Professional Documents
Culture Documents
ACC 400 Risk and Controls
ACC 400 Risk and Controls
Uploaded by
youngo1Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
ACC 400 Risk and Controls
ACC 400 Risk and Controls
Uploaded by
youngo1Copyright:
Available Formats
ACCOUNTING CYCLES RISKS AND CONTROLS
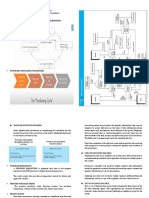
EXPENDITURE CYCLE – PURCHASING/REQUISITIONING
Risk Control(s) to mitigate that risk
Purchasing items that are not needed Purchase orders must have the appropriate authorization
Purchasing items that have high prices Vendors should be approved and purchase agents should only use vendors from the
approved vendor list. They can also improve by requesting competitive bids or request for
quotations directly from multiple vendors.
Purchasing items of poor quality Vendors should be approved and purchase agents should only use vendors from the
approved vendor list. They can also improve by requesting competitive bids or request for
quotations directly from multiple vendors.
Purchasing from unauthorized supplies Vendors should be approved and purchase agents should only use vendors from the
approved vendor list. They can also improve by requesting competitive bids or request for
quotations directly from multiple vendors.
EXPENDITURE CYCLE – RECEIVING
Risk Control(s) to mitigate that risk
Receiving unordered items The receiving clerk should have an approved purchase order prior to receiving the items
Receiving items of poor quality The receiving clerks should count and properly inspect the goods for possible damage or
defects. The PO copy used by the Receiving Department should not include the quantity
that wasordered. Using bar codes to scan items reduces mistakes in counting.
Mistakes in inventory The receiving clerks should count and properly inspect the goods for possible damage or
defects. The PO copy used by the Receiving Department should not include the quantity
that wasordered. Using bar codes to scan items reduces mistakes in counting.
Theft of inventory Physical access to the warehouse should be restricted and inventory should be periodically
counted and reconciled to the accounting records.
EXPENDITURE CYCLE – ACCOUNTS PAYABLE
Risk Control(s) to mitigate that risk
Vendor invoice errors The vendor invoice should be compared to the purchase order, to the receiving report, and
to a price list. The extensions and totals should be checked.
Accounts payable posting errors the date of the posting to accounts payable should be the date the goods are received, not
the invoice date.
EXPENDITURE CYCLE – CASH DISBURSEMENTS
Risk Control(s) to mitigate that risk
Paying for items not received An authorized check signer should review the supporting documentation (purchase order,
receiving report, and vendor invoice), to ensure invoice is apprpoved for payment.
Paying the same invoice twice After check is signed, all supporting documentation should be marked PAID.
Theft of cash Checks should be processed by a separate department or person that has no access to the
accounting records.
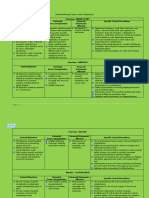
REVENUE CYCLE – ORDER ENTRY AND CREDIT
Risk Control(s) to mitigate that risk
Inaccurate/incomplete sales orders Computerized accounting systems include data entry controls, such as requiring all fields to
be completed before accepting the order.
Invalid/fake order All sales orders shoul be supported by a customer order for approval.
Uncollectible customer orders The customers credit must be approved before the goods are shipped.
Inventory stockouts Good inventory control practices (using a perpetual inventory method, automatic ordering
of items with low inventory, periodic inventory counts with reconciliation to the accounting
records.
REVENUE CYCLE – WAREHOUSE AND SHIPPING
Risk Control(s) to mitigate that risk
Picking the wrong items Barcodes or RFID systems should be used with inventory.
Picking the wrong quantity of items ordered Barcodes or RFID systems should be used with inventory.
Theft of inventory Only authorized employees should be allowed in inventory storage areas.
Not shipping ordered items to customer Sales orders, picking tickets, packing slips and shipping documents should be
compared to ensure information is consistent.
