Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Name"sarween Robitan Alassade Hawzhen Mohssan Shema Abad Alwahad
Name"sarween Robitan Alassade Hawzhen Mohssan Shema Abad Alwahad
Uploaded by
sarweenOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Name"sarween Robitan Alassade Hawzhen Mohssan Shema Abad Alwahad
Name"sarween Robitan Alassade Hawzhen Mohssan Shema Abad Alwahad
Uploaded by
sarweenCopyright:
Available Formats
Name"sarween robitan alassade hawzhen mohssan shema abad alwahad
Deb" Food Technology
Principles of dairy science Dr"narin mhamed nanakali
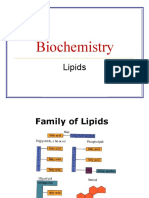
Types of fat and its characteristics
There is milk fat emulsion in the form of a natural compound because of a fatty substance, including: fat phosphorous, and carotenoids, and a vehicle Algelesarad a high melting point which is the membrane around the three pools Algelesarad and its compounds, similar to the rule of squalene (Squalen). And fatty granules formed in this way vary in size composed of milk with sugar and protein in the case of colloid in a liquid genuine, and granules can be seen clearly Bamajahr normal. Milk fat consists mainly of a mixture which is a threeAlgelesarad the esterification of fatty acids and glycerol which are distributed irregularly on the glycerol carbonate. There are about 14 different fatty acids in milk fat, as has been identified (30) fatty acids and the last but the quantity is very small. Glycerol and manufactured in the mammary gland of the blood sugar, and then combine with the fatty acids. The table shows (5) fatty acids that are found in both human colostrum and bovine colostrum (the milk raw). Is produced short-chain fatty acids in the carbon mammary gland of vinegar (derived from blood sugar) (Acetate) or Betahadroxad Biotirat B - hydroxybutyrate, or blood sugar directly. The vinegar, which consists in the intestine by the process of enteric fermentation of sugars move with the blood
circulation to the mammary gland is configured as fatty acids (short-chain carbon). It should be noted that the fatty acids (short chain) are not found in human milk, or non-existent and there is a small percentage in the milk of animals other than ruminants. The triglyceride, which is transmitted with the blood it offers what seems Albmutaik acid (Palmitic acid) and oleic acid (Oleic acid), which Aktran in milk fat. And provides that in addition to other saturated fatty acids and long chain from a acids Aloliakih. Apparently, the triglyceride in the blood is divided, and is re-distribution of fatty acids in the triglyceride by mammary gland, using glycerol (Glycerol) produced by this gland. (Linoleic and arachideonic acid) and for fatty acids (long carbon chain), it is derived from fat food directly, and carries blood to the mammary gland in the image of esters (esters) cholesterol, and composed acid Aleracedona (Arachidonic acid) in the tissues of the body from acid Allenoleik (Linoleic) Because these acids belong to the same (metabolic group). The tissues of the body is unable to produce these acids or fatty acids, the acid group Allenoliynyh. The acids and Allenolieckih Alercedonah Allenoliynyh and necessary for the metabolism of fatty tissue as it supplies food. And provide high levels of these fatty acids and various unsaturated (Polyunsaturated) to dairy cows does not increase the amount of detachment in the milk. The bowel hydrogenated unsaturated fatty acids quickly, and mammary gland, it does not take linoleic acid from the blood stream quickly and easily. Although the amount of fat phosphorous are very small (0.2 1.0%) of the total milk fat, but it is one of the important components of the fat, and be distributed.
As it appears on the components of the cells of the body is composed of fatty acids, phosphoric acid and other groups Kalgelesarol Choline in lecithin, and all of Alaithanolamyin (ethanolamine) and serine (Serine) in cephalin) and Ambassnjosen (Sphingosine) in Ambassnjamilan (Sphingomyelin). The fatty acids with a low nuclear weight are found only very small amounts. Other vehicle and fat in the milk: (Alserreauseid Ambasszjusyn + galactose + long-chain fatty acid and carbon Albulazemalogin (Plasmalogens) glycerol (Glycerol) + Aldehidz aldehydes + fatty acid + phosphoric acid + choline Choline or Ethanolamine Athanolamin And plasma to the neutral Lejeune does not contain phosphoric acid and phosphorous fats are found individually, but be united with the proteins in milk (1). It is therefore clear that the components of milk fat (ie, glycerol and fatty acids) are taken from each of the blood and Alvrth (directly or indirectly, is glucose and its metabolites (Setilobatem) the source of glycerol. And fatty acids that its series of 16 or more carbon (saturated or non saturated) fat comes from the blood or tissues after degradation (Hydrolysis) in the mammary gland. The fatty acids derived from tissue shall be taken from Alvrth. Here, there is congruence between what is indicated by the verse (66) of Surat bees and the scientific discoveries regarding milk fats.
