Professional Documents
Culture Documents
CNS Cancer Pathology
CNS Cancer Pathology
Uploaded by
lindseycallierCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Oncology Nursing (Word) Bulleted For NSG RevieweesDocument8 pagesOncology Nursing (Word) Bulleted For NSG Revieweesswitlipz100% (1)
- PHA611 - Unit 2 - Lesson 2 - Plant StemDocument9 pagesPHA611 - Unit 2 - Lesson 2 - Plant StemJonah Dane BautistaNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Traumatic Brain Injury: Melissa J. Mcginn,, John T. PovlishockDocument11 pagesPathophysiology of Traumatic Brain Injury: Melissa J. Mcginn,, John T. Povlishocksiska misaliNo ratings yet
- Squash Cytology Vs Frozen Section Ver2Document54 pagesSquash Cytology Vs Frozen Section Ver2Shruthi N.RNo ratings yet
- Malignant Epithelial Slides-1Document5 pagesMalignant Epithelial Slides-1Cenonina Paola TapiaNo ratings yet
- Micro - Male Repro (Sec A) PDFDocument5 pagesMicro - Male Repro (Sec A) PDFKaren ValdezNo ratings yet
- Cytology of Normal Epithelial CellsDocument31 pagesCytology of Normal Epithelial CellsNatalia HaikaliNo ratings yet
- AAD BF Paisley Tie DiagnosisDocument2 pagesAAD BF Paisley Tie Diagnosiskahkashanahmed065No ratings yet
- WBC SlidesDocument5 pagesWBC SlidesCenonina Paola TapiaNo ratings yet
- Neoplasms of The KidneyDocument5 pagesNeoplasms of The KidneyEMILY N CRUZ-VARGASNo ratings yet
- Roots, Stems and Leaves Grade 10 2022 Learners FinalDocument29 pagesRoots, Stems and Leaves Grade 10 2022 Learners Finalanelisancokwana14No ratings yet
- Histology of The Testicle Spermatogenesis TZsDocument21 pagesHistology of The Testicle Spermatogenesis TZsYogita BhansaliNo ratings yet
- Skull Base Tumors NBNDocument30 pagesSkull Base Tumors NBNAbdullah Yeamin PeyalNo ratings yet
- Arasitology: Intestinal AmoebaeDocument5 pagesArasitology: Intestinal AmoebaeMa. Mil Adrianne PamaNo ratings yet
- Parasitology (Lect #5) TransDocument3 pagesParasitology (Lect #5) TransSherlyn Giban InditaNo ratings yet
- Lymphatic System ReviewerDocument49 pagesLymphatic System ReviewerJess Lejarde100% (1)
- Intellectual FunctionsDocument13 pagesIntellectual Functionsrrkn9njjhzNo ratings yet
- EpitheliaDocument1 pageEpitheliaTarlan SharifiNo ratings yet
- The OrgansDocument13 pagesThe OrgansFAITH ELLA MARIE PARMANo ratings yet
- Brain TumorsDocument3 pagesBrain TumorsDrashty DesaiNo ratings yet
- Spindle Cell TumorsDocument138 pagesSpindle Cell TumorsMadhura ShekatkarNo ratings yet
- Blood and Tissue Flagellates para LecDocument8 pagesBlood and Tissue Flagellates para LecLian MallareNo ratings yet
- SurgPatho Thyroid 2018Document8 pagesSurgPatho Thyroid 2018John Paulo CatacutanNo ratings yet
- 17174-Imging of Cerebellopontine Angle - Prof El BeltagiDocument10 pages17174-Imging of Cerebellopontine Angle - Prof El BeltagiPugazhenthi CNo ratings yet
- Haematoxylin and Eosin (H+E) - Aldehyde-Fuchsin - Van Geison's Picro Fuchsin Technique - Masson's Trichrome - Nuclei - Blue/backDocument9 pagesHaematoxylin and Eosin (H+E) - Aldehyde-Fuchsin - Van Geison's Picro Fuchsin Technique - Masson's Trichrome - Nuclei - Blue/backsilentscreamsofloveNo ratings yet
