Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Safety and Rules in Biology Laboratory
Safety and Rules in Biology Laboratory
Uploaded by
Sierenttra BrittoCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- MT 304 - Gas Liquid Absorption: CL 333 Chemical Engineering Lab-III (2021)Document13 pagesMT 304 - Gas Liquid Absorption: CL 333 Chemical Engineering Lab-III (2021)Shivansh SinghNo ratings yet
- Structuring of Edible Oils by Alternatives To Crystalline Fat DatDocument11 pagesStructuring of Edible Oils by Alternatives To Crystalline Fat DatNedelcu AdelinaNo ratings yet
- Basic GreaseDocument20 pagesBasic Greasefahreez100% (3)
- Life Cycle Assessment PneuDocument44 pagesLife Cycle Assessment PneuatpontesNo ratings yet
- Bio f4 Eng-1Document63 pagesBio f4 Eng-1pic6004No ratings yet
- f4 Chapter 1Document8 pagesf4 Chapter 1Zy KianNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document8 pagesChapter 1Danish AhmadNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of BiologyDocument5 pagesFundamentals of BiologyChan PNo ratings yet
- Hazards in Your LabDocument2 pagesHazards in Your LabSamantha BolanteNo ratings yet
- Chemical Safety and Laboratory RulesDocument3 pagesChemical Safety and Laboratory RulesKate ManaloNo ratings yet
- Week 1 - Introduction To General Pathology and HistotechniquesDocument8 pagesWeek 1 - Introduction To General Pathology and HistotechniquesRubenne Miles ElagasNo ratings yet
- Lab Saftey MeasuresDocument8 pagesLab Saftey MeasuresRayehaNo ratings yet
- C. Work Safely in The Laboratory A. Risk Prevention in The LaboratoryDocument2 pagesC. Work Safely in The Laboratory A. Risk Prevention in The LaboratoryYoselin MamaniNo ratings yet
- Org Chem Lab Manual - ContentDocument42 pagesOrg Chem Lab Manual - ContentAugold UrbanoNo ratings yet
- Sign/Symbol: A. Microbiology Laboratory Equipment/ToolsDocument4 pagesSign/Symbol: A. Microbiology Laboratory Equipment/ToolsGwendolyn CalatravaNo ratings yet
- Safety in LaboratoryDocument11 pagesSafety in LaboratorybassamqabahaNo ratings yet
- Lab Safety Physiology LabDocument58 pagesLab Safety Physiology Labmaheen aurangzaibNo ratings yet
- CHEM 503 Lab Manual-2024Document85 pagesCHEM 503 Lab Manual-2024Hussain RazaNo ratings yet
- Bio F3 New Curr NotesDocument380 pagesBio F3 New Curr NotesreunkosiNo ratings yet
- Laboratory SafetyDocument15 pagesLaboratory SafetyHardik VyasNo ratings yet
- Micro para Lab - PrelimsDocument7 pagesMicro para Lab - PrelimsEingel Mer EvangelistaNo ratings yet
- Safety Rules in A Microbiology LaboratoryDocument5 pagesSafety Rules in A Microbiology LaboratoryTsedey bereketNo ratings yet
- Science Laboratory ManualDocument14 pagesScience Laboratory ManualSir Josh100% (3)
- Lab Safety SymbolsDocument1 pageLab Safety SymbolsKing Mat100% (1)
- PHAR303 Lab ManualDocument30 pagesPHAR303 Lab ManualNuhu SibaNo ratings yet
- Safety PrecautionsDocument3 pagesSafety PrecautionsAbegail Frias CalvoNo ratings yet
- Handling Laboratory Equipments Grade-8 ResearchDocument43 pagesHandling Laboratory Equipments Grade-8 ResearchMark JoshuaNo ratings yet
- Lab 1 Safety Rules ChemistryDocument23 pagesLab 1 Safety Rules Chemistrykarim samirNo ratings yet
- FIS3013 Safety RulesDocument3 pagesFIS3013 Safety RuleshudaNo ratings yet
- Lab Safety and Standard PrecautionDocument11 pagesLab Safety and Standard PrecautionAlex Kim Ren JyeNo ratings yet
- Policy On Laboratory Biosafety and Biosecurity For Print Amd ApprovalDocument7 pagesPolicy On Laboratory Biosafety and Biosecurity For Print Amd ApprovalgravadorceciliaNo ratings yet
