Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Culture Media (MLT 1st)
Culture Media (MLT 1st)
Uploaded by
SAJID MALIKCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Worksheet Activity No. 4: Preparation of Nutrient BrothDocument3 pagesWorksheet Activity No. 4: Preparation of Nutrient BrothPandangan MatiynNo ratings yet
- The Neuroscience of Leadership PDFDocument10 pagesThe Neuroscience of Leadership PDFgimmeanearfulNo ratings yet
- Microbial Culture Media Definition: The Media Is A Source of Nutrients To Support The Growth of The Micro-Organisms inDocument10 pagesMicrobial Culture Media Definition: The Media Is A Source of Nutrients To Support The Growth of The Micro-Organisms inARG ShovonNo ratings yet
- Culture Media Presentation by DR Irfan Final VersionDocument24 pagesCulture Media Presentation by DR Irfan Final Versionyaseenahmad544No ratings yet
- Microbiology NotesDocument9 pagesMicrobiology Notesshreevidya4gurunagesNo ratings yet
- Culture MediaDocument5 pagesCulture MediaMuhammad Abu HurairaNo ratings yet
- Chapter X Culture Media Preparation, InoculationDocument71 pagesChapter X Culture Media Preparation, InoculationBenyam ZenebeNo ratings yet
- Types of Culture MediaDocument7 pagesTypes of Culture MediaSurbhi GuptaNo ratings yet
- Bacterial Culture MediaDocument10 pagesBacterial Culture Medianosila_oz854No ratings yet
- Controlling Microbial Growth in VitroDocument4 pagesControlling Microbial Growth in VitroWingielyn Honculada BaldozaNo ratings yet
- 21030Document9 pages21030ARG ShovonNo ratings yet
- CULTURINGDocument10 pagesCULTURINGpeterNo ratings yet
- CULTURINGDocument12 pagesCULTURINGvictor mangataNo ratings yet
- Lab 3 Media W23Document6 pagesLab 3 Media W23devaanshNo ratings yet
- XL RemovedDocument11 pagesXL RemovedbhavyaNo ratings yet
- BACTERIAL CULTIVATION IN THE LAB CULTURE MEDIA PART 2Document48 pagesBACTERIAL CULTIVATION IN THE LAB CULTURE MEDIA PART 2kamiliaabdazizNo ratings yet
- Culture Media Used in Microbiology: Salman Tausif Senior Technologist Clinical MicrobiologyDocument36 pagesCulture Media Used in Microbiology: Salman Tausif Senior Technologist Clinical MicrobiologyZeeshan YousufNo ratings yet
- Culture MediaDocument36 pagesCulture MediaPatricia Anne Nicole CuaresmaNo ratings yet
- Histopathology QuestionsDocument5 pagesHistopathology QuestionsRey AlegrosoNo ratings yet
- Culture Media & Culture MethodsDocument25 pagesCulture Media & Culture Methodsryan100% (1)
- BacteriaDocument8 pagesBacteriaAmalNo ratings yet
- Culturing of Bacteria and Culture MethodsDocument47 pagesCulturing of Bacteria and Culture MethodsQawiyy 55No ratings yet
- Microbial Culture MediaDocument19 pagesMicrobial Culture Mediaabhijeetpadhi001No ratings yet
- MCB 222. Culturing of MicroorganismsDocument8 pagesMCB 222. Culturing of Microorganismsosibomu41No ratings yet
- 10 Culture Media Preparation, Inoculation (2) (Autosaved)Document68 pages10 Culture Media Preparation, Inoculation (2) (Autosaved)Firaol ManNo ratings yet
- Culture Media Preparation, InoculationDocument67 pagesCulture Media Preparation, InoculationGebrekidanhaftayNo ratings yet
- Types of Culture Media Used in MicrobiologyDocument3 pagesTypes of Culture Media Used in MicrobiologyAzriel BeronNo ratings yet
- Lab 3Document17 pagesLab 3mahirrasho75No ratings yet
- Micro Lec MidDocument171 pagesMicro Lec MidJustine Vens G. AgustinNo ratings yet
- EXERCISE 3 and 4Document15 pagesEXERCISE 3 and 4Andrei RoqueNo ratings yet
- Week 6 Culture Media UpdateDocument23 pagesWeek 6 Culture Media Updateaishabahaa03No ratings yet
