Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Al-assaf NOTES 10 (4)
Al-assaf NOTES 10 (4)
Uploaded by
mohamedalawy1979Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Al-assaf NOTES 10 (4)
Al-assaf NOTES 10 (4)
Uploaded by
mohamedalawy1979Copyright:
Available Formats
Al-Assaf NOTES (PART 10), 11-15 January 2022
1. Dose of ibuprofen for a 10-year-old child:
• 4 - 10 mg
• 4 - 10 g
• Pediatric Dentistry - Infancy Through Adolescence
2. Anterior diastema, what is its effect on the gingiva
• Flat (could be the correct answer).
• Retention
•
• Carranza’s Clinical Periodontology
3. Anterior diastema with mobility of teeth, what is major connector use?
• Interrupted linguoplate (notched lingual plate).
•
• McCracken's Removable Partial Prosthodontics
4. Case with 12 mm vestibule, what major connectors is most suitable?
• Lingual bar.
NOTES By: Moath Al-assaf Twitter: @mo3ath44
Al-Assaf NOTES (PART 10), 11-15 January 2022
5. Which of the following is the suitable maxillary major connector in case with large palatal tori?
• Horse-shoe shape / U-shaped
•
• McCracken's Removable Partial Prosthodontics
6. Which of the following is the most destructive direct retainer in class I Kennedy case
• Aker
• RPI
• RPA
•
• McCracken's Removable Partial Prosthodontics
7. Saucer shaped radiolucency around implant, this indicates which of the following?
• Peri-implantitis
•
• Carranza’s Clinical Periodontology
8. Pocket depth of 4-5 around implant, the likely diagnosis is:
• Peri-implantitis
• Peri-implant mucositis
•
• Carranza’s Clinical Periodontology
9. Which of the following is considered determinant of implant success?
• Primary stability
• Secondary stability (Osteointegration)
• Carranza’s Clinical Periodontology
NOTES By: Moath Al-assaf Twitter: @mo3ath44
Al-Assaf NOTES (PART 10), 11-15 January 2022
10. Question about iodine test:
• Frey’s syndrome
•
• Neville, Oral & Maxillofacial Pathology
11. You add violet stain to yellow crown?
• Increase chroma and value
• Decrease chroma abs value
• Increase chroma decrease value
• Decrease chroma increase value
•
• Contemporary Fixed Prosthodontics
12. Drug cause swelling in lower lip
• Question not clear, I think it is related to allergic reaction, hence, angioedema.
•
• Dental Management of the Medically Compromised Patient
NOTES By: Moath Al-assaf Twitter: @mo3ath44
Al-Assaf NOTES (PART 10), 11-15 January 2022
13. A question about Addison’s disease
• Cushing syndrome refers to a condition caused by excessive cortisol in the body.
• Addison disease (Primary adrenal insufficiency) is caused by the lack of the major hormones of the
adrenal cortex (aldosterone, cortisol, androgens).
• Secondary and tertiary adrenal insufficiency:
•
• Dental Management of the Medically Compromised Patient
14. Considerations for diabetic patient
• Short treatment
•
• Contemporary Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery
15. Multiple questions about VRF
• Covered in detail in previous files.
NOTES By: Moath Al-assaf Twitter: @mo3ath44
Al-Assaf NOTES (PART 10), 11-15 January 2022
16. INR level that contraindicates dental treatment:
• 2.5
• 3 (for major oral surgeries).
• 3.5 (for invasive dental and surgical procedures).
•
• Dental Management of the Medically Compromised Patient
17. Patient with fractured complete denture after 10 years of use, what is the likely cause?
• Porosity? (I don’t think that it is the correct answer).
• Causes of fracture could be:
▪ Ridge resorption with loss of relief effect causes delay fracture.
▪ Dropped on the hard surface
▪ Fracture of ill-fitting denture due to:
• Alveolar ridge resorption
• Warpage of the denture base
• Inadequate relief or excessive relief inaccurate impression
▪ Maxillary teeth set outside the ridge
▪ Inadequate thickness of the denture base
• Online source
18. Alginate impression poured after long time, what is the effect of cast size?
• Smaller than real
• Larger than real
•
• McCracken's Removable Partial Prosthodontics
NOTES By: Moath Al-assaf Twitter: @mo3ath44
Al-Assaf NOTES (PART 10), 11-15 January 2022
19. Multiple questions about decreased and increased vertical dimensions:
• Reduced occlusal vertical dimension can cause:
▪ Temporomandibular joint damage,
▪ Facial distortion,
▪ Loss of muscle tone,
▪ Angular cheilitis. (Related to saliva)
▪ The patient often has the appearance of the “nose being too close to the chin.”
• Increased occlusal vertical dimension can cause
▪ Most often the patient’s face does not appear relaxed,
▪ Lips cannot lightly touch when the patient is at rest, result in facial distortion.
▪ Damage to supporting tissues includes soreness, possible ischemia, and eventual resorption.
▪ Increased gag reflex
•
• Textbook of Complete Dentures, 6th Edition
20. Adenoid related to:
• Increased lower facial height:
