Professional Documents
Culture Documents
12_physics_electrostaticpotentialandcapacitance_tp02
12_physics_electrostaticpotentialandcapacitance_tp02
Uploaded by
Lakshit ManchandaCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Lab Report 2: Phase Change: Name Class Matrix No. Lecturer'S NameDocument18 pagesLab Report 2: Phase Change: Name Class Matrix No. Lecturer'S NameGnabryNo ratings yet
- Sample Paper Physics Grade 12Document7 pagesSample Paper Physics Grade 12chandram654321No ratings yet
- Physics-XII Board Important QuestionsDocument30 pagesPhysics-XII Board Important QuestionsDisha SinghalNo ratings yet
- 12 Physics Electricchargesfield Tp04Document6 pages12 Physics Electricchargesfield Tp04AVNEESH CHAUBEYNo ratings yet
- CH 2Document21 pagesCH 2terasaini77No ratings yet
- CLASS XII - CH - 2 - ELECTROSTATIC POTENTIAlAND CAPACITANCE (COMPETENCY - BASED TEST ITEMS) MARKS WISEDocument32 pagesCLASS XII - CH - 2 - ELECTROSTATIC POTENTIAlAND CAPACITANCE (COMPETENCY - BASED TEST ITEMS) MARKS WISERohan SNo ratings yet
- 2.electrostatic Potential & Capacitance.Document11 pages2.electrostatic Potential & Capacitance.Arshdeep singhNo ratings yet
- Xii Phy Holidayhomework 2Document13 pagesXii Phy Holidayhomework 2Amar Prasad DashNo ratings yet
- Physics Term 1Document48 pagesPhysics Term 1harsh dugharNo ratings yet
- XII Revision Sheet 7 PhysicsDocument2 pagesXII Revision Sheet 7 PhysicsVipin VNo ratings yet
- Xii Physics June Set 2Document4 pagesXii Physics June Set 2shreyasinghchampNo ratings yet
- Kendriya Vidyalaya Sangathan Ziet Chandigarh: Practice Paper Unit-Ii - Electrostatic-Potential and CapacitanceDocument2 pagesKendriya Vidyalaya Sangathan Ziet Chandigarh: Practice Paper Unit-Ii - Electrostatic-Potential and Capacitanceanime loverNo ratings yet
- Mycbseguide: Class 12 - Physics Term 1 - Electric Charges and Fields - 01Document5 pagesMycbseguide: Class 12 - Physics Term 1 - Electric Charges and Fields - 01Utsav ShawNo ratings yet
- Physics - XII (Holiday Home Work)Document10 pagesPhysics - XII (Holiday Home Work)VIVAAS .SNo ratings yet
- Electrostatic Potential - WSDocument3 pagesElectrostatic Potential - WSmy4025093No ratings yet
- PSVT 23-24Document4 pagesPSVT 23-24Pritish KumarNo ratings yet
- Delhi Public School Navi Mumbai Online Revision Assessment 2021-22Document4 pagesDelhi Public School Navi Mumbai Online Revision Assessment 2021-22palash guptaNo ratings yet
- Class 12 Physics QBDocument263 pagesClass 12 Physics QBRohit KumarNo ratings yet
- Physics (Code No. 042) Maximum Marks: 40 TIME: 2 Hours General InstructionsDocument4 pagesPhysics (Code No. 042) Maximum Marks: 40 TIME: 2 Hours General InstructionsHemelatha NairNo ratings yet
- Electrostatic Potential and CapascitanceDocument9 pagesElectrostatic Potential and CapascitancemapuclouddigitalworldNo ratings yet
- Cbse - Current ElectricityDocument4 pagesCbse - Current Electricityrajkumar465987No ratings yet
- XIIPhysicsI 11.07.2022Document2 pagesXIIPhysicsI 11.07.2022sanskritiparihar10No ratings yet
- Class - Xii: (Physics)Document8 pagesClass - Xii: (Physics)kamalmeena2rkNo ratings yet
- Ans. (C) Understanding: Electrostatic Potential and Capacitance - 2 (I) Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument10 pagesAns. (C) Understanding: Electrostatic Potential and Capacitance - 2 (I) Multiple Choice QuestionspaigeNo ratings yet
- STEP-Physics-Ch#12(A)Document10 pagesSTEP-Physics-Ch#12(A)longliveimcbg104No ratings yet
- MLL Physics - 240110 - 133626Document49 pagesMLL Physics - 240110 - 133626Gowtham KNo ratings yet
- XII Monthly Test QPDocument3 pagesXII Monthly Test QPermaharajanNo ratings yet
- PB - I Physics Xii 2023-24Document7 pagesPB - I Physics Xii 2023-24hari008091No ratings yet
- Phy ppr 2024-2025Document4 pagesPhy ppr 2024-2025astrophysicistharshit2007No ratings yet
- 12 Physics Electricchargesfield Tp01Document7 pages12 Physics Electricchargesfield Tp01Aryan KulratanNo ratings yet
- FT Gr-12 SET ADocument8 pagesFT Gr-12 SET ARAIRSNo ratings yet
- Physics XII CH 2 CASE STUDY Electrostatic Potential and CapacitanceDocument18 pagesPhysics XII CH 2 CASE STUDY Electrostatic Potential and CapacitanceNjan KL16么PorottaNo ratings yet
- Class 12Document10 pagesClass 12Vicky mishraNo ratings yet
- 10 Sci Electricity tp01Document6 pages10 Sci Electricity tp0142rwgwnjg5No ratings yet
