxyriboseabdulkareemfarida4No ratings yet
- Unit-13 Onc 2023Document16 pagesUnit-13 Onc 2023jagannathanNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry Reaction Summary SheetDocument30 pagesOrganic Chemistry Reaction Summary SheetKylo RenNo ratings yet
- Lecture 11, Sulphonation, DiazotizationDocument22 pagesLecture 11, Sulphonation, DiazotizationMALIK ZARYABBABARNo ratings yet
- UreacycleDocument18 pagesUreacycleChudasama DhruvrajsinhNo ratings yet
- Chemistry AllDocument4 pagesChemistry Allcandy.rajput02No ratings yet
- Key Chem TheoryDocument8 pagesKey Chem Theoryalex.holdcroft23No ratings yet
- Nisa Slide Icnp2015Document19 pagesNisa Slide Icnp2015Yun NikNo ratings yet
- Pharmaceutical Organic Chemistry LecDocument51 pagesPharmaceutical Organic Chemistry Lecبن آجرومNo ratings yet
- Aldehydes Notes 27 May 2023Document7 pagesAldehydes Notes 27 May 2023Aafia AlamNo ratings yet
- CHEM F311 Lecture 40 Use of Aliphatic Nitro Compounds 1,2-Difunctionalised CompoundsDocument8 pagesCHEM F311 Lecture 40 Use of Aliphatic Nitro Compounds 1,2-Difunctionalised Compoundsliving luxuriousNo ratings yet
- 04 Reactive IntermediatesDocument115 pages04 Reactive IntermediatesMuhammad ArsalanNo ratings yet
- Scan 4 Oct 2020 Alcohol, Phenol, EtherDocument6 pagesScan 4 Oct 2020 Alcohol, Phenol, Ethernikhilpise2006No ratings yet
- Amines: (I) Basic Character of AminesDocument1 pageAmines: (I) Basic Character of AmineseliyachrisNo ratings yet
- Natural ProductsDocument18 pagesNatural ProductsSankar AdhikariNo ratings yet
- FF - MC Lecture PPT 2.en - IdDocument18 pagesFF - MC Lecture PPT 2.en - IdRegina SyafinatullahNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Online NotesDocument16 pagesChemistry Online NotesBharti YadavNo ratings yet
- Neet Sample PaparDocument6 pagesNeet Sample PaparSuman LattaNo ratings yet
- C3- Chemical ReactionDocument17 pagesC3- Chemical ReactionNapassorn WongduangpaNo ratings yet
- 5 6145477749600419915Document15 pages5 6145477749600419915Ihtisham Ul HaqNo ratings yet
- Amines and Nitrogen Compounds-1Document8 pagesAmines and Nitrogen Compounds-1CBIT CIVIL A1No ratings yet
- Name of Ligands in Coordination CompoundsDocument1 pageName of Ligands in Coordination CompoundsUpendra Shukla50% (4)
- Handbook of Reagents for Organic Synthesis: Reagents for Heteroarene FunctionalizationFrom EverandHandbook of Reagents for Organic Synthesis: Reagents for Heteroarene FunctionalizationNo ratings yet
- Executive Summary: BackgroundDocument16 pagesExecutive Summary: BackgroundUsman KulkarniNo ratings yet
- 4-Seminar Uji Efikasi Fumigan Berbahan Aktif Sulfuryl Flouride Pada Komoditas Beras An Ilham MendrofaDocument8 pages4-Seminar Uji Efikasi Fumigan Berbahan Aktif Sulfuryl Flouride Pada Komoditas Beras An Ilham MendrofasuryanaNo ratings yet
- Studies On Liver Marker Enzymes (SGOT and SGPT) of Fish Heteropneustes Fossilis (Bloch.) After Famfos IntoxicationDocument4 pagesStudies On Liver Marker Enzymes (SGOT and SGPT) of Fish Heteropneustes Fossilis (Bloch.) After Famfos IntoxicationKanhiya MahourNo ratings yet
- Aqa 8464C1F QP Jun18 PDFDocument24 pagesAqa 8464C1F QP Jun18 PDFMustafa NabeihNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document24 pagesChapter 1moltot getahunNo ratings yet
- ASTM D4243 99 Standard Test Method For Measurement of Average Viscometric DPDocument6 pagesASTM D4243 99 Standard Test Method For Measurement of Average Viscometric DPNatália Rufino Tavares de MouraNo ratings yet
- Earth As A Physicochemical SystemDocument2 pagesEarth As A Physicochemical SystemJuan Sebastian Barbosa MejiaNo ratings yet
- 11 Chemistry Solutions Chapter 12 Q 1 18Document20 pages11 Chemistry Solutions Chapter 12 Q 1 18Arbia WahidNo ratings yet