- 1.2 Safety & Rules in Biology LaboratoryDocument32 pages1.2 Safety & Rules in Biology LaboratoryasyuraNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry LAB MANUALDocument26 pagesBiochemistry LAB MANUALGulab khanNo ratings yet
- TB Biology f4 Chapter 1Document71 pagesTB Biology f4 Chapter 1ASYURA BINTI DILLAH MoeNo ratings yet
- lab-1-Lab-safety-Document3 pageslab-1-Lab-safety-AmalNo ratings yet
- A211 Chem203 SafetyDocument7 pagesA211 Chem203 SafetyramezbazziNo ratings yet
- ITU Chemistry Lab Safety RulesDocument26 pagesITU Chemistry Lab Safety RulesGarip DenizNo ratings yet
- Experiment No. 1 Laboratory Safety and Preventive Measures: I. ObjectivesDocument33 pagesExperiment No. 1 Laboratory Safety and Preventive Measures: I. ObjectivesShanedy SumagangNo ratings yet
- Manual Basic ConceptsDocument68 pagesManual Basic ConceptsDhaya VNo ratings yet
- Biosafety in Toxicology LaboratoryDocument29 pagesBiosafety in Toxicology LaboratoryScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- Activity NoDocument9 pagesActivity NoVincent DayangcoNo ratings yet
- Activity No. 1 - Laboratory Safety and Preventive MeasuresDocument3 pagesActivity No. 1 - Laboratory Safety and Preventive MeasuresVincent DayangcoNo ratings yet
- Lab Safety Symbols 1Document1 pageLab Safety Symbols 1api-367424443No ratings yet
- 68-1911 Foamguard AFFF SDSDocument6 pages68-1911 Foamguard AFFF SDSdwinanda fortuna warmanNo ratings yet
- PMLS 2 LaboratoryDocument11 pagesPMLS 2 LaboratoryJanna EchavezNo ratings yet
- Safety Rules EXP 0Document28 pagesSafety Rules EXP 0Ahmad Abu NiajNo ratings yet
- FBD LAB SAFETY TRAININGDocument12 pagesFBD LAB SAFETY TRAININGPankaj KrisnatarNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Safety Guidelines: Department of Biology College of Science University of The Philippines BaguioDocument25 pagesLaboratory Safety Guidelines: Department of Biology College of Science University of The Philippines BaguioGeorgette Nicole San AgustinNo ratings yet
- Pure Biology NotesDocument205 pagesPure Biology NotesAdora MaitaNo ratings yet
- EXPERIMENT NO.1B Polo, David Jonathan S.Document2 pagesEXPERIMENT NO.1B Polo, David Jonathan S.Jonathan PoloNo ratings yet
- Pengurusan Makmal Sains 7Document12 pagesPengurusan Makmal Sains 7namlyNo ratings yet
- LSS Lab Safety Lab ManualDocument6 pagesLSS Lab Safety Lab ManualJazNo ratings yet
- 1-Medical Bio 1 (Lab Safety - 23-24)Document21 pages1-Medical Bio 1 (Lab Safety - 23-24)mh7146572No ratings yet
- Oberon F737 SDS 1673320560880157Document6 pagesOberon F737 SDS 1673320560880157Cosmic TitusNo ratings yet
- Microbiology Lab Manual:: Discovering Your Tiny NeighborsDocument222 pagesMicrobiology Lab Manual:: Discovering Your Tiny NeighborsRaj PatelNo ratings yet
- Biosafety in Toxicology LaboratoryDocument29 pagesBiosafety in Toxicology LaboratoryScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Safety: General Safety Precaution and ProceduresDocument3 pagesLaboratory Safety: General Safety Precaution and ProceduresREIGNE KRISTY CA�ADANo ratings yet
- Bio 302L - Activity 1Document5 pagesBio 302L - Activity 1larraNo ratings yet
- Safety Briefing NotesDocument11 pagesSafety Briefing NotesasdfNo ratings yet
- Solvent SDS Version 8 2021Document7 pagesSolvent SDS Version 8 2021johanbesarNo ratings yet
- BSMT-MED224 BiosafetyDocument8 pagesBSMT-MED224 BiosafetyKatleen DugenioNo ratings yet
- Histo Histopath Safety ManualDocument14 pagesHisto Histopath Safety ManualJanielle Medina FajardoNo ratings yet
- Good Microbiological Lab PracticesDocument2 pagesGood Microbiological Lab PracticesaicssssNo ratings yet
- Teroson Ms 935-EnDocument2 pagesTeroson Ms 935-EnakosirhockzNo ratings yet