•
• Contemporary Orthodontics
NOTES By: Moath Al-assaf Twitter: @mo3ath44
Al-Assaf NOTES (PART 10), 11-15 January 2022
21. Which of the following has the least chance of impaction?
• Maxillary molar
• Mandibular molar
• Maxillary premolar
• Maxillary incisor
•
• Neville, Oral & Maxillofacial Pathology
22. When “S” sound like “th” sound, which of the following is correct?
• Posterior setting problem
• Anterior setting problem
•
• Textbook of Complete Dentures, 6th Edition
23. Regarding chipping of porcelain, what type of failure?
• Cohesive failure
•
• Contemporary Fixed Prosthodontics
24. Regarding chipping of porcelain, which of the following is a cause?
• Metal-ceramic interface at occlusal contact
•
• Contemporary Fixed Prosthodontics
25. Management of white spot lesions after orthodontic treatment
• Bleaching
• Micro-abrasion
•
NOTES By: Moath Al-assaf Twitter: @mo3ath44
Al-Assaf NOTES (PART 10), 11-15 January 2022
26. Which of the following procedures includes the use of bur?
• Macro abrasion
• Micro abrasion
• Bleaching
27. What type of burs is used during macro-abrasion procedure?
• 12-fluted composite finishing bur
•
• Sturdevant’s Art and Science of Operative Dentistry, 5e
28. Which of the following procedures includes the use of rubber cup and paste?
• Macro abrasion
• Micro abrasion
• Bleaching
•
• Sturdevant’s Art and Science of Operative Dentistry, 5e
•
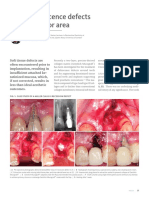
29. Type of cement used for cementatin of orthodontic bands: (Note: Not bracket)
• Glass-ionomer cements
•
30. After laser gingivectomy, patient return with bleeding, which could be the cause?
• Overuse of leaser
• Violation of biologic width
31. Patient with upper complete denture and lower natural teeth for long time, this case is describe as
• Combination syndrome (AKA: Anterior hyperfunction syndrome / Kelly’s Syndrome)
• Hyperplasia syndrome
•
• Textbook of Complete Dentures, 6th Edition
32. Christensen’s phenomena
•
• Textbook of Complete Dentures, 6th Edition
NOTES By: Moath Al-assaf Twitter: @mo3ath44
Al-Assaf NOTES (PART 10), 11-15 January 2022
33. Two pictures for swellings in pregnant female:
34. Picture for mandibular tori:
35. Local delivery of antibiotics,
•
• Carranza’s Clinical Periodontology
36. Picture of PerioChip:
•
• Carranza’s Clinical Periodontology
NOTES By: Moath Al-assaf Twitter: @mo3ath44
Al-Assaf NOTES (PART 10), 11-15 January 2022
37. Root amputation definition:
• Split roots
• Remove one root
• Keep crown
• Root resection (amputation) is the process by which one or more roots of a tooth are removed at
the level of the furcation while leaving the crown and remaining roots in function.
• Periodontics: Medicine, Surgery and Implants
38. Hemi section definition:
• Split roots
• Remove one root
• Keep crown
•
• Carranza’s Clinical Periodontology
39. Upper 1st molar radiograph asking about number of roots:
•
40. Patient with anterior flappy tissue, what impression technique to use?
• Open try
• Closed tray
• Functional impression
• Answer should be open window impression
41. Splinting of alveolar fracture
• Semi-rigid 2-3 weeks
• Rigid 8 weeks
• Flexible splint for 4 weeks (answered in previous parts).
• International Association of Dental Traumatology Guidelines for
the Management of Traumatic Dental Injuries: 1. Fractures and
Luxations
NOTES By: Moath Al-assaf Twitter: @mo3ath44
Al-Assaf NOTES (PART 10), 11-15 January 2022
42. Softening of wax which use for bite registration
• 10 s
• 20 s
• 30 s
•
• Prosthodontic Treatment for Edentulous Patients
43. What is the likely cause of loosing the retention of complete denture at rest?
•
• Textbook of Complete Dentures, 6th Edition
44. Which muscle moves the mandible downward?
• Masseter
• Temporalis
• Lateral pterygoid (Inferior head) – A table for each muscle function in previous parts
• Medial pterygoid
45. The condyle of non-working side, which of the following is the path it moves to?
• Downward backward median
• Downward foreword lateral
• Downward, foreword, and medially
•
• Contemporary Fixed Prosthodontics
46. How many rests for a case with Kennedy class IV RPD?
• 2
• 3
• 4
• Class I: 2 rests, Class II, 3 rests, Class III: 4 rests, Class IV: 4 rests.
NOTES By: Moath Al-assaf Twitter: @mo3ath44
Al-Assaf NOTES (PART 10), 11-15 January 2022
47. RPD color coding
• Red: Means ‘required action’ to be prepared, recontoured and relieved.
▪ Solid red shows where occlusal rest is to be prepared.
▪ Diagonal red lines show where recontouring is necessary.
▪ Tripod marks are also marked in red.
• Black: Denotes survey lines, depth of undercut is also written in black.
• Blue: Denotes portions that will be made of acrylic – mostly denture bases and acrylic teeth.
• Brown: Denotes all metallic portions.
• Textbook of Prosthodontics
48. Premolar clamp?
• W8 (upper molar)
• A2
• 212 (anterior)
•
• “W” means wingless, “A” means active or apically directed prongs.
49. #12 missing, which Kennedy classification?
• Class III, because it does not cross the midline.
• Kennedy classification and Applegate’s rules mentioned in previous parts in details.
NOTES By: Moath Al-assaf Twitter: @mo3ath44
Al-Assaf NOTES (PART 10), 11-15 January 2022
50. Case for a patient on bisphosphonate for 10 years, present for tooth extraction:
•
• Contemporary Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery
•
• Dental Management of the Medically Compromised Patient
51. Which of the following is a feature in patient with Apert syndrome?
• Long face
• Long skull (Acrobrachycephaly / Tower skull)
• Small face
•
• Neville, Oral & Maxillofacial Pathology
NOTES By: Moath Al-assaf Twitter: @mo3ath44
Al-Assaf NOTES (PART 10), 11-15 January 2022
52. Most effective irrigation for endo Tx:
• EDTA (For inorganic portion - Ethylenediamine Tetra-Acetic Acid)
• NaOCl
•
• Cohen's Pathways of the Pulp Expert Consult
53. Patient complains from left side pain referred to ear, which of the following is the likely offending tooth?
• Lower molars.
•
• Essentials of Oral Pathology
54. Scrofula
• Unpasteurized milk
•
• Neville, Oral & Maxillofacial Pathology
NOTES By: Moath Al-assaf Twitter: @mo3ath44
Al-Assaf NOTES (PART 10), 11-15 January 2022
55. Picture of large swelling due to odontogenic infection, what is the management?
• Extraoral incision
• Intra oral incision
• Extraction of the destructed tooth
• If an option with extraction & incision and drainage is available, it is the correct answer.
• Management of Fascial Space Infections:
1) Medical support of the patient, especially to airway and host defense.
2) Surgical removal of the source of infection as early as possible.
3) Surgical drainage of the infection, with proper placement of drains.
4) Administration of correct antibiotics in appropriate doses.
5) Frequent re-evaluation of the patient’s progress toward resolution.
•
• Contemporary Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery
56. Sleep apnea:
• Management:
▪ Weight loss is one of the most effective measures that can be instituted; however, it may
not result in normalization alone.
▪ Positive Airway Pressure (gold standard): Delivery of PAP modalities:
• 1. Continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP)
• 2. Bilevel positive airway pressure (BiPAP or BPAP)
• 3. Auto-adjusting positive airway pressure (APAP)
▪ Oral Appliances:
• Indications:
o (1) as a primary treatment option.
o (2) in patients who are unable to tolerate the use of PAP.
o (3) in patients who refuse to use PAP.
• The two basic types of oral appliances:
o Mandibular advancement devices (MADs), which engage the mandible and
reposition it (and indirectly, the tongue) in an anterior or forward position.
o Tongue-retaining devices (TRDs), which directly engage the tongue and hold
it in a forward position.
NOTES By: Moath Al-assaf Twitter: @mo3ath44
Al-Assaf NOTES (PART 10), 11-15 January 2022
57. Tongue thrust
•
• Contemporary Orthodontics
58. The Most common cause of allergic reaction in dentistry:
• Latex
• Stainless steel crown
• The most common causes of anaphylactic death
are penicillin, bee stings, and wasp stings.