- AISSCE ASGNMT2class 12 Chapter 2Document4 pagesAISSCE ASGNMT2class 12 Chapter 2Sajid KhanNo ratings yet
- Potential Energy & CapacitanceDocument11 pagesPotential Energy & Capacitanceshlokshukla280300No ratings yet
- Based On Cbse Sample Question PaperDocument9 pagesBased On Cbse Sample Question Paperlakshaydhall123No ratings yet
- Class 12 Electric Potential and Capacitance WorksheetDocument4 pagesClass 12 Electric Potential and Capacitance Worksheetmanikmaurya227No ratings yet
- CH 2 Electric Potential and CapacitanceDocument7 pagesCH 2 Electric Potential and CapacitanceShaurya SinghNo ratings yet
- XII UT 2 PhysicsDocument4 pagesXII UT 2 Physicsharsh JoshiNo ratings yet
- +2 Physics DCM PT1Document5 pages+2 Physics DCM PT1Muskan MongaNo ratings yet
- +2 Physics DCM PT1Document5 pages+2 Physics DCM PT1Muskan MongaNo ratings yet
- 12 - Phy - Electric Chargest Field - Question With SolutionDocument7 pages12 - Phy - Electric Chargest Field - Question With Solutionjayamadhavan2007No ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Electrostatic Potential and Capacitance-1Document3 pagesChapter 2 Electrostatic Potential and Capacitance-1hitharesmi07No ratings yet
- 12 Physics 2017 18 Pre Board Exam PDFDocument8 pages12 Physics 2017 18 Pre Board Exam PDFAshish ChaharNo ratings yet
- 6185-Revision Test 1 Class XII Physics Dec 16Document5 pages6185-Revision Test 1 Class XII Physics Dec 16Rehan AhmadNo ratings yet
- Electric Potential and Capacitance (Revised Ws 1)Document3 pagesElectric Potential and Capacitance (Revised Ws 1)3D SAMINo ratings yet
- Adharsheela Global School Revision Worksheet (2022-23) Physics (042) - Class Xi I A Ch-2-Capacitance and PotentialDocument2 pagesAdharsheela Global School Revision Worksheet (2022-23) Physics (042) - Class Xi I A Ch-2-Capacitance and PotentialNovaNo ratings yet
- Jee Practice Questions-12thDocument88 pagesJee Practice Questions-12thVIKAS SHARMANo ratings yet
- CH2 Electric Potential and Capacitance 2019Document6 pagesCH2 Electric Potential and Capacitance 2019PrachiNo ratings yet
- 12 PhysicsDocument6 pages12 PhysicsMohammed AmmaarNo ratings yet
- Class 12 Physics PA 1 WorksheetDocument3 pagesClass 12 Physics PA 1 Worksheetmd.muzzamil2007No ratings yet
- 10 Years of Electrostatic QuestionsDocument6 pages10 Years of Electrostatic QuestionsBharti KakkarNo ratings yet
- Practice Test, PHYSICS, CE & POTENTIAL, CAPACITANCEDocument3 pagesPractice Test, PHYSICS, CE & POTENTIAL, CAPACITANCEViplavNo ratings yet
- PB - II Physics Xii 2023-24Document7 pagesPB - II Physics Xii 2023-24hari008091No ratings yet
- Chapter 13 Drill: Section I: Multiple ChoiceDocument7 pagesChapter 13 Drill: Section I: Multiple ChoiceRadhika C.No ratings yet
- Worksheet 01 Phy (2021) STEPDocument10 pagesWorksheet 01 Phy (2021) STEPkirki pNo ratings yet
- STEP Physics (1-18) All Worksheets 2020 PDFDocument221 pagesSTEP Physics (1-18) All Worksheets 2020 PDFMUHAMMAD AHMADNo ratings yet
- GP2 - Q3 - Melc 17 - Mod 8Document27 pagesGP2 - Q3 - Melc 17 - Mod 8Aguila Ronz EnguerraNo ratings yet
- Feynman Lectures Simplified 2B: Magnetism & ElectrodynamicsFrom EverandFeynman Lectures Simplified 2B: Magnetism & ElectrodynamicsNo ratings yet
- An Introduction to the Physics and Electrochemistry of Semiconductors: Fundamentals and ApplicationsFrom EverandAn Introduction to the Physics and Electrochemistry of Semiconductors: Fundamentals and ApplicationsNo ratings yet
- Revision Practice 5 markers problemsDocument3 pagesRevision Practice 5 markers problemsLakshit ManchandaNo ratings yet
- solution-1361182Document9 pagessolution-1361182Lakshit ManchandaNo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan 08-Jan-2024 (1)Document3 pagesAdobe Scan 08-Jan-2024 (1)Lakshit ManchandaNo ratings yet
- TTN TEST-1Document1 pageTTN TEST-1Lakshit ManchandaNo ratings yet
- Relation and FunctionDocument4 pagesRelation and FunctionLakshit ManchandaNo ratings yet
- solution-1395763-1Document5 pagessolution-1395763-1Lakshit ManchandaNo ratings yet
- AOD WORD PROBLEMSDocument1 pageAOD WORD PROBLEMSLakshit ManchandaNo ratings yet
- DeterminantsDocument3 pagesDeterminantsLakshit ManchandaNo ratings yet
- Rescheduling of Periodic TestDocument1 pageRescheduling of Periodic TestLakshit ManchandaNo ratings yet