- Corrosion GuideDocument32 pagesCorrosion Guidedarsh2001patelNo ratings yet
- Cross-Linking Polymers - Alginate Worms: CO Na CO NaDocument3 pagesCross-Linking Polymers - Alginate Worms: CO Na CO NanarutotriyanNo ratings yet
- Self Cleaning DocumentINTRODUCTION-WPS OfficeDocument10 pagesSelf Cleaning DocumentINTRODUCTION-WPS OfficeSuryanshdeepak AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Soil Chemistry PDFDocument25 pagesSoil Chemistry PDFChynna Kaye GregorioNo ratings yet
- Table UCS-56-11 Postweld Heat Treatment Requirements For Carbon and Low Alloy Steels - P-No. 15EDocument1 pageTable UCS-56-11 Postweld Heat Treatment Requirements For Carbon and Low Alloy Steels - P-No. 15ECITRIXNo ratings yet
- Btech Project ReportDocument23 pagesBtech Project ReportS RNo ratings yet
- Simulation of A Natural Gas Processing Plant With An Amine-Based System For The Removal of h2SDocument11 pagesSimulation of A Natural Gas Processing Plant With An Amine-Based System For The Removal of h2SAntonio EngenhariasNo ratings yet
- CL CARB 9 enDocument2 pagesCL CARB 9 enmikael8118No ratings yet
- B.I Welded Pipe Fittings-Clayton BrandDocument12 pagesB.I Welded Pipe Fittings-Clayton BrandAndrei SabaterNo ratings yet
- What Is NanocelluloseDocument5 pagesWhat Is NanocelluloseAbhishek GadhwalNo ratings yet
- XRD 63 Quantitative XRD Phase Analysis in Minerals Mining - Bauxite LowDocument4 pagesXRD 63 Quantitative XRD Phase Analysis in Minerals Mining - Bauxite LowJosue David Mago ArredondoNo ratings yet
- Is.8188.1999 0 PDFDocument25 pagesIs.8188.1999 0 PDFArunkumar ChandaranNo ratings yet
- Capsules Part-1 MaterialDocument21 pagesCapsules Part-1 Materialsimbi beliseNo ratings yet
- Definitions of Standard Enthalpy ChangesDocument9 pagesDefinitions of Standard Enthalpy ChangesWang RuyiNo ratings yet
- Astm D2386Document5 pagesAstm D2386sawitri diah ayu komalaNo ratings yet
- MC MX 6-2960 Corrosion InhibitorDocument1 pageMC MX 6-2960 Corrosion InhibitorRicardo ValeraNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Imp QuestionsDocument4 pagesChemistry Imp QuestionsRasi MathiNo ratings yet
- Journal of Alloys and Compounds - 2021Document12 pagesJournal of Alloys and Compounds - 2021Eugene YiNo ratings yet
- Kolliphor RH 40Document6 pagesKolliphor RH 40farmacia scerboNo ratings yet
- Experiment 3 - Carboxylic Acid and DerivativesDocument3 pagesExperiment 3 - Carboxylic Acid and DerivativesFaris SyahmiNo ratings yet
- Understanding Solubility: Preparing Spreadsheets & Graphs With ExcelDocument6 pagesUnderstanding Solubility: Preparing Spreadsheets & Graphs With ExcelnandagamersNo ratings yet
- PFI Filtration String Wound Filter Cartridges Data SheetDocument1 pagePFI Filtration String Wound Filter Cartridges Data Sheetbennypartono407No ratings yet
- Corrosion Control LectruresDocument143 pagesCorrosion Control Lectruresyamen sayedNo ratings yet
- Exp.1-Distillation, Simple and FractionalDocument18 pagesExp.1-Distillation, Simple and FractionalzazoNo ratings yet
- Pharmaceutical Calculation: Pharmaceutical Dosage Forms & MeasurementDocument32 pagesPharmaceutical Calculation: Pharmaceutical Dosage Forms & MeasurementMarwanNo ratings yet
Safety and Rules in Biology Laboratory
Safety and Rules in Biology Laboratory
Uploaded by
Sierenttra BrittoCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Safety and Rules in Biology Laboratory
Safety and Rules in Biology Laboratory
Uploaded by
Sierenttra BrittoCopyright:
Available Formats
Safety and Rules in Biological Laboratory
1.2 Safety and Rules in Biological Laboratory
Self-protection equipment:
Self-protection equipment Descriptions and functions
Made from latex/rubber/plastics.