- L6-PATHO-Neoplasia (Sept2821)Document12 pagesL6-PATHO-Neoplasia (Sept2821)Erald PaderangaNo ratings yet
- Tissue Type Sketch Function Location Notes Simple Squamous EpitheliumDocument9 pagesTissue Type Sketch Function Location Notes Simple Squamous EpitheliumKaitlin NooneyNo ratings yet
- Bengin SGT 2023Document11 pagesBengin SGT 2023Hazem MouradNo ratings yet
- Male Reproductive HistologyDocument7 pagesMale Reproductive HistologyCarmela MarianoNo ratings yet
- Pineal Sellar Pituitary Dr. RitaDocument112 pagesPineal Sellar Pituitary Dr. RitaAkifa NailaNo ratings yet
- Annotated OneShotANAT, DR Ashwani - 230208 - 143653Document90 pagesAnnotated OneShotANAT, DR Ashwani - 230208 - 143653KabbuNo ratings yet
- Histology: Histology Slide Diagrams, Discussion Questions and Slide PicturesDocument45 pagesHistology: Histology Slide Diagrams, Discussion Questions and Slide Picturesmarjanggyamar7No ratings yet
- Anatomy One Shot DR AshwiniDocument95 pagesAnatomy One Shot DR Ashwinienthusiast383No ratings yet
- SECTION 6: Spleen: and OverviewDocument38 pagesSECTION 6: Spleen: and Overviewtudoranluciana1No ratings yet
- Surgical Pathology - CNSDocument2 pagesSurgical Pathology - CNSIsabel CastilloNo ratings yet
- Atrial Flagellates LabDocument3 pagesAtrial Flagellates LabLeinard ClaveroNo ratings yet
- Epithelium: Dr. Lalit MehraDocument39 pagesEpithelium: Dr. Lalit Mehramus zaharaNo ratings yet
- Hole's Human Anatomy and Physiology: 5 Skeletal SystemDocument73 pagesHole's Human Anatomy and Physiology: 5 Skeletal SystemLongyapon Sheena StephanieNo ratings yet
- AAD BF Cutaneous Smooth Muscle TumorsDocument2 pagesAAD BF Cutaneous Smooth Muscle Tumorskahkashanahmed065No ratings yet
- Activity 4 Organogenesis in The Frog Embryo Activity Worksheet A. 4 MM Frog EmbryoDocument4 pagesActivity 4 Organogenesis in The Frog Embryo Activity Worksheet A. 4 MM Frog Embryojhayyypee jhayypsNo ratings yet
- Gastrulation Somites and Folding TSRDocument27 pagesGastrulation Somites and Folding TSRAsia SattiNo ratings yet
- Dr. Praveen - Important Topcs UPDATED 2023Document33 pagesDr. Praveen - Important Topcs UPDATED 2023Sakshi SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- 四下micro 2Document77 pages四下micro 2q124415669No ratings yet
- Extra-Adrenal Paraganglioma: A Brief OverviewDocument19 pagesExtra-Adrenal Paraganglioma: A Brief Overviewpperez1863No ratings yet
- Cancer 1 - 2022 - LectureDocument42 pagesCancer 1 - 2022 - LectureJoshua KaoNo ratings yet
- Epithelial Tumours - SreejaDocument184 pagesEpithelial Tumours - SreejaaakiNo ratings yet
- Paediatric Liver TumoursDocument22 pagesPaediatric Liver TumoursMohamed HelmiNo ratings yet
- 4.3 Intestinal FlagellatesDocument7 pages4.3 Intestinal FlagellatesJudith Dianne Ignacio100% (1)
- Salv GLND Histopath Slides 051116Document64 pagesSalv GLND Histopath Slides 051116Amesz Itzu Tsang SynysterNo ratings yet
- c4k 06 Jenkins Nrsoft Tissue SarcomasDocument11 pagesc4k 06 Jenkins Nrsoft Tissue SarcomasAde CahyanaNo ratings yet
- Male Reproductive Path and SurgeryDocument36 pagesMale Reproductive Path and SurgeryThimira WaidyasekaraNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 Neoplasia 1 2 Robbins and Cotran Pathologic Basis of Disease PDFDocument9 pagesChapter 7 Neoplasia 1 2 Robbins and Cotran Pathologic Basis of Disease PDFChethranNo ratings yet
