Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Takina-Job-Safety-Analysis-and-Training-register_V2
Takina-Job-Safety-Analysis-and-Training-register_V2
Uploaded by
satishdawane2390Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Takina-Job-Safety-Analysis-and-Training-register_V2
Takina-Job-Safety-Analysis-and-Training-register_V2
Uploaded by
satishdawane2390Copyright:
Available Formats
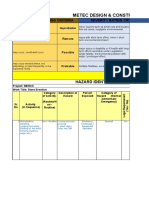
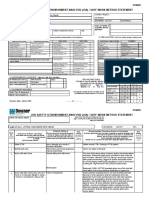
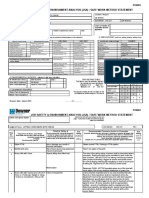
JOB SAFETY ANALYSIS (JSA)
This Job Safety Analysis (JSA) is a site-specific documented approach to tasks, which are required to be risk rated and managed.
SECTION 1: JSA DETAILS
Event Name JHA No.
Task Description
Is a Permit Required? What type? ☐ Confined Space ☐ Hot Work ☐ Working At Height Other
List procedures and other documents related to the
work that should be available and understood prior
to undertaking task.
SECTION 2: TOOLS AND EQUIPMENT
List PPE required. ☐ High Vis Vest ☐ Ear Protection ☐ Hand Protection ☐ Foot Protection ☐ Safety Glasses ☐ Hard Hat
List training / licenses / certificates
required for workers
Note: Work requiring high-risk activities,
e.g., scaffolding, dogging, rigging, crane,
hoist, and forklift operation.
SECTION 3: EMERGENCY DETAILS
Emergency Details: (Enter phone or contact points in the event of an emergency)
SECTION 4: SIGN OFF
Supervisor Name Signature Date
H&S Manager Signature Date
JSA Team
Members Names
JOB SAFETY ANALYSIS AND TRAINING REGISTER - TĀKINA EVENTS Page 1 of 8
JOB SAFETY ANALYSIS (JSA)
SECTION 5: JSA TABLE
Job Steps What ‘Hazards’ (damaging energies) What ‘Controls’ will you use? After you apply the Control,
are associated with the job step? what is the risk reduced to?
(List job steps one at a time, (Elimination, Substitution, Engineering,
answering ‘hazards’ and (Refer to appendix – damaging energies Administration, PPE) (Refer to appendix - low, medium-
‘controls’ for each before - Is there something that can injure or low, medium-high, high)
proceeding to the next job step) harm you, damage equipment or the
environment)
1. List the job step. 2. Identify the hazards- use your hazard 3. List your controls – refer to 4. Using the risk matrix, determine
table if you need help. procedures, permits, hazard/risk the risk level.
register or other information.
JOB SAFETY ANALYSIS AND TRAINING REGISTER - TĀKINA EVENTS Page 2 of 8
JOB SAFETY ANALYSIS (JSA)
WORKGROUP MUST SIGN ONTO JSA
I acknowledge that I have read, understood, and will comply with the requirements of the JSA and any associated documentation. I am fit, trained and competent
to complete the risks assigned to me.
NAME DATE SIGNED NAME DATE SIGNED
The JSA is valid for the duration of the task. If significant changes occur, then a new JSA must be completed.
JOB SAFETY ANALYSIS AND TRAINING REGISTER - TĀKINA EVENTS Page 3 of 8
JOB SAFETY ANALYSIS (JSA)
APPENDIX 1: ASSESSING THE RISK OF A WORK ACTIVITY (REFER TO SECTION 4 OF JSA TABLE)
Step 1: JSA Detail - Complete Sections 1, 2 and 3 of the JSA.
Step 2: List Job Steps - In Section 5 of the JSA table, list the job steps required for the activity in the order that they will be performed.
Step 3: Identify Hazards (damaging energies) associated with the work activity (What can injure or harm?) Complete section 5 of the JHA.
