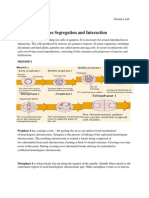
Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Advance DPP_A and B + Solutions
Advance DPP_A and B + Solutions
Uploaded by
9-E PRADYOT SINHACopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Advance DPP_A and B + Solutions
Advance DPP_A and B + Solutions
Uploaded by
9-E PRADYOT SINHACopyright:
Available Formats
The Fundamental Unit of Life (Class 9)
ss
The Fundamental Unit of Life DPP – 01
Section - A
Q.1 to Q.9 are multiple choice questions. Each has four options (1), (2), (3) and (4) out of which only one option
is correct.
1. Which of the following cells have the same components as shown in the cell given below?
Cell membrane
Cytoplasm
Nucleus
(1) Muscle cell
(2) Nerve cell
(3) Human red blood cells
(4) Both (1) and (2)
2. Identify the organism that contains nerve cell.
(1) Yeast
(2) Spirogyra
(3) Earthworm
(4) Amoeba
3. ________ was the first one to observe free living cells. The term cell was given by __________. Cell theory was
proposed by __________ and __________. All cells arise from preexisting cells was suggested by __________.
Select the correct sequence of names to complete the above paragraph.
(1) Robert Hooke, Virchow, Anton Von Leeuwenhoek, Schleiden, Schwann
(2) Anton Von Leeuwenhoek, Robert Hooke, Schleiden, Schwann, Virchow
(3) Robert Hooke, Virchow, Schleiden, Schwann, Anton Von Leeuwenhoek
(4) Anton Von Leeuwenhoek, Virchow, Schleiden, Schwann, Robert Hooke
4. Cells are of different shapes and sizes. Some cells are irregular in shape such as __________
(1) Amoeba
(2) Red Blood cell
(3) Leucocyte
(4) Both (1) & (3)
Digital Pvt. Ltd. [1]
The Fundamental Unit of Life (Class 9)
5. What is an exception to cell theory?
ss
(1) Algae
(2) Bacteria
(3) Virus
(4) Fungi
6. Robert Hooke is a well-known scientist as he discovered _________
(1) Lysosome
(2) Vacuole
(3) Cell
(4) Nucleus
7. Knoll and Ruska invented
(1) Simple microscope
(2) Electron microscope
(3) Compound microscope
(4) All of the above
8. How many cells are there in hen’s egg?
(1) 1
(2) 10
(3) 100
(4) 1000
9. “Omnis cellula-e-cellula”, an idea of Rudolf Virchow means that
(1) All organisms are composed of cells
(2) All living cells arise from pre existing cells.
(3) Cells are basic unit of life.
(4) Every organism starts life as a single cell.
Q. 10 is multiple choice question. It has four options (1), (2), (3) and (4) out of which ONE or MORE THAN ONE
option may be correct.
10. The cell theory states that
(1) The cell is the basic unit of life.
(2) Cells arise from pre-existing cells.
(3) Bodies of living beings are made up of cells.
(4) Activities of an organism are the sum total of activities of its cells.
s Digital Pvt. Ltd. [2]
The Fundamental Unit of Life (Class 9)
SECTION B
ss
1. From the given image of compound microscope. Identify X and Y.
2. Match the Column I with the Column II.
Column - I Column - II
A Elongated and branched P Paramecium
B Slipper Shaped Q Nerve Cell
C Cuboidal R RBC
D Discoidal Shaped S Germ cells of gonads
3. Match the column I with the column II.
Column - I Column - II
A Robert Hooke P Nucleus
B J.E. Purkinje Q Dead Cell
C Robert Brown R Living Cell
D Anton Van Leeuwenhoek S Protoplasm
Analogy Type Questions
4. Germ cells : Cuboidal : : Liver cell : _____
5. Robert Hooke : Cell : : Robert Brown : _____
Read the following statements and give your answer as true or false.
6. The size of an organism is dependent upon the number of cells and not on the size of the cell.
s Digital Pvt. Ltd. [3]
The Fundamental Unit of Life (Class 9)
7. Muscle cell is spindle shaped.
ss
Read the following statements and fill in the blanks.
8. A cell is the ________ and functional unit of life.
9. The smallest cell known is that of ____________.
Subjective Question
10. What is cell theory?
s Digital Pvt. Ltd. [4]
The Fundamental Unit of Life (Class 9)
ss SOLUTIONS DPP – 1
Section - A
Answer Key
Question 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
Answer 4 3 2 4 3 3 2 1 1 1,2,3, 4
1. Option (4)
Muscle cell and Nerve cell consists of cell membrane, nucleus and cytoplasm.
2. Option (3)
Earthworm contains nerve cell.
3. Option (2)
Anton Von Leeuwenhoek was the first one to observe free living cells. The term cell was given by Robert Hooke.
Cell theory was proposed by Schleiden and Schwann. All cells arise from pre-existing cells was suggested by
Virchow.
4. Option (4)
Cells which are irregular in shape include amoeba and leucocyte.
5. Option (3)
Virus is an exception to cell theory.
6. Option (3)
Robert Hooke is a well-known scientist as he discovered cell.
7. Option (2)
Knoll and Ruska invented the electron microscope.
8. Option (1)
Hen’s egg is a single cell.
9. Option (1)
PPLO stands for Pleuro pneumonia like organism.
10. Option (1,2,3,4)
The cell theory states that the cell is the basic unit of life, Cells arise from pre-existing cells, Bodies of living
beings are made up of cells. Activities of an organism are the sum total of activities of its cells.
s Digital Pvt. Ltd. [5]
The Fundamental Unit of Life (Class 9)
Section - B
ss
1. X - Eyepiece
Y - Stage
2. A - q, B - p, C - s, D - r
3. A- q, B - s, C - p, D - r
4. Polygonal
5. Nucleus
6. True
7. True
8. Structural
9. PPLO
10. The "cell theory" was formulated by two biologists, M. J. Schleiden (1838), and T. Schwann (1839).
According to them, the cell is the structural and functional unit of all living beings. The cell theory was further
expanded by Virchow.
Cell theory, states that
(i) Bodies of the living beings are made up of cells. The cell is the basic unit of life.
(ii) Activities of an organism are the sum total of activities of its cells.
(iii) Every new cell arises from pre-existing cells.
s Digital Pvt. Ltd. [6]
The Fundamental Unit of Life (Class 9)
ss
The Fundamental Unit of Life DPP – 02
Section - A
Q.1 to Q.5 are multiple choice questions. Each has four options (1), (2), (3) and (4) out of which only one option
is correct.
1. The shape of the cell determines the function it performs. Which of these best represents the shape of
the RBC?
(1)
(2)
(3)
(4)
2. A mature plant cell has
(1) Protoplasm and vacuole
(2) Vacuole and cell wall
(3) Cell wall and protoplasm
(4) Protoplasm, cell wall and vacuole
3. Amongst the following which is not a single membrane bound cell organelle?
(1) Plastid
(2) Endoplasmic Reticulum
(3) Golgi Body
(4) Lysosomes
s Digital Pvt. Ltd. [7]
The Fundamental Unit of Life (Class 9)
4. The figure shows two different types of cells
ss
(P) (Q)
Which of the following statements is NOT true about the given cells?
(1) All of them have a nucleus.
(2) All of them carry out life processes.
(3) All of them are animal cells.
(4) P is a nerve cell.
5. Sakshi stated that protoplasm consists of cytoplasm and nucleus.
(1) The statement she gave was incorrect.
(2) The statement she gave was totally correct.
(3) The statement she gave was partially correct.
(4) None of the above.
s Digital Pvt. Ltd. [8]
The Fundamental Unit of Life (Class 9)
SECTION B
ss
1. Identify the organisms given below.
(i) (ii)
Classify them as unicellular or multicellular?
2. Match the Column - I with Column - II.
Column - I Column - II
A Paramecium P Multicellular
B Plastid Q Unicellular
C Plant R Single membrane bound
D Lysosome S Double membrane bound
Read the following statements and give your answer as true or false.
3. All the cells of multicellular organisms have similar basic structure and undertake similar basic
functions.
4. Mitochondria is a single membranous cell organelle.
Read the following statements and fill in the blanks.
5. Chlamydomonas is an example of ______________ organism.
6. Cytoplasm includes ___________ and _________________.
Subjective Questions
7. Name two examples of multicellular organisms.
8. Draw a flow chart of structure of cell.
9. Name two cell organelles which are covered by double membrane.
10. Name two examples of unicellular organisms.
s Digital Pvt. Ltd. [9]
The Fundamental Unit of Life (Class 9)
ss SOLUTIONS DPP – 2
Section - A
Answer Key
Question 1 2 3 4 5
Answer 3 2 1 1 2
1. Option (3)
RBC has discoidal shape and lacks nucleus
2. Option (2)
A mature plant cell has Protoplasm, cell wall and vacuole
3. Option (1)
Plastid are double membrane bound cell organelles.
4. Option (1)
RBC does not have nucleus.
5. Option (2)
The statement made by Sakshi that protoplasm consist of cytoplasm and nucleus is correct.
s Digital Pvt. Ltd. [10]
The Fundamental Unit of Life (Class 9)
Section - B
ss
1. (i) Chlamydomonas - unicellular
(ii) Amoeba - unicellular
2. A -Q, B- S, C- P, D- R
3. True
4. False
5. Unicellular
6. Cytosol, cell organelles
7. Plants, Animals
8.
Structure of Cell
Cell membrane Protoplasm
Cytoplasm Nucleus
Nuclear membrane
Cytosol Cell organelles Nucleoplasm
Nucleolus
Chromatin threads
Single Double Non
membranous membranous membranous
Endoplasmic Plastid Ribosomes
Reticulum Mitochondria Centrosomes
Golgi body
Lysosomes
9. Mitochondria
Plastid
10. Amoeba
Paramecium
s Digital Pvt. Ltd. [11]
The Fundamental Unit of Life (Class 9)
ss
The Fundamental Unit of Life DPP – 03
Section - A
Q.1 to Q.5 are multiple choice questions. Each has four options (1), (2), (3) and (4) out of which only one option
is correct.
1. Human cheek cells stained in methylene blue and mounted in glycerine were observed with the help of
a compound microscope. The components of the cell which were seen are:
(1) Cell wall, cytoplasm, nucleus
(2) Plasma membrane, cytoplasm, nucleus, mitochondria
(3) Plasma membrane, cytoplasm, nucleus
(4) Plasma membrane, cytoplasm, nucleus, mitochondria, lysosomes, Golgi bodies.
2. Given below are four operations for preparing a temporary mount of human cheek cells:
(i) Taking a scraping from the inner side of the cheek and spreading it on a clean slide
(ii) Putting a drop of glycerine on the material
(iii) Adding two or three drops of methylene blue
(iv) Rinsing the mouth with fresh water and disinfectant solution
Identify the correct sequence of these operations.
(1) (i)—(ii)—(iii)—(iv)
(2) (iv)—(i)—(iii)—(ii)
(3) (iv)—(i)—(iii)—(ii)
(4) (i)—(iii)—(ii)—(iv)
3. Cells are first focused in microscope under
(1) 40 X
(2) 10 X
(3) 100 X
(4) Any of these
4. The materials commonly used for staining and mounting human cheek cells are respectively
(1) Safranin and glycerin
(2) Methylene blue and glycerin
(3) Safranin and methylene blue
(4) Fast green and glycerin
s Digital Pvt. Ltd. [12]
The Fundamental Unit of Life (Class 9)
5. While observing an onion peel slide under the microscope, Paheli noted its characteristics. Which of
ss
these does she not see?
(1) Cells attached edge to edge without intercellular space
(2) Presence of single nucleus in the cell
(3) Presence of cell wall around each rectangular cell
(4) All of these
s Digital Pvt. Ltd. [13]
The Fundamental Unit of Life (Class 9)
SECTION B
ss
1. These are diagrams showing steps of onion peel experiments. Give the statement for each step.
(i) ..................................................................................................................... .
