Professional Documents
Culture Documents
AIC IAT -1 Answer key
AIC IAT -1 Answer key
Uploaded by
HeeraCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
AIC IAT -1 Answer key
AIC IAT -1 Answer key
Uploaded by
HeeraCopyright:
Available Formats
SURYA GROUP OF INSTITUTIONS
SURYA COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY
CEC334 – ANALOG IC DESIGN
Year / Sem : III / VI Marks : 50
IAT – 1 ANSWER KEY
PART - A 10x2=20
1) Define Noise & Gain.
There is a range of noise sources in analog and mixed-signal systems. Some common types of noise
include white noise, pink noise, Johnson noise, quantization noise, and popcorn noise. White noise has a flat
spectrum and is distributed uniformly throughout the frequency domain.
2) Write some advantages of Cascade amplifier.
There are two primary advantages of cascade amplifiers:
a) Increased gain and input,
b) Output impedance flexibility.
3) Define Wilson current mirror
A Wilson current mirror or Wilson current source, named after George Wilson, is an improved mirror
circuit configuration designed to provide a more constant current source or sink. It provides a much more
accurate input to output current gain.
4) What do you mean by Power dissipation/Voltage swing?
The definition of power dissipation is the process by which an electronic or electrical device produces heat
(energy loss or waste) as an undesirable derivative of its primary action.
Voltage swing, defined here as the voltage difference between the peak voltage and the projected peak voltage,
is independent of series resistance, and thus directly impacts the noise margin in hybrid tunnel diode memory
and logic applications.
5) What is the purpose of using a differential amplifier with an active load?
The purpose of a differential amplifier with active load is to provide an increase in the voltage gain. The total
gain of a differential amplifier with active load is the product of the voltage gains of the discrete stages.
6) Define Miller Effect.
The Miller effect refers to the phenomenon where the input capacitance of a transistor or electronic component
appears to be larger than it actually is due to the voltage gain of the amplifier. This effect is named after John
M. Miller, an American electrical engineer who described it in the 1920s
7) Write down the Statistical characteristics of noise.
This discussion assumes the noise sources have two characteristics: First, multiple sources are uncorrelated.
Second, the probability of a particular amplitude at a point in time follows a Gaussian or normal distribution
which is the case for many sources
8) Write the difference between External & Internal noise.
The internal noise, generated within the equipment or device, and the external noise that come from other
sources outside the equipment.
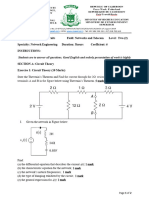
9) Draw a High frequency model of a cascade stage.
10) Write the types of Noise encountered in op amps.
There are a number of noise sources within an op amp (resistor noise, current noise, KT/C noise, etc.), but it is
customary to model them externally as a voltage noise which appears differentially across the two inputs and
two current noise sources, one in each input.
PART – B 2x10=20
11) a) Explain MOS Equivalent Circuits & Models.
Definition - 2m
Diagram - 4m
Operations & Equations - 4m
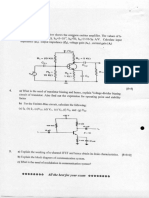
11) b) Explain Cascode & Folded cascode configurations with Active load.
Definition - 2m (cascode & folded cascode)
Diagram - 4m
Operations & Equations - 4m
12) a) Draw the circuits of CG Amplifier with Active load & Expression for input resistance, output
resistance and voltage gain.
Definition - 2m
Diagram - 4m
Operations & Equations - 4m
12) b) Explain the Noise in differential amplifier.
Definition - 2m
Diagram - 4m
Operations & Equations - 4m
PART – C 1x10=10
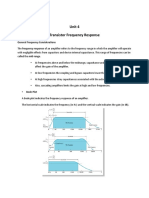
13) Discuss the Frequency of CS, CG & Source Follower.
