Professional Documents
Culture Documents
191105082_MCN_Exp4
191105082_MCN_Exp4
Uploaded by
gaonkarsaish1112Copyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Manual Do Modem Da Valenet - Quick Start ManualDocument10 pagesManual Do Modem Da Valenet - Quick Start ManualItalo Almeida100% (2)
- Forcepoint NGFW Mobile VPN ConfigDocument18 pagesForcepoint NGFW Mobile VPN ConfigGeorge JR BagsaoNo ratings yet
- Cisco CCNA Command Guide: An Introductory Guide for CCNA & Computer Networking Beginners: Computer Networking, #3From EverandCisco CCNA Command Guide: An Introductory Guide for CCNA & Computer Networking Beginners: Computer Networking, #3No ratings yet
- CCNA Study SummaryDocument15 pagesCCNA Study SummaryJaimal Singh JaimalNo ratings yet
- CCNA 1 Chapter 11 Study GuideDocument11 pagesCCNA 1 Chapter 11 Study GuideGreg MillerNo ratings yet
- CCNA - Day School 2Document25 pagesCCNA - Day School 2Jonathan EckloffNo ratings yet
- Jitsi Meet /W Call-In and Active Directory: Home MusicDocument11 pagesJitsi Meet /W Call-In and Active Directory: Home MusicmircammNo ratings yet
- Lab#4 (Basic Networks Commonds)Document5 pagesLab#4 (Basic Networks Commonds)NomanNo ratings yet
- Cisco Router Configuration Tutorial PDFDocument8 pagesCisco Router Configuration Tutorial PDFHamami InkaZoNo ratings yet
- CN Lab 3Document7 pagesCN Lab 3Esha JavaidNo ratings yet
- It010 707 (Reference) Internetworking LabDocument109 pagesIt010 707 (Reference) Internetworking LabDivya K.SNo ratings yet
- Cisco Routers and Switches: Phoenix Cisco User Group (PCUG)Document55 pagesCisco Routers and Switches: Phoenix Cisco User Group (PCUG)Denis ManicNo ratings yet
- CCNA Cheat Sheet: Experts in NetworkingDocument8 pagesCCNA Cheat Sheet: Experts in NetworkingHeribertus BudhihartoNo ratings yet
- Cisco IOS Router CommandsDocument7 pagesCisco IOS Router CommandsbatousaiNo ratings yet
- Cisco® Router Configuration & Troubleshooting - 3 - Initial Router SetupDocument10 pagesCisco® Router Configuration & Troubleshooting - 3 - Initial Router SetupDev VishwakarmaNo ratings yet
- E2 Lab 1 5 2Document11 pagesE2 Lab 1 5 2Ninja NuggetNo ratings yet
- Routing: Engr. Neriza V. Bustillo, Mpa, MitDocument35 pagesRouting: Engr. Neriza V. Bustillo, Mpa, Mitsamiza1122No ratings yet
- Practical 1 (CN)Document9 pagesPractical 1 (CN)Sonal RathvaNo ratings yet
- Lab 3 ManualDocument16 pagesLab 3 ManualDeep Narayan ChaudhuriNo ratings yet
- Basic Router ConfigDocument13 pagesBasic Router Configelvis page kamunanwireNo ratings yet
- Laboratory 1Document2 pagesLaboratory 1dkhanNo ratings yet
- Ccna Certifications BasiDocument4 pagesCcna Certifications BasiAnupam MishraNo ratings yet
- Perintah Untuk Memberikan Deskripsi Mengenai Interface RouterDocument5 pagesPerintah Untuk Memberikan Deskripsi Mengenai Interface RouterLeonardo HutapeaNo ratings yet
- Cisco Router Configuration Tutorial: Cisco Inter-Network Operating SystemDocument11 pagesCisco Router Configuration Tutorial: Cisco Inter-Network Operating Systemheruye mulugetaNo ratings yet
- Department of Computer Science & Engineering: Independent University, Bangladesh (IUB)Document11 pagesDepartment of Computer Science & Engineering: Independent University, Bangladesh (IUB)Zulker NienNo ratings yet