- Protozoans - Amebae: Medically Important ParasitesDocument10 pagesProtozoans - Amebae: Medically Important ParasitesBrylle LumberioNo ratings yet
- Soft Tissue Tumor SeminarDocument39 pagesSoft Tissue Tumor SeminarAhmad SyahmiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3-4 - TablesDocument6 pagesChapter 3-4 - TablesvallecerajamaicaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy MS University IMP'sDocument4 pagesAnatomy MS University IMP'spatelsharmistha415No ratings yet
- Mindmap - AnatomyDocument9 pagesMindmap - AnatomyPushpa DhruvNo ratings yet
- OPD Surgery Complete PDFDocument22 pagesOPD Surgery Complete PDFPeter Paul RecaboNo ratings yet
- Slides - 01-03 - Gastrulation and Trilaminar EmbryoDocument16 pagesSlides - 01-03 - Gastrulation and Trilaminar EmbryoSebastian RuaNo ratings yet
- SURGICAL PATHOLOGY SOFT TISSUES TableDocument4 pagesSURGICAL PATHOLOGY SOFT TISSUES TableIsabel CastilloNo ratings yet
- Case Study Cva Gr1Document72 pagesCase Study Cva Gr1Divina Gracia Fabicon Arana100% (1)
- Glioblastoma: in This Fact SheetDocument17 pagesGlioblastoma: in This Fact SheetSunil GvalaniNo ratings yet
- Levin - Godukhin - 2017 - Modulating Effect of Cytokines On Mechanisms of Synaptic Plasticity in The BrainDocument11 pagesLevin - Godukhin - 2017 - Modulating Effect of Cytokines On Mechanisms of Synaptic Plasticity in The Brainkeon.arbabi.altNo ratings yet
- Neuroinflammation and Neuroprogression in DepressionDocument14 pagesNeuroinflammation and Neuroprogression in DepressionAldehydeNo ratings yet
- 10 1 1 110Document135 pages10 1 1 110khaled1512No ratings yet
- The Retinal Muller Cell PDFDocument293 pagesThe Retinal Muller Cell PDFkemalasari8818No ratings yet
- The Effects of 528 HZ Sound Wave To Reduce Cell Death in Human Astrocyteprimary Cell Culture Treated With Ethanol 2155 6105 1000335Document5 pagesThe Effects of 528 HZ Sound Wave To Reduce Cell Death in Human Astrocyteprimary Cell Culture Treated With Ethanol 2155 6105 1000335kaoscodedNo ratings yet
- Role of Glia in Optic NerveDocument21 pagesRole of Glia in Optic NerveSi PuputNo ratings yet
- CBT 2 Paper PDFDocument140 pagesCBT 2 Paper PDFkarthikNo ratings yet
- Science - Abo7257 SMDocument105 pagesScience - Abo7257 SM张议No ratings yet
- Neural Cell BiologyDocument348 pagesNeural Cell BiologySrinivas PingaliNo ratings yet
- TMP F578Document10 pagesTMP F578FrontiersNo ratings yet
- Actcr 1 (3) 15Document11 pagesActcr 1 (3) 15Robinson Trujillo CabanillaNo ratings yet
- PTAH Principle and Dignostic ApplicationDocument1 pagePTAH Principle and Dignostic ApplicationSuman MandalNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 AllDocument95 pagesUnit 1 Allaloysius limNo ratings yet
- Glutamate and GABA in Appetite Regulation: Teresa C. DelgadoDocument8 pagesGlutamate and GABA in Appetite Regulation: Teresa C. DelgadoFia NisaNo ratings yet
- Fisiologi SSP NEUDocument59 pagesFisiologi SSP NEUCeyvira ArsytaNo ratings yet
- Journal - Formaldehyde in Brain An Overlooked Player in Neurodegeneration PDFDocument15 pagesJournal - Formaldehyde in Brain An Overlooked Player in Neurodegeneration PDFtriNo ratings yet