Definition - 2m (CS, CG & Source Follower)
Diagram - 4m (CS, CG & Source Follower)
Operations & Equations - 4m (CS, CG & Source Follower)
You might also like
- An Operational Amplifier Architecture With A Single Gain Stage and Distortion CancellationDocument21 pagesAn Operational Amplifier Architecture With A Single Gain Stage and Distortion CancellationLuis Freitas100% (1)
- Chapter 9 Frequency Response of BJT & MosfetDocument54 pagesChapter 9 Frequency Response of BJT & Mosfetshubhankar palNo ratings yet
- Elec4602 NotesDocument34 pagesElec4602 NotesDavid VangNo ratings yet
- AIC IAT - 2 Answer keyDocument3 pagesAIC IAT - 2 Answer keyHeeraNo ratings yet
- Aec Model Question 2021Document2 pagesAec Model Question 2021Ajay kumar GuptaNo ratings yet
- Lica Model Question Paper TemplateDocument1 pageLica Model Question Paper Templategowri thumburNo ratings yet
- Eee 4234 Analogue Electronics IiDocument5 pagesEee 4234 Analogue Electronics IiSylvester WasongaNo ratings yet
- Bansal Group of InstitutesDocument3 pagesBansal Group of Instituteskkp0650No ratings yet
- 13A99101 Basic Electrial & Electronics EngineeringDocument2 pages13A99101 Basic Electrial & Electronics EngineeringjagadeeshNo ratings yet
- EDC - Old Question Papers For Unit 3, 4, 5Document19 pagesEDC - Old Question Papers For Unit 3, 4, 5Deepak SahuNo ratings yet
- Question Paper Code:: Reg. No.Document3 pagesQuestion Paper Code:: Reg. No.Samraj JebasinghNo ratings yet
- NR 320204 HIgh Voltge EngineeringDocument4 pagesNR 320204 HIgh Voltge EngineeringSrinivasa Rao GNo ratings yet
- UEE001Document1 pageUEE001ishuNo ratings yet
- ECAD Question BankDocument5 pagesECAD Question Bank20BF1A04M6 sumanthNo ratings yet
- Sheet 6Answer OLdDocument8 pagesSheet 6Answer OLdmohamedalaas103No ratings yet
- r5100406 Network AnalysisDocument4 pagesr5100406 Network AnalysissivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- Electric Circuit Exam INIESATDocument2 pagesElectric Circuit Exam INIESATMBIEDA NGOMEGNI FRANK GAETANNo ratings yet
- Bee Cia IiDocument2 pagesBee Cia IiRavi KannappanNo ratings yet
- Following Paper ID and Roll No. To Be Filled in Your Answer BookDocument4 pagesFollowing Paper ID and Roll No. To Be Filled in Your Answer BookNivedita BasuNo ratings yet
- Cs It 04 304 Basic Electronics EngineeringDocument2 pagesCs It 04 304 Basic Electronics EngineeringVipin jNo ratings yet
- Ec 303Document2 pagesEc 303jeetendrasidhiNo ratings yet
- Ee 501 SeriesDocument5 pagesEe 501 SeriesFLOWERNo ratings yet
- Institute of Aeronautical Engineering: (Autonomous)Document4 pagesInstitute of Aeronautical Engineering: (Autonomous)VigneshNo ratings yet
- Scenario:: Internal Verification Form D1Document10 pagesScenario:: Internal Verification Form D1tanmoyr2001No ratings yet
- 2012 Basic Electrical Engineering: CS/B.TECH (OLD) /SEM-2/EE-201/2012Document7 pages2012 Basic Electrical Engineering: CS/B.TECH (OLD) /SEM-2/EE-201/2012abhrajitsahaNo ratings yet
- ANE - Tut 1-Merged-MergedDocument10 pagesANE - Tut 1-Merged-MergedadityaNo ratings yet
- JNTUK May June 2015-2-2 R13 Electronic Circuit Analysis Common To ECE EIEDocument5 pagesJNTUK May June 2015-2-2 R13 Electronic Circuit Analysis Common To ECE EIEJaswanth PatnaikNo ratings yet
- Time: 3 Hours Max. Marks: 100 Note: Be Precise in Your Answer. in Case of Numerical Problem Assume Data Wherever Not ProvidedDocument1 pageTime: 3 Hours Max. Marks: 100 Note: Be Precise in Your Answer. in Case of Numerical Problem Assume Data Wherever Not ProvidedAdarsh MishraNo ratings yet