(ii) ..................................................................................................................... .
Onion peel
(iii) ..................................................................................................................... .
Onion peel
(iv) ..................................................................................................................... .
Safranin
s Digital Pvt. Ltd. [14]
The Fundamental Unit of Life (Class 9)
(v) ..................................................................................................................... .
ss
Glycerine
Read the following statements and give your answer as true or false.
2. Cheek cells having cell wall.
3. Onion peel cells have large vacuole.
Read the following statements and fill in the blanks.
4. _____________stain is used to stain plant cells usually.
5. _________stain is used for staining the human cheek cell during the experiment.
6. Human cheek cells are flat and _________________ in shape.
Subjective Questions
7. Why is glycerine used for mounting of the onion peel cells or human cheek cells ?
8. Why is it essential to place the coverslip gently to avoid entry of air bubbles?
9. Why is staining done before mounting?
10. What are the precautions we should use during human cheek cell experiment ?
s Digital Pvt. Ltd. [15]
The Fundamental Unit of Life (Class 9)
ss SOLUTIONS DPP – 3
Section - A
Answer Key
Question 1 2 3 4 5
Answer 3 3 2 2 3
1. Option (3)
The components of the human cheek cell which were seen are plasma membrane, cytoplasm, nucleus.
2. Option (3)
Rinsing the mouth with fresh water and disinfectant solution ; Taking a scraping from the inner side of the
cheek and spreading it on a clean slide ; Adding two or three drops of methylene blue and Putting a drop of
glycerine on the material.
3. Option (2)
Cells are first focused in microscope under 10 X.
4. Option (2)
Methylene blue and glycerine are commonly used for staining and mounting human cheek cells.
5. Option (3)
She did not observed presence of cell wall around each rectangular cell.
s Digital Pvt. Ltd. [16]
The Fundamental Unit of Life (Class 9)
Section - B
ss
1. (i) Take an onion.
(ii) Separate out a thin onion scale from an onion. Tear it from the concave side to get a transparent, thin
and membranous onion peel piece called epidermis.
(iii) Now keep this onion peel piece in a watch glass containing water.
(iv) Cut out a small portion of this peel and place it flat on a glass slide on a drop of water with the help of
a thin camel-hair paint brush. Add a drop of safranin.
(v) Drain out the excess stain and mount the onion peel in a drop of glycerine under a coverslip. Examine
the slide under low and high powers of a compound microscope.
2. False
3. True
4. Safranin
5. Methylene blue
6. Polygonal
7. It prevents drying up the specimen.
8. It is essential to place the coverslip gently as in case of soft specimens there is the possibility of damaging it.
But the main purpose is to avoid the entry of air bubbles in the slide that hinders the clear vision.
9. Staining of specimen is done so as to get a better look at it. Staining does more than just highlighting the outline
of cells. Some stains can penetrate cell wall and highlight cell components, and this helps in visualising metabolic
process. After all this is completed, then the specimen is mounted so that changes in the specimen can be seen
for a period of time. Hence mounting is done after staining.
10. (i) Do not scrap the cheek too hard as it may injure the buccal lining.
(ii) Scrapped material should be spread uniformly on the slide.
(iii) Excess of stain should be drained off.
(iv) There should be no air-bubble under the coverslip.
s Digital Pvt. Ltd. [17]
The Fundamental Unit of Life (Class 9)
ss
The Fundamental Unit of Life DPP – 04
Section - A
Q.1 to Q.8. are multiple choice questions. Each has four options (1), (2), (3) and (4) out of which only one option
is correct.
1. The lipid molecules present in plasma membrane have polar heads and non-polar tails (as shown in
figure). Which option represents the correct arrangement of lipids in lipid bilayer?
Polar head
Non polar tail
(1)
(2)
(3)
(4)
2. Which of the following statements best describes the composition of plasma membrane?
(1) Plasma membrane is composed of two layers - One layer of phospholipid and one layer of proteins.
(2) Plasma membrane is bilayer of proteins with associated lipids and carbohydrates.
(3) Plasma membrane is bilayer of phospholipids with associated proteins.
(4) None of these.
3. Find out the incorrect statement
(1) The movement of water across a semipermeable membrane is affected by the amount of substances
dissolved in it.
(2) Membranes are made up of organic molecules like proteins and lipids.
(3) Molecules soluble in organic solvents can easily pass through the membrane.
(4) Plasma membrane contains chitin sugar in plants.
s Digital Pvt. Ltd. [18]
The Fundamental Unit of Life (Class 9)
4. Which labelled part in the diagram below help in cell - cell recognition?
ss
A
B
(1) A
(2) B
(3) C
(4) D
5. Carbohydrates of plasma membrane help in
(1) Passive transport
(2) Active transport
(3) Cell adhesion
(4) Cell-cell recognition
6. Study the figure carefully. In which direction the net movement of water will take place?
Solution 1 Solution 2
(1) From solution 1 to solution 2
(2) From solution 2 to solution 1
(3) Both A and B
(4) No movement will take place
7. Most cell membrane are principally composed of__________.
(1) DNA and ATP
(2) Protein and starch
(3) Chitin and starch
(4) Nucleotides and amino acid
s Digital Pvt. Ltd. [19]
The Fundamental Unit of Life (Class 9)
8. Plasma membrane is fluid structure due to presence of -
ss
(1) Carbohydrate
(2) Lipid
(3) Glycoprotein
(4) Polysaccharide
Q. 9 to Q.10 is multiple choice question. It has four options (1), (2), (3) and (4) out of which ONE or MORE THAN
ONE option may be correct.
9. Function of plasma membrane is/are
(1) The lipid bilayer is selectively permeable which allows only selected molecules to diffuse across the
membrane.
(2) It separates the content of the cell from its outside environment.
(3) It helps in maintaining the shape of the animal cell.
(4) It permits the animal cells to withstand hypotonic condition without bursting.
10. Molecules that can freely pass through cell membrane are
(1) Oxygen
(2) Carbon dioxide
(3) Amino acids
(4) Water
s Digital Pvt. Ltd. [20]
The Fundamental Unit of Life (Class 9)
SECTION B
ss
1. Observe the diagram given below and answer the question.
(i) The hydrophilic portion of a lipid molecule is ______________.
(ii) The proteins involved in transport is _____________.
2. Match the column - I with column - II.
Column - I Column -II
A Freely movable P Selectively permeable
B Plasma membrane Q Oxygen
C Fluid mosaic model R Singer and Nicolson
D Amoeba S Endocytosis
Read the following statements and give your answer as true or false.
3. Structure of plasma membrane was explained by Singer and Nicolson.
4. Plasma membrane provides shape to the cell.
Read the following statements and fill in the blanks.
5. The plasma membrane is flexible and made up of organic molecules called _________ and _____________.
6. Plasma membrane allows materials to enter and leave the cell through the tiny holes called__________.
Subjective Questions
7. What is active transport?
8. What is passive transport?
9. What are the functions of plasma membrane?
10. Who gave the fluid mosaic model of plasma membrane?
s Digital Pvt. Ltd. [21]
The Fundamental Unit of Life (Class 9)
ss SOLUTIONS DPP – 4
Section - A
Answer Key
Question 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
Answer 2 3 4 1 4 1 2 2 1, 2, 3 1, 2, 4
1. Option (2)
The lipid molecules present in plasma membrane have polar heads and non-polar tails (as shown in figure).
2. Option (3)
Plasma membrane is bilayer of phospholipids with associated proteins best describes the composition of
plasma membrane,
3. Option (4)
Plasma membrane do not contain chitin sugar in plants.
4. Option (1)
Part (A) labelled in the diagram below help in cell - cell recognition.
5. Option (4)
Carbohydrates of plasma membrane help in cell-cell recognition.
6. Option (1)
The semipermeable barrier between the protoplasm and outer environment in a plant cell is membrane.
7. Option (2)
Most cell membrane are principally composed of protein and starch.
8. Option (2)
Plasma membrane is fluid structure due to presence of lipid.
s Digital Pvt. Ltd. [22]
The Fundamental Unit of Life (Class 9)
9. Option (1, 2, 3)
ss
Function of plasma membrane is
The lipid bilayer is selectively permeable which allows only selected molecules to diffuse across the
membrane. It separates the content of the cell from its outside environment. It helps in maintaining the shape
of the animal cell.
10. Option (1, 2, 4)
Molecules that can freely pass through cell membrane are Oxygen, Carbon dioxide, Water
s Digital Pvt. Ltd. [23]
The Fundamental Unit of Life (Class 9)
Section - B
ss
1. (i) D
(ii) E
2. A -Q, B-P, C -R, D - S
3. True
4. True
5. Lipids, proteins
6. Pores
7. Transport of substances across plasma membrane against the concentration gradient with expenditure of
energy is called active transport.
8. Transport of substances across plasma membrane along the concentration gradient i.e. from higher
concentration to lower concentration without expenditure of energy is called passive transport.
9 (i) It protects the internal components of the cell.
(ii) It provides shape to the cell.
(iii) It allows materials to enter and leave the cell through the tiny holes called pores.
10. Singer and Nicolson
s Digital Pvt. Ltd. [24]
The Fundamental Unit of Life (Class 9)
ss
The Fundamental Unit of Life DPP – 05
Section - A
Q.1 to Q5. are multiple choice questions. Each has four options (1), (2), (3) and (4) out of which only one option
is correct.
1. Four strips are cut from a fresh potato. The length of each strip is measured. One strip is placed in water
and others in different concentrations of sugar solution. After an hour, the strips were measured again.
The results are shown in the table. Which of the liquids P, Q, R and S in water?
Liquid Original length of strip (mm) Final length of strip (mm)
P 75 75
Q 78 80
R 82 80
S 86 85
(1) P
(2) Q
(3) R
(4) S
2. Ali performed an experiment in which he put two different cells P and Q in pure water. Cell P swelled
up and burst eventually while cell Q became tight and firm but did not burst. Which of the following is
the most appropriate inference?
(1) Cell sap of cell P is isotonic to the pure water.
(2) Cell sap of cell Q is isotonic to pure water.
(3) Cell P has been obtained from a plant.
(4) Cell Q is a bacterium.
3. A unicellular protist X, which has contractile vacuole to remove excess intracellular water, was placed in
salt solution of increasing osmolarity. The given graph shows the rate of contraction of vacuole to pump
out excess water against osmolarity of solution. Select the option that gives the correct explanation of
the data.
s Digital Pvt. Ltd. [25]
The Fundamental Unit of Life (Class 9)
(1) In an isotonic solution there is no diffusion of water in or out of the X, so the contraction rate is zero.
ss
(2) At higher osmolarity, more salt diffuses into X, therefore lower rates of contractions are required.
(3) The rate of contraction increases as osmolarity decreases because the amount of water entering X by
osmosis increases.
(4) The contractile vacuole is less efficient in solution of high osmolarity because of reduced respiration and
less production of ATP.
4. Study the given diagram representing the process of osmosis and select the correct statement
regarding this.
(1) Limb P of the U-tube functions like the root hair of a plant for the absorption of water.
(2) Net movement of sucrose molecules takes place from limb Q to limb P of the U-tube.
(3) Net movement of water molecules takes place from limb P to limb Q of the U-tube.
(4) Semi-permeable membrane allows only solute sucrose molecules to pass through it.
5. Find out the incorrect statement.
(1) Osmosis is a slow process, occurs down the concentration gradient and does not expand energy.
(2) Electron microscope uses very high voltage electricity. It uses electromagnets instead of glass lenses and
beam of electrons instead of light.
(3) A semi permeable membrane does not allow both solvent and solute molecules to pass through it.
