Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chemistry Alvel grade13 first term 2024 Thurstan college Essay English medium
Chemistry Alvel grade13 first term 2024 Thurstan college Essay English medium
Uploaded by
dhwi123Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Chemistry Alvel grade13 first term 2024 Thurstan college Essay English medium
Chemistry Alvel grade13 first term 2024 Thurstan college Essay English medium
Uploaded by
dhwi123Copyright:
Available Formats
ish¿u ysñlï weúßKs / All Rights Reserved ]
තර්ස්ටන් විද්යාලය-ක ාළඹ 07
Thurstan College - Colombo-07
தர்ஸ்டன் கல்லூரி-ககரழும்பு 07
අධ්යය කදාු සතික ද්ර උසසස් කදළ විාායය 2024 අකයෝස්ු
General Certificate of Education (Adv. Level) Examination, August 2024
First term test - 2024 May
රසායන විද්යාව II 13 කර්ණිය
Chemistry II 02 E II Grade 13
Universal gas constant R = 8.314 J K–1 mol–1 Plank constant h = 6.626 x 10-34 J s
Avogadro constant NA = 6.022 x 1023 mol–1 speed of light c = 3 x 108 m s–1
Part B – Essay
Answer only two questions. (Each question carries 150 marks).
05. (a) A student used the following method to find the
enthalpy of combustion of spirits with the help of spirit
lamp . For that, water is heated using a spirit lamp.
First, the mass of the burner is measured when it is
filled with a certain amount of spirit . The heat from the
burner slowly boils the water in the calorimeter,
causing the temperature of the water to rise . At the end
of the test , after all the spirits have been burnt, the
burner is switched off and its dry mass is measured .
The results are as follows.
Initial temperature of water = 27.0 0C
Final temperature of water = 34.9 0C
Initial mass of spirit burner = 28.2 g
Final mass of spirit burner = 23.6 g
(i) Find the enthalpy of combustion of the spirit assuming that 17250 J is required to raise
the temperature of the calorimeter and its water by one degree Celsius. Consider the
molar mass of alcohol to be 46 g mol-1.
(ii) Write two assumptions that you used in the calculation which are not mentioned above.
(45 marks)
(b) Consider the equilibrium reaction given below.
aA(g) + bB(g) cC(g) + dD(g)
1) Write the KC expression for the above equilibrium
2) Write the KP expression for the above equilibrium
3) Derive the relationship between the above KC and KP expressions by using the gas laws.
(35 marks)
(c) Consider the equilibrium reaction given below.
P(g) + 2Q(g) PQ2(g)
A closed system of volume 6 dm3 at 327 0C containing 0.2 mol of P(g) and a catalyst was allowed
to equilibrate by introducing gas Q into the system. After equilibration the total pressure of the
system was 5.0 x 105 Pa and the amount of PQ2 gas produced was 0.1 mol
1) What is the number of moles of Q(g) contained in the system at equilibrium?
2) Find the partial pressures of each gas in the equilibrium system
3) Calculate the KP and KC values for the system at 327 0C
4) State an assumption you used in the above calculations.
(70 marks)
Chemistry - Thurstan college-Colombo-07 9
06. (a) The results of an experiment carried out on the gaseous reaction P(g) + Q(g) → R(g) + S(g) are
as follows.
Experiment Initial concentration of P Initial concentration of Q Initial rate of reaction
(mol dm-3) (mol dm-3) (mol dm-3 s-1)
1 0.033 0.034 6.75 x 10-4
2 0.033 0.137 1.08 x 10-2
3 0.136 0.137 1.08 x 10-2
4 0.202 0.233 R1
(i) Find the order of the reaction with respect to P and Q.
(ii) Write the rate expression for the overall reaction.
6.75 1.08
(iii) Find the value of the rate constant k. Hint–: 2
2
0.575
3.4 1.37
(iv) Find the initial rate of reaction in Experiment No. 4 . Hint –: {0.575 x (2.33)2 = 3.12}
(v) The following mechanism is proposed for the above reaction.
