Professional Documents
Culture Documents
14-Addition-to-alkenes_2019
14-Addition-to-alkenes_2019
Uploaded by
Djarkasi RoxaneCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
14-Addition-to-alkenes_2019
14-Addition-to-alkenes_2019
Uploaded by
Djarkasi RoxaneCopyright:
Available Formats
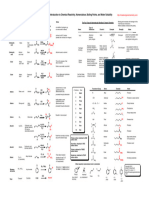
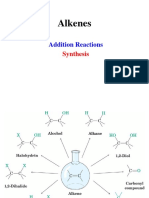
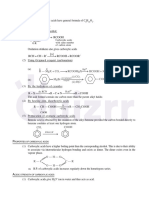
Additions to Alkenes "Master Organic Chemistry" Note - this sheet is not meant to be comprehensive.
Your course
masterorganicchemistry.com may provide additional material, or may not cover some of the
Reaction "Regiochemistry" "Stereochemistry" reactions shown here. Your course instructor is the final authority.
H OH
R R 1) BH 3 R R Sometimes you might see BH 3•THF or B 2H 6 used here: it's the same reagent in a slightly different form.
Anti-Markovnikoff syn addition
Hydroboration The base (can be NaOH, KOH, identity unimportant) helps make H 2O2 more reactive. The reaction is anti -
R H 2) NaOH, R H
Markovnikoff because the H–B bond is polarized toward H (electronegativity of H = 2.2, B = 2.0) - the H
H 2O 2 adds to the carbon best able to stabilize positive charge (i.e. the most substituted one).
1) Hg(OAc) 2
H 2O HO H
R R This reaction goes through 3-membered "mercurinium" ion. The NaBH 4 step removes the
Oxymercuration Markovnikoff syn + anti mercury. While the addition is anti, the overall reaction is stereorandom because this step involves a carbon
R H 2) NaBH 4 R R
R H based free radical (usually not discussed). Alternatively, an alcohol used in place of water will produce an ether.
HO H
R R H 2SO4 Strong acid protonates the alkene, generating free carbocation. Watch out for
Markovnikoff syn + anti
Acid-catalyzed addition of H 2O R possibility of rearrangements when a tertiary carbocation could be generated through a 1,2 shift.
R H H 2O R
(hydration) R H HSO 4– anion is not strongly nucleophilic, hence it does not add. Gives a mixture of syn and anti products
due to the free carbocation.
Cl H
R R HCl Markovnikoff syn + anti
Addition of HX
R H R R
R H HCl and HBr (as well as HI, not pictured) protonate the alkene to give a free
carbocation which can then be trapped by the halide anion. Gives a mixture of syn and anti
Br H
R R HBr
Addition of HX Markovnikoff syn + anti
R H R R
R H
Br
Br R R Bromonium ion mechanism
Br 2 R R R H
Bromination N/A anti addition
R H Br or H 2O/ROH depending on solvent
R R Br
The key detail in these reactions is solvent: water and alcohol solvents will form the
R H HO halohydrin products (the ones containing the OH and Br). All other solvents (you might
Br 2 R
Halohydrin Formation R
Markovnikoff anti addition see CCl4, CHCl 3, hexane, etc. ) provide the dibromide.
H 2O R H
Br
Cl
R R Cl2 R R As with bromination, above. Although not depicted, use of water or alcohol as solvent
Chlorination N/A anti addition
R H R H will also lead to formation of the halohydrin product (also anti).
Cl
HO OH
R R OsO 4 R R Osmium is a transition metal. The tools won't be given in this course to fully understand how this reaction
Dihydroxylation N/A syn addition
R H works. Occasionally a second reagent like NaHSO 3, H 2S, or Na 2S2O3 is also given as a reactant in this
R H reaction - minor detail, it's used to remove the osmium from the hydroxyl groups.
HO OH Keywords are "cold, dilute". NOTE: If "heat" or "acid" is mentioned in the conditions, the diol will
R R KMnO 4 R R N/A syn addition be cleaved to provide carbonyl compounds (same reaction as ozonolysis with oxidative workup,
Dihydroxylation R H cold, dilute R H below).
NOTE: "anti" hydroxylation can be achieved through epoxidation followed by treatment with NaOH (basic)
or aqueous acid ( H 3O+ )
O
OH O
R O O R RCO 3H is a peroxyacid. A common peroxy acid for this reaction is m-CPBA
R R R N/A syn addition Cl OH
Epoxidation (m-chloroperoxybenzoic acid). If H 3O+, heat is written afterwards, this
R H R H O
is opening of the epoxide to give the diol (anti-selective) m-CPBA
H2 H H
R R R R N/A syn addition The catalyst can vary - you might see Pt or Ni as well. All provide the same product with the same
Hydrogenation
R H Pd/C R H stereochemistry.
