Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 viewsTABLE_TO_UPLOAD philosophy
TABLE_TO_UPLOAD philosophy
Uploaded by
carolina orlandoCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Philosophy Matrices Assignment Final SubmissionDocument3 pagesPhilosophy Matrices Assignment Final SubmissionDraft Night Investing50% (2)
- Philosophy and Education Continuum ChartDocument2 pagesPhilosophy and Education Continuum ChartJeson Galgo75% (4)
- Helmut Zander, Anthroposophie in DeutschlandDocument14 pagesHelmut Zander, Anthroposophie in DeutschlandBibliorare100% (1)
- Module 2 - Ped 02 The Teaching Profession 2 (Revised - Final)Document16 pagesModule 2 - Ped 02 The Teaching Profession 2 (Revised - Final)Lawrence DiolaNo ratings yet
- Philosophical Roots of EducationDocument28 pagesPhilosophical Roots of EducationFatin Nadirah AqilahNo ratings yet
- PhilosophyDocument12 pagesPhilosophyAlhumdulillah Hi Rabil AlameenNo ratings yet
- Philosophy and Education Continuum Chart: Originator(s)Document2 pagesPhilosophy and Education Continuum Chart: Originator(s)Umme Ammara100% (1)
- Alvin Philosophy and Education Continuum Chart 1Document2 pagesAlvin Philosophy and Education Continuum Chart 1CHERRY LYNN Y. ROLOYANNo ratings yet
- Philosophy and Education Continuum Chart F3 6 BCE2 AJ JMCDocument1 pagePhilosophy and Education Continuum Chart F3 6 BCE2 AJ JMCPrakash Chandra PandeyNo ratings yet
- Philosophy of Education and Personal Philosophy: Beed 1A-Group 3 Zafra Villaronte Capuno Diamada MalachicoDocument20 pagesPhilosophy of Education and Personal Philosophy: Beed 1A-Group 3 Zafra Villaronte Capuno Diamada MalachicoMaria Laila Jane MalachicoNo ratings yet
- eLFD TASK 1.3Document23 pageseLFD TASK 1.3DC TpcNo ratings yet
- Notes Teach ProfDocument15 pagesNotes Teach ProfKristine Anne IgotNo ratings yet
- Ch-5 Overview PhilosophyDocument35 pagesCh-5 Overview Philosophyrommel legaspiNo ratings yet
- Philosophy Key Words Proponent Rule of TeachersDocument3 pagesPhilosophy Key Words Proponent Rule of TeacherskennethNo ratings yet
- Ch-5 Overview PhilosophyDocument35 pagesCh-5 Overview Philosophyseigfred john BallesterosNo ratings yet
- TABLE 2.1 Five Major Educational PhilosophiesDocument2 pagesTABLE 2.1 Five Major Educational PhilosophiesTeam TheaLleaNo ratings yet
- PHILOS and EDUCATIONAL IMPLICATIONSDocument5 pagesPHILOS and EDUCATIONAL IMPLICATIONSmarnylieNo ratings yet
- Psychological Foundation Sociological FoundationDocument3 pagesPsychological Foundation Sociological FoundationVallada, FebroseNo ratings yet
- Philosophy of EdDocument36 pagesPhilosophy of Edning setiaNo ratings yet
- Philosophy of Education Part 1Document29 pagesPhilosophy of Education Part 1Jamer PelotinNo ratings yet
- PHILO Ver. 2Document4 pagesPHILO Ver. 2MAFNo ratings yet
- Philosophies Philosophies MeaningDocument20 pagesPhilosophies Philosophies Meaninggems gamesNo ratings yet
- STS Prelims ReviewDocument12 pagesSTS Prelims ReviewAve RobbinsNo ratings yet
- Metaphysics and EducationDocument29 pagesMetaphysics and EducationMaria Shiela Cantonjos MaglenteNo ratings yet
- Health EducationDocument11 pagesHealth Educationkrishnamaecortega09No ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document2 pagesChapter 1Josh SumabonNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Lesson-2 Philosophy-Of-EducationDocument9 pagesChapter 3 Lesson-2 Philosophy-Of-EducationGray Yan HolmesNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 PDF Teaching AptitudeDocument188 pagesUnit 1 PDF Teaching Aptitudeneelam khattarNo ratings yet