Step I Q+Q→A+S slow
Step II A+P Q+R fast
a. Can this mechanism be accepted for the above reaction? Briefly explain your answer
b. Which of the above steps is the rate determining step of this mechanism?
c. Confirm your chosen rate determination step with the values you obtained for the order.
d. State whether A is a catalyst or an intermediate according to the above mechanism and
give reasons for it.
(90 marks)
(b) CO2 gas is contained in a rigid container X whose volume is 4.157 dm3 and SO2 gas is contained
in a rigid container Y. The volume of container Y is twice the volume of container X. These two
vessels are connected by a tube whose volume is negligible. Initially, when the tap is closed, the
pressure in container X is 3 x 105 Pa and the temperature is 177 0C, and the pressure in container
Y is 1 x 105 Pa and the temperature is 327 0C.
1) Find the initial number of gas moles in vessels X and Y separately.
2) Find the total number of moles of gas in each container separately when the tap is opened and
the temperatures in the containers are kept constant and the gases are allowed to mix.
3) Calculate the partial pressures of CO2 and SO2 in each container when the gases are mixed.
4) The temperature of the system was raised to 477 0C. Then calculate the final pressure in the
system.
5) State two assumptions you made in the above calculations
(60 marks)
Chemistry - Thurstan college-Colombo-07 10
07. (a)
(i) According to collision theory, state three conditions that must be satisfied for a chemical
reaction to occur.
(ii) An increase in temperature increases the rate of a chemical reaction. Confirm that statement
with two facts.
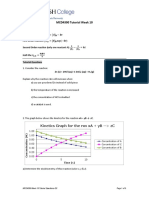
(iii) Consider the reaction X → Q. The initial concentration of X was 0.5 mol dm-3 and after 30
minutes 50% of X had been consumed.
I. Roughly plot the rate of the reaction versus the concentration of X when the reaction is
zero-order with respect to X
II. Roughly plot the rate of the reaction versus the concentration of X when the reaction
is first-order with respect to X.
III. Sketch the concentration of X versus time considering the reaction is zero-order with
respect to X. Then determine the concentration of X remaining after one hour. (Indicate
if X is completely consumed).
IV. Sketch the concentration of X versus time considering the reaction is first-order with
respect to X. Using knowledge of the half-life for a first-order reaction, determine the
concentration of X remaining after one hour.
V. If the initial concentration of X is 0.25 mol dm-3 and the reaction with X is first order,
determine the concentration of X remaining after one hour.
(75 marks)
(b) P and Q are two octahedral coordination compounds whose molecular formula is CoN5H12Cl2O2.
All H atoms in these exist only as NH3. Cobalt is in the same oxidation state in both compounds.
Only compound P gives a white precipitate with aqueous AgNO3
i) Identify the ligands in P and Q.
ii) Deduce the chemical formulas of compounds P and Q.
iii) State the oxidation state of cobalt in the above compounds and write its electron
configuration .
(50 marks)
(c) W is a coordination complex ion with octahedral geometry. Its atomic composition is MnO5H8N
. It contains two types of ligands and when this ion is mixed with an aqueous solution of KCl, it
gives compound Y, and that compound Y gives 4 ions in aqueous solution..
i) Identify the ligands contained in W
ii) Write the chemical formulas of W and Y.
iii) State the oxidation state of Mn in W above and write its electron configuration
(25 marks)
Chemistry - Thurstan college-Colombo-07 11
Part C – Essay
Answer only two questions. (Each question carries 150 marks).
08. (a)
(i) The steps of a process for the synthesis of organic compound U using ethene and ethyene as
starting materials are given below. Copy the step diagram in your answer sheet and complete
the chain of reactions mentioning compounds P, Q, R, S, T and reagents 1, 2, 3, 4.
Reagent 1
HC CH H2C CH2
Reagent 2 Reagent 3
P Q
T
Reagent 4 H3C
R S C N
CH3CH2
U
(ii) Write the major product and its IUPAC name from the reaction of organic compound T with
liquid Br2.