- CCNADocumentV7 ITN Module10 BasicRouterConfigurationDocument16 pagesCCNADocumentV7 ITN Module10 BasicRouterConfigurationPHONG TRẦN HỒNGNo ratings yet
- CCN Exp2Document11 pagesCCN Exp2Palaash GandhiNo ratings yet
- Configuring A Router: Nescot Catc 1Document10 pagesConfiguring A Router: Nescot Catc 1DidierJairUranAvendañoNo ratings yet
- Ethernet CablingDocument8 pagesEthernet CablingOctav EnachiNo ratings yet
- Answer of CCNA DiscoveryGBDocument34 pagesAnswer of CCNA DiscoveryGBChimdi KweksNo ratings yet
- Cisco IOS Tips and TricksDocument16 pagesCisco IOS Tips and TricksChavara MatekweNo ratings yet
- CLI Command HierarchyDocument6 pagesCLI Command HierarchyddiixxyyNo ratings yet
- Networking CommandsDocument5 pagesNetworking CommandsChristina JosephNo ratings yet
- Basic Router Configuration: Honolulu Community College Cisco Academy Training Center Semester 2Document19 pagesBasic Router Configuration: Honolulu Community College Cisco Academy Training Center Semester 2elia maulaNo ratings yet
- Configuring A Router: CCNA 2 v3 - Module 3Document10 pagesConfiguring A Router: CCNA 2 v3 - Module 3Vladimir OleynikovNo ratings yet
- 10 Commandos CiscoDocument2 pages10 Commandos CiscoCarlos SolisNo ratings yet
- RAM. Most of The Configuration Commands Deal With Moving Information Into and Out From RAMDocument53 pagesRAM. Most of The Configuration Commands Deal With Moving Information Into and Out From RAMEdara PrasaadNo ratings yet
- CS-356 Computer Networks Lab 1Document13 pagesCS-356 Computer Networks Lab 1atishkumar20180No ratings yet
- Quick CommandsDocument9 pagesQuick CommandsMark WoffardNo ratings yet
- CCNA PresentationDocument127 pagesCCNA PresentationVVNAGESWARNo ratings yet
- Router CommandsDocument7 pagesRouter Commandsmuneebali445No ratings yet
- Use The Following Diagram For The Following ConfigurationsDocument15 pagesUse The Following Diagram For The Following ConfigurationsmkumbleNo ratings yet
- NDC Chapter 3Document9 pagesNDC Chapter 3Aschalew Getnet MengistuNo ratings yet
- Mode Prompt Command To Enter Command To ExitDocument8 pagesMode Prompt Command To Enter Command To ExitManjunathNo ratings yet
- CN - 60004200117 - Expt 2Document14 pagesCN - 60004200117 - Expt 2bhavik shahNo ratings yet
- Lab Name: Networking Commands EmulationDocument2 pagesLab Name: Networking Commands EmulationAriful HaqueNo ratings yet
- CN Exp-3Document7 pagesCN Exp-33017 Antara Mudi Cse AiNo ratings yet
- CN Exp-3Document7 pagesCN Exp-33017 Antara Mudi Cse AiNo ratings yet
- Cisco RoutersDocument15 pagesCisco Routerssmara_1009No ratings yet
- Experiment 5 - Basic Networking Commands in MsdosDocument5 pagesExperiment 5 - Basic Networking Commands in MsdosM ZahidNo ratings yet
- CCNA 2 Exams SolvedDocument70 pagesCCNA 2 Exams Solvedvisky100% (9)
- CN PR 10Document9 pagesCN PR 10dkchauhanNo ratings yet
- Ping Command:: Assignment No: 1Document16 pagesPing Command:: Assignment No: 1Ninad ShetkarNo ratings yet
- Modules 1 - 3 - EnglishDocument25 pagesModules 1 - 3 - EnglishChabi HonoratNo ratings yet
- Welcome To CCNA 2/3/4: Some Important Info To FollowDocument60 pagesWelcome To CCNA 2/3/4: Some Important Info To FollowPaul Kruger KokNo ratings yet
- CNS Lab Manual 2019 Course - UpdatedDocument96 pagesCNS Lab Manual 2019 Course - Updatedswapnil khandareNo ratings yet