- Policy-7000154096-01Document18 pagesPolicy-7000154096-01Lakshit ManchandaNo ratings yet
- Tesys D Lc1d38m7Document4 pagesTesys D Lc1d38m7Alen HusagićNo ratings yet
- SemiconductorsDocument122 pagesSemiconductorsArpita JaiswalNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 ElectromagneticDocument26 pagesChapter 3 ElectromagneticAdsham100% (2)
- Monthly RE-Dec-21 Final JMKResearchDocument26 pagesMonthly RE-Dec-21 Final JMKResearchkrishna prasadNo ratings yet
- TEMA 2 ACT 2 PROBLEMARIO Balance de MomentumDocument1 pageTEMA 2 ACT 2 PROBLEMARIO Balance de MomentumMichelleNo ratings yet
- Battery Energy Storage System - Edi LeksonoDocument73 pagesBattery Energy Storage System - Edi LeksonoFahmy Rinanda SaputriNo ratings yet
- This PDF Is The Sample PDF Taken From Our Comprehensive Study Material For NEET & AiimsDocument13 pagesThis PDF Is The Sample PDF Taken From Our Comprehensive Study Material For NEET & AiimsVikash Rao khatodiyaNo ratings yet
- Circuits WorksheetDocument3 pagesCircuits WorksheetTawan PetpaiboonNo ratings yet
- Relee ElmarkDocument2 pagesRelee ElmarkwawinNo ratings yet
- Capacitance Group 3Document2 pagesCapacitance Group 3Jhon Cris CorañesNo ratings yet
- Inverter GZ PDFDocument50 pagesInverter GZ PDFZika StojanovicNo ratings yet
- DET40073 - Topic 2cDocument26 pagesDET40073 - Topic 2cKuhaanProNo ratings yet
- American University of Sharjah Department of Electrical EngineeringDocument5 pagesAmerican University of Sharjah Department of Electrical EngineeringNajmul Puda PappadamNo ratings yet
- Tally BookDocument53 pagesTally BookAnyer SalazarNo ratings yet
- ComputationDocument18 pagesComputationKaren Anne JavierNo ratings yet
- ASK-M 72cells Monocrystalline Module: Key FeaturesDocument2 pagesASK-M 72cells Monocrystalline Module: Key FeaturesNam Tran HoangNo ratings yet
- SCIENCE 7 Q3 Week 2Document9 pagesSCIENCE 7 Q3 Week 2Khryzha Mikalyn GaligaNo ratings yet
- The Gaudium School Kollur Campus VectorsDocument4 pagesThe Gaudium School Kollur Campus VectorsROHAN REDDY CHINTALANo ratings yet
- NCMA 215: Course Task #4 Laboratory - MODULE WEEK 2: Healthy Overweight Healthy Overweight HealthyDocument4 pagesNCMA 215: Course Task #4 Laboratory - MODULE WEEK 2: Healthy Overweight Healthy Overweight HealthyMaurice BeltranNo ratings yet
- Astm D 126Document8 pagesAstm D 126Alfonso MartínezNo ratings yet
- Capstone ResearchDocument25 pagesCapstone ResearchEdward John AlawagNo ratings yet
- 2 1 4 A CalculatingforcevectorsDocument6 pages2 1 4 A Calculatingforcevectorsapi-325609547No ratings yet
- STULZ CyberAir CFD-1080Document2 pagesSTULZ CyberAir CFD-1080AsadNo ratings yet
- Taps in Autos-1Document60 pagesTaps in Autos-1ThiyagarjanNo ratings yet
- Xii - Physics - LdaDocument46 pagesXii - Physics - LdaMihir VyasNo ratings yet
- Fault Code 154: Intake Manifold Air Temperature Sensor Circuit - Voltage Below Normal or Shorted To Low SourceDocument3 pagesFault Code 154: Intake Manifold Air Temperature Sensor Circuit - Voltage Below Normal or Shorted To Low Sourcehamilton mirandaNo ratings yet
- Physics Quiz Chapter 5, 6, 7Document6 pagesPhysics Quiz Chapter 5, 6, 7Tariq MahmoodNo ratings yet
- Chemical Energetics: Igcse ChemistryDocument12 pagesChemical Energetics: Igcse ChemistrySherly LeticiaNo ratings yet
- Star DeltaDocument7 pagesStar DeltagopikrishnaraoNo ratings yet
12_physics_electrostaticpotentialandcapacitance_tp02
12_physics_electrostaticpotentialandcapacitance_tp02
Uploaded by
Lakshit ManchandaCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
12_physics_electrostaticpotentialandcapacitance_tp02
12_physics_electrostaticpotentialandcapacitance_tp02
Uploaded by
Lakshit ManchandaCopyright:
Available Formats
myCBSEguide
Class 12 - Physics
Electrostatic Potential and Capacitance Test 02
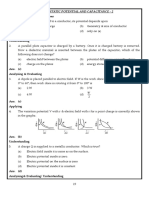
Question No. 1 to 5 are based on the given text. Read the text carefully and answer the questions:
The potential at any observation point P of a static electric field is defined as the work done by the external agent (or negative of
work done by electrostatic field) in slowly bringing a unit positive point charge from infinity to the observation point. Figure
shows the potential variation along the line of charges. Two point charges Q1 and Q2 lie along a line at a distance from each
other.
