Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Block Diagram of Computer & Input Output Units
Block Diagram of Computer & Input Output Units
Uploaded by
himanshu.bcastudent23.236640 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1 views40 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1 views40 pagesBlock Diagram of Computer & Input Output Units
Block Diagram of Computer & Input Output Units
Uploaded by
himanshu.bcastudent23.23664Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 40
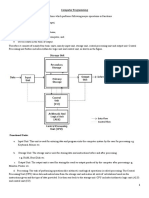
Block Diagram of Computer
Input Unit
All the data received by the computer goes
through the input unit. The input unit
comprises different devices. Like a mouse,
keyboard, scanner, etc. In other words,
each of these devices acts as a mediator
between the users and the computer.
The data that is to be processed is put
through the input unit. The computer
accepts the raw data in binary form. It
then processes the data, and produces the
desired output.
The 3 major functions of the input unit
are-
Take the data to be processed by the user.
Convert the given data into machine-
readable form.
And then, transmit the converted data into
the main memory of the computer. The sole
purpose is to connect the user and the
computer. In addition, this creates easy
communication between them.
CPU – Central Processing Unit
Central Processing Unit or the CPU, is the
brain of the computer. It works the same
way a human brain works. As the brain
controls all human activities, the CPU too
controls all tasks.
Moreover, the CPU conducts all the
arithmetical and logical operations in the
computer.
Now the CPU comprises of two units, namely
– ALU (Arithmetic Logic Unit) and CU
(Control Unit). Both of these units work in
sync. The CPU processes the data as a
whole.
ALU – Arithmetic Logic Unit
The Arithmetic Logic Unit is made of two terms,
arithmetic and logic. There are two major functions
that this unit performs.
1) Data inserted through the input unit into the
primary memory. Performs the basic arithmetical
operation on it. Like addition, subtraction,
multiplication, and division. It performs all sorts
of calculations required on the data. Then sends
back data to the storage.
2) The unit is also responsible for performing logical
operations like, AND, OR, Equal to, Less than,
etc. In addition to this it conducts merging,
sorting, and selection of the given data.
CU – Control Unit
The control unit as the name suggests is the
controller of all the activities/tasks and
operations. All this is performed inside the
computer.
The memory unit sends a set of instructions
to the control unit. Then the control unit in
turn converts those instructions. After that
these instructions are converted to control
signals.
These control signals help in prioritizing and
scheduling the activities. Thus, the control
unit coordinates the tasks inside the
computer in sync with the input and output
units.
Memory Unit
All the data that has to be processed or has
been processed is stored in the memory unit.
The memory unit acts as a hub of all the data.
It transmits it to the required part of the
computer whenever necessary.
The memory unit works in sync with the CPU.
This helps in faster accessing and processing
of the data. Thus, making tasks easier and
faster.
Memory Unit……
There are two types of computer memory-
1) Primary memory – This type of memory cannot
store a vast amount of data. Therefore, it is
only used to store recent data. The data
stored in this is temporary. It can get erased
once the power is switched off. Therefore, is
also called temporary memory or the main
memory.
RAM stands for Random Access Memory. It is
an example of primary memory. This memory is
directly accessible by the CPU. It is used for
reading and writing purposes. For data to be
processed, it has to be first transferred to
the RAM and then to the CPU.
Memory Unit……
2) Secondary memory – As explained above, the
primary memory stores temporary data. Thus it
cannot be accessed in the future. For permanent
storage purposes, secondary memory is used. It is
also called the permanent memory or the auxiliary
memory. The hard disk is an example of secondary
memory. Even in a power failure data does not get
erased easily.
Output
There is nothing to be amazed by what the output
unit is used for. All the information sent to the
computer once processed is received by the user
through the output unit. Devices like printers,
monitors, projector, etc. all come under the output
unit.
The output unit displays the data either in the form
of a soft copy or hard copy. The printer is for the
hard copy. The monitor is for the display. The
output unit accepts the data in binary form from
the computer. It then converts it into a readable
form for the user.