- Experiment 2Document5 pagesExperiment 2Noor Aini JaafarNo ratings yet
- Arogyajagratha Calendar 2022 FHC AmbalavayalDocument25 pagesArogyajagratha Calendar 2022 FHC AmbalavayalJafar SheriefNo ratings yet
- Aqa A Level Chemistry Cheatsheet 3Document24 pagesAqa A Level Chemistry Cheatsheet 3David AdigboNo ratings yet
- Spectrophotometric Determination of Selenium by Use of ThioninDocument4 pagesSpectrophotometric Determination of Selenium by Use of ThioninSena KulaksızNo ratings yet
- 2022 SUP EXAM QP 83E A VersionDocument16 pages2022 SUP EXAM QP 83E A VersionZaheerAhmedAhmedNo ratings yet
- Rice Husk AshDocument7 pagesRice Husk Ashian yuhuNo ratings yet
- Final SHS Gen - Chem. Q3 Module 3 Colligative PropertiesDocument25 pagesFinal SHS Gen - Chem. Q3 Module 3 Colligative PropertiesAllan Jay DaligdigNo ratings yet
- Class Test-6 - Carboxylic Acid - Amines JEE Adv - CC - AnsDocument6 pagesClass Test-6 - Carboxylic Acid - Amines JEE Adv - CC - Ansbruh pogNo ratings yet
- Percentage Ascorbic AcidDocument2 pagesPercentage Ascorbic AcidVinodNo ratings yet
- Answer Script For Textiles Fourth SemesterDocument8 pagesAnswer Script For Textiles Fourth SemestermansiagrawalNo ratings yet
- Osmosis R. SERIE R200Document68 pagesOsmosis R. SERIE R200Ron VillaNo ratings yet
- Paper Sludge PDFDocument13 pagesPaper Sludge PDFDanie RoyNo ratings yet
- Chemistry - Weekend Task-Grade 8Document3 pagesChemistry - Weekend Task-Grade 8kavyaNo ratings yet
- Science of SlimeDocument3 pagesScience of SlimeMax Is hereNo ratings yet
- Process Development For Separation of Lignin From OrganoCat LignocelluloseDocument14 pagesProcess Development For Separation of Lignin From OrganoCat LignocelluloseYudanis TaqwinNo ratings yet
- 10 1002@jctb 6502Document46 pages10 1002@jctb 6502Quynh Anh NguyenNo ratings yet
- DEGALAN 66 02 N eDocument2 pagesDEGALAN 66 02 N echungyang.gohNo ratings yet
- Ivan Zaman: Element (Metal) Symbol Valency Atomic Element Symbol Valency AtomicDocument2 pagesIvan Zaman: Element (Metal) Symbol Valency Atomic Element Symbol Valency AtomicJobayer Mahin100% (2)
- IUPAC Naming ExampleDocument2 pagesIUPAC Naming ExampleShimanta EasinNo ratings yet
- Noakhali Science and Technology University: Department of PharmacyDocument26 pagesNoakhali Science and Technology University: Department of PharmacyMd Ismail HosenNo ratings yet
- Analysis QBDocument167 pagesAnalysis QBChethan PrabhuNo ratings yet
Important unidentate and multidentate ligand
Important unidentate and multidentate ligand
Uploaded by
Abhilasha SharmaCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Important unidentate and multidentate ligand
Important unidentate and multidentate ligand
Uploaded by
Abhilasha SharmaCopyright:
Available Formats
nenswe CHEASTR
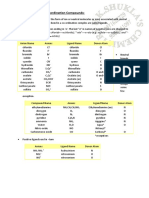
Table 9.2. Some Common Unidentate Ligands
CO-ORDINAT
Charge
Name Formula Name of Ligand
Zero
Ammonia GNH, ammine
Water H,Ö: zero
aquo or aqua
-1 halo
Halide ion X
(X = Cl, Br, I)
Hydroxide ion :OH -1 hydroxo
Cyanide ion :CN -1 cyano
Oxide ion -2 OX0
Peroxide ion 2 peroxo
Carbonate ion Co, carbonato
Phosphine zero phosphine
Nitrogen oxide NO zero nitrosyl
Carbon monoxide CO Zero carbonyl
Sulphate ion So, -2 sulphato
Nitrite ion NO, -1 nitro or nitrito*
Thiocyanate ion SCN -1 thiocyanato or
isothiocyanato*
-1 acetato
Acetate ion CH,CO0
Pyridine C,H,N zero pyridine (py)
Sulphide ion -2 sulphido
Thiosulphate S,0, -2 thiosulphato
Nitrate ion --1 nitrato
Sulphite ion SO,2 -2 sulphito
Triphenyl phosphine (C,H,),P zero triphenyl phosphine
Thiocarbonyl CS zero thiocarbonyl
nitrosonium
Nitrosonium NO+ +1
Nitronium NO,* + 1 nitronium
Imide ion NH -2 imido
Nitrate ion nitrato
NO, -1
Amide ion amido
NH, -1
Thio urea thiourea (tu)
H,NCSNH, Zero
*See -Linkage isomerism.