(4) Active transport of materials is rapid and usually occurs against the concentration gradient involving carrier
proteins and energy in the form of ATP.
s Digital Pvt. Ltd. [26]
The Fundamental Unit of Life (Class 9)
SECTION B
ss
1. The plant cell was placed in three different solution named as A, B and C. The following were the
observations made -
Normal cell placed Normal cell placed Cytoplasm shrinks
Solution A Solution B cell placed
in Solution C
Identify the nature of solution A, B and C.
2. What does following experimental setup depicts?
Read the following statements and give your answer as true or false.
3. Absorption of water by plant root is the example of osmosis.
4. Absorption of water by unicellular fresh water organism is the example of diffusion.
Read the following statements and fill in the blanks.
5. _______________is the osmotic entry of water into a cell.
6. _______________is the osmotic withdrawal of water from a cell.
Subjective Questions
7. What is hypotonic solution?
8. If the human blood cells are placed in hypotonic solution, it is observed that they burst. Give reasons.
9. When a perfume bottle opens in a room, it spread uniformly in the room. Which process is responsible
for this?
10. What is diffusion?
s Digital Pvt. Ltd. [27]
The Fundamental Unit of Life (Class 9)
ss SOLUTIONS DPP – 5
Section - A
Answer Key
Question 1 2 3 4 5
Answer 2 4 3 1 4
1. Option (2)
The Liquid Q is water as the final length of strip expands while in case of others the strip either remain the
same or shrink.
2. Option (4)
Cell P swelled up and burst eventually so it could be animal cell while cell Q became tight and firm but did not
burst so it could be either plant or bacterial cell.
3. Option (3)
The rate of contraction increases as osmolarity decreases because the amount of water entering X by osmosis
increases.
4. Option (1)
Limb P of the U-tube functions like the root hair of a plant for the absorption of water.
5. Option (4)
Active transport of materials is slow process and usually occurs against the concentration gradient involving
the usage of ATP.
s Digital Pvt. Ltd. [28]
The Fundamental Unit of Life (Class 9)
Section - B
ss
1. Solution A - Isotonic solution.
Solution B - Hypotonic solution.
Solution C - Hypertonic solution.
2. Endosmosis
3. True
4. False
5. Endosmosis
6. Exosmosis
7. The external solution is dilute as compared to cell contents. It has more water content while the water content
is lower inside the cell. The cell membrane allows passage of water in both directions. Due to difference in
concentration of water molecules, there is net flow of water molecules into the cells. The phenomenon is as
called endosmosis.
8. If the human blood cells are placed in hypotonic solution, it is observed that they burst, because human blood
cells lack cell wall.
9. Diffusion
10. The process of movement of substance (solid, liquid & gas) from the region of its higher concentration to the
region of its lower concentration to spread uniformly in the given space is called diffusion.
s Digital Pvt. Ltd. [29]
The Fundamental Unit of Life (Class 9)
ss
The Fundamental Unit of Life DPP – 06
Section - A
Q.1 to 10. are multiple choice questions. Each has four options (1), (2), (3) and (4) out of which ONLY ONE option
is correct.
1. Animal cell do not show plasmolysis because
(1) They do not exhibit osmosis
(2) They do not possess cell wall
(3) They are living cells
(4) They have intercellular spaces
2. Cell wall of which one of these is not made of cellulose?
(1) Bacteria
(2) Hydrilla
(3) Mango tree
(4) Cactus
3. Take a clean glass slide and put few drops of water on it. Now place a complete rheo leaf on water
droplets and examine the cells of leaf under the high power of compound microscope. Put a few drops
of concentrated salt / sugar solution on the mounted rheo leaf on the glass slide. Wait for few minutes
and again observe the leaf under the high power of microscope.
What will be your observation after few minutes?
(1) Cell contents are separated from the cell wall.
(2) Cytoplasm along with plasma membrane has come to lie on one side of cell wall.
(3) A clear space is seen between the cell wall and protoplast of the cells.
(4) All of these.
4. The Bacterial cell wall is composed of?
(1) A phospholipid matrix
(2) A lipoprotein
(3) Chitin
(4) A polymer of sugars
5. The process of plasmolysis in plant cell is defined as:
(1) Breakdown of plasma membrane in hypotonic solution.
(2) Shrinkage of cytoplasm in hypertonic medium.
(3) Shrinkage of Nucleoplasm.
(4) None of these.
s Digital Pvt. Ltd. [30]
The Fundamental Unit of Life (Class 9)
6. Number of which of the following cell component remain fixed for a particular species?
ss
(1) Mitochondria
(2) Chromosome
(3) Cytoplasm
(4) Ribosome
7. A strain of an animal exists in wild in which there is only one nucleolus in the nucleus of each cell instead
of the usual two. When such animals are mated, approximately one quarter of the offspring have two
nucleoli per nucleus, one half have one nucleolus per nucleus and one quarter have no nucleolus at all.
Offspring without nucleoli die about four days after hatching. These offspring die because they do not
possess
(1) Mitochondria and are unable to obtain energy
(2) Centrioles and are unable to undergo cell division
(3) Golgi apparatus and are unable to remove dead cells
(4) Ribosomes are unable to manufacture proteins
8. The undefined nuclear region of prokaryote is
(1) Nucleus
(2) Nucleolus
(3) Nucleic acid
(4) Nucleoid
9. The structure of nuclear membrane facilitates
(1) Organization of spindle
(2) Nucleocytoplasmic exchange of materials.
(3) Chloroplast
(4) Golgi apparatus
10. Read the given statements and select the correct option.
Statement 1 : Nucleus of the cell can be compared to brain in animals.
Statement 2 : Nucleus contains genes responsible for transmission of characters from parents to
offspring.
(1) Both statements 1 and 2 are true and statement 2 is the correct explanation of statement 1.
(2) Both statements 1 and 2 are true but statement 2 is not the correct explanation of statement 1.
(3) Statement 1 is true but statement 2 is false.
(4) Both statements 1 and 2 are false.
s Digital Pvt. Ltd. [31]
The Fundamental Unit of Life (Class 9)
Section - B
ss
1. From the given picture of bacterial cell, mention the composition of the part labelled as Q?
2. From the diagram given below, identify the parts labelled as B and C.
3. Match the Column -I with Column - II.
Column I Column II
A Plant cell wall P Chitin
B Bacterial cell wall Q Cellulose
C Fungi cell wall R Peptidoglycan
Read the following statements and give your answer as true or false.
4. Cell wall is a protective and supportive coat.
5. Cell wall does not provide definite shape to the cell.
Read the following statements and fill in the blanks.
6. Cell wall is not present in ________________.
7. A cell can exist without ___________ like animal cell but can not exist without cell membrane.
Subjective Questions
8. What is the structure of cell wall?
9. What is the function of chromatin thread in nucleus?
10. What is the importance of nuclear pores in nucleus?
s Digital Pvt. Ltd. [32]
The Fundamental Unit of Life (Class 9)
ss SOLUTIONS DPP – 6
Section - A
Answer Key
Question 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
Answer 2 1 4 4 2 2 4 4 2 2
1. Option (2)
Animal cell do not show plasmolysis because they do not possess cell wall.
2. Option (1)
Bacterial cell wall is not made up of cellulose rather it is made up of polysaccharide.
3. Option (4)
Cell contents are separated from the cell wall, cytoplasm along with plasma membrane has come to lie on one
side of cell wall and a clear space is seen between the cell wall and protoplast of the cells is observed.
4. Option (4)
The Bacterial cell wall is composed of a polymer of sugars.
5. Option (2)
The process of plasmolysis in plant cell is defined as shrinkage of cytoplasm in hypertonic medium.
6. Option (2)
The number of chromosomes are fixed for a species.
7. Option (4)
Offspring without nucleoli die about four days after hatching. These offspring die because they do not possess
ribosomes.
8. Option (4)
The undefined nuclear region of prokaryote is nucleoid.
9. Option (2)
The structure of nuclear membrane facilitates nucleocytoplasmic exchange of materials.
10 Option (2)
Both statements 1 and 2 are true but statement 2 is not the correct explanation of statement 1.
s Digital Pvt. Ltd. [33]
The Fundamental Unit of Life (Class 9)
Section - B
ss
1. Q is cell wall. It is made up of peptidoglycan in bacteria.
2. B – chromatin material
C – Nucleolus
3. A -Q, B -R, C - P
4. True
5. True
6. Animals
7. Cell wall
8. Cell wall of plant cells is formed of a fibrous polysaccharide called cellulose, while it is formed of peptidoglycan
in bacteria and blue-green algae. It is formed of chitin in most of fungi.
9. Chromatin threads are intermingled with one another forming a network called chromatin reticulum.
Whenever the cell is about to divide the chromatin material gets organized into chromosomes.
10. Nucleopore takes part in exchange of different substances between nucleoplasm and cytoplasm.
s Digital Pvt. Ltd. [34]
The Fundamental Unit of Life (Class 9)
ss
The Fundamental Unit of Life DPP – 07
Q.1 to Q.10 are multiple choice questions. Each has four options (1), (2), (3) and (4) out of which only one option
is correct.
1. Animal cell lacking nuclei would also lack in
(1) Chromosome
(2) Ribosome
(3) Lysosome
(4) Endoplasmic reticulum
2. Read the following terms and select the pair that is related to inheritance of characters
(1) Cell wall and cell membrane
(2) Chromosome and mitochondria
(3) Chloroplast and cell membrane
(4) Chromosome and genes
3. Look at the given diagram.
Which of the following best describes the area marked P?
(1) It contains genes.
(2) Most of the cell processes takes place here.
(3) It controls the substance entering and leaving the cell.
(4) It protects the cell.
4. All the members of gupta family can roll their tongues. Which of the part of the nucleus carries
information regarding this characteristic?
(1) Nucleolus
(2) Chromatin thread
(3) Endoplasmic reticulum
(4) Nucleoplasm
s Digital Pvt. Ltd. [35]
The Fundamental Unit of Life (Class 9)
5. Which of the following is true about the Chromatids?
ss
(1) It is a haploid chromosome.
(2) It is a complete chromosome.
(3) It is a duplicate chromosome.
(4) It is one-half of the replicated chromosome.
6. The centromere is that part of the chromosome where___________.
(1) Nicking occurs.
(2) Chromatids are attached.
(3) Nucleoli are formed.
(4) Crossing-over takes place.
7. The ends of the chromosome are called ___________.
(1) Satellites.
(2) Centromeres.
(3) Telomeres.
(4) Kinetochore.
8. Chromosomes were first observed by___________.
(1) Fleming.
(2) Waldeyer.
(3) Strass burger.
(4) Hoffmeister.
9. A chromosome with sub-terminal centromere is___________.
(1) Acrocentric
(2) Acentric
(3) Metacentric
(4) Telocentric
10. A chromosome with centromere near the middle is called___________.
(1) Metacentric
(2) Acrocentric
(3) Telocentric
(4) Submetacentric
s Digital Pvt. Ltd. [36]
The Fundamental Unit of Life (Class 9)
SECTION B
ss
1. From the given picture, identify the acrocentric chromosomes.
(a) (b) (c) (d)
Read the following statements and give your answer as true or false.
2. Each sister chromatid has centromere, a specialised protein structure.
3. Centromeres are rod shaped or thread like DNA containing structure located in the nucleus.
Read the following statements and fill in the blanks.
4. A chromosome may either have equal or unequal arms depending on the position of the ______________.
5. The part of the DNA that connects two adjacent nucleosomes is called ________________.
s Digital Pvt. Ltd. [37]
The Fundamental Unit of Life (Class 9)
ss SOLUTIONS DPP – 07
Section - A
Answer Key
Question 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
Answer 1 4 2 2 4 2 3 4 1 4
1. Option (1)
Animal cell lacking nuclei would also lack in chromosome.
2. Option (4)
Chromosome and genes are the pair that is related to inheritance of characters.
3. Option (2)
P is cytoplasm where most of the cell processes takes place here.
4. Option (2)
Chromatin thread carries genetic information.
