Professional Documents
Culture Documents
MATH9-CVIF-DLP-MIMs-4-1STQ-SOLVING-QE-COMPLETING-THE-SQUARE
MATH9-CVIF-DLP-MIMs-4-1STQ-SOLVING-QE-COMPLETING-THE-SQUARE
Uploaded by
Marvin FloresCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Precalculus Graphical Numerical Algebraic 8th Edition Demana Solutions ManualDocument35 pagesPrecalculus Graphical Numerical Algebraic 8th Edition Demana Solutions Manualmikadischerpro100% (13)
- Harcourt - Advanced Functions and Introductory Calculus - SolutionsDocument299 pagesHarcourt - Advanced Functions and Introductory Calculus - SolutionsTom S100% (4)
- Lie Groups and Lie Algebras For PhysicistsDocument50 pagesLie Groups and Lie Algebras For PhysicistsJoel CurtisNo ratings yet
- Differential EquationDocument134 pagesDifferential EquationHalzinashein Abella100% (1)
- Lesson 2 3 Solving Quadratic Equation by Completing The SquareDocument9 pagesLesson 2 3 Solving Quadratic Equation by Completing The SquareflyleafNo ratings yet
- Test 1 Review W2022Document4 pagesTest 1 Review W2022pissyonchrissyNo ratings yet
- Notes 2 Quadratic Equation by Extracting The RootsDocument2 pagesNotes 2 Quadratic Equation by Extracting The RootsKenneth AcostaNo ratings yet
- WEEK 1 - 2math 8Document8 pagesWEEK 1 - 2math 8Gerald TorresNo ratings yet
- V1663930820koswaal CBSE Class-9 Mathematics - Self Assessment Paper-3Document6 pagesV1663930820koswaal CBSE Class-9 Mathematics - Self Assessment Paper-3Ryan TakkarNo ratings yet
- SDLP - Completing The SquareDocument5 pagesSDLP - Completing The Squarekylene.abante.sNo ratings yet
- Algebra 101 DDocument7 pagesAlgebra 101 DjohannyNo ratings yet
- Gr9math Q1W1 - LasDocument22 pagesGr9math Q1W1 - LasIvanhoe BalaroteNo ratings yet
- Rational ExpressionsDocument9 pagesRational ExpressionsShineNo ratings yet
- Module in Mathematics 9: Department of Education-National Capital Region Schools Division of Pasay CityDocument5 pagesModule in Mathematics 9: Department of Education-National Capital Region Schools Division of Pasay CityShein SheilaNo ratings yet
- Juancho PDFDocument1 pageJuancho PDFJacinto Huamani SulcaNo ratings yet
- Maths MSDocument20 pagesMaths MSsavoupNo ratings yet
- Mathematics Notes Gr.11Document59 pagesMathematics Notes Gr.11iyermagsNo ratings yet
- Week 2Document10 pagesWeek 2lalaineNo ratings yet
- Edexcel IAL P2 Exercise 5C (Solution)Document3 pagesEdexcel IAL P2 Exercise 5C (Solution)Kaif HasanNo ratings yet
- Ial Maths Pure 2 Ex5cDocument3 pagesIal Maths Pure 2 Ex5cAhmadNo ratings yet
- Quadratic Equations: Solving A Quadratic Equation Completing The Square The Quadratic FormulaDocument24 pagesQuadratic Equations: Solving A Quadratic Equation Completing The Square The Quadratic FormulaJerard BalalaNo ratings yet
- Quadratic Formula ProjectDocument6 pagesQuadratic Formula ProjectCameron TomNo ratings yet
- Y8 Linear Equations 2Document18 pagesY8 Linear Equations 2Jackie TsoiNo ratings yet
- Math 99 Short SetsDocument3 pagesMath 99 Short SetscmcavoyNo ratings yet
- Mathematics: Quarter 2 - Module 9: Solve Equations Involving Radical ExpressionsDocument24 pagesMathematics: Quarter 2 - Module 9: Solve Equations Involving Radical ExpressionsKitkattyNo ratings yet
