Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Class Ix Consitution
Class Ix Consitution
Uploaded by
killeramit1060 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views2 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views2 pagesClass Ix Consitution
Class Ix Consitution
Uploaded by
killeramit106Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 2
GYAN DEEP SR. SEC.
SCHOOL
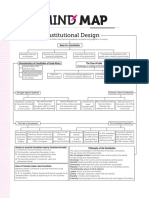
CH:2 CONSITITUTIONAL DESIGN
Teminology
Constitution : Supreme law of a country, containing fundamental rules
governing the policies and society in a country.
Clause : A distinct section of a document.
Constituent Assembly : An assembly of people’s representatives that
drafts a constitution for a country.
Constitutional amendment : A change in the constitution made by the
supreme legislative body in a country.
Draft : A preliminary version of a legal document.
Philosophy : The most fundamental principles underlying one’s
thoughts and actions.
Preamble : An introductory statement in a constitution which states the
reasons and guiding values of the constitution.
Universal adult franchise : Every adult, rich or poor, irrespective of
their religion-caste or education , colour , race, economic conditions, is
free to vote.
African National Congress (ANC) : The umbrella organization that led
the struggle against the policies of segregation.
Treason : The offence of attempting to overthrow the government of
the state for which the offender owes allegiance.
GYAN DEEP SR. SEC. SCHOOL
Chapter-2 Political ScienceConstitutional Design
Democratic Constitution in South Africa
Nelson Mandela, the South African leader of African National Congress,
fought a longbattle against Apartheid.
Imprisoned for 28 years (1964–1992) emerged as the First President of
the Republic ofSouth Africa.
People struggled against the horrible discrimination practised against them
by the whiteminority rulers.
Apartheid finally defeated in 1994 and a new constitution made in 1996.
Remarkable constitution, forgot past sufferings, sought co-operation of all
the raceswhich make S. Africa based on equality, democratic values and
social justice.
Do We Need a Constitution?
Yes. A constitution has written laws accepted by people living together in a
country.
It generates trust and co-ordination.
It specifies how a government should be constituted.
It lays down limits on the powers of the government.
It expresses the aspirations of the people about creating a good society.
Making of the Indian Constitution
The process began during the national struggle for freedom.
First draft 1928, then 1931. Motilal Nehru and 8 leaders demanded in the
draft : universaladult franchise, social justice, right to freedom and liberty.
Participation in Provincial Legislatures helped Indians in framing their
constitution.
z Leaders inspired by French Revolution, British parliamentary system
and the Bill ofRights of the US.
They also learnt what the British were denying Indian citizens.
The Constituent Assembly
Elections to the Constituent Assembly held in July 1946.
Dr. B.R. Ambedkar appointed chairman of the drafting committee.
Constitution adopted on 26 November 1949, and enacted on 26 January,
1950, whenIndia became a republic.
The Constitution reflects the best minds of the country. Its members
represented mini-India.
Every law was debated clause by clause and a consensus arrived at.
It is the longest written constitution.
