Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Side Effects of Amoxicillin
Side Effects of Amoxicillin
Uploaded by
Aphro DhiteOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Side Effects of Amoxicillin
Side Effects of Amoxicillin
Uploaded by
Aphro DhiteCopyright:
Available Formats
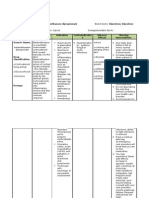
Drug name
Generic:AMOXICILLIN Brand:Apo-Amoxi
Action: antiinfective; antibiotic; aminopenicillin System:
Mechanism of action Side effects Adverse effects
Amoxicillin is bactericidal to susceptible microorganisms. It inhibits cell wall synthesis.
Side Effects of Amoxicillin
GI disturbances (mild diarrhea, nausea, or vomiting) Headache Oral and Vaginal Candidiasis Generalized Rash Urticaria
Adverse Reactions of Amoxicillin
Superinfections Severe hypersensitivity reactions (anaphylaxis, acute interstitial nephritis) Potentially fatal antibiotic colitis ( abdominal cramps, watery svere diarrhea, fever) Nursing Implication Determine previous hypersensitivity reactions to penicillins, cephalosporins, and other allergens prior to therapy. Lab tests: Baseline C&S tests prior to initiation of therapy, start drug pending results; periodic assessments of renal, hepatic, and hematologic functions should be made during prolonged therapy. Monitor for S&S of an urticarial rash (usually occurring within a few days after start of drug) suggestive of a hypersensitivity reaction. If it occurs, look for other signs of hypersensitivity (fever, wheezing, generalized itching, dyspnea), and report to physician immediately. Report onset of generalized, erythematous, maculopapular rash (ampicillin rash) to physician. Ampicillin rash is not due to hypersensitivity; however, hypersensitivity should be ruled out. Closely monitor diarrhea to rule out pseudomembranous colitis. Patient & Family Education Take drug around the clock, do not miss a dose, and continue therapy until all medication is taken, unless otherwise directed by physician. Report onset of diarrhea and other possible symptoms of superinfection to physician (see Appendix F). Do not breast feed while taking this drug without consulting physician
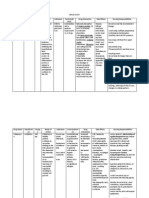
Drug name
Generic:Clindamycin Brand: Klindex
Action: antiinfective; antibiotic System:
Mechanism of action
Bacteriostatic. Clindamycin binds to bacterial ribosomal receptor sites. Topically, it decreases fatty acid concentration on skin. It inhibits protein synthesis of bacterial cell wall and prevents outbreak of acne vulgaris.
Side Effects of Clindamycin Abdominal pain Nausea and Vomiting Diarrhea Vaginitis and itching Dry scaly skin Phlebitis, thrombophlebitis with IV administration Pain, induration, at the IM injection site Allergic reaction, urticaria, pruritus Headache and dizziness Contact dermatitis Hypersensitivity reaction
Side effects Adverse effects
Adverse Reactions or Toxic Effects of Clindamycin Antibiotic-associated colitis (Severe abdominal pain, tenderness, fever, watery and severe diarrhea) Blood dyscrasias (Leukopenia and thrombocytopenia) Nephrotoxicity (Proteinuria, azotemia, oliguria)
Nursing Implication
Store capsules at room temperature After reconstitution, oral solution is stable for 2 weeks at room temperature. Do not refrigerate oral solution to avoid thickening. Give with 8 oz water. Question patient for history of allergies, particularly to clindamycin, lincomycin, and aspirin. Avoid concurrent use of neuromuscular blocking agents. Monitor bowel activity, stool consistency; report diarrhea promptly due to potential for serious colitis. Assess skin for rash with topical application. Assess for superinfection: severe diaarhea, genital/anal pruritus, increase fever, and change of oral mucosa.
Continue therapy for full length of treatment. Doses should be evenly spaced. Oral doses should be taken with 8 oz water. Caution should be used when applying topical clindamycin concurrently with peeling/abrasive acne agents, soaps, alcohol-containing cosmetics to avoid cumulative effect Do not apply topical preparations near eyes, abraded areas. If accidental contact with eyes, rinse with cool tap water. Do not engage in sexual intercourse during treatment.
Drug name Mechanism of action
Generic:Ferrous sulfate Brand: Feosol
Action: supplemental vitamins System:
Ferrous Sulfate is an essential component in the formation of hemoglobin, myoglobin and enzymes. It is necessary for effective erythropoiesis and transport or utilization of oxygen.