NOTES By: Moath Al-assaf Twitter: @mo3ath44
Al-Assaf NOTES (PART 10), 11-15 January 2022
•
• Dental Management of the Medically Compromised Patient
59. Most common mandibular fracture
• Condylar
• Body
• Regarding mid-face fractures:
•
• Contemporary Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery
60. Age of trauma:
• 2-4
• 7-8
•
• Pediatric Dentistry - Infancy Through Adolescence,
61. TB skin test result that indicates “patient not at risk”
• Less 5 mm
• More 5 mm
• 15 mm (15 mm or greater is considered positive evidence of TB in all persons tested.).
• Dental Management of the Medically Compromised Patient
NOTES By: Moath Al-assaf Twitter: @mo3ath44
Al-Assaf NOTES (PART 10), 11-15 January 2022
62. Anti-HBc negative:
• To possible diagnosis
▪ Susceptible
▪ Immune due to hepatitis B vaccination
63. Prognosis of single rooted tooth with vertical root fracture
• Good
• Poor
• Hopeless
• Questionable
•
• Carranza’s Clinical Periodontology
64. Treatment of pseudo class III:
• Chain (Incorrect)
• Headgear (Incorrect)
• Definition: shifting into anterior crossbite because of incisor interferences.
• Management: treat maxillary or mandibular incisor to eliminate interference.
• Contemporary Orthodontics
65. ANB in class 2:
• Increased
• Decreased
• Class II Division 1: Increased
• Class II Division 2: Decreased
NOTES By: Moath Al-assaf Twitter: @mo3ath44
Al-Assaf NOTES (PART 10), 11-15 January 2022
66. 5 years pediatric patient worried about diastema?
• Just reassure the patient
•
• Contemporary Orthodontics
67. 14 years old patient with unerupted upper canine, how to manage?
• Palpation
• Ortho extrusion
•
• Contemporary Orthodontics
68. What is the most difficult pontic design to clean?
• Ridge lab
• Modified ridge lab
• Ovate
•
• The table with other pontics details was mentioned in previous parts.
69. What is the largest sinus?
• Maxillary
• Frontal
70. What is the prognosis of fractured file middle third of the root?
• No answer is straightforward, the following factors affect the prognosis:
NOTES By: Moath Al-assaf Twitter: @mo3ath44
Al-Assaf NOTES (PART 10), 11-15 January 2022
71. X-ray to identify a separated instrument in the middle third of the root:
72. Low of quantity of minerals in enamel is defined as:
• Hypo-calcification
• Amelogenesis imperfecta
73. Cross section of wrought wire
• Round (Flexible).
• Half-round (Rigid, cannot be modified)
•
• McCracken's Removable Partial Prosthodontics
74. Patient who needs simple restoration, but he wants to do crown and it is considered destructive procedure:
• Refer and politely dismiss
• Refer to another physician
• Do what he wants
75. Extracted tooth for training:
• 10% formalin (if containing amalgam)
• Autoclave (No amalgam)
76. - MB2 location?
• Mesial
• Distal
• Location of MB2: The mesiolingual canal orifice (commonly referred to as the MB2 canal) is located
1 to 3 mm lingual to the main mesiobuccal canal (MB1 canal) and is slightly mesial to a line drawn
from the mesiobuccal to the lingual or palatal canal.
• Endodontics, Principles and Practice
NOTES By: Moath Al-assaf Twitter: @mo3ath44
Al-Assaf NOTES (PART 10), 11-15 January 2022
77. Which of the following is the appropriate size of implant if the MD & BL width is 7mm?
• 3
• 4 (details are in precious files)
• 5
78. Multiple endo Clinical Cases (endo diagnosis was covered before)
• Necrotic
• Reversible and irreversible pulpits
79. Best pulp test:
• Cold
80. Filler and resin matrix are linked by which of the following:
• Silane coupling agent (3- Methacryloxypropyl-trimethoxy Silane)
81. Splint time for the following cases:
• Extrusion: 2 weeks
• Lateral laxation: 4 weeks
• Alveolar bone fracture: 4 weeks
• Avulsion: 2 weeks
• Table of splinting time was mentioned before
82. Regarding rubber dam: if holes too far and holes too close
•
• Sturdevant’s Art and Science of Operative Dentistry, 5e
83. Poor prognosis:
• Cervical root fracture
• Mentioned before
84. Multiple cases to select appropriate size of implant
• Methods and dimensions mentioned before
85. Probing depth of implant after one year of placement:
• Same as natural
• Increase
• Shallow
•
• Carranza’s Clinical Periodontology
86. Distance between two implants
• 3mm (mentioned before)
87. Radiographs about Periimplantitis (Carranza’s Clinical Periodontology)
NOTES By: Moath Al-assaf Twitter: @mo3ath44
Al-Assaf NOTES (PART 10), 11-15 January 2022
88. Distance between plaque and alveolar crest:
• 4-5 mm
• 0.5 mm – 2.7 mm (Correct)
•
• Carranza’s Clinical Periodontology
89. Fluorosis affect permanent dentition at which age (Conflict)
• 18 months to 3 years (1.5 - 3 years).
• For primary dentition: middle of first year.
•
• McDonald and Avery's Dentistry for the Child and Adolescent
•
• Pediatric Dentistry - Infancy Through Adolescence
NOTES By: Moath Al-assaf Twitter: @mo3ath44
Al-Assaf NOTES (PART 10), 11-15 January 2022
90. Junctional epithelium length
• 0.97 mm (answered before)
91. Connective tissue attachment length
• 1.07 mm (answered before)
92. Periodontal probes:
• WHO: 0.5 mm ball at the end.
