Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 viewsModule 7. Intro to Project Financing in the Private Sector
Module 7. Intro to Project Financing in the Private Sector
Uploaded by
jbcruz2Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Build, Own and Operate (BOO) Concept For Power Projects PDFDocument8 pagesBuild, Own and Operate (BOO) Concept For Power Projects PDFAbdulrahman Al HuribyNo ratings yet
- PWC - Overview of Public Private PartnershipsDocument34 pagesPWC - Overview of Public Private Partnershipsspratiwia100% (2)
- PAWCM PPT 3 - Principles of Project FinanceDocument44 pagesPAWCM PPT 3 - Principles of Project FinanceYashodhan JoshiNo ratings yet
- Summary Project Finance in Theory and PracticeDocument30 pagesSummary Project Finance in Theory and PracticeroseNo ratings yet
- Case Project FinanceDocument9 pagesCase Project FinanceaamritaaNo ratings yet
- Peng Man Infra Dan Pembiayaan ProyekDocument25 pagesPeng Man Infra Dan Pembiayaan Proyekagus supriyatnoNo ratings yet
- Project Appraisal & FinanceDocument30 pagesProject Appraisal & FinanceNikhilRPandeyNo ratings yet
- 750 P3 Week 5 (2021)Document26 pages750 P3 Week 5 (2021)Khanh DamNo ratings yet
- Presentation On Concession AgreementDocument31 pagesPresentation On Concession AgreementnikimeeraNo ratings yet
- Infrastructure FinancingDocument12 pagesInfrastructure Financingharesh swaminathanNo ratings yet
- Project Finance-Day 6Document23 pagesProject Finance-Day 6Piyush BhatnagarNo ratings yet
- PF 2018 - 2019 Lecture 2 - Structuring A Project FinanceDocument29 pagesPF 2018 - 2019 Lecture 2 - Structuring A Project FinanceAnton AliagaNo ratings yet
- Large Project Financiers: Chapter 4: Who Finances Large Projects?Document33 pagesLarge Project Financiers: Chapter 4: Who Finances Large Projects?k bhargavNo ratings yet
- UNIT-2 ContinuationDocument28 pagesUNIT-2 ContinuationLikitha GangaramNo ratings yet
- PF 2018 - 2019 Lecture 3 - Public Private PartnershipDocument49 pagesPF 2018 - 2019 Lecture 3 - Public Private PartnershipAnton AliagaNo ratings yet
- Joint Venture Agreements in Project Development and Finance - An IntroductionDocument2 pagesJoint Venture Agreements in Project Development and Finance - An Introductionmayorlad100% (1)
- Test 11 (Economy Chapter On Resource Mobilisation in India)Document29 pagesTest 11 (Economy Chapter On Resource Mobilisation in India)CyrilMaxNo ratings yet
- Oagbc Understanding p3 Public Private PartnershipsDocument4 pagesOagbc Understanding p3 Public Private PartnershipsSangwa StevenNo ratings yet
- Presentation - Cigdem - 20 Oct 2022Document32 pagesPresentation - Cigdem - 20 Oct 2022Bob KoudstaalNo ratings yet
- Public Private Partnerships: Finances For Infrastructural and Building ProjectsDocument24 pagesPublic Private Partnerships: Finances For Infrastructural and Building ProjectsVivek BNo ratings yet
- International CDM Projects:: Financing Requirements and Project CyclesDocument12 pagesInternational CDM Projects:: Financing Requirements and Project Cyclescyaboo100% (1)
- Alternative Financing - PPPDocument18 pagesAlternative Financing - PPPNaomi Alberg-BlijdNo ratings yet
- What We Will Cover: Project Bond DifferencesDocument14 pagesWhat We Will Cover: Project Bond DifferencesMeenal AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Project FinanceDocument63 pagesProject FinanceAdeel Ahmad100% (2)
- Hemodialysis Center PPPS: Project Structures and TermsDocument47 pagesHemodialysis Center PPPS: Project Structures and TermsKevin mogatas100% (1)