5. Option (4)
Chromatid is one-half of the replicated chromosome.
6. Option (2)
The centromere is that part of the chromosome where chromatids are attached.
7. Option (3)
The ends of the chromosome are called telomeres.
8. Option (4)
Chromosomes were first observed by Hoffmeister.
9. Option (1)
A chromosome with sub-terminal centromere is acrocentric.
10. Option (4)
A chromosome with centromere near the middle is called submetacentric.
s Digital Pvt. Ltd. [38]
The Fundamental Unit of Life (Class 9)
Section - B
ss
1. Option (c) represents acrocentric chromosome whereas (a) represents metacentric, (b) represents
submetacentric and (d) represents telocentric.
2. The statement is false.
Each sister chromatid has kinetochore, a specialised protein structure located at the centromere.
3. The statement is false.
Chromosomes are rod shaped or thread like DNA containing structure located in the nucleus.
4. A chromosome may either have equal or unequal arms depending on the position of the centromere.
5. The part of the DNA that connects two adjacent nucleosomes is called Linker DNA.
s Digital Pvt. Ltd. [39]
The Fundamental Unit of Life (Class 9)
ss
The Fundamental Unit of Life DPP – 08
Section - A
Q.1 to Q.5 are multiple choice questions. Each has four options (1), (2), (3) and (4) out of which only one option
is correct.
1. Uridine present in RNA is
(1) Nucleotides
(2) Pyrimidine
(3) Purine
(4) Nucleoside
2. Nucleic acids are a polymer of nucleotide monomeric units. Each nucleotide consists of
(1) Base-sugar-OH
(2) Sugar-phosphate
(3) Base-sugar-phosphate
(4) Base-sugar-OH
3. A DNA segment contains 100 Adenine and 100 cytosines, how many nucleotides are present in the
segment?
(1) 100
(2) 200
(3) 400
(4) 50
4. Nucleoside contains
(1) Base-sugar
(2) Base-phosphate
(3) Base-sugar-phosphate
(4) Sugar-phosphate
5. Which of the following nucleotide contains only ribose sugar and not deoxyribose?
(1) Thymine – pentose sugar-phosphate
(2) Uracil – pentose sugar-phosphate
(3) Thymine – pentose sugar-phosphate
(4) Cytosine – pentose sugar-phosphate
s Digital Pvt. Ltd. [40]
The Fundamental Unit of Life (Class 9)
SECTION B
ss
1. What does the given picture depicts?
Observe the picture and answer the following question.
2. What does the picture depicts?
3. What are the three components required for making the structure?
Read the following statements and give your answer as true or false.
4. There are 10 nitrogen base pairs in one complete turn of helical form of ds DNA.
5. DNA & RNA are the two types of nucleic acids found in every living organism.
Read the following statements and fill in the blanks.
6. Double stranded helical structure of DNA was proposed by ______________ & ________________
7. The strands in double stranded DNA are joined together by __________________
Subjective Questions
8. What type of nucleic acid is found in prokaryotic cells?
9. In how many forms RNA usually occurs?
10. What is the significance of DNA?
s Digital Pvt. Ltd. [41]
The Fundamental Unit of Life (Class 9)
ss SOLUTIONS DPP – 8
Section - A
Answer Key
Question 1 2 3 4 5
Answer 4 3 3 1 2
1. Option (4)
Uridine present in RNA is nucleoside.
2. Option (3)
Nucleic acids are a polymer of nucleotide monomeric units. Each nucleotide consists of Base- sugar- Phosphate.
3. Option (3)
A DNA segment contains 100 Adenine and 100 cytosines, 400 nucleotides are present in the segment
4. Option (1)
Nucleoside contains base-sugar.
5. Option (2)
Uracil – pentose sugar-phosphate contains only ribose sugar and not deoxyribose.
s Digital Pvt. Ltd. [42]
The Fundamental Unit of Life (Class 9)
Section - B
ss
1. The picture shows single stranded nucleic acid
2. The given picture depicts diagrammatic representation of double stranded polynucleotide chain in helical form.
3. The three components required for making this structure are –
a. Polynucleotide chain
b. Pentose sugar
c. Nitrogen bases
4. True
5. Ture
6. Watson, Crick
7. Hydrogen bonds
8. DNA found in prokaryotic cells is generally circular due to joining of two ends. It is not covered with protein and
is, therefore called naked.
9. RNA usually occurs in three forms-
a. messenger RNA (m- RNA)
b. transfer RNA (t-RNA)
c. ribosomal RNA (r-RNA)
10. Significance of DNA can be explained as –
a. DNA controls all the activities of cell, both directly & indirectly.
b. It is the genetic material in most of the living organisms which contain the information which guides the
synthesis of proteins.
c. DNA can undergo mutation & recombination to bring about variations, which play an important role in
specification.
s Digital Pvt. Ltd. [43]
The Fundamental Unit of Life (Class 9)
ss
The Fundamental Unit of Life DPP - 9
Section - A
Q.1 to Q.5 are multiple choice questions. Each has four options (1), (2), (3) and (4) out of which only one option
is correct.
1. Select the incorrect option about the cell inclusions.
(1) It is a living material inside cytoplasm.
(2) Pigment granules and starch granules are called cell inclusion.
(3) Non-living material inside cytoplasm.
(4) Both (1) and (2)
2. If the ribosomes of a cell are destroyed then
(1) Respiration will not take place.
(2) Fats will not be stored.
(3) Carbon assimilation will not occur.
(4) Proteins will not be formed.
3. Which is not a function of the cytoplasm?
(1) Provide support.
(2) Make proteins.
(3) Provide protection.
(4) Stores molecules.
4. What type of material is the cytoplasm?
(1) Water soluble material
(2) Permeable material
(3) Fat soluble material
(4) Colloidal material
5. Which of the following ions are required for binding of ribosomal subunits?
(1) Na+
(2) Mg++
(3) Mn++
(4) Fe++
s Digital Pvt. Ltd. [44]
The Fundamental Unit of Life (Class 9)
SECTION B
ss
1. Identify the picture given below. What is the function of it?
Read the following statements and give your answer as true or false.
2. In mammals 55 S type of ribosome are present in mitochondrial matrix.
4. Each ribosome is made up with two equal sub units which join together at the time of protein synthesis.
Read the following statements and fill in the blanks.
5. The prokaryotic ribosome is made up of __________ and ____________ sub units.
6. Functional segments of DNA are called _____________.
Subjective Questions
7. ‘Organelle within an organelle’ term is used for?
8. Cytoplasm consists of how many components/parts? Name them.
9. Explain the term ‘polyribosome’.
10. What are the functions of nucleus?
s Digital Pvt. Ltd. [45]
The Fundamental Unit of Life (Class 9)
ss SOLUTIONS DPP – 9
Section - A
Answer Key
Question 1 2 3 4 5
Answer 1 4 2 4 2
1. Option (1)
Cell inclusions. It is a living material inside cytoplasm.
2. Option (4)
If the ribosomes of a cell are destroyed then proteins will not be formed.
3. Option (2)
Cytoplasm do not contribute in making proteins.
4. Option (4)
Cytoplasm is Colloidal material
5. Option (2)
Mg++ ions are required for binding of ribosomal subunits.
s Digital Pvt. Ltd. [46]
The Fundamental Unit of Life (Class 9)
Section - B
ss
1. It is ribosome.
Function of ribosome is protein synthesis.
2. True
3. False
5. 30 S, 50 S
6. Gene
7. Ribosome is known as ‘organelles within an organelle’.
8. Cytoplasm is made up of two components known as cytosol & cell organelles.
9. At the time of protein synthesis, when many ribosomes attach to a single m-RNA, then the resultant structure
formed is called as polyribosome.
10. The nucleus performs following functions:
(i) It controls all the metabolic activities of the cell.
(ii) It brings about growth of the cell by directing the synthesis of structural proteins.
(iii) It takes part in the formation of ribosomes.
(iv) It regulates cell cycle.
(v) It contains genetic information and is concerned with the transmission of hereditary traits from one
generation to another.
s Digital Pvt. Ltd. [47]
The Fundamental Unit of Life (Class 9)
ss
The Fundamental Unit of Life DPP – 10
Section - A
Q.1 to 10. are multiple choice questions. Each has four options (1), (2), (3) and (4) out of which only one option
is correct.
1. Find out the correct sentence.
(1) Enzymes packed in lysosomes are made through RER (Rough endoplasmic reticulum).
(2) Rough endoplasmic reticulum and smooth endoplasmic reticulum produce lipid and protein respectively.
(3) Endoplasmic reticulum is related with the destruction of plasma membrane.
(4) Nucleoid is present inside the nucleoplasm of eukaryotic nucleus.
2. The cell organelle involved in forming complex sugars from simple sugars are
(1) Endoplasmic Reticulum
(2) Ribosomes
(3) Plastids
(4) Golgi apparatus
3. Based on the given features, identify the cell organelle and select the correct option regarding it.
• It is single membrane bound cell organelle.
• Enzymes of this cell organelle reabsorbed the tail of tadpole during metamorphosis.
(1) The cell organelle is formed by the joint activity of ER and Golgi apparatus.
(2) The cell organelle is present in almost all the animal cells except mature mammalian RBCs.
(3) The cell organelle is equally abundant in plant and animal cells.
(4) Both A and B
4. Membrane biogenesis is associated with which of the following cell organelles?
(1)
(2)
(3)
(4) All of the above
s Digital Pvt. Ltd. [48]
The Fundamental Unit of Life (Class 9)
5. The transportation of materials in the cell is by
ss
(1) Golgi complex
(2) Lysosomes
(3) Mitochondria
(4) Endoplasmic reticulum
6. The cytoplasm surrounding golgi body is also called as
(1) Centrosphere.
(2) Dictyosomes.
(3) Zone of exclusion.
(4) All of the above.
7. Of the following organelles, which group is involved in manufacturing substances needed by the cell?
(1) Ribosome, rough ER, smooth ER
(2) Vacuole, rough ER, smooth ER
(3) Smooth ER, ribosome, vacuole
(4) Rough ER, lysosome, vacuole
8. Which of the following statement is correct for a secretory cell?
(1) Golgi apparatus is absent.
(2) Rough endoplasmic reticulum is abundantly present in the cell.
(3) Only smooth endoplasmic reticulum is present.
(4) Secretory granules are formed in nucleus.
9. In which organism is golgi body known as dictyosomes?
(1) Bacteria
(2) Virus
(3) Plants
(4) Animals
10. The diagram shows five different structures that can be observed in cells.
1 2 3 4 5
Which structures would be present in large quantities in lipid synthesizing cells?
(1) 1, 2, 4 and 5
(2) 1, 3 and 4
(3) 2, 3 and 5
(4) 3, 4 and 5
s Digital Pvt. Ltd. [49]
The Fundamental Unit of Life (Class 9)
SECTION B
ss
1. Diagram of endoplasmic reticulum is given below. Identify the labelled structure P and Q .
Q P
2. Figure of golgi body is given below. Identify the labelled structure X and Y.
3. Match the Column - I with Column - II.
Column - I Column - II
A RER P Detoxification
B SER Q Golgi body of plants
C Golgi body R Protein synthesis
D Dictyosomes S Camillo Golgi
Read the following statements and give your answer as true or false.
4. Golgi complex was discovered by Camillo Golgi in the nerve cells of dog.
5. Golgi bodies are pleomorphic structures.
Read the following statements and fill in the blanks.
6. _________________is the site of formation of glycolipids and glycoprotein.
7. ___________ plays an important role in detoxification of drugs and poisons.
s Digital Pvt. Ltd. [50]
The Fundamental Unit of Life (Class 9)
Subjective Questions
ss
8. Which organelle is associated with the surface of RER?
9. What are the functions of endoplasmic reticulum?
10. What do you understand by the term "membrane biogenesis"?
s Digital Pvt. Ltd. [51]
The Fundamental Unit of Life (Class 9)
ss SOLUTIONS DPP – 10
Section - A
Answer Key
Question 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
Answer 1 1 4 1 4 3 1 2 3 3
1. Option (1)
Enzymes packed in lysosomes are made through RER (Rough endoplasmic reticulum.