You might also like
- China Doll (Issues and Recommendation)Document8 pagesChina Doll (Issues and Recommendation)Murayysn Chandra100% (1)
- 13 Week Cash Flow ModelDocument16 pages13 Week Cash Flow ModelASChipLeadNo ratings yet
- 09 Social Science Key Notes Pol SC Ch3 Constitutional DesignDocument2 pages09 Social Science Key Notes Pol SC Ch3 Constitutional DesignJIO CINEMA0% (1)
- Chapter-2 Constitutional DesignDocument31 pagesChapter-2 Constitutional DesignNodiaNo ratings yet
- Pol. Sci Class Ix CH 2 NotesDocument4 pagesPol. Sci Class Ix CH 2 Notessonal chaudharyNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 9 Political Science (Civics) Chapter 2 Notes - Constitutional DesignDocument4 pagesCBSE Class 9 Political Science (Civics) Chapter 2 Notes - Constitutional DesignDeepak GuptaNo ratings yet
- Cbse Class 9 Social Science Political Science Chapter 2 NotesDocument4 pagesCbse Class 9 Social Science Political Science Chapter 2 Notessk0editor0666No ratings yet
- Constitutional Design Class 9 Notes Social Science Civics Chapter 3Document2 pagesConstitutional Design Class 9 Notes Social Science Civics Chapter 3atharvashende806No ratings yet
- CBSE-Notes-Class-9-Social-Science-Political-Science-Chapter-2-Constitutional-Design 2Document5 pagesCBSE-Notes-Class-9-Social-Science-Political-Science-Chapter-2-Constitutional-Design 2Praneeth ReddyNo ratings yet
- Constitutional DesignsDocument12 pagesConstitutional Designsfamkmr11No ratings yet
- 09 Social Science Key Notes Pol SC ch3 Constitutional DesignDocument1 page09 Social Science Key Notes Pol SC ch3 Constitutional DesignPrem KukrejaNo ratings yet
- Making of The South African ConstitutionDocument5 pagesMaking of The South African ConstitutionAchilles HussainNo ratings yet
- Chapter-3 Political Science Constitutional Design: Democratic Constitution in South AfricaDocument1 pageChapter-3 Political Science Constitutional Design: Democratic Constitution in South AfricaKishlay AnandNo ratings yet
- Class9 Social Science Chapter 21.constitutional DesignDocument1 pageClass9 Social Science Chapter 21.constitutional Designvinod kumar wahiNo ratings yet
- 09 Social Science Key Notes Pol SC ch3 Constitutional Design UnlockedDocument1 page09 Social Science Key Notes Pol SC ch3 Constitutional Design Unlockedaryabhorkade22No ratings yet
- Constitutional DesignDocument1 pageConstitutional DesignNikhat SiddiqueNo ratings yet
- Chapter-3 Political Science Constitutional Design: Democratic Constitution in South AfricaDocument1 pageChapter-3 Political Science Constitutional Design: Democratic Constitution in South AfricaArun HoodaNo ratings yet
- Chapter-3 Political Science Constitutional Design: Democratic Constitution in South AfricaDocument1 pageChapter-3 Political Science Constitutional Design: Democratic Constitution in South AfricaShekhar Upadhyay0% (1)
- Constitutional Design: Nelson MandelaDocument6 pagesConstitutional Design: Nelson MandelaAnonymous 8fpvYy9ihNo ratings yet
- Constitutional Design Forest Society and ColonialismDocument23 pagesConstitutional Design Forest Society and ColonialismthinkiitNo ratings yet
- CONSTITUTIONAL DESIGN - Class Notes - SprintDocument73 pagesCONSTITUTIONAL DESIGN - Class Notes - SprintArav AroraNo ratings yet
- St. Joseph's Sr. Sec. Co Ed School Social Science (Democratic Politics) Class IXDocument6 pagesSt. Joseph's Sr. Sec. Co Ed School Social Science (Democratic Politics) Class IXom guptaNo ratings yet
- constitutional design class 9Document16 pagesconstitutional design class 9myaiphabi21deviNo ratings yet
- Constitutional DesignDocument1 pageConstitutional DesignHafalath UL HajaraNo ratings yet
- Constitutional Design Notes PDFDocument39 pagesConstitutional Design Notes PDFSanjay GenwaNo ratings yet
- Constitution Why and How L-3Document29 pagesConstitution Why and How L-3aanjnay1234No ratings yet