- $rmentation Technology and MicroorganismsDocument9 pages$rmentation Technology and MicroorganismsAhsan AhmadNo ratings yet
- Microbiology Assignment: Name: Laiba Ali Registartion No.: L1F20Bsft0040Document8 pagesMicrobiology Assignment: Name: Laiba Ali Registartion No.: L1F20Bsft0040Laiba AliNo ratings yet
- Transport MediaDocument5 pagesTransport MediaIremey Reyes100% (3)
- Culture MethodsDocument64 pagesCulture MethodsMisbah ShabbirNo ratings yet
- Types of MediaDocument9 pagesTypes of Mediamaria zaheerNo ratings yet
- Serial No. Name of The Content Page NoDocument11 pagesSerial No. Name of The Content Page NoMd. Mohib UllahNo ratings yet
- Classification of Bacterial Culture Media On The Basis of PurposeDocument2 pagesClassification of Bacterial Culture Media On The Basis of PurposeNuel EsguerraNo ratings yet
- Culture MediaDocument20 pagesCulture MediaSchola De san joseNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5Document3 pagesLecture 5maria zaheerNo ratings yet
- Practical MicrobiologyDocument14 pagesPractical MicrobiologyLaksilu Viduraga Peiris100% (2)
- Types of Culture Media Used in Microbiology: A. On ConsistencyDocument3 pagesTypes of Culture Media Used in Microbiology: A. On Consistencyvidushi srivastavaNo ratings yet
- Unit 2Document31 pagesUnit 2Jo AnNo ratings yet
- Bacteriology (Methods of Studying Bacteria) : Anne Lorraine Magarette Dulay MLS 3.1 JULY 3, 2018Document15 pagesBacteriology (Methods of Studying Bacteria) : Anne Lorraine Magarette Dulay MLS 3.1 JULY 3, 2018Anne Lorraine Margarette DulayNo ratings yet
- CULTURE MEDIA and CULTURE METHODS-54887478Document41 pagesCULTURE MEDIA and CULTURE METHODS-54887478Sandro ManuNo ratings yet
- Practical 1 MediaDocument35 pagesPractical 1 MediaPatrisha BuanNo ratings yet
- CultureDocument4 pagesCultureyam pdNo ratings yet
- Microbial Culture MediaDocument5 pagesMicrobial Culture MediaARG ShovonNo ratings yet
- Culture MediaDocument6 pagesCulture MediaTryfingNo ratings yet
- Bacterial Culture Media: Types and Applications: Mlt422: Clinical Microbiology IDocument13 pagesBacterial Culture Media: Types and Applications: Mlt422: Clinical Microbiology Inuraini sofeaNo ratings yet
- 3.ist April Media PrepDocument17 pages3.ist April Media PrepUmme RubabNo ratings yet
- Culture MediaDocument8 pagesCulture MediaHershey BaconNo ratings yet
- Media Preparation SterilizationDocument13 pagesMedia Preparation SterilizationJessica GutierrezNo ratings yet
- Culture MediaDocument34 pagesCulture MediaIsak Isak IsakNo ratings yet
- Microbiological Media Pre-Lecture 3Document27 pagesMicrobiological Media Pre-Lecture 3nadeen moughrabiNo ratings yet
- Types of Culture Media Used in MicrobiologyDocument3 pagesTypes of Culture Media Used in MicrobiologyMoonsoul ChildNo ratings yet
- 5 - CULTURE MEDIA AnimeshDocument35 pages5 - CULTURE MEDIA Animeshsouvikmaity2024No ratings yet
- Micro 11Document44 pagesMicro 11Hend maarofNo ratings yet
- Practical 1 Mediums 2024Document9 pagesPractical 1 Mediums 2024sitholesabelo440No ratings yet
- Starter Cultures in Food ProductionFrom EverandStarter Cultures in Food ProductionBarbara SperanzaNo ratings yet
- MHRA Approved Manufacturers ListDocument265 pagesMHRA Approved Manufacturers ListWFree100% (1)
- Fruit Fly Reference ManualDocument18 pagesFruit Fly Reference Manualgermain figueroaNo ratings yet
- Ts of Ethanolic Leaf Extract of Justicia Carnea On The Kidney Function Parameters in Alloxan-Induced Diabetic Albino Wistar RatsDocument39 pagesTs of Ethanolic Leaf Extract of Justicia Carnea On The Kidney Function Parameters in Alloxan-Induced Diabetic Albino Wistar RatsNwigwe Promise ChukwuebukaNo ratings yet