2. Option (1)
The cell organelle involved in forming complex sugars from simple sugars are endoplasmic reticulum.
3. Option (4)
The cell organelle is lysosome which is found in all animal cells except human RBC & it is responsible for
reabsorption of tail of tadpole during metamorphosis. It is formed by the joint activity of ER and Golgi.
4. Option (1)
Membrane biogenesis is associated with endoplasmic reticulum.
5. Option (4)
The transportation of materials in the cell is by endoplasmic reticulum.
6. Option (3)
The cytoplasm surrounding golgi body is also called as zone of exclusion.
7. Option (1)
Ribosome; rough ER & smooth ER is associated with manufacturing substance needed the cell.
8. Option (2)
Rough endoplasmic reticulum is abundantly present in a secretory cell.
9. Option (3)
Golgi body is known as dictyosomes in plants.
10. Option (3)
Golgi, smooth endoplasmic reticulum & lysosomes are present in large quantities in lipid synthesizing cells.
s Digital Pvt. Ltd. [52]
The Fundamental Unit of Life (Class 9)
Section - B
ss
1. P - Rough endoplasmic reticulum
Q - Smooth endoplasmic reticulum
2. X - Cisternae
Y - Vesicles
3. A - R, B - P, C - S, D - Q
4. False
5. True
6. Golgi complex
7. Smooth endoplasmic reticulum
8. Ribosomes
9. (i) ER serve as channels for the transport of materials between various regions of cytoplasm or between
cytoplasm and nucleus.
(ii) It also functions as a cytoplasmic framework providing a surface for some of the biochemical activities of
the cell.
(iii) SER plays an important role in detoxifying many poisons and drugs and is also a site of lipid synthesis.
(iv) RER is engaged in synthesizing proteins and enzymes.
10. The proteins and lipids synthesized by RER and SER respectively help in building the cell membrane which is
known as membrane biogenesis.
s Digital Pvt. Ltd. [53]
The Fundamental Unit of Life (Class 9)
ss
The Fundamental Unit of Life DPP – 11
Section - A
Q.1 to Q.9 are multiple choice questions. Each has four options (1), (2), (3) and (4) out of which only one option
is correct.
1. Cell organelle having its own DNA is
(1) Endoplasmic reticulum
(2) Golgi apparatus
(3) Mitochondria
(4) Lysosome
2. Find out the false statement
(1) Nucleus, plastids and mitochondria contain DNA and hence are able to make their own structural proteins.
(2) Mitochondria are said to be the powerhouse of the cell.
(3) Grana
(4) Cristernae
3. Mitochondria are organelles found in cells. Cells with high activity rate, such as muscle cells, contain a
lot of these organelles. What is the function of the mitochondria?
(1) To store food and waste.
(2) To produce energy.
(3) To produce protein.
(4) To support the shape of the cell.
4. Which cell organelle is site of aerobic respiration within the cell?
(1) Glyoxisomes
(2) Mitochondria
(3) Lysosomes
(4) Chloroplast
5. Which organelle is composed of cristae and matrix?
(1) Chloroplast
(2) Nucleolus
(3) Mitochondrion
(4) Nucleus
s Digital Pvt. Ltd. [54]
The Fundamental Unit of Life (Class 9)
6. Which of the cell organelle liberate heat for the maintenance of constant body temperature in aves and
ss
mammals?
(1) Lysosomes
(2) Ribosomes
(3) Endoplasmic reticulum
(4) Mitochondria
7. Polysomes are
(1) Multiple units of ribosomes.
(2) Attachment of many ribosomes to a common mRNA
(3) Attachment of many m-RNA to common ribosomes.
(4) Lysosomal aggregations
8. These are membrane bound sac like organelles, they are concerned with the waste disposal system of
the cell. The cell organelles referred to in above description are
(1) Mitochondria
(2) Golgi Body
(3) Peroxisome
(4) Lysosome
9. Lysosomes are also known as
(1) Powerhouse of the cell
(2) Suicide bags
(3) Lipids
(4) None of them
Q. 10 is multiple choice question. It has four options (1), (2), (3) and (4) out of which ONE or MORE THAN ONE
option may be correct.
10. Which of the following statements about mitochondria is/are correct?
(1) They serve as sites for cellular respiration.
(2) They are enclosed by a double membrane.
(3) They are the sites where most of the cell's ATP is produced.
(4) They are found in animal cells only; plant cells have chloroplasts instead.
s Digital Pvt. Ltd. [55]
The Fundamental Unit of Life (Class 9)
SECTION B
ss
1. Identify the labelled structure in the diagram given below.
A
B
2. Match the column - I with column - II.
Column - I Column - II
A Lysosome P Power house of cell
B Mitochondria Q Suicidal bags
C ATP R Tennis racket shaped
D F1 particles S Energy currency
Read the following statements and give your answer as true or false.
3. Mitochondria is the double membrane bound cell organelle.
4. Lysosomes are called semi-autonomous cell organelle.
Read the following statements and fill in the blanks.
5. _____________ of mitochondria increases the inner surface area to hold a variety of enzymes.
6. Mitochondria has ______________ type of ribosome.
Subjective Questions
7. Draw the diagram of mitochondria.
8. Why are lysosomes known as "suicidal bags"?
9. Write a short note on origin of mitochondria.
10. What are the functions of mitochondria?
s Digital Pvt. Ltd. [56]
The Fundamental Unit of Life (Class 9)
ss SOLUTIONS DPP – 11
Section - A
Answer Key
Question 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
Answer 3 1 2 2 3 4 2 4 2 1,2,3
1. Option (3)
Cell organelle having its own DNA is Mitochondria.
2. Option (1)
Mitochondrial infoldings are known as cristae.
3. Option (2)
The organelle mitochondria help in ATP generation (energy).
4. Option (2)
Site of aerobic respiration is mitochondria.
5. Option (3)
Mitochondrion is composed of cristae and matrix.
6. Option (4)
Mitochondria liberate heat for the maintenance of constant body temperature in aves and mammals.
7. Option (2)
Polysome are attachment of many ribosomes to a common mRNA.
8. Option (4)
Lysosomes which is known as the suicidal bag of the cell so they are concerned with the waste disposal system
of the cell.
9. Option (2)
Lysosomes are also known as suicide bags.
10. Option (1,2,3)
Mitochondria serve as sites for cellular respiration, they are enclosed by a double membrane and they are the
sites where most of the cell's ATP is produced.
s Digital Pvt. Ltd. [57]
The Fundamental Unit of Life (Class 9)
Section - B
ss
1. A - Cristae
B - Matrix
2. A - Q, B - P, C - S, D - R
3. True
4. False
5. Cristae
6. 70 s
7.
8. At the time of cellular damage, the lysosomes burst to release its enzyme and they digest its own cell. Therefore,
lysosomes are also known as suicidal bags of a cell.
9. Mitochondria have a small and circular chromosome and 70S ribosome of their own and make some of their
own proteins, showing that they were once aerobic bacteria.
10. Mitochondria are the main sites of cellular respiration. They bring about complete oxidation of food stuffs or
respiratory substrates into carbon dioxide and water.
They are commonly known as 'power house of the cell' because they contain enzymes necessary for the
complete oxidation of food and for release of high amount of energy in the form of ATP (Adenosine
triphosphate) molecules. The body uses energy stored in ATP for synthesis of new chemical compounds and for
mechanical work. ATP is also known as energy currency of the cell.
s Digital Pvt. Ltd. [58]
The Fundamental Unit of Life (Class 9)
ss
The Fundamental Unit of Life DPP – 12
Section - A
Q.1 to Q.9 are multiple choice questions. Each has four options (1), (2), (3) and (4) out of which only one option
is correct.
1. Within chloroplasts, light is captured by -
(1) Thylakoids within grana
(2) Grana within cisternae
(3) Cisternae within grana
(4) Grana within thylakoids
2. Plastids differ from mitochondria on the basis of which of the following features?
(1) Presence of two layers of membrane
(2) Presence of green pigments
(3) Presence of DNA
(4) Plastids are present in plant cell while mitochondria are present in animal cell.
3. The radiant energy of sunlight is converted to chemical energy and stored as –
(1) AMP
(2) ADP
(3) ATP
(4) APP
4. Identify A, B and C in the given figure and select the correct option.
A C
B
s Digital Pvt. Ltd. [59]
The Fundamental Unit of Life (Class 9)
ss A B C
(1) Granum Stroma DNA
(2) Stroma Grana Ribosomes
(3) Frets Thyllakoid Mitochondria
(4) Thyllakoid Granum Vacuole
5. Select the correct statement for the given picture.
c
b a
(1) The part labelled “b” is called intergranal thylakoid.
(2) The part labelled “c” is called granum.
(3) The part labelled “a” is the site of dark reaction.
(4) The part labelled as ‘’a’’, ‘’b’’, ‘’c’, all possess photosynthetic pigments such as chlorophyll.
6. Which type of plastid is found in roots and seeds?
(1) Chloroplasts
(2) Chromoplasts
(3) Leucoplasts
(4) None of these
7. Read the given statements.
(i) Flat membranous sacs in stroma of chloroplasts.
(ii) Infoldings in mitochondria.
(iii) Disc shaped sacs in golgi apparatus.
Select the correct option as per the codes given above.
Cristae Cisternae Thylakoids
(1) (i) (iii) (ii)
(2) (i) (ii) (iii)
(3) (ii) (iii) (i)
(4) (iii) (ii) (i)
s Digital Pvt. Ltd. [60]
The Fundamental Unit of Life (Class 9)
8. An unripe green fruit changes colour when it ripens. The reason being:
ss
(1) Chromoplasts changes to chlorophyll
(2) Chromoplasts changes to chromosomes
(3) Chromosomes changes to chromoplasts
(4) Chloroplast changes to chromoplasts
9. Which cell organelles is/ are absent in an animal cell?
(1) A nucleus
(2) A cell wall
(3) A Chloroplast
(4) Both (2) & (3)
Q. 10 is multiple choice question. It has four options (1), (2), (3) and (4) out of which ONE or MORE THAN ONE
option may be correct.
10. Which of these functions are performed by plastids?
(1) Storage of substances like starch, lipid
(2) Synthesis of carbohydrates
(3) Determine cell's colour
(4) Photosynthesis
s Digital Pvt. Ltd. [61]
The Fundamental Unit of Life (Class 9)
SECTION B
ss
1. Identify the labelled structure A, B and C in the diagram given below.
2. Match the column - I with Column - II.
Column -I Column - II
A Leucoplast P Double membranous organelle
B Chloroplast Q Xanthophyll
C Chromoplast R Chlorophyll
D Plastids S Starch
Read the following statements and give your answer as true or false.
3. Chromoplasts are red, yellow and orange in colour and are found in petals of flower and in fruits.
4. Chloroplasts are usually disc-shaped and surrounded by a single membrane.
Read the following statements and fill in the blanks.
5. Chloroplasts are the sites of __________________.
6. Plastid has ___________ type of ribosomes.
Subjective Questions
7. Draw the diagram of plastid.
8. Write the name of different types of plastids.
9. There would be no animal life if chloroplasts did not exist. Justify.
10. Why are plastids termed as semi - autonomous?
s Digital Pvt. Ltd. [62]
The Fundamental Unit of Life (Class 9)
ss SOLUTIONS DPP – 12
Section - A
Answer Key
Question 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
Answer 1 2 3 1 3 3 3 4 4 1, 2, 3, 4
1. Option (1)
Within chloroplasts, light is captured by thylakoids within grana.
2. Option (2)
Plastids differ from mitochondria due to the presence of green pigment.