- Research Methodology Unit 1Document18 pagesResearch Methodology Unit 1hanna.avery666No ratings yet
- Philosophy of EducationDocument4 pagesPhilosophy of EducationClaire YingNo ratings yet
- Teaching Profession - Educational PhilosophyDocument23 pagesTeaching Profession - Educational PhilosophyRon louise PereyraNo ratings yet
- Educ 3202 MD Reviewer FileDocument11 pagesEduc 3202 MD Reviewer FileVia Iana RagayNo ratings yet
- Foundation of Social Studies SSM1 M4Document15 pagesFoundation of Social Studies SSM1 M4HAZEL JANE ABAPONo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 The Nature and History of PsychologyDocument8 pagesLesson 1 The Nature and History of PsychologyAllison MaañoNo ratings yet
- Pursuing WisdomDocument18 pagesPursuing WisdomCEDRICK NICOLAS CUGAS VALERANo ratings yet
- PhilosophyDocument16 pagesPhilosophyMa.Jessica SiblagNo ratings yet
- EDUC 6 Midterm Exam Reviewer All CoveragesDocument8 pagesEDUC 6 Midterm Exam Reviewer All Coveragescharlot besasNo ratings yet
- Isnain, Erich C - BSED 1A 08/22/2020: Educational Philosophy Philosophical Roots Idealism Realism PragmatismDocument3 pagesIsnain, Erich C - BSED 1A 08/22/2020: Educational Philosophy Philosophical Roots Idealism Realism PragmatismErichIsnainNo ratings yet
- Philosophical Foundations of CurriculumDocument16 pagesPhilosophical Foundations of CurriculumUshna ShahNo ratings yet
- Government Elementary College of Education (Qasimabad) : Name: Sitara RiazDocument8 pagesGovernment Elementary College of Education (Qasimabad) : Name: Sitara RiazSitara RiazNo ratings yet
- Philedu2016 05 RationalismDocument13 pagesPhiledu2016 05 RationalismKathrina De CastroNo ratings yet
- PART 3 - Educational ThoughtDocument18 pagesPART 3 - Educational ThoughtReshNo ratings yet
- Philosophical Foundations of EducationDocument33 pagesPhilosophical Foundations of EducationAnilyn CelisNo ratings yet
- ODB - Soc Dim 1Document5 pagesODB - Soc Dim 1edenj rodrigoNo ratings yet
- Philosophy and Education - OverviewDocument18 pagesPhilosophy and Education - OverviewRhenan LoseoNo ratings yet
- Topic 2 - Philosophical Foundations of CurriculumDocument51 pagesTopic 2 - Philosophical Foundations of Curriculumaton hudaNo ratings yet
- Educational Philosophy: For The Intellectual Foundations of Indonesia EducationDocument27 pagesEducational Philosophy: For The Intellectual Foundations of Indonesia EducationMiraNurmayantiNo ratings yet
- JMN 451 - Teaching Philosphy Part 2Document12 pagesJMN 451 - Teaching Philosphy Part 2Ntuthu TshoksNo ratings yet
- Foundations of EducationDocument35 pagesFoundations of EducationElla CamelloNo ratings yet
- Module 1Document6 pagesModule 1johnemmanuel oreaNo ratings yet
- Theory of Learning From Time To Time: Christina Lhaksmita Anandari, Ed.MDocument13 pagesTheory of Learning From Time To Time: Christina Lhaksmita Anandari, Ed.Mfriska nadiaNo ratings yet
- Western Perspective PhilosophyDocument29 pagesWestern Perspective PhilosophyEmynordiana JamilNo ratings yet
- Summary of Philosophies - TableDocument3 pagesSummary of Philosophies - Tableabdusabur2535No ratings yet
- LESSON 1 - Introduction To The Philosophy of The Human PersonDocument49 pagesLESSON 1 - Introduction To The Philosophy of The Human PersonMauie Uy JonasNo ratings yet
- 1 Doing PhilosophyDocument32 pages1 Doing PhilosophyAilener ZednanrehNo ratings yet
- Focus: Nature of Ultimate Reality (Beyond The Physical) : MetaphysicsDocument10 pagesFocus: Nature of Ultimate Reality (Beyond The Physical) : MetaphysicsChristy Lou RollorataNo ratings yet
