Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Product of electrolysis-1
Product of electrolysis-1
Uploaded by
ms02073450 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
0 views2 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
0 views2 pagesProduct of electrolysis-1
Product of electrolysis-1
Uploaded by
ms0207345Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 2
Product of electrolysis
Product of electrolysis depends on :
(i) Nature of the material that is to be electrolysed
(ii) Oxidising and reducing species and their E° value
(iii) Type of electrode used (inert/reactive)
Inert electrode: Do not participate in the reaction and act as a source of electron.
Reactive electrode : It participate in the electrode reaction
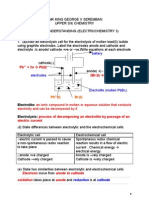
Example 1: Electrolysis of Molten Sodium Chloride
2NaCl ⇌ 2Na+ +2Cl−
At cathode: 2Na+ + 2e−→2Na E∘=−2.71V
− −
At anode: 2Cl →Cl2+2e E∘=1.36V
Overall reaction:
2Na++2Cl−− electrolysis 2Na + Cl2
Electrolysis of an aqueous solution of Sodium Chloride:
NaCl(aq) →Na+(aq) + Cl−(aq)
H2O(l) ⇌H+(aq) + OH−(aq)
At cathode:
Na+ +e− → Na , E∘=−2.71V
2H2O + 2e−→H2 + 2OH− , E∘=−0.83V
Higher the value of E°is preferred thus H2 gas is deposited at cathode
Thus, the reaction taking place at cathode 2H2O + 2e−→H2 + 2OH−
At Anode:
2H2O → O2+ 4H++ 4e− , E∘= 1.23V
2Cl− → Cl2 +2e− E∘= 1.36V
Due to over voltage or over potential of oxygen oxidation of water will not take place hence chlorine gas is
liberated at anode. Thus the reaction at anode
2Cl− → Cl2 +2e−
Over Potential : During electrochemical process , some reactions are kinetically slow at low voltage and
do not seems to takes place thus an extra potential is applied to make such reaction more difficult to occur.
Electrolysis of aqueous copper sulphate solution
Copper sulphate and water ionise as:
CuSO4 (aq) ⇔ Cu2+(aq) + SO42¯
H2O (l) ⇔ H+(aq) + OH¯ (aq)
During electrolysis, copper is deposited at the cathode while oxygen is liberated at the anode.
At anode (oxidation)
2 H2O (l) ——-> 4 H+ + O2 +4 e¯
At cathode (reduction)
Cu2+ (aq) +2e‾ ———> Cu(s) x 2
The overall reaction is :
2Cu2+ (aq) + 2 H2O (l) ———> Cu(s) + 4 H+ + O2 (g)
Electrolysis Of Sulphuric acid
During the electrolysis of sulphuric acid, hydrogen is liberated at cathode:
At cathode
H+ + e¯ ——-> ½ H2
The following two reactions occur at anode:
2 H2O (l) ———–> O2 (g) + 4 e¯ Eø = 1.23 V
2 SO42¯ (aq) ——> S2O82¯ (aq) + 2 e¯ Eø = 1.96 V
You might also like
- Chapter 11Document20 pagesChapter 11helloblarg100% (1)
- ElectrolysisDocument12 pagesElectrolysisShofwa AnnisaNo ratings yet
- A. Electrolysis of Acidified Water (Dilute Sulphuric Acid) : Notes Myp 5 ChemistryDocument10 pagesA. Electrolysis of Acidified Water (Dilute Sulphuric Acid) : Notes Myp 5 Chemistrywama ojhaNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 9 - Level 2 Worked SolutionsDocument11 pagesTutorial 9 - Level 2 Worked SolutionsBloodCypherNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 - ElectrochemistryDocument74 pagesChapter 4 - Electrochemistryhoboslayer97No ratings yet
- Electro Chemistry One PageDocument2 pagesElectro Chemistry One Pageshankaranand200517No ratings yet
- Electrochemistry - ApplicationsDocument18 pagesElectrochemistry - ApplicationsMNo ratings yet
- Electrochemistry - 2 - 1Document6 pagesElectrochemistry - 2 - 1Mandeep PediredlaNo ratings yet
- UNIT 2 Electrochemistry FinalDocument26 pagesUNIT 2 Electrochemistry FinalA HNo ratings yet
- UNIT 2 Electrochemistry FinalDocument25 pagesUNIT 2 Electrochemistry FinalPisces SandNo ratings yet
- BATTERYDocument19 pagesBATTERYRaja PRNo ratings yet
- Chapter9 AnswersDocument5 pagesChapter9 AnswersedytfuyNo ratings yet
- A Chemistry Electrolysis ProjectDocument10 pagesA Chemistry Electrolysis ProjectLij WynterNo ratings yet
- Lesson 8 - Electrolysis Part 2Document16 pagesLesson 8 - Electrolysis Part 2Dishna KarunasekaraNo ratings yet
- Topic 9 (Galvanic Cell) - Tutorial - Level 2 AnswerDocument7 pagesTopic 9 (Galvanic Cell) - Tutorial - Level 2 AnswerCheng Xun LeeNo ratings yet
- Lesson 8 - Electrolysis Part 3Document16 pagesLesson 8 - Electrolysis Part 3Dishna KarunasekaraNo ratings yet
- Chapter 20Document77 pagesChapter 20XYRUS MARAMOTNo ratings yet
- Electrochemistry NotesDocument4 pagesElectrochemistry NotesAyush RorNo ratings yet
- Electrochem Understanding - AnswersDocument11 pagesElectrochem Understanding - AnswersSiva NeshNo ratings yet
- Chapter 17 ElectrochemistryDocument68 pagesChapter 17 ElectrochemistryBeastUnleashed28No ratings yet
- IB CHEM HL Oxidation and Reduction Note CardsDocument9 pagesIB CHEM HL Oxidation and Reduction Note Cards陳定均No ratings yet