- Csec Add Maths June 2015Document24 pagesCsec Add Maths June 2015ValNo ratings yet
- Y10 Maths - Algebra - I Can ListDocument2 pagesY10 Maths - Algebra - I Can ListMicah SharpNo ratings yet
- Quadratic FunctionsDocument37 pagesQuadratic FunctionsHadi Alnaher100% (3)
- Instant Download PDF College Algebra An Early Functions Approach 1st Edition Blitzer Solutions Manual Full ChapterDocument144 pagesInstant Download PDF College Algebra An Early Functions Approach 1st Edition Blitzer Solutions Manual Full Chaptermickeykepple100% (5)
- Factoring Polynomials Perfect Square TrinomialsDocument3 pagesFactoring Polynomials Perfect Square TrinomialsCARYL FAITH ROSALLO GADIANNo ratings yet
- Math Solving EquationDocument12 pagesMath Solving EquationgeloloNo ratings yet
- Project in Math: Fourth QuarterDocument2 pagesProject in Math: Fourth QuarterJiyahnBayNo ratings yet
- Hand-Outs in MATH 9Document9 pagesHand-Outs in MATH 9Lee EspeletaNo ratings yet
- Grade 9 Solving Quadratic Equations by Using The Quadratic FormulaDocument2 pagesGrade 9 Solving Quadratic Equations by Using The Quadratic FormulaJowelyn MaderalNo ratings yet
- Solving Quadratic Equations by Completing The Square: ObjectivesDocument6 pagesSolving Quadratic Equations by Completing The Square: ObjectivesBaems AmborNo ratings yet
- Equation of Quadratic FunctionsDocument5 pagesEquation of Quadratic FunctionsJerson YhuwelNo ratings yet
- Rational Functions : X 2 X 4 X 2 X 4Document1 pageRational Functions : X 2 X 4 X 2 X 4Angel CariñoNo ratings yet
- 2014 EFsolnsDocument3 pages2014 EFsolnsBo WangNo ratings yet
- Q1 Math9Module1 Module2 PrintDocument9 pagesQ1 Math9Module1 Module2 PrintBrigida MaglalangNo ratings yet
- LESSON 7 Part 1Document12 pagesLESSON 7 Part 1phython 1109No ratings yet
- Math Reviewer - Sa1q1Document3 pagesMath Reviewer - Sa1q1AudreyNo ratings yet
- Factoring Brochure 2022-2023Document4 pagesFactoring Brochure 2022-2023Louela OrozcoNo ratings yet
- Any Trinomial of The Form Ax Factored To Be A (BINOMIAL Factor) SquaredDocument12 pagesAny Trinomial of The Form Ax Factored To Be A (BINOMIAL Factor) SquaredAml AmlNo ratings yet
- Pre-Cal Final ExamDocument8 pagesPre-Cal Final ExamJasmina Angelevska KostadinoskaNo ratings yet
- College and Advance Algebra MODULE 4Document6 pagesCollege and Advance Algebra MODULE 4Jefferson SociasNo ratings yet
- Year 9 Maths Test - Yearly Exam - AnswersDocument9 pagesYear 9 Maths Test - Yearly Exam - Answershannah20400oNo ratings yet
- Instant Download PDF College Algebra Essentials 2nd Edition Blitzer Solutions Manual Full ChapterDocument131 pagesInstant Download PDF College Algebra Essentials 2nd Edition Blitzer Solutions Manual Full Chaptermickeykepple100% (4)
- Algebra 1 Test and SolutionDocument11 pagesAlgebra 1 Test and SolutionZulfan AhmadiNo ratings yet
- MST129 - Applied Calculus 2021-2022 / Spring 1Document13 pagesMST129 - Applied Calculus 2021-2022 / Spring 1Hatem AlsofiNo ratings yet