- CCN Practical No.2Document11 pagesCCN Practical No.2Gaurang GawasNo ratings yet
- CNE Tutorial 02 - Real - LAN and LAN With Packet TracerDocument18 pagesCNE Tutorial 02 - Real - LAN and LAN With Packet TracerThơm VũNo ratings yet
- CISCO PACKET TRACER LABS: Best practice of configuring or troubleshooting NetworkFrom EverandCISCO PACKET TRACER LABS: Best practice of configuring or troubleshooting NetworkNo ratings yet
- Network with Practical Labs Configuration: Step by Step configuration of Router and Switch configurationFrom EverandNetwork with Practical Labs Configuration: Step by Step configuration of Router and Switch configurationNo ratings yet
- LEARN MPLS FROM SCRATCH PART-B: A Beginners guide to next level of networkingFrom EverandLEARN MPLS FROM SCRATCH PART-B: A Beginners guide to next level of networkingNo ratings yet
- 191105082_exp2_MCNDocument6 pages191105082_exp2_MCNgaonkarsaish1112No ratings yet
- 191105082_MCN_Exp3Document5 pages191105082_MCN_Exp3gaonkarsaish1112No ratings yet
- 191105082_EXP1_MCNDocument8 pages191105082_EXP1_MCNgaonkarsaish1112No ratings yet
- 191105082_Exp8_MCNDocument3 pages191105082_Exp8_MCNgaonkarsaish1112No ratings yet
- 191105082_MCN_Exp10Document2 pages191105082_MCN_Exp10gaonkarsaish1112No ratings yet
- CN Lab ManualDocument72 pagesCN Lab Manualvino dhiniNo ratings yet
- How To Connect To iSCSI Targets On QNAP NAS Using MPIO On Windows 2008Document30 pagesHow To Connect To iSCSI Targets On QNAP NAS Using MPIO On Windows 2008Jazz OberoiNo ratings yet
- FiberHome FTTX SoluciónDocument54 pagesFiberHome FTTX Soluciónmacias_marlon100% (2)
- Lantv Television On IP NetworksDocument8 pagesLantv Television On IP NetworksdhanushkasuriyaNo ratings yet
- 3800x3600x-Software Configuration Guide 15.4.1sDocument1,292 pages3800x3600x-Software Configuration Guide 15.4.1sscorcdNo ratings yet
- PTZ Camera TycoDocument3 pagesPTZ Camera Tycogokul krishnaNo ratings yet
- TCP Model (Net101)Document2 pagesTCP Model (Net101)Yhuber BalbidinaNo ratings yet
- Voxai Solutions Firewall Ruleset Review H1 Report v1.1 February 28 2023 CDocument11 pagesVoxai Solutions Firewall Ruleset Review H1 Report v1.1 February 28 2023 Cmuddassir.nocNo ratings yet
- Brocade ICX 6430 and 6450 Switches: Enterprise-Class Stackable Switching at An Entry-Level PriceDocument16 pagesBrocade ICX 6430 and 6450 Switches: Enterprise-Class Stackable Switching at An Entry-Level PricedimydeskyNo ratings yet
- VoLTE Overview and Features IntroductionDocument45 pagesVoLTE Overview and Features Introductionahmed wedattallahNo ratings yet
- PTCL DSL Installation GuideDocument133 pagesPTCL DSL Installation GuideFarhan ShuaibNo ratings yet
- Network Pentesting Gaining Access 1 PDFDocument17 pagesNetwork Pentesting Gaining Access 1 PDFPhilippNo ratings yet
- 08 XMLDocument9 pages08 XMLMarcela DobreNo ratings yet
- Networks-Lab 6632853 PowerpointDocument22 pagesNetworks-Lab 6632853 PowerpointVivek Kumar SinhaNo ratings yet
- Network ProjectDocument18 pagesNetwork Projectpramodh kumar0% (2)
- IS-IS Segment RoutingDocument21 pagesIS-IS Segment RoutingChristopheProustNo ratings yet
- Tutorial - 02 ADocument8 pagesTutorial - 02 AChanduni GamageNo ratings yet