- Order Pictorial KeyDocument8 pagesOrder Pictorial KeyNova Tri Kusuma DewiNo ratings yet
- Reviewer For MapehDocument63 pagesReviewer For MapehElly MarbellaNo ratings yet
- Brochure PDFDocument8 pagesBrochure PDFBabbooNo ratings yet
- Anaphy Lab Reviewer Midterm 1st SemDocument26 pagesAnaphy Lab Reviewer Midterm 1st SemSeaniah Faith ApolonaNo ratings yet
- Combinatorics 2 Solutions UHSMCDocument5 pagesCombinatorics 2 Solutions UHSMCWalker KroubalkianNo ratings yet
- Biggest Man Boob MistakesDocument21 pagesBiggest Man Boob Mistakesjuventus200067% (3)
- Modern Biology - Lab Report 1Document7 pagesModern Biology - Lab Report 1BAUAN Al DominicNo ratings yet
- BIOA01 F2021 SyllabusDocument10 pagesBIOA01 F2021 Syllabusthisis throwawayxDNo ratings yet
- Daftar PustakaDocument5 pagesDaftar PustakaPramitha YustiaNo ratings yet
- Referat Engleza Tigrul AlbDocument2 pagesReferat Engleza Tigrul Albandrei0891No ratings yet
- COVID-19 mRNA VaccinesDocument1 pageCOVID-19 mRNA Vaccinesdcscsdss56No ratings yet
- Comparative Assessment of Salivary Level of Cortisol Anxiety and Depression in Patients With Oral Conditions A Case Control StudyDocument6 pagesComparative Assessment of Salivary Level of Cortisol Anxiety and Depression in Patients With Oral Conditions A Case Control StudyAthenaeum Scientific PublishersNo ratings yet
- Case StudyDocument23 pagesCase StudyVinson Pacheco SerranoNo ratings yet
- 7th Grade Scope and Sequence 15 16Document4 pages7th Grade Scope and Sequence 15 16api-292474936No ratings yet
- Animal Parts QuizDocument13 pagesAnimal Parts QuizLarisa M.No ratings yet
- Pathophysiology - Rheumatoid ArthritisDocument1 pagePathophysiology - Rheumatoid ArthritisAngel FiloteoNo ratings yet
- PreviewpdfDocument24 pagesPreviewpdfarienne.baptistellaNo ratings yet
- Ficks Law 12Document4 pagesFicks Law 12Katarina BoracNo ratings yet
- Que Es Un Individuo Concreto. Mario BungeDocument9 pagesQue Es Un Individuo Concreto. Mario BungeManuel Antonio Requena ArriolaNo ratings yet
- Sophia Roosth: Crafting Life: A Sensory Ethnography of Fabricated Biologies (2010)Document326 pagesSophia Roosth: Crafting Life: A Sensory Ethnography of Fabricated Biologies (2010)Hodie CsillaNo ratings yet
- Origin of Lymphoid Neoplasms: CLP: BLB: NBC: MC: GC: MZDocument26 pagesOrigin of Lymphoid Neoplasms: CLP: BLB: NBC: MC: GC: MZSri Naharindah NingNo ratings yet
- New Antibiotics: From The Sea Bed To The Hospital Bed DR Andrew Mearns Spragg, CEO, Aquapharm Bio-Discovery LTD 3 March 2008Document3 pagesNew Antibiotics: From The Sea Bed To The Hospital Bed DR Andrew Mearns Spragg, CEO, Aquapharm Bio-Discovery LTD 3 March 2008The Royal Society of EdinburghNo ratings yet
- GalactosemiaDocument41 pagesGalactosemiaArlene DaroNo ratings yet
- 4 Movement of Substances Across The Cell Membrane: A. Concept CheckingDocument11 pages4 Movement of Substances Across The Cell Membrane: A. Concept CheckingRyo LamNo ratings yet
- Guidance On Registration of Similar Biological Products in SingaporeDocument13 pagesGuidance On Registration of Similar Biological Products in SingaporeWilliam ChandraNo ratings yet
- Class9 NSO 2017 SetB - SolutionsDocument15 pagesClass9 NSO 2017 SetB - SolutionsAmbica JainNo ratings yet
Culture Media (MLT 1st)
Culture Media (MLT 1st)
Uploaded by
SAJID MALIKCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Culture Media (MLT 1st)
Culture Media (MLT 1st)
Uploaded by
SAJID MALIKCopyright:
Available Formats
Culture media
“A culture medium is a solid or liquid mixture of chemicals that can support the growth of
microorganisms.”