You might also like
- LIPID METABOLISM Notes PDFDocument8 pagesLIPID METABOLISM Notes PDFToga BrandonNo ratings yet
- ProjectDocument56 pagesProjectPramod KumarNo ratings yet
- Fatty Acids and GlyceridesDocument17 pagesFatty Acids and GlyceridesAngelia PedrenoNo ratings yet
- Tsi New-1Document8 pagesTsi New-1Markos sitotawNo ratings yet
- Chem2OB3 - Experiment 5Document7 pagesChem2OB3 - Experiment 5MarsXplorerNo ratings yet
- CYL456: Chemistry of Life - An Introduction Biomolecules: LipidsDocument45 pagesCYL456: Chemistry of Life - An Introduction Biomolecules: LipidsMegraj MeenaNo ratings yet
- Milk Fat Composition: 1. Blood LipidsDocument3 pagesMilk Fat Composition: 1. Blood Lipidszarqa zulfiqarNo ratings yet
- LIPIDS ReportDocument38 pagesLIPIDS ReportcharmsterNo ratings yet
- FST 3210 Milk and Dairy Products Part OneDocument23 pagesFST 3210 Milk and Dairy Products Part OneAhmad MukhtarNo ratings yet
- Lipids MLT and DPTDocument89 pagesLipids MLT and DPTZille HummaNo ratings yet
- What Are Lipids?Document16 pagesWhat Are Lipids?Khazel CasimiroNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7chemistry of LipidDocument31 pagesChapter 7chemistry of Lipidbayan.grNo ratings yet
- Fat - WikipediaDocument29 pagesFat - WikipediaWaqar AhmadNo ratings yet
- Lipids NotesDocument4 pagesLipids NoteskatNo ratings yet
- Tsi NewDocument7 pagesTsi NewMarkos sitotawNo ratings yet
- Chemistry of LipidsDocument7 pagesChemistry of Lipidsbossbaby18105No ratings yet
- Nutritional Components in MilkDocument7 pagesNutritional Components in MilkJenny V. BajoNo ratings yet
- Biochem Lec (Part 2)Document248 pagesBiochem Lec (Part 2)Rainier Vincent LeonardoNo ratings yet
- Structure of LipidDocument11 pagesStructure of LipidAfrah Alatas100% (1)
- Hormone Like, Help Regulate Blood Pressure, Clotting, and Produce Pain and FeverDocument87 pagesHormone Like, Help Regulate Blood Pressure, Clotting, and Produce Pain and FeverReyana BaderNo ratings yet
- Composition of Milk PDFDocument5 pagesComposition of Milk PDFghanashyam tomarNo ratings yet
- From "Lipos", A Greek Word For Fat.: Six Essential Nutrients: FatsDocument5 pagesFrom "Lipos", A Greek Word For Fat.: Six Essential Nutrients: FatsBumanghat ElviraNo ratings yet
- Glucose-6-Phosphate in Metabolic Processes: ProcessDocument3 pagesGlucose-6-Phosphate in Metabolic Processes: ProcessEL-nina Liebt U VaterNo ratings yet
- Lipids BiochemistryDocument188 pagesLipids BiochemistryfayanNo ratings yet
- Lipid: Endah PuspitasariDocument13 pagesLipid: Endah Puspitasaritnep21No ratings yet
- Lipids FatsDocument21 pagesLipids FatsMona Riza PagtabonanNo ratings yet
- LipidsDocument6 pagesLipidsMUHAMMAD SHOAIB MUNAWARNo ratings yet
- Chem 113 Lipid ActivityDocument3 pagesChem 113 Lipid ActivityAlliah MendozaNo ratings yet
- Lecture No. 3: Lipid ChemistryDocument22 pagesLecture No. 3: Lipid ChemistrySafura IjazNo ratings yet
- Structure of Fats: Saturated and Unsaturated FatsDocument4 pagesStructure of Fats: Saturated and Unsaturated FatsClaudia Rosela GabrieliaNo ratings yet