(iii) Name another organic compound you have learned which gives the same observation as
compound T with liquid Br2.
(60 marks)
(b) Perform the following conversions in minimum number of steps.
O OH H
i) CH3CH2 C H CH3CH2 C C CH2CH3
H H
O O
ii) CH3 C CH3 CH3CH2 C O CH2CH2CH3
(80 marks)
(c) State the major product of self-condensation of propanal with dilute NaOH at room temperature
and suggest a plausible mechanism for it.
(10 marks)
Chemistry - Thurstan college-Colombo-07 12
09.(a) Four cations are contained in the four aqueous solutions A, B, C, D. Tests done to identify them
And the related observations are as follows..
Experiment Observations
A colorless gas with a pungent odor (G1)
Dilute NaOH solution was added to a small was released.
1 The gas turned the filter paper soaked with
portion of the aqueous solution A.
the Nessler reagent brown.
First a gelatinous white precipitate (P1)
occurs and when excess more NaOH was
added it dissolves (P2) by releasing a
Add a small amount of dilute NaOH to a colorless diatomic odorless gas (G2)
2
portion of the aqueous solution B. A yellow solid (P3) was obtained when the
gelatinous precipitate was heated strongly.
and on cooling the white precipitate is
formed again.
A white precipitate (P4) was formed . It
Add a diluted HCl to a portion of the aqueous
3 dissolves well in dilute NH4OH and is
solution C.
colorless solution (P5) is given.
A portion of solution D is acidified and H2S No precipitate.
4 gas is bubbled. Then base was added and
again H2S gas was bubbled. A black precipitate was obtained (P6) .
Dissolve the P6 precipitate in dilute HNO 3
5 A pink precipitate (P 7 ) is formed.
Add NaOH solution.
(i) Identify the cations present in solutions A, B, C and D
(ii) Identify the compounds G1, G2, P1, P2, P3, P4, P5, P6, and P7.
(iii) State a reagent that can be used to detect gas G1 and the observations obtained there.
(Litmus papers are not accepted)
(iv) Give balanced ionic equations for the cation in solution B to form a precipitate when
NaOH is added and to dissolve when excess NaOH is added.
(85 marks)
(b) The steps of an experiment carried out in the laboratory to find the molar ratio of Fe(NO3)2 and
Fe2(CO3)3 in a solid mixture containing Fe(NO3)2 and Fe2(CO3)3 are as follows.
Dissolve 5.83 g of the given solid mixture completely in dilute H2SO4 and add distilled water.
Dilute to 600 cm3 and prepare solution Y.
When 25.00 cm3 of the prepared Y solution was accurately measured into a volumetric flask
and titrated with the 0.01 mol dm-3 KMnO4(aq) solution in the burette, the volume of KMnO4
solution consumed during the reaction was 20.00 cm3.
SO2 gas was bubbled through 30.00 cm3 of the prepared Y solution and after all the Fe3+ in
the medium was converted to Fe2+, all the remaining SO2(g) was removed.
Then again, when the same SO2 removed solution is titrated by KMnO4(aq) solution of 0.01
mol dm-3, the volume of KMnO4 solution consumed in the reaction is 48.00 cm3.
(Fe = 56, Mn = 55, K = 39, N = 14, O = 16, C = 12)
Chemistry - Thurstan college-Colombo-07 13
i) Write the balanced ionic equation for the reaction between Fe2+ and MnO4-
ii) Write the balanced ionic equation for the reaction between Fe3+ and SO2
iii) By suitable calculation and calculate the mole ratio of Fe(NO3)2 and Fe2(CO3)3 contained in the
initial solid mixture.
iv) Write the color change that occurs at the endpoint of the titration.
v) In the above titration, a small amount of tribasic acid is added to clearly observe the color change
at the endpoint. Mention the acid thus added and how it makes it easy to clearly observe the color
change at the endpoint..
(65 marks)
10. (a) The tests and observations made to identify the ions present in the aqueous solutions of P, Q, R
consisting of three anions and one cation belonging to the s block are as follows.