453
NCOMPOUNDS
Table 9.3. Some Multidentate Ligands
Formula Abbreviation Donor Sites
Species
the
Charge
Nlameof
Bihvlenediamine
NH,CH,CH,NH, Zero en 2
2
Zero bipy
22-Biyridyl
2
-2 OX
Oxalate i0n
CH-C C-CH,
acac 2
-1
Acetylacetonate
2
CH,C= NO -1 dmg
Dimethylglyoxime ion
CH,C =NOH
CH, C=0 gly
2
-1
H,N
Glycinato
zero
0-phen
1, 10 phenanthroline
or ortho-phenanthroline
CH,NH, dien 3
zero
H,C:
Diethylene triamine CNH
or
N-2-aminoethyl))-1,
2ethanediamine H,CKCH.NH,
3
tery
Zero
2,2: 6, 2"terpyridine
4
trien
zero
Triethylene tetraamine CH,NHCH,), NH,
CH,GHCH,)NH,
NN-bhisanedi
12-et -42-aamiminnoete hyl)
454
CH, N<
CH,CO0>
Qomprehense CHEMIST,
Ethylenediamine CH,CO0 3
triacetate ion H EDTA
CH-N 5
CH,CO0 ->
CH,CO0 ’
CH.-N
Ethylenediamine tetra CH,CO0 ’ -4
acetate ion EDT+
CH,CO0 ’ 6
H-N CH,CO0 ’
8-hydroxyquinolinato -1 (Oxin) or 2
:0: (oxinate)
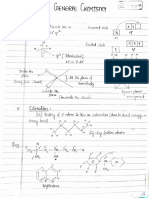
Some common chelating ligands are shown below:
H
Knoukedge Plus.
HC CH
INNER METALLIC COMPLEXES
H H When ligands like acetyl acetonato, glycinata.
which possess both neutral and anionic g
Oxalate ion Ortho-phenanthroline (ph) Carbonate co-ordinate with metallic cation, they form comp
(0X) 10n in which both the co-ordination number and char;
the cation are satisfied simultaneously. Such oam
are called inner-metallic complexes or simply i
ODafow Kuou?. complexes. For example
(i) Chelating ligands form more stable
than the monodentate ligands. For example, complexes
of ethylenediammine with cobalt is more the complex
complex with water.
stable than the CH, NH, III
Co
(CoH,0)J +3en ’ (Colen),J'* +6NH, |co-o
This is because when
chelation occurs entropy
increases and the process becomes more favourable.
effect is called macrocyclic effect. In the This
above reaction ¬0
particles/species of reactants is four and after chelation
the number increases H,C
toseven.
(ü) Ligands with larger groups
than the ligands with form unstable rings -0
tosteric hinderance smaller groups.This is ascribable CCo Or
(iü) All types produced by a larger group. HC
of bidentate,
polydentate ligands can act as chelatingtridentate
ligands.
and =0
(iv) Metal chelates having
stable when atoms in the ring5-membered ring are most
are joined only by single H,C
bonds.