• UNC 15 color code: (5-10-15)
• Plastic probe for implants
• All mentioned before
•
93. Drugs cause cleft palate at pregnant:
• Steroids (Not sure)
• List for drugs causing cleft lip and palate:
▪ Aspirin, Cigarette smoke (hypoxia), Dilantin,
▪ Cleft palate: 6-Mercaptopurine
▪ Contemporary Orthodontics
94. White spots appear only when dry
• Incipient caries
95. White spots when dry and wet
• Enamel Hypoplasia
• Enamel hypocalcification
•
• Sturdevant’s Art and Science of Operative Dentistry, 5e
96. Nasopalatine nerve block (2 questions)
NOTES By: Moath Al-assaf Twitter: @mo3ath44
Al-Assaf NOTES (PART 10), 11-15 January 2022
• Handbook of Local Anesthesia by Stanley F. Malamed
97. Ethics:
• Veracity
• Non-maleficence
• Confidentiality
• Questions about how to deal with complicated cases -> refer to specialist
• Covered before
98. Vomiting on floor
• Intermediate
99. Extracted tooth without restoration for dental students
• Autoclave for 40 min
•
• Basic Guide to Infection Prevention and Control in Dentistry
100. Extracted tooth with amalgam
• Hazardous waste
•
• Basic Guide to Infection Prevention and Control in Dentistry
101. Wiping vomit with napkins
• Infectious
•
• Basic Guide to Infection Prevention and Control in Dentistry
102. Best sterilization method:
• Dry heat (used in most dental offices)
• Moist heat
•
• Contemporary Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery
NOTES By: Moath Al-assaf Twitter: @mo3ath44
Al-Assaf NOTES (PART 10), 11-15 January 2022
103. Oral conditions associated with HIV:
•
• Neville, Oral & Maxillofacial Pathology
104. Clinical appearance of erythema multiform:
• Target-like skin lesions
•
• Neville, Oral & Maxillofacial Pathology
105. Asthma Allergy to which component of LA
• Sodium Metabisulphite
• Answered before
•
106. Laboratory test result of a case with Aplastic anemia
• Definition:
•
• To identify the lab test results, normal count of each category should be memorized:
▪ White blood cells: 4500–10,000/mL.
▪ Red blood cells: 4.5–5.9 × 106 106 /µL.
▪ Platelets: 150,000–450,000/µL.
▪ Hemoglobin:
• Male: 13.5–17.5 g/dl
• Female: 12.3–15.3 g/dL
• For your knowledge:
NOTES By: Moath Al-assaf Twitter: @mo3ath44
Al-Assaf NOTES (PART 10), 11-15 January 2022
•
• Dental Management of the Medically Compromised Patient
NOTES By: Moath Al-assaf Twitter: @mo3ath44
Al-Assaf NOTES (PART 10), 11-15 January 2022
107. Asthmatic patient started to wheeze during treatment, how to manage?
• Give bronchodilator
•
• Dental Management of the Medically Compromised Patient
108. 70-year-old with xerostomia and caries what is the likely cause?
• Hyposalivation due to age (This option is mostly incorrect).
•
• Dental Management of the Medically Compromised Patient
•
• Neville, Oral & Maxillofacial Pathology
109. Cause gingival enlargement
• Beta blockers (likely incorrect)
•
• Neville, Oral & Maxillofacial Pathology
• Beta-blocker cause: Taste changes, lichenoid reactions. (Frequently asked).
• Dental Management of the Medically Compromised Patient
NOTES By: Moath Al-assaf Twitter: @mo3ath44
Al-Assaf NOTES (PART 10), 11-15 January 2022
110. Stage 3 of NUG:
• STAGE 3: Necrosis extending to the gingival margin
• Al-Assaf NOTES (PART 7), 7-9 December 2021
111. Kennedy classifications (7 cases)
• Mentioned in detail in part 7
112. Clasps (multiple cases related to clinical case and esthetic preference)
• Infrabulge clasps such I-bar, T-bar, Y-bar.
•
• McCracken's Removable Partial Prosthodontics
• Textbook of Prosthodontics - 2nd Edition
113. Lingual plate (4 cases)
• Indications for lingual plate:
▪ If less than 8 mm between gingival margins
and the movable floor of the mouth.
▪ For stabilizing periodontally weakened
teeth, splinting with a linguo-plate can be of
some value when used with definite rests on
sound adjacent teeth.
▪ When the future replacement of one or more
incisor teeth.
• McCracken's Removable Partial Prosthodontics
NOTES By: Moath Al-assaf Twitter: @mo3ath44
Al-Assaf NOTES (PART 10), 11-15 January 2022
114. Risk of using Aker’s clasp:
• Caries - recession - periodontal disease – sensitivity
• Because more tooth surface is covered.
• McCracken's Removable Partial Prosthodontics
115. Circumferential clasp
• McCracken's Removable Partial Prosthodontics
116. Investment material for FPD crown:
• Phosphate bonded investment
•
• Textbook of Prosthodontics - 2nd Edition
117. Attrition:
118. Erosion in case of bulimia nervosa:
•
119. Abfraction
NOTES By: Moath Al-assaf Twitter: @mo3ath44
Al-Assaf NOTES (PART 10), 11-15 January 2022
120. Which of the following is a component of FPD:
• Retainer
• Abutment (Incorrect)
•
• Contemporary Fixed Prosthodontics
121. FPD pier abutment connector:
• A nonrigid connector or a cantilever can minimize problems often encountered with pier abutments.
• Contemporary Fixed Prosthodontics
122. Nickel chromium sensitivity
•
• Type IV hypersensitivity (contact stomatitis) begins in hours and peaks in 2 to 3 days. (Delayed hypersensitivity.)
• Contemporary Fixed Prosthodontics
NOTES By: Moath Al-assaf Twitter: @mo3ath44
Al-Assaf NOTES (PART 10), 11-15 January 2022
123. Cobalt chromium
•
• McCracken's Removable Partial Prosthodontics
124. Lefort II fracture
•
• Contemporary Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery
125. Flushing waterlines between patients
• 20 -30 second
• Answered in part 1
126. Airway management
• Head tilt -chin lift
•
• Dental Management of the Medically Compromised Patient
127. Ledge Bypass
• Using smaller files
128. Direct temporary
• Avoid polymethyl methacrylate
• A polymethyl methacrylate resin produced significantly higher temperatures than did the others
• Contemporary Fixed Prosthodontics
129. Access cavity of three canals premolar
• Triangular
•
• Cohen's Pathways of the Pulp Expert Consult
NOTES By: Moath Al-assaf Twitter: @mo3ath44
Al-Assaf NOTES (PART 10), 11-15 January 2022
130. 3rd molar extraction may cause
• Vertical bone loss
•
• Carranza’s Clinical Periodontology
131. When preparing for extraction of lower 3rd molar how to Prevent formation of distal pocket on 2nd molar
• Partial thickness flap (Not logical answer, not sure if correct, see previous question).
•
• Carranza’s Clinical Periodontology
132. Glossopharyngeal neuralgia
•
• Neville, Oral & Maxillofacial Pathology
133. Fluoride toxic dose
• 5 mg/kg
134. Color of #6 k file
• Pink
NOTES By: Moath Al-assaf Twitter: @mo3ath44
Al-Assaf NOTES (PART 10), 11-15 January 2022
135. Prophylaxis AB
• Previous infective endocarditis
• Indications were mentioned in previous parts
136. Class II camouflage
• Extract upper 1st premolars
• Class II Camouflage by Extraction of Upper First Premolars
•
• Contemporary Orthodontics
137. Class III camouflage
• Extract lower 4 and upper 5
•
• Contemporary Orthodontics
To remember extraction in orthodontics for camouflage, think about the direction of teeth
movement needed to correct the malocclusion.