1. At which of the points 1, 2 and 3 is the electric field is zero?
a. both 1 and 2
b. 1
c. 2
d. 3
2. The signs of charges Q1 and Q2 respectively are
a. negative and positive
b. positive and positive
c. positive and negative
d. negative and negative
3. Which of the two charges Q1 and Q2 is greater in magnitude?
a. Q2
b. Q1
c. Same
d. Can't determined
To practice more questions & prepare well for exams, download myCBSEguide App. It provides complete study
material for CBSE, NCERT, JEE (main), NEET-UG and NDA exams. Teachers can use Examin8 App to create similar
papers with their own name and logo.
4. Which of the following statement is not true?
i. Electrostatic force is a conservative force.
ii. Potential energy of charge q at a point is the work done per unit charge in bringing a charge from any point to
infinity.
iii. When two like charges lie infinite distance apart, their potential energy is zero.
iv. Both (i) and (ii)
a. Option (ii)
b. Option (iv)
c. Option (i)
d. Option (iii)
Copyright © myCBSEguide.com. Mass distribution in any mode is strictly prohibited.
1/6
myCBSEguide
5. Positive and negative point charges of equal magnitude are kept at (0, 0, a
2
) and (0, 0, −a
2
) respectively. The work done
by the electric field when another positive point charge is moved from (-a, 0, 0) to (0, a, 0) is
a. negative
b. positve
c. zero
d. depends on the path connecting the initial and final positions
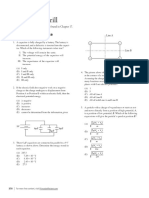
6. In the circuit given below, the charge in μ C, on the capacitor having capacitance 5 μ F is:
a. 7
b. 4.5
c. 9
d. 12
7. Assertion: When charges are shared between any two bodies by conduction, no charge is really lost but some loss of
energy does occurs.
Reason: Some energy disappears in the form of heat, sparking etc.
a. If both Assertion & Reason are true and the reason is the correct explanation of the assertion.
b. If both Assertion and Reason are false statements.
c. If Assertion is true statement but Reason is false.
d. If both Assertion & Reason are true but the reason is not the correct explanation of the assertion.
8. Assertion (A): Two concentric charged shells are given. The potential difference between the shells depends on charge
of inner shell.
Reason (R): Potential due to charge of outer shell remains same at every point inside the sphere.
a. Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
b. Both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of A.
c. A is true but R is false.
d. A is false but R is true.
9. Assertion (A): A metallic shield in form of a hollow shell may be built to block an electric field.
Reason (R): In a hollow spherical shield, the electric field inside it is zero at every point.
a. Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
b. Both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of A.
c. A is true but R is false.
d. A is false but R is true.
10. State True or False:
i. Electric potential of earth is taken to be zero because earth is a good conductor.
a. True
b. False
ii. As radius of the earth is very large, so the potential on the earth can be taken equal to zero.
Copyright © myCBSEguide.com. Mass distribution in any mode is strictly prohibited.
2/6
myCBSEguide
a. True
b. False
11. Fill in the blanks:
a. The potential at a point, due to a positive charge of 100μ F at a distance of 9 m, is ________.
b. When a dielectric material is introduced between the plates of a charged condenser, then the electric field between the
plates will ________.
To practice more questions & prepare well for exams, download myCBSEguide App. It provides complete study
material for CBSE, NCERT, JEE (main), NEET-UG and NDA exams. Teachers can use Examin8 App to create similar
papers with their own name and logo.
12. Match the following:
(a) common potential (i) inversely proportional to distance between plates
(b) energy of capacitor (ii) potential acquired when two capacitors are connected
(c) capacity of parallel plate capacitor (iii) capacity increases
(d) capacity of capacitor with dielectric material (iv) energy stored in capacitor plates
13. Why does a configuration of charges possess potential energy?
14. In a certain 0.1 m3 of space, an electric potential is found to be 5V throughout. What is the electric field in this region?
15. A test charge q is moved without acceleration from A to C along the path from A to B and then from B to C in electric
field E as Fig.
i. Calculate the potential difference between A and C.
ii. At which point (of the two) is the electric potential more and why?
16. Prove that the total energy stored in a series combination of capacitors is equal to the sum of energies stored in the
individual capacitors.
17. The following data was obtained for the dependence of the magnitude of an electric field with distance from a reference
point O, within the charge distribution in the shaded region shown in the figure.
Field Point A B C A' B' C'
Magnitude of electric field E E/8 E/27 E/2 E/16 E/64
i. Identify the charge distribution and justify your answer.
ii. If the potential due to this charge distribution has a value V at the point A, what is its value at the point A'?