Side Effects of Ferrous Sulfate Mild, transient nausea Heartburn Anorexia Constipation Diarrhea Adverse Reactions of Ferrous Sulfate Large doses may aggravate peptic ulcer, regional enteritis, and ulcerative colitis. Severe Iron Poisoning: Vomiting Severe abdominal pain Diarrhea Dehydration Hyperventilation Pallor or cyanosis Cardiovascular collapse
Side effects Adverse effects
Nursing Implication
Store all forms at room temperature. Give between meals with water but may give with meals if gastrointestinal discomfort occurs. Transient staining of mucous membranes and teeth will occur with liquid iron preparation. To avoid, place liquid on the back of the tongue with dropper or use straw. Avoid simultaneous administration of antacids or tetracycline. Do not crush sustained-release preparations. Eggs and milk inhibit absorption. Monitor serum iron, total iron-binding capacity, reticulocyte count, hemoglobin, and ferritin. Monitor daily pattern of bowel activity and stool consistency. Assess for clinical improvement, record of relief of symptoms (fatigue, irritability, pallor, paresthesia, and headache). Expect stools to darken in color. If gastrointestinal discomfort occurs, take after meals or with food.
Drug name Mechanism of action Side effects Adverse effects Nursing Implication
Generic: Brand:
Action: System:
Drug name Mechanism of action Side effects Adverse effects Nursing Implication
Generic: Brand:
Action: System:
You might also like
- Pharma CardsDocument5 pagesPharma CardsazancheNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument21 pagesDrug StudyRemedios Bandong100% (1)
- Nursing Pharmacology Handouts For ZamboDocument7 pagesNursing Pharmacology Handouts For ZamboAlexa Abidin Oldenborg100% (8)
- Naplex Complete Study Outline A Topic-Wise Approach DiabetesFrom EverandNaplex Complete Study Outline A Topic-Wise Approach DiabetesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (3)
- Drug StudyDocument6 pagesDrug StudyFloramae Celine BosqueNo ratings yet
- Clindamycin (: Drug ClassDocument8 pagesClindamycin (: Drug ClassWilliam CiferNo ratings yet
- Drugs Study, Nursing, PreoperativeDocument9 pagesDrugs Study, Nursing, PreoperativeKevin Sam AguirreNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument5 pagesDrug StudyDick Morgan FerrerNo ratings yet
- AmoxicillinDocument5 pagesAmoxicillinKyle DelrosarioNo ratings yet
- Drusadg Study For Paracetamol Omeprazole and Vitamin B ComplexDocument3 pagesDrusadg Study For Paracetamol Omeprazole and Vitamin B ComplexzerpthederpNo ratings yet
- Snakebite Drug StudyDocument7 pagesSnakebite Drug StudyDevon RevillaNo ratings yet
- DrugsDocument11 pagesDrugsElisa Libo-onNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument4 pagesDrug StudyAbigail LonoganNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument7 pagesDrug StudyNatnath FernandoNo ratings yet
- Name of Drug Indications Action Contraindication Side Effects Adverse Side Effects Nursing ManagementDocument3 pagesName of Drug Indications Action Contraindication Side Effects Adverse Side Effects Nursing Managementjhappo31No ratings yet
- Drug Study (FINAL)Document31 pagesDrug Study (FINAL)iamjenivicNo ratings yet
- Hernia Medical ManagementDocument5 pagesHernia Medical ManagementCherilyn MedalleNo ratings yet
- Drug Study - LeptospirosisDocument19 pagesDrug Study - LeptospirosisCamille PinedaNo ratings yet
- AmoxicillinDocument2 pagesAmoxicillindheng05No ratings yet
- DRug StudyDocument6 pagesDRug StudyRochell Torres ArtatesNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument14 pagesDrug StudyRoderick BajamundiNo ratings yet
- CHN Drug StudyDocument10 pagesCHN Drug StudyJoshua Cyryll ComiaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study OssamDocument3 pagesDrug Study OssamCharmaine IdologNo ratings yet