- ElectrochemistryDocument38 pagesElectrochemistryShannon Smith100% (1)
- A - Ahl Electrochemical CellsDocument1 pageA - Ahl Electrochemical CellsAlyasin FrougaNo ratings yet
- Redox Dan Electrochemistry (Kimia)Document65 pagesRedox Dan Electrochemistry (Kimia)Rocky Simon HiaNo ratings yet
- Electrolysis: Electrolysis of Molten SaltsDocument2 pagesElectrolysis: Electrolysis of Molten SaltsSunnyNo ratings yet
- Production of NaOHDocument16 pagesProduction of NaOHminingforverus1No ratings yet
- Electrolysis O LevelDocument17 pagesElectrolysis O LevelInnocent EbilNo ratings yet
- CH 18Document6 pagesCH 18France Mico SobrevegaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 ElectrochemistryDocument76 pagesChapter 10 ElectrochemistryPatrickNo ratings yet
- The Aqueous Phase ReactionDocument16 pagesThe Aqueous Phase ReactionRSL100% (1)
- Unit 5.1Document10 pagesUnit 5.1Tilak K CNo ratings yet
- Chem121-Reactions in Aqueous SolutionsDocument87 pagesChem121-Reactions in Aqueous SolutionsberkitenberkanNo ratings yet
- Electrolysis in SolutionsDocument13 pagesElectrolysis in SolutionsTeandraNo ratings yet
- 2 Electrochemistry (Electrolytic Cells)Document45 pages2 Electrochemistry (Electrolytic Cells)Gerald Paul SumagpaoNo ratings yet
- Electrochemical Cells: Electronic Conductor + Surrounding ElectrolyteDocument7 pagesElectrochemical Cells: Electronic Conductor + Surrounding ElectrolyteMou RakshitNo ratings yet
- ElectrochemistryDocument39 pagesElectrochemistryHaider AliNo ratings yet
- Electricity and Chemicals - AKHS Edition 2020 - Complete NotesDocument20 pagesElectricity and Chemicals - AKHS Edition 2020 - Complete NotesKim SewoonNo ratings yet
- New Note Chapter 22 Electrolysis_2020_suggested answers to More Challenging QuestionsDocument11 pagesNew Note Chapter 22 Electrolysis_2020_suggested answers to More Challenging QuestionsmtauNo ratings yet
- 2122 Course Revision Questions Chemistry Level M T2 MSDocument127 pages2122 Course Revision Questions Chemistry Level M T2 MSDana JrabNo ratings yet
- ElectrochemistryDocument28 pagesElectrochemistryNgô Minh KhuêNo ratings yet
- Matriculation Chemistry (Electrochemistry)Document77 pagesMatriculation Chemistry (Electrochemistry)ridwan100% (3)
- Electrolysis: Electrolysis Electric Current Ionic To Form ElementsDocument11 pagesElectrolysis: Electrolysis Electric Current Ionic To Form ElementsLana Arsyad100% (2)
- ElectrolysisDocument4 pagesElectrolysisCaroline ThuNo ratings yet
- Electrolysis of Solutions: Earning UtcomesDocument13 pagesElectrolysis of Solutions: Earning UtcomesNicaliaNo ratings yet
- 2 Electrochemistry (Semester 2)Document49 pages2 Electrochemistry (Semester 2)Esther Ngieng100% (1)
- Electrochemistry NotesDocument54 pagesElectrochemistry NotesAkash Roy67% (6)
- KimiaDocument46 pagesKimiaErvina RetnaningtyasNo ratings yet
- CHM432 Fundamental Physical Chemistry: ElectrochemistryDocument102 pagesCHM432 Fundamental Physical Chemistry: ElectrochemistryPriscyyNo ratings yet
- New Note Chapter 22 Electrolysis_2020_suggested answers to More Challenging QuestionsDocument12 pagesNew Note Chapter 22 Electrolysis_2020_suggested answers to More Challenging QuestionsmtauNo ratings yet
- CHEM2310 Electrochemistry Tutorial Solutions - Typed - Nov 2013Document4 pagesCHEM2310 Electrochemistry Tutorial Solutions - Typed - Nov 2013ClaytonMitchellJr.No ratings yet
- Materi Aplikasi Reaksi RedoksDocument28 pagesMateri Aplikasi Reaksi Redokszaharo putriNo ratings yet
- ElectrochemistryDocument10 pagesElectrochemistrySsNo ratings yet
- Electrolytic CellsDocument32 pagesElectrolytic CellsHendi PratamaNo ratings yet
- ch21 Electrochem SILBERBERGDocument101 pagesch21 Electrochem SILBERBERGSiskaWahyuniNo ratings yet
- EpotppsDocument31 pagesEpotppsHelpful HandNo ratings yet
- Topic 9 First Year MCAT (Electrochemistry)Document39 pagesTopic 9 First Year MCAT (Electrochemistry)Khubaib KhanNo ratings yet
- 14.3 NotesDocument28 pages14.3 NotesCarmen PurewalNo ratings yet
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-ReductionFrom EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-ReductionRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-Reduction with AnswersFrom EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-Reduction with AnswersNo ratings yet
- Advances in Organometallic Chemistry and Catalysis: The Silver / Gold Jubilee International Conference on Organometallic Chemistry Celebratory BookFrom EverandAdvances in Organometallic Chemistry and Catalysis: The Silver / Gold Jubilee International Conference on Organometallic Chemistry Celebratory BookArmando J. L. PombeiroRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)