Gloves Protects the hands from heat and dangerous chemical substances; strong acid and strong alkali.
Lab coat: aids to protect the skin and clothes from chemicals spillage.
Lab coat and lab shoes Lab shoes: protects the legs from chemical spillage and broken glass.
Protects the face and eyes from chemicals splash and protects from inhaling chemicals that can interrupt the respiratory system.
Goggle and face mask
Washing both hands before leaving the lab is a must.
Handwash
Contains salt solution used to wash the eyes if chemical substances/foreign particles get into the eyes.
Eye washer
Station for work that involved with fumes or toxic gas; chlorine, bromine and nitrogen dioxide.
Fume hood
Station used to wash the hand and body when someone exposed to dangerous chemicals.
Emergency shower station
Station for work involved with plant tissue culture, medium preparation that provides a sterile environment to the workplace.
Laminar flow cabinet
Station for work involved with bacteria, fungi and virus cultures helps to prevent the cultures from contaminating the environment.
Biosafety cabinet
Substances that cannot thrown in the sink:
1. Chemical substances, glass, metals, plastics, woods or any solid substances.
2. Grease, oil and oil paint.
3. Toxic substances; benzene, chloroform, hydrogen cyanide, argentum.
4. Heavy metals; mercury, lead, cadmium.
5. Radioactive wastes.
6. Reactive substances that are unstable; sodium metal, ether, hydrogen peroxide.
Substances that can be thrown in the sink:
1. Any liquid/solution that has low concentration, not dangerous and biodegradable.
Methods of handling biological wastes:
Waste category Example Methods of handling
Sharp waste Syringe with needle, needle, glass and scalple Throw it in the sharp-bin waste
Non-sharp waste Gloves, tissue paper, Petri dish, agar, culture waste Throw it in the biohazard bag, sterilize it and throw it in the biohazard bin
Animal carcass Organs, animal tissue waste, carcass Wrap it with tissue paper, put it in the biohazard bag and freeze it
Liquid Broth culture, liquid media, blood and blood product Decontaminate the waste through autoclave before throw it in the biohazard bin
Accidents in the laboratory:
Steps to handle general chemical spills
1. Inform your teacher
2. Declare the spill area as a restricted zone.
3. Prevent the chemical spill from spreading using sand.
4. Scoop up the chemical spill from using appropriate equipment.
p p p g pp p q p
5. Dispose it safely.
Steps to handle mercury spills
1. Inform your teacher
2. Declare the spill area as a restricted zone.
3. Sprinkle sulphur to cover the mercury spills
4. Call the fire and rescue department.
Practices in a biological laboratory:
Practices Explainations
Use a lab coat,gloves,safety shoes and goggles when appropriate.
Clothing ethics
Do not work alone in the laboratory without supervision.
Wash your hand after conducting an experiment.
Do not bring in irrelevant items into the laboratory.
Clean your workstation using disinfectant.
Laboratory safety rules
Dispose wastes according to the set procedures.
Do not eat and drink in the laboratory.
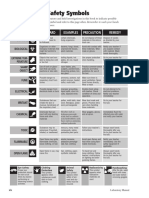
Identify all safety symbols on substances and equipment before use.
Stop work immediately and switch off all nearby power sources.
Unplug appliances
Exit the laboratory according to the emergency exit plan.
Call the fire and rescue department.
Safety measures for fires
Do not panic and stay calm.
Do not turn back to collect your belongings.
Assemble at the assembly point.
Be cautions when handling hot glassware.
Report any damaged equipment or glassware to teachers immediately.
Handling glass and chemicals Keep flammable chemicals away from fire sources.
Do not touch,taste and smell chemicals directly.
Use appropriate gloves when handling biological specimens.
Speciements that are not harmful and have been dissected should be buried or frozen.
Handling live specimens Wash hands with antiseptic detergents before and after experiment.
All surafaces and workstations should be cleaned with disinfectant before leaving the lab.