18. Two parallel metal plates P and Q are inserted at equal distances into a plane capacitor as shown in fig. Plates A and B of
the capacitor are connected to a battery of e.m.f. V.
Copyright © myCBSEguide.com. Mass distribution in any mode is strictly prohibited.
3/6
myCBSEguide
a. What are the potentials of the four plates?
b. How will the potentials of plates P and Q and the intensities of the fields in each of the three spaces change after
plates P and Q have been connected by a wire?
c. What will happen to the charges on plates A and B, when plates P and Q are connected with a wire?
d. Will there be charges on the plates P and Q after connecting them with a wire?
Copyright © myCBSEguide.com. Mass distribution in any mode is strictly prohibited.
4/6
myCBSEguide
Class 12 - Physics
Electrostatic Potential and Capacitance Test 02
Solution
1. (d) 3
−dV
Explanation: As dr
= Er, the negative of the slop of V versus r curve represents the component of electric field along
r. Slope of curve is zero only at point 3. Therefore, the electric field vector is zero at point 3.
2. (c) positive and negative
Explanation: Near positive charge, net potential is positive and near a negative charge, net potential is negative. Thus,
charge Q1 is positive and Q2 is negative.
3. (b) Q1
Explanation: From the figure, it can be seen that net potential due to two charges is positive everywhere in the region
left to charge Q1. Therefore the magnitude of potential due to charge Q1 is greater than due to Q2.
To practice more questions & prepare well for exams, download myCBSEguide App. It provides complete study
material for CBSE, NCERT, JEE (main), NEET-UG and NDA exams. Teachers can use Examin8 App to create similar
papers with their own name and logo.
4. (a) Option (ii)
Explanation: Option (ii)
5. (c) zero
Explanation: It can be seen that potential at the points both A and B are zero. When the charge is moved from A to B,
work done by the electric field on the charge will be zero.
6. (c) 9
Explanation: The potential difference across the branch de is 6 V.
The net capacitance of de branch is 2.1 μ F
So, q = CV = 2.1 × 6 μ C = 12.6 μ C
Potential across 2 and 5 combination in parallel is
6 - 4.2 = 1.8 V
So, q = (1.8) (5) = 9 μ C
7. (c) If Assertion is true statement but Reason is false.
Explanation: If Assertion is true statement but Reason is false.
8. (a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
Explanation: Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
9. (a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
Explanation: Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
10. State True or False:
i. (a) True
ii. (a) True
Copyright © myCBSEguide.com. Mass distribution in any mode is strictly prohibited.
5/6
myCBSEguide
11. Fill in the blanks:
a. 105 V
b. Decrease
12. (a) - (ii), (b) - (iv), (c) - (i), (d) - (iii)
13. Work was done in putting the charges at their present locations which get stored in the configuration as its potential
energy.
14. Now, E = - dV
dr
As electric potential is 5 V throughout i.e. constant, electric field in the region will be zero.
VC −VA VC −VA
15. i. E = −
dV
dx
= −
2−6
=
4
or VC - VA = 4E
⇒ VC > VA
ii. The direction of the electric field is in the direction of decreasing potential, so VC > VA.
To practice more questions & prepare well for exams, download myCBSEguide App. It provides complete study
material for CBSE, NCERT, JEE (main), NEET-UG and NDA exams. Teachers can use Examin8 App to create similar
papers with their own name and logo.
16. Suppose that three capacitors of capacitances C1, C2 and C3 are connected in series to a battery. The equivalent
capacitance of the series combination is given by
1 1 1 1
= + +
C C1 C2 C3
Further, when a series combination of the capacitors is charged through a battery, the charge on the left plate of each
capacitor is q, while the induced charges -q and +q are produced on the right plate of each capacitor. Thus, the net charge
stored in the series combination is just q. Therefore, the total energy stored in the series combination,
2
q2 (
q
U= 1
2 C
=
1
2 C1
1
+
1
C2
+
1
C3
)
2 2 2
q q q
=
1 1 1
+ +
2 C1 2 C2 2 C3
or U = U1 + U2 + U3
Thus, the total energy stored in a series combination of the capacitors is equal to the sum of the energies stored in the
individual capacitors.
17. i. The charge distribution in the shaded region is an electric dipole.
It is because, the electric field at points A, B and C varies inversely as the cube of their distances from the centre of
the charge distribution. The electric field varies in this manner (E ∝ 1/r3) due to an electric dipole. Further, if the
points A, B and C lie on the axial line of the electric dipole, then the points A', B' and C' lie on its equatorial line and
electric fields at these points is exactly half of those at the corresponding points A, B, and C on the axial line.
ii. The electric potential at the point A' is zero. It is because the electric potential at a point on the equatorial line of an
electric dipole is zero.
18. a. The plates P and Q divide the space between the plates A and B in three equal parts. Since V = Ed, the potentials of
the plates A, P, Q, and B will be respectively V, 2V/3, V/3 and 0.
b. When the plates P and Q are connected with a wire, the space between the plates A and B gets divided into two equal
parts. Hence, the potentials of plates A, P, Q, and B will be respectively V, V/2, V/2 and 0.