- r5100506 Basic Electrical EngineeringDocument4 pagesr5100506 Basic Electrical EngineeringsivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- 9A04402 Electronic Circuit AnalysisDocument4 pages9A04402 Electronic Circuit AnalysissivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- 10 Hve mqp1476880070Document3 pages10 Hve mqp1476880070vpzfarisNo ratings yet
- Time: 3 Hours Max. Marks: 100 Note: Be Precise in Your Answer. in Case of Numerical Problem Assume Data Wherever Not ProvidedDocument2 pagesTime: 3 Hours Max. Marks: 100 Note: Be Precise in Your Answer. in Case of Numerical Problem Assume Data Wherever Not ProvidedIsha TripathiNo ratings yet
- R19-EEE-EC-II QP - Set-2Document3 pagesR19-EEE-EC-II QP - Set-2kisnamohanNo ratings yet
- Model Answer Summer 2016Document30 pagesModel Answer Summer 2016haiderNo ratings yet
- ELECTRONICS-ENGINEERING-NEC201 (1)Document2 pagesELECTRONICS-ENGINEERING-NEC201 (1)nikhildev516No ratings yet
- Lecture 5 and 6 Mist SpecialDocument26 pagesLecture 5 and 6 Mist SpecialGaffar KhanNo ratings yet
- E3-238: Analog VLSI Circuits Lab 2: InstructionsDocument4 pagesE3-238: Analog VLSI Circuits Lab 2: InstructionsR SHARMANo ratings yet
- Iare Ac Model QPDocument5 pagesIare Ac Model QPVigneshNo ratings yet
- 2 MarksDocument45 pages2 MarkshidhanaaNo ratings yet
- KTU EC205 ELECTRONIC CIRCUITS (AE, EC) - MAin - Jan - 2017 - Ktu Qbank-MergedDocument16 pagesKTU EC205 ELECTRONIC CIRCUITS (AE, EC) - MAin - Jan - 2017 - Ktu Qbank-MergedsunNo ratings yet
- Ece 1071 - Ece-1071 - Basic ElectronicsDocument2 pagesEce 1071 - Ece-1071 - Basic ElectronicsChalla SaiNo ratings yet
- Ac 1Document8 pagesAc 1andhracollegesNo ratings yet
- 2019-Dec EC-101 232Document2 pages2019-Dec EC-101 232Rajesh SharmaNo ratings yet
- 9A04402 Electronic Circuit AnalysisDocument8 pages9A04402 Electronic Circuit AnalysissivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- Microwave Engineering May2004 NR 320403Document5 pagesMicrowave Engineering May2004 NR 320403Nizam Institute of Engineering and Technology LibraryNo ratings yet
- R7410207-High Voltage EngineeringDocument4 pagesR7410207-High Voltage EngineeringsivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- Harrisob Laboratory No.1Document4 pagesHarrisob Laboratory No.1Harrison VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- IA2 Question PaperDocument18 pagesIA2 Question PaperravirayappaNo ratings yet
- Koneru Lakshmaiah Education Foundation: Department of Electronics and Communication EngineeringDocument13 pagesKoneru Lakshmaiah Education Foundation: Department of Electronics and Communication EngineeringLakshmi JagupillaNo ratings yet
- Cat 1Document7 pagesCat 1aksdafNo ratings yet
- B.E./E.Tech. D E G R E E Examination, April / May 2011Document2 pagesB.E./E.Tech. D E G R E E Examination, April / May 2011Ramkumar SivakaminathanNo ratings yet
- PSG College of Technology, Coimbatore - 641 004 Semester Examinations, SemesterDocument2 pagesPSG College of Technology, Coimbatore - 641 004 Semester Examinations, SemesterAravindh AadhityaNo ratings yet
- R7221005 Linear IC ApplicationsDocument1 pageR7221005 Linear IC ApplicationssivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- Question Bank: Krishna School of Emerging Technology and Applied Research (KSET)Document7 pagesQuestion Bank: Krishna School of Emerging Technology and Applied Research (KSET)Vraj PatelNo ratings yet
- NR 311701 Microwave EngineeringDocument7 pagesNR 311701 Microwave EngineeringSrinivasa Rao GNo ratings yet
- Anallysis and Design of Analog Integrated Circuits QuestionsDocument5 pagesAnallysis and Design of Analog Integrated Circuits QuestionsshankarNo ratings yet
- 3rd Sem Analog and LA Sem QPDocument5 pages3rd Sem Analog and LA Sem QP22u211No ratings yet
- Our Official Android App - REJINPAUL NETWORK FromDocument2 pagesOur Official Android App - REJINPAUL NETWORK FromAngelinNo ratings yet