- The Possibility of A Transcendental Subject by Zosimo LeeDocument15 pagesThe Possibility of A Transcendental Subject by Zosimo LeeNicoelNo ratings yet
- Approaches To Human CognitionDocument19 pagesApproaches To Human Cognitionbobadilla.sarah19No ratings yet
- DISS Chapter-2.2Document5 pagesDISS Chapter-2.2minajayron9No ratings yet
- Eria Rhona L. - Assignment in Foundation of Education-2Document3 pagesEria Rhona L. - Assignment in Foundation of Education-2LIBERTY VALVERDENo ratings yet
- Ag Test Package FormatDocument25 pagesAg Test Package FormatoparoystNo ratings yet
- SafeGrid Tutorial How To Perform A Simple Earthing DesignDocument10 pagesSafeGrid Tutorial How To Perform A Simple Earthing DesignAnwesh Kumar MaddikuntaNo ratings yet
- English Project CompileDocument33 pagesEnglish Project CompileAbdul QayyumNo ratings yet
- D. Raghuram: Work ExperienceDocument3 pagesD. Raghuram: Work ExperienceNaveen KumarNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan in Science 1.3Document38 pagesLesson Plan in Science 1.3Heidi Dalyagan DulnagonNo ratings yet
- Pengaruh Motivasi, Kepemimpinan Dan Budaya Organisasi Terhadap Kepuasan Kerja Serta Dampaknya Pada Kinerja KaryawanDocument7 pagesPengaruh Motivasi, Kepemimpinan Dan Budaya Organisasi Terhadap Kepuasan Kerja Serta Dampaknya Pada Kinerja KaryawanAnggi PutraNo ratings yet
- Free - Space W - Band Setup For The Electrical Characterization of Materials and MM - Wave ComponentsDocument44 pagesFree - Space W - Band Setup For The Electrical Characterization of Materials and MM - Wave ComponentsthomasNo ratings yet
- Half-Cell Potential Test From The Upper-Side and The Lower-Side of Reinforced Concrete Slabs: A Comparative StudyDocument6 pagesHalf-Cell Potential Test From The Upper-Side and The Lower-Side of Reinforced Concrete Slabs: A Comparative StudyANNADURAINo ratings yet
- R Reference Manual Volume 1Document736 pagesR Reference Manual Volume 1PH1628No ratings yet
- 3 Generations of Human RightsDocument1 page3 Generations of Human RightsDzenan HakalovicNo ratings yet
- Reasons For Diminishing Returns To A FactorDocument2 pagesReasons For Diminishing Returns To A FactorRobert AyalaNo ratings yet
- E4nb71 PDFDocument99 pagesE4nb71 PDFtambache69100% (1)
- Asme Sa-29 1018Document1 pageAsme Sa-29 1018Nelson RangelNo ratings yet
- Artificial Intelligence On Digital Marketing - An OverviewDocument14 pagesArtificial Intelligence On Digital Marketing - An Overviewammar zNo ratings yet
- Ims555 Grouping Assignment (Ai Deepfakes)Document23 pagesIms555 Grouping Assignment (Ai Deepfakes)NUR A'ISYAH AZIZINo ratings yet
- UPS Technical Data Sheet (MS-DD-SAP01-ELE-DS-0015 - Rev2)Document6 pagesUPS Technical Data Sheet (MS-DD-SAP01-ELE-DS-0015 - Rev2)Muhammad YusufNo ratings yet
- On Arushi Murder CaseDocument8 pagesOn Arushi Murder Case0000No ratings yet
- Heater: Hydrate PreventionDocument12 pagesHeater: Hydrate PreventionMahmoud Ahmed Ali AbdelrazikNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan in English 8Document66 pagesLesson Plan in English 8Mhairo Akira100% (1)
- AHU Vibration Data - PostingDocument2 pagesAHU Vibration Data - PostingNeal JohnsonNo ratings yet
- Mayank Selection & Recruitment Process BluedartDocument5 pagesMayank Selection & Recruitment Process BluedartMayank SahuNo ratings yet
- SCIETECHNODocument19 pagesSCIETECHNOChini ChanNo ratings yet
- Performance: Task in Math 8 House Floor PlanDocument10 pagesPerformance: Task in Math 8 House Floor PlanJoshua Emmanuel LedesmaNo ratings yet