3. Option (3)
The solar energy of sunlight is converted to chemical energy and stored as ATP.
4. Option (1)
Part labelled A is Granum, B is stroma & C is DNA.
5. Option (3)
The part labelled as ‘’a’’ is stroma where dark reaction occurs.
6. Option (3)
Leucoplast is found in roots and seeds.
7. Option (3)
Flat membranous sacs in stroma of chloroplast is thylakoids; Infoldings in mitochondria is cristate and disc
shaped sacs in golgi apparatus is cisternae.
8. Option (4)
The reason for change in colour of green fruit when it ripens is chloroplast changes to chromoplasts
9. Option (4)
Cell wall and chloroplast are absent in an animal cell.
10. Option (1, 2, 3, 4)
Palisade help in storage of substances like starch, lipid; help in synthesis of carbohydrates, determines cell
colour & perform photosynthesis.
s Digital Pvt. Ltd. [63]
The Fundamental Unit of Life (Class 9)
SECTION B
ss
1. A - Thylakoid
B - Stroma
C - Grana
2. A - S, B- R, C -Q, D- P
3. True
4. False
5. photosynthesis
6. 70s
7.
Stroma
Outer Membrane
granum
Inner membrane
thylakoid
8. (i) Chromoplasts
(ii) Leucoplasts
(iii) Chloroplast
9. If chloroplasts did not exist, there would be no plant life because if chloroplast did not exist then there will be
no oxygen for animals and there will be no food for animals. So, survival of animals cannot be possible.
10. Plastids and mitochondria are semi-autonomous cell organelle as they are having their own DNA and ribosomes
which are useful in protein synthesis.
s Digital Pvt. Ltd. [64]
The Fundamental Unit of Life (Class 9)
ss
The Fundamental Unit of Life DPP – 13
Section - A
Q.1 to Q.8 are multiple choice questions. Each has four options (1), (2), (3) and (4) out of which only one option
is correct.
1. Cell vacuole contains
(1) Water
(2) Metabolic gases
(3) Cytoplasm
(4) Water and dissolved substances
2. Which of the following statements is correct about the lack of organelles in prokaryotes?
(1) The lack of organelles in prokaryotes means that their basic cellular processes are different from eukaryotes.
(2) It suggests that the amount of DNA remains the same throughout the life cycle.
(3) Absence of organelles in prokaryotes means that they cannot perform the function of photosynthesis.
(4) It suggests that they contain more variety of phospholipids in their cell membrane.
3. Study the given diagram of an animal cell. Which of the following statements are correct regarding P,
Q, R and S?
(i) S fuses with R to release its content into the extracellular space.
(ii) Proteins formed in Q are modified into glycoproteins in P.
(iii) If radioactively labelled amino acids are provided to the cell then radioactivity will first appear in S.
(iv) Q is involved in the synthesis of R.
(v) S buds off from cis face of Q.
R
P
Q
S
(1) (i) and (iii) only
(2) (ii), (iii) and (v) only
(3) (i), (ii) and (iv) only
(4) (i) and (iv) only
s Digital Pvt. Ltd. [65]
The Fundamental Unit of Life (Class 9)
4. Match column I with column II and select the correct option from the given codes.
ss
Column I Column II
(a) Ribosomes (i) Jelly like substance
(b) Lysosomes (ii) Powerhouse of the cell
(c) Endoplasmic reticulum (iii) Site of protein synthesis
(d) Cytoplasm (iv) Synthesis of lipids
(e) Mitochondria (v) Suicide bags
(1) (a) - (iii), (b) - (v), (c) - (iv), (d) - (i), (e) - (ii)
(2) (a) - (iv), (b) - (v), (c) - (iii), (d) - (i), (e) - (ii)
(3) (a) - (iii), (b) - (iv), (c) - (i), (d) - (v), (e) - (ii)
(4) (a) - (iv), (b) - (v), (c) - (ii), (d) - (i), (e) - (iii)
5. Which is these is true regarding a prokaryotic cell?
(1) 80S ribosomes present
(2) Cell wall is usually present
(3) Multiple linear chromosomes present
(4) All of the above
6. Nucleolus in prokaryotic cell is
(1) Site of packaging of RNA
(2) Store house of RNA
(3) Both (1) and (2)
(4) None of these
7. Select the incorrect statements among the following.
(A) Generally prokaryotic cells and plant cells both have cell wall while animal cells do not.
(B) Plant cells have peripheral nucleus while animal cells have central nucleus
(C) Ribosomes of prokaryotic cells are 70s, made up of 40s + 30s subunits while in eukaryotic cells it is80s,
made up of 50s + 30s subunits.
(D) Rough endoplasmic reticulum helps in detoxification of drugs whereas smooth endoplasmic reticulum
helps in lipid synthesis.
(1) A and B
(2) B and C
(3) C and D
(4) A and C
s Digital Pvt. Ltd. [66]
The Fundamental Unit of Life (Class 9)
8. Which of the following organelle is absent in plant cell?
ss
(1) Cell wall
(2) Centriole
(3) Mitochondria
(4) Chloroplast
Q.9 to Q.10 is multiple choice question. It has four options (1), (2), (3) and (4) out of which ONE or MORE THAN
ONE option may be correct.
9. Which out of the following is not a function of vacuole?
(1) Storage
(2) Locomotion
(3) Power house of the cell
(4) Providing turgidity and rigidity to the cell
10. Which of the following cell organelle are common in both plant & animal cell?
(1) Cell membrane
(2) Cell wall
(3) Nucleus
(4) Cytoplasm
s Digital Pvt. Ltd. [67]
The Fundamental Unit of Life (Class 9)
SECTION B
ss
1. Which of the following structure is present in both animal and plant cell? Identify and name them.
2. Match the column - I with Column - II.
Column -I Column - II
A Centriole P 80s type of ribosome
B Prokaryotes Q Present only in lower plants
C Eukaryotes R Provide turgidity to the cell
D Vacuole S Single circular DNA
Read the following statements and give your answer as true or false.
3. Centrioles are present only in higher plants.
4. 80s type of ribosomes are present in eukaryotes.
Read the following statements and fill in the blanks.
5. ________ act as dump house for excretory products in plants cells.
6. _________ DNA is found in prokaryotes.
Subjective Questions
7. Write four differences between animal and plant cell.
8. Write four differences between prokaryotes and eukaryotes.
9. What is centrosome?
10. What are the functions of vacuoles?
s Digital Pvt. Ltd. [68]
The Fundamental Unit of Life (Class 9)
ss SOLUTIONS DPP – 13
Section - A
Answer Key
Question 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
Answer 4 2 4 1 2 4 2 2 2, 4 1, 3, 4
1. Option (4)
Vacuole contains water and dissolved substances like salts, sugar, amino acids, organic acids and some proteins.
2. Option (2)
The amount of DNA remains the same throughout the life cycle.
3. Option (4)
Vesicles (S) fuses with plasma membrane (R) to release its content into the extracellular space
Golgi body (Q) is involved in the synthesis of plasma membrane (R).
4. Option (1)
Ribosome – site of photosynthesis; lysosome – suicidal bag; endoplasmic reticulum – synthesis of lipids;
cytoplasm – jelly like substance ; mitochondria – power house of the cell .
5. Option (2)
Cell wall is usually present in a prokaryotic cell.
6. Option (4)
Nucleolus in prokaryotic cell is nucleoid.
7. Option (2)
Incorrect statement is statement B & C
8. Option (2)
Centriole is absent in plant cell.
9. Option (2, 4)
Storage of salt, sugar, organic acids etc. Helps in maintaining turgidity of cell. It is a dump for waste products in
plants of vacuole.
10. Option (1, 3, 4)
Cell membrane, Nucleus and cytoplasm are common in both plant and animal cells. Cell wall is only present in
plants.
s Digital Pvt. Ltd. [69]
The Fundamental Unit of Life (Class 9)
Section - B
ss
1. A - Nucleus
B - Cell Membrane
C - Cytoplasm
A, B and C all are present in both animal and plant cell.
2. A- Q, B- S, C- P, D- R
3. False
4. True
5. Vacuoles
6. Single circular
7.
Comparison between Animal cell and Plant cell
Animal Cell Plant Cell
Cell wall Absent Present
Plasma membrane Present Present
Lysosomes Lysosomes occur in Lysosomes usually not evident
cytoplasm
Nucleus Present in center Present in periphery
8.
Comparison between Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes
Characteristic Prokaryotes Eukaryotes
Nucleus No nuclear membrane or True nucleus, consisting of nuclear
nucleoli membrane and nucleoli
Membrane enclosed Absent Present; examples include Lysosomes,
cell organelles Golgi complex, Endoplasmic reticulum
Mitochondria, Chloroplasts
Cell Wall Usually present; When When present, made up of cellulose or
present, made up of chitin
made up of peptidoglycan
Plasma No carbohydrates and Steroid and carbohydrates
membrane generally lacks steroid are present
s Digital Pvt. Ltd. [70]
The Fundamental Unit of Life (Class 9)
9. Centrioles and centrosphere are collectively called centrosome. Two centrioles are located just outside the
ss
nucleus and lie at right angle (90°). It initiates cell division by arranging spindle fibres between 2 poles of cell.
10. (i) In plant cell, vacuoles are full of cell sap and provide turgidity and rigidity to the cell.
(ii) Vacuoles store amino acid, sugars, various organic acids and some proteins.
(iii) They act as dump house for excretory products in plant cells.
(iv) In single celled organisms like Amoeba, the food vacuole contains the food items that the Amoeba
has consumed.
s Digital Pvt. Ltd. [71]
The Fundamental Unit of Life (Class 9)
ss
The Fundamental Unit of Life DPP – 14
Section - A
Q.1 to Q.5. are multiple choice questions. Each has four options (1), (2), (3) and (4) out of which only one option
is correct.
1. Centrosome is found in
(1) Cytoplasm
(2) Nucleus
(3) Chromosomes
(4) Nucleolus
2. The part of the cell responsible for maintaining cell shape, internal organization and cell movement is
the
(1) Vesicle
(2) Nucleus
(3) Endoplasmic reticulum
(4) Cytoskeleton.
3. A plant cell differs from the animal cell in the absence of
(1) Endoplasmic reticulum
(2) Mitochondria
(3) Ribosomes
(4) Centrioles
4. Microbodies which help to convert stored lipid into carbohydrates so they can be used for plant growth
are
(1) Peroxisome
(2) Spaerosome
(3) Glyoxisome
(4) Lysosome
5. What is the major role of peroxisomes in our body?
(1) Breakdown of Formaldehyde
(2) Breakdown of proteins
(3) Breakdown of Hydrogen Peroxide
(4) Breakdown of Phthalates
s Digital Pvt. Ltd. [72]
The Fundamental Unit of Life (Class 9)
SECTION B
ss
Fill in the blanks-
1. In animal cells ____________ are concerned with peroxide (H 2O2) metabolism.
2. _____________are major site of lipid storage and synthesis in plants.
Answer the following questions based on the diagram given below-
3. What is the name given to parts labelled as X and Y?
4. X and Y are chiefly involved in Locomotion of these organisms, name one more function these are
involved in.
5. Are X and Y same in size? Write about the sizes of these two structures?
6. What is centriole?
Answer the following. Name the types of components of cytoskeleton for following statements-
7. Composed of protein Tubulin.
8. Composed of contractile protein Actin. ___________
9. These filaments form basket like structure around the nucleus. ____________
10. Name the following structure
s Digital Pvt. Ltd. [73]
The Fundamental Unit of Life (Class 9)
ss SOLUTIONS DPP – 1
Section - A
Answer Key
Question 1 2 3 4 5
Answer 1 4 4 3 3
1. Option (1)
Centrosome is found in cytoplasm.
2. Option (4)
The part of the cell responsible for maintaining cell shape, internal organization and cell movement is the
cytoskeleton.
3. Option (4)
A plant cell differs from the animal cell in the absence of centrioles.
