Professional Documents
Culture Documents
QuadraticEquation_DPP-5_Question_JEE_@Gb_Sir
QuadraticEquation_DPP-5_Question_JEE_@Gb_Sir
Uploaded by
mrindianmysteryCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
QuadraticEquation_DPP-5_Question_JEE_@Gb_Sir
QuadraticEquation_DPP-5_Question_JEE_@Gb_Sir
Uploaded by
mrindianmysteryCopyright:
Available Formats
TM
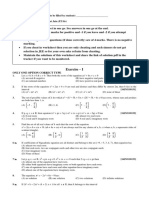
QUADRATIC EQUATION
DPP - 5
JEE [MAIN + ADV.] DIVISION
1. If and are roots of 2x 2 – 3x – 6 = 0, then the equation whose roots are 2 + 2 and
2 + 2 will be -
(A) 4x2 + 49 x – 118 = 0 (B) 4x2 – 49 x – 118 = 0
(C) 4x2 – 49 x + 118 = 0 (D) 4x2 + 49 x + 118 = 0
2. If and are roots of x 2 – 2x + 3 = 0, then the equation whose roots are
1 1
and will be-
1 1
(A) 3x2 – 2x + 1 = 0 (B) 3x2 + 2x + 1 = 0
(C) 3x2 – 2x – 1 = 0 (D) x2 – 3x + 1 = 0
3. The sum of the roots of a equation is 2 and sum of their cubes is 98, then the equation is -
(A) x2 + 2x + 15 = 0 (B) x2 + 15 x + 2 = 0
(C) 2x2 – 2x + 15 = 0 (D) x2 – 2x – 15 = 0
4. If a > 0, b > 0, c > 0, then both the roots of the equation ax 2 + bx + c = 0 -
(A) Are real and negative (B) Have negative real parts
(C) are rational numbers (D) None of these
3 5i
5. If one root of the equation 2x2 – 6x + c = 0 is , then the value of c will be -
2
(A) 7 (B) – 7 (C) 17 (D) – 17
6. The roots of the equation (p – 2) x 2 + 2 (p – 2) x + 2 = 0 are not real when -
(A) p [1, 2] (B) p [2, 3] (C) p ( 2,4) (D) p [ 3, 4]
7. The values of a for which 9x2 – 2x + a = 6 – ax posseses equal roots
1 1
(A) 20 ± 6 5 (B) 9 (C) (D) –
9 9
8. The value of k for which the equation (k – 1)x2 + (k + 4) x + k + 7 = 0 has equal roots
(A) 2 (B) – 2 (C) 22/3 (D) None
Multiple type
2 3a
9. The equation cx + 2bx – 3a = 0, has no real roots and < (b + c) then ‘a’ can be
4
(a, b, c R)
(A) –1 (B) –2 (C) –17 (D) –34
10. Let a, b, c and d be non-zero numbers such that x = c and x = d are the roots of the equation
x2 + ax + b = 0 and x = a and x = b are the roots of the equation x2 + cx + d = 0 then
(a + b + c + d) is
(A) a perfect square (B) even integer
(C) prime number (D) divisible by 2
Answer Key
1. C 2. A 3. D 4. B 5. C
6. C 7. A 8. A 9. A,B,C,D 10. B,C,D
Corporate Office : Motion Education Pvt. Ltd., 394 - Rajeev Gandhi Nagar, Kota 8003899588
8 Page : 1
You might also like
- Advanced Problems in Algebra by Vikas GuptaDocument577 pagesAdvanced Problems in Algebra by Vikas Guptasid75% (64)
- Chapter 4 Matrices and Systems of Linear EquationsDocument10 pagesChapter 4 Matrices and Systems of Linear Equationszan2812No ratings yet
- STA 314 Operations Research I Lecture Note 2017/2018 ACADEMIC SESSIONDocument50 pagesSTA 314 Operations Research I Lecture Note 2017/2018 ACADEMIC SESSIONAbdulKareem Wasiu100% (4)
- 2b. Other Surveys With TapeDocument7 pages2b. Other Surveys With TapeMarc Dared CagaoanNo ratings yet
- QuadraticEquation_DPP-7_Question_JEE_@Gb_SirDocument1 pageQuadraticEquation_DPP-7_Question_JEE_@Gb_SirmrindianmysteryNo ratings yet
- QuadraticEquation_DPP-10_Question_JEE_@Gb_SirDocument2 pagesQuadraticEquation_DPP-10_Question_JEE_@Gb_SirmrindianmysteryNo ratings yet