Since the potential difference between the plates A and P; and between the plates, Q and B have increased from V/3
to V/2, the electric field between these plates will increase. As the potential difference the plates P and Q is zero, the
electric field will also be zero.
c. Since the potential difference between the plates A and P and between the plates Q and B have increased, the charge
on the plates A and B will increase.
d. Yes, the plate P will have a positive charge and the plate Q will have a negative charge.
Copyright © myCBSEguide.com. Mass distribution in any mode is strictly prohibited.
6/6
You might also like
- Lab Report 2: Phase Change: Name Class Matrix No. Lecturer'S NameDocument18 pagesLab Report 2: Phase Change: Name Class Matrix No. Lecturer'S NameGnabryNo ratings yet
- Sample Paper Physics Grade 12Document7 pagesSample Paper Physics Grade 12chandram654321No ratings yet
- Physics-XII Board Important QuestionsDocument30 pagesPhysics-XII Board Important QuestionsDisha SinghalNo ratings yet
- 12 Physics Electricchargesfield Tp04Document6 pages12 Physics Electricchargesfield Tp04AVNEESH CHAUBEYNo ratings yet
- CH 2Document21 pagesCH 2terasaini77No ratings yet
- CLASS XII - CH - 2 - ELECTROSTATIC POTENTIAlAND CAPACITANCE (COMPETENCY - BASED TEST ITEMS) MARKS WISEDocument32 pagesCLASS XII - CH - 2 - ELECTROSTATIC POTENTIAlAND CAPACITANCE (COMPETENCY - BASED TEST ITEMS) MARKS WISERohan SNo ratings yet
- 2.electrostatic Potential & Capacitance.Document11 pages2.electrostatic Potential & Capacitance.Arshdeep singhNo ratings yet
- Xii Phy Holidayhomework 2Document13 pagesXii Phy Holidayhomework 2Amar Prasad DashNo ratings yet
- Physics Term 1Document48 pagesPhysics Term 1harsh dugharNo ratings yet
- XII Revision Sheet 7 PhysicsDocument2 pagesXII Revision Sheet 7 PhysicsVipin VNo ratings yet
- Xii Physics June Set 2Document4 pagesXii Physics June Set 2shreyasinghchampNo ratings yet
- Kendriya Vidyalaya Sangathan Ziet Chandigarh: Practice Paper Unit-Ii - Electrostatic-Potential and CapacitanceDocument2 pagesKendriya Vidyalaya Sangathan Ziet Chandigarh: Practice Paper Unit-Ii - Electrostatic-Potential and Capacitanceanime loverNo ratings yet
- Mycbseguide: Class 12 - Physics Term 1 - Electric Charges and Fields - 01Document5 pagesMycbseguide: Class 12 - Physics Term 1 - Electric Charges and Fields - 01Utsav ShawNo ratings yet
- Physics - XII (Holiday Home Work)Document10 pagesPhysics - XII (Holiday Home Work)VIVAAS .SNo ratings yet
- Electrostatic Potential - WSDocument3 pagesElectrostatic Potential - WSmy4025093No ratings yet
- PSVT 23-24Document4 pagesPSVT 23-24Pritish KumarNo ratings yet
- Delhi Public School Navi Mumbai Online Revision Assessment 2021-22Document4 pagesDelhi Public School Navi Mumbai Online Revision Assessment 2021-22palash guptaNo ratings yet
- Class 12 Physics QBDocument263 pagesClass 12 Physics QBRohit KumarNo ratings yet
- Physics (Code No. 042) Maximum Marks: 40 TIME: 2 Hours General InstructionsDocument4 pagesPhysics (Code No. 042) Maximum Marks: 40 TIME: 2 Hours General InstructionsHemelatha NairNo ratings yet
- Electrostatic Potential and CapascitanceDocument9 pagesElectrostatic Potential and CapascitancemapuclouddigitalworldNo ratings yet
- Cbse - Current ElectricityDocument4 pagesCbse - Current Electricityrajkumar465987No ratings yet
- XIIPhysicsI 11.07.2022Document2 pagesXIIPhysicsI 11.07.2022sanskritiparihar10No ratings yet
- Class - Xii: (Physics)Document8 pagesClass - Xii: (Physics)kamalmeena2rkNo ratings yet
- Ans. (C) Understanding: Electrostatic Potential and Capacitance - 2 (I) Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument10 pagesAns. (C) Understanding: Electrostatic Potential and Capacitance - 2 (I) Multiple Choice QuestionspaigeNo ratings yet
- STEP-Physics-Ch#12(A)Document10 pagesSTEP-Physics-Ch#12(A)longliveimcbg104No ratings yet
- MLL Physics - 240110 - 133626Document49 pagesMLL Physics - 240110 - 133626Gowtham KNo ratings yet
- XII Monthly Test QPDocument3 pagesXII Monthly Test QPermaharajanNo ratings yet
- PB - I Physics Xii 2023-24Document7 pagesPB - I Physics Xii 2023-24hari008091No ratings yet