Experiment observation
HCl solution was added to a little portion of
1 A brown gas (G1) was released.
the aqueous solution P.
The purple solution turned to a green
Add concentrated KOH to a portion of the
solution (S1). A colorless diatomic
aqueous solution Q
oxidizing gas (G2) was released.
2
H2SO4 again to the obtained green solution S1
A purple aqueous solution and a dark
to was acidified it.
brown precipitate (P1 ) were obtained.
Add dilute HNO3 and ammonium molybdate
3 for a portion of the aqueous solution R and A yellow precipitate was observed.
heat the solution.
For flame test was performed for Aqueous
4 gives off a Lilac purple flame.
solutions of P, Q, R .
(i) Identify the ions present in the solutions P, Q, and R.
(ii) Identify the compounds G1, G2, S1 and P1.
(iii) Give the balanced chemical equation for the reaction that occurs when dilute HCl is added
to an aqueous solution of P.
(iv) Give the balanced chemical equation for the reaction that takes place in strongly basifying
aqueous solution Q.
(v) Give the balanced chemical equation for the reaction of aqueous solution S1 in the
presence of dilute H2SO4. Which of the processes of oxidation, reduction, and
disproportionation will the compound S1 undergo?
(65 marks)
(b) Determine whether the given reaction is spontaneous at 300 K using the following data
CO(g) + ½ O2(g) → CO2(g)
ΔfHθ [CO2(g)] = – 393.5 kJ mol-1 ΔfHθ [CO(g)] = – 110.5 kJ mol-1
Sθ [CO2(g)] = 213.7 J mol-1 K-1 Sθ [CO(g)] = 197.7 J mol-1 K-1
Sθ [O2(g)] = 205.1 J mol-1 K-1
(40 marks)
Chemistry - Thurstan college-Colombo-07 14
(c) Consider the following reaction mechanism.
Step I NO + O2 NO3 fast
Step II NO3 + NO → 2NO2 slow
a. Write the overall reaction according to this reaction mechanism
b. Identify the intermediate in this reaction mechanism.
c. Construct a rate expression for the reaction.
(45 marks)
Chemistry - Thurstan college-Colombo-07 15
You might also like
- Chemistry Unit 1 P2 2017 PDFDocument18 pagesChemistry Unit 1 P2 2017 PDFNalini Gangaram33% (6)
- Dec Exam AnswersDocument17 pagesDec Exam Answersvivivihohoho1No ratings yet
- Workbook Grade 11&12 Chemistry - 1Document34 pagesWorkbook Grade 11&12 Chemistry - 1Kamil Ali75% (8)
- PHAR 526 - Physical Chemistry Lab 2: Kinetics of Aspirin Degradation in Aqueous SolutionDocument4 pagesPHAR 526 - Physical Chemistry Lab 2: Kinetics of Aspirin Degradation in Aqueous SolutioninnoxyzNo ratings yet
- Mid Term General Chem II Fall 2001Document6 pagesMid Term General Chem II Fall 2001dr.ibrahimsalemvpNo ratings yet
- Tutorial1 CML101Document4 pagesTutorial1 CML101DeveshNo ratings yet
- Exam 1 ReviewDocument3 pagesExam 1 ReviewShanty FelizNo ratings yet
- Assignment 03Document3 pagesAssignment 03Rashmi SahooNo ratings yet
- Gen Chem II Exam 2 Practice Problems f08Document8 pagesGen Chem II Exam 2 Practice Problems f08Nikka LopezNo ratings yet
- Nai (Yai (G Concept Test Ciiemistry (Advanced Level)Document24 pagesNai (Yai (G Concept Test Ciiemistry (Advanced Level)NgoVietCuongNo ratings yet
- Big Idea 4 AnswersDocument4 pagesBig Idea 4 AnswersSreeyaNo ratings yet