(u) 6-membered
chelates having
in the ring are moredouble bond or
unsaturation
You might also like
- BS en ISO 11114-2 - Compatibility of MaterialsDocument26 pagesBS en ISO 11114-2 - Compatibility of MaterialsAndy HowlettNo ratings yet
- Preparation of P-Nitroacetanilide, Hydrolysis of P-Nitroacetanilide, Preparation of P-Nitroaniline (Student's Handout)Document6 pagesPreparation of P-Nitroacetanilide, Hydrolysis of P-Nitroacetanilide, Preparation of P-Nitroaniline (Student's Handout)Dotsha Raheem100% (4)
- Coordination Chemistry - Handout 1Document3 pagesCoordination Chemistry - Handout 1Thisali RathnayakaNo ratings yet
- Coordination Compounds 2022Document16 pagesCoordination Compounds 2022SIDHARTH SINHNo ratings yet
- 02-Nomenclature of LigandsDocument2 pages02-Nomenclature of LigandsAshmit SinhaNo ratings yet
- 1group and 2 Group Disconnections 04-Mar-2021Document10 pages1group and 2 Group Disconnections 04-Mar-2021Sowmya N DNo ratings yet
- chemical reactions of cyanide and isocyanide summaryDocument1 pagechemical reactions of cyanide and isocyanide summaryAbhilasha SharmaNo ratings yet
- Diazonium Salts, Azo DyesDocument8 pagesDiazonium Salts, Azo DyesDotsha Raheem100% (4)
- Diazonium Salts Azo DyesDocument8 pagesDiazonium Salts Azo DyesAnthony Basanta100% (1)
- Chemistry: S.No Negative LigandDocument1 pageChemistry: S.No Negative Ligandvedang agarwalNo ratings yet
- Halogen Derivative 3Document11 pagesHalogen Derivative 3atharva kadgiNo ratings yet
- Asset-V1 HKVU+COSAS+2021 Q4 R1+type@asset+block@metal-SeminarDocument37 pagesAsset-V1 HKVU+COSAS+2021 Q4 R1+type@asset+block@metal-Seminar1126playpubgNo ratings yet
- ShortNotes-6. Aldehyde and Ketone - 22128886Document6 pagesShortNotes-6. Aldehyde and Ketone - 22128886PranavNo ratings yet
- Unit-13 Onc - SPL TPDocument14 pagesUnit-13 Onc - SPL TPjagannathanNo ratings yet
- DGT Organic Compounds C NitrogenDocument15 pagesDGT Organic Compounds C Nitrogensc5753972No ratings yet
- Coordination 1Document59 pagesCoordination 1akbar azamNo ratings yet
- Coordination CompoundDocument16 pagesCoordination CompoundRahul PrajapatiNo ratings yet
- 01-Classification OfligandsDocument2 pages01-Classification OfligandsAshmit SinhaNo ratings yet
- Amines, Reactions: Basic NucleophilicDocument37 pagesAmines, Reactions: Basic NucleophilicM. MoizNo ratings yet
- CH 17 PDFDocument15 pagesCH 17 PDFkrishnaNo ratings yet
- Zadaci Za Vezbanje - 02Document14 pagesZadaci Za Vezbanje - 02leontina.goncacalvesNo ratings yet
- Molecular Rearrangement (Electron Deficient Nitrogen), AsynchronousDocument45 pagesMolecular Rearrangement (Electron Deficient Nitrogen), AsynchronousAzka AmandaNo ratings yet
- Vitamin PDFDocument19 pagesVitamin PDFSrivikashini KNo ratings yet
- بحث د.ابتهال كاظمDocument11 pagesبحث د.ابتهال كاظمالباحثة عن الحقNo ratings yet
- Chem-353-Lecture 2Document10 pagesChem-353-Lecture 2Caleb AsharleyNo ratings yet
- Nitrogen CompoundsDocument20 pagesNitrogen Compoundsapi-3734333No ratings yet
- CCN MHT CET Synopsis PDFDocument7 pagesCCN MHT CET Synopsis PDFAbhishek Mandlik100% (1)
- 65bc787665022d00198279d3 - ## - Amines Short NotesDocument7 pages65bc787665022d00198279d3 - ## - Amines Short NotesImdadullah AkbarNo ratings yet
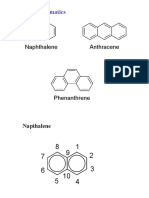
- Polynuclear Aromatics: Anthracene NaphthaleneDocument26 pagesPolynuclear Aromatics: Anthracene NaphthaleneRonak Modi0% (1)