INPUT UNIT
Keyboard Most common and very popular input
device is keyboard. The keyboard helps in
inputting the data to the computer.
The layout of the keyboard is like that of
traditional typewriter, although there are some
additional keys provided for performing some
additional functions.
Keyboards are of two sizes 84 keys or 101/102
keys, but now 104 keys or 108 keys keyboard is
also available for Windows and Internet.
Portable computers such as laptops quite often
have custom keyboards have slightly different key
arrangements than a standard keyboard.
It is the easiest input device as it does not require
any special skill. The keys are following
Screen, but it cannot be used to enter text into the computer. The
mouse may be classified as a mechanical mouse or an optical
mouse.
A mechanical mouse uses a rubber ball at the bottom surface which
rotates as the mouse is moved along a flat surface to move the
cursor. It is the most common and least expensive pointing device.
An optical mouse uses a light beam instead of a rotating ball to
detect movement across a specially patterned mouse pad. As the
user rolls the mouse on a flat surface the cursor on a flat surface
the cursor on the screen also moves in the direction of the mouse’s
movement. Modern mouse does not required mouse pad.
THE OUTPUT UNIT
Printer :- A printer prints information and data
from the computer onto a paper. Printing is the
art of moving ink from one place to another. A
printer is used to produce printouts of the
documents stored on a computer’s disk drive.
There are two types of printer according to
printing technology.
Impact Printer:- An impact printer has
mechanisms resembling those of a typewriter.
It forms characters or images by striking a
mechanism such as a print hammer or wheel
against an inked ribbon, leaving an image on
paper. Impact printers are dying out; however,
you may still come in contact with a dot-matrix
printer. Such as Dot matrix printer, Daisy
wheel Printer, Drum printer.
Characteristics of Impact Printer
In impact printer there is physical
contact with the paper to produce
text and image.
They have relatively low consumable
costs.
Due to being robust and low cost they
are useful for bulk printing.
They can withstand dusty
environment, vibrations and extreme
temperature.
Due to its striking activity, impact
printers are very noisy.
Since they are mechanical in nature,
they tend to be slow.
Non- Impact Printer
A non impact printer forms characters and
images without making direct physical
contact between printing mechanism and
paper.
In this printer the print head does not make
contact with the paper and no inked ribbon is
required.
Ink can be sprayed against the paper and
then heat and pressure are used to fuse a
fine black powder into the shape of a
character. Such as Ink-jet printer, Laser
Printer.
Characteristics of Non-impact printer
Non impact printers are faster than impact printers
because they have fewer moving parts.
They are quieter than impact printers because there
is no striking mechanism involved and only few moving
parts are used.
They possess the ability to change typefaces
automatically.
These printers produce high quality graphics.
These printers usually support the transparencies.
MONITOR
A computer display is also called a display screen or
video display terminal (VDT). A monitor is a screen
used to display the output. Images are represented on
monitors by individual dots called pixels. A pixel is the
smallest unit on the screen that can be turned on and
off or made different shades. The density of the dots
determines the clarity of the images, the resolution.
Screen resolution: This is the degree of sharpness of
a displayed character or image. The screen resolution
is usually expressed as the number of columns by the
number rows. A 1024x768 resolution means that it has
1024 dots in a line and 768 lines. A smaller screen
looks sharper on the same resolution. Another measure
of display resolution is a dot pitch.
Interlaced/Non-interlaced:
An interlaced technique refreshes the lines of the
screen by exposing all odd lines first then all even
lines next.
A non-interlaced technology that is developed later
refreshes all the lines on the screen form top to
bottom. The non- interlaced method gives more
stable video display than interlaced method. It also
requires twice as much signal information as
interlaced technology.
There are two forms of display: cathode-ray
tubes (CRTs) and flat-panel display.
Cathode Ray Tubes (CRT)
A CRT is a vacuum tube used as a display
screen for a computer output device.
Although the CRT means only a tube, it
usually refers to all monitors. IBM and IBM
compatible microcomputers operate two
modes unlike Macintosh based entirely on
graphics mode. They are a text mode and a
graphics mode. Application programs switch
computers into appropriate display mode.