H Br
R H HBr Peroxides generate the Br• radical, which adds to the double bond in the way that will generate the
Radical addition of HBr Anti-Markovnikoff syn + anti most stable radical (i.e. the radical will go on to the most substituted carbon). This explains the
H H peroxides R H
H H selectivity for the anti-Markovnikoff product. It gives a mixture of syn and anti because it goes through
(RO-OR) a free radical process.
O3
Ozonolysis (Reductive workup) R R
O + O
S R H Reductive workup: Zinc (Zn), or dimethyl sulfide (DMS, Me 2S) is a reducing agent. It reduces excess ozone, allowing for isolation
R R CH3 CH3 (or Zn/H+)
of the aldehyde.
R H
O3 R R Oxidative workup: Hydrogen peroxide is used to obtain the carboxylic acid instead of the aldehyde.
O + O Can also use KMnO 4 and acid
Ozonolysis (Oxidative Workup) R OH
H 2O 2 Omissions, Mistakes, Suggestions?
This reaction goes through addition of a carbene (actually, "carbenoid") to james@masterorganicchemistry.com
H H
CH2I 2 C the double bond. The reaction is stereospecific.
R R R R This sheet copyright 2019, James A. Ashenhurst
Cyclopropanation N/A syn addition Another set of conditions to provide a cyclopropane is CHCl3 with strong
R H masterorganicchemistry.com
Zn/Cu R H base (NaOH), which makes the dichlorocyclopropane.
You might also like
- Schaum's Easy Outline of Organic Chemistry, Second EditionFrom EverandSchaum's Easy Outline of Organic Chemistry, Second EditionRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- ACS Study GuideDocument7 pagesACS Study GuideRachel Garner100% (1)
- Addition To Alkenes CheatsheetDocument1 pageAddition To Alkenes CheatsheetChinmay MhatreNo ratings yet
- 14 Addition To Alkenes 2019Document1 page14 Addition To Alkenes 2019ayushupadhyay548No ratings yet
- DH AmakaDocument91 pagesDH AmakaazsaNo ratings yet
- Sample Study Material: IIT-JAM ChemistryDocument74 pagesSample Study Material: IIT-JAM ChemistryPradeep PrajapatiNo ratings yet
- Physical Organic Chemistry Chapter ThreeDocument40 pagesPhysical Organic Chemistry Chapter ThreeMULUKEN TILAHUNNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 Lecture Slides PDFDocument179 pagesChapter 8 Lecture Slides PDFjoseph changNo ratings yet
- Synthesis of ImidazolesDocument5 pagesSynthesis of ImidazolesMuhammad SalehNo ratings yet
- CHEM F111 General Chemistry: Electrophilic Addition ReactionDocument18 pagesCHEM F111 General Chemistry: Electrophilic Addition ReactionUtkarsh BansalNo ratings yet
- Winstein: Concept of Ion Pairs: Contact or Tight Ion PairDocument14 pagesWinstein: Concept of Ion Pairs: Contact or Tight Ion PairAnil Kumar100% (1)
- Organic (Nag3)Document25 pagesOrganic (Nag3)riaz.atom4No ratings yet
- Learning Guide For Chapter 12 - Alkenes (II) : I. Addition Reactions of AlkenesDocument21 pagesLearning Guide For Chapter 12 - Alkenes (II) : I. Addition Reactions of AlkenesJaqen H'gharNo ratings yet
- Summary of Reactions chm2120Document4 pagesSummary of Reactions chm2120sabrinasameja75No ratings yet
- Plij Gib Me BookDocument16 pagesPlij Gib Me BookDarsheel AmbasthaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Elimination Reaction - 2016Document19 pagesChapter 5 Elimination Reaction - 2016Syuhadah NoordinNo ratings yet
- Solutions Test 3Document4 pagesSolutions Test 3roorayNo ratings yet
- Organic Assignment 2119317Document11 pagesOrganic Assignment 2119317Pranali ParabNo ratings yet
- Nature - White - 2011 (Desaturacions) PDFDocument7 pagesNature - White - 2011 (Desaturacions) PDFCarlotaNo ratings yet
- Organic Reaction Mechanisms (Lecture 3) : Reaction Mechanism Bonding ChangesDocument22 pagesOrganic Reaction Mechanisms (Lecture 3) : Reaction Mechanism Bonding ChangesDoris GladiaNo ratings yet