- Rollarc 400Document48 pagesRollarc 400m khNo ratings yet
- Nepal National Building Code: Draft Final NBC 205: 2012Document52 pagesNepal National Building Code: Draft Final NBC 205: 2012Sudan ShresthaNo ratings yet
- Optare Electric Vehicles: Embracing The EnvironmentDocument4 pagesOptare Electric Vehicles: Embracing The EnvironmentarrenNo ratings yet
- Allen Bradley 160 C SeriesDocument28 pagesAllen Bradley 160 C SeriesTihomir Matulić100% (1)
- Chapter 9: TidesDocument40 pagesChapter 9: TidesCarol GirottoNo ratings yet
- Models - Acdc.capacitor Fringing FieldsDocument16 pagesModels - Acdc.capacitor Fringing FieldsAnonymous pWNBPuMcf100% (1)
TABLE_TO_UPLOAD philosophy
TABLE_TO_UPLOAD philosophy
Uploaded by
carolina orlando0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views1 pageCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views1 pageTABLE_TO_UPLOAD philosophy
TABLE_TO_UPLOAD philosophy
Uploaded by
carolina orlandoCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 1
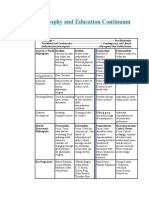
COMPARISONS
CATEGORY Traditional & Conservative Contemporary & Liberal
World Idealism: Realism: Pragmatism: Existentialism:
Philosophies Ideas are the only true reality, Reality exists independent of Universe is dynamic, Reality is subjective, within
the only thing worth human mind. World of evolving. Purpose of thought the individual. Individual
knowing. Focus: Mind physical objects ultimate is action. Truth is relative. rather than external
reality. Focus: Body Focus: Experience standards. Focus: Freedom
People Involved Socrates, Plato Aristotle Charles Sanders Pierce, William Søren Kierkegaard, Jean-Paul Sartre
James, John Dewey
Emphasis Subject matter of mind: Subject matter of social
Subject matter of physical Subject matter of personal
literature, history, experience. Creation of new
world: science, math choice
philosophy, religion social order
Educational Progressivism:
Perennialism: Reconstructionism:
Philosophies Focus: Ideas should be tested
Focus: Teach ideas that are Essentialism: Focus: Critical pedagogy:
by active experimentation.
everlasting, enduring unchanging Focus: Teach the common Analysis of world events,
Learning rooted in questions
constant truths through core, "the basics" of information controversial issues and
of learners in interaction
literature, art, philosophy, and skills diversity to provide vision
with others. Experience and
religion. for better world and social change.
student centred.
People involved Robert Hutchins, Mortimer Adler William Bagley, Herman John Locke, Jean-Jacques Rousseau, Theodore Brameld, George Counts
Home, Chester Finn John Dewey, William Kilpatrick
Associated Educational Psychological (Learning) Theories
Educational Behaviourism:
Information Processing: Cognitivism/Constructivism”
Psychological Behaviour is shaped by the Humanism:
Involves three stages of memory, the Learner actively constructs
Theories learning environment. Learning Personal freedom and choice of
sensory memory to receive information, own understandings of
occurs as result of subject matter. Achievement
the short-term memory to process the reality through interaction
reinforcing responses to motivation and responsibility towards
information and the long-term memory with environment and
stimuli. highest levels. Learner centred.
to store knowledge structures (schema) reflection on actions.
Social Learning: Learning by Interaction with others.
in a systematic manner. Student-centred learning.
observing and imitating others.