Monochrome Monitors
A monochrome monitor has two colors, one for
foreground and the other for background. The
colors can be white, amber or green on a dark
(black) background. The monochrome monitors
display both text and graphics modes.
Color Monitors A color monitor is a display
peripheral that displays more than two colors.
Color monitors have been developed through
the following paths.
Flat Panel Displays
Portable computers such as a laptop use flat
panel displays, because they are more compact
and consume less power than CRTs. Portable
computers use several kinds of flat panel
screens:
Liquid-Crystal Displays (LCDs) A display
technology that creates characters by means
of reflected light and is commonly used in
digital watches and laptop computers. LCDs
replaced LEDs (light emitting diodes) because
LCDs use less power. LCDs are difficult to
read in a strong light, because they do not
emit their own light. Portable computers
wanted to have brighter and easier to read
displays. Backlit LCDs are used for the
purpose now.
Backlit LCDs: This is a type of LCD display
having its own light source provided from the
back of the screen. The backlit makes the
background brighter and clear, as a result the
texts and images appear sharper. However,
this still is much less clear than CRTs. Thus,
better technology is needed.
Active Matrix LCDs: This is an LCD display
technique in which every dot on the screen has
a transistor to control it more accurately. This
uses a transistor for each monochrome or each
red, green and blue dot. It provides better
contrast, speeds up screen refresh and
reduces motion smearing
Plotters
A plotter is a special-purpose output device
that draws images with ink pens. That is, the
plotter is a graphics printer for making
sophisticated graphs, charts, maps, and 3D
graphics as well as high-quality colored
documents. It can also produce larger size of
documents. Plotters require data in a vector
graphics format that can produce images with a
series of lines.
There are two main types of plotters:
STORAGE UNIT
Storage Devices are the data storage
devices that are used in the computers to
store the data.
The computer has many types of data
storage devices. Some of them can be
classified as the removable data Storage
Devices and the others as the non
removable data Storage Devices.
The memory is of two types; one is the
primary memory and the other one is the
secondary memory.
Primary Memory
The primary memory is the volatile
memory and the secondary memory is
the non volatile memory.
The volatile memory is the kind of the
memory that is erasable and the non
volatile memory is the one where in the
contents cannot be erased.
Basically when we talk about the data
storage devices it is generally assumed
to be the secondary memory.
Secondary Memory
The secondary memory is used to store
the data permanently in the computer.
The secondary storage devices are
usually as follows: hard disk drives – this
is the most common type of storage
device that is used in almost all the
computer systems.
The other ones include the floppy disk
drives, the CD ROM, DVD ROM, flash
memory, the USB data card etc.
RAM vs ROM
Read-only memory or ROM is a form of
data storage in computers and other
electronic devices that cannot be easily
altered or reprogrammed.
RAM is referred to as volatile memory
and is lost when the power is turned off
whereas ROM in non-volatile and the
contents are retained even after the
power is switched off.
Random Access Memory
Random Access Memory or RAM is a
form of data storage that can be
accessed randomly at any time, in any
order and from any physical location in
contrast to other storage devices, such
as hard drives, where the physical
location of the data determines the
time taken to retrieve it.
RAM is measured in megabytes and the
speed is measured in nanoseconds and
RAM chips can read data faster than
ROM.
ROM Types : PROM
PROM : Short for programmable read-only
memory, a memory chip on which data can be
written only once. Once a program has been
written onto a PROM, it remains there forever.
Unlike RAM, PROMs retain their contents when
the computer is turned off.
The difference between a PROM and a ROM
(read-only memory) is that a PROM is
manufactured as blank memory, whereas a ROM
is programmed during the manufacturing
process.
To write data onto a PROM chip, you need a
special device called a PROM programmer or
PROM burner. The process of programming a
PROM is sometimes called burning the PROM.
EPROM
EPROM : It stands for erasable
programmable read-only memory, and
pronounced ee-prom, EPROM is a special type
of memory that retains its contents until it
is exposed to ultraviolet light.