- Drug Study NRMFDocument11 pagesDrug Study NRMFKristine ReyesNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument5 pagesDrug StudyKristine-Joy Legaspi FrancoNo ratings yet
- Ciprofloxacin CiproDocument1 pageCiprofloxacin CiproKristi WrayNo ratings yet
- Ward6 Drug StudyDocument6 pagesWard6 Drug StudyMichael Lloyd T. SabijonNo ratings yet
- Nicu Drug StudyDocument8 pagesNicu Drug StudyMike SoySauce LibrojoNo ratings yet
- Pott's Drug Study. AdelDocument6 pagesPott's Drug Study. AdelAdelle SmithNo ratings yet
- Drug Study GranjaDocument5 pagesDrug Study GranjajolibeecaldonaNo ratings yet
- DrugsDocument11 pagesDrugsClarence Lyndyll ToldingNo ratings yet
- CeftriaxoneDocument2 pagesCeftriaxoneArianne Rose100% (2)
- Drug StudyDocument23 pagesDrug StudyEdward Baes33% (3)
- Drug Study (AFP)Document10 pagesDrug Study (AFP)Summer SuarezNo ratings yet
- Medications For Primary ComplexDocument8 pagesMedications For Primary ComplexMary CruzNo ratings yet
- Toxic Effects, Drug CalculationDocument185 pagesToxic Effects, Drug CalculationAntonette Africa MercadoNo ratings yet
- Mefenamic Acid: CefuroximeDocument9 pagesMefenamic Acid: CefuroximeGregory LitangNo ratings yet
- Drug Cefaclor IsoxsuprineDocument6 pagesDrug Cefaclor IsoxsuprineJelly Ong 王金玉No ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument10 pagesDrug StudyFritzie Beatrice NomusNo ratings yet
- Drug Study 408Document13 pagesDrug Study 408Jheryck SabadaoNo ratings yet
- Topic 2.1: Antibiotics: Unit 2: Anti-Infective MedicationsDocument50 pagesTopic 2.1: Antibiotics: Unit 2: Anti-Infective MedicationsNirali ParmarNo ratings yet
- 5th Draft DrugsDocument7 pages5th Draft DrugsShayne Jessemae AlmarioNo ratings yet
- Quinocil: Ophthalmic Use: Treatment of Conjunctivitis Caused by Susceptible Strains of Aerobic GramDocument3 pagesQuinocil: Ophthalmic Use: Treatment of Conjunctivitis Caused by Susceptible Strains of Aerobic GramTallal KhanNo ratings yet
- CloxacillinDocument3 pagesCloxacillinRoberto Manuel IINo ratings yet
- WarfarinDocument10 pagesWarfarinMar Ordanza100% (1)
- Drug StudyDocument9 pagesDrug StudyShiara Ruth EdrosoloNo ratings yet
- Cefadroxil (Cephalosporin Generasi I)Document5 pagesCefadroxil (Cephalosporin Generasi I)Yustia SariNo ratings yet
- Name of Drug Classification Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Effects Nursing Responsibilities Ampicillin Sulbactam GI: Diarrhea, NauseaDocument10 pagesName of Drug Classification Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Effects Nursing Responsibilities Ampicillin Sulbactam GI: Diarrhea, NauseaVictor BiñasNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument8 pagesDrug StudyJoel MadjosNo ratings yet
- Drug Study: Postpartum Care ActivityDocument13 pagesDrug Study: Postpartum Care ActivityJohn Paul DimaunahanNo ratings yet
- MetoclopramideDocument5 pagesMetoclopramideyliahsamNo ratings yet
- Drug Study FINALDocument32 pagesDrug Study FINALhomeworkping1No ratings yet
- DexamethasoneDocument4 pagesDexamethasoneMits Valencia Karlsson0% (2)
- Drug Study FinalDocument3 pagesDrug Study FinalJazel OpinionNo ratings yet
- AcyclovirDocument20 pagesAcyclovirBrian Enrile Dorado0% (1)
- Drug StudyDocument3 pagesDrug StudyArra Cristine SeraficaNo ratings yet
- Name: Sophia Angela Famor BSN12EDocument4 pagesName: Sophia Angela Famor BSN12EZumi IskakNo ratings yet
- Drug Study (Pedia)Document7 pagesDrug Study (Pedia)Caurrine Monsalud100% (1)
- Drug StudyDocument8 pagesDrug Studysarah1217No ratings yet
- Anda - of AndaDocument46 pagesAnda - of AndaTarikNo ratings yet
- SOP Template For Preparation of A Clinical Trial Authorisation V4 1Document5 pagesSOP Template For Preparation of A Clinical Trial Authorisation V4 1DrSyeda Rima100% (1)