- Risks in A PPP Project:: Development RiskDocument21 pagesRisks in A PPP Project:: Development RiskKaran AggarwalNo ratings yet
- Infrastructure in Indonesia Sounds Decisions Sounds InvestmentsDocument6 pagesInfrastructure in Indonesia Sounds Decisions Sounds InvestmentschienNo ratings yet
- Public Private PartnershipDocument38 pagesPublic Private PartnershipAvnish NarulaNo ratings yet
- Asa 2Document15 pagesAsa 2raghav VarmaNo ratings yet
- Nistha - Sona PresentationDocument38 pagesNistha - Sona PresentationNisthaNakarmiNo ratings yet
- Formulating Global Infra ProjectsDocument27 pagesFormulating Global Infra ProjectsYusuke HigakiNo ratings yet
- Topic 3 - Introduction To PPPDocument21 pagesTopic 3 - Introduction To PPPADNo ratings yet
- Project Finance and Obtaining Sufficient Funding For The Successful Completion of Your ProjectDocument17 pagesProject Finance and Obtaining Sufficient Funding For The Successful Completion of Your ProjectSky walkingNo ratings yet
- Session 1 To 3Document32 pagesSession 1 To 3nisargpritamlondheNo ratings yet
- Session 1 ToDocument127 pagesSession 1 TonisargpritamlondheNo ratings yet
- Session 3 - PPP Options - S RahmanDocument22 pagesSession 3 - PPP Options - S RahmanFarukHossainNo ratings yet
- Workshop On Evaluation and Public-Private PartnershipDocument16 pagesWorkshop On Evaluation and Public-Private PartnershipLUAY BREAMNo ratings yet
- Financing Infra ProjectsDocument12 pagesFinancing Infra Projectssaurabhkokane96.skNo ratings yet
- Blcok-3 MCO-7 Unit-3Document24 pagesBlcok-3 MCO-7 Unit-3Tushar SharmaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Project FinancingDocument88 pagesIntroduction To Project FinancingE B100% (1)
- Farid Jafarov ENG Project FinanceDocument27 pagesFarid Jafarov ENG Project FinanceSky walkingNo ratings yet
- 15 Invesmnet ModelsDocument14 pages15 Invesmnet ModelsTanay BansalNo ratings yet
- Viability Gap Funding For InfrastructureDocument2 pagesViability Gap Funding For InfrastructurePrashanthi AtukuriNo ratings yet
- Bot Structures: What Is A BOT?Document8 pagesBot Structures: What Is A BOT?mhabeeb9127No ratings yet
- PF 2018 - 2019 Lecture 1 Introduction - v1Document44 pagesPF 2018 - 2019 Lecture 1 Introduction - v1Anton AliagaNo ratings yet
- Public Private PartnershipsDocument25 pagesPublic Private PartnershipsTHOMASKUTTYNo ratings yet
- Financing Infrastructure ProjectDocument9 pagesFinancing Infrastructure ProjectsargunkaurNo ratings yet
- PPP Presen-2019Document28 pagesPPP Presen-2019Raymon PrakashNo ratings yet
- Public Private PartnershipsDocument32 pagesPublic Private PartnershipsThe GravelsNo ratings yet
- A. Preliminary EvaluationDocument8 pagesA. Preliminary EvaluationNanette Rose HaguilingNo ratings yet
- Experience Sharing & Workshop On Public-Private Partnership (PPP) : PPP Project ConceptsDocument32 pagesExperience Sharing & Workshop On Public-Private Partnership (PPP) : PPP Project ConceptsThe Outer Marker100% (1)
- 06Document49 pages06bpsc08No ratings yet
- 6 Plenary - Thematic PPP by AGaliev 20mar2017Document9 pages6 Plenary - Thematic PPP by AGaliev 20mar2017Butch D. de la Cruz100% (1)
- PDI Complete SlidesDocument151 pagesPDI Complete SlidesAbrar AkmalNo ratings yet
- 2 - Project Structure and Financing Sources For Wind FarmsDocument28 pages2 - Project Structure and Financing Sources For Wind Farmsviethoa_uehNo ratings yet
- Engineering, Procurement and Construction (ECP) ContractsDocument124 pagesEngineering, Procurement and Construction (ECP) ContractsPopeyeNo ratings yet