- Phy ppr 2024-2025Document4 pagesPhy ppr 2024-2025astrophysicistharshit2007No ratings yet
- 12 Physics Electricchargesfield Tp01Document7 pages12 Physics Electricchargesfield Tp01Aryan KulratanNo ratings yet
- FT Gr-12 SET ADocument8 pagesFT Gr-12 SET ARAIRSNo ratings yet
- Physics XII CH 2 CASE STUDY Electrostatic Potential and CapacitanceDocument18 pagesPhysics XII CH 2 CASE STUDY Electrostatic Potential and CapacitanceNjan KL16么PorottaNo ratings yet
- Class 12Document10 pagesClass 12Vicky mishraNo ratings yet
- 10 Sci Electricity tp01Document6 pages10 Sci Electricity tp0142rwgwnjg5No ratings yet
- AISSCE ASGNMT2class 12 Chapter 2Document4 pagesAISSCE ASGNMT2class 12 Chapter 2Sajid KhanNo ratings yet
- Potential Energy & CapacitanceDocument11 pagesPotential Energy & Capacitanceshlokshukla280300No ratings yet
- Based On Cbse Sample Question PaperDocument9 pagesBased On Cbse Sample Question Paperlakshaydhall123No ratings yet
- Class 12 Electric Potential and Capacitance WorksheetDocument4 pagesClass 12 Electric Potential and Capacitance Worksheetmanikmaurya227No ratings yet
- CH 2 Electric Potential and CapacitanceDocument7 pagesCH 2 Electric Potential and CapacitanceShaurya SinghNo ratings yet
- XII UT 2 PhysicsDocument4 pagesXII UT 2 Physicsharsh JoshiNo ratings yet
- +2 Physics DCM PT1Document5 pages+2 Physics DCM PT1Muskan MongaNo ratings yet
- +2 Physics DCM PT1Document5 pages+2 Physics DCM PT1Muskan MongaNo ratings yet
- 12 - Phy - Electric Chargest Field - Question With SolutionDocument7 pages12 - Phy - Electric Chargest Field - Question With Solutionjayamadhavan2007No ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Electrostatic Potential and Capacitance-1Document3 pagesChapter 2 Electrostatic Potential and Capacitance-1hitharesmi07No ratings yet
- 12 Physics 2017 18 Pre Board Exam PDFDocument8 pages12 Physics 2017 18 Pre Board Exam PDFAshish ChaharNo ratings yet
- 6185-Revision Test 1 Class XII Physics Dec 16Document5 pages6185-Revision Test 1 Class XII Physics Dec 16Rehan AhmadNo ratings yet
- Electric Potential and Capacitance (Revised Ws 1)Document3 pagesElectric Potential and Capacitance (Revised Ws 1)3D SAMINo ratings yet
- Adharsheela Global School Revision Worksheet (2022-23) Physics (042) - Class Xi I A Ch-2-Capacitance and PotentialDocument2 pagesAdharsheela Global School Revision Worksheet (2022-23) Physics (042) - Class Xi I A Ch-2-Capacitance and PotentialNovaNo ratings yet
- Jee Practice Questions-12thDocument88 pagesJee Practice Questions-12thVIKAS SHARMANo ratings yet
- CH2 Electric Potential and Capacitance 2019Document6 pagesCH2 Electric Potential and Capacitance 2019PrachiNo ratings yet
- 12 PhysicsDocument6 pages12 PhysicsMohammed AmmaarNo ratings yet
- Class 12 Physics PA 1 WorksheetDocument3 pagesClass 12 Physics PA 1 Worksheetmd.muzzamil2007No ratings yet
- 10 Years of Electrostatic QuestionsDocument6 pages10 Years of Electrostatic QuestionsBharti KakkarNo ratings yet
- Practice Test, PHYSICS, CE & POTENTIAL, CAPACITANCEDocument3 pagesPractice Test, PHYSICS, CE & POTENTIAL, CAPACITANCEViplavNo ratings yet
- PB - II Physics Xii 2023-24Document7 pagesPB - II Physics Xii 2023-24hari008091No ratings yet
- Chapter 13 Drill: Section I: Multiple ChoiceDocument7 pagesChapter 13 Drill: Section I: Multiple ChoiceRadhika C.No ratings yet
- Worksheet 01 Phy (2021) STEPDocument10 pagesWorksheet 01 Phy (2021) STEPkirki pNo ratings yet
- STEP Physics (1-18) All Worksheets 2020 PDFDocument221 pagesSTEP Physics (1-18) All Worksheets 2020 PDFMUHAMMAD AHMADNo ratings yet
- GP2 - Q3 - Melc 17 - Mod 8Document27 pagesGP2 - Q3 - Melc 17 - Mod 8Aguila Ronz EnguerraNo ratings yet
- Feynman Lectures Simplified 2B: Magnetism & ElectrodynamicsFrom EverandFeynman Lectures Simplified 2B: Magnetism & ElectrodynamicsNo ratings yet
- An Introduction to the Physics and Electrochemistry of Semiconductors: Fundamentals and ApplicationsFrom EverandAn Introduction to the Physics and Electrochemistry of Semiconductors: Fundamentals and ApplicationsNo ratings yet
- Revision Practice 5 markers problemsDocument3 pagesRevision Practice 5 markers problemsLakshit ManchandaNo ratings yet