Shipping items to the wrong shipping address Sales orders, picking tickets, packing slips and shipping documents should be
compared to ensure information is consistent.
REVENUE CYCLE – BILLING AND ACCOUNTS RECEIVABLE
Risk Control(s) to mitigate that risk
Not billing the customer Reconcile all itmes from shipping reports to invoices.
Errors on invoice Review the accounts receivable aging report regularly.
Not posting transaction to the proper accounting period Use data entry controls to automatically post to appropriate period.
Posting to the wrong customer account Use data entry controls to automatically post to appropriate period.
REVENUE CYCLE – CASH RECEIPTS
Risk Control(s) to mitigate that risk
Theft of cash Use proper segregation duties or use a bank lockbox.
FIXED ASSETS CYCLE
Risk Control(s) to mitigate that risk
Asset theft Proper authorization to aquire or dispose of assets, tagging, reconcile
physical list to the General Ledger.
Improperly accounting for the asset acquisition price Good asset policies and knowledgeable employees. Some exampales include
an appriopriate threshold amount that makes the company capitalize the
cost rather than expensing it. Also, having approval required for asset
acquisitions and having a budgeting process for asset acquisitions.
Improperly expensing or capitalizing repairs Good asset policies and knowledgeable employees. Some exampales include
an appriopriate threshold amount that makes the company capitalize the
cost rather than expensing it. Also, having approval required for asset
acquisitions and having a budgeting process for asset acquisitions.
Improperly calculating depreciation expense Good asset policies and knowledgeable employees. Some exampales include
an appriopriate threshold amount that makes the company capitalize the
cost rather than expensing it. Also, having approval required for asset
acquisitions and having a budgeting process for asset acquisitions.
Lack of authorization for asset acquisition/disposal Proper authorization to acquire or dispost of assets, tagging, reconcoile
physical list to the General Ledger.
Inadequate insurance levels on assets Annual review to ensure adequate coverage
FINANCING CYCLE - EQUITY
Risk Control(s) to mitigate that risk
Improperly accounting for equity Good corporate governance and a strong Board of Directors.
Improperly accounting for dividends Transactions should be verified through board minutes
Improperly accounting for treasure stock Transactions should be verified through board minutes
Improperly accounting for stock options Proper authorization and segregation of duties
FINANCING CYCLE - DEBT
Risk Control(s) to mitigate that risk
Improperly accounting for debt Proper authorization
Improperly classifying debt as short or long-term Verification through loan documents and use
Improperly calculating interest Use of amortization tables provided by bank or leasing company
PAYROLL CYCLE
Risk Control(s) to mitigate that risk
Theft of cash Limiting access to authorized personnel. Use of an imprest account to limit
liability.
Unauthorized changes to the payroll system Proper authorization required for any changes. Payroll change report should
periodically be run and reviewed to prevent fraudulent payment or ‘ghost
employees’
Inaccurate wage or tax calculations Manager or automated system should review payroll before processing.
Variance analysis can identify any unexpected changes.
Incorrect posting to the wrong accounting period Manager or automated system should review payroll before processing.
Variance analysis can identify any unexpected changes.