Hazard Type Hazard Hazard Hazard Hazard Hazard
Type Type
Climatic / Wind, hail, rain, extreme weather Electrical / Low / high voltage, AC voltage, DC Gravity Stability (ground / structural stability, fall from
Natural conditions magnetic voltage, loss of power, magnetic one level to another (object, person,
events fields, static electricity, control material),
systems, DC earth leakage
Work Confined spaces, remote activities / Mechanical Pinching, crushing, pulling, Substance Chemicals, hydrocarbons, raw materials,
Environment isolation, slippery conditions, uneven or severing, grinding, scraping, s products, gases, fumes, fibres, dust,
broken ground, pedestrians / people in impact, puncturing, moving/rotating flammables.
work area, use of ladders / scaffolding equip.
Lighting Low/high level glare Waste Pollution, waste creation/disposal / Vehicles/ Vehicles (heavy, light, medium 4WD)
recycling, spill transport
Ergonomics Lifting, pushing, pulling, bending, twisting, Thermal / Ambient/radiant heat, cold stress, Radiation Electromagnetic, infrared, laser, radio
whole body/hand and arm vibration, work Fire / heat stress, contact (cold, hot), frequency, microwave, ultraviolet, welding
area design, hand tool, use Explosion extreme cold/heat, fire. flash, x-ray
awkward/sustained postures, repetitive
motion actions
Personal / Fatigue, shift work, fitness for work Sound / Continuous/impact noise, Biological Legionella, infection (viral, bacterial), bites
behaviours (medication effects, reduced Vibration community issue noise/vibration (animal, insect) fauna, flora,
physical/mental capacity)
JOB SAFETY ANALYSIS AND TRAINING REGISTER - TĀKINA EVENTS Page 4 of 8
JOB SAFETY ANALYSIS (JSA)
STEP 4: DETERMINE AND IMPLEMENT CONTROLS (USE THE HIERARCHY OF CONTROLS BELOW TO DECIDE THE TYPE OF CONTROL TO BE
IMPLEMENTED, ELIMINATION BEING THE MOST PREFERRED OPTION
Controls are identified in job procedures however if these are not available, this JSA becomes your Safe Work Method statement therefore controls shall be in
accordance with industry / Australian / New Zealand Standards and any legislative requirements. Controls are then applied in order of effectiveness. Determine
controls required for the work, add to Section 5 and implement.
Controls (Hierarchy of Effectiveness Descriptor Examples
Control)
Elimination Wherever possible, eliminate the hazard in the first Removing the hazard Completing tasks at ground level instead of at
(most effective) instance. from the work sequence height thereby removing the risk of a fall from
height
Isolation Where elimination is not possible, isolate the area Isolating to a risk with Using a less hazardous chemical
something posing a
lesser risk
Engineering Where neither elimination nor substitution is Physical measures to Applying barricading to prevent inadvertent
possible, consider an engineering solution, such as separate workers from access or handrails to prevent a fall from height
isolation, barricading or guarding. hazards
Minimisation Where neither elimination, substitution nor Application of training, Provision of training in hazards associated with
engineering is possible, develop safe work procedures, method the work to increase awareness
procedures that will assist persons perform the statements
work safely.
Personal Protective This is the least effective method and relies heavily Use of PPE to reduce Use of P2 masks when working with asbestos to
Equipment on persons selecting, using and maintaining PPE in exposure reduce the risk of exposure to airborne
(least effective) accordance with their specifications. PPE on its contaminants
own cannot be used as the only source of control.
JOB SAFETY ANALYSIS AND TRAINING REGISTER - TĀKINA EVENTS Page 5 of 8
JOB SAFETY ANALYSIS (JSA)
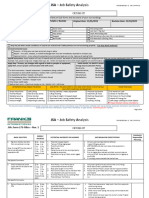
STEP 5: ASSESS THE RISK (CALCULATE THE RISKS USING THE LIKELIHOOD, CONSEQUENCE AND RISK MATRIX)
Determine the possible consequences of an incident should only the existing controls be in place. This calculation is done by looking at the hazards identified
within the job step and determining the likelihood of the incident happening (use the likelihood table) and the consequence should it happen (use the consequence
table). Using the risk matrix (consequence on the left and likelihood on the top), the risk level is determined where these two columns meet. Enter the risk level
to your JSA table at Section 5.