- Fizyoloji Kongresi FEPS 2011 Abstract Book PDFDocument522 pagesFizyoloji Kongresi FEPS 2011 Abstract Book PDFH. Fehmi OZELNo ratings yet
- Renato Anghinah, Wellingson Paiva, Linamara Rizzo Battistella, Robson Amorim - Topics in Cognitive Rehabilitation in The TBI Post-Hospital Phase-Springer International Publishing (2018)Document129 pagesRenato Anghinah, Wellingson Paiva, Linamara Rizzo Battistella, Robson Amorim - Topics in Cognitive Rehabilitation in The TBI Post-Hospital Phase-Springer International Publishing (2018)basti_aka_slim0% (1)
- Functional NeuroanatomyDocument23 pagesFunctional NeuroanatomyDaniela GrigoraşNo ratings yet
- Brain Tumors - Classifications, Symptoms, Diagnosis and TreatmentsDocument10 pagesBrain Tumors - Classifications, Symptoms, Diagnosis and TreatmentsshamimNo ratings yet
- Glial CaellsDocument4 pagesGlial CaellsEmerson BartleyNo ratings yet
- Astrocyte: Structure & FunctionDocument7 pagesAstrocyte: Structure & Functionمحمود الموسويNo ratings yet
- Seminar 4 Glia Nature Feb09Document3 pagesSeminar 4 Glia Nature Feb09dr_dicere_929212728No ratings yet
- Neuropathology PDFDocument205 pagesNeuropathology PDFNarendraNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 3 PART A - Anatomy of The Nervous SystemDocument88 pagesCHAPTER 3 PART A - Anatomy of The Nervous Systemyusijusmine21No ratings yet
- The Cause of AutismDocument47 pagesThe Cause of Autismjoeimbriano100% (1)
- Blood Brain Barrier PDFDocument5 pagesBlood Brain Barrier PDFRoxanA BocaNo ratings yet
CNS Cancer Pathology
CNS Cancer Pathology
Uploaded by
lindseycallierCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
CNS Cancer Pathology
CNS Cancer Pathology
Uploaded by
lindseycallierCopyright:
Available Formats
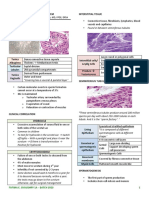
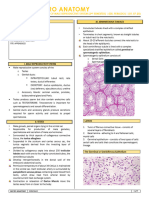
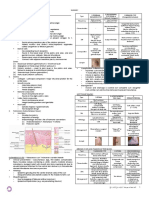
Tumor Histology 2024- Karim/McConnel/ Callier
Overview of pediatric primary brain tumors
Tumor Precursor Typical location Typical histology
Supratentorial
Craniopharyngioma • Rathke pouch (ectoderm) • Suprasellar region • Nests of stratified squamous
epithelium with internal
areas of
lamellar keratin deposits
• Cholesterol crystals
Infratentorial
Pinealoma • Pineal gland • Dorsal midbrain (compression • Large vacuolated cells with
of tectum, cerebral round nuclei (fried egg
aqueduct, cells)
and hypothalamic inhibiting • Lymphoid stroma
pathways)
• Similar to germ cell
tumors such as testicular
seminoma
Pilocytic • Astrocytes • Posterior cranial fossa • Rosenthal fibers: eosinophilic
astrocytoma fibers with corkscrew-
like configuration
• GFAP positive
Medulloblastoma • Primitive, neuroectodermal tissue • Cerebellar vermis • Small, round blue cells
• Homer-Wright rosette
• Synaptophysin positive
Ependymoma • Ependymal cells • 4th ventricle • Perivascular
pseudorosettes: tumor cells
that are arranged in
a papillary structure around
a central blood vessel
Tumor Histology 2024- Karim/McConnel/ Callier
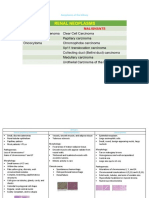
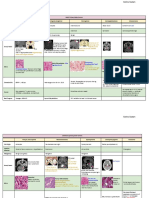
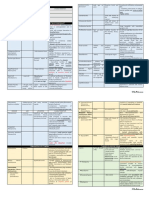