People involved Atkinson-Shiffrin Skinner, Thorndike, Bandura Piaget, Vygotsky, Ausubel J.J. Rousseau, A. Maslow
Teaching Teacher Centred: Teacher Centred:
Learner Centred: Learner Centred:
Approach Teach for core unchanging knowledge: Direction given for Knowledge &
Direct Experiences, Discovery & Individuality, Self-Actualization,
Conformity, Compliance with Authority, Discipline. Teach for mastery of
Exploration encouraged Direct Experiences. Individual as
Knowledge & Discipline facts and basic skills:
Problem solving: Project method entity within social context
Lecture, Discussion Demonstration, Recitation
You might also like
- Philosophy Matrices Assignment Final SubmissionDocument3 pagesPhilosophy Matrices Assignment Final SubmissionDraft Night Investing50% (2)
- Philosophy and Education Continuum ChartDocument2 pagesPhilosophy and Education Continuum ChartJeson Galgo75% (4)
- Helmut Zander, Anthroposophie in DeutschlandDocument14 pagesHelmut Zander, Anthroposophie in DeutschlandBibliorare100% (1)
- Module 2 - Ped 02 The Teaching Profession 2 (Revised - Final)Document16 pagesModule 2 - Ped 02 The Teaching Profession 2 (Revised - Final)Lawrence DiolaNo ratings yet
- Philosophical Roots of EducationDocument28 pagesPhilosophical Roots of EducationFatin Nadirah AqilahNo ratings yet
- PhilosophyDocument12 pagesPhilosophyAlhumdulillah Hi Rabil AlameenNo ratings yet
- Philosophy and Education Continuum Chart: Originator(s)Document2 pagesPhilosophy and Education Continuum Chart: Originator(s)Umme Ammara100% (1)
- Alvin Philosophy and Education Continuum Chart 1Document2 pagesAlvin Philosophy and Education Continuum Chart 1CHERRY LYNN Y. ROLOYANNo ratings yet
- Philosophy and Education Continuum Chart F3 6 BCE2 AJ JMCDocument1 pagePhilosophy and Education Continuum Chart F3 6 BCE2 AJ JMCPrakash Chandra PandeyNo ratings yet
- Philosophy of Education and Personal Philosophy: Beed 1A-Group 3 Zafra Villaronte Capuno Diamada MalachicoDocument20 pagesPhilosophy of Education and Personal Philosophy: Beed 1A-Group 3 Zafra Villaronte Capuno Diamada MalachicoMaria Laila Jane MalachicoNo ratings yet
- eLFD TASK 1.3Document23 pageseLFD TASK 1.3DC TpcNo ratings yet
- Notes Teach ProfDocument15 pagesNotes Teach ProfKristine Anne IgotNo ratings yet
- Ch-5 Overview PhilosophyDocument35 pagesCh-5 Overview Philosophyrommel legaspiNo ratings yet
- Philosophy Key Words Proponent Rule of TeachersDocument3 pagesPhilosophy Key Words Proponent Rule of TeacherskennethNo ratings yet
- Ch-5 Overview PhilosophyDocument35 pagesCh-5 Overview Philosophyseigfred john BallesterosNo ratings yet
- TABLE 2.1 Five Major Educational PhilosophiesDocument2 pagesTABLE 2.1 Five Major Educational PhilosophiesTeam TheaLleaNo ratings yet
- PHILOS and EDUCATIONAL IMPLICATIONSDocument5 pagesPHILOS and EDUCATIONAL IMPLICATIONSmarnylieNo ratings yet
- Psychological Foundation Sociological FoundationDocument3 pagesPsychological Foundation Sociological FoundationVallada, FebroseNo ratings yet
- Philosophy of EdDocument36 pagesPhilosophy of Edning setiaNo ratings yet
- Philosophy of Education Part 1Document29 pagesPhilosophy of Education Part 1Jamer PelotinNo ratings yet
- PHILO Ver. 2Document4 pagesPHILO Ver. 2MAFNo ratings yet
- Philosophies Philosophies MeaningDocument20 pagesPhilosophies Philosophies Meaninggems gamesNo ratings yet
- STS Prelims ReviewDocument12 pagesSTS Prelims ReviewAve RobbinsNo ratings yet
- Metaphysics and EducationDocument29 pagesMetaphysics and EducationMaria Shiela Cantonjos MaglenteNo ratings yet
- Health EducationDocument11 pagesHealth Educationkrishnamaecortega09No ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document2 pagesChapter 1Josh SumabonNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Lesson-2 Philosophy-Of-EducationDocument9 pagesChapter 3 Lesson-2 Philosophy-Of-EducationGray Yan HolmesNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 PDF Teaching AptitudeDocument188 pagesUnit 1 PDF Teaching Aptitudeneelam khattarNo ratings yet