LIKELIHOOD TABLE (descriptors) CONSEQUENCE TABLE (descriptors)
Likelihood Description Consequence Description - Personal (Health and Safety) Financial (loss/damage)
Rare Unlikely to occur and only Severe 4-10 fatalities (or permanent Total Disabilities) $50M to $250M
in exceptional
circumstances
Unlikely Once in the life of the Major 1-3 Fatality (or permanent Total Disabilities) $5M to $50M
business
Possible Once a year Moderate Major Injury / Illness Permanent loss of bodily function $500K to $5M
(<30%), Lost Time Case > 2 days
Likely Once a month Minor Slight Injury / Illness (reversible), Medical Treatment Case $50K to $500K
Almost Certain Once a week Slight Low level short term impact / Minor First Aid / No <$50K
medical treatment
JOB SAFETY ANALYSIS AND TRAINING REGISTER - TĀKINA EVENTS Page 6 of 8
JOB SAFETY ANALYSIS (JSA)
RISK MATRIX MINIMAL MINOR MODERATE MAJOR SEVERE
Almost Certain
Expected to occur in most instances
<86% probability of occurring 5 10 20 30 70
Event occurs on a frequent basis
Likely
Will probably occur in most instances
66 - 85% probability of occurring 4 8 16 24 56
Event occurs several times per year
Possible
50/50 that it might occur at some time
3 6 12 18 42
35 - 65% probability of occurring
Event occurs once or twice per year
Unlikely
Could occur at some time
2 4 8 12 28
15-34% probability of occurring
Event occurs from time to time
Rare
May occur in exceptional circumstances
1 2 4 6 14
<14% probability of occurring
Event known to occur
STEP 6: APPROVAL TO PROCEED
Arrange sign off of Section 4 of the JSA. Note: All JSA’s shall be signed off by the Supervisor. Where hazards are identified as ‘high’ or higher and where these
cannot be reduced further, the Te Papa Health and Safety Manager shall review to determine if the work should continue and what strategies shall be implemented
address the risks raised.
JOB SAFETY ANALYSIS AND TRAINING REGISTER - TĀKINA EVENTS Page 7 of 8
TRAINING AND QUALIFICATION REGISTER
TRAINING AND QUALIFICATION REGISTER
First and last name Key role or task on this job Training and/or qualifications relevant to this job Training expiry No. of years
(EWP, forklift, first aid) date experience
Examples – EWP (elevated work platform), FL (fork lift), FA (fall arrest), SCA (scaffold), DOG (dogman), MP (mobile plant – specify type), RELECT (registered electrical worker), ELTAG (electrical
testing and tagging)
JOB SAFETY ANALYSIS AND TRAINING REGISTER - TĀKINA EVENTS Page 8 of 8
You might also like
- Working Heights Risk Assessment TemplateDocument8 pagesWorking Heights Risk Assessment TemplatemahmoudmakladNo ratings yet
- SWMS - Glass PartitionDocument11 pagesSWMS - Glass PartitionParasNo ratings yet
- Hard Hat, Safety Glasses, Safety Boots Compulsory: PowerDocument9 pagesHard Hat, Safety Glasses, Safety Boots Compulsory: PowerEbeneshwar Anthony71% (7)
- 25-Risk Assessment For Fabrication & NDT During Night ShiftDocument2 pages25-Risk Assessment For Fabrication & NDT During Night Shiftgulryz84100% (9)
- JHA Template BlankDocument5 pagesJHA Template BlankChristopher Newby100% (1)
- JSA For Elevator InstallationDocument11 pagesJSA For Elevator InstallationHamid RazaNo ratings yet