138. Impacted canine
• Resorption of lateral incisor root
•
• Contemporary Orthodontics
139. Headgear
• High-pull headgear, distal & upward effect. (For class II with deep bite).
• Cervical pull headgear, distal & downward effect. (For class II with open bite, VME).
• Straight- pull headgear, Distal effect only. (For class II).
• Mentioned before
140. ANB - SNA - SNB
• All mentioned before
141. Palatal crib appliance
• Mentioned before
142. Hass appliance is considered
• Tooth-Tissue borne expander
• Mentioned before
143. Enamel extended to CEJ and to the furcation will cause
• Hypersensitivity (I think incorrect)
• Cervical enamel projection can lead to:
▪ Furcation involvement.
▪ Plaque accumulation.
▪ Attachment loss.
•
• Carranza’s Clinical Periodontology
NOTES By: Moath Al-assaf Twitter: @mo3ath44
Al-Assaf NOTES (PART 10), 11-15 January 2022
144. Most common form of enamel - cementum junction:
• Overlapping of enamel by cementum
•
• Carranza’s Clinical Periodontology
145. Rapid progression of periodontal disease in Sri Lanka (Frequently asked)
• 8%
• Rapid progression = 8%
• Moderate progression = 81%
• No progression of periodontal disease beyond gingivitis = 11%
•
• Carranza’s Clinical Periodontology
146. Periodontal abscess
•
• Carranza’s Clinical Periodontology
147. Patient came after 1 day
• Delayed latex allergy (delayed hypersensitivity).
• Mentioned before
NOTES By: Moath Al-assaf Twitter: @mo3ath44
Al-Assaf NOTES (PART 10), 11-15 January 2022
148. Neglected child
•
• McDonald and Avery's Dentistry for the Child and Adolescent
149. Management of vertical bone defect
• Guided bone regeneration
• Carranza’s Clinical Periodontology
150. Patency file
•
• Cohen's Pathways of the Pulp Expert Consult
151. Types of gypsum products:
• Type 1: Dental plaster, impression.
• Type 2: Dental plaster, model.
• Type 3: Dental stone, model.
• Type 4: Dental stone, die, high strength, low expansion.
• Type 5: Dental stone, die, high strength, high expansion.
• Type 1 and 2 are Beta form of calcium sulfate hemihydrates.
• Type 3, 4, and 5 are Alpha form of calcium sulfate hemihydrates.
NOTES By: Moath Al-assaf Twitter: @mo3ath44
Al-Assaf NOTES (PART 10), 11-15 January 2022
152. Frankfort line
• This plane extends from the upper border of the external auditory canal (Porion) anteriorly to the
upper border of the lower orbital rim (Orbitale).
• Contemporary Orthodontics
•
• Textbook of Complete Dentures, 6th Edition
153. Reline and rebase
•
• More details are mentioned before.
154. Serial Extraction, sequence in Moyer method:
• B -> C -> D -> 4.
• Methods for serial extraction:
▪ Dewel’s method: C -> D -> 4.
▪ Tweed’s method: D -> C & 4.
▪ Moyer’s method: B -> C -> D -> 4.
155. Pregnant female in second trimester, what is the safest antibiotic?
• Amoxicillin and clindamycin are safe.
• Table of safe drugs in previous parts
NOTES By: Moath Al-assaf Twitter: @mo3ath44
Al-Assaf NOTES (PART 10), 11-15 January 2022
156. Crouzon’s syndrome
•
• NOTE: Apert syndrome -> long head.
•
• Neville, Oral & Maxillofacial Pathology
157. Bur used for pin hole preparation:
• Kodex drill, Twist drill.
NOTE: No. 1 ⁄ 4 bur is first used to prepare a pilot hole (dimple) then Kodex drill.
Sturdevant’s Art and Science of Operative Dentistry, 5e
Contemporary Fixed Prosthodontics
158. Picture of bony defect of reverse architecture:
•
• Carranza’s Clinical Periodontology
NOTES By: Moath Al-assaf Twitter: @mo3ath44
Al-Assaf NOTES (PART 10), 11-15 January 2022
159. First step of osseous surgery
• Vertical grooving
•
• Carranza’s Clinical Periodontology
160. X-ray use to determine biological width
• Bite-wing
•
• Carranza’s Clinical Periodontology
161. Disinfection of impression and how to send it to lap
•
• Textbook of Prosthodontics - 2nd Edition
NOTES By: Moath Al-assaf Twitter: @mo3ath44
Al-Assaf NOTES (PART 10), 11-15 January 2022
162. Normal Water fluoride
• 0.7 to 1.2 ppm
•
• Pediatric Dentistry - Infancy Through Adolescence
163. Percentage of osseous craters
• 35.2%
•
• Carranza’s Clinical Periodontology
164. Trismus:
• Incorrect technique of IANB
• Mentioned before (medial pterygoid muscle).
165. Danger zone
• Distal wall of MB root of lower molar
▪ Concavity on the distal aspect of the mesio-buccal root of maxillary molars.
▪ Concavities on the distal aspect of the mesial roots of mandibular molar.
•
• Cohen's Pathways of the Pulp Expert Consult
166. Shearing Cusp
• The lingual cusps of the upper teeth and the buccal cusps of the lower teeth are called Stamp Cusps.
The buccal cusps of the upper teeth and the lingual cusps of the lower are called the Shear Cusps.
• Functional = supporting = Stamp cusps
• Non-functional = guiding = shearing cusps
167. Which of the following conditions has increased chance of periodontal abscess?
• Uncontrol diabetes mellitus
• Mentioned before
168. Infection that on involve lower eyelids
• Canine tooth
• A table with spaces and the likely tooth that cause the
infection was mentioned before.
NOTES By: Moath Al-assaf Twitter: @mo3ath44
Al-Assaf NOTES (PART 10), 11-15 January 2022
169. Which of the following is a sign of Hypoglycemia?
• Increase heart rate
•
• Dental Management of the Medically Compromised Patient
170. Which of the following is a manifestation in patient with end stag renal disease?
• Ammonia in the mouth
•
• Dental Management of the Medically Compromised Patient
171. Most common feature of polyether material
• Rigidity
• Elasticity
• Dimension stability
•
• McCracken's Removable Partial Prosthodontics
•
• Textbook of Prosthodontics - 2nd Edition
NOTES By: Moath Al-assaf Twitter: @mo3ath44
Al-Assaf NOTES (PART 10), 11-15 January 2022
172. Most common feature of polysilicon/Polysiloxane?
• Rigidity
• Elasticity
•
• McCracken's Removable Partial Prosthodontics
• A table with all impression materials and their properties was mentioned before.