- Session 2-Milk and Milk ProductDocument39 pagesSession 2-Milk and Milk ProductZul Fiqriyani SafitriNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3: LIPIDSDocument77 pagesChapter 3: LIPIDSOltagon Nicole DupingayNo ratings yet
- FatsDocument6 pagesFatsro_sheenNo ratings yet
- Biological MoleculeDocument14 pagesBiological MoleculeRaidioactiveguyNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Fat Rich Dairy ProductsDocument9 pagesIntroduction To Fat Rich Dairy ProductsMonty KushwahaNo ratings yet
- FatsDocument45 pagesFatsManshad AbbasNo ratings yet
- BiochemistryDocument9 pagesBiochemistryshubhm008No ratings yet
- 4 LipidsDocument59 pages4 LipidsDESIGNERICLELYN SORONIONo ratings yet
- Lipis ReportDocument11 pagesLipis ReportEnnavy YongkolNo ratings yet
- BP U8 LipidsDocument69 pagesBP U8 Lipidsjada germaineNo ratings yet
- Return To Lab Menu: Analysis of The Chemical Components of Milk ObjectivesDocument7 pagesReturn To Lab Menu: Analysis of The Chemical Components of Milk Objectivesgailluna112795No ratings yet
- Structure and Classification of Lipids: PresentDocument4 pagesStructure and Classification of Lipids: Presentsamantha laurenthNo ratings yet
- Fat Digestion and Metabolism in RuminantsDocument23 pagesFat Digestion and Metabolism in Ruminantsshahbaz zafarNo ratings yet
- Lipids: Guide Questions Group 1-BDocument12 pagesLipids: Guide Questions Group 1-BMarie Christy Blancaflor JuanitoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Biochemistry and Clinical Pathology Complete Notes by Noteskarts Acc To ER20Document8 pagesChapter 4 Biochemistry and Clinical Pathology Complete Notes by Noteskarts Acc To ER20yplsinghNo ratings yet
- Milk and Milk ProductsDocument10 pagesMilk and Milk ProductsNirmal SharmaNo ratings yet
- Milk CompositionDocument1 pageMilk CompositionAndreea Andrei100% (2)
- MacronutrientsDocument107 pagesMacronutrientsPaul DeliyosNo ratings yet
- 6 Lipids Diagestion Absoption NewDocument45 pages6 Lipids Diagestion Absoption Newamel elabassNo ratings yet
- Lipid PDFDocument5 pagesLipid PDFKhổng Tiến ĐạtNo ratings yet
- Blue Illustrated Heart Health Fair FlyerDocument7 pagesBlue Illustrated Heart Health Fair FlyerFelipeMorenoNo ratings yet
- Lipids: Prepared By: de Torres, Angelica M. Che-4102Document37 pagesLipids: Prepared By: de Torres, Angelica M. Che-4102Angelica de TorresNo ratings yet
- Fatty AcidsDocument13 pagesFatty AcidsRaviraj MalaniNo ratings yet
- Lipids (脂质) : Michel-Eugene ChevreulDocument73 pagesLipids (脂质) : Michel-Eugene ChevreulAdeeb NawahdaNo ratings yet
- (WWW - Indowebster.com) Lipid Transport Amp StorageDocument33 pages(WWW - Indowebster.com) Lipid Transport Amp StorageRs93No ratings yet
- Isolation of Casein, Lactose and Albumin From MilkDocument9 pagesIsolation of Casein, Lactose and Albumin From MilkkimradaNo ratings yet
- Cleansing Mechanism of SoapDocument3 pagesCleansing Mechanism of SoapAlexis Nacionales AguinaldoNo ratings yet
- Nutritional Quality of Milkfat: 1 What's in Milkfat?Document10 pagesNutritional Quality of Milkfat: 1 What's in Milkfat?test testNo ratings yet
- End of Year Test A : GrammarDocument3 pagesEnd of Year Test A : GrammarMaks SlobodianNo ratings yet