- Project Financing: Asset-Based Financial EngineeringFrom EverandProject Financing: Asset-Based Financial EngineeringRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2)
- COVID-19 and Public–Private Partnerships in Asia and the Pacific: Guidance NoteFrom EverandCOVID-19 and Public–Private Partnerships in Asia and the Pacific: Guidance NoteNo ratings yet
- Module 8Document1 pageModule 8jbcruz2No ratings yet
- Module 2. Sustainable DevelopmentDocument2 pagesModule 2. Sustainable Developmentjbcruz2No ratings yet
- Module 4. Forest and Land ResourcesDocument4 pagesModule 4. Forest and Land Resourcesjbcruz2No ratings yet
- P201 Module 10 NotesDocument4 pagesP201 Module 10 Notesjbcruz2No ratings yet
- Castro Mapping Gis PiepDocument53 pagesCastro Mapping Gis Piepjbcruz2No ratings yet
- P203 Module 2 Notes - Land Use Planning Principles and Contemporary IssuesDocument10 pagesP203 Module 2 Notes - Land Use Planning Principles and Contemporary Issuesjbcruz2No ratings yet
- Concepts in Planning - 2Document28 pagesConcepts in Planning - 2jbcruz2No ratings yet
- Nature and Types of Planning Jan 7Document152 pagesNature and Types of Planning Jan 7jbcruz2No ratings yet
- Day 4 DR Regunay SeaDocument41 pagesDay 4 DR Regunay Seajbcruz2No ratings yet
- Project Planning Development - 2Document38 pagesProject Planning Development - 2jbcruz2No ratings yet
- Promoting Public Private Partnership in Disaster Risk Reduction Japanese CasesDocument69 pagesPromoting Public Private Partnership in Disaster Risk Reduction Japanese Casesjbcruz2No ratings yet
- Early Trends in PLG in The Phil Add To History of PLG - 2Document11 pagesEarly Trends in PLG in The Phil Add To History of PLG - 2jbcruz2No ratings yet
- Dynamics of Land Use Planning and Its Effects On Socio-Economic DevelopmentDocument123 pagesDynamics of Land Use Planning and Its Effects On Socio-Economic Developmentjbcruz2No ratings yet
- Spatial Disaggregation of Landsat-Derived Land Surface Temperature Over A Heterogeneous Urban Landscape Using Planetscope Image DerivativesDocument8 pagesSpatial Disaggregation of Landsat-Derived Land Surface Temperature Over A Heterogeneous Urban Landscape Using Planetscope Image Derivativesjbcruz2No ratings yet
- Public Private Partnership PPP Case Studies - PhilippinesDocument19 pagesPublic Private Partnership PPP Case Studies - Philippinesjbcruz2No ratings yet
- Land and Its Basic CharacteristicsDocument41 pagesLand and Its Basic Characteristicsjbcruz2No ratings yet
- Land Use Planning IssuesDocument6 pagesLand Use Planning Issuesjbcruz2No ratings yet
- Annual Marketing CalendarDocument20 pagesAnnual Marketing CalendarRia ThoNo ratings yet
- Proposal On Management of A Consulting FirmDocument4 pagesProposal On Management of A Consulting FirmOlufemi MoyegunNo ratings yet
- Marketing Management Journal: Professor: Dr. Shalini GulechaDocument17 pagesMarketing Management Journal: Professor: Dr. Shalini GulechatejashreeNo ratings yet
- Arts Council EnglandDocument21 pagesArts Council EnglandShankeyNo ratings yet
- The Importance of Diversity in WorkplaceDocument2 pagesThe Importance of Diversity in WorkplaceNavjot Singh RaiNo ratings yet
- Wa0018.Document7 pagesWa0018.jar070888No ratings yet
- 2016 Puma Energy Annual ReportDocument212 pages2016 Puma Energy Annual ReportKA-11 Єфіменко ІванNo ratings yet
- Owfm6013 Corporate Finance - Individual AssignmentDocument27 pagesOwfm6013 Corporate Finance - Individual AssignmentPK LNo ratings yet