- Carbonyls - Alpha SubstitutionsDocument8 pagesCarbonyls - Alpha SubstitutionsRavi Kiran KoduriNo ratings yet
- SynrxnsDocument48 pagesSynrxnsRonak MantriNo ratings yet
- Amino Acid and BiochemistryDocument10 pagesAmino Acid and BiochemistryUNKNOWNNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13Document24 pagesChapter 13abubakarabubakarbah563No ratings yet
- 686bMkQ0N7YppKfBrnE2 PDFDocument13 pages686bMkQ0N7YppKfBrnE2 PDFMayank BaghelNo ratings yet
- Alkenerxnsrevise s15 PDFDocument12 pagesAlkenerxnsrevise s15 PDFBädắrđîńJāmẳlīNo ratings yet
- Chapter 16 Lecture NotesDocument15 pagesChapter 16 Lecture NotesJSGINo ratings yet
- Course 201N 1 Semester 2006-2007 Inorganic Chemistry Instructor: Jitendra K. BeraDocument10 pagesCourse 201N 1 Semester 2006-2007 Inorganic Chemistry Instructor: Jitendra K. BeraNITU KUMARINo ratings yet
- Organic ChemistryDocument15 pagesOrganic ChemistryVedant SharmaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12Document46 pagesChapter 12Eshita SharmaNo ratings yet
- Iit Reductions PDFDocument71 pagesIit Reductions PDFAshish SinghNo ratings yet
- Lecture Series 5 Organic ChemistryDocument36 pagesLecture Series 5 Organic ChemistryWiza MulengaNo ratings yet
- 29 Carboxylic Acids Formula Sheets QuizrrDocument9 pages29 Carboxylic Acids Formula Sheets Quizrrpowerranger34873No ratings yet
- Intro SummaryDocument1 pageIntro SummaryChastine CruzNo ratings yet
- Alkenes ReactionsDocument69 pagesAlkenes ReactionsAhmad SayyedahmadNo ratings yet
- 11H Alkene2Document35 pages11H Alkene2henriquejfdsantos4No ratings yet
- ORM-II TH EDocument12 pagesORM-II TH EelonmuskonmoonNo ratings yet
- Xii OrganicDocument25 pagesXii OrganicArindam GoswamiNo ratings yet
- HaloalkanesDocument12 pagesHaloalkanescoding727treeNo ratings yet
- 16H Carbonyl PDFDocument60 pages16H Carbonyl PDFJose Erick Ortega ValenciaNo ratings yet
- HalogenoalkanesDocument11 pagesHalogenoalkanesmrmemer6996No ratings yet
- 29 Carboxylic Acids Formula Sheets QuizrrDocument8 pages29 Carboxylic Acids Formula Sheets QuizrrArjunNo ratings yet
- 16 Cie HalogenoalkanesDocument5 pages16 Cie HalogenoalkanesAnanNo ratings yet
- Named Reaction ProjectDocument2 pagesNamed Reaction Projectrajnibhati437No ratings yet
- Organic ChemistryDocument32 pagesOrganic Chemistryj.obriain94No ratings yet
- Indoles and IsoindolesDocument16 pagesIndoles and IsoindolesSylvester AsareNo ratings yet
- 5L ReductionsDocument20 pages5L ReductionsCarlos Javier Orellana OrtizNo ratings yet
- General Organic ChemistryDocument5 pagesGeneral Organic ChemistryG RNo ratings yet
- 3 3 Revision Guide HalogenoalkanesDocument5 pages3 3 Revision Guide HalogenoalkanesmarieNo ratings yet
- Hydrocarbon (Ncert Punch)Document17 pagesHydrocarbon (Ncert Punch)Raj DoneNo ratings yet
- Organic Synthesis. ReductionsDocument64 pagesOrganic Synthesis. ReductionsKartik RanaNo ratings yet
- Acid - Base Equilibria: Prof. Dr. Elham Y. HashemDocument12 pagesAcid - Base Equilibria: Prof. Dr. Elham Y. HashemMoamen MohamedNo ratings yet
- Addition Reactions of AlkenesDocument18 pagesAddition Reactions of AlkenesPinaNo ratings yet
- AlkyneDocument11 pagesAlkyneAnil KumarNo ratings yet
- Functional Group InterconversionDocument28 pagesFunctional Group InterconversionIvy JoyceNo ratings yet
- 9 Alkenes Alkynes PostDocument26 pages9 Alkenes Alkynes Postapi-3767370No ratings yet
- Intro To Organic Reactions CHM457Document73 pagesIntro To Organic Reactions CHM457Zafrel ZaffNo ratings yet
- L2 Alkynes and AromaticsDocument17 pagesL2 Alkynes and AromaticsCheng FuNo ratings yet
- Inorganic Reactions and Methods, The Formation of Bonds to Hydrogen (Part 1)From EverandInorganic Reactions and Methods, The Formation of Bonds to Hydrogen (Part 1)No ratings yet
- 9701/22/M/J/20 © Ucles 2020Document10 pages9701/22/M/J/20 © Ucles 2020Fire stormNo ratings yet