- Iupac Nomenclature of Cod CompoundsDocument11 pagesIupac Nomenclature of Cod CompoundsVenkatesh VNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13 Compound Contaning NitrogenDocument27 pagesChapter 13 Compound Contaning NitrogenTanvi ShahNo ratings yet
- 01 Nitrogen Containging Compound Part 1 Theory Final EDocument8 pages01 Nitrogen Containging Compound Part 1 Theory Final EImtiaz AliNo ratings yet
- Lect. 7 Nitro CompoundsDocument13 pagesLect. 7 Nitro CompoundsAbdo HaiderNo ratings yet
- The Sandmeyer Reaction: Replacement of The Diazonium Group by CL, BR, or CNDocument2 pagesThe Sandmeyer Reaction: Replacement of The Diazonium Group by CL, BR, or CNUsman GhaniNo ratings yet
- Table of Common LigandsDocument1 pageTable of Common LigandsLet's work today For better tomorrow100% (2)
- AnilineDocument21 pagesAnilineDr M K GuptaNo ratings yet
- Phosphate Group (Double-Ringed: DeoxyriboseDocument6 pagesPhosphate Group (Double-Ringed: Deoxyriboseabdulkareemfarida4No ratings yet
- Unit-13 Onc 2023Document16 pagesUnit-13 Onc 2023jagannathanNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry Reaction Summary SheetDocument30 pagesOrganic Chemistry Reaction Summary SheetKylo RenNo ratings yet
- Lecture 11, Sulphonation, DiazotizationDocument22 pagesLecture 11, Sulphonation, DiazotizationMALIK ZARYABBABARNo ratings yet
- UreacycleDocument18 pagesUreacycleChudasama DhruvrajsinhNo ratings yet
- Chemistry AllDocument4 pagesChemistry Allcandy.rajput02No ratings yet
- Key Chem TheoryDocument8 pagesKey Chem Theoryalex.holdcroft23No ratings yet
- Nisa Slide Icnp2015Document19 pagesNisa Slide Icnp2015Yun NikNo ratings yet
- Pharmaceutical Organic Chemistry LecDocument51 pagesPharmaceutical Organic Chemistry Lecبن آجرومNo ratings yet
- Aldehydes Notes 27 May 2023Document7 pagesAldehydes Notes 27 May 2023Aafia AlamNo ratings yet
- CHEM F311 Lecture 40 Use of Aliphatic Nitro Compounds 1,2-Difunctionalised CompoundsDocument8 pagesCHEM F311 Lecture 40 Use of Aliphatic Nitro Compounds 1,2-Difunctionalised Compoundsliving luxuriousNo ratings yet
- 04 Reactive IntermediatesDocument115 pages04 Reactive IntermediatesMuhammad ArsalanNo ratings yet
- Scan 4 Oct 2020 Alcohol, Phenol, EtherDocument6 pagesScan 4 Oct 2020 Alcohol, Phenol, Ethernikhilpise2006No ratings yet
- Amines: (I) Basic Character of AminesDocument1 pageAmines: (I) Basic Character of AmineseliyachrisNo ratings yet
- Natural ProductsDocument18 pagesNatural ProductsSankar AdhikariNo ratings yet
- FF - MC Lecture PPT 2.en - IdDocument18 pagesFF - MC Lecture PPT 2.en - IdRegina SyafinatullahNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Online NotesDocument16 pagesChemistry Online NotesBharti YadavNo ratings yet
- Neet Sample PaparDocument6 pagesNeet Sample PaparSuman LattaNo ratings yet
- C3- Chemical ReactionDocument17 pagesC3- Chemical ReactionNapassorn WongduangpaNo ratings yet
- 5 6145477749600419915Document15 pages5 6145477749600419915Ihtisham Ul HaqNo ratings yet
- Amines and Nitrogen Compounds-1Document8 pagesAmines and Nitrogen Compounds-1CBIT CIVIL A1No ratings yet
- Name of Ligands in Coordination CompoundsDocument1 pageName of Ligands in Coordination CompoundsUpendra Shukla50% (4)
- Handbook of Reagents for Organic Synthesis: Reagents for Heteroarene FunctionalizationFrom EverandHandbook of Reagents for Organic Synthesis: Reagents for Heteroarene FunctionalizationNo ratings yet
- Executive Summary: BackgroundDocument16 pagesExecutive Summary: BackgroundUsman KulkarniNo ratings yet