Overview of adult primary brain tumors
Tumor Precursor Typical locations Typical histology
Glioblastoma • Glial • Cerebral hemispheres • Pleomorphic cells that
multiforme (WHO grade cells (e.g., astrocytes) (supratentorial) form pseudopalisades due
IV astrocytoma) o May cross to central necrosis or hemorrhage
the corpus • Microvascular proliferation
callosum • GFAP positive
(butterfly
glioma)
Meningioma • Arachnoid cap cells • Extra- • Spindle cells arranged in whorls
parenchymal tumor that • Psammoma bodies
can occur
in supratentorial (often
parasagittal)
or infratentorial regions
Hemangioblastoma • Vascular system origin • Cerebellum (infratentorial) • Densely packed thin-walled capillaries
Schwannoma • Schwann cells • Cerebellopontine • Spindle cells in palisades (Antoni A tissue)
angle (infratentorial) alternating with myxoid areas (Antoni B
tissue)
• S-100 positive
Oligodendroglioma • Oligodendrocytes • Frontal • Large vacuolated cells with round nuclei (fried
lobes (supratentorial) egg cells)
• Chicken-wire pattern of capillary anastomoses
Pituitary adenoma • Pituitary adenotrophic • Sella • Monomorphic, acidophilic or basophilic,
cells turcica (supratentorial) polygonal cells arranged in sheets or cords
(typically lactotrophs)
Tumor Histology 2024- Karim/McConnel/ Callier
References:
- Kumar, V., Abbas, A. K., Aster, J. C., & Robbins, S. L. (2015). Neoplasia. In Robbins & Cotran Pathologic Basis of Disease (Ninth
edition, pp. 299-382). Elsevier Saunders.
- AMBoss. (n.d.). Benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH). In AMBOSS (Version [insert version number]). Retrieved from
https://next.amboss.com/us/article/H50Klg#Zf87f826ac9e4518d42d934f4e082e9d6
You might also like
- Oncology Nursing (Word) Bulleted For NSG RevieweesDocument8 pagesOncology Nursing (Word) Bulleted For NSG Revieweesswitlipz100% (1)
- PHA611 - Unit 2 - Lesson 2 - Plant StemDocument9 pagesPHA611 - Unit 2 - Lesson 2 - Plant StemJonah Dane BautistaNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Traumatic Brain Injury: Melissa J. Mcginn,, John T. PovlishockDocument11 pagesPathophysiology of Traumatic Brain Injury: Melissa J. Mcginn,, John T. Povlishocksiska misaliNo ratings yet
- Squash Cytology Vs Frozen Section Ver2Document54 pagesSquash Cytology Vs Frozen Section Ver2Shruthi N.RNo ratings yet
- Malignant Epithelial Slides-1Document5 pagesMalignant Epithelial Slides-1Cenonina Paola TapiaNo ratings yet
- Micro - Male Repro (Sec A) PDFDocument5 pagesMicro - Male Repro (Sec A) PDFKaren ValdezNo ratings yet
- Cytology of Normal Epithelial CellsDocument31 pagesCytology of Normal Epithelial CellsNatalia HaikaliNo ratings yet
- AAD BF Paisley Tie DiagnosisDocument2 pagesAAD BF Paisley Tie Diagnosiskahkashanahmed065No ratings yet
- WBC SlidesDocument5 pagesWBC SlidesCenonina Paola TapiaNo ratings yet
- Neoplasms of The KidneyDocument5 pagesNeoplasms of The KidneyEMILY N CRUZ-VARGASNo ratings yet
- Roots, Stems and Leaves Grade 10 2022 Learners FinalDocument29 pagesRoots, Stems and Leaves Grade 10 2022 Learners Finalanelisancokwana14No ratings yet
- Histology of The Testicle Spermatogenesis TZsDocument21 pagesHistology of The Testicle Spermatogenesis TZsYogita BhansaliNo ratings yet