Inform your teacher
Call the fire and rescue emergency number.
Remove the victim from the scene.
Emergency help
Give emergency treatment.
Make the place of accident as a restricted area.
© 2023 Pandai.org All Rights Reserved Made with in Malaysia
You might also like
- MT 304 - Gas Liquid Absorption: CL 333 Chemical Engineering Lab-III (2021)Document13 pagesMT 304 - Gas Liquid Absorption: CL 333 Chemical Engineering Lab-III (2021)Shivansh SinghNo ratings yet
- Structuring of Edible Oils by Alternatives To Crystalline Fat DatDocument11 pagesStructuring of Edible Oils by Alternatives To Crystalline Fat DatNedelcu AdelinaNo ratings yet
- Basic GreaseDocument20 pagesBasic Greasefahreez100% (3)
- Life Cycle Assessment PneuDocument44 pagesLife Cycle Assessment PneuatpontesNo ratings yet
- Bio f4 Eng-1Document63 pagesBio f4 Eng-1pic6004No ratings yet
- f4 Chapter 1Document8 pagesf4 Chapter 1Zy KianNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document8 pagesChapter 1Danish AhmadNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of BiologyDocument5 pagesFundamentals of BiologyChan PNo ratings yet
- Hazards in Your LabDocument2 pagesHazards in Your LabSamantha BolanteNo ratings yet
- Chemical Safety and Laboratory RulesDocument3 pagesChemical Safety and Laboratory RulesKate ManaloNo ratings yet
- Week 1 - Introduction To General Pathology and HistotechniquesDocument8 pagesWeek 1 - Introduction To General Pathology and HistotechniquesRubenne Miles ElagasNo ratings yet
- Lab Saftey MeasuresDocument8 pagesLab Saftey MeasuresRayehaNo ratings yet
- C. Work Safely in The Laboratory A. Risk Prevention in The LaboratoryDocument2 pagesC. Work Safely in The Laboratory A. Risk Prevention in The LaboratoryYoselin MamaniNo ratings yet
- Org Chem Lab Manual - ContentDocument42 pagesOrg Chem Lab Manual - ContentAugold UrbanoNo ratings yet
- Sign/Symbol: A. Microbiology Laboratory Equipment/ToolsDocument4 pagesSign/Symbol: A. Microbiology Laboratory Equipment/ToolsGwendolyn CalatravaNo ratings yet
- Safety in LaboratoryDocument11 pagesSafety in LaboratorybassamqabahaNo ratings yet
- Lab Safety Physiology LabDocument58 pagesLab Safety Physiology Labmaheen aurangzaibNo ratings yet
- CHEM 503 Lab Manual-2024Document85 pagesCHEM 503 Lab Manual-2024Hussain RazaNo ratings yet
- Bio F3 New Curr NotesDocument380 pagesBio F3 New Curr NotesreunkosiNo ratings yet
- Laboratory SafetyDocument15 pagesLaboratory SafetyHardik VyasNo ratings yet
- Micro para Lab - PrelimsDocument7 pagesMicro para Lab - PrelimsEingel Mer EvangelistaNo ratings yet
- Safety Rules in A Microbiology LaboratoryDocument5 pagesSafety Rules in A Microbiology LaboratoryTsedey bereketNo ratings yet
- Science Laboratory ManualDocument14 pagesScience Laboratory ManualSir Josh100% (3)
- Lab Safety SymbolsDocument1 pageLab Safety SymbolsKing Mat100% (1)
- PHAR303 Lab ManualDocument30 pagesPHAR303 Lab ManualNuhu SibaNo ratings yet
- Safety PrecautionsDocument3 pagesSafety PrecautionsAbegail Frias CalvoNo ratings yet
- Handling Laboratory Equipments Grade-8 ResearchDocument43 pagesHandling Laboratory Equipments Grade-8 ResearchMark JoshuaNo ratings yet
- Lab 1 Safety Rules ChemistryDocument23 pagesLab 1 Safety Rules Chemistrykarim samirNo ratings yet
- FIS3013 Safety RulesDocument3 pagesFIS3013 Safety RuleshudaNo ratings yet
- Lab Safety and Standard PrecautionDocument11 pagesLab Safety and Standard PrecautionAlex Kim Ren JyeNo ratings yet