- Algorithmic StrategiesDocument1 pageAlgorithmic Strategiesamir khNo ratings yet
- Understanding Ebix IP Asset TransferDocument41 pagesUnderstanding Ebix IP Asset TransferspinvestorNo ratings yet
- 2 Creativity Innovation and EntrepreneurshipDocument28 pages2 Creativity Innovation and EntrepreneurshipNarayan MaharjanNo ratings yet
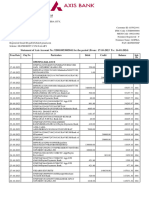
- Statement of Account: Date Narration Chq./Ref - No. Value DT Withdrawal Amt. Deposit Amt. Closing BalanceDocument2 pagesStatement of Account: Date Narration Chq./Ref - No. Value DT Withdrawal Amt. Deposit Amt. Closing BalanceDRISHTI MEHRANo ratings yet
- Manufacturing ManagementDocument332 pagesManufacturing ManagementPugdug 209No ratings yet
- Team 1 Moot 3 (Appellant)Document25 pagesTeam 1 Moot 3 (Appellant)Amal M SNo ratings yet
- 2020 - VN Market Trend - Q - MeDocument15 pages2020 - VN Market Trend - Q - MeGame AccountNo ratings yet
- Managing The Venture's Financial ResourcesDocument28 pagesManaging The Venture's Financial ResourcesAnto DNo ratings yet
- Business Law 10Th Edition Cheeseman Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFDocument28 pagesBusiness Law 10Th Edition Cheeseman Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFkathleenjonesswzrqcmkex100% (18)
- Ass1 Macro sp20Document3 pagesAss1 Macro sp20NoorNo ratings yet
- Team Battleship TransactionsDocument2 pagesTeam Battleship TransactionsJacob SheridanNo ratings yet
- Research Methodology: "Research Is A Formalized Curiosity. It Is Poking and Prying With A Purpose."Document10 pagesResearch Methodology: "Research Is A Formalized Curiosity. It Is Poking and Prying With A Purpose."azhagu sundaramNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Book Scheme Topic 2 Sequence (pg.4-pg32)Document29 pagesTutorial Book Scheme Topic 2 Sequence (pg.4-pg32)Fatin AqilahNo ratings yet
- Destination Zero An Action Plan For Shipping CeosDocument11 pagesDestination Zero An Action Plan For Shipping CeosromainNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument4 pagesUntitledRudra PrakashNo ratings yet
- Case Study of Mobile BankingDocument5 pagesCase Study of Mobile BankingShefali Garg100% (1)
- 0036 - Accounting For Business - EditedDocument4 pages0036 - Accounting For Business - EditedAwais AhmedNo ratings yet
- Petition For Voluntary Liquidation Sample Scribd - Google SearchDocument3 pagesPetition For Voluntary Liquidation Sample Scribd - Google SearchNielgem Beja0% (2)
- Company Certifications Fire Classifications Product ApprovalsDocument4 pagesCompany Certifications Fire Classifications Product ApprovalsHussein BeqaiNo ratings yet
- FAQsDocument1 pageFAQsJeg GillNo ratings yet
- The Self-Made Copywriter: Steal The Syllabus That Produced The Greatest Copywriters in The WorldDocument9 pagesThe Self-Made Copywriter: Steal The Syllabus That Produced The Greatest Copywriters in The WorldJosé Alias Blake0% (1)
- Crafton IndustriesDocument7 pagesCrafton IndustriesS KNo ratings yet
Module 7. Intro to Project Financing in the Private Sector
Module 7. Intro to Project Financing in the Private Sector
Uploaded by
jbcruz20 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views2 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views2 pagesModule 7. Intro to Project Financing in the Private Sector
Module 7. Intro to Project Financing in the Private Sector
Uploaded by
jbcruz2Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 2
MODULE 7.