- Exhibitor ListDocument9 pagesExhibitor ListflinstonesNo ratings yet
- Centurion, CorrectHealth NegotiationsDocument16 pagesCenturion, CorrectHealth Negotiationssavannahnow.comNo ratings yet
- 1401 - List of Companies Contains Products in Need For Validation and CompletionDocument17 pages1401 - List of Companies Contains Products in Need For Validation and CompletionNader Samir50% (2)
- JohnsonDocument21 pagesJohnsonNeha SinghNo ratings yet
- What Is BMR (Batch Manufacturing Record) ?Document2 pagesWhat Is BMR (Batch Manufacturing Record) ?Yousif100% (1)
- Internship Report Template - DPSDocument8 pagesInternship Report Template - DPSsiti nadzirahNo ratings yet
- Directorate General of Drug Administration: SL Name of The Pharmaceutical Address Location Licence No. Present StatusDocument2 pagesDirectorate General of Drug Administration: SL Name of The Pharmaceutical Address Location Licence No. Present StatusAnamika SahaNo ratings yet
- Generic Name: Ceftriaxone Brand Name: (Kept Rix) IV, 1g, q12Document5 pagesGeneric Name: Ceftriaxone Brand Name: (Kept Rix) IV, 1g, q12De Sesto Rhys CarloNo ratings yet
- Swetha ResumeDocument4 pagesSwetha ResumeSushma VallamdasNo ratings yet
- 85 - 161 - Virosil Pharma Brochure - (New)Document34 pages85 - 161 - Virosil Pharma Brochure - (New)vkNo ratings yet
- Perencanaan Sediaan Farmasi Di RSDocument54 pagesPerencanaan Sediaan Farmasi Di RSkuingNo ratings yet
- Drug Study: Anti-InfectiveDocument8 pagesDrug Study: Anti-InfectiveTri ShaNo ratings yet
- The Work of Alfred Adask - A Summary of Man or Other AnimalsDocument3 pagesThe Work of Alfred Adask - A Summary of Man or Other AnimalsVen GeanciaNo ratings yet
- List of BoilersDocument17 pagesList of Boilersrmnkmr120% (1)
- Interaction Between Amlodipine and Simvastatin in Patients With Hypercholesterolemia and HypertensionDocument5 pagesInteraction Between Amlodipine and Simvastatin in Patients With Hypercholesterolemia and HypertensionSuci Ika PratiwiNo ratings yet
- NO Nama Obat Kemasan Harga SatuanDocument77 pagesNO Nama Obat Kemasan Harga SatuanArty Lestari IINo ratings yet
- Accord Product ListDocument14 pagesAccord Product ListANIRUDDHA KAPADNISNo ratings yet
- RSSM OkDocument28 pagesRSSM OkKanza Azalea PlayNo ratings yet
- Drug Sale ServiceDocument4 pagesDrug Sale Serviceaim4toeflNo ratings yet
- Assignment Number: MRTS-1 File Name: Market Research Transcript - Simple Duration: 0:04:48 Total Pages: 2Document2 pagesAssignment Number: MRTS-1 File Name: Market Research Transcript - Simple Duration: 0:04:48 Total Pages: 2Ummi NadhillahNo ratings yet
- DermatotherapyDocument56 pagesDermatotherapyRushda100% (1)
- (Depo) SO JANUARI 2022Document70 pages(Depo) SO JANUARI 2022NANDANo ratings yet
- Phytochemical Evaluation of MarchantiapolymorphamontivagansDocument5 pagesPhytochemical Evaluation of MarchantiapolymorphamontivagansjujuadrianNo ratings yet
- Annex 4 WHO Guidelines 4 Sampling of Pharmaceutical ProductsDocument23 pagesAnnex 4 WHO Guidelines 4 Sampling of Pharmaceutical ProductsJakobus Benny SalimNo ratings yet
- Insulin Price IncreasesDocument13 pagesInsulin Price IncreasesGazetteonlineNo ratings yet
- List of Selected Applicants To Join Health Institutions (Batch 1) Year 2014/15Document123 pagesList of Selected Applicants To Join Health Institutions (Batch 1) Year 2014/15nacte_tz86% (7)
- Kakatiya University, Warangal: Department of Pharmaceutics University College of Pharmaceutical SciencesDocument27 pagesKakatiya University, Warangal: Department of Pharmaceutics University College of Pharmaceutical SciencesJohn OmandacNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Lit. RevDocument10 pagesChapter 2 Lit. RevSAI ASSOCIATENo ratings yet