- Constitutional Design CBSE Grade 9Document14 pagesConstitutional Design CBSE Grade 9Anagha Krishna PrasadNo ratings yet
- Class 9 Constitutional DesignDocument27 pagesClass 9 Constitutional DesignaannoosandhuNo ratings yet
- Class9 Constitutional Design TermIDocument5 pagesClass9 Constitutional Design TermIvinod15770% (1)
- CLASS IX Politics Chapter 3 Constitutional DesignDocument7 pagesCLASS IX Politics Chapter 3 Constitutional DesignAksa Merlin ThomasNo ratings yet
- Constitution Design-ChapterDocument3 pagesConstitution Design-ChapterAshmit SarkarNo ratings yet
- Constitutional Design: Apartheid - Racial Discrimination Unique To South AfricaDocument3 pagesConstitutional Design: Apartheid - Racial Discrimination Unique To South AfricaommNo ratings yet
- Ch-4 Working of InstitutionDocument8 pagesCh-4 Working of Institutionmukeshwithvirat9595No ratings yet
- 03 Constitutional DesignDocument15 pages03 Constitutional DesignKamalKumawatNo ratings yet
- Constitution Design PPT by KanishkaDocument17 pagesConstitution Design PPT by KanishkaKanishka SharmaNo ratings yet
- Polity 03 - Daily Class Notes - UPSC Prarambh 2026Document8 pagesPolity 03 - Daily Class Notes - UPSC Prarambh 2026fake11226465No ratings yet
- SOC.G7.U3 - Handout - Updated 7th Nov 2023Document6 pagesSOC.G7.U3 - Handout - Updated 7th Nov 2023Nivesh Programming and GamingNo ratings yet
- Constitutional Design Class-9th PDocument24 pagesConstitutional Design Class-9th PSudipta BhattacharyyaNo ratings yet
- Constitutional DesignDocument52 pagesConstitutional Designjaiprakash adwaniNo ratings yet
- Constitutionn of India Class 7Document5 pagesConstitutionn of India Class 7jecom79703No ratings yet
- Constitutional Design Chap 3Document5 pagesConstitutional Design Chap 3nandita singhNo ratings yet
- Constitutionaldesign 150605114722 Lva1 App6892Document43 pagesConstitutionaldesign 150605114722 Lva1 App6892divyapoornachand petetiNo ratings yet
- Democracy and ConstitutionDocument19 pagesDemocracy and ConstitutionSanchit MukherjeeNo ratings yet
- Explain The Philosophy of Indian ConstitutionDocument15 pagesExplain The Philosophy of Indian ConstitutionSupport E LaxmiNo ratings yet
- ch-2 NotesDocument9 pagesch-2 NotesDipanshu JainNo ratings yet
- Constitutional Design Q and AnsDocument5 pagesConstitutional Design Q and AnsAKSHARA TYAGI100% (1)
- Ch2 CivicsDocument16 pagesCh2 CivicsBhagyashreeNo ratings yet
- CSL NotesDocument50 pagesCSL Notestf2hzfkbnmNo ratings yet
- Constitutional DesignDocument4 pagesConstitutional DesignManas AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Constitution of IndiaDocument84 pagesConstitution of Indianingegowda0% (1)
- Indian Constitution Module 1 Philosophy and FramingDocument12 pagesIndian Constitution Module 1 Philosophy and FramingPriya AhujaNo ratings yet
- Constitutional Design (1-8)Document2 pagesConstitutional Design (1-8)rajputmanas77No ratings yet
- The Indian Constitution PDFDocument6 pagesThe Indian Constitution PDFEeshan SharmaNo ratings yet
- Polity Ncert Compilation (ST)Document81 pagesPolity Ncert Compilation (ST)journeybpscNo ratings yet
- Indian Constitution NotesDocument26 pagesIndian Constitution NotesNisarga H PNo ratings yet
- Polity RevisionDocument11 pagesPolity Revision22D011 AROCKIAVIMALJAPSON ANo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 The Indian Constitution WatermarkDocument20 pagesChapter 1 The Indian Constitution WatermarkKrypton HalideNo ratings yet
- The Constitution of IndiaDocument39 pagesThe Constitution of Indiasagar oza100% (1)
- Constitutional Design IXDocument30 pagesConstitutional Design IXIndu KumariNo ratings yet
- ConstitutionDocument21 pagesConstitutionNISHTA SHARMANo ratings yet
- XI PRINT (E) .OdDocument28 pagesXI PRINT (E) .OdAmjada YasminNo ratings yet