- Delhi Public School Bangalore - East Mathematics Rational Numbers (Answer Key) NAME: - CLASS: VIII SEC: - DATEDocument26 pagesDelhi Public School Bangalore - East Mathematics Rational Numbers (Answer Key) NAME: - CLASS: VIII SEC: - DATESaket TNo ratings yet
- 9.3 Complete The Square PDFDocument9 pages9.3 Complete The Square PDFJoby ChenNo ratings yet
- EMT 1101 End of Semester Supplementary Exam December 2015Document6 pagesEMT 1101 End of Semester Supplementary Exam December 2015jonathane nhlaneNo ratings yet
- 12333Document144 pages12333jubaerkuroe5No ratings yet
- Algebra Task 2 - SolutionsDocument5 pagesAlgebra Task 2 - SolutionsJames BangNo ratings yet
- S22 FinalDocument11 pagesS22 FinalGathai MundiaNo ratings yet
- 02 Algebraic Fractional EquationsDocument9 pages02 Algebraic Fractional EquationsDivyaNo ratings yet
- The Graph of A Quadratic FunctionDocument30 pagesThe Graph of A Quadratic FunctionIr HeriawanNo ratings yet
- Determining Roots Using The Methods of Soving Quadratic EquationDocument6 pagesDetermining Roots Using The Methods of Soving Quadratic EquationBaems Ambor0% (1)
- Notre Dame of Jaro, Inc.: Motivation/DrillDocument5 pagesNotre Dame of Jaro, Inc.: Motivation/DrillVia Terrado CañedaNo ratings yet
- Inbound 580570974400447793Document3 pagesInbound 580570974400447793Jomaili A. JamalolNo ratings yet
- Math 10 Module 2Document27 pagesMath 10 Module 2regilynNo ratings yet
- A-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandA-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (8)
- MATH9-CVIF-DLP-MODULE 7Document1 pageMATH9-CVIF-DLP-MODULE 7Marvin FloresNo ratings yet
- 3RD Q Summative Test 1 Math 9Document2 pages3RD Q Summative Test 1 Math 9Marvin FloresNo ratings yet
- 3RD Q Summative Test 2 Math 9Document3 pages3RD Q Summative Test 2 Math 9Marvin Flores100% (1)
- 3rd and 4th Summative Test Math 9 2nd QDocument2 pages3rd and 4th Summative Test Math 9 2nd QMarvin FloresNo ratings yet
- 8th Maths Chapter 14 PDFDocument27 pages8th Maths Chapter 14 PDFRaj dhareNo ratings yet
- Notes For Finding The Inverse Laplace TransformDocument6 pagesNotes For Finding The Inverse Laplace TransformMukesh Kumar MeherNo ratings yet
- Soal Tugas 3Document4 pagesSoal Tugas 3Auliya Nusyura Al IslamiNo ratings yet
- SolutionDocument9 pagesSolutionParkVegasNo ratings yet
- Q1 - W8 - MATH6 - D1 - Dividing Decimals Up To 4 Decimal Places by 0.1, 0.01, and 0.001Document11 pagesQ1 - W8 - MATH6 - D1 - Dividing Decimals Up To 4 Decimal Places by 0.1, 0.01, and 0.001jigs michelle pasamonteNo ratings yet
- Lecture 16 - Matrix Method of Analysis of TrussesDocument16 pagesLecture 16 - Matrix Method of Analysis of TrussesAkshayNo ratings yet
- Write A Program To Store and Calculate The Sum of 5 Numbers Entered by The User Using ArraysDocument5 pagesWrite A Program To Store and Calculate The Sum of 5 Numbers Entered by The User Using Arraystarek mahmoudNo ratings yet
- Discrete Time Markov ChainsDocument59 pagesDiscrete Time Markov ChainsIsabella AlvarengaNo ratings yet
- 2 - Matrix Displacement Method For Plane TrussesDocument8 pages2 - Matrix Displacement Method For Plane TrussestrixiaNo ratings yet