- 11 Chemistry Impq Ch07 Equilibrium KvsDocument67 pages11 Chemistry Impq Ch07 Equilibrium KvsDevarajan VeeraraghavanNo ratings yet
- Class Xi CH-6 Question BankDocument6 pagesClass Xi CH-6 Question Bankmohita vigNo ratings yet
- GZB - Xii - WS-8 - Chemistry - Chemical Kinetics - OctoberDocument3 pagesGZB - Xii - WS-8 - Chemistry - Chemical Kinetics - OctoberSaman PanwarNo ratings yet
- Full Marks: 60: 2K) (H) (BR) (HBR) (BR) 1 +Document2 pagesFull Marks: 60: 2K) (H) (BR) (HBR) (BR) 1 +Ashu1803No ratings yet
- Class 11 Chemistry Worksheet Chapter 1 Some Basic Concepts of Chemistry Answers Set 1Document9 pagesClass 11 Chemistry Worksheet Chapter 1 Some Basic Concepts of Chemistry Answers Set 1smartlearningggg249No ratings yet
- Gujarat Technological UniversityDocument2 pagesGujarat Technological Universityyicef37689No ratings yet
- PAC 314 Assignment 1Document1 pagePAC 314 Assignment 1Andiswa patoNo ratings yet
- HW Solutions AP Ch. 12-13Document25 pagesHW Solutions AP Ch. 12-13kleosi50% (2)
- PCP Diag 2 Trial 1Document4 pagesPCP Diag 2 Trial 1Paulo Emmanuele BetitaNo ratings yet
- Vidyasagar University: B.Sc. General Examinations 2021 Semester - III Subject: PHYSICS Question PaperDocument7 pagesVidyasagar University: B.Sc. General Examinations 2021 Semester - III Subject: PHYSICS Question PaperRajani Kanta DolaiNo ratings yet
- Chemical Kinetics 119 Ques!!!Document27 pagesChemical Kinetics 119 Ques!!!elifnazNo ratings yet
- Chemistry TestDocument12 pagesChemistry TestKimmy KuoNo ratings yet
- 04 GasesDocument3 pages04 Gaseschilekwamichael26No ratings yet
- Chemical Reaction Engineering-I Part-A QDocument4 pagesChemical Reaction Engineering-I Part-A Qleela2008No ratings yet
- CT 1 ChemistryDocument7 pagesCT 1 Chemistrykiruthikpranav147No ratings yet
- Assignment 4Document3 pagesAssignment 4Duy Do MinhNo ratings yet
- Physical Chemistry Reference 2Document33 pagesPhysical Chemistry Reference 2Kuo SarongNo ratings yet
- Class XI Chem SAMPLEDocument4 pagesClass XI Chem SAMPLEFIITJEE DPSNo ratings yet
- CHM271 - Tutorial 5 - Chemical KineticsDocument6 pagesCHM271 - Tutorial 5 - Chemical KineticsisfaNo ratings yet
- Chm271 - Tutorial 5 - Chemical KineticsDocument6 pagesChm271 - Tutorial 5 - Chemical Kineticsfiefy zmrNo ratings yet
- Chm271 - Tutorial 5 - Chemical KineticsDocument6 pagesChm271 - Tutorial 5 - Chemical KineticsisfaNo ratings yet
- MCD4390 Week 10 Tutorial QuestionsDocument5 pagesMCD4390 Week 10 Tutorial QuestionsGabbar100% (1)
- I Puc Chemistry Mock PaperDocument2 pagesI Puc Chemistry Mock Papertranquil_452889939No ratings yet
- Class Xi Chemistry 2017Document3 pagesClass Xi Chemistry 2017disha moharanaNo ratings yet
- Gujarat Technological UniversityDocument2 pagesGujarat Technological Universityvyomjavia092003No ratings yet
- Set A Final Exam QuestionDocument8 pagesSet A Final Exam QuestionDhayalan RamachandranNo ratings yet
- Department of Chemistry - Model Question Papers PDFDocument27 pagesDepartment of Chemistry - Model Question Papers PDFRamNo ratings yet