- solution-1361182Document9 pagessolution-1361182Lakshit ManchandaNo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan 08-Jan-2024 (1)Document3 pagesAdobe Scan 08-Jan-2024 (1)Lakshit ManchandaNo ratings yet
- TTN TEST-1Document1 pageTTN TEST-1Lakshit ManchandaNo ratings yet
- Relation and FunctionDocument4 pagesRelation and FunctionLakshit ManchandaNo ratings yet
- solution-1395763-1Document5 pagessolution-1395763-1Lakshit ManchandaNo ratings yet
- AOD WORD PROBLEMSDocument1 pageAOD WORD PROBLEMSLakshit ManchandaNo ratings yet
- DeterminantsDocument3 pagesDeterminantsLakshit ManchandaNo ratings yet
- Rescheduling of Periodic TestDocument1 pageRescheduling of Periodic TestLakshit ManchandaNo ratings yet
- Policy-7000154096-01Document18 pagesPolicy-7000154096-01Lakshit ManchandaNo ratings yet
- Tesys D Lc1d38m7Document4 pagesTesys D Lc1d38m7Alen HusagićNo ratings yet
- SemiconductorsDocument122 pagesSemiconductorsArpita JaiswalNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 ElectromagneticDocument26 pagesChapter 3 ElectromagneticAdsham100% (2)
- Monthly RE-Dec-21 Final JMKResearchDocument26 pagesMonthly RE-Dec-21 Final JMKResearchkrishna prasadNo ratings yet
- TEMA 2 ACT 2 PROBLEMARIO Balance de MomentumDocument1 pageTEMA 2 ACT 2 PROBLEMARIO Balance de MomentumMichelleNo ratings yet
- Battery Energy Storage System - Edi LeksonoDocument73 pagesBattery Energy Storage System - Edi LeksonoFahmy Rinanda SaputriNo ratings yet
- This PDF Is The Sample PDF Taken From Our Comprehensive Study Material For NEET & AiimsDocument13 pagesThis PDF Is The Sample PDF Taken From Our Comprehensive Study Material For NEET & AiimsVikash Rao khatodiyaNo ratings yet
- Circuits WorksheetDocument3 pagesCircuits WorksheetTawan PetpaiboonNo ratings yet
- Relee ElmarkDocument2 pagesRelee ElmarkwawinNo ratings yet
- Capacitance Group 3Document2 pagesCapacitance Group 3Jhon Cris CorañesNo ratings yet
- Inverter GZ PDFDocument50 pagesInverter GZ PDFZika StojanovicNo ratings yet
- DET40073 - Topic 2cDocument26 pagesDET40073 - Topic 2cKuhaanProNo ratings yet
- American University of Sharjah Department of Electrical EngineeringDocument5 pagesAmerican University of Sharjah Department of Electrical EngineeringNajmul Puda PappadamNo ratings yet
- Tally BookDocument53 pagesTally BookAnyer SalazarNo ratings yet
- ComputationDocument18 pagesComputationKaren Anne JavierNo ratings yet
- ASK-M 72cells Monocrystalline Module: Key FeaturesDocument2 pagesASK-M 72cells Monocrystalline Module: Key FeaturesNam Tran HoangNo ratings yet
- SCIENCE 7 Q3 Week 2Document9 pagesSCIENCE 7 Q3 Week 2Khryzha Mikalyn GaligaNo ratings yet
- The Gaudium School Kollur Campus VectorsDocument4 pagesThe Gaudium School Kollur Campus VectorsROHAN REDDY CHINTALANo ratings yet
- NCMA 215: Course Task #4 Laboratory - MODULE WEEK 2: Healthy Overweight Healthy Overweight HealthyDocument4 pagesNCMA 215: Course Task #4 Laboratory - MODULE WEEK 2: Healthy Overweight Healthy Overweight HealthyMaurice BeltranNo ratings yet
- Astm D 126Document8 pagesAstm D 126Alfonso MartínezNo ratings yet
- Capstone ResearchDocument25 pagesCapstone ResearchEdward John AlawagNo ratings yet
- 2 1 4 A CalculatingforcevectorsDocument6 pages2 1 4 A Calculatingforcevectorsapi-325609547No ratings yet
- STULZ CyberAir CFD-1080Document2 pagesSTULZ CyberAir CFD-1080AsadNo ratings yet
- Taps in Autos-1Document60 pagesTaps in Autos-1ThiyagarjanNo ratings yet
- Xii - Physics - LdaDocument46 pagesXii - Physics - LdaMihir VyasNo ratings yet
- Fault Code 154: Intake Manifold Air Temperature Sensor Circuit - Voltage Below Normal or Shorted To Low SourceDocument3 pagesFault Code 154: Intake Manifold Air Temperature Sensor Circuit - Voltage Below Normal or Shorted To Low Sourcehamilton mirandaNo ratings yet
- Physics Quiz Chapter 5, 6, 7Document6 pagesPhysics Quiz Chapter 5, 6, 7Tariq MahmoodNo ratings yet
- Chemical Energetics: Igcse ChemistryDocument12 pagesChemical Energetics: Igcse ChemistrySherly LeticiaNo ratings yet
- Star DeltaDocument7 pagesStar DeltagopikrishnaraoNo ratings yet