Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Document
Document
Uploaded by
Shreeyaa Mehta0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views3 pagesOutline on presentation on chapter 15 of economics as and a level
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentOutline on presentation on chapter 15 of economics as and a level
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views3 pagesDocument
Document
Uploaded by
Shreeyaa MehtaOutline on presentation on chapter 15 of economics as and a level
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 3
### Slide 1: Introduction
- **Story/Example**: Imagine a bustling shareholder meeting where passionate individuals
debate the company's future. Mention Warren Buffett, the legendary investor known for his
wisdom and long-term vision.
- **Key Point**: This presentation will delve into the fascinating world of owners and
shareholders, exploring their influence and impact on businesses.
### Slide 2: Uncovering the Essence
- **Main Idea**: This presentation aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of the
dynamic roles, rights, and responsibilities of owners and shareholders.
### Slide 3: Interactive Exploration
- **Engagement**: We'll use interactive elements including quizzes, role-playing, and case
studies to make learning engaging and impactful.
### Slide 4: Real-World Insights
- **Practical Application**: By exploring real-world examples and discussions, you'll gain
practical insights into the world of shareholders.
### Slide 5: Roles of Owners/Shareholders
- **Overview**: Owners and shareholders are the backbone of a company, providing
financial capital and driving growth.
- **Decision-Making**: Shareholders participate in crucial decisions affecting the
company's future through voting rights. They impact major strategies, acquisitions, and more.
- **Oversight**: They actively monitor the company's performance, ensuring accountability
and responsible management. This involves scrutinizing financial reports and executive
actions.
- **Active Participation**: Shareholders engage in company affairs by attending meetings,
voicing concerns, and advocating for responsible practices, shaping the company's trajectory.
### Slide 6: Rights of Owners/Shareholders
- **Overview**: As owners, shareholders possess certain rights that empower them to
participate in the company's affairs and receive benefits from their investment.
- **Voting Rights**: Shareholders have the right to vote on crucial decisions like electing
board members, approving mergers, and authorizing significant expenditures.
- **Dividends**: They are entitled to receive a share of the company's profits in the form of
dividends, a direct financial reward for their investment.
- **Information Rights**: Shareholders have access to essential information about the
company's performance, financial reports, and corporate governance practices.
- **Pre-emptive Rights**: In some cases, shareholders have the right to purchase new
shares issued by the company before they are offered to the public, protecting their ownership
stake.
### Slide 7: Responsibilities of Owners/Shareholders
- **Overview**: Beyond their rights, owners and shareholders also bear responsibilities
towards the company and its stakeholders.
- **Ethical Decision-Making**: Shareholders should consider the ethical implications of
their decisions, supporting companies that operate responsibly and contribute to society.
- **Long-Term Planning**: They have a responsibility to think about the long-term health
and sustainability of the company, advocating for investments that promote future growth.
- **Accountability**: Owners must hold management accountable for their actions,
ensuring transparency, ethical behavior, and responsible financial practices.
- **Stakeholder Engagement**: Shareholders should actively engage with stakeholders,
considering the interests of employees, customers, and the community, promoting a
responsible and sustainable business environment.
### Slide 8: Case Study - Apple Inc.
- **Example**: Apple Inc., a renowned tech giant, offers a fascinating case study of
shareholder activism and engagement.
- **2020**: Shareholders debated and voted on environmental initiatives, pushing Apple to
embrace more sustainable practices.
- **2021**: The company faced scrutiny regarding its app store policies, with shareholders
demanding greater transparency and fairness.
- **2022**: Shareholders advocated for increased diversity and inclusion within Apple's
leadership team, pushing for greater representation.
### Slide 9: Conclusion
- **Wrap Up**: Thank the audience for their attention.
- **Encouragement**: Encourage questions and invite further discussion.
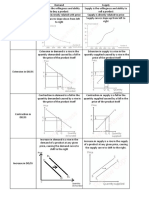
In the context of India, GDP is typically used as the primary measure of economic
performance and size because it captures the total value of goods and services produced
within the country’s borders, making it a comprehensive indicator of domestic economic
activity. This focus on domestic production is crucial for policymakers to design and
implement effective economic policies that directly impact the local economy. Additionally,
GDP allows for consistent international comparisons, aiding in trade and investment
decisions. It also provides essential data for economic planning, helping identify key growth
sectors and informing strategies. Furthermore, GDP is a vital metric for investors and
businesses, signaling economic stability and growth potential, while also correlating closely
with employment rates and income levels. Overall, GDP serves as a crucial tool for
understanding, managing, and enhancing India’s economic performance and growth.