- Chemistry 122 Kinetics and Equilibrium Exam ReviewDocument12 pagesChemistry 122 Kinetics and Equilibrium Exam ReviewKyle GeryczNo ratings yet
- 11 Worksheet 8-10-23 - 06102023 - 204200Document3 pages11 Worksheet 8-10-23 - 06102023 - 204200Adithya PramodNo ratings yet
- Plus One Sample Question Paper: ChemistryDocument4 pagesPlus One Sample Question Paper: ChemistrynafidfdNo ratings yet
- Unit 6.problem Set 2Document5 pagesUnit 6.problem Set 2Aryaa KapilNo ratings yet
- XII - Revision Sheet - 2 - ChemistryDocument3 pagesXII - Revision Sheet - 2 - ChemistryVipin VNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 ThermodynamicsDocument12 pagesChapter 6 ThermodynamicsYash PlayNo ratings yet
- CLASS 11 CHEMISTRY NCERT SOLUTION Chapter - 6 - ThermodynamicsDocument29 pagesCLASS 11 CHEMISTRY NCERT SOLUTION Chapter - 6 - ThermodynamicsAnantNo ratings yet
- Chem 3Document14 pagesChem 3Ellaine NacisNo ratings yet
- Chem 1120 - Chapter 14: Chemical Equilibrium Practice Quiz 1Document10 pagesChem 1120 - Chapter 14: Chemical Equilibrium Practice Quiz 1Danielle Lois AbagNo ratings yet
- Exercise 18.1ah - Equilibrium ExpressionsDocument2 pagesExercise 18.1ah - Equilibrium Expressionsxr aimNo ratings yet
- PLTL Ch. 16 AssignmentDocument6 pagesPLTL Ch. 16 AssignmentJules BrunoNo ratings yet
- Numericals Assignment - Chemical KineticsDocument6 pagesNumericals Assignment - Chemical KineticsSwastik DasNo ratings yet
- Kinetics Revision Worksheet 2 (Solutions)Document8 pagesKinetics Revision Worksheet 2 (Solutions)Lee Jun HuiNo ratings yet
- Test 1 PhysChem - May 2022 - W - AnsDocument5 pagesTest 1 PhysChem - May 2022 - W - Ansmarc jacobs davisNo ratings yet
- Chemical Reaction Engineering Exam QuestionDocument2 pagesChemical Reaction Engineering Exam QuestionnadyahginiceNo ratings yet
- Chemical Thermodynamics Class 12th Practice PaperDocument8 pagesChemical Thermodynamics Class 12th Practice PaperLiyutsa ZirangeNo ratings yet
- Assignment 4Document3 pagesAssignment 4Đạt Trương MinhNo ratings yet
- Chem. Assig.Document8 pagesChem. Assig.aryan asliaNo ratings yet
- Answer All Question: Sk027 / Chapter 3: Reaction Kinetics / Exercise 1Document5 pagesAnswer All Question: Sk027 / Chapter 3: Reaction Kinetics / Exercise 1kjjkimkmkNo ratings yet
- Equilibrium ConceptsDocument4 pagesEquilibrium ConceptsAlex IoannouNo ratings yet
- Kinetic Theory of GasesDocument5 pagesKinetic Theory of GasesOm TipsetwarNo ratings yet
- 2023CML101 Tutorial ChemKin-1Document3 pages2023CML101 Tutorial ChemKin-1Bhoomika Singh SirohiNo ratings yet
- Kinetics & Photochemistry Tutorial ProblemsDocument4 pagesKinetics & Photochemistry Tutorial ProblemsAmbuj Yadav 4-Year B.Tech. Chemical EngineeringNo ratings yet
- CRE Assignment - 1 (Kinetics - Rate Constant and Mole Balance Over Chemical Reactions With Answer Keys)Document6 pagesCRE Assignment - 1 (Kinetics - Rate Constant and Mole Balance Over Chemical Reactions With Answer Keys)Ankush GuptaNo ratings yet
- A Modern Course in Statistical PhysicsFrom EverandA Modern Course in Statistical PhysicsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- Chemical KineticsDocument60 pagesChemical KineticsThe Rock75% (4)