INTRO TO PROJECT FINANCING IN o Remuneration through user fees,
THE PRIVATE SECTOR availability payments (govt pays fixed
fees to private operator)
Reference 1: Project Finance Video
o No public funds are disbursed during
Project Finance the construction phase – spread
throughout lifetime of the project once
Non-recourse loans and obligations
operational
o Creditors are relying only to the
SPV to repay the loan Duration
o Financial obligations are
o Relationship between the government
recourse only to the project
and private sector continues after the
company, they are non-
construction of the project
recourse to the investors of the
o Private sector is responsible for
project
operating it for a set number of years
o Special Purpose Vehicle (SPV)
(more than 20 yrs)
o Company will borrow a lot of
o Asset rights revert back to public
money to buy assets but the
authority after set number of years
obligation to return the loan
stays on the level of the Output vs Input
company, not on the investors
o Requirements are defined based on
Cash Flow-based
output – what we want to achieve
o Basis of valuation is cash flow,
(traditional – input – how to achieve
not collateral
what we want)
o Project must operate to
o Project specifications for road infra
generate cash
might include road surface quality
Allocation of Risks
rather than specific details of
o Strong network of contracts
construction
o Counterparties must be reliable
o Provide the private sector with the
and experienced
opportunity to deliver innovative
o Proven technology
solutions for delivering public services
Public-Private Partnership
Risk Allocation
A long-term contract between a private
o Risks are shared among public and
party and government entity, for the
private partners
provision of public services and/or
o Private sector usually supports
development of public infrastructure, in
construction and operational risks
which responsibilities and rewards are
shared Benefits of PPP
Funding Sources Private capital – finance projects that
are not feasible in the government due
o Private sector is financing the project,
to budget constraints
expecting to gain profit out of the
Efficiency gains
investment
Creation of long-term solutions
Risk transfer to the private sector
Limitations of PPP
Not suitable for all projects (does not
work well in sectors with rapid change
unless there is long-term predictable
need
Complex/high transaction cost
Lack of local private sector capacity
Political and social sensitivity
Limited flexibility – hard to modify
project specifications once awarded
Mega Manila Infrastructure Roadmap
You might also like
- Build, Own and Operate (BOO) Concept For Power Projects PDFDocument8 pagesBuild, Own and Operate (BOO) Concept For Power Projects PDFAbdulrahman Al HuribyNo ratings yet
- PWC - Overview of Public Private PartnershipsDocument34 pagesPWC - Overview of Public Private Partnershipsspratiwia100% (2)
- PAWCM PPT 3 - Principles of Project FinanceDocument44 pagesPAWCM PPT 3 - Principles of Project FinanceYashodhan JoshiNo ratings yet
- Summary Project Finance in Theory and PracticeDocument30 pagesSummary Project Finance in Theory and PracticeroseNo ratings yet
- Case Project FinanceDocument9 pagesCase Project FinanceaamritaaNo ratings yet
- Peng Man Infra Dan Pembiayaan ProyekDocument25 pagesPeng Man Infra Dan Pembiayaan Proyekagus supriyatnoNo ratings yet
- Project Appraisal & FinanceDocument30 pagesProject Appraisal & FinanceNikhilRPandeyNo ratings yet
- 750 P3 Week 5 (2021)Document26 pages750 P3 Week 5 (2021)Khanh DamNo ratings yet
- Presentation On Concession AgreementDocument31 pagesPresentation On Concession AgreementnikimeeraNo ratings yet
- Infrastructure FinancingDocument12 pagesInfrastructure Financingharesh swaminathanNo ratings yet
- Project Finance-Day 6Document23 pagesProject Finance-Day 6Piyush BhatnagarNo ratings yet
- PF 2018 - 2019 Lecture 2 - Structuring A Project FinanceDocument29 pagesPF 2018 - 2019 Lecture 2 - Structuring A Project FinanceAnton AliagaNo ratings yet