- Skull Base Tumors NBNDocument30 pagesSkull Base Tumors NBNAbdullah Yeamin PeyalNo ratings yet
- Arasitology: Intestinal AmoebaeDocument5 pagesArasitology: Intestinal AmoebaeMa. Mil Adrianne PamaNo ratings yet
- Parasitology (Lect #5) TransDocument3 pagesParasitology (Lect #5) TransSherlyn Giban InditaNo ratings yet
- Lymphatic System ReviewerDocument49 pagesLymphatic System ReviewerJess Lejarde100% (1)
- Intellectual FunctionsDocument13 pagesIntellectual Functionsrrkn9njjhzNo ratings yet
- EpitheliaDocument1 pageEpitheliaTarlan SharifiNo ratings yet
- The OrgansDocument13 pagesThe OrgansFAITH ELLA MARIE PARMANo ratings yet
- Brain TumorsDocument3 pagesBrain TumorsDrashty DesaiNo ratings yet
- Spindle Cell TumorsDocument138 pagesSpindle Cell TumorsMadhura ShekatkarNo ratings yet
- Blood and Tissue Flagellates para LecDocument8 pagesBlood and Tissue Flagellates para LecLian MallareNo ratings yet
- SurgPatho Thyroid 2018Document8 pagesSurgPatho Thyroid 2018John Paulo CatacutanNo ratings yet
- 17174-Imging of Cerebellopontine Angle - Prof El BeltagiDocument10 pages17174-Imging of Cerebellopontine Angle - Prof El BeltagiPugazhenthi CNo ratings yet
- Haematoxylin and Eosin (H+E) - Aldehyde-Fuchsin - Van Geison's Picro Fuchsin Technique - Masson's Trichrome - Nuclei - Blue/backDocument9 pagesHaematoxylin and Eosin (H+E) - Aldehyde-Fuchsin - Van Geison's Picro Fuchsin Technique - Masson's Trichrome - Nuclei - Blue/backsilentscreamsofloveNo ratings yet
- L6-PATHO-Neoplasia (Sept2821)Document12 pagesL6-PATHO-Neoplasia (Sept2821)Erald PaderangaNo ratings yet
- Tissue Type Sketch Function Location Notes Simple Squamous EpitheliumDocument9 pagesTissue Type Sketch Function Location Notes Simple Squamous EpitheliumKaitlin NooneyNo ratings yet
- Bengin SGT 2023Document11 pagesBengin SGT 2023Hazem MouradNo ratings yet
- Male Reproductive HistologyDocument7 pagesMale Reproductive HistologyCarmela MarianoNo ratings yet
- Pineal Sellar Pituitary Dr. RitaDocument112 pagesPineal Sellar Pituitary Dr. RitaAkifa NailaNo ratings yet
- Annotated OneShotANAT, DR Ashwani - 230208 - 143653Document90 pagesAnnotated OneShotANAT, DR Ashwani - 230208 - 143653KabbuNo ratings yet
- Histology: Histology Slide Diagrams, Discussion Questions and Slide PicturesDocument45 pagesHistology: Histology Slide Diagrams, Discussion Questions and Slide Picturesmarjanggyamar7No ratings yet
- Anatomy One Shot DR AshwiniDocument95 pagesAnatomy One Shot DR Ashwinienthusiast383No ratings yet
- SECTION 6: Spleen: and OverviewDocument38 pagesSECTION 6: Spleen: and Overviewtudoranluciana1No ratings yet
- Surgical Pathology - CNSDocument2 pagesSurgical Pathology - CNSIsabel CastilloNo ratings yet
- Atrial Flagellates LabDocument3 pagesAtrial Flagellates LabLeinard ClaveroNo ratings yet
- Epithelium: Dr. Lalit MehraDocument39 pagesEpithelium: Dr. Lalit Mehramus zaharaNo ratings yet
- Hole's Human Anatomy and Physiology: 5 Skeletal SystemDocument73 pagesHole's Human Anatomy and Physiology: 5 Skeletal SystemLongyapon Sheena StephanieNo ratings yet
- AAD BF Cutaneous Smooth Muscle TumorsDocument2 pagesAAD BF Cutaneous Smooth Muscle Tumorskahkashanahmed065No ratings yet