In practice, GDP is the primary measure used for assessing Germany's economic activity and
performance because it provides a comprehensive view of all economic production within the
country's borders. This makes GDP the most relevant metric for policy-making, as it directly
reflects the effectiveness of domestic economic policies and initiatives. Additionally, GDP
allows for consistent and standardized comparisons with other countries, which is crucial for
international trade and investment decisions. It also aids in economic analysis and planning
by identifying key sectors driving growth and informing resource allocation. Consequently,
GDP is considered the best measure for evaluating Germany's economic output and overall
performance, as it offers a clear and complete picture of the nation’s economic health and
development.
You might also like
- NYSF Leveraged Buyout Model TemplateDocument20 pagesNYSF Leveraged Buyout Model TemplateBenNo ratings yet
- Controller Investor Relations RoleDocument4 pagesController Investor Relations RoleNoel MiñanoNo ratings yet
- Project On Kotak Mutual FundDocument63 pagesProject On Kotak Mutual FundAnupamJena33% (3)
- Financial AccountingDocument6 pagesFinancial AccountingAnushkaa DattaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Financial ManagementDocument11 pagesIntroduction To Financial Managementamina.94664No ratings yet
- MGT 406 - STRAT-WPS OfficeDocument17 pagesMGT 406 - STRAT-WPS OfficeClarissa Atillano FababairNo ratings yet
- Ethics Notes GptDocument26 pagesEthics Notes GptCute GirlNo ratings yet
- Accounting Mid Term DefinitionsDocument8 pagesAccounting Mid Term Definitions619ahadNo ratings yet
- Understanding BusinessDocument2 pagesUnderstanding BusinessAbirham GetieNo ratings yet
- EntrpreneurshipDocument5 pagesEntrpreneurship1-F NikhithaNo ratings yet
- Gse202 Compete SummaryDocument27 pagesGse202 Compete SummaryabdulwaritholawepoNo ratings yet
- Accounting and ModalitiesDocument5 pagesAccounting and Modalitiesjaphetnkunika34No ratings yet
- Dividend Decision Indiabulls Financial Services LTD 2011Document78 pagesDividend Decision Indiabulls Financial Services LTD 2011Vinathy PalleNo ratings yet
- What Is AuditingDocument8 pagesWhat Is Auditingalbhome pcNo ratings yet
- Cash Crop Farming FeasibilityDocument7 pagesCash Crop Farming FeasibilitytatawalatatuNo ratings yet
- Fundamental of Finance ManagementDocument49 pagesFundamental of Finance ManagementShashank SonkarNo ratings yet
- GP - Password@sameer20240223182614Document8 pagesGP - Password@sameer20240223182614mohdsameerali143No ratings yet
- Project MF - Kuldeep SinghDocument73 pagesProject MF - Kuldeep SinghJoanna HernandezNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document28 pagesChapter 1JonNo ratings yet
- Business Finance Guide WK 1Document4 pagesBusiness Finance Guide WK 1Efren Grenias JrNo ratings yet
- 01 Financial Management and The Firm and Review of Financial Statements (Session 1)Document68 pages01 Financial Management and The Firm and Review of Financial Statements (Session 1)creamellzNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 FinanceDocument2 pagesUnit 1 Financearmish24uk11No ratings yet
- LEARNING MODULE-Financial Accounting and ReportingDocument7 pagesLEARNING MODULE-Financial Accounting and ReportingAira AbigailNo ratings yet
- Financial Management CH 1Document22 pagesFinancial Management CH 1Gadisa TarikuNo ratings yet
- Unit - 3 Public Issue Management Investment BankingDocument27 pagesUnit - 3 Public Issue Management Investment Bankinghansikagupta2611No ratings yet
- 3rd Sem Assignment StrategicDocument3 pages3rd Sem Assignment StrategicurstrulytejaguptaNo ratings yet
- FM TheoryDocument42 pagesFM TheoryMeenakshi PradeepNo ratings yet
- Finance CompilationDocument14 pagesFinance CompilationNo NameNo ratings yet