Characteristic of ideal Culture Medium:
Must give a satisfactory growth from a small inoculation.
Should promote a rapid growth
Should be easy to prepare
Should be reasonably cheap
Should be easily reproducible
Uses of Culture media:
To identify cause of infection.
To study the characteristics or properties of microorganisms.
To prepare biological products such as vaccine.
Common ingredients/ composition of culture media:
Peptone- source of carbon and nitrogen.
Beef extract- source of amino acid, vitamins, minerals.
Yeast extract- source of vitamin, carbon, nitrogen.
Distilled water:
Agar- solidifying agent.
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
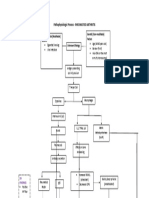
Classification of culture media:
BASED ON PHYSICAL NATURE:
1. Solid medium
2. Semi-solid medium
3. Liquid medium
1. Solid media
It is for the isolation of bacteria as a pure culture on a solid medium.
Agar is used to hardening the media at 1.5- 2.0% concentration. Solid media allows the growth of bacteria
as colonies by streaking on the medium. It solidified at 37 degrees Celsius.
Agar is an un-branched polysaccharide extracted from red algae species like Gelidium. Colonies
identification is done on this medium.
Examples of Solid Media
Nutrient agar, MacConkey agar, Blood agar, Chocolate agar.
Growth of bacteria on solid medium appear as smooth, rough, mucoid, round, irregular, filamentous,
punctiform.
2. Semi-solid media
This media shows the motility of bacteria and the cultivation of microaerophilic bacteria. This media has
agar at a concentration of 0.5% or less. It has a jelly consistency.
Examples of Semi-solid media
Mannitol motility media.
The growth of bacteria in semi-solid appears as a thick line in the medium.
3. Liquid media
This media shows the growth of a large number of bacteria.
It is called Broth that allows bacteria to grow uniformly with turbidity. The growth occurs at 37ºC in an
incubator for 24hrs.
Liquid media don’t have the addition of agar; it is for fermentation studies.
Examples of Liquid media
Nutrient broth, soy broth, phenol red carbohydrate broth.
Growth of bacteria in liquid media- Turbidity is seen at the end of the broth.
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Types of culture media based on chemical composition
1. Basal media or Simple media
2. Defined media or synthetic
3. Undefined or complex media
1. Basal media/ Simple media
This media is simple as it enhances the growth of many microorganisms. It’s a routinely used medium in
the lab, having Carbon and Nitrogen. This media allows the growth; of non- fastidious bacteria without
any enrichment source; used for sub-culturing. It’s a non-selective medium.
Staphylococcus and Enterobacteriaceae grow in this media.
Examples of Basal media
Nutrient Agar, Peptone water.
2. Defined medium or synthetic media
A defined medium has a known quantity of all ingredients, like carbon source (Glucose or Glycerol) and
nitrogen source (Ammonium salt or Nitrate as inorganic nitrogen). The medium needs in metabolic,
nutritional, and physiological growth experiments. (Example: Simmons citrate agar, mineral glucose
medium.)