- Activity 4 Organogenesis in The Frog Embryo Activity Worksheet A. 4 MM Frog EmbryoDocument4 pagesActivity 4 Organogenesis in The Frog Embryo Activity Worksheet A. 4 MM Frog Embryojhayyypee jhayypsNo ratings yet
- Gastrulation Somites and Folding TSRDocument27 pagesGastrulation Somites and Folding TSRAsia SattiNo ratings yet
- Dr. Praveen - Important Topcs UPDATED 2023Document33 pagesDr. Praveen - Important Topcs UPDATED 2023Sakshi SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- 四下micro 2Document77 pages四下micro 2q124415669No ratings yet
- Extra-Adrenal Paraganglioma: A Brief OverviewDocument19 pagesExtra-Adrenal Paraganglioma: A Brief Overviewpperez1863No ratings yet
- Cancer 1 - 2022 - LectureDocument42 pagesCancer 1 - 2022 - LectureJoshua KaoNo ratings yet
- Epithelial Tumours - SreejaDocument184 pagesEpithelial Tumours - SreejaaakiNo ratings yet
- Paediatric Liver TumoursDocument22 pagesPaediatric Liver TumoursMohamed HelmiNo ratings yet
- 4.3 Intestinal FlagellatesDocument7 pages4.3 Intestinal FlagellatesJudith Dianne Ignacio100% (1)
- Salv GLND Histopath Slides 051116Document64 pagesSalv GLND Histopath Slides 051116Amesz Itzu Tsang SynysterNo ratings yet
- c4k 06 Jenkins Nrsoft Tissue SarcomasDocument11 pagesc4k 06 Jenkins Nrsoft Tissue SarcomasAde CahyanaNo ratings yet
- Male Reproductive Path and SurgeryDocument36 pagesMale Reproductive Path and SurgeryThimira WaidyasekaraNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 Neoplasia 1 2 Robbins and Cotran Pathologic Basis of Disease PDFDocument9 pagesChapter 7 Neoplasia 1 2 Robbins and Cotran Pathologic Basis of Disease PDFChethranNo ratings yet
- Protozoans - Amebae: Medically Important ParasitesDocument10 pagesProtozoans - Amebae: Medically Important ParasitesBrylle LumberioNo ratings yet
- Soft Tissue Tumor SeminarDocument39 pagesSoft Tissue Tumor SeminarAhmad SyahmiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3-4 - TablesDocument6 pagesChapter 3-4 - TablesvallecerajamaicaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy MS University IMP'sDocument4 pagesAnatomy MS University IMP'spatelsharmistha415No ratings yet
- Mindmap - AnatomyDocument9 pagesMindmap - AnatomyPushpa DhruvNo ratings yet
- OPD Surgery Complete PDFDocument22 pagesOPD Surgery Complete PDFPeter Paul RecaboNo ratings yet
- Slides - 01-03 - Gastrulation and Trilaminar EmbryoDocument16 pagesSlides - 01-03 - Gastrulation and Trilaminar EmbryoSebastian RuaNo ratings yet
- SURGICAL PATHOLOGY SOFT TISSUES TableDocument4 pagesSURGICAL PATHOLOGY SOFT TISSUES TableIsabel CastilloNo ratings yet
- Case Study Cva Gr1Document72 pagesCase Study Cva Gr1Divina Gracia Fabicon Arana100% (1)
- Glioblastoma: in This Fact SheetDocument17 pagesGlioblastoma: in This Fact SheetSunil GvalaniNo ratings yet
- Levin - Godukhin - 2017 - Modulating Effect of Cytokines On Mechanisms of Synaptic Plasticity in The BrainDocument11 pagesLevin - Godukhin - 2017 - Modulating Effect of Cytokines On Mechanisms of Synaptic Plasticity in The Brainkeon.arbabi.altNo ratings yet
- Neuroinflammation and Neuroprogression in DepressionDocument14 pagesNeuroinflammation and Neuroprogression in DepressionAldehydeNo ratings yet