- Large Project Financiers: Chapter 4: Who Finances Large Projects?Document33 pagesLarge Project Financiers: Chapter 4: Who Finances Large Projects?k bhargavNo ratings yet
- UNIT-2 ContinuationDocument28 pagesUNIT-2 ContinuationLikitha GangaramNo ratings yet
- PF 2018 - 2019 Lecture 3 - Public Private PartnershipDocument49 pagesPF 2018 - 2019 Lecture 3 - Public Private PartnershipAnton AliagaNo ratings yet
- Joint Venture Agreements in Project Development and Finance - An IntroductionDocument2 pagesJoint Venture Agreements in Project Development and Finance - An Introductionmayorlad100% (1)
- Test 11 (Economy Chapter On Resource Mobilisation in India)Document29 pagesTest 11 (Economy Chapter On Resource Mobilisation in India)CyrilMaxNo ratings yet
- Oagbc Understanding p3 Public Private PartnershipsDocument4 pagesOagbc Understanding p3 Public Private PartnershipsSangwa StevenNo ratings yet
- Presentation - Cigdem - 20 Oct 2022Document32 pagesPresentation - Cigdem - 20 Oct 2022Bob KoudstaalNo ratings yet
- Public Private Partnerships: Finances For Infrastructural and Building ProjectsDocument24 pagesPublic Private Partnerships: Finances For Infrastructural and Building ProjectsVivek BNo ratings yet
- International CDM Projects:: Financing Requirements and Project CyclesDocument12 pagesInternational CDM Projects:: Financing Requirements and Project Cyclescyaboo100% (1)
- Alternative Financing - PPPDocument18 pagesAlternative Financing - PPPNaomi Alberg-BlijdNo ratings yet
- What We Will Cover: Project Bond DifferencesDocument14 pagesWhat We Will Cover: Project Bond DifferencesMeenal AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Project FinanceDocument63 pagesProject FinanceAdeel Ahmad100% (2)
- Hemodialysis Center PPPS: Project Structures and TermsDocument47 pagesHemodialysis Center PPPS: Project Structures and TermsKevin mogatas100% (1)
- Risks in A PPP Project:: Development RiskDocument21 pagesRisks in A PPP Project:: Development RiskKaran AggarwalNo ratings yet
- Infrastructure in Indonesia Sounds Decisions Sounds InvestmentsDocument6 pagesInfrastructure in Indonesia Sounds Decisions Sounds InvestmentschienNo ratings yet
- Public Private PartnershipDocument38 pagesPublic Private PartnershipAvnish NarulaNo ratings yet
- Asa 2Document15 pagesAsa 2raghav VarmaNo ratings yet
- Nistha - Sona PresentationDocument38 pagesNistha - Sona PresentationNisthaNakarmiNo ratings yet
- Formulating Global Infra ProjectsDocument27 pagesFormulating Global Infra ProjectsYusuke HigakiNo ratings yet
- Topic 3 - Introduction To PPPDocument21 pagesTopic 3 - Introduction To PPPADNo ratings yet
- Project Finance and Obtaining Sufficient Funding For The Successful Completion of Your ProjectDocument17 pagesProject Finance and Obtaining Sufficient Funding For The Successful Completion of Your ProjectSky walkingNo ratings yet
- Session 1 To 3Document32 pagesSession 1 To 3nisargpritamlondheNo ratings yet
- Session 1 ToDocument127 pagesSession 1 TonisargpritamlondheNo ratings yet
- Session 3 - PPP Options - S RahmanDocument22 pagesSession 3 - PPP Options - S RahmanFarukHossainNo ratings yet
- Workshop On Evaluation and Public-Private PartnershipDocument16 pagesWorkshop On Evaluation and Public-Private PartnershipLUAY BREAMNo ratings yet
- Financing Infra ProjectsDocument12 pagesFinancing Infra Projectssaurabhkokane96.skNo ratings yet
- Blcok-3 MCO-7 Unit-3Document24 pagesBlcok-3 MCO-7 Unit-3Tushar SharmaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Project FinancingDocument88 pagesIntroduction To Project FinancingE B100% (1)
- Farid Jafarov ENG Project FinanceDocument27 pagesFarid Jafarov ENG Project FinanceSky walkingNo ratings yet
- 15 Invesmnet ModelsDocument14 pages15 Invesmnet ModelsTanay BansalNo ratings yet
- Viability Gap Funding For InfrastructureDocument2 pagesViability Gap Funding For InfrastructurePrashanthi AtukuriNo ratings yet