- Applications Involving Fourier TransformsDocument60 pagesApplications Involving Fourier TransformsHimanshu MeenaNo ratings yet
- F3a 1Document126 pagesF3a 1Ng Kwan YinNo ratings yet
- Fractional Fourier TransformDocument12 pagesFractional Fourier Transformvolly666No ratings yet
- 5131 Week 2Document5 pages5131 Week 2Jeanneth Tatiana GuamanNo ratings yet
- Integral Calculus and Differential Equations Using MathematicaDocument223 pagesIntegral Calculus and Differential Equations Using MathematicaAlexander P. BelkaNo ratings yet
- Linear Algebra For Machine Learning: Sargur N. Srihari Srihari@cedar - Buffalo.eduDocument62 pagesLinear Algebra For Machine Learning: Sargur N. Srihari Srihari@cedar - Buffalo.eduHost Van BraundNo ratings yet
- W s-5 Vectors Vector CoordinatesDocument3 pagesW s-5 Vectors Vector Coordinatesapi-253679034No ratings yet
- Worksheet 7: Math3 (814013) - Group F31 - Fall 2006Document2 pagesWorksheet 7: Math3 (814013) - Group F31 - Fall 2006dennieboyNo ratings yet
- Calc05 4Document13 pagesCalc05 4Noli NogaNo ratings yet
- 10th Preboard (C) SchoolDocument7 pages10th Preboard (C) Schooljm2ccmukul35No ratings yet
- Gauss ExamplesDocument5 pagesGauss ExamplesHerath Mudiyanselage Indika HerathNo ratings yet
- An Integer-Arithmetic Algorithm For Observability Analysis of Systems With SCADA and PMU MeasurementsDocument15 pagesAn Integer-Arithmetic Algorithm For Observability Analysis of Systems With SCADA and PMU Measurementswvargas926No ratings yet
- RBHS GR 12 June P1 MEMO 2017Document12 pagesRBHS GR 12 June P1 MEMO 2017Chey1242No ratings yet
- Aops Community 1960 Amc 12/ahsmeDocument7 pagesAops Community 1960 Amc 12/ahsmeQFDqNo ratings yet
- C2 Exponentials & Logs - Laws of Logs PDFDocument16 pagesC2 Exponentials & Logs - Laws of Logs PDFtechang1No ratings yet
- Consolidated Test-1Document26 pagesConsolidated Test-1UnknownNo ratings yet
MATH9-CVIF-DLP-MIMs-4-1STQ-SOLVING-QE-COMPLETING-THE-SQUARE
MATH9-CVIF-DLP-MIMs-4-1STQ-SOLVING-QE-COMPLETING-THE-SQUARE
Uploaded by
Marvin FloresCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
MATH9-CVIF-DLP-MIMs-4-1STQ-SOLVING-QE-COMPLETING-THE-SQUARE
MATH9-CVIF-DLP-MIMs-4-1STQ-SOLVING-QE-COMPLETING-THE-SQUARE
Uploaded by
Marvin FloresCopyright:
Available Formats
Republic of the Philippines
Department of Education
National Capital Region
SCHOOLS DIVISION OFFICE-MALABON CITY
COL. RAMON CAMUS INTEGRATED SCHOOL
CVIF-DL Learning Activity Sheet
4th Quarter: Week 3
Name: _________________________________________ Score: ___________________________
Grade & Section:___________________ Date: _________________ Teacher:__________________
Subject: Mathematics 9, Quadratic Equation
Activity Title: Solving Quadratic Equation by Completing the Square
Learning Target: Solve quadratic equations by completing the square.
Reference: Quarter 1 – Module 4 – New Normal Math for G9
SOLVING QUADRATIC EQUATIONS BY COMPLETING THE SQUARE
Steps in Solving Quadratic Equation by “Completing the Square”
1. Place the constant term on the right side of the equation. All the terms with unknowns are on
the left side.