- 10 1 1 110Document135 pages10 1 1 110khaled1512No ratings yet
- The Retinal Muller Cell PDFDocument293 pagesThe Retinal Muller Cell PDFkemalasari8818No ratings yet
- The Effects of 528 HZ Sound Wave To Reduce Cell Death in Human Astrocyteprimary Cell Culture Treated With Ethanol 2155 6105 1000335Document5 pagesThe Effects of 528 HZ Sound Wave To Reduce Cell Death in Human Astrocyteprimary Cell Culture Treated With Ethanol 2155 6105 1000335kaoscodedNo ratings yet
- Role of Glia in Optic NerveDocument21 pagesRole of Glia in Optic NerveSi PuputNo ratings yet
- CBT 2 Paper PDFDocument140 pagesCBT 2 Paper PDFkarthikNo ratings yet
- Science - Abo7257 SMDocument105 pagesScience - Abo7257 SM张议No ratings yet
- Neural Cell BiologyDocument348 pagesNeural Cell BiologySrinivas PingaliNo ratings yet
- TMP F578Document10 pagesTMP F578FrontiersNo ratings yet
- Actcr 1 (3) 15Document11 pagesActcr 1 (3) 15Robinson Trujillo CabanillaNo ratings yet
- PTAH Principle and Dignostic ApplicationDocument1 pagePTAH Principle and Dignostic ApplicationSuman MandalNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 AllDocument95 pagesUnit 1 Allaloysius limNo ratings yet
- Glutamate and GABA in Appetite Regulation: Teresa C. DelgadoDocument8 pagesGlutamate and GABA in Appetite Regulation: Teresa C. DelgadoFia NisaNo ratings yet
- Fisiologi SSP NEUDocument59 pagesFisiologi SSP NEUCeyvira ArsytaNo ratings yet
- Journal - Formaldehyde in Brain An Overlooked Player in Neurodegeneration PDFDocument15 pagesJournal - Formaldehyde in Brain An Overlooked Player in Neurodegeneration PDFtriNo ratings yet
- Fizyoloji Kongresi FEPS 2011 Abstract Book PDFDocument522 pagesFizyoloji Kongresi FEPS 2011 Abstract Book PDFH. Fehmi OZELNo ratings yet
- Renato Anghinah, Wellingson Paiva, Linamara Rizzo Battistella, Robson Amorim - Topics in Cognitive Rehabilitation in The TBI Post-Hospital Phase-Springer International Publishing (2018)Document129 pagesRenato Anghinah, Wellingson Paiva, Linamara Rizzo Battistella, Robson Amorim - Topics in Cognitive Rehabilitation in The TBI Post-Hospital Phase-Springer International Publishing (2018)basti_aka_slim0% (1)
- Functional NeuroanatomyDocument23 pagesFunctional NeuroanatomyDaniela GrigoraşNo ratings yet
- Brain Tumors - Classifications, Symptoms, Diagnosis and TreatmentsDocument10 pagesBrain Tumors - Classifications, Symptoms, Diagnosis and TreatmentsshamimNo ratings yet
- Glial CaellsDocument4 pagesGlial CaellsEmerson BartleyNo ratings yet
- Astrocyte: Structure & FunctionDocument7 pagesAstrocyte: Structure & Functionمحمود الموسويNo ratings yet
- Seminar 4 Glia Nature Feb09Document3 pagesSeminar 4 Glia Nature Feb09dr_dicere_929212728No ratings yet
- Neuropathology PDFDocument205 pagesNeuropathology PDFNarendraNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 3 PART A - Anatomy of The Nervous SystemDocument88 pagesCHAPTER 3 PART A - Anatomy of The Nervous Systemyusijusmine21No ratings yet
- The Cause of AutismDocument47 pagesThe Cause of Autismjoeimbriano100% (1)
- Blood Brain Barrier PDFDocument5 pagesBlood Brain Barrier PDFRoxanA BocaNo ratings yet