3. Undefined or complex media
This medium has different complex ingredients in unknown quantities, for example- yeast extract, beef,
various salts, and enzymatic protein. (Example: blood agar, milk agar)
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Types of culture media based on function
1. Enriched media
2. Selective media
3. Enrichment media
4. Indicator media or differential media
5. Transport media
6. Storage media
1. Enriched media
This media requires the addition of other substances like blood, egg, or serum. An enriched media allows
the growth of devised microorganisms but inhibits other and fastidious microbes grow as they require
nutrients like vitamins and growth-promoting substances.
Example of Enriched media
Blood agar, Chocolate agar, Lowenstein Jensen media.
2. Selective media
This media shows the growth of selective; microbes or desired microorganisms and inhibits the growth of
unwanted microbes. The inhibition occurs by adding bile salts, antibiotics, dyes, PH adjustments.
Examples of Selective media
S.N. Media Bacteria
1. Mannitol Agar– It has 7% of Selective for Staphylococcus aureus
sodium chloride that inhibits
the growth of other microbes
and promotes the growth
of Staphylococci. It has phenol
red dye that produces acid
Staphylococcus used the
mannitol for the acid
production and the color of
phenol red changes from red to
yellow.
It is used for the isolation
Salmonella-Shigella Agar of Salmonella bacteria that causes
2.
Deoxycholate agar typhoid.
Selective for Shigella.
MacConkey Agar- It has bile
Selective isolation
3. salts that inhibit the growth of
for Enterobacteriaceae
gram-positive bacteria
TCBS Agar– Light green
translucent media Bile salt Selective for Vibrio cholera.
4.
inhibits the growth of unwanted
bacteria
Lowenstein Jensen Media- It is
made selective by adding
5. Selective for M. tuberculosis
malachite green and stops the
unwanted growth of pathogens.
3. Enrichment media
It is a liquid medium, which also permits the growth of desired bacteria at a low density. The media
provides an environment and conditions as selective media and inhibits unwanted bacteria from growing.
It is for the isolation of the soil and fecal microorganisms.
Examples of Enrichment media
Selenite F-broth does the isolation of Salmonella Typhi from a fecal sample.
4. Differential media or Indicator
This media shows visible changes due to biochemical properties or the presence of an indicator. It
differentiates bacteria based on colony color growing on the same plate.
Examples of Indicator or differential media
Mannitol salt agar shows yellow color colonies, MacConkey agar produces pink colonies.
5. Transport media
The media is use to transport specimens after collection to control the overgrowth of organisms. This
media act as temporary storage. It also maintains the viability of pathogens in the specimen and prevents
them from drying.
Examples of Transport media
Stuart’s transport medium. Pikes medium
6. Storage media
Media used for storing the bacteria for a long period of time. Examples are- cooked meat broth.
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Types of culture media based on oxygen requirement
Microorganisms have different requirements for growth depending on oxygen requirements.
1. Aerobic media
Aerobic media is the media that support the growth of bacteria that require oxygen to grow. Availability
of oxygen is through exposure to the air or by incorporating oxygen releasing components
Examples
Blood agar, Nutrient agar
2. Anaerobic media
Anaerobic media is the media that support growth of bacteria that don not require oxygen. Anaerobic
media contain reducing agent that help to remove oxygen.
Examples of Anaerobic media
RCM (Robertson cooked meat) isolation for Clostridium sp.
Thioglycolate broth– It has sodium glycolate that maintains low oxygen.