- Make in India: WelcomeDocument25 pagesMake in India: Welcomevkumar_345287No ratings yet
- Some Any A - An ActivityDocument4 pagesSome Any A - An Activitygeraldine.laraNo ratings yet
- Tsunami and One Year AfterDocument84 pagesTsunami and One Year Aftersherinedavidsa100% (3)
- Golden Era Muscle BookDocument50 pagesGolden Era Muscle BookRick Gaines100% (1)
- Sandeep IBDocument73 pagesSandeep IBSandy RanaNo ratings yet
- Business GoalsDocument7 pagesBusiness GoalsMariel Generalao MacapazNo ratings yet
- Proposal Effect of Processing Methods On Mineral Contents of Selected Lentils in EthiopiaDocument6 pagesProposal Effect of Processing Methods On Mineral Contents of Selected Lentils in EthiopiaTäð Œvê MîðNo ratings yet
- Ilmu Gizi DasarDocument36 pagesIlmu Gizi DasarJuliana AskimNo ratings yet
- Feasibility Study of ProjectDocument15 pagesFeasibility Study of ProjectMauliddha RachmiNo ratings yet
- Sbl-Report3 ProteinDocument8 pagesSbl-Report3 Proteinapi-383715002No ratings yet
- Social Welfare Programs and Social Safety Nets in The Philippines: in Times of Crisis and BeyondDocument38 pagesSocial Welfare Programs and Social Safety Nets in The Philippines: in Times of Crisis and BeyondAsian Development BankNo ratings yet
- Information Sheet 5.1.1 Common Culinary Terms Used With Regard To SandwichesDocument4 pagesInformation Sheet 5.1.1 Common Culinary Terms Used With Regard To SandwichesZeyya Nikka Cordova Pingad50% (2)
- Du Gruyere: The Restaurant 7/7 InformationDocument2 pagesDu Gruyere: The Restaurant 7/7 InformationLeo MoltoNo ratings yet
- Representations of The Table of WisdomDocument20 pagesRepresentations of The Table of WisdomАнђелија КозакијевићNo ratings yet
- Design For Social Innovation As A Form of Designing Activism. An Action FormatDocument13 pagesDesign For Social Innovation As A Form of Designing Activism. An Action FormatNesta100% (1)
- A Lifeless Soul s1Document154 pagesA Lifeless Soul s1priscillarachel40No ratings yet
- Wine ListDocument2 pagesWine ListeatlocalmenusNo ratings yet
- Chuys 2023 Menu Pricing Updates Tier 2 WEBDocument2 pagesChuys 2023 Menu Pricing Updates Tier 2 WEBDavid RothwellNo ratings yet
- Pahiyas FestivalDocument3 pagesPahiyas FestivalAnne Marlaine MagbanuaNo ratings yet
- Muraco MenuDocument1 pageMuraco MenuJeje DengiNo ratings yet
- Karnataka MinWages FY17Document183 pagesKarnataka MinWages FY17Navin SanjeevNo ratings yet
- MYZ - Zone HumansDocument8 pagesMYZ - Zone HumansCristian Rubio-Quintanilla Alcalá100% (1)
- Jurnal Agroekoteknologi FP Usu E-Issn No. 2337-659 Vol.7.No.2, Maret 2019 (45) : 361-367Document7 pagesJurnal Agroekoteknologi FP Usu E-Issn No. 2337-659 Vol.7.No.2, Maret 2019 (45) : 361-367mdnhllNo ratings yet
- Coca ColaDocument28 pagesCoca ColaTayyeba NoureenNo ratings yet
- Joel Andrews Abraham - 19BSPHH01C0475 - Final ReportDocument70 pagesJoel Andrews Abraham - 19BSPHH01C0475 - Final Report1787AshishBishtaniaNo ratings yet
- P.4 Scie Package 26TH May To 2ND June 2020Document8 pagesP.4 Scie Package 26TH May To 2ND June 2020Monydit santinoNo ratings yet
- Ish300 Chapter 4&5Document29 pagesIsh300 Chapter 4&5Amanina AyuniNo ratings yet