- Questoes Lpi 2 202 PDFDocument103 pagesQuestoes Lpi 2 202 PDFRomero CostaNo ratings yet
- List of TCP and UDP Port Numbers: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument41 pagesList of TCP and UDP Port Numbers: From Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopediadescargas6xNo ratings yet
- TN303 SW OnuDataPathDocument40 pagesTN303 SW OnuDataPath박철민No ratings yet
- sf300 24ppDocument9 pagessf300 24ppdark musNo ratings yet
- AXS1800 GPON Optical Line Terminal Data Sheet PDFDocument2 pagesAXS1800 GPON Optical Line Terminal Data Sheet PDFKy Pham HongNo ratings yet
- 13 Introducing Basic IPv6Document43 pages13 Introducing Basic IPv6Lorenzo Maria MASELLINo ratings yet
- Phy&Logical Design of IoTDocument45 pagesPhy&Logical Design of IoTVydeki Vijayakumar40% (5)
- Palo-Alto-Firewall-Training I-MEDITADocument4 pagesPalo-Alto-Firewall-Training I-MEDITAspgethicalNo ratings yet
- Introduction To LTE Feature Part4 Updated (VoLTE)Document46 pagesIntroduction To LTE Feature Part4 Updated (VoLTE)brahiti3100% (1)
- Sonicwall Network Security Appliance (Nsa) SeriesDocument14 pagesSonicwall Network Security Appliance (Nsa) Seriesandroid klien01No ratings yet
191105082_MCN_Exp4
191105082_MCN_Exp4
Uploaded by
gaonkarsaish1112Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
191105082_MCN_Exp4
191105082_MCN_Exp4
Uploaded by
gaonkarsaish1112Copyright:
Available Formats
Name: Trusha Neogi Date: 24/4/22
Roll No: 191105082
Branch: TE Comp
EXPERIMENT 4
TITLE: Study of basic network command and Network configuration command.
APPARATUS (SOFTWARE): Command Prompt and Packet Tracer.
PROCEDURE: To do this experiment- follows these steps: In this experiment- students
have to understand basic networking commands e.g., ping, tracert etc.
All commands related to Network configuration which includes how to switch to
privilege mode and normal mode and how to configure router interface and how to
save this configuration to flash memory or permanent memory.
This command includes:
. Configuring the Router commands
. General Commands to configure network
. Privileged Mode commands of a router
. Router Processes & Statistics
. IP Commands
. Other IP Commands e.g., show IP route etc.
ping:
ping(8) sends an ICMP ECHO_REQUEST packet to the specified host. If the host
responds, you get an ICMP packet back. Sound strange? Well, you can “ping” an IP
address to see if a machine is alive. If there is no response, you know something is
wrong.
Trusha Neogi 191105082 Batch E
Traceroute:
Tracert is a command which can show you the path a packet of information taken from
your computer to one you specify. It will list all the routers it passes through until it
reaches its destination, or fails to and is discarded. In addition to this, it will tell you
how long each 'hop' from router to router takes.
nslookup:
Displays information from Domain Name System (DNS) name servers. NOTE: If you
write the command as above it shows as default your pc's server name firstly.
pathping:
A better version of tracert that gives you statics about packet lost and latency.
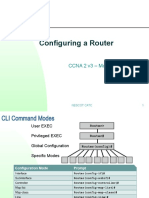
Getting Help
In any command mode, you can get a list of available commands by entering a
question mark (?).
Trusha Neogi 191105082 Batch E
Router>?