173. Patient taking 325mg aspirin, what is the proper management?
• Stope it 5-7 days (in case if the dose is more than 325 mg).
•
• Contemporary Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery
•
• Carranza’s Clinical Periodontology
NOTES By: Moath Al-assaf Twitter: @mo3ath44
Al-Assaf NOTES (PART 10), 11-15 January 2022
174. Drug lead to more saliva secretion?
• Anticholinergic drugs (e.g., Atropine) (Incorrect)
• Cholinergic agonist drugs (Pilocarpine)
•
• Neville, Oral and Maxillofacial Pathology
175. Procedure types used in orthognathic surgery:
• Body ostectomy:
176. Epinephrine in retraction cord has an adverse effect on wish patient.
• Asthmatic
• Hypertension
•
• Dental Management of the Medically Compromised Patient
•
• Retraction cords with aluminum chloride should be used.
• Sturdevant’s Art and Science of Operative Dentistry, 5e
NOTES By: Moath Al-assaf Twitter: @mo3ath44
Al-Assaf NOTES (PART 10), 11-15 January 2022
177. The proper case to use incisional or excisional biopsy?
Excisional biopsy:
•
• Contemporary Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery
178. Picture of gingival recession, what is the likely cause?
• Improper brushing
• Periodontitis
• Violation supra-crestal attachment (biologic attachment)
• Answer depends on the picture
NOTES By: Moath Al-assaf Twitter: @mo3ath44
Al-Assaf NOTES (PART 10), 11-15 January 2022
179. Difference between apexo-genesis and apexification?
•
• Pediatric Dentistry - Infancy Through Adolescence
180. Which of the following is the material used for coronal perforation seal?
• BioCeram
•
• Cohen's Pathways of the Pulp Expert Consult
NOTES By: Moath Al-assaf Twitter: @mo3ath44
Al-Assaf NOTES (PART 10), 11-15 January 2022
181. Fibromyalgia diagnosis?
• By muscle test
• Serology
• Tender points test
•
• Dental Management of the Medically Compromised Patient
182. During RCT sudden pain occurred, what is the likely cause? (Missing data)
• Perforation
• Sodium hypochlorite accident
• Early signs of perforation may include one or more of the following:
▪ sudden pain during the working length determination
▪ the sudden appearance of hemorrhage.
▪ burning pain or a bad taste during irrigation with sodium hypochlorite.
▪ radiographically malpositioned file.
▪ PDL reading from an apex locator that is short of the working length on an initial file entry.
• Extrusion of irrigant:
▪ Wedging of a needle in the canal41,42 (or particularly out of a perforation) with forceful
expression of irrigant.
▪ Sudden, prolonged, and sharp pain during irrigation, followed by rapid, diffuse swelling
(“sodium hypochlorite accident”),
▪ The acute episode subsides spontaneously with time.
▪ In teeth with open apices, the use of less concentrated irrigants, or saline.
▪ Management: Initially there is no reason to prescribe antibiotics or attempt surgical
drainage. Treatment is palliative. Analgesics are prescribed, and the patient is reassured.
• Endodontics, Principles and Practice
NOTES By: Moath Al-assaf Twitter: @mo3ath44
Al-Assaf NOTES (PART 10), 11-15 January 2022
183. General unlocalized pain. How to find the exact place of the pain?
• Endo test
• Selective anesthesia
•
• Endodontics, Principles and Practice
•
• Cohen's Pathways of the Pulp Expert Consult
184. Time for complete mineralization crown and root for third molar?
• 15 – 19 years (Incorrect)
• 8-10 years -> Hard Tissue Formation Begins
• 12-16 years -> Enamel Completed
• 17-21 years -> Eruption
• 18-25 years -> Root Completed
• McDonald and Avery's Dentistry for the Child and Adolescent
185. Splinting time for the following traumas:
• Subluxation: 1 to 2 weeks (if discernibly loosened).
• Intrusion: 4 weeks.
• Alveolar fracture: 4 weeks.
• Splinting time after TDI mentioned before.
186. In periodontal surgery, intact periosteum on the bone, what type of flap?
• Partial thickness flap
187. Part inside implant fixture, what is it called?
• Abutment
•
• Contemporary Fixed Prosthodontics
NOTES By: Moath Al-assaf Twitter: @mo3ath44
Al-Assaf NOTES (PART 10), 11-15 January 2022
188. When implant has mobility, it is considered
• Implant failure
189. Distance between implant and anatomic structure should be?
• About 2mm
• Critical measurements specific to implant placement include the following:
▪ At least 1 mm inferior to the floor of the maxillary and nasal sinuses
▪ Incisive canal (maxillary midline implant placement) to be avoided
▪ 5 mm anterior to the mental foramen
▪ 2 mm superior to the mandibular canal
▪ 3 mm from adjacent implants
▪ 1.5 mm from roots of adjacent teeth
• Contemporary Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery
190. Picture for semilunar incision in periodontal surgery:
• Carranza’s Clinical Periodontology
NOTES By: Moath Al-assaf Twitter: @mo3ath44
You might also like
- Schoenbaum Implant Prosthetics in The Aesthetic Zone Science Protocol TechniquesDocument24 pagesSchoenbaum Implant Prosthetics in The Aesthetic Zone Science Protocol TechniquesЮля КолмаковаNo ratings yet
- Mandibular FractureDocument56 pagesMandibular FractureFeat Bezer Ebenezer TadeNo ratings yet
- Viva MFD Book - Sample With Link To Full VersionDocument20 pagesViva MFD Book - Sample With Link To Full Versiongarima100% (1)
- A New Method To Eliminate The Risk of Maxillary Sinusitis With Zygomatic ImplantsDocument9 pagesA New Method To Eliminate The Risk of Maxillary Sinusitis With Zygomatic ImplantsCaioSelaimenNo ratings yet
- Al-Assaf NOTES 02Document9 pagesAl-Assaf NOTES 02alidyab128No ratings yet