- Copper ElectroplatingDocument21 pagesCopper ElectroplatingRahul PandeyNo ratings yet
- MC Acids and AlkalisDocument12 pagesMC Acids and Alkalisapi-3826629100% (1)
- United States Patent: Ca (OH) 2, P7 CasoDocument8 pagesUnited States Patent: Ca (OH) 2, P7 CasoViolanda PranajayaNo ratings yet
- Ball ValvesDocument112 pagesBall ValvesAlexjohn2009No ratings yet
- Is 1367 - 13 PDFDocument4 pagesIs 1367 - 13 PDFsat palNo ratings yet
- Solids Specific Heat Capacity TableDocument3 pagesSolids Specific Heat Capacity TableDominic LibradillaNo ratings yet
- 12 Chemistry Impq CH08 D and F Block Elements 01Document17 pages12 Chemistry Impq CH08 D and F Block Elements 01L38Santanu DebnathNo ratings yet
- Phosphor Bronze and Nickel Silver Sheet and Strip StandardDocument3 pagesPhosphor Bronze and Nickel Silver Sheet and Strip StandardScott Kramer100% (1)
- BT Soldamoll 220 enDocument1 pageBT Soldamoll 220 enSyed Noman AhmedNo ratings yet
- Refining of Stainless SteelsDocument27 pagesRefining of Stainless SteelsirajfarjiNo ratings yet
- 6.5 Electricity and Chemistry Ms - Igcse Cie Chemistry - Extended Theory PaperDocument6 pages6.5 Electricity and Chemistry Ms - Igcse Cie Chemistry - Extended Theory PaperBerryNo ratings yet
- Selective Process Steps For The Recovery of Scandium From Jamaican Bauxite ResidueDocument11 pagesSelective Process Steps For The Recovery of Scandium From Jamaican Bauxite ResidueŞerifKayaNo ratings yet
- Neutrophiles and ElectrophilesDocument2 pagesNeutrophiles and Electrophileswhydaspam joeNo ratings yet
- Sample Paper-Ftre-2022-Class-X-P2-PcmDocument20 pagesSample Paper-Ftre-2022-Class-X-P2-Pcmhipakin454100% (1)
- Unit - 2 Cutting-Tool MaterialsDocument23 pagesUnit - 2 Cutting-Tool MaterialsRavichandran G100% (3)
- IGCSE O Level Essential Chemistry Third Edition Answer Key by OxfordDocument40 pagesIGCSE O Level Essential Chemistry Third Edition Answer Key by OxfordHninn Aye WaiNo ratings yet
- J K NorskovDocument27 pagesJ K Norskovvazzoleralex6884No ratings yet
- Ion Chromatography in Environmental AnalysisDocument23 pagesIon Chromatography in Environmental AnalysisCompras FQ AnaltecNo ratings yet
- Inert GasesDocument8 pagesInert Gasesbiswajit.ghoshNo ratings yet
- Cast Iron Pipe Fittings Corrosion AnalysisDocument6 pagesCast Iron Pipe Fittings Corrosion AnalysisTeby RodoNo ratings yet
- Astm F2215 15Document10 pagesAstm F2215 15Jed Kevin MendozaNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 9 Science Chapter 3 Atoms and Molecules Revision NotesDocument45 pagesCBSE Class 9 Science Chapter 3 Atoms and Molecules Revision NotesOm KumarNo ratings yet
- Chm101: Introductory Chemistry 1 MODULE 1: Methods of Science Lecture Four: Types of Chemical ReactionsDocument34 pagesChm101: Introductory Chemistry 1 MODULE 1: Methods of Science Lecture Four: Types of Chemical ReactionsOluwabusolami Akinola100% (1)
- PR-Request FormDocument2 pagesPR-Request FormVajid MadathilNo ratings yet
- PKa Table of AcidsDocument1 pagePKa Table of AcidsGuery SaenzNo ratings yet
- ASTM E415-21 Standard Test Method For Analysis For Carbon and Low-Aloy Steel by Spart Atomic Emissision SpectrometryDocument12 pagesASTM E415-21 Standard Test Method For Analysis For Carbon and Low-Aloy Steel by Spart Atomic Emissision SpectrometryMOHD SAZALI BIN SALLEHNo ratings yet
- PP1 Kimia F5 K2Document27 pagesPP1 Kimia F5 K2Zul Adli AliNo ratings yet
- As 3515.2-2002 Gold and Gold Bearing Alloys Determination of Gold Content 30 Percent To 99.5 Percent - GravimDocument7 pagesAs 3515.2-2002 Gold and Gold Bearing Alloys Determination of Gold Content 30 Percent To 99.5 Percent - GravimSAI Global - APACNo ratings yet
- Micro Electro DosDocument9 pagesMicro Electro DosCesar Segales HillpaNo ratings yet