To obtain a list of commands that begin with a particular character sequence, type in
those characters followed immediately by the question mark (?).
Router#co?
configure connect copy
To list keywords or arguments, enter a question mark in place of a keyword or
argument. Include a space before the question mark.
Router#configure ?
memory Configure from NV memory
network Configure from a TFTP network host
terminal Configure from the terminal
You can also abbreviate commands and keywords by entering just enough characters
to make the command unique from other commands. For example, you can abbreviate
the show command to sh.
Configuration Files
Any time you make changes to the router configuration, you must save the changes to
memory because if you do not, they will be lost if there is a system reload or power
outage. There are two types of configuration files: the running (current operating)
configuration and the startup configuration.
Use the following privileged mode commands to work with configuration files.
configure terminal – modify the running configuration manually from the terminal.
show running-config – display the running configuration.
show startup-config – display the startup configuration.
copy running-config startup-config – copy the running configuration to the startup
configuration.
copy startup-config running-config – copy the startup configuration to the running
configuration.
erase startup-config – erase the startup-configuration in NVRAM.
copy tftp running-config – load a configuration file stored on a Trivial File Transfer
Protocol (TFTP) server into the running configuration.
copy running-config tftp – store the running configuration on a TFTP server.
IP Address Configuration
Take the following steps to configure the IP address of an interface.
Step 1: Enter privileged EXEC mode:
Router>enable password
Step 2: Enter the configure terminal command to enter global configuration mode.
Router#config terminal
Trusha Neogi 191105082 Batch E
Step 3: Enter the interface type slot/port (for Cisco 7000 series) or interface type port
(for Cisco 2500 series) to enter the interface configuration mode.
Example: Router (config)#interface ethernet 0/1
Step 4: Enter the IP address and subnet mask of the interface using the IP address IP
address subnet mask command.
Example, Router (config-if)#ip address 192.168.10.1 255.255.255.0
Step 5: Exit the configuration mode by pressing Ctrl-Z
Router(config-if)#[Ctrl-Z]
CONCLUSION: Basic network command and Network configuration commands were
studied successfully.
Trusha Neogi 191105082 Batch E
You might also like
- Manual Do Modem Da Valenet - Quick Start ManualDocument10 pagesManual Do Modem Da Valenet - Quick Start ManualItalo Almeida100% (2)
- Forcepoint NGFW Mobile VPN ConfigDocument18 pagesForcepoint NGFW Mobile VPN ConfigGeorge JR BagsaoNo ratings yet
- Cisco CCNA Command Guide: An Introductory Guide for CCNA & Computer Networking Beginners: Computer Networking, #3From EverandCisco CCNA Command Guide: An Introductory Guide for CCNA & Computer Networking Beginners: Computer Networking, #3No ratings yet
- CCNA Study SummaryDocument15 pagesCCNA Study SummaryJaimal Singh JaimalNo ratings yet
- CCNA 1 Chapter 11 Study GuideDocument11 pagesCCNA 1 Chapter 11 Study GuideGreg MillerNo ratings yet
- CCNA - Day School 2Document25 pagesCCNA - Day School 2Jonathan EckloffNo ratings yet