- Policy On Laboratory Biosafety and Biosecurity For Print Amd ApprovalDocument7 pagesPolicy On Laboratory Biosafety and Biosecurity For Print Amd ApprovalgravadorceciliaNo ratings yet
- 1.2 Safety & Rules in Biology LaboratoryDocument32 pages1.2 Safety & Rules in Biology LaboratoryasyuraNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry LAB MANUALDocument26 pagesBiochemistry LAB MANUALGulab khanNo ratings yet
- TB Biology f4 Chapter 1Document71 pagesTB Biology f4 Chapter 1ASYURA BINTI DILLAH MoeNo ratings yet
- lab-1-Lab-safety-Document3 pageslab-1-Lab-safety-AmalNo ratings yet
- A211 Chem203 SafetyDocument7 pagesA211 Chem203 SafetyramezbazziNo ratings yet
- ITU Chemistry Lab Safety RulesDocument26 pagesITU Chemistry Lab Safety RulesGarip DenizNo ratings yet
- Experiment No. 1 Laboratory Safety and Preventive Measures: I. ObjectivesDocument33 pagesExperiment No. 1 Laboratory Safety and Preventive Measures: I. ObjectivesShanedy SumagangNo ratings yet
- Manual Basic ConceptsDocument68 pagesManual Basic ConceptsDhaya VNo ratings yet
- Biosafety in Toxicology LaboratoryDocument29 pagesBiosafety in Toxicology LaboratoryScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- Activity NoDocument9 pagesActivity NoVincent DayangcoNo ratings yet
- Activity No. 1 - Laboratory Safety and Preventive MeasuresDocument3 pagesActivity No. 1 - Laboratory Safety and Preventive MeasuresVincent DayangcoNo ratings yet
- Lab Safety Symbols 1Document1 pageLab Safety Symbols 1api-367424443No ratings yet
- 68-1911 Foamguard AFFF SDSDocument6 pages68-1911 Foamguard AFFF SDSdwinanda fortuna warmanNo ratings yet
- PMLS 2 LaboratoryDocument11 pagesPMLS 2 LaboratoryJanna EchavezNo ratings yet
- Safety Rules EXP 0Document28 pagesSafety Rules EXP 0Ahmad Abu NiajNo ratings yet
- FBD LAB SAFETY TRAININGDocument12 pagesFBD LAB SAFETY TRAININGPankaj KrisnatarNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Safety Guidelines: Department of Biology College of Science University of The Philippines BaguioDocument25 pagesLaboratory Safety Guidelines: Department of Biology College of Science University of The Philippines BaguioGeorgette Nicole San AgustinNo ratings yet
- Pure Biology NotesDocument205 pagesPure Biology NotesAdora MaitaNo ratings yet
- EXPERIMENT NO.1B Polo, David Jonathan S.Document2 pagesEXPERIMENT NO.1B Polo, David Jonathan S.Jonathan PoloNo ratings yet
- Pengurusan Makmal Sains 7Document12 pagesPengurusan Makmal Sains 7namlyNo ratings yet
- LSS Lab Safety Lab ManualDocument6 pagesLSS Lab Safety Lab ManualJazNo ratings yet
- 1-Medical Bio 1 (Lab Safety - 23-24)Document21 pages1-Medical Bio 1 (Lab Safety - 23-24)mh7146572No ratings yet
- Oberon F737 SDS 1673320560880157Document6 pagesOberon F737 SDS 1673320560880157Cosmic TitusNo ratings yet
- Microbiology Lab Manual:: Discovering Your Tiny NeighborsDocument222 pagesMicrobiology Lab Manual:: Discovering Your Tiny NeighborsRaj PatelNo ratings yet
- Biosafety in Toxicology LaboratoryDocument29 pagesBiosafety in Toxicology LaboratoryScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Safety: General Safety Precaution and ProceduresDocument3 pagesLaboratory Safety: General Safety Precaution and ProceduresREIGNE KRISTY CA�ADANo ratings yet
- Bio 302L - Activity 1Document5 pagesBio 302L - Activity 1larraNo ratings yet
- Safety Briefing NotesDocument11 pagesSafety Briefing NotesasdfNo ratings yet
- Solvent SDS Version 8 2021Document7 pagesSolvent SDS Version 8 2021johanbesarNo ratings yet
- BSMT-MED224 BiosafetyDocument8 pagesBSMT-MED224 BiosafetyKatleen DugenioNo ratings yet