- EntraaaapinuarDocument12 pagesEntraaaapinuar6.9.6.9.thats.what.she.said.6.9.6.9No ratings yet
- CFDocument15 pagesCFmauryaveer11No ratings yet
- Financial ManagementDocument3 pagesFinancial ManagementSharanNo ratings yet
- IDM Assignment AllDocument15 pagesIDM Assignment AllmejabahadurNo ratings yet
- RuruDocument18 pagesRuruShreyash PatilNo ratings yet
- Financial ManagementDocument10 pagesFinancial ManagementSameer ShaikhNo ratings yet
- Stock Holding Corporation of India LimitedDocument10 pagesStock Holding Corporation of India LimitedSOMA15No ratings yet
- Stock MarketDocument4 pagesStock Marketvyash ashNo ratings yet
- Fundamental Aanalysis On ICICI BankDocument56 pagesFundamental Aanalysis On ICICI BankAsif KhanNo ratings yet
- BUSINESS ORGANISATION 1stDocument19 pagesBUSINESS ORGANISATION 1stmohammadham242No ratings yet
- Eb p2Document4 pagesEb p2lifeofmeowbdNo ratings yet
- Numero 5Document2 pagesNumero 5stephan bomaNo ratings yet
- Fyp-Equity Research For India InfolineDocument70 pagesFyp-Equity Research For India InfolinePranay DagaNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument63 pagesUntitledHari NathNo ratings yet
- Entrepreneurial Skills: Introduction To The StudyDocument19 pagesEntrepreneurial Skills: Introduction To The Studyaminkhizer377No ratings yet
- SDocument16 pagesSdieungo.31211023417No ratings yet
- LN07 Smart3075419 12 FI C07Document60 pagesLN07 Smart3075419 12 FI C07trevorsum123No ratings yet
- Investment AssignmentDocument4 pagesInvestment AssignmentthorseiratyNo ratings yet
- Alternative Investment 20240226101737Document2 pagesAlternative Investment 20240226101737manjusri2327No ratings yet
- Company's Shareholders: Chairperson's CEO's Auditor's Mission Statement Corporate GovernanceDocument5 pagesCompany's Shareholders: Chairperson's CEO's Auditor's Mission Statement Corporate GovernanceRoshanrvNo ratings yet
- Stock Market Main Project PDFDocument57 pagesStock Market Main Project PDFshridhar gadeNo ratings yet
- 20Document2 pages20GeniuS GSMNo ratings yet
- Equity Research For India InfolineDocument70 pagesEquity Research For India Infolinejyoti rNo ratings yet
- Reviewer 1Document2 pagesReviewer 1Atulo FebrimanNo ratings yet
- Principles of Corporate GovernanceDocument11 pagesPrinciples of Corporate Governancefor thierNo ratings yet
- Cooperative PhilosophyDocument7 pagesCooperative Philosophyndunguloren96No ratings yet
- Baterisna - REVIEWER (FinMan)Document5 pagesBaterisna - REVIEWER (FinMan)Regine BaterisnaNo ratings yet
- ### Introduction To Workplace Ethics: ### Factors Affecting Ethical Behaviour at WorkDocument19 pages### Introduction To Workplace Ethics: ### Factors Affecting Ethical Behaviour at Workkvyas4861No ratings yet
- Important of Accountant by ChatGPTDocument2 pagesImportant of Accountant by ChatGPTTalaNo ratings yet
- What Is Accounting?: Philippines Reporting Standards (PFRS)Document3 pagesWhat Is Accounting?: Philippines Reporting Standards (PFRS)Anonymous yvHbTK4XoNo ratings yet
- Features of Stock Exchange: Fundamental AnalysisDocument8 pagesFeatures of Stock Exchange: Fundamental AnalysisShanmuka SreenivasNo ratings yet
- Entrepreneur an-WPS OfficeDocument2 pagesEntrepreneur an-WPS OfficeJustin AdarosNo ratings yet
- PowerPoint PresentationDocument8 pagesPowerPoint PresentationShreeyaa MehtaNo ratings yet
- Shreeyaa Mehta - FLE - Comprehension - Ws 6 and 7 - Grade 9A - February 19 2023Document4 pagesShreeyaa Mehta - FLE - Comprehension - Ws 6 and 7 - Grade 9A - February 19 2023Shreeyaa MehtaNo ratings yet
- Style Analysis November 2011Document4 pagesStyle Analysis November 2011Shreeyaa MehtaNo ratings yet
- Practice For Month June and July 2023Document35 pagesPractice For Month June and July 2023Shreeyaa MehtaNo ratings yet
- Acc Mixed PaperDocument11 pagesAcc Mixed PaperShreeyaa MehtaNo ratings yet
- Inc RecdsDocument3 pagesInc RecdsShreeyaa MehtaNo ratings yet