The ultraviolet light clears its contents,
making it possible to reprogram the memory.
To write to and erase an EPROM, you need a
special device called a PROM programmer or
PROM burner.
EEPROM :
EEPROM : It stands for electrically erasable
programmable read-only memory.
EEPROM is a special type of PROM that can
be erased by exposing it to an electrical
charge.
Like other types of PROM, EEPROM retains
its contents even when the power is turned
off. Also like other types of ROM, EEPROM
is not as fast as RAM
You might also like
- Manual Monitor Contec 6000 PDFDocument116 pagesManual Monitor Contec 6000 PDFLuisa Fernandez100% (1)
- Unit 2. Hardware ComponentsDocument10 pagesUnit 2. Hardware ComponentsRaju KumaarNo ratings yet
- QP MEP Q0202 Office AssistantDocument28 pagesQP MEP Q0202 Office AssistantAmbrish UpadhyayNo ratings yet
- Coa Lab ManualDocument33 pagesCoa Lab ManualSENTHIL RNo ratings yet
- Computer of PgdcaDocument11 pagesComputer of PgdcaGANESH KISANNo ratings yet
- Computer Input and Output DevicesDocument3 pagesComputer Input and Output Devicesgabriel chinechenduNo ratings yet
- What Is A ComputerDocument39 pagesWhat Is A Computerசுதாகரன் கோபாலகிருஷ்ணன்No ratings yet
- Project For Internship On MS OFFICEDocument51 pagesProject For Internship On MS OFFICEpriyankatiwari070No ratings yet
- LBS Data Entry and Office Automation NotesDocument26 pagesLBS Data Entry and Office Automation NotesNIJEESH RAJ N100% (2)
- DCA 101 NotesDocument95 pagesDCA 101 NoteswesiteguidesNo ratings yet
- Computer StudiesDocument5 pagesComputer Studiesgabriel chinechenduNo ratings yet
- Module 1 Basic Computer Concept Part 2Document37 pagesModule 1 Basic Computer Concept Part 2Manilyn NunezNo ratings yet
- Chapter Two:-: Computer SystemDocument134 pagesChapter Two:-: Computer SystemTolera TamiruNo ratings yet
- Basic Power PointDocument10 pagesBasic Power PointPaul Anthony Gerona JacerNo ratings yet
- 9th ppt1Document28 pages9th ppt1buvaneswari saravananNo ratings yet
- 9th ppt1Document28 pages9th ppt1buvaneswari saravananNo ratings yet
- Fundamental FinalDocument24 pagesFundamental FinalJaiSainiNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 2Document134 pagesChapter - 2elias asefaNo ratings yet
- Practical Exam DCO-315Document31 pagesPractical Exam DCO-315زین العابدینNo ratings yet
- Complete CP NotesDocument91 pagesComplete CP NotesAnonymous 1HlNy6nNo ratings yet
- ComputersDocument140 pagesComputersAnonymous sENwj8nwqNo ratings yet
- BCA3RDPC Assembly TroubleshootingDocument62 pagesBCA3RDPC Assembly TroubleshootingARTIST Urban sahilNo ratings yet
- Input and Output Devices of ComputerDocument3 pagesInput and Output Devices of ComputerFull Study0% (1)
- Central Processing Unit (CPU)Document5 pagesCentral Processing Unit (CPU)EllaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2computer SystemDocument12 pagesChapter 2computer Systemaddisyawkal18No ratings yet
- CpfdfileDocument27 pagesCpfdfileSukhpal KaurNo ratings yet
- unit 1Document26 pagesunit 1internationaldegreecollegeNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Computers Notes OUTPUT DevicesDocument20 pagesIntroduction To Computers Notes OUTPUT Devicesmunaxemimosa8No ratings yet
- AECC Basic Computer SkillsDocument118 pagesAECC Basic Computer SkillsAnkit YadavNo ratings yet