- Bot Structures: What Is A BOT?Document8 pagesBot Structures: What Is A BOT?mhabeeb9127No ratings yet
- PF 2018 - 2019 Lecture 1 Introduction - v1Document44 pagesPF 2018 - 2019 Lecture 1 Introduction - v1Anton AliagaNo ratings yet
- Public Private PartnershipsDocument25 pagesPublic Private PartnershipsTHOMASKUTTYNo ratings yet
- Financing Infrastructure ProjectDocument9 pagesFinancing Infrastructure ProjectsargunkaurNo ratings yet
- PPP Presen-2019Document28 pagesPPP Presen-2019Raymon PrakashNo ratings yet
- Public Private PartnershipsDocument32 pagesPublic Private PartnershipsThe GravelsNo ratings yet
- A. Preliminary EvaluationDocument8 pagesA. Preliminary EvaluationNanette Rose HaguilingNo ratings yet
- Experience Sharing & Workshop On Public-Private Partnership (PPP) : PPP Project ConceptsDocument32 pagesExperience Sharing & Workshop On Public-Private Partnership (PPP) : PPP Project ConceptsThe Outer Marker100% (1)
- 06Document49 pages06bpsc08No ratings yet
- 6 Plenary - Thematic PPP by AGaliev 20mar2017Document9 pages6 Plenary - Thematic PPP by AGaliev 20mar2017Butch D. de la Cruz100% (1)
- PDI Complete SlidesDocument151 pagesPDI Complete SlidesAbrar AkmalNo ratings yet
- 2 - Project Structure and Financing Sources For Wind FarmsDocument28 pages2 - Project Structure and Financing Sources For Wind Farmsviethoa_uehNo ratings yet
- Engineering, Procurement and Construction (ECP) ContractsDocument124 pagesEngineering, Procurement and Construction (ECP) ContractsPopeyeNo ratings yet
- Project Financing: Asset-Based Financial EngineeringFrom EverandProject Financing: Asset-Based Financial EngineeringRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2)
- COVID-19 and Public–Private Partnerships in Asia and the Pacific: Guidance NoteFrom EverandCOVID-19 and Public–Private Partnerships in Asia and the Pacific: Guidance NoteNo ratings yet
- Module 8Document1 pageModule 8jbcruz2No ratings yet
- Module 2. Sustainable DevelopmentDocument2 pagesModule 2. Sustainable Developmentjbcruz2No ratings yet
- Module 4. Forest and Land ResourcesDocument4 pagesModule 4. Forest and Land Resourcesjbcruz2No ratings yet
- P201 Module 10 NotesDocument4 pagesP201 Module 10 Notesjbcruz2No ratings yet
- Castro Mapping Gis PiepDocument53 pagesCastro Mapping Gis Piepjbcruz2No ratings yet
- P203 Module 2 Notes - Land Use Planning Principles and Contemporary IssuesDocument10 pagesP203 Module 2 Notes - Land Use Planning Principles and Contemporary Issuesjbcruz2No ratings yet
- Concepts in Planning - 2Document28 pagesConcepts in Planning - 2jbcruz2No ratings yet
- Nature and Types of Planning Jan 7Document152 pagesNature and Types of Planning Jan 7jbcruz2No ratings yet
- Day 4 DR Regunay SeaDocument41 pagesDay 4 DR Regunay Seajbcruz2No ratings yet
- Project Planning Development - 2Document38 pagesProject Planning Development - 2jbcruz2No ratings yet
- Promoting Public Private Partnership in Disaster Risk Reduction Japanese CasesDocument69 pagesPromoting Public Private Partnership in Disaster Risk Reduction Japanese Casesjbcruz2No ratings yet
- Early Trends in PLG in The Phil Add To History of PLG - 2Document11 pagesEarly Trends in PLG in The Phil Add To History of PLG - 2jbcruz2No ratings yet
- Dynamics of Land Use Planning and Its Effects On Socio-Economic DevelopmentDocument123 pagesDynamics of Land Use Planning and Its Effects On Socio-Economic Developmentjbcruz2No ratings yet
- Spatial Disaggregation of Landsat-Derived Land Surface Temperature Over A Heterogeneous Urban Landscape Using Planetscope Image DerivativesDocument8 pagesSpatial Disaggregation of Landsat-Derived Land Surface Temperature Over A Heterogeneous Urban Landscape Using Planetscope Image Derivativesjbcruz2No ratings yet
- Public Private Partnership PPP Case Studies - PhilippinesDocument19 pagesPublic Private Partnership PPP Case Studies - Philippinesjbcruz2No ratings yet
- Land and Its Basic CharacteristicsDocument41 pagesLand and Its Basic Characteristicsjbcruz2No ratings yet