- GR 9 Math - Sem 1 Revision Sheet 2Document20 pagesGR 9 Math - Sem 1 Revision Sheet 2Shreeyaa MehtaNo ratings yet
- 2020 Specimen Paper 4 Mark SchemeDocument12 pages2020 Specimen Paper 4 Mark SchemeShreeyaa MehtaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 & 8 NotesDocument3 pagesChapter 7 & 8 NotesShreeyaa MehtaNo ratings yet
- Ict - PrintDocument1 pageIct - PrintShreeyaa MehtaNo ratings yet
- Thatate Sansar MajhaDocument2 pagesThatate Sansar Majhalaxmi sambreNo ratings yet
- AYALA - Commercial Banking 3Document3 pagesAYALA - Commercial Banking 3French D. AyalaNo ratings yet
- Life Cycle Costing (LLC) in Value EngineeringDocument37 pagesLife Cycle Costing (LLC) in Value EngineeringanantarajkhanalNo ratings yet
- Rebar Cage AssemblyDocument18 pagesRebar Cage Assemblyajit karandikarNo ratings yet
- Bitboy Marketing DeckDocument2 pagesBitboy Marketing DeckDragomir DanielNo ratings yet
- Core White Paper v1.0.6Document35 pagesCore White Paper v1.0.6damasealexisNo ratings yet
- What Are Food Stamps Worth - PongpipatDocument32 pagesWhat Are Food Stamps Worth - PongpipatPhanita PhakdiNo ratings yet
- Broad 1901Document98 pagesBroad 1901Criss MorillasNo ratings yet
- Ca Foundation Paper 3 MTP Ques 2023Document17 pagesCa Foundation Paper 3 MTP Ques 2023OLD ACCOUNTNo ratings yet
- Into To Supply Graduation ProjectDocument27 pagesInto To Supply Graduation ProjectMahmoud AhmadNo ratings yet
- Business Mathematics: Department of EducationDocument2 pagesBusiness Mathematics: Department of EducationSharlyn Marie An Noble-BadilloNo ratings yet
- SBOTS - 26 - State Bank of Pakistan. Career DevelopmentDocument3 pagesSBOTS - 26 - State Bank of Pakistan. Career DevelopmentshakeelahmedNo ratings yet
- Dinotefuram: DINNO TÉCNICO (Registro MAPA Nº 29119)Document22 pagesDinotefuram: DINNO TÉCNICO (Registro MAPA Nº 29119)alexandrealves10No ratings yet
- Gammon: Heavy Duty Dry Break Quick DisconnectDocument2 pagesGammon: Heavy Duty Dry Break Quick DisconnectAdolfo Eduardo García BraunNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 3 Accounting For Public Sector & Civil SocietyDocument88 pagesChapter - 3 Accounting For Public Sector & Civil Societyfekadegebretsadik478729No ratings yet
- L.M. No. 2. Interest and Usury (Catholic and Islamic Tradition) and The Merchant of VeniceDocument17 pagesL.M. No. 2. Interest and Usury (Catholic and Islamic Tradition) and The Merchant of Venicemarkchristopher.agustin.engNo ratings yet
- Applied Economics Is The Application of Economic Theory and Econometrics in Specific SettingsDocument8 pagesApplied Economics Is The Application of Economic Theory and Econometrics in Specific SettingsNoemi Elgincolin ManlapazNo ratings yet
- IAS 32 - Financial InstrumentsDocument28 pagesIAS 32 - Financial InstrumentsJaaNo ratings yet
- Community Support Worker Job Description 1Document2 pagesCommunity Support Worker Job Description 1ghalib ahmedNo ratings yet
- Hotanakatte SchoolDocument21 pagesHotanakatte Schoolsunilkumar1988No ratings yet
- Supply Chain Management Module 1Document37 pagesSupply Chain Management Module 1Random MusicNo ratings yet
- HDFC Statement - 01.11.021 - 13.04.2022Document9 pagesHDFC Statement - 01.11.021 - 13.04.2022Raghav SharmaNo ratings yet
- Personal DictionaryDocument2 pagesPersonal DictionaryAlfia RoyaniNo ratings yet
- Eq 2391 AbbDocument2 pagesEq 2391 AbbMahyar MashayekhiNo ratings yet
- Mbaf 605 Lecture Week 2-4Document135 pagesMbaf 605 Lecture Week 2-4Gen AbulkhairNo ratings yet
- FSR 2018 19 1Document96 pagesFSR 2018 19 1Prashant chaudharyNo ratings yet
- Handouts PDICDocument3 pagesHandouts PDICKhiara Jansz P. BeltranNo ratings yet
- Chap 2 ReviewDocument10 pagesChap 2 ReviewK59 Du Ngoc Phuong UyenNo ratings yet
- Allama Iqbal Open University, Islamabad: (Department of Economics)Document3 pagesAllama Iqbal Open University, Islamabad: (Department of Economics)ilyas muhammadNo ratings yet