Noncompliance with laws Management or third-party review
FINANCIAL REPORTING CYCLE
Risk Control(s) to mitigate that risk
Material misstatements Segregation of duties and thorough review and approval process
You might also like
- Chart of AccountsDocument22 pagesChart of AccountsaddyNo ratings yet
- I. Case BackgroundDocument7 pagesI. Case BackgroundHiya BhandariBD21070No ratings yet
- ACC 400 Risk and ControlsDocument4 pagesACC 400 Risk and Controlsyoungo1No ratings yet
- Chapter+11 Transactional+CycleDocument35 pagesChapter+11 Transactional+Cyclemohazka hassan100% (1)
- AA - Internal Control: The Auditors Approach To Internal ControlsDocument10 pagesAA - Internal Control: The Auditors Approach To Internal ControlsTapiwa K NgungunyaniNo ratings yet
- The Credit Approval Process Involves Which of The Following?Document9 pagesThe Credit Approval Process Involves Which of The Following?June KooNo ratings yet
- Revenue and Expenditure AuditDocument38 pagesRevenue and Expenditure AuditPavitra MohanNo ratings yet
- (Type The Document Title) : The Expenditure Cycle: Purchasing To Cash DisbursementsDocument13 pages(Type The Document Title) : The Expenditure Cycle: Purchasing To Cash DisbursementsLet it beNo ratings yet
- Auditing Part 3Document10 pagesAuditing Part 3Trisha BanzonNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 Audit f8 - 2.3Document33 pagesChapter 10 Audit f8 - 2.3JosephineMicheal17No ratings yet
- Pear CoDocument3 pagesPear CoSITI SARAH JAUHARINo ratings yet
- Chapter 15Document6 pagesChapter 15Joy RubioNo ratings yet
- Isa 240 Auditor Responsibility Relating To FraudDocument6 pagesIsa 240 Auditor Responsibility Relating To Fraudnurmaisarahnurazim1No ratings yet
- PBL Session 2Document3 pagesPBL Session 2Muhammad ZulhisyamNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 - Purchase - InventoryDocument29 pagesChapter 5 - Purchase - Inventoryhasan jabrNo ratings yet
- Reviewer 5Document14 pagesReviewer 5Cyrene CruzNo ratings yet
- Exam Kit Specimen (Cases)Document6 pagesExam Kit Specimen (Cases)Mayurika DassaniNo ratings yet
- AAPreJun24MockAns21Document3 pagesAAPreJun24MockAns21Phạm Việt BáchNo ratings yet
- Week 10lecture InventoryDocument34 pagesWeek 10lecture InventoryShalin LataNo ratings yet
- Lecture 9Document33 pagesLecture 9lawlokyiNo ratings yet
- Week 10 The Expenditure CycleDocument8 pagesWeek 10 The Expenditure CycleAldwin CalambaNo ratings yet
- The Revenue CycleDocument10 pagesThe Revenue CycleMarjorie IsonNo ratings yet
- Sim-Ge: Q1) Suggested AnswersDocument12 pagesSim-Ge: Q1) Suggested AnswersDương DươngNo ratings yet
- Controls in Revenue - Expenditure CycleDocument28 pagesControls in Revenue - Expenditure CycleKhen CaballesNo ratings yet
- converted-RR Control ObjectivesDocument3 pagesconverted-RR Control ObjectivesWillowNo ratings yet
- Bac416 1M Abit-1Document2 pagesBac416 1M Abit-1janus lopezNo ratings yet
- Multiple Choice - Chapter10 To Chapter20Document22 pagesMultiple Choice - Chapter10 To Chapter20Aditya Agung SatrioNo ratings yet
- Auditing Business Processes - Operations Auditing (1)Document68 pagesAuditing Business Processes - Operations Auditing (1)adulusman501No ratings yet
- Audit-II-Chapter 6Document11 pagesAudit-II-Chapter 6mulunehNo ratings yet
- AUDIT PROGRAM For Cash Disbursements 2Document5 pagesAUDIT PROGRAM For Cash Disbursements 2jezreel dela mercedNo ratings yet
- Chapter 07 The Revenue CycleDocument22 pagesChapter 07 The Revenue CycleClaire Denisse AilesNo ratings yet