- ELPs - Quadratic EquationDocument15 pagesELPs - Quadratic EquationKamran AkbarNo ratings yet
- Batch Maths & Log - EnglishDocument10 pagesBatch Maths & Log - EnglishAvijeet kumar MishraNo ratings yet
- Amj Mathematics 1Document16 pagesAmj Mathematics 1sonalimandal.1985No ratings yet
- 3.quadratic Equation - PMDDocument10 pages3.quadratic Equation - PMDAshwani ChaurasiaNo ratings yet
- Theory of Equations DPP-1Document6 pagesTheory of Equations DPP-1SaήjaγKsNo ratings yet
- Quadratic 2Document5 pagesQuadratic 2Arihant KumarNo ratings yet
- Quadratic Equation SheetDocument21 pagesQuadratic Equation SheetMandeep RanaNo ratings yet
- Angle and Its MeasurementDocument7 pagesAngle and Its MeasurementHarshika KatariyaNo ratings yet
- 10+1 - Assignment-4 - Quadratic Equation - MathsDocument4 pages10+1 - Assignment-4 - Quadratic Equation - Mathsnaman kansalNo ratings yet
- Qee-1 MajDocument12 pagesQee-1 Maj25.Karthik Rao 9FNo ratings yet
- PolynomialDocument2 pagesPolynomialshitalsamant10No ratings yet
- 02march MainsDocument34 pages02march Mainsprakash karnaNo ratings yet
- DPPS - 1 - Quadratic EquationDocument2 pagesDPPS - 1 - Quadratic EquationyashNo ratings yet
- 09851a60-eeec-401f-98e0-711ffb8a760cDocument3 pages09851a60-eeec-401f-98e0-711ffb8a760ckundumanik43No ratings yet
- MathsDocument64 pagesMathsAshish GiriNo ratings yet
- QB AlgebraLogQuadraticProgressionDocument12 pagesQB AlgebraLogQuadraticProgressionIshhuNo ratings yet
- Subject: Mathematics Rank Booster Course (RBC) : Worksheet - 1 Time: 3 Hrs. Unit - 1Document3 pagesSubject: Mathematics Rank Booster Course (RBC) : Worksheet - 1 Time: 3 Hrs. Unit - 1Akshay GuptaNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 6 SCQDocument5 pagesWorksheet 6 SCQpriyanshu rawatNo ratings yet
- Quadratic Equations - JEE Main and Advanced-1-5Document5 pagesQuadratic Equations - JEE Main and Advanced-1-5Sakshi RaiNo ratings yet
- Answer All The Following Questions Which Are Single Option CorrectDocument7 pagesAnswer All The Following Questions Which Are Single Option CorrectiamrockyNo ratings yet
- race_02_quadratic_e_1615015748Document2 pagesrace_02_quadratic_e_1615015748Singh NikhilNo ratings yet
- Quadratic Question BankDocument25 pagesQuadratic Question BankArihant KumarNo ratings yet
- QuadraticEquation_DPP-(3+4)_Question_JEE_@Gb_SirDocument1 pageQuadraticEquation_DPP-(3+4)_Question_JEE_@Gb_SirmrindianmysteryNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument72 pagesUntitledParth NikamNo ratings yet
- Qee QDocument2 pagesQee QMayank VatsaNo ratings yet
- BM I (E)Document6 pagesBM I (E)priyanshisehrawat30No ratings yet
- Maths Class Xii Sample Paper Test 11 For Board Exam 2023Document5 pagesMaths Class Xii Sample Paper Test 11 For Board Exam 2023Rahul KumarNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Mathematics-1: Section (A) : Number SystemDocument6 pagesFundamentals of Mathematics-1: Section (A) : Number SystemSushila TanwarNo ratings yet
- Class-X MCQDocument2 pagesClass-X MCQStorage AccountNo ratings yet
- DPP-3 Quadratic Equation - OmgDocument6 pagesDPP-3 Quadratic Equation - OmgSumit RajNo ratings yet