- JSA For Install Instrument Sample Point HousingDocument3 pagesJSA For Install Instrument Sample Point HousingNasrullah JanNo ratings yet
- SWMS 2 Fixing CarpenterDocument3 pagesSWMS 2 Fixing CarpenterJonasNo ratings yet
- Generator RADocument16 pagesGenerator RABaher MohamedNo ratings yet
- Working Heights Risk Assessment TemplateDocument8 pagesWorking Heights Risk Assessment TemplateJUAN NICANOR ALIAGA GIRONNo ratings yet
- Risk Assessment Form1Document3 pagesRisk Assessment Form1Elites ChoraleNo ratings yet
- JSA - Unloading & Positioning of Pre Action EquipmentDocument7 pagesJSA - Unloading & Positioning of Pre Action EquipmentRAJKUMAR MUTHINENINo ratings yet
- JSA 08 Laying of Conduit WiringDocument8 pagesJSA 08 Laying of Conduit Wiringsyed khaja misbhuddinNo ratings yet
- Working Heights Risk Assessment TemplateDocument8 pagesWorking Heights Risk Assessment TemplatePanchdev KumarNo ratings yet
- Job Safety Analysis Form 0Document2 pagesJob Safety Analysis Form 0ahmar javedNo ratings yet
- Jsa-Installation Roof Truss Steel Structure For ShelterDocument10 pagesJsa-Installation Roof Truss Steel Structure For ShelterAisha purconNo ratings yet
- Daily Plant InspectionDocument5 pagesDaily Plant InspectionSteve O'DonoghueNo ratings yet
- JSA G20 Scaffolding Erection DismantlingDocument4 pagesJSA G20 Scaffolding Erection DismantlingemmyNo ratings yet
- Working Heights Risk Assessment TemplateDocument8 pagesWorking Heights Risk Assessment TemplateeddieNo ratings yet
- JSA Template HVH CoverDocument10 pagesJSA Template HVH CoverAisha purconNo ratings yet
- Mazzella FallProtectionJSABundle 1218Document7 pagesMazzella FallProtectionJSABundle 1218mostafa zakiNo ratings yet
- JSA Assessement geeneral updatedDocument11 pagesJSA Assessement geeneral updatedhabib42833No ratings yet
- Sewing Machine Risk AssessmentDocument2 pagesSewing Machine Risk Assessmenteunicemabena664No ratings yet
- Ro3 Co2co2 TBV Hse Ra 006.00Document12 pagesRo3 Co2co2 TBV Hse Ra 006.00like saddamNo ratings yet
- Job Safety & Environment Analysis (Jsa) : Activity or TaskDocument3 pagesJob Safety & Environment Analysis (Jsa) : Activity or TaskLusy Gusti EfendiNo ratings yet
- Safety Engineering and JhaDocument29 pagesSafety Engineering and JhaDarren Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- General Heat Stress Prevention Risk AssessmentDocument4 pagesGeneral Heat Stress Prevention Risk Assessmentprecivalcamilus19No ratings yet
- MS-AS-FRM-0063 Job Hazard Analysis Worksheet Form-1 (1)Document3 pagesMS-AS-FRM-0063 Job Hazard Analysis Worksheet Form-1 (1)reda ihsaneNo ratings yet
- Electrical, Rev 01Document235 pagesElectrical, Rev 01Samy KsNo ratings yet
- Job Hazard Analysis (Jha) Instructions: Job or Activity: Sequence of Job Steps: Hazards and ConsequencesDocument2 pagesJob Hazard Analysis (Jha) Instructions: Job or Activity: Sequence of Job Steps: Hazards and ConsequencesTanri Andita WicaksonoNo ratings yet
- The Form Should Be Used in Accordance With The Job Hazard Analysis Standard MS-AS-STD-0064Document3 pagesThe Form Should Be Used in Accordance With The Job Hazard Analysis Standard MS-AS-STD-0064Mounir HammoutiNo ratings yet
- Instructions For Completing Job Analysis FormDocument3 pagesInstructions For Completing Job Analysis Formghada gattouchNo ratings yet