- Tinkerbell: Key Control Test of ControlDocument2 pagesTinkerbell: Key Control Test of ControlIanNo ratings yet
- Summary SIA Ch.13 - Expenditure CycleDocument3 pagesSummary SIA Ch.13 - Expenditure CycleAthiyya Nabila AyuNo ratings yet
- Audit of Acquisition Cycle and Inventory: Rittenberg/Schwieger/Johnstone Auditing: A Business Risk Approach Sixth EditionDocument28 pagesAudit of Acquisition Cycle and Inventory: Rittenberg/Schwieger/Johnstone Auditing: A Business Risk Approach Sixth EditionQin YunNo ratings yet
- PPT7-Auditing Inventory, Goods and Services, and Accounts Payable The Acquisition and Payment CycleDocument28 pagesPPT7-Auditing Inventory, Goods and Services, and Accounts Payable The Acquisition and Payment CycleHerman LiemNo ratings yet
- Revision of Control SystemsDocument8 pagesRevision of Control Systemstramng12No ratings yet
- Control Objectives, Threats, and Procedures: Order GoodsDocument4 pagesControl Objectives, Threats, and Procedures: Order GoodsJuliet PeñarandaNo ratings yet
- AnswerDocument16 pagesAnswerHassleBustNo ratings yet
- Audit Procedur ES Cash Accounts Receivable Accounts Payable InventoryDocument2 pagesAudit Procedur ES Cash Accounts Receivable Accounts Payable InventoryRoseyy GalitNo ratings yet
- Purchase Controls QuestionnaireDocument3 pagesPurchase Controls QuestionnaireMarieJoiaNo ratings yet
- Auditing The Revenue Cycle: ©Mcgraw-Hill EducationDocument36 pagesAuditing The Revenue Cycle: ©Mcgraw-Hill EducationNabila SedkiNo ratings yet
- Audit Mock 2Document6 pagesAudit Mock 2Jiya RajputNo ratings yet
- Audit MidtermDocument2 pagesAudit MidtermconsulivyNo ratings yet
- PBL Session 2Document5 pagesPBL Session 2liyanahamzahNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals Level - Skills Module, F8 (INT) Audit and AssuranceDocument12 pagesFundamentals Level - Skills Module, F8 (INT) Audit and AssurancekhengmaiNo ratings yet
- Purchase System - BIG Picture: 1. Purchase Process 2. Ordering PhaseDocument4 pagesPurchase System - BIG Picture: 1. Purchase Process 2. Ordering PhaseShahid MahmudNo ratings yet
- Case Study of Max SDN BHDDocument5 pagesCase Study of Max SDN BHDIan RKONo ratings yet
- Day 24Document7 pagesDay 24Reem JavedNo ratings yet
- Day 24-1Document11 pagesDay 24-1Reem JavedNo ratings yet
- Audit and Assurance CrqDocument6 pagesAudit and Assurance Crqraj580481No ratings yet
- Sample DocumentDocument13 pagesSample DocumentRuann Albete FernandezNo ratings yet
- Audit Risk NotesDocument14 pagesAudit Risk NotesRana NadeemNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document4 pagesChapter 3Angela Erish CastroNo ratings yet
- Audit of Acquisition and Payment CycleDocument30 pagesAudit of Acquisition and Payment CycleontykerlsNo ratings yet
- Slide Audit On Revenue - Latest - 1Document22 pagesSlide Audit On Revenue - Latest - 1黄勇添No ratings yet
- MERCADO, Erica Kaye M. Acctsys A2B April 28, 2020: AnswerDocument3 pagesMERCADO, Erica Kaye M. Acctsys A2B April 28, 2020: AnswerMila MercadoNo ratings yet
- Internal Control and Tests of Control For Inventory and Production CycleDocument6 pagesInternal Control and Tests of Control For Inventory and Production Cyclecriselda salazar100% (1)
- Internal Controls-Sales and Collection CycleDocument4 pagesInternal Controls-Sales and Collection CyclebabyNo ratings yet
- Audit of Acquisition and Payment Cycle PDFDocument36 pagesAudit of Acquisition and Payment Cycle PDFZi VillarNo ratings yet
- ControlDocument3 pagesControlHäbizhita IbruckiNo ratings yet