4. Option (3)
Microbodies which help to convert stored lipid into carbohydrates so they can be used for plant growth are
Glyoxisome.
5. Option (3)
The peroxisomes have an enzyme called catalase. This enzyme is used to breakdown Hydrogen Peroxide into
water.
s Digital Pvt. Ltd. [74]
The Fundamental Unit of Life (Class 9)
Section - B
ss
1. Peroxisomes
In animal cells peroxisomes are concerned with peroxide (H2O2) metabolism.
2. Sphaerosomes
Sphaerosomes are major site of lipid storage and synthesis in plants.
3. A X- Cilia
Y- Flagella
4. Cilia and Flagella play a very important role in Ingestion of food as well.
5. The cilia range in size 5–10mm. Flagella are up to 150 mm long in size.
6. Centrioles are paired barrel-shaped organelles located in the cytoplasm of animal cells near the nuclear envelope
7. Composed of protein Tubulin is Microtubules.
8. Composed of contractile protein Actin is Microfilaments.
9. These filaments form basket like structure around the nucleus is Intermediate filaments.
10. Its an image of a centriole.
s Digital Pvt. Ltd. [75]
The Fundamental Unit of Life (Class 9)
ss
The Fundamental Unit of Life DPP – 15
Section - A
Q.1 to Q.5 are multiple choice questions. Each has four options (1), (2), (3) and (4) out of which only one option
is correct.
1. Which of the following processes involve meiosis?
(a) Production of pollen grains.
(b) Formation of the zygote.
(c) Production of ova.
(d) Formation of new potato plants from buds on an existing tuber.
(1) a only
(2) a and c only
(3) a, b and c only
(4) a, b, c and d
2. Chromosome structure can be observed best during ____
(1) Anaphase
(2) Metaphase
(3) Prophase
(4) None of the above
3. The _______ state implies the exit of cells from the cell cycle
(1) S
(2) G1
(3) G2
(4) G0
4. Mitosis can be observed in _____
(1) Polyploid individual
(2) Diploid individual
(3) Haploid individual
(4) Both (1,) (2) and (3)
5. ____________is the number of DNA in the chromosome at the G2 stage of the cell cycle
(1) 1
(2) 2
(3) 3
(4) 0
s Digital Pvt. Ltd. [76]
The Fundamental Unit of Life (Class 9)
SECTION B
ss
1. What is cell division?
2. What are the two main types of cell division?
3. Write a short note on mitosis.
4. Write a short note on meiosis.
5. Which type of cell division helps in growth and repair of tissues?
s Digital Pvt. Ltd. [77]
The Fundamental Unit of Life (Class 9)
ss SOLUTIONS DPP – 15
Section - A
Answer Key
Question 1 2 3 4 5
Answer 3 2 4 4 2
1. Option (3)
Production of pollen grains, formation of zygote and production of ova involve meiosis.
2. Option (2)
Chromosome structure can be observed best during metaphase.
3. Option (4)
The G0 state implies the exit of cells from the cell cycle.
4. Option (4)
Mitosis can be observed in Polyploid individual, Diploid individual as well as Haploid individual.
5. Option (2)
2 is the number of DNA in the chromosome at the G2 stage of the cell cycle.
s Digital Pvt. Ltd. [78]
The Fundamental Unit of Life (Class 9)
Section - B
ss
1. New cells are formed in organisms in order to grow, to replace old, dead and injured cells, and to form gametes
required for reproduction. The process by which new cells are made is called cell division.
2. (i) Mitosis
(ii) Meiosis
3. The process of cell division by which most of the cells divide for growth is called mitosis. In this process, each
cell called mother cell divides to form two identical daughter cells. The daughter cells have the same number of
chromosomes as mother cell. It helps in growth and repair of tissues in organisms.
4. Specific cells of reproductive organs or tissues in animals and plants divide to form gametes, which after
fertilisation give rise to offspring. They divide by a different process called meiosis which involves two
consecutive divisions. When a cell divides by meiosis it produces four new cells instead of just two. The new cells
only have half the number of chromosomes than that of the mother cells.
5. Mitosis.
s Digital Pvt. Ltd. [79]
The Fundamental Unit of Life (Class 9)
ss
The Fundamental Unit of Life DPP – 16
Section - A
Q.1 to Q.5 are multiple choice questions. Each has four options (1), (2), (3) and (4) out of which only one option
is correct.
1. The condensation of chromosomes is observed in ______
(5) Prophase 1
(6) Anaphase 1
(7) Metaphase 1
(8) None of the above
2. The stage which serves as a connecting link between meiosis 1 and meiosis 2
(1) Interphase 2
(2) Interphase 1
(3) Interkinesis
(4) None of the above
3. One of these events does not take place during meiosis:
(1) One successive division without any DNA replication
(2) Chiasmata formation and crossing over
(3) Segregation of homologous chromosomes
(4) Separation of sister chromatids
4. Name the event wherein the paternal and maternal chromosomes change their material with each other
in cell division.
(1) Crossing over
(2) Synapsis
(3) Dyad forming
(4) Bivalent forming
5. Meiosis I is reductional division and meiosis II is equational division because of
(1) Separation of chromatids
(2) Crossing over
(3) The disjunction of homologous chromosomes
(4) The pairing of homologous chromosomes
s Digital Pvt. Ltd. [80]
The Fundamental Unit of Life (Class 9)
SECTION B
ss
1. Write the name of the following stage of Meiosis?
2. How can you differentiate between the Prophase stages of Mitosis and Meiosis?
3. Complete the statements for Meiosis II
(a) The chromosome number remains____________, and daughter cells are genetically ________to the parent
cell.
(b) Meiosis II is functionally the same as ______________and consists of the same phases: prophase-II,
metaphase-II, anaphase-II, telophase-II, and cytokinesis.
4. Assertion: Metaphase-II of meiosis involve formation of bivalents on equatorial plate.
Reason: Bivalent is formed during leptotene.
(1) Both Assertion and Reason are true, and Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion.
(2) Both Assertion and Reason are true, but Reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion.
(3) Assertion is true but Reason is false.
(4) Both Assertion and Reason are false.
5. Assertion: Cells are haploid with double DNA content after meiosis I.
Reason: No S-phase occurs in between two phases of Meiosis, i.e. Meiosis I and II.
(1) Both Assertion and Reason are true and Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion.
(2) Both Assertion and Reason are true but Reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion.
(3) Assertion is true but Reason is false.
(4) Both Assertion and Reason are false
s Digital Pvt. Ltd. [81]
The Fundamental Unit of Life (Class 9)
ss SOLUTIONS DPP – 16
Section - A
Answer Key
Question 1 2 3 4 5
Answer 1 3 1 1 1
1. Option (1)
The condensation of chromosomes is observed in Prophase 1.
2. Option (3)
The stage which serves as a connecting link between meiosis 1 and meiosis is interkinesis.
3. Option (1)
One successive division without any DNA replication does not occur during meiosis.
4. Option (1)
The event wherein the paternal and maternal chromosomes change their material with each other in cell
division is crossing over.
5. Option (1)
Meiosis I is reductional division and meiosis II is equational division because of separation of chromatids.
s Digital Pvt. Ltd. [82]
The Fundamental Unit of Life (Class 9)
Section - B
ss
1. Anaphase
2. Meiotic prophase I is much longer that mitotic prophase as it further involves stages such as leptotene, zygotene,
pachytene, diplotene, and diakinesis whereas mitotic prophase does not.
3. (a) The chromosome number remains haploid, and daughter cells are genetically identical to the parent cell.
(b) Meiosis II is functionally the same as mitosis and consists of the same phases: prophase-II, metaphase-II,
anaphase-II, telophase-II, and cytokinesis.
4. (4) Both assertion and reason are false.
5. (2) Both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
s Digital Pvt. Ltd. [83]
You might also like
- Test Bank For Cell and Molecular Biology 8th Edition Gerald Karp Janet Iwasa Wallace MarshallDocument31 pagesTest Bank For Cell and Molecular Biology 8th Edition Gerald Karp Janet Iwasa Wallace MarshallRosalinda Byrd100% (37)
- ANSWERS Worksheets Cell Structure FunctionsDocument24 pagesANSWERS Worksheets Cell Structure FunctionsAnghel LopezNo ratings yet
- Testbank Urry Ch5Document29 pagesTestbank Urry Ch5Jan Defr0% (1)
- Cell Test Paper MDocument2 pagesCell Test Paper Mkritikatusid17No ratings yet
- Cell - The Unit of LIfe - DPPsDocument23 pagesCell - The Unit of LIfe - DPPsMd Faijal100% (1)
- Biology Science Class 9 Reference BookDocument198 pagesBiology Science Class 9 Reference BookJeevraj MedhiNo ratings yet
- Cell - The Unit of Life - DPP 01 - Yakeen 2.0 2024 (Legend)Document3 pagesCell - The Unit of Life - DPP 01 - Yakeen 2.0 2024 (Legend)kdxrfn79txNo ratings yet
- RESTART 2025 Cell: The Unit of Life: Subtopic-Cell Theory and An Overview of CellDocument3 pagesRESTART 2025 Cell: The Unit of Life: Subtopic-Cell Theory and An Overview of Cellwww.ksarma55No ratings yet
- Biology Part - 1Document68 pagesBiology Part - 1SantoshNo ratings yet
- 6 Cell: The Unit of Life: SolutionsDocument34 pages6 Cell: The Unit of Life: SolutionsyoteshNo ratings yet
- 01 - Fundamental Unit of LifeDocument19 pages01 - Fundamental Unit of Lifeaditya biswabandhuNo ratings yet
- DPP-01 - Cell The Unit of Life CORRECTEDDocument3 pagesDPP-01 - Cell The Unit of Life CORRECTEDSiazzzNo ratings yet
- CLASS 8 CHAPTER-8 CELL STRUCTURE & FUNCTIONSDocument5 pagesCLASS 8 CHAPTER-8 CELL STRUCTURE & FUNCTIONSaditya rajputNo ratings yet
- Cell TheoryDocument18 pagesCell TheoryAika NaNo ratings yet
- BTY223 Quizz 1 Set 1,2 3 With AnswersDocument13 pagesBTY223 Quizz 1 Set 1,2 3 With Answerssanjog kshetriNo ratings yet
- DPP LiveDocument15 pagesDPP Livep11925885No ratings yet
- Biology Week 1Document11 pagesBiology Week 1nitsuaNo ratings yet
- Ch. 5 The Fundamental Unit of Life: 1 Mark QuestionsDocument3 pagesCh. 5 The Fundamental Unit of Life: 1 Mark QuestionsTanush RaghavNo ratings yet
- Evardo, Nathan Nyle Eddor C.-Q1-MODULE1-ANSWERSDocument3 pagesEvardo, Nathan Nyle Eddor C.-Q1-MODULE1-ANSWERSEvardoNathanNyleNo ratings yet
- Biology Cell Assignment 4Document1 pageBiology Cell Assignment 4chaudharyhansika95No ratings yet