- Research Methodology Unit 1Document18 pagesResearch Methodology Unit 1hanna.avery666No ratings yet
- Philosophy of EducationDocument4 pagesPhilosophy of EducationClaire YingNo ratings yet
- Teaching Profession - Educational PhilosophyDocument23 pagesTeaching Profession - Educational PhilosophyRon louise PereyraNo ratings yet
- Educ 3202 MD Reviewer FileDocument11 pagesEduc 3202 MD Reviewer FileVia Iana RagayNo ratings yet
- Foundation of Social Studies SSM1 M4Document15 pagesFoundation of Social Studies SSM1 M4HAZEL JANE ABAPONo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 The Nature and History of PsychologyDocument8 pagesLesson 1 The Nature and History of PsychologyAllison MaañoNo ratings yet
- Pursuing WisdomDocument18 pagesPursuing WisdomCEDRICK NICOLAS CUGAS VALERANo ratings yet
- PhilosophyDocument16 pagesPhilosophyMa.Jessica SiblagNo ratings yet
- EDUC 6 Midterm Exam Reviewer All CoveragesDocument8 pagesEDUC 6 Midterm Exam Reviewer All Coveragescharlot besasNo ratings yet
- Isnain, Erich C - BSED 1A 08/22/2020: Educational Philosophy Philosophical Roots Idealism Realism PragmatismDocument3 pagesIsnain, Erich C - BSED 1A 08/22/2020: Educational Philosophy Philosophical Roots Idealism Realism PragmatismErichIsnainNo ratings yet
- Philosophical Foundations of CurriculumDocument16 pagesPhilosophical Foundations of CurriculumUshna ShahNo ratings yet
- Government Elementary College of Education (Qasimabad) : Name: Sitara RiazDocument8 pagesGovernment Elementary College of Education (Qasimabad) : Name: Sitara RiazSitara RiazNo ratings yet
- Philedu2016 05 RationalismDocument13 pagesPhiledu2016 05 RationalismKathrina De CastroNo ratings yet
- PART 3 - Educational ThoughtDocument18 pagesPART 3 - Educational ThoughtReshNo ratings yet
- Philosophical Foundations of EducationDocument33 pagesPhilosophical Foundations of EducationAnilyn CelisNo ratings yet
- ODB - Soc Dim 1Document5 pagesODB - Soc Dim 1edenj rodrigoNo ratings yet
- Philosophy and Education - OverviewDocument18 pagesPhilosophy and Education - OverviewRhenan LoseoNo ratings yet
- Topic 2 - Philosophical Foundations of CurriculumDocument51 pagesTopic 2 - Philosophical Foundations of Curriculumaton hudaNo ratings yet
- Educational Philosophy: For The Intellectual Foundations of Indonesia EducationDocument27 pagesEducational Philosophy: For The Intellectual Foundations of Indonesia EducationMiraNurmayantiNo ratings yet
- JMN 451 - Teaching Philosphy Part 2Document12 pagesJMN 451 - Teaching Philosphy Part 2Ntuthu TshoksNo ratings yet
- Foundations of EducationDocument35 pagesFoundations of EducationElla CamelloNo ratings yet
- Module 1Document6 pagesModule 1johnemmanuel oreaNo ratings yet
- Theory of Learning From Time To Time: Christina Lhaksmita Anandari, Ed.MDocument13 pagesTheory of Learning From Time To Time: Christina Lhaksmita Anandari, Ed.Mfriska nadiaNo ratings yet
- Western Perspective PhilosophyDocument29 pagesWestern Perspective PhilosophyEmynordiana JamilNo ratings yet
- Summary of Philosophies - TableDocument3 pagesSummary of Philosophies - Tableabdusabur2535No ratings yet
- LESSON 1 - Introduction To The Philosophy of The Human PersonDocument49 pagesLESSON 1 - Introduction To The Philosophy of The Human PersonMauie Uy JonasNo ratings yet
- 1 Doing PhilosophyDocument32 pages1 Doing PhilosophyAilener ZednanrehNo ratings yet
- Focus: Nature of Ultimate Reality (Beyond The Physical) : MetaphysicsDocument10 pagesFocus: Nature of Ultimate Reality (Beyond The Physical) : MetaphysicsChristy Lou RollorataNo ratings yet
- The Possibility of A Transcendental Subject by Zosimo LeeDocument15 pagesThe Possibility of A Transcendental Subject by Zosimo LeeNicoelNo ratings yet
- Approaches To Human CognitionDocument19 pagesApproaches To Human Cognitionbobadilla.sarah19No ratings yet