- Al-assaf NOTES 11 (7)Document29 pagesAl-assaf NOTES 11 (7)mohamedalawy1979No ratings yet
- OjojDocument7 pagesOjojmohammed alsaadNo ratings yet
- Al-assaf NOTES 04 (2)Document9 pagesAl-assaf NOTES 04 (2)mohamedalawy1979No ratings yet
- Al-assaf NOTES 07 (2)Document34 pagesAl-assaf NOTES 07 (2)mohamedalawy1979No ratings yet
- Al-assaf NOTES 08 (3)Document19 pagesAl-assaf NOTES 08 (3)mohamedalawy1979No ratings yet
- Al-assaf NOTES 06 (2)Document7 pagesAl-assaf NOTES 06 (2)mohamedalawy1979No ratings yet
- DENTALA EXAM2Al-assaf NOTES 12 (4)Document36 pagesDENTALA EXAM2Al-assaf NOTES 12 (4)mohamedalawy1979No ratings yet
- Session 1Document13 pagesSession 1El FaresNo ratings yet
- Bds Final Professional Examination 2007: Model PaperDocument15 pagesBds Final Professional Examination 2007: Model PaperMostafa FayadNo ratings yet
- Ortho - Prostho RelationshipDocument40 pagesOrtho - Prostho RelationshipAshis Biswas100% (1)
- Indications of Early Ortho RX-4Document50 pagesIndications of Early Ortho RX-4Kifamulusi ErisaNo ratings yet
- Al-assaf NOTES 03Document7 pagesAl-assaf NOTES 03mohamedalawy1979No ratings yet
- Omr Seminar CystDocument51 pagesOmr Seminar CystJohann GeorgeNo ratings yet
- Journalclub-3: Primary Eruption FailureDocument30 pagesJournalclub-3: Primary Eruption FailurechaitreeNo ratings yet
- Sdle 19 PDFDocument11 pagesSdle 19 PDFQq qNo ratings yet
- Non Caries LeasionDocument33 pagesNon Caries LeasionmayaherabiNo ratings yet
- Maxillary Orthognathic Procedures - PPT / Orthodontic Courses by Indian Dental AcademyDocument53 pagesMaxillary Orthognathic Procedures - PPT / Orthodontic Courses by Indian Dental Academyindian dental academyNo ratings yet
- Prosthetic Rehabilitation For Oral Cleft Patients: - R. Madhuvathani Cri (I2 Batch) Department of ProsthodonticsDocument34 pagesProsthetic Rehabilitation For Oral Cleft Patients: - R. Madhuvathani Cri (I2 Batch) Department of ProsthodonticsEazhil RajNo ratings yet
- Management of An Endodontic-Periodontal Lesion Caused by IatrogenicDocument8 pagesManagement of An Endodontic-Periodontal Lesion Caused by IatrogenicDebora GultomNo ratings yet
- Implant Soft Tissue ConsiderationsDocument43 pagesImplant Soft Tissue ConsiderationsCORTES MAJALIA GUADA LINDA L.100% (2)
- Enhancement of Orthodontic Anchoring by The Use of Bone Anchorage A Case ReportDocument6 pagesEnhancement of Orthodontic Anchoring by The Use of Bone Anchorage A Case ReportAthenaeum Scientific PublishersNo ratings yet
- Periodontal Plastic and Esthetic SurgeryDocument173 pagesPeriodontal Plastic and Esthetic SurgerySaman MohammadzadehNo ratings yet
- Adult Orthodontics: P.Sivakalyani PGDocument161 pagesAdult Orthodontics: P.Sivakalyani PGMini RobertNo ratings yet
- Anterior Dental Crossbite and Class III Malocclusion1Document83 pagesAnterior Dental Crossbite and Class III Malocclusion1Nagi H. AlawdiNo ratings yet
- Pediatric DentistryDocument36 pagesPediatric DentistrySaba SaqerNo ratings yet
- 29 - Unusual - Extraoral SinusDocument29 pages29 - Unusual - Extraoral SinussonalyadavchinuNo ratings yet
- Multidisciplin Ary Approach IN Prosthodonti CS: Veena PG III YearDocument111 pagesMultidisciplin Ary Approach IN Prosthodonti CS: Veena PG III Yearbharathi krishnaNo ratings yet
- Diagnosis of Partially Edentulous PatientDocument82 pagesDiagnosis of Partially Edentulous PatientMostafa Fayad0% (1)
- Anterior Cross BiteDocument19 pagesAnterior Cross BiteatikaNo ratings yet
- Alternatives To Routine Endodontic TreatmentDocument55 pagesAlternatives To Routine Endodontic TreatmentMaryam Mohamed Abdelkarim AbdelfattahNo ratings yet
- Lec TRAUMADocument19 pagesLec TRAUMAFlorida ManNo ratings yet
- Endodontic Surgery: Bilog Falloran Ferrer Delos Reyes Palor Quinones'Document42 pagesEndodontic Surgery: Bilog Falloran Ferrer Delos Reyes Palor Quinones'Michael Francis MendozaNo ratings yet
- Anterior and Posterior Cross BiteDocument22 pagesAnterior and Posterior Cross BiteatikaNo ratings yet
- Presented By:: Aya Adel Abd El-Hafez Rana Mohamed EL-AbasseryDocument36 pagesPresented By:: Aya Adel Abd El-Hafez Rana Mohamed EL-AbasseryRisky Anita OktavianiNo ratings yet
- Pedo - Trauma 3Document27 pagesPedo - Trauma 3Florida ManNo ratings yet
- Prosthetic Management of Craniofacial Congenital DisoderDocument101 pagesProsthetic Management of Craniofacial Congenital DisoderKassim OboghenaNo ratings yet
- Preprosthetic SurgeryDocument22 pagesPreprosthetic Surgeryjerin thomasNo ratings yet
- Cervical LesionsDocument40 pagesCervical LesionsnishthaNo ratings yet
- Extraction in Orthodontics FHDocument60 pagesExtraction in Orthodontics FHsahar emadNo ratings yet
- Pulp Therapy For ChildrenDocument5 pagesPulp Therapy For ChildrenathenaNo ratings yet
- Immediate Dentures - S2Document41 pagesImmediate Dentures - S2Nikita AggarwalNo ratings yet
- Treatment Options For The Compromised Tooth:: A Decision GuideDocument16 pagesTreatment Options For The Compromised Tooth:: A Decision GuideYuttapol Pimpison100% (1)
- Mock Test Nmcle (Only For Symbol No N091-N180)Document8 pagesMock Test Nmcle (Only For Symbol No N091-N180)Young FlameNo ratings yet
- Tutor 1 SK 4 Blok 19Document16 pagesTutor 1 SK 4 Blok 19WIFA RAHMINo ratings yet
- Detectie Carie MarginalaDocument10 pagesDetectie Carie Marginala1980ssNo ratings yet
- 2000+ Prometric Questions PDFDocument254 pages2000+ Prometric Questions PDFMohsen Saeed OzaibiNo ratings yet
- Pit and Fissure SealantsDocument56 pagesPit and Fissure SealantsهجرسNo ratings yet