- Land Use Planning IssuesDocument6 pagesLand Use Planning Issuesjbcruz2No ratings yet
- Annual Marketing CalendarDocument20 pagesAnnual Marketing CalendarRia ThoNo ratings yet
- Proposal On Management of A Consulting FirmDocument4 pagesProposal On Management of A Consulting FirmOlufemi MoyegunNo ratings yet
- Marketing Management Journal: Professor: Dr. Shalini GulechaDocument17 pagesMarketing Management Journal: Professor: Dr. Shalini GulechatejashreeNo ratings yet
- Arts Council EnglandDocument21 pagesArts Council EnglandShankeyNo ratings yet
- The Importance of Diversity in WorkplaceDocument2 pagesThe Importance of Diversity in WorkplaceNavjot Singh RaiNo ratings yet
- Wa0018.Document7 pagesWa0018.jar070888No ratings yet
- 2016 Puma Energy Annual ReportDocument212 pages2016 Puma Energy Annual ReportKA-11 Єфіменко ІванNo ratings yet
- Owfm6013 Corporate Finance - Individual AssignmentDocument27 pagesOwfm6013 Corporate Finance - Individual AssignmentPK LNo ratings yet
- Algorithmic StrategiesDocument1 pageAlgorithmic Strategiesamir khNo ratings yet
- Understanding Ebix IP Asset TransferDocument41 pagesUnderstanding Ebix IP Asset TransferspinvestorNo ratings yet
- 2 Creativity Innovation and EntrepreneurshipDocument28 pages2 Creativity Innovation and EntrepreneurshipNarayan MaharjanNo ratings yet
- Statement of Account: Date Narration Chq./Ref - No. Value DT Withdrawal Amt. Deposit Amt. Closing BalanceDocument2 pagesStatement of Account: Date Narration Chq./Ref - No. Value DT Withdrawal Amt. Deposit Amt. Closing BalanceDRISHTI MEHRANo ratings yet
- Manufacturing ManagementDocument332 pagesManufacturing ManagementPugdug 209No ratings yet
- Team 1 Moot 3 (Appellant)Document25 pagesTeam 1 Moot 3 (Appellant)Amal M SNo ratings yet
- 2020 - VN Market Trend - Q - MeDocument15 pages2020 - VN Market Trend - Q - MeGame AccountNo ratings yet
- Managing The Venture's Financial ResourcesDocument28 pagesManaging The Venture's Financial ResourcesAnto DNo ratings yet
- Business Law 10Th Edition Cheeseman Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFDocument28 pagesBusiness Law 10Th Edition Cheeseman Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFkathleenjonesswzrqcmkex100% (18)
- Ass1 Macro sp20Document3 pagesAss1 Macro sp20NoorNo ratings yet
- Team Battleship TransactionsDocument2 pagesTeam Battleship TransactionsJacob SheridanNo ratings yet
- Research Methodology: "Research Is A Formalized Curiosity. It Is Poking and Prying With A Purpose."Document10 pagesResearch Methodology: "Research Is A Formalized Curiosity. It Is Poking and Prying With A Purpose."azhagu sundaramNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Book Scheme Topic 2 Sequence (pg.4-pg32)Document29 pagesTutorial Book Scheme Topic 2 Sequence (pg.4-pg32)Fatin AqilahNo ratings yet
- Destination Zero An Action Plan For Shipping CeosDocument11 pagesDestination Zero An Action Plan For Shipping CeosromainNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument4 pagesUntitledRudra PrakashNo ratings yet
- Case Study of Mobile BankingDocument5 pagesCase Study of Mobile BankingShefali Garg100% (1)
- 0036 - Accounting For Business - EditedDocument4 pages0036 - Accounting For Business - EditedAwais AhmedNo ratings yet
- Petition For Voluntary Liquidation Sample Scribd - Google SearchDocument3 pagesPetition For Voluntary Liquidation Sample Scribd - Google SearchNielgem Beja0% (2)
- Company Certifications Fire Classifications Product ApprovalsDocument4 pagesCompany Certifications Fire Classifications Product ApprovalsHussein BeqaiNo ratings yet
- FAQsDocument1 pageFAQsJeg GillNo ratings yet
- The Self-Made Copywriter: Steal The Syllabus That Produced The Greatest Copywriters in The WorldDocument9 pagesThe Self-Made Copywriter: Steal The Syllabus That Produced The Greatest Copywriters in The WorldJosé Alias Blake0% (1)
- Crafton IndustriesDocument7 pagesCrafton IndustriesS KNo ratings yet