- Jitsi Meet /W Call-In and Active Directory: Home MusicDocument11 pagesJitsi Meet /W Call-In and Active Directory: Home MusicmircammNo ratings yet
- Lab#4 (Basic Networks Commonds)Document5 pagesLab#4 (Basic Networks Commonds)NomanNo ratings yet
- Cisco Router Configuration Tutorial PDFDocument8 pagesCisco Router Configuration Tutorial PDFHamami InkaZoNo ratings yet
- CN Lab 3Document7 pagesCN Lab 3Esha JavaidNo ratings yet
- It010 707 (Reference) Internetworking LabDocument109 pagesIt010 707 (Reference) Internetworking LabDivya K.SNo ratings yet
- Cisco Routers and Switches: Phoenix Cisco User Group (PCUG)Document55 pagesCisco Routers and Switches: Phoenix Cisco User Group (PCUG)Denis ManicNo ratings yet
- CCNA Cheat Sheet: Experts in NetworkingDocument8 pagesCCNA Cheat Sheet: Experts in NetworkingHeribertus BudhihartoNo ratings yet
- Cisco IOS Router CommandsDocument7 pagesCisco IOS Router CommandsbatousaiNo ratings yet
- Cisco® Router Configuration & Troubleshooting - 3 - Initial Router SetupDocument10 pagesCisco® Router Configuration & Troubleshooting - 3 - Initial Router SetupDev VishwakarmaNo ratings yet
- E2 Lab 1 5 2Document11 pagesE2 Lab 1 5 2Ninja NuggetNo ratings yet
- Routing: Engr. Neriza V. Bustillo, Mpa, MitDocument35 pagesRouting: Engr. Neriza V. Bustillo, Mpa, Mitsamiza1122No ratings yet
- Practical 1 (CN)Document9 pagesPractical 1 (CN)Sonal RathvaNo ratings yet
- Lab 3 ManualDocument16 pagesLab 3 ManualDeep Narayan ChaudhuriNo ratings yet
- Basic Router ConfigDocument13 pagesBasic Router Configelvis page kamunanwireNo ratings yet
- Laboratory 1Document2 pagesLaboratory 1dkhanNo ratings yet
- Ccna Certifications BasiDocument4 pagesCcna Certifications BasiAnupam MishraNo ratings yet
- Perintah Untuk Memberikan Deskripsi Mengenai Interface RouterDocument5 pagesPerintah Untuk Memberikan Deskripsi Mengenai Interface RouterLeonardo HutapeaNo ratings yet
- Cisco Router Configuration Tutorial: Cisco Inter-Network Operating SystemDocument11 pagesCisco Router Configuration Tutorial: Cisco Inter-Network Operating Systemheruye mulugetaNo ratings yet
- Department of Computer Science & Engineering: Independent University, Bangladesh (IUB)Document11 pagesDepartment of Computer Science & Engineering: Independent University, Bangladesh (IUB)Zulker NienNo ratings yet
- CCNADocumentV7 ITN Module10 BasicRouterConfigurationDocument16 pagesCCNADocumentV7 ITN Module10 BasicRouterConfigurationPHONG TRẦN HỒNGNo ratings yet
- CCN Exp2Document11 pagesCCN Exp2Palaash GandhiNo ratings yet
- Configuring A Router: Nescot Catc 1Document10 pagesConfiguring A Router: Nescot Catc 1DidierJairUranAvendañoNo ratings yet
- Ethernet CablingDocument8 pagesEthernet CablingOctav EnachiNo ratings yet
- Answer of CCNA DiscoveryGBDocument34 pagesAnswer of CCNA DiscoveryGBChimdi KweksNo ratings yet
- Cisco IOS Tips and TricksDocument16 pagesCisco IOS Tips and TricksChavara MatekweNo ratings yet
- CLI Command HierarchyDocument6 pagesCLI Command HierarchyddiixxyyNo ratings yet
- Networking CommandsDocument5 pagesNetworking CommandsChristina JosephNo ratings yet
- Basic Router Configuration: Honolulu Community College Cisco Academy Training Center Semester 2Document19 pagesBasic Router Configuration: Honolulu Community College Cisco Academy Training Center Semester 2elia maulaNo ratings yet