- Management of Deepbite Malocclusion: by Assist. Prof. Dr. Hadi M IsmailDocument68 pagesManagement of Deepbite Malocclusion: by Assist. Prof. Dr. Hadi M Ismailyounisismail935No ratings yet
- MBT Familly: Resists RetroclinationDocument24 pagesMBT Familly: Resists RetroclinationCernei Eduard Radu100% (1)
- Ankita KhandelwalDocument26 pagesAnkita Khandelwaldr. saNo ratings yet
- Eruption Cyst 22Document40 pagesEruption Cyst 22Taki EmmanuelNo ratings yet
- dental exams 25Aug2022. (1)Document8 pagesdental exams 25Aug2022. (1)mohamedalawy1979No ratings yet
- Twin BlockDocument95 pagesTwin BlockAnandNo ratings yet
- Screenshot 2023-11-14 at 9.09.26 PMDocument126 pagesScreenshot 2023-11-14 at 9.09.26 PMMagie FaragNo ratings yet
- 10 - Prevention of MalocclusionDocument46 pages10 - Prevention of MalocclusionMimo HemadNo ratings yet
- Research Project PowerpointDocument14 pagesResearch Project PowerpointbrendaNo ratings yet
- All August 2021 (1)Document210 pagesAll August 2021 (1)mohamedalawy1979No ratings yet
- All May 2021 by Dr Afnan (8)Document251 pagesAll May 2021 by Dr Afnan (8)mohamedalawy1979No ratings yet
- Al-assaf NOTES 07 (2)Document34 pagesAl-assaf NOTES 07 (2)mohamedalawy1979No ratings yet
- Al-assaf NOTES 04 (2)Document9 pagesAl-assaf NOTES 04 (2)mohamedalawy1979No ratings yet
- Al-assaf NOTES 03Document7 pagesAl-assaf NOTES 03mohamedalawy1979No ratings yet
- all January 2022 (4)Document79 pagesall January 2022 (4)mohamedalawy1979No ratings yet
- All February 2022 (6)Document74 pagesAll February 2022 (6)mohamedalawy1979No ratings yet
- DENTY All March.. 2021 (5)Document488 pagesDENTY All March.. 2021 (5)mohamedalawy1979No ratings yet
- dentisi examAll July 2021 By Dr.NASSER F. (3)Document214 pagesdentisi examAll July 2021 By Dr.NASSER F. (3)mohamedalawy1979No ratings yet
- dental exams 25Aug2022. (1)Document8 pagesdental exams 25Aug2022. (1)mohamedalawy1979No ratings yet
- list al hamaed foe wsftyDocument75 pageslist al hamaed foe wsftymohamedalawy1979No ratings yet
- Unilateral Removable Partial DenturesDocument8 pagesUnilateral Removable Partial DenturesIvan Fadhillah NurdinNo ratings yet
- A Concept For The Treatment of Various Dental Bone Defects.Document6 pagesA Concept For The Treatment of Various Dental Bone Defects.Jaime FrancoNo ratings yet
- Straumann BLX Implants System - 702115 D 03 en - LowDocument64 pagesStraumann BLX Implants System - 702115 D 03 en - LowabeqaNo ratings yet
- BASIC IMPLANT SCIENCES.20.Sabtu, 29 April 2017Document27 pagesBASIC IMPLANT SCIENCES.20.Sabtu, 29 April 2017dehaaNo ratings yet
- 5 PDFDocument8 pages5 PDFoskar ORTIZNo ratings yet
- Question TemplateDocument21 pagesQuestion TemplateSally MohamadNo ratings yet
- Zirconia Dental Implants: A Literature Review: Journal of Oral Implantology June 2011Document11 pagesZirconia Dental Implants: A Literature Review: Journal of Oral Implantology June 2011Seno FauziNo ratings yet
- Surface Treatment of PekkDocument6 pagesSurface Treatment of PekkmustafaNo ratings yet
- Impacts of Orthodontic Treatment On PeriDocument10 pagesImpacts of Orthodontic Treatment On PeriCatia Sofia A PNo ratings yet
- OsseointegrationDocument3 pagesOsseointegrationImtiyaz MagrayNo ratings yet
- Microstructures of Plasma-Sprayed Hydroxyapatite-Coated Ti-6Al-4V Dental ImplantsDocument14 pagesMicrostructures of Plasma-Sprayed Hydroxyapatite-Coated Ti-6Al-4V Dental ImplantsMedstudNo ratings yet
- SQ Implant 200110Document30 pagesSQ Implant 200110김문규No ratings yet
- Dental Implant Therapy in A Patient With Acromegaly: A Clinical ReportDocument6 pagesDental Implant Therapy in A Patient With Acromegaly: A Clinical ReportAkanksha MahajanNo ratings yet
- Anchorage in Orthodontics (2) / Orthodontic Courses by Indian Dental AcademyDocument177 pagesAnchorage in Orthodontics (2) / Orthodontic Courses by Indian Dental Academyindian dental academyNo ratings yet
- Heymann & Tulloch (2006) Implantable Devices As Orthodontic AnchorageDocument12 pagesHeymann & Tulloch (2006) Implantable Devices As Orthodontic AnchorageDominikaSkórkaNo ratings yet
- Mucositis PeriDocument9 pagesMucositis PerianonimoNo ratings yet
- Immediate Dental ImplantsDocument13 pagesImmediate Dental ImplantsDevanyNataniaNo ratings yet
- Mis Implant Connccal Connection ProductDocument208 pagesMis Implant Connccal Connection ProductdrgunNo ratings yet
- Ectodermal Dysplasia ADocument7 pagesEctodermal Dysplasia AFatima AliNo ratings yet
- 10th World Veterinary Dental Congress 2007 BrazilDocument127 pages10th World Veterinary Dental Congress 2007 BrazilHumberto FustesNo ratings yet
- Photoelastic Stress Analysis of MandibularDocument6 pagesPhotoelastic Stress Analysis of MandibularOdilon SouzaNo ratings yet
- Full-Arch Implant Surgical and Restorative Considerations: ImplantsDocument4 pagesFull-Arch Implant Surgical and Restorative Considerations: ImplantsTín ĐăngNo ratings yet
- Journal of Periodontology - 2018 - Schwarz - Peri ImplantitisDocument24 pagesJournal of Periodontology - 2018 - Schwarz - Peri ImplantitisFrancisca Cardenas OñateNo ratings yet
- Koutouzisetal 2013IJOMIAbutmentdisconnectionClinicalDocument8 pagesKoutouzisetal 2013IJOMIAbutmentdisconnectionClinicalKyoko CPNo ratings yet
- Digital Dentistry Sydney 2020Document13 pagesDigital Dentistry Sydney 2020Michael XuNo ratings yet
- Good Morning.: @areebazainabDocument42 pagesGood Morning.: @areebazainabshabana waniNo ratings yet
- The Future of ProsthodonticsDocument22 pagesThe Future of ProsthodonticsGoutham SunilNo ratings yet
- Aesthetic Zone Shakeel ShahdadDocument3 pagesAesthetic Zone Shakeel ShahdadAhsan NaseerNo ratings yet