- 4-Seminar Uji Efikasi Fumigan Berbahan Aktif Sulfuryl Flouride Pada Komoditas Beras An Ilham MendrofaDocument8 pages4-Seminar Uji Efikasi Fumigan Berbahan Aktif Sulfuryl Flouride Pada Komoditas Beras An Ilham MendrofasuryanaNo ratings yet
- Studies On Liver Marker Enzymes (SGOT and SGPT) of Fish Heteropneustes Fossilis (Bloch.) After Famfos IntoxicationDocument4 pagesStudies On Liver Marker Enzymes (SGOT and SGPT) of Fish Heteropneustes Fossilis (Bloch.) After Famfos IntoxicationKanhiya MahourNo ratings yet
- Aqa 8464C1F QP Jun18 PDFDocument24 pagesAqa 8464C1F QP Jun18 PDFMustafa NabeihNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document24 pagesChapter 1moltot getahunNo ratings yet
- ASTM D4243 99 Standard Test Method For Measurement of Average Viscometric DPDocument6 pagesASTM D4243 99 Standard Test Method For Measurement of Average Viscometric DPNatália Rufino Tavares de MouraNo ratings yet
- Earth As A Physicochemical SystemDocument2 pagesEarth As A Physicochemical SystemJuan Sebastian Barbosa MejiaNo ratings yet
- 11 Chemistry Solutions Chapter 12 Q 1 18Document20 pages11 Chemistry Solutions Chapter 12 Q 1 18Arbia WahidNo ratings yet
- Experiment 2Document5 pagesExperiment 2Noor Aini JaafarNo ratings yet
- Arogyajagratha Calendar 2022 FHC AmbalavayalDocument25 pagesArogyajagratha Calendar 2022 FHC AmbalavayalJafar SheriefNo ratings yet
- Aqa A Level Chemistry Cheatsheet 3Document24 pagesAqa A Level Chemistry Cheatsheet 3David AdigboNo ratings yet
- Spectrophotometric Determination of Selenium by Use of ThioninDocument4 pagesSpectrophotometric Determination of Selenium by Use of ThioninSena KulaksızNo ratings yet
- 2022 SUP EXAM QP 83E A VersionDocument16 pages2022 SUP EXAM QP 83E A VersionZaheerAhmedAhmedNo ratings yet
- Rice Husk AshDocument7 pagesRice Husk Ashian yuhuNo ratings yet
- Final SHS Gen - Chem. Q3 Module 3 Colligative PropertiesDocument25 pagesFinal SHS Gen - Chem. Q3 Module 3 Colligative PropertiesAllan Jay DaligdigNo ratings yet
- Class Test-6 - Carboxylic Acid - Amines JEE Adv - CC - AnsDocument6 pagesClass Test-6 - Carboxylic Acid - Amines JEE Adv - CC - Ansbruh pogNo ratings yet
- Percentage Ascorbic AcidDocument2 pagesPercentage Ascorbic AcidVinodNo ratings yet
- Answer Script For Textiles Fourth SemesterDocument8 pagesAnswer Script For Textiles Fourth SemestermansiagrawalNo ratings yet
- Osmosis R. SERIE R200Document68 pagesOsmosis R. SERIE R200Ron VillaNo ratings yet
- Paper Sludge PDFDocument13 pagesPaper Sludge PDFDanie RoyNo ratings yet
- Chemistry - Weekend Task-Grade 8Document3 pagesChemistry - Weekend Task-Grade 8kavyaNo ratings yet
- Science of SlimeDocument3 pagesScience of SlimeMax Is hereNo ratings yet
- Process Development For Separation of Lignin From OrganoCat LignocelluloseDocument14 pagesProcess Development For Separation of Lignin From OrganoCat LignocelluloseYudanis TaqwinNo ratings yet
- 10 1002@jctb 6502Document46 pages10 1002@jctb 6502Quynh Anh NguyenNo ratings yet
- DEGALAN 66 02 N eDocument2 pagesDEGALAN 66 02 N echungyang.gohNo ratings yet
- Ivan Zaman: Element (Metal) Symbol Valency Atomic Element Symbol Valency AtomicDocument2 pagesIvan Zaman: Element (Metal) Symbol Valency Atomic Element Symbol Valency AtomicJobayer Mahin100% (2)
- IUPAC Naming ExampleDocument2 pagesIUPAC Naming ExampleShimanta EasinNo ratings yet
- Noakhali Science and Technology University: Department of PharmacyDocument26 pagesNoakhali Science and Technology University: Department of PharmacyMd Ismail HosenNo ratings yet
- Analysis QBDocument167 pagesAnalysis QBChethan PrabhuNo ratings yet