- Wa0003.Document10 pagesWa0003.amgita2021No ratings yet
- Computer Orgnization: Dr. Chaitali ShahDocument38 pagesComputer Orgnization: Dr. Chaitali ShahRohan sondharvaNo ratings yet
- Computer and Its ComponentsDocument4 pagesComputer and Its ComponentsIsmail MswNo ratings yet
- Input Devices OF ComputerDocument12 pagesInput Devices OF ComputerAjoyNo ratings yet
- Computer Notes by GV SirDocument60 pagesComputer Notes by GV Sirrishabhjangra1694No ratings yet
- Intro. Computer HardwareDocument12 pagesIntro. Computer HardwareKwadwo PeprahNo ratings yet
- Component of ComputerDocument27 pagesComponent of ComputerHuleshwar Kumar SinghNo ratings yet
- FCPIT Practical FileDocument6 pagesFCPIT Practical FileShefali GuptaNo ratings yet
- DC 102 Module 1 Lesson 1Document12 pagesDC 102 Module 1 Lesson 1jerome paulinesNo ratings yet
- 1 Computers FundamentalsDocument13 pages1 Computers Fundamentalsdevil's doubleNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Computer Hardware and SoftwareDocument12 pagesIntroduction To Computer Hardware and Software60 - R - OP ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- Input and Output DevicesDocument12 pagesInput and Output DevicesArshdeep SinghNo ratings yet
- Components of ComputerDocument4 pagesComponents of ComputerSheikh Hammad Bin KhalidNo ratings yet
- Computer Notes 2019Document139 pagesComputer Notes 2019anesumandaraza0No ratings yet
- FCPIT Practical FileDocument78 pagesFCPIT Practical Filekaushal2442100% (1)
- Computer Hardware and Software UcuDocument58 pagesComputer Hardware and Software UcuvianneloroNo ratings yet
- Input Output Devices: KeyboardDocument6 pagesInput Output Devices: KeyboardAdipudi Srinivasa RaoNo ratings yet
- Componet of A Computer SystemDocument13 pagesComponet of A Computer System✬ SHANZA MALIK ✬No ratings yet
- Block DiagramDocument21 pagesBlock DiagramBhoomi JindalNo ratings yet
- 7 - 8 CSS - WK 4-5 Computer System - Jesucrtina NimenzoDocument8 pages7 - 8 CSS - WK 4-5 Computer System - Jesucrtina NimenzoEdelmar BenosaNo ratings yet
- Pre Grade Computer Book 5 - 7 Introduction To Computers. Book Vol Ume - 1Document21 pagesPre Grade Computer Book 5 - 7 Introduction To Computers. Book Vol Ume - 1andsenNo ratings yet
- Asap Unit 3Document4 pagesAsap Unit 3AswathyNo ratings yet
- Basic Fundamentals of ComputerDocument5 pagesBasic Fundamentals of ComputerAyushi AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Computer System: By-Abc 11/3/2016Document16 pagesComputer System: By-Abc 11/3/2016Bijen ShahiNo ratings yet
- GEE2Document15 pagesGEE2Ronimarie Nicole ZapataNo ratings yet
- (OS) Operating SystemDocument21 pages(OS) Operating SystemSa Kh AauNo ratings yet
- Assignment IictDocument11 pagesAssignment IictZohaib JoyiaNo ratings yet
- B.ED 2Document26 pagesB.ED 2manshinain08No ratings yet
- It - 802 - Study MaterialDocument24 pagesIt - 802 - Study Materialkavya shreeNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Hand Out ItcDocument12 pagesUnit 2 Hand Out ItcMukhtaar CaseNo ratings yet
- Features To Consider When Buying A Laptop.Document2 pagesFeatures To Consider When Buying A Laptop.Alphonce MulwaNo ratings yet
- Acer V173Document62 pagesAcer V173Hernan Ortiz EnamoradoNo ratings yet