- Topic 2-1Document35 pagesTopic 2-1fbicia218No ratings yet
- How To Build An Email List On Ebay PDF Ebook Make Money PDFDocument2 pagesHow To Build An Email List On Ebay PDF Ebook Make Money PDFNyasclemNo ratings yet
- Ca Final Financial Reporting 50 Important Questions 1643352280Document91 pagesCa Final Financial Reporting 50 Important Questions 1643352280Indhumathi ThangaveluNo ratings yet
- Manufacturing ManagementDocument332 pagesManufacturing ManagementPugdug 209No ratings yet
- Cib ExamDocument3 pagesCib ExamAhmed HakimNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12 - Revenue Recognition: Revenue From Contracts With CustomerDocument21 pagesChapter 12 - Revenue Recognition: Revenue From Contracts With CustomerCruxzelle BajoNo ratings yet
- Principles of Corporate GovernanceDocument6 pagesPrinciples of Corporate GovernanceTrần Ánh NgọcNo ratings yet
- Intermediate Accounting 2 ReportDocument2 pagesIntermediate Accounting 2 ReportYna Herrera's VlogNo ratings yet
- PaytmDocument11 pagesPaytmaddankisai24No ratings yet
- Gebi Shuka FinalDocument70 pagesGebi Shuka FinalDerara UmetaNo ratings yet
- Segment Reporting Lecture NotesDocument3 pagesSegment Reporting Lecture Noteszein lopezNo ratings yet
- 1693812937balmer Lawrrie Annual Report 2023Document280 pages1693812937balmer Lawrrie Annual Report 2023pavithranrk1353No ratings yet
- Mba Finance Dissertation Project PDFDocument5 pagesMba Finance Dissertation Project PDFApaPapersForSaleFargo100% (1)
- 0036 - Accounting For Business - EditedDocument4 pages0036 - Accounting For Business - EditedAwais AhmedNo ratings yet
- 7 Perceive Quality and Customer SatisfactionDocument17 pages7 Perceive Quality and Customer SatisfactionFarhanAnsariNo ratings yet
- Lecture # 5: Dr. Pawan KumarDocument42 pagesLecture # 5: Dr. Pawan Kumarsweta mishra lovelyNo ratings yet
- The Business of InfluenceDocument9 pagesThe Business of InfluencevvvasimmmNo ratings yet
- Public Opinion Poll: Residents of MongoliaDocument55 pagesPublic Opinion Poll: Residents of Mongoliashinkaron88No ratings yet
- Lecture 2.2 Value Creation Revisited and Pro Forma Cash FlowsDocument37 pagesLecture 2.2 Value Creation Revisited and Pro Forma Cash FlowsWahidNo ratings yet
- Bylaws RevisedDocument6 pagesBylaws RevisedJanie S. RobertsNo ratings yet
- Skills Audit WorksheetDocument2 pagesSkills Audit WorksheetNguyễn Kim NgânNo ratings yet
- Company Certifications Fire Classifications Product ApprovalsDocument4 pagesCompany Certifications Fire Classifications Product ApprovalsHussein BeqaiNo ratings yet
- Timothy - Chap 10Document44 pagesTimothy - Chap 10Chaeyeon JungNo ratings yet
- Neuroethics of Neuromarketing: Emily R. Murphy, Judy Illes and Peter B. ReinerDocument10 pagesNeuroethics of Neuromarketing: Emily R. Murphy, Judy Illes and Peter B. ReinerShaheryar HasanNo ratings yet
- 3M: Rethinking Innovation: Joe Tidd, John Bessant, Keith PavittDocument5 pages3M: Rethinking Innovation: Joe Tidd, John Bessant, Keith PavittArbresh RaveniNo ratings yet
- RexDocument17 pagesRexErick KinotiNo ratings yet
- Detailed Unit Price Analysis (Dupa) : PART II - Other General RequirementsDocument76 pagesDetailed Unit Price Analysis (Dupa) : PART II - Other General RequirementsCed LucasNo ratings yet
- Constellation Software Inc.: To Our ShareholdersDocument4 pagesConstellation Software Inc.: To Our ShareholdersrNo ratings yet
- Form 13A (Request For Availability of Name)Document2 pagesForm 13A (Request For Availability of Name)Zaim Adli100% (1)