2. If the coefficient of the quadratic term, 𝑎≠1, divide each term of the equation by the numerical
coefficient.
3. To get the constant term needed to complete the square, get the numerical coefficient of linear
term, divide it by 2 and square it. Add the result to both sides of the equation.
4. Factor the perfect square trinomial.
5. Extract the square root from both sides. Two values will be obtained for the right side of the
equation.
6. Equate the linear expressions to each of the two values.
7. Solve each of the resulting linear equations.
8. Check your answer by substituting to the original equation.
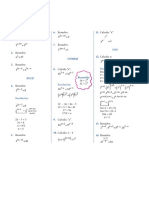
Example 1: Example 2:
A. Solve x 2−8 x−9=0 by completing the B. Solve 3 x 2−4 x+1=0 by completing the
square. square.
Solution: Solution:
2 2
x −8 x−9=0 Original Equation 3 x −4 x +1=0 Original Equation
2 2
x −8 x=9 Add 9 to both sides 3 x −4 x =−1 Add -1 to both sides
2 2
x −8 x +16=9+16 Add 16 to both sides 3 x 4 x −1
− = Divide by 3
Note: To get the constant that will complete the 3 3 3
2 4 x −1 −4
square take the coefficient of x, divide it by 2, x− = The coefficient of x is .
3 3 3
then square it. We have -8 as the numerical
( ) ( )
2 2
−4 −2 4
÷2 = =
( −82 ) =16
2
coefficient of -8x. Thus, 3 3 9
2 4 4 −1 4 4
2 x − x+ = + Add to both sides
x −8 x +16=25 3 9 3 9 9
( x−4 )2=25 2 4 4 1
Factor the perfect square trinomial x − x+ =
3 9 9
x−4=√ 25 Extract the square root of both sides
( )
2
2 1
x−4=±5 x− = Factor the trinomial square
3 9
x−4=5 x−4=−5
(√ x− 23 ) =√ 19
Equate the linear expressions to
2
x−4+ 4=5+4 x−4+ 4=−5+4 each of the two values. Extract the root of both sides
x=9 x=−1 Solve each resulting equation
The solutions set is {−1 , 9 }. 2
x− =±
1
3 3
2 1 2 −1
x− = x− = Equate the linear expressions to
3 3 3 3
2 2 1 2 2 2 −1 2
x− + = + x− + = + each of the two
3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3
values.
1
x=1 x= Solve each resulting equation
3
The solutions set is {13 , 1}.
Example 3:
C. Solve x 2−4 x−8=0 by completing the square.
Solution:
2
x −4 x−8=0 Original Equation
2
x −4 x=8 Adding 8 on both sides of the equation
The coefficient of x is -4
(−4 ÷ 2 )2=(−2 )2=4
2
x −4 x+ 4=8+ 4 Add 4 on both sides
2
x −4 x+ 4=12
( x−2 )2=12 Factor the trinomial square
x−2=± √ 12 Extract the square root of both sides
x−2=± √ 4 ∙3
x−2=±2 √ 3
x=2 ± 2 √ 3
x=2+2 √ 3 Solve each resulting equation
x=2−2 √ 3
The solutions set is { 2−2 √ 3 , 2+2 √ 3 }.
Activity: Complete Me!
Directions: To master your skills in solving quadratic equation by completing the square, solve and
check your solutions for the following:
1. x 2+ 6 x+5=0 2. 2 x 2+3 x−2=0 3. x 2−4 x+12=0
You might also like
- Precalculus Graphical Numerical Algebraic 8th Edition Demana Solutions ManualDocument35 pagesPrecalculus Graphical Numerical Algebraic 8th Edition Demana Solutions Manualmikadischerpro100% (13)
- Harcourt - Advanced Functions and Introductory Calculus - SolutionsDocument299 pagesHarcourt - Advanced Functions and Introductory Calculus - SolutionsTom S100% (4)