- Karloboard - D05-Jan-2024Document40 pagesKarloboard - D05-Jan-2024jainil2536No ratings yet
- DPP 1 Quadratic Equation by Om SirDocument5 pagesDPP 1 Quadratic Equation by Om SirItsYour OmNo ratings yet
- Daily Practice Problems (DPP) : Sub: Maths Chapter: Quadratic Equation DPP No.: 1Document2 pagesDaily Practice Problems (DPP) : Sub: Maths Chapter: Quadratic Equation DPP No.: 1Sanchit MukherjeeNo ratings yet
- ALGEBRA (Practice Sheet) PDFDocument132 pagesALGEBRA (Practice Sheet) PDFManavSaksariaNo ratings yet
- ATP Star DPP Math 2Document360 pagesATP Star DPP Math 2shriteshNo ratings yet
- Mathematics: Daily Practice ProblemsDocument3 pagesMathematics: Daily Practice ProblemsArihant KumarNo ratings yet
- Single Choice Type (+2, 1) : STUDENT NAME: - Quadratic EquationsDocument1 pageSingle Choice Type (+2, 1) : STUDENT NAME: - Quadratic EquationsGitanshu AroraNo ratings yet
- A Ab A B A Ab B A Ab: DPP - V PolynomialsDocument3 pagesA Ab A B A Ab B A Ab: DPP - V PolynomialsGeeth SagarNo ratings yet
- Theory of Equations DPP-3Document4 pagesTheory of Equations DPP-3SaήjaγKsNo ratings yet
- Revision Module Mathematics AdvancedDocument48 pagesRevision Module Mathematics AdvancedSatish RajNo ratings yet
- Quadratic Equation (2) .PMD PDFDocument2 pagesQuadratic Equation (2) .PMD PDFJatin SinglaNo ratings yet
- Mathematics Ntse Class - X Linear EquationsDocument2 pagesMathematics Ntse Class - X Linear EquationsKeerthi Reddy MadaNo ratings yet
- Topic Wise WB JEE Master Question Bank-20210702182059221938Document27 pagesTopic Wise WB JEE Master Question Bank-20210702182059221938PRIYANSHNo ratings yet
- DPP 4polynomialsDocument8 pagesDPP 4polynomialsBitan DasNo ratings yet
- Maths - Race#022Document2 pagesMaths - Race#022animalinda088No ratings yet
- EnglishDocument19 pagesEnglishmarmaduke32No ratings yet
- Mathematics: Rapid Crash CourseDocument13 pagesMathematics: Rapid Crash CourseHudsun HornetNo ratings yet
- FOM ExercisesDocument25 pagesFOM ExercisesKRITANTNo ratings yet
- Yellow BookDocument577 pagesYellow BookAnuJ Mishra100% (4)
- JA Quadratic VGDocument44 pagesJA Quadratic VGAarush KaletwadNo ratings yet
- Quadratic Home AssignmentDocument4 pagesQuadratic Home AssignmentSunilSutharNo ratings yet
- Xii - Mock Test - 2 (11) Ans KeyDocument14 pagesXii - Mock Test - 2 (11) Ans KeyKartik ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Quadratic Equations Advanced AssignmentDocument3 pagesQuadratic Equations Advanced AssignmentNeeravNo ratings yet
- Maths Class Xii Sample Paper Test 11 For Board Exam 2023 AnswersDocument14 pagesMaths Class Xii Sample Paper Test 11 For Board Exam 2023 AnswersOm ZambareNo ratings yet
- Time: 3 Hrs. Xii-Main - PCM MM: 300Document10 pagesTime: 3 Hrs. Xii-Main - PCM MM: 3000901AI201047 SAMAR JAINNo ratings yet
- QuadraticEquation_DPP-8_Solution_JEE_@Gb_SirDocument2 pagesQuadraticEquation_DPP-8_Solution_JEE_@Gb_SirmrindianmysteryNo ratings yet
- QuadraticEquation_DPP-11_Solution_JEE_@Gb_SirDocument3 pagesQuadraticEquation_DPP-11_Solution_JEE_@Gb_SirmrindianmysteryNo ratings yet