- Configuring A Router: CCNA 2 v3 - Module 3Document10 pagesConfiguring A Router: CCNA 2 v3 - Module 3Vladimir OleynikovNo ratings yet
- 10 Commandos CiscoDocument2 pages10 Commandos CiscoCarlos SolisNo ratings yet
- RAM. Most of The Configuration Commands Deal With Moving Information Into and Out From RAMDocument53 pagesRAM. Most of The Configuration Commands Deal With Moving Information Into and Out From RAMEdara PrasaadNo ratings yet
- CS-356 Computer Networks Lab 1Document13 pagesCS-356 Computer Networks Lab 1atishkumar20180No ratings yet
- Quick CommandsDocument9 pagesQuick CommandsMark WoffardNo ratings yet
- CCNA PresentationDocument127 pagesCCNA PresentationVVNAGESWARNo ratings yet
- Router CommandsDocument7 pagesRouter Commandsmuneebali445No ratings yet
- Use The Following Diagram For The Following ConfigurationsDocument15 pagesUse The Following Diagram For The Following ConfigurationsmkumbleNo ratings yet
- NDC Chapter 3Document9 pagesNDC Chapter 3Aschalew Getnet MengistuNo ratings yet
- Mode Prompt Command To Enter Command To ExitDocument8 pagesMode Prompt Command To Enter Command To ExitManjunathNo ratings yet
- CN - 60004200117 - Expt 2Document14 pagesCN - 60004200117 - Expt 2bhavik shahNo ratings yet
- Lab Name: Networking Commands EmulationDocument2 pagesLab Name: Networking Commands EmulationAriful HaqueNo ratings yet
- CN Exp-3Document7 pagesCN Exp-33017 Antara Mudi Cse AiNo ratings yet
- CN Exp-3Document7 pagesCN Exp-33017 Antara Mudi Cse AiNo ratings yet
- Cisco RoutersDocument15 pagesCisco Routerssmara_1009No ratings yet
- Experiment 5 - Basic Networking Commands in MsdosDocument5 pagesExperiment 5 - Basic Networking Commands in MsdosM ZahidNo ratings yet
- CCNA 2 Exams SolvedDocument70 pagesCCNA 2 Exams Solvedvisky100% (9)
- CN PR 10Document9 pagesCN PR 10dkchauhanNo ratings yet
- Ping Command:: Assignment No: 1Document16 pagesPing Command:: Assignment No: 1Ninad ShetkarNo ratings yet
- Modules 1 - 3 - EnglishDocument25 pagesModules 1 - 3 - EnglishChabi HonoratNo ratings yet
- Welcome To CCNA 2/3/4: Some Important Info To FollowDocument60 pagesWelcome To CCNA 2/3/4: Some Important Info To FollowPaul Kruger KokNo ratings yet
- CNS Lab Manual 2019 Course - UpdatedDocument96 pagesCNS Lab Manual 2019 Course - Updatedswapnil khandareNo ratings yet
- CCN Practical No.2Document11 pagesCCN Practical No.2Gaurang GawasNo ratings yet
- CNE Tutorial 02 - Real - LAN and LAN With Packet TracerDocument18 pagesCNE Tutorial 02 - Real - LAN and LAN With Packet TracerThơm VũNo ratings yet
- CISCO PACKET TRACER LABS: Best practice of configuring or troubleshooting NetworkFrom EverandCISCO PACKET TRACER LABS: Best practice of configuring or troubleshooting NetworkNo ratings yet
- Network with Practical Labs Configuration: Step by Step configuration of Router and Switch configurationFrom EverandNetwork with Practical Labs Configuration: Step by Step configuration of Router and Switch configurationNo ratings yet
- LEARN MPLS FROM SCRATCH PART-B: A Beginners guide to next level of networkingFrom EverandLEARN MPLS FROM SCRATCH PART-B: A Beginners guide to next level of networkingNo ratings yet
- 191105082_exp2_MCNDocument6 pages191105082_exp2_MCNgaonkarsaish1112No ratings yet
- 191105082_MCN_Exp3Document5 pages191105082_MCN_Exp3gaonkarsaish1112No ratings yet