- Ec6503 - TLW - Iq - Nov - Dec 2018 - Rejinpaul PDFDocument2 pagesEc6503 - TLW - Iq - Nov - Dec 2018 - Rejinpaul PDFAngelinNo ratings yet
- Manipal Institute of Technology: Reg. NoDocument2 pagesManipal Institute of Technology: Reg. Nodreamivory29No ratings yet
- R7310403 Linear IC ApplicationsDocument1 pageR7310403 Linear IC ApplicationssivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC) Design and Test Case AnalysisFrom EverandElectromagnetic Compatibility (EMC) Design and Test Case AnalysisNo ratings yet
- Active LoadsDocument9 pagesActive LoadsGowndaManiNo ratings yet
- Grid-Stoppers and Miller CapacitanceDocument3 pagesGrid-Stoppers and Miller CapacitanceDiego García MedinaNo ratings yet
- EC8351 Electronic Circuits I IQDocument20 pagesEC8351 Electronic Circuits I IQRekha SharmilyNo ratings yet
- 4th Sem ReportDocument93 pages4th Sem ReportAbhishek MatNo ratings yet
- Ecen 326 - Lab 11 ReportDocument9 pagesEcen 326 - Lab 11 Reportapi-241454978No ratings yet
- Radio Frequency CircuitsDocument29 pagesRadio Frequency CircuitsNano Gomesh100% (2)
- A 2.4 GHZ CMOS Low Noise Amplifier Using An Inter-Stage Matching InductorDocument4 pagesA 2.4 GHZ CMOS Low Noise Amplifier Using An Inter-Stage Matching InductorphithucNo ratings yet
- Vacuum Tube BasicsDocument9 pagesVacuum Tube BasicsCIELO OLEANo ratings yet
- Amplifier Frequency ResponseDocument33 pagesAmplifier Frequency ResponseHidayah HadiNo ratings yet
- VN/VP13 Series Application Note: Circuit Description/Design ConsiderationsDocument4 pagesVN/VP13 Series Application Note: Circuit Description/Design ConsiderationsGerardo TexisNo ratings yet
- BJT and FET Frequency Response - Lec2Document51 pagesBJT and FET Frequency Response - Lec2Toota TuttaNo ratings yet
- Eca Unit 2 2024Document20 pagesEca Unit 2 2024Manchana PadamajaNo ratings yet
- Miller EffectDocument4 pagesMiller EffectMukundKomatiNo ratings yet
- Miller ApproximationDocument14 pagesMiller ApproximationRobeul AhmedNo ratings yet
- 3.5 Chapter 3 - FET Frequency Response Wo QRDocument18 pages3.5 Chapter 3 - FET Frequency Response Wo QRAnsar AnsarNo ratings yet
- LINEAR INTEGRATED CIRCUITS Unit3 Raghudathesh VTUDocument30 pagesLINEAR INTEGRATED CIRCUITS Unit3 Raghudathesh VTUraghudatheshNo ratings yet
- Ccsmodel PPTDocument25 pagesCcsmodel PPTRam Prasad100% (1)
- Chap2 (RF)Document4 pagesChap2 (RF)ReivenNo ratings yet
- Communication EngineeringDocument66 pagesCommunication EngineeringOlvaNo ratings yet
- Class AB Push-Pull Vacuum Tube Guitar Amplifier Analysis, Design, and ConstructionDocument14 pagesClass AB Push-Pull Vacuum Tube Guitar Amplifier Analysis, Design, and ConstructiontekellamerZ aka tekellamer100% (2)
- Unit 4 Transistor Frequency ResponseDocument6 pagesUnit 4 Transistor Frequency ResponseShaina MabborangNo ratings yet
- Lecture 10Document22 pagesLecture 10mkrasanNo ratings yet
- DC To Ac Inverter Card With IgbtDocument26 pagesDC To Ac Inverter Card With IgbtedgarpolNo ratings yet
- EC Lab Manual (08.407)Document101 pagesEC Lab Manual (08.407)Assini HussainNo ratings yet
- Implementation and Simulation of Half Bridge Series Resonant Inverter in Zero Voltage SwitchingDocument5 pagesImplementation and Simulation of Half Bridge Series Resonant Inverter in Zero Voltage Switchingwhite_lonelinessNo ratings yet
- Design and Simulation of 4T-Cascode Amplifier at 45 Nanometer Technology NodeDocument4 pagesDesign and Simulation of 4T-Cascode Amplifier at 45 Nanometer Technology NodeHassan El-kholyNo ratings yet
- Burt 2006Document8 pagesBurt 2006Zhenyu YangNo ratings yet
- Application Note 5314: Active Miller ClampDocument6 pagesApplication Note 5314: Active Miller ClampDavid ZammitNo ratings yet