- Histo Histopath Safety ManualDocument14 pagesHisto Histopath Safety ManualJanielle Medina FajardoNo ratings yet
- Good Microbiological Lab PracticesDocument2 pagesGood Microbiological Lab PracticesaicssssNo ratings yet
- Teroson Ms 935-EnDocument2 pagesTeroson Ms 935-EnakosirhockzNo ratings yet
- Corrosion GuideDocument32 pagesCorrosion Guidedarsh2001patelNo ratings yet
- Cross-Linking Polymers - Alginate Worms: CO Na CO NaDocument3 pagesCross-Linking Polymers - Alginate Worms: CO Na CO NanarutotriyanNo ratings yet
- Self Cleaning DocumentINTRODUCTION-WPS OfficeDocument10 pagesSelf Cleaning DocumentINTRODUCTION-WPS OfficeSuryanshdeepak AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Soil Chemistry PDFDocument25 pagesSoil Chemistry PDFChynna Kaye GregorioNo ratings yet
- Table UCS-56-11 Postweld Heat Treatment Requirements For Carbon and Low Alloy Steels - P-No. 15EDocument1 pageTable UCS-56-11 Postweld Heat Treatment Requirements For Carbon and Low Alloy Steels - P-No. 15ECITRIXNo ratings yet
- Btech Project ReportDocument23 pagesBtech Project ReportS RNo ratings yet
- Simulation of A Natural Gas Processing Plant With An Amine-Based System For The Removal of h2SDocument11 pagesSimulation of A Natural Gas Processing Plant With An Amine-Based System For The Removal of h2SAntonio EngenhariasNo ratings yet
- CL CARB 9 enDocument2 pagesCL CARB 9 enmikael8118No ratings yet
- B.I Welded Pipe Fittings-Clayton BrandDocument12 pagesB.I Welded Pipe Fittings-Clayton BrandAndrei SabaterNo ratings yet
- What Is NanocelluloseDocument5 pagesWhat Is NanocelluloseAbhishek GadhwalNo ratings yet
- XRD 63 Quantitative XRD Phase Analysis in Minerals Mining - Bauxite LowDocument4 pagesXRD 63 Quantitative XRD Phase Analysis in Minerals Mining - Bauxite LowJosue David Mago ArredondoNo ratings yet
- Is.8188.1999 0 PDFDocument25 pagesIs.8188.1999 0 PDFArunkumar ChandaranNo ratings yet
- Capsules Part-1 MaterialDocument21 pagesCapsules Part-1 Materialsimbi beliseNo ratings yet
- Definitions of Standard Enthalpy ChangesDocument9 pagesDefinitions of Standard Enthalpy ChangesWang RuyiNo ratings yet
- Astm D2386Document5 pagesAstm D2386sawitri diah ayu komalaNo ratings yet
- MC MX 6-2960 Corrosion InhibitorDocument1 pageMC MX 6-2960 Corrosion InhibitorRicardo ValeraNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Imp QuestionsDocument4 pagesChemistry Imp QuestionsRasi MathiNo ratings yet
- Journal of Alloys and Compounds - 2021Document12 pagesJournal of Alloys and Compounds - 2021Eugene YiNo ratings yet
- Kolliphor RH 40Document6 pagesKolliphor RH 40farmacia scerboNo ratings yet
- Experiment 3 - Carboxylic Acid and DerivativesDocument3 pagesExperiment 3 - Carboxylic Acid and DerivativesFaris SyahmiNo ratings yet
- Understanding Solubility: Preparing Spreadsheets & Graphs With ExcelDocument6 pagesUnderstanding Solubility: Preparing Spreadsheets & Graphs With ExcelnandagamersNo ratings yet
- PFI Filtration String Wound Filter Cartridges Data SheetDocument1 pagePFI Filtration String Wound Filter Cartridges Data Sheetbennypartono407No ratings yet
- Corrosion Control LectruresDocument143 pagesCorrosion Control Lectruresyamen sayedNo ratings yet
- Exp.1-Distillation, Simple and FractionalDocument18 pagesExp.1-Distillation, Simple and FractionalzazoNo ratings yet
- Pharmaceutical Calculation: Pharmaceutical Dosage Forms & MeasurementDocument32 pagesPharmaceutical Calculation: Pharmaceutical Dosage Forms & MeasurementMarwanNo ratings yet