- RBSE Class 12 Chemistry Previous Year Paper 2020Document12 pagesRBSE Class 12 Chemistry Previous Year Paper 2020Sheetal meenaNo ratings yet
- CBRE Module 1 Part 3Document38 pagesCBRE Module 1 Part 3Ronima RajiveNo ratings yet
- Substitution Reactions of Transition Metal ComplexesDocument18 pagesSubstitution Reactions of Transition Metal ComplexesManadip SutradharNo ratings yet
- 2021 EJC JC2 Prelim H2 Chemistry Paper 2 Suggested SolutionDocument20 pages2021 EJC JC2 Prelim H2 Chemistry Paper 2 Suggested Solutionclarissa yeoNo ratings yet
- STPM 962/2: (40 Marks) Answer All QuestionsDocument7 pagesSTPM 962/2: (40 Marks) Answer All QuestionsLim Tze ChuenNo ratings yet
- Burrows3e Solutions Ch09Document60 pagesBurrows3e Solutions Ch09Patricia de LeonNo ratings yet
- Fucking KineticsDocument28 pagesFucking KineticsReginal MoralesNo ratings yet
- DPPS-3 - Chemical KineticsDocument2 pagesDPPS-3 - Chemical KineticsShrish PratapNo ratings yet
- Design For Parallel Reactions (Compatibility Mode)Document8 pagesDesign For Parallel Reactions (Compatibility Mode)Jeetendra YadavNo ratings yet
- Student 3 Stage 2 UpdateDocument10 pagesStudent 3 Stage 2 UpdateMeck LotfiNo ratings yet
- Chemical Stability of Pharmaceuticals: A Handbook For PharmacistsDocument3 pagesChemical Stability of Pharmaceuticals: A Handbook For PharmacistsMiguel SNo ratings yet
- The Fate of The Peroxyl Radical in AutoxidationDocument8 pagesThe Fate of The Peroxyl Radical in AutoxidationforeverskNo ratings yet
- MN Removal by Electrocoagulation-Adsorption KineticsDocument12 pagesMN Removal by Electrocoagulation-Adsorption KineticsassinalevagaiNo ratings yet
- Navneet Chemistry Question BankDocument34 pagesNavneet Chemistry Question BankshriNo ratings yet
- Simplified Material Chemistry FieldDocument32 pagesSimplified Material Chemistry Fieldrohiniharchand786No ratings yet
- Practice Questions For Viva-Class-12Document5 pagesPractice Questions For Viva-Class-12DDNo ratings yet
- Lecture 7 Internal DiffusionDocument46 pagesLecture 7 Internal DiffusionTysir SarhanNo ratings yet
- RKDocument6 pagesRKKou UrakiNo ratings yet
- Yogurt ViscosityDocument6 pagesYogurt Viscosityhuntervog9631No ratings yet
- Exercise For Basic ChemistryDocument31 pagesExercise For Basic Chemistryaqila salmaagistaNo ratings yet
- 101DPP 1 Chemical Kinetics C4U Sahendra KumarDocument3 pages101DPP 1 Chemical Kinetics C4U Sahendra KumarR K Meena JhopadiNo ratings yet
- Chemistry FinalDocument57 pagesChemistry FinalChutvinder LanduliyaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4-: Determination of Rate Law For Batch ReactorDocument25 pagesChapter 4-: Determination of Rate Law For Batch ReactorWonda 005No ratings yet
- Chemical Reaction Engineering: Cap Iii: Rate Laws and StoichiometryDocument53 pagesChemical Reaction Engineering: Cap Iii: Rate Laws and StoichiometryMarthaAlbaGuevaraNo ratings yet
- Lab 1 - Iodine ClockDocument13 pagesLab 1 - Iodine ClockHân LêNo ratings yet
- Tutorial (Kinetics) AnswersDocument4 pagesTutorial (Kinetics) Answersoh khang chiangNo ratings yet