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
You might also like
- Worksheet Activity No. 4: Preparation of Nutrient BrothDocument3 pagesWorksheet Activity No. 4: Preparation of Nutrient BrothPandangan MatiynNo ratings yet
- The Neuroscience of Leadership PDFDocument10 pagesThe Neuroscience of Leadership PDFgimmeanearfulNo ratings yet
- Microbial Culture Media Definition: The Media Is A Source of Nutrients To Support The Growth of The Micro-Organisms inDocument10 pagesMicrobial Culture Media Definition: The Media Is A Source of Nutrients To Support The Growth of The Micro-Organisms inARG ShovonNo ratings yet
- Culture Media Presentation by DR Irfan Final VersionDocument24 pagesCulture Media Presentation by DR Irfan Final Versionyaseenahmad544No ratings yet
- Microbiology NotesDocument9 pagesMicrobiology Notesshreevidya4gurunagesNo ratings yet
- Culture MediaDocument5 pagesCulture MediaMuhammad Abu HurairaNo ratings yet
- Chapter X Culture Media Preparation, InoculationDocument71 pagesChapter X Culture Media Preparation, InoculationBenyam ZenebeNo ratings yet
- Types of Culture MediaDocument7 pagesTypes of Culture MediaSurbhi GuptaNo ratings yet
- Bacterial Culture MediaDocument10 pagesBacterial Culture Medianosila_oz854No ratings yet
- Controlling Microbial Growth in VitroDocument4 pagesControlling Microbial Growth in VitroWingielyn Honculada BaldozaNo ratings yet
- 21030Document9 pages21030ARG ShovonNo ratings yet
- CULTURINGDocument10 pagesCULTURINGpeterNo ratings yet
- CULTURINGDocument12 pagesCULTURINGvictor mangataNo ratings yet
- Lab 3 Media W23Document6 pagesLab 3 Media W23devaanshNo ratings yet
- XL RemovedDocument11 pagesXL RemovedbhavyaNo ratings yet
- BACTERIAL CULTIVATION IN THE LAB CULTURE MEDIA PART 2Document48 pagesBACTERIAL CULTIVATION IN THE LAB CULTURE MEDIA PART 2kamiliaabdazizNo ratings yet
- Culture Media Used in Microbiology: Salman Tausif Senior Technologist Clinical MicrobiologyDocument36 pagesCulture Media Used in Microbiology: Salman Tausif Senior Technologist Clinical MicrobiologyZeeshan YousufNo ratings yet
- Culture MediaDocument36 pagesCulture MediaPatricia Anne Nicole CuaresmaNo ratings yet
- Histopathology QuestionsDocument5 pagesHistopathology QuestionsRey AlegrosoNo ratings yet
- Culture Media & Culture MethodsDocument25 pagesCulture Media & Culture Methodsryan100% (1)
- BacteriaDocument8 pagesBacteriaAmalNo ratings yet
- Culturing of Bacteria and Culture MethodsDocument47 pagesCulturing of Bacteria and Culture MethodsQawiyy 55No ratings yet
- Microbial Culture MediaDocument19 pagesMicrobial Culture Mediaabhijeetpadhi001No ratings yet
- MCB 222. Culturing of MicroorganismsDocument8 pagesMCB 222. Culturing of Microorganismsosibomu41No ratings yet
- 10 Culture Media Preparation, Inoculation (2) (Autosaved)Document68 pages10 Culture Media Preparation, Inoculation (2) (Autosaved)Firaol ManNo ratings yet
- Culture Media Preparation, InoculationDocument67 pagesCulture Media Preparation, InoculationGebrekidanhaftayNo ratings yet
- Types of Culture Media Used in MicrobiologyDocument3 pagesTypes of Culture Media Used in MicrobiologyAzriel BeronNo ratings yet
- Lab 3Document17 pagesLab 3mahirrasho75No ratings yet
- Micro Lec MidDocument171 pagesMicro Lec MidJustine Vens G. AgustinNo ratings yet
- EXERCISE 3 and 4Document15 pagesEXERCISE 3 and 4Andrei RoqueNo ratings yet
- Week 6 Culture Media UpdateDocument23 pagesWeek 6 Culture Media Updateaishabahaa03No ratings yet