- P10 - H12 - JSA - Electrical - Rev 00 - 20221204Document6 pagesP10 - H12 - JSA - Electrical - Rev 00 - 20221204imranNo ratings yet
- Safety Case TemplateDocument23 pagesSafety Case TemplateOluwagbemi SundayNo ratings yet
- Ws Job Safety Assessment 11Document8 pagesWs Job Safety Assessment 11liveconnectionz282No ratings yet
- P10 - H12 - JSA - Lifting - Rev 00 - 20221204Document6 pagesP10 - H12 - JSA - Lifting - Rev 00 - 20221204imranNo ratings yet
- Ro3 Co2co2 TBV Hse Ra 005.00Document19 pagesRo3 Co2co2 TBV Hse Ra 005.00like saddamNo ratings yet
- MS-As-FRM-0063 Job Hazard Analysis Worksheet FormDocument3 pagesMS-As-FRM-0063 Job Hazard Analysis Worksheet Formأم رهامNo ratings yet
- Continuous Medical Education (Cme)Document28 pagesContinuous Medical Education (Cme)Kyle VanrynNo ratings yet
- Logistic Management-Risk AssessmentDocument10 pagesLogistic Management-Risk Assessmentlike saddamNo ratings yet
- iFUEL CON Risk AssessmentDocument3 pagesiFUEL CON Risk AssessmentHoang Quoc DungNo ratings yet
- Instructions For Completing Job Analysis FormDocument2 pagesInstructions For Completing Job Analysis Formghada gattouchNo ratings yet
- General Risk AssessmentDocument2 pagesGeneral Risk AssessmentlisaconnollyNo ratings yet
- OSH Inspection HIRAC - GOV - SO2210531-0604Document31 pagesOSH Inspection HIRAC - GOV - SO2210531-0604James RecañaNo ratings yet
- OHSW Plant Specific Hazard IdentificationDocument3 pagesOHSW Plant Specific Hazard IdentificationGokul pNo ratings yet
- General RA TemplateDocument2 pagesGeneral RA TemplateGeorgeNo ratings yet
- Skanska Pretask Planning PlaybookDocument98 pagesSkanska Pretask Planning PlaybookKannon TamNo ratings yet
- Cutting A Hole in The Gratings On The Shale Shakers AreaDocument2 pagesCutting A Hole in The Gratings On The Shale Shakers Areaghada gattouchNo ratings yet
- JSA G17 Lift Container With Crane PDFDocument4 pagesJSA G17 Lift Container With Crane PDFsetiawanaji407100% (1)
- JSA G17 Lift Container With CraneDocument4 pagesJSA G17 Lift Container With Cranesetiawanaji407No ratings yet
- Waterproofing WorkDocument10 pagesWaterproofing WorkNisanth ThulasidasNo ratings yet
- Instructions For Completing Job Analysis FormDocument2 pagesInstructions For Completing Job Analysis Formghada gattouchNo ratings yet
- Field Level Risk AssessmentDocument23 pagesField Level Risk AssessmentTammyNo ratings yet
- Job Safety Analysis KFS-IMSF-HRA-01-Job Safety AnalysisDocument2 pagesJob Safety Analysis KFS-IMSF-HRA-01-Job Safety AnalysisAmit ChahandeNo ratings yet
- JSA 173 - CRT RIG UP - Updated 21.10.2019Document11 pagesJSA 173 - CRT RIG UP - Updated 21.10.2019tafhim rashidNo ratings yet
- TRA Strainer Cleaning 01Document7 pagesTRA Strainer Cleaning 01Ijaz Hussain50% (2)
- Plant and Equipment Risk AssesmentDocument5 pagesPlant and Equipment Risk Assesmentmjradley79No ratings yet
- Grading Risk AssessmentDocument5 pagesGrading Risk AssessmentLawrence adeleke OmisakinNo ratings yet
- The Handbook of Safety Engineering: Principles and ApplicationsFrom EverandThe Handbook of Safety Engineering: Principles and ApplicationsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Physical Hazard Control: Preventing Injuries in the WorkplaceFrom EverandPhysical Hazard Control: Preventing Injuries in the WorkplaceNo ratings yet