- MIAA V CA, 495 SCRA 591, 622Document181 pagesMIAA V CA, 495 SCRA 591, 622HNo ratings yet
- Tax 2 - Unit 2. Chapter 2.Document7 pagesTax 2 - Unit 2. Chapter 2.Rujean Salar AltejarNo ratings yet
- WS - QHSE - S23 - G05 - Cement Head - 3313701 - 07Document17 pagesWS - QHSE - S23 - G05 - Cement Head - 3313701 - 07CiprianHnNo ratings yet
- AJSK CentersDocument34 pagesAJSK CentersRoopa P JadhavNo ratings yet
- SecretaryDocument2 pagesSecretaryNicolo Jay PajaritoNo ratings yet
- Language Programs and Policies in Multilingual Societies - Activity 3Document4 pagesLanguage Programs and Policies in Multilingual Societies - Activity 3Angel Rodriguez75% (4)
- Sample MCQ Topics 1-5Document12 pagesSample MCQ Topics 1-5horace000715No ratings yet
- TELEBAP v. COMELEC - LandongDocument2 pagesTELEBAP v. COMELEC - LandongNamiel Maverick D. Balina100% (1)
- Lufthansa German Airlines V IAC & SPS Alcantara (G.R. No. 71238) PDFDocument4 pagesLufthansa German Airlines V IAC & SPS Alcantara (G.R. No. 71238) PDFAlainah ChuaNo ratings yet
- Jamuna BankDocument35 pagesJamuna BankMd ShahnewazNo ratings yet
- Lab 15 - Applying A Pricing Rule To A CatalogDocument6 pagesLab 15 - Applying A Pricing Rule To A CatalogSushantgupta015No ratings yet
- Carino Vs Carino (2001)Document1 pageCarino Vs Carino (2001)CECILIA TALLANo ratings yet
- The Fathers of The Church. A New Translation. Volume 31.Document408 pagesThe Fathers of The Church. A New Translation. Volume 31.Patrologia Latina, Graeca et Orientalis100% (7)
- RA CUSTOMSBROKER CEBU Nov2017 PDFDocument7 pagesRA CUSTOMSBROKER CEBU Nov2017 PDFPhilBoardResultsNo ratings yet
- Insurance Law in India Question and AnswerDocument15 pagesInsurance Law in India Question and AnswerMaitrayee NandyNo ratings yet
- Theodore Whitmore Stanley v. Darlington County School District, Elaine Whittenberg v. School District of Greenville County, Etc., 424 F.2d 195, 4th Cir. (1970)Document6 pagesTheodore Whitmore Stanley v. Darlington County School District, Elaine Whittenberg v. School District of Greenville County, Etc., 424 F.2d 195, 4th Cir. (1970)Scribd Government DocsNo ratings yet
- 4th Grade Indian in The CupboardDocument16 pages4th Grade Indian in The Cupboardapi-251212745No ratings yet
- Chordu Guitar Chords Ensamble Tejedora Manabita Expresarte Música Chordsheet Id GiY7U7AjCaYDocument3 pagesChordu Guitar Chords Ensamble Tejedora Manabita Expresarte Música Chordsheet Id GiY7U7AjCaYAngelita;3 Neko:3No ratings yet
- International Arbitration Conference - MNLU Mumbai - 6 December PDFDocument4 pagesInternational Arbitration Conference - MNLU Mumbai - 6 December PDFRCR 75No ratings yet
- Palanca Vs CommonwealthDocument2 pagesPalanca Vs CommonwealthReal TaberneroNo ratings yet
- Tax Audit Reference Manual - Tally TDL - College Management Software - Tally Implementation ServicesDocument48 pagesTax Audit Reference Manual - Tally TDL - College Management Software - Tally Implementation ServicesjohnabrahamstanNo ratings yet
- GOMs No 58Document14 pagesGOMs No 58PRAKASHNo ratings yet
- 803E Incoterms 2020 Wallchart A4Document1 page803E Incoterms 2020 Wallchart A4bd6999No ratings yet
- American West and Industrialization Part 2Document13 pagesAmerican West and Industrialization Part 2Christian JonesNo ratings yet
- Au Abhi 31-MarchDocument2 pagesAu Abhi 31-MarchShubhra Kanti GopeNo ratings yet
- Audit of Not For Profit OrganizationsDocument172 pagesAudit of Not For Profit OrganizationsDeepak JainNo ratings yet
- ADR Sec 35 - Group 2 Fundamentals of ADR Report (Angiwan, Bandal Sanchez, Sobrevega)Document8 pagesADR Sec 35 - Group 2 Fundamentals of ADR Report (Angiwan, Bandal Sanchez, Sobrevega)Jeanrose B. CarenanNo ratings yet
- Mind Map For Prophet's Life - TaskadeDocument7 pagesMind Map For Prophet's Life - TaskadeUniba WajidNo ratings yet