- DISS Chapter-2.2Document5 pagesDISS Chapter-2.2minajayron9No ratings yet
- Eria Rhona L. - Assignment in Foundation of Education-2Document3 pagesEria Rhona L. - Assignment in Foundation of Education-2LIBERTY VALVERDENo ratings yet
- Ag Test Package FormatDocument25 pagesAg Test Package FormatoparoystNo ratings yet
- SafeGrid Tutorial How To Perform A Simple Earthing DesignDocument10 pagesSafeGrid Tutorial How To Perform A Simple Earthing DesignAnwesh Kumar MaddikuntaNo ratings yet
- English Project CompileDocument33 pagesEnglish Project CompileAbdul QayyumNo ratings yet
- D. Raghuram: Work ExperienceDocument3 pagesD. Raghuram: Work ExperienceNaveen KumarNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan in Science 1.3Document38 pagesLesson Plan in Science 1.3Heidi Dalyagan DulnagonNo ratings yet
- Pengaruh Motivasi, Kepemimpinan Dan Budaya Organisasi Terhadap Kepuasan Kerja Serta Dampaknya Pada Kinerja KaryawanDocument7 pagesPengaruh Motivasi, Kepemimpinan Dan Budaya Organisasi Terhadap Kepuasan Kerja Serta Dampaknya Pada Kinerja KaryawanAnggi PutraNo ratings yet
- Free - Space W - Band Setup For The Electrical Characterization of Materials and MM - Wave ComponentsDocument44 pagesFree - Space W - Band Setup For The Electrical Characterization of Materials and MM - Wave ComponentsthomasNo ratings yet
- Half-Cell Potential Test From The Upper-Side and The Lower-Side of Reinforced Concrete Slabs: A Comparative StudyDocument6 pagesHalf-Cell Potential Test From The Upper-Side and The Lower-Side of Reinforced Concrete Slabs: A Comparative StudyANNADURAINo ratings yet
- R Reference Manual Volume 1Document736 pagesR Reference Manual Volume 1PH1628No ratings yet
- 3 Generations of Human RightsDocument1 page3 Generations of Human RightsDzenan HakalovicNo ratings yet
- Reasons For Diminishing Returns To A FactorDocument2 pagesReasons For Diminishing Returns To A FactorRobert AyalaNo ratings yet
- E4nb71 PDFDocument99 pagesE4nb71 PDFtambache69100% (1)
- Asme Sa-29 1018Document1 pageAsme Sa-29 1018Nelson RangelNo ratings yet
- Artificial Intelligence On Digital Marketing - An OverviewDocument14 pagesArtificial Intelligence On Digital Marketing - An Overviewammar zNo ratings yet
- Ims555 Grouping Assignment (Ai Deepfakes)Document23 pagesIms555 Grouping Assignment (Ai Deepfakes)NUR A'ISYAH AZIZINo ratings yet
- UPS Technical Data Sheet (MS-DD-SAP01-ELE-DS-0015 - Rev2)Document6 pagesUPS Technical Data Sheet (MS-DD-SAP01-ELE-DS-0015 - Rev2)Muhammad YusufNo ratings yet
- On Arushi Murder CaseDocument8 pagesOn Arushi Murder Case0000No ratings yet
- Heater: Hydrate PreventionDocument12 pagesHeater: Hydrate PreventionMahmoud Ahmed Ali AbdelrazikNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan in English 8Document66 pagesLesson Plan in English 8Mhairo Akira100% (1)
- AHU Vibration Data - PostingDocument2 pagesAHU Vibration Data - PostingNeal JohnsonNo ratings yet
- Mayank Selection & Recruitment Process BluedartDocument5 pagesMayank Selection & Recruitment Process BluedartMayank SahuNo ratings yet
- SCIETECHNODocument19 pagesSCIETECHNOChini ChanNo ratings yet
- Performance: Task in Math 8 House Floor PlanDocument10 pagesPerformance: Task in Math 8 House Floor PlanJoshua Emmanuel LedesmaNo ratings yet
- Rollarc 400Document48 pagesRollarc 400m khNo ratings yet
- Nepal National Building Code: Draft Final NBC 205: 2012Document52 pagesNepal National Building Code: Draft Final NBC 205: 2012Sudan ShresthaNo ratings yet
- Optare Electric Vehicles: Embracing The EnvironmentDocument4 pagesOptare Electric Vehicles: Embracing The EnvironmentarrenNo ratings yet
- Allen Bradley 160 C SeriesDocument28 pagesAllen Bradley 160 C SeriesTihomir Matulić100% (1)
- Chapter 9: TidesDocument40 pagesChapter 9: TidesCarol GirottoNo ratings yet
- Models - Acdc.capacitor Fringing FieldsDocument16 pagesModels - Acdc.capacitor Fringing FieldsAnonymous pWNBPuMcf100% (1)