- 191105082_EXP1_MCNDocument8 pages191105082_EXP1_MCNgaonkarsaish1112No ratings yet
- 191105082_Exp8_MCNDocument3 pages191105082_Exp8_MCNgaonkarsaish1112No ratings yet
- 191105082_MCN_Exp10Document2 pages191105082_MCN_Exp10gaonkarsaish1112No ratings yet
- CN Lab ManualDocument72 pagesCN Lab Manualvino dhiniNo ratings yet
- How To Connect To iSCSI Targets On QNAP NAS Using MPIO On Windows 2008Document30 pagesHow To Connect To iSCSI Targets On QNAP NAS Using MPIO On Windows 2008Jazz OberoiNo ratings yet
- FiberHome FTTX SoluciónDocument54 pagesFiberHome FTTX Soluciónmacias_marlon100% (2)
- Lantv Television On IP NetworksDocument8 pagesLantv Television On IP NetworksdhanushkasuriyaNo ratings yet
- 3800x3600x-Software Configuration Guide 15.4.1sDocument1,292 pages3800x3600x-Software Configuration Guide 15.4.1sscorcdNo ratings yet
- PTZ Camera TycoDocument3 pagesPTZ Camera Tycogokul krishnaNo ratings yet
- TCP Model (Net101)Document2 pagesTCP Model (Net101)Yhuber BalbidinaNo ratings yet
- Voxai Solutions Firewall Ruleset Review H1 Report v1.1 February 28 2023 CDocument11 pagesVoxai Solutions Firewall Ruleset Review H1 Report v1.1 February 28 2023 Cmuddassir.nocNo ratings yet
- Brocade ICX 6430 and 6450 Switches: Enterprise-Class Stackable Switching at An Entry-Level PriceDocument16 pagesBrocade ICX 6430 and 6450 Switches: Enterprise-Class Stackable Switching at An Entry-Level PricedimydeskyNo ratings yet
- VoLTE Overview and Features IntroductionDocument45 pagesVoLTE Overview and Features Introductionahmed wedattallahNo ratings yet
- PTCL DSL Installation GuideDocument133 pagesPTCL DSL Installation GuideFarhan ShuaibNo ratings yet
- Network Pentesting Gaining Access 1 PDFDocument17 pagesNetwork Pentesting Gaining Access 1 PDFPhilippNo ratings yet
- 08 XMLDocument9 pages08 XMLMarcela DobreNo ratings yet
- Networks-Lab 6632853 PowerpointDocument22 pagesNetworks-Lab 6632853 PowerpointVivek Kumar SinhaNo ratings yet
- Network ProjectDocument18 pagesNetwork Projectpramodh kumar0% (2)
- IS-IS Segment RoutingDocument21 pagesIS-IS Segment RoutingChristopheProustNo ratings yet
- Tutorial - 02 ADocument8 pagesTutorial - 02 AChanduni GamageNo ratings yet
- Questoes Lpi 2 202 PDFDocument103 pagesQuestoes Lpi 2 202 PDFRomero CostaNo ratings yet
- List of TCP and UDP Port Numbers: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument41 pagesList of TCP and UDP Port Numbers: From Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopediadescargas6xNo ratings yet
- TN303 SW OnuDataPathDocument40 pagesTN303 SW OnuDataPath박철민No ratings yet
- sf300 24ppDocument9 pagessf300 24ppdark musNo ratings yet
- AXS1800 GPON Optical Line Terminal Data Sheet PDFDocument2 pagesAXS1800 GPON Optical Line Terminal Data Sheet PDFKy Pham HongNo ratings yet
- 13 Introducing Basic IPv6Document43 pages13 Introducing Basic IPv6Lorenzo Maria MASELLINo ratings yet
- Phy&Logical Design of IoTDocument45 pagesPhy&Logical Design of IoTVydeki Vijayakumar40% (5)
- Palo-Alto-Firewall-Training I-MEDITADocument4 pagesPalo-Alto-Firewall-Training I-MEDITAspgethicalNo ratings yet
- Introduction To LTE Feature Part4 Updated (VoLTE)Document46 pagesIntroduction To LTE Feature Part4 Updated (VoLTE)brahiti3100% (1)
- Sonicwall Network Security Appliance (Nsa) SeriesDocument14 pagesSonicwall Network Security Appliance (Nsa) Seriesandroid klien01No ratings yet