- $rmentation Technology and MicroorganismsDocument9 pages$rmentation Technology and MicroorganismsAhsan AhmadNo ratings yet
- Microbiology Assignment: Name: Laiba Ali Registartion No.: L1F20Bsft0040Document8 pagesMicrobiology Assignment: Name: Laiba Ali Registartion No.: L1F20Bsft0040Laiba AliNo ratings yet
- Transport MediaDocument5 pagesTransport MediaIremey Reyes100% (3)
- Culture MethodsDocument64 pagesCulture MethodsMisbah ShabbirNo ratings yet
- Types of MediaDocument9 pagesTypes of Mediamaria zaheerNo ratings yet
- Serial No. Name of The Content Page NoDocument11 pagesSerial No. Name of The Content Page NoMd. Mohib UllahNo ratings yet
- Classification of Bacterial Culture Media On The Basis of PurposeDocument2 pagesClassification of Bacterial Culture Media On The Basis of PurposeNuel EsguerraNo ratings yet
- Culture MediaDocument20 pagesCulture MediaSchola De san joseNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5Document3 pagesLecture 5maria zaheerNo ratings yet
- Practical MicrobiologyDocument14 pagesPractical MicrobiologyLaksilu Viduraga Peiris100% (2)
- Types of Culture Media Used in Microbiology: A. On ConsistencyDocument3 pagesTypes of Culture Media Used in Microbiology: A. On Consistencyvidushi srivastavaNo ratings yet
- Unit 2Document31 pagesUnit 2Jo AnNo ratings yet
- Bacteriology (Methods of Studying Bacteria) : Anne Lorraine Magarette Dulay MLS 3.1 JULY 3, 2018Document15 pagesBacteriology (Methods of Studying Bacteria) : Anne Lorraine Magarette Dulay MLS 3.1 JULY 3, 2018Anne Lorraine Margarette DulayNo ratings yet
- CULTURE MEDIA and CULTURE METHODS-54887478Document41 pagesCULTURE MEDIA and CULTURE METHODS-54887478Sandro ManuNo ratings yet
- Practical 1 MediaDocument35 pagesPractical 1 MediaPatrisha BuanNo ratings yet
- CultureDocument4 pagesCultureyam pdNo ratings yet
- Microbial Culture MediaDocument5 pagesMicrobial Culture MediaARG ShovonNo ratings yet
- Culture MediaDocument6 pagesCulture MediaTryfingNo ratings yet
- Bacterial Culture Media: Types and Applications: Mlt422: Clinical Microbiology IDocument13 pagesBacterial Culture Media: Types and Applications: Mlt422: Clinical Microbiology Inuraini sofeaNo ratings yet
- 3.ist April Media PrepDocument17 pages3.ist April Media PrepUmme RubabNo ratings yet
- Culture MediaDocument8 pagesCulture MediaHershey BaconNo ratings yet
- Media Preparation SterilizationDocument13 pagesMedia Preparation SterilizationJessica GutierrezNo ratings yet
- Culture MediaDocument34 pagesCulture MediaIsak Isak IsakNo ratings yet
- Microbiological Media Pre-Lecture 3Document27 pagesMicrobiological Media Pre-Lecture 3nadeen moughrabiNo ratings yet
- Types of Culture Media Used in MicrobiologyDocument3 pagesTypes of Culture Media Used in MicrobiologyMoonsoul ChildNo ratings yet
- 5 - CULTURE MEDIA AnimeshDocument35 pages5 - CULTURE MEDIA Animeshsouvikmaity2024No ratings yet
- Micro 11Document44 pagesMicro 11Hend maarofNo ratings yet
- Practical 1 Mediums 2024Document9 pagesPractical 1 Mediums 2024sitholesabelo440No ratings yet
- Starter Cultures in Food ProductionFrom EverandStarter Cultures in Food ProductionBarbara SperanzaNo ratings yet
- MHRA Approved Manufacturers ListDocument265 pagesMHRA Approved Manufacturers ListWFree100% (1)
- Fruit Fly Reference ManualDocument18 pagesFruit Fly Reference Manualgermain figueroaNo ratings yet