- Cell Structure and Functions Question AnswserDocument5 pagesCell Structure and Functions Question AnswserSifat Monga100% (2)
- Cell and Molecular Biology Concepts and Experiments 7th Edition Test Bank Gerald KarpDocument27 pagesCell and Molecular Biology Concepts and Experiments 7th Edition Test Bank Gerald KarpBernard Dalessio100% (40)
- Downloaded For Personal Use Only: Column-I Column-IIDocument7 pagesDownloaded For Personal Use Only: Column-I Column-IIMohit SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- 31 Mar Cells HWDocument10 pages31 Mar Cells HWNiladri ChatterjeeNo ratings yet
- gr 8 ws 2 pdfDocument3 pagesgr 8 ws 2 pdfJaimukeshNo ratings yet
- Ch-8, Cell Class - 8, Science Textbook QuestionsDocument5 pagesCh-8, Cell Class - 8, Science Textbook Questionsbucks GamingNo ratings yet
- Joez 3 Odf RKB VMKPzo HACDocument6 pagesJoez 3 Odf RKB VMKPzo HACKawaljit KaurNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 5: The Fundamental Unit of LifeDocument78 pagesChapter - 5: The Fundamental Unit of LifeRoboNo ratings yet
- Session No 1.1. A Tour of The CellDocument40 pagesSession No 1.1. A Tour of The CellShekaina Faith Cuizon LozadaNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 - Cell OrganizationDocument2 pagesUnit 2 - Cell OrganizationSouhardhNo ratings yet
- Cell For 9 11Document13 pagesCell For 9 11ossama44zidaniNo ratings yet
- UggigDocument36 pagesUggigSubhadip DindaNo ratings yet
- CLS Aipmt 19 20 XIII Bot Study Package 1 Level 1 Chapter 1Document26 pagesCLS Aipmt 19 20 XIII Bot Study Package 1 Level 1 Chapter 1ÃthårNo ratings yet
- Grade 8 - Chap 8 (Qns & Ans)Document5 pagesGrade 8 - Chap 8 (Qns & Ans)Sri DharshanNo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan 16 Sept 2023Document7 pagesAdobe Scan 16 Sept 2023Koushikci KanjilalNo ratings yet
- Grade 8: Science TestDocument32 pagesGrade 8: Science TestJatmiko Eko SaputroNo ratings yet
- TEST BANK For Karp's Cell and Molecular Biology, 9th Edition by Gerald Karp, Janet Iwasa, Verified Chapters 1 - 18, Complete Newest VersionDocument51 pagesTEST BANK For Karp's Cell and Molecular Biology, 9th Edition by Gerald Karp, Janet Iwasa, Verified Chapters 1 - 18, Complete Newest Versionkevinkariuki227No ratings yet
- CMBCE7ESKDocument27 pagesCMBCE7ESKAllyson OffreyNo ratings yet
- I. Multiple Choice. Choose The Letter of The Best AnswerDocument3 pagesI. Multiple Choice. Choose The Letter of The Best AnswerKeannoNo ratings yet
- 8 Science NCERT Solutions Chapter 8Document6 pages8 Science NCERT Solutions Chapter 8Raj AnandNo ratings yet
- 9 BiologyDocument54 pages9 BiologygirishtiwaskarNo ratings yet
- Ils62018 ExamwDocument32 pagesIls62018 ExamwMargie CochingNo ratings yet
- Cell-Structure and Functions - Class 8 - NCERT Exercise Questions - PANTOMATHDocument4 pagesCell-Structure and Functions - Class 8 - NCERT Exercise Questions - PANTOMATHsourav9823No ratings yet
- Ejercicios Tema 1 y 2Document2 pagesEjercicios Tema 1 y 2janire cabezasNo ratings yet
- Class 8 Cell and Cell Structure Questions and AnswDocument10 pagesClass 8 Cell and Cell Structure Questions and AnswAalooooNo ratings yet
- (E-Module) BNA - Science - Class 9 - Part 1Document73 pages(E-Module) BNA - Science - Class 9 - Part 1Neetu SinhaNo ratings yet
- General Biology Midterm 1 BackupDocument5 pagesGeneral Biology Midterm 1 BackupJf CatubayNo ratings yet
- Science 7 - Quarter 2 - Week 4 Learning Activity SheetDocument4 pagesScience 7 - Quarter 2 - Week 4 Learning Activity SheetTricia BrunoNo ratings yet
- BIOLOGY Sample Questions 1Document3 pagesBIOLOGY Sample Questions 1Mohit SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Class 9 PWDocument16 pagesClass 9 PW2982No ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of The Human BodyDocument51 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of The Human BodyEight AlykNo ratings yet
- Bio Lo Gym 2 Cell Structure FunctionDocument24 pagesBio Lo Gym 2 Cell Structure FunctionMarmorn ArborshateNo ratings yet
- Aakash Botany Study Package 2 SolutionsDocument116 pagesAakash Botany Study Package 2 Solutionsrekim23414No ratings yet
- CLS Aipmt-18-19 XIII Bot Study-Package-1 SET-1 Chapter-1 PDFDocument38 pagesCLS Aipmt-18-19 XIII Bot Study-Package-1 SET-1 Chapter-1 PDFKunal GuptaNo ratings yet
- M-Caps-01: Botany: NEET - XI StudyingDocument3 pagesM-Caps-01: Botany: NEET - XI StudyingAlokSinghNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - Cell: The Unit of Life Exercise Ex. 1: Solution 1Document8 pagesChapter 2 - Cell: The Unit of Life Exercise Ex. 1: Solution 1Arpan KaurNo ratings yet
- TEST I. TRUE or FALSE. Write TRUE If The Statement Is True, Otherwise Write FALSE If The StatementDocument3 pagesTEST I. TRUE or FALSE. Write TRUE If The Statement Is True, Otherwise Write FALSE If The StatementHasnairah Mautin LimbotonganNo ratings yet
- Quiz 2 (Cell Parts and Functions)Document3 pagesQuiz 2 (Cell Parts and Functions)Reyzel Pahunao100% (1)
- Full Download PDF of Test Bank For Karp's Cell and Molecular Biology, 9th Edition, Gerald Karp, Janet Iwasa Wallace Marshall All ChapterDocument62 pagesFull Download PDF of Test Bank For Karp's Cell and Molecular Biology, 9th Edition, Gerald Karp, Janet Iwasa Wallace Marshall All Chapterklgaiert04100% (7)
- CLASS VIII QUESTION BANK - 8. CellDocument8 pagesCLASS VIII QUESTION BANK - 8. CellSurbhi NayarNo ratings yet
- DPPhkshdahfaDocument4 pagesDPPhkshdahfa9-E PRADYOT SINHANo ratings yet
- Exercise01and02 +SolutionDocument28 pagesExercise01and02 +Solution9-E PRADYOT SINHANo ratings yet
- Exercise_03 + SolutionsDocument12 pagesExercise_03 + Solutions9-E PRADYOT SINHANo ratings yet
- 9th_Test Paper_Diversity_AdvanceDocument6 pages9th_Test Paper_Diversity_Advance9-E PRADYOT SINHANo ratings yet
- Test+SolutionDocument7 pagesTest+Solution9-E PRADYOT SINHANo ratings yet
- DPP_Diversity in living organisms_AdvanceDocument82 pagesDPP_Diversity in living organisms_Advance9-E PRADYOT SINHANo ratings yet
- 1. Verbal Series DPPDocument9 pages1. Verbal Series DPP9-E PRADYOT SINHANo ratings yet
- Exercise + SolutionsDocument25 pagesExercise + Solutions9-E PRADYOT SINHANo ratings yet
- Test+SolutionDocument5 pagesTest+Solution9-E PRADYOT SINHANo ratings yet
- NotesDocument4 pagesNotes9-E PRADYOT SINHANo ratings yet
- Motion ex 3Document35 pagesMotion ex 39-E PRADYOT SINHANo ratings yet
- Test+SolutionDocument5 pagesTest+Solution9-E PRADYOT SINHANo ratings yet
- Test FNLMDocument10 pagesTest FNLM9-E PRADYOT SINHANo ratings yet
- Motion NOTES N AND ODocument23 pagesMotion NOTES N AND O9-E PRADYOT SINHANo ratings yet
- Motion DPPDocument64 pagesMotion DPP9-E PRADYOT SINHANo ratings yet
- Motion Exercise 1 AND 2Document25 pagesMotion Exercise 1 AND 29-E PRADYOT SINHANo ratings yet
- EXERCISE 1 AND 2Document28 pagesEXERCISE 1 AND 29-E PRADYOT SINHANo ratings yet
- Exercise - 3Document22 pagesExercise - 39-E PRADYOT SINHANo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Tissue Level of OrganisationDocument66 pagesUnit 1 Tissue Level of Organisationkrystal1994100% (1)
- Parts of A CellDocument16 pagesParts of A CellThomas417No ratings yet
- Biology Grade 11 3rd Quarter DLLDocument21 pagesBiology Grade 11 3rd Quarter DLLkyru Schatten100% (1)
- Epigenetic and Cancer Therapy, 2019Document12 pagesEpigenetic and Cancer Therapy, 2019AbsjeyNo ratings yet
- Protein Synthesis: Teacher Answer Key: Code CrackingDocument10 pagesProtein Synthesis: Teacher Answer Key: Code CrackingMariana SuescúnNo ratings yet
- Genes Segregation and Interaction: Meiosis IDocument3 pagesGenes Segregation and Interaction: Meiosis IDhine Dhine ArguellesNo ratings yet
- Identify & Describe The Type - Describe The Function - Name One LocationDocument22 pagesIdentify & Describe The Type - Describe The Function - Name One LocationSpencer WebbNo ratings yet
- bk978 0 7503 1302 5ch1Document31 pagesbk978 0 7503 1302 5ch1Vaibhav RAJ KUMAR GUPTANo ratings yet
- H2 Receptor BlockersDocument11 pagesH2 Receptor BlockersApurba Sarker ApuNo ratings yet
- IHC Dako HandbookDocument67 pagesIHC Dako Handbooksusilorini100% (23)
- EnzymesDocument41 pagesEnzymesYing Fei LimNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13 - Platelet Production, Structure and FunctionDocument6 pagesChapter 13 - Platelet Production, Structure and FunctionAira UsiNo ratings yet
- Oxidative PhosphorylationDocument47 pagesOxidative PhosphorylationSadaf BegNo ratings yet
- Drug DistributionDocument27 pagesDrug DistributionLailaturrahmi LailaturrahmiNo ratings yet
- MUST To KNOW in Hematology1-1Document45 pagesMUST To KNOW in Hematology1-1Jez Mendoza ManuelNo ratings yet
- Medical Biochemistry Course Syllabus 2010Document6 pagesMedical Biochemistry Course Syllabus 2010Sheryl ShohamNo ratings yet
- Department of Education: Republic of The PhilippinesDocument1 pageDepartment of Education: Republic of The PhilippinesSuzuri LNo ratings yet
- Cape Biology 2018 U1 p2 MsDocument16 pagesCape Biology 2018 U1 p2 MsYagna Lall81% (16)
- 03 Epithelium 2022Document78 pages03 Epithelium 2022AlkadafeNo ratings yet
- Metabolism of BacteriaDocument39 pagesMetabolism of BacteriaPinaki ChatterjeeNo ratings yet
- Epigenetics of The Yeast Galactose Genetic Switch: P J B and R SIDocument10 pagesEpigenetics of The Yeast Galactose Genetic Switch: P J B and R SIChad ChouNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 Respiration Bio f4Document10 pagesChapter 7 Respiration Bio f4Saidatul Atyah Mohd ApendaiNo ratings yet
- Tricarboxylic Acid CycleDocument25 pagesTricarboxylic Acid CycleJulia Mae LabajoNo ratings yet
- Final ReportDocument27 pagesFinal Reportapi-340511124No ratings yet
- 06 9700 42 2013 62592.inddDocument2 pages06 9700 42 2013 62592.inddRaphael JosephNo ratings yet
- Barbara J Bain - Haemoglobinopathy DiagnosisDocument440 pagesBarbara J Bain - Haemoglobinopathy DiagnosisMantavya PurohitNo ratings yet
- 2.2 Drug Absorption From The GITDocument15 pages2.2 Drug Absorption From The GITCari MosehuusNo ratings yet
- MeiosisSEDocument10 pagesMeiosisSEtheodougy17No ratings yet
- 1St Unit Test (Foundation Course) Class-Ix Sub: - BIOLOGY Full Marks: - 35 Time: - 1hr 20 MinsDocument2 pages1St Unit Test (Foundation Course) Class-Ix Sub: - BIOLOGY Full Marks: - 35 Time: - 1hr 20 MinsJoyabrata SarkarNo ratings yet