- MERI-College of Engineering and TechnologyDocument43 pagesMERI-College of Engineering and TechnologyDhriti SalujaNo ratings yet
- Bharat Heavy Electricals LimitedDocument15 pagesBharat Heavy Electricals LimitedDipti BhanjaNo ratings yet
- AlltablesDocument784 pagesAlltablescgrzywinskiNo ratings yet
- Brosur ZX470LC-5GDocument13 pagesBrosur ZX470LC-5Gjohan gantoheNo ratings yet
- 3500-77M Recip Cylinder Pressure Monitor Datasheet - 147485Document9 pages3500-77M Recip Cylinder Pressure Monitor Datasheet - 147485ernst22No ratings yet
- Igcse Ict Chapter 1 To 3 NotesDocument42 pagesIgcse Ict Chapter 1 To 3 Notesasfas asf asNo ratings yet
- Aesculap PV440 Camera System - User ManualDocument192 pagesAesculap PV440 Camera System - User Manualprzy3_14No ratings yet
- FVS Spring 2016 CatalogueDocument28 pagesFVS Spring 2016 CataloguefvsNo ratings yet
- Qcs 2010 Part 10 Pipeline Cleaning and Inspection SurveyDocument18 pagesQcs 2010 Part 10 Pipeline Cleaning and Inspection SurveyRotsapNayrbNo ratings yet
- VEIKK A30 Instruction ManualDocument22 pagesVEIKK A30 Instruction ManualLQ530No ratings yet
- cetisPV Contact1Document4 pagescetisPV Contact1Venkatramana ThotaNo ratings yet
- Launching High-End Technology Products: A Samsung Case StudyDocument5 pagesLaunching High-End Technology Products: A Samsung Case Studyjanuarius123No ratings yet
- DVR 8 Canales Cpcam Avc796z (MDR686Z)Document55 pagesDVR 8 Canales Cpcam Avc796z (MDR686Z)TecnoSmartNo ratings yet
- Service Manual: CPD-110GS/110ESTDocument39 pagesService Manual: CPD-110GS/110ESTManuel HernandezNo ratings yet
- Philips Azurion使用说明Document472 pagesPhilips Azurion使用说明service iyadMedicalNo ratings yet
- Summer Internship Training Report (Pyrotech Electronics UdaipurDocument54 pagesSummer Internship Training Report (Pyrotech Electronics UdaipurAnsh Bhardwaj50% (4)
- Ln26r71bd Ln-s2652d Ln26r71b Ln32r71bd LN s3252d DiagramaDocument261 pagesLn26r71bd Ln-s2652d Ln26r71b Ln32r71bd LN s3252d DiagramaVictor Julio AlvarezNo ratings yet
- LEDStudio User GuideDocument85 pagesLEDStudio User GuideivanNo ratings yet
- Flexible System Design: Checkpoint Security: Small Baggage and Parcel InspectionDocument2 pagesFlexible System Design: Checkpoint Security: Small Baggage and Parcel InspectionAbdou MohNo ratings yet
- Series: Intuitively Innovative!Document48 pagesSeries: Intuitively Innovative!Hector Velez PizaNo ratings yet
- Auto Script BrochureDocument24 pagesAuto Script BrochureMalay K GhoshNo ratings yet
- Applied Information and Communication Technology NotesDocument129 pagesApplied Information and Communication Technology NotesNadim AhmedNo ratings yet
- Circular 20240527150243 3rd Class Summer Holidays Homework 2024-25Document21 pagesCircular 20240527150243 3rd Class Summer Holidays Homework 2024-25sarpanchzharryNo ratings yet
- Manual: Height Changes Your Aesthetic ViewDocument21 pagesManual: Height Changes Your Aesthetic ViewChitrarekha ChaudhariNo ratings yet
- 1168 E Smart Grid Trainer Electrical Power Engineering ShortDocument189 pages1168 E Smart Grid Trainer Electrical Power Engineering ShortMongkon BenjawanNo ratings yet
- Ict 1 Handout: Notre Dame of Salaman College, IncDocument13 pagesIct 1 Handout: Notre Dame of Salaman College, IncOh Den NiNo ratings yet
- Fr355 - 375 Service ManualDocument158 pagesFr355 - 375 Service ManualMariana Henry Henry75% (4)