- Ts of Ethanolic Leaf Extract of Justicia Carnea On The Kidney Function Parameters in Alloxan-Induced Diabetic Albino Wistar RatsDocument39 pagesTs of Ethanolic Leaf Extract of Justicia Carnea On The Kidney Function Parameters in Alloxan-Induced Diabetic Albino Wistar RatsNwigwe Promise ChukwuebukaNo ratings yet
- Order Pictorial KeyDocument8 pagesOrder Pictorial KeyNova Tri Kusuma DewiNo ratings yet
- Reviewer For MapehDocument63 pagesReviewer For MapehElly MarbellaNo ratings yet
- Brochure PDFDocument8 pagesBrochure PDFBabbooNo ratings yet
- Anaphy Lab Reviewer Midterm 1st SemDocument26 pagesAnaphy Lab Reviewer Midterm 1st SemSeaniah Faith ApolonaNo ratings yet
- Combinatorics 2 Solutions UHSMCDocument5 pagesCombinatorics 2 Solutions UHSMCWalker KroubalkianNo ratings yet
- Biggest Man Boob MistakesDocument21 pagesBiggest Man Boob Mistakesjuventus200067% (3)
- Modern Biology - Lab Report 1Document7 pagesModern Biology - Lab Report 1BAUAN Al DominicNo ratings yet
- BIOA01 F2021 SyllabusDocument10 pagesBIOA01 F2021 Syllabusthisis throwawayxDNo ratings yet
- Daftar PustakaDocument5 pagesDaftar PustakaPramitha YustiaNo ratings yet
- Referat Engleza Tigrul AlbDocument2 pagesReferat Engleza Tigrul Albandrei0891No ratings yet
- COVID-19 mRNA VaccinesDocument1 pageCOVID-19 mRNA Vaccinesdcscsdss56No ratings yet
- Comparative Assessment of Salivary Level of Cortisol Anxiety and Depression in Patients With Oral Conditions A Case Control StudyDocument6 pagesComparative Assessment of Salivary Level of Cortisol Anxiety and Depression in Patients With Oral Conditions A Case Control StudyAthenaeum Scientific PublishersNo ratings yet
- Case StudyDocument23 pagesCase StudyVinson Pacheco SerranoNo ratings yet
- 7th Grade Scope and Sequence 15 16Document4 pages7th Grade Scope and Sequence 15 16api-292474936No ratings yet
- Animal Parts QuizDocument13 pagesAnimal Parts QuizLarisa M.No ratings yet
- Pathophysiology - Rheumatoid ArthritisDocument1 pagePathophysiology - Rheumatoid ArthritisAngel FiloteoNo ratings yet
- PreviewpdfDocument24 pagesPreviewpdfarienne.baptistellaNo ratings yet
- Ficks Law 12Document4 pagesFicks Law 12Katarina BoracNo ratings yet
- Que Es Un Individuo Concreto. Mario BungeDocument9 pagesQue Es Un Individuo Concreto. Mario BungeManuel Antonio Requena ArriolaNo ratings yet
- Sophia Roosth: Crafting Life: A Sensory Ethnography of Fabricated Biologies (2010)Document326 pagesSophia Roosth: Crafting Life: A Sensory Ethnography of Fabricated Biologies (2010)Hodie CsillaNo ratings yet
- Origin of Lymphoid Neoplasms: CLP: BLB: NBC: MC: GC: MZDocument26 pagesOrigin of Lymphoid Neoplasms: CLP: BLB: NBC: MC: GC: MZSri Naharindah NingNo ratings yet
- New Antibiotics: From The Sea Bed To The Hospital Bed DR Andrew Mearns Spragg, CEO, Aquapharm Bio-Discovery LTD 3 March 2008Document3 pagesNew Antibiotics: From The Sea Bed To The Hospital Bed DR Andrew Mearns Spragg, CEO, Aquapharm Bio-Discovery LTD 3 March 2008The Royal Society of EdinburghNo ratings yet
- GalactosemiaDocument41 pagesGalactosemiaArlene DaroNo ratings yet
- 4 Movement of Substances Across The Cell Membrane: A. Concept CheckingDocument11 pages4 Movement of Substances Across The Cell Membrane: A. Concept CheckingRyo LamNo ratings yet
- Guidance On Registration of Similar Biological Products in SingaporeDocument13 pagesGuidance On Registration of Similar Biological Products in SingaporeWilliam ChandraNo ratings yet
- Class9 NSO 2017 SetB - SolutionsDocument15 pagesClass9 NSO 2017 SetB - SolutionsAmbica JainNo ratings yet