- QuadraticEquation_DPP-11_Question_JEE_@Gb_SirDocument1 pageQuadraticEquation_DPP-11_Question_JEE_@Gb_SirmrindianmysteryNo ratings yet
- physical education class 12th practical file (1)Document63 pagesphysical education class 12th practical file (1)mrindianmysteryNo ratings yet
- Grade 9 2nd ExamDocument7 pagesGrade 9 2nd ExamAmelia Moreno100% (1)
- Quantitative Cheat SheetDocument6 pagesQuantitative Cheat SheethfchchNo ratings yet
- Y4 FYE CMath + AMath Notes (Condensed Version)Document56 pagesY4 FYE CMath + AMath Notes (Condensed Version)Kaja RajalakshmiNo ratings yet
- ME424 201516 Unit4 PDFDocument56 pagesME424 201516 Unit4 PDFharshaNo ratings yet
- STS Reviewer PDFDocument6 pagesSTS Reviewer PDFdiannexNo ratings yet
- LEARNING ACTIVITY Sheet Math 7 q3 M 1Document4 pagesLEARNING ACTIVITY Sheet Math 7 q3 M 1Mariel PastoleroNo ratings yet
- 6 TrigonometryDocument64 pages6 Trigonometryshaannivas0% (1)
- Artificial Intelligence - Mirrors For The Mind - H. Henderson (2007) WWDocument209 pagesArtificial Intelligence - Mirrors For The Mind - H. Henderson (2007) WWTrịnh Hữu Tâm100% (3)
- Ese559 Jul2021 FinalDocument7 pagesEse559 Jul2021 FinalAmirul HazzmiNo ratings yet
- Floating Bodies in Neutral EquilibriumDocument5 pagesFloating Bodies in Neutral EquilibriumCarlos JoseNo ratings yet
- Quadratic Equations - DPP 02 - Arjuna JEE 2024Document2 pagesQuadratic Equations - DPP 02 - Arjuna JEE 2024bhavyansh1707No ratings yet
- Angular Momentum 1Document29 pagesAngular Momentum 1Atif ImamNo ratings yet
- The Importance of Using Manipulatives in Teaching Math TodayDocument26 pagesThe Importance of Using Manipulatives in Teaching Math TodayROMNICK DIANZONNo ratings yet
- COMSATS University Islamabad, Lahore Campus: Lab Terminal Exam (Spring-2020)Document5 pagesCOMSATS University Islamabad, Lahore Campus: Lab Terminal Exam (Spring-2020)Hafiz Hassan JawadNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 Operators and ExpressionsDocument13 pagesUnit 3 Operators and ExpressionsLawrence OrewaNo ratings yet
- BDAT 4 Mathematics Paper 3 Problem SolvingDocument5 pagesBDAT 4 Mathematics Paper 3 Problem SolvingZuri NoveloNo ratings yet
- Math Iecep GeasDocument4 pagesMath Iecep GeasMark JasonNo ratings yet
- Class QuestionsDocument161 pagesClass QuestionsKeithNo ratings yet
- H6Document2 pagesH6groziolNo ratings yet
- Creating A Scatter Plot in ExcelDocument8 pagesCreating A Scatter Plot in ExcelanisumiNo ratings yet
- Chia Green PaperDocument44 pagesChia Green PaperMuhammad TabishNo ratings yet
- VIP - Solving Systems of Equations by GraphingDocument21 pagesVIP - Solving Systems of Equations by Graphingtree5215No ratings yet
- 2ND Year Math Guess PaperDocument6 pages2ND Year Math Guess PaperM ShabanNo ratings yet
- Nonlinear Modeling and Control of Hydraulic ActuatorsDocument7 pagesNonlinear Modeling and Control of Hydraulic ActuatorsNachiketNo ratings yet
- Griffiths QMCH 1 P 1Document2 pagesGriffiths QMCH 1 P 1abc xyzNo ratings yet
- LPoverallDocument139 pagesLPoverallTanmay BelavadiNo ratings yet
- DSA - Linked List PDFDocument37 pagesDSA - Linked List PDFArun KumarNo ratings yet