- Confined Space (Underfloor Entry)Document6 pagesConfined Space (Underfloor Entry)Tony ZhangNo ratings yet
- NEBOSH IG1 2023 WWP AnswersDocument12 pagesNEBOSH IG1 2023 WWP Answersaliceughi1No ratings yet
- Construction Safety and Health ProgramDocument13 pagesConstruction Safety and Health ProgramDeosrock SalvadorNo ratings yet
- AOV Operating ManualDocument40 pagesAOV Operating ManualThanh Tung NguyenNo ratings yet
- MSDS - Regal - R&o - 32, 46, 68 - Oils - UsDocument7 pagesMSDS - Regal - R&o - 32, 46, 68 - Oils - UsAustin UdofiaNo ratings yet
- Rewinder STD Extra5 GB01Document126 pagesRewinder STD Extra5 GB01ruboNo ratings yet
- 3075 SWMS RendererDocument13 pages3075 SWMS Renderernik KooNo ratings yet
- Safety Data Sheet: Hempel'S Curing Agent 98550Document12 pagesSafety Data Sheet: Hempel'S Curing Agent 98550akhilsyam21No ratings yet
- TabunDocument24 pagesTabunMiftakul SururiNo ratings yet
- 2018 Chapter 3-4 Ergonomics PDFDocument76 pages2018 Chapter 3-4 Ergonomics PDFLove StrikeNo ratings yet
- Inge UF Dizzerl55 Vertical Assembly Instructions Manual 45 D02229 enDocument45 pagesInge UF Dizzerl55 Vertical Assembly Instructions Manual 45 D02229 enSamoel Anjos0% (1)
- Safety Data Sheet: Flowback Surfactant B.525Document9 pagesSafety Data Sheet: Flowback Surfactant B.525Pranav DubeyNo ratings yet
- Chemical Safety PresentationDocument16 pagesChemical Safety Presentationrahul100% (1)
- SUDAIR-HSE-PR-012-01-PPE ManagementDocument19 pagesSUDAIR-HSE-PR-012-01-PPE ManagementGerardoNo ratings yet
- PSIS - BISCO Silicones HT-1510Document5 pagesPSIS - BISCO Silicones HT-1510mukeshNo ratings yet
- MSDS SunlightDocument3 pagesMSDS SunlightAri RamadhanNo ratings yet
- MSDS AminofilinDocument5 pagesMSDS AminofilinDiana SekarNo ratings yet
- Hazard Recognition & Control Training: Exercise ADocument23 pagesHazard Recognition & Control Training: Exercise Amd azmiNo ratings yet
- Jha - SW - 22 - Spandex Wall ReplacementDocument5 pagesJha - SW - 22 - Spandex Wall ReplacementFikri HidayatNo ratings yet
- Carpentry NC II - 21 DaysDocument75 pagesCarpentry NC II - 21 Dayselizabeth olarveNo ratings yet
- MS For Paint & Repair WorksDocument12 pagesMS For Paint & Repair WorksmasroorNo ratings yet
- Week 06 Senior Management HSE EvaluationDocument13 pagesWeek 06 Senior Management HSE EvaluationwajiNo ratings yet
- SWP 03 - Hacking WorksDocument3 pagesSWP 03 - Hacking WorksGerald Wong NttNo ratings yet
- Aquasoft CI - MSDSDocument3 pagesAquasoft CI - MSDSJaleel AhmedNo ratings yet
- Bamboo U Online - Module 7 - Step by Step Guide To Traditional JointsDocument9 pagesBamboo U Online - Module 7 - Step by Step Guide To Traditional Jointsreno otoNo ratings yet
- DMA+Legal+Requirements UnlockedDocument20 pagesDMA+Legal+Requirements UnlockedAli ZafarNo ratings yet
- Vanquish Pumps (VH-P10) - Operating ManualDocument228 pagesVanquish Pumps (VH-P10) - Operating ManualNguyễnHoàngDanhNo ratings yet
- 26071-100-530-GST-00013 Method Statement For Instrument Logic Function Test - 00ADocument47 pages26071-100-530-GST-00013 Method Statement For Instrument Logic Function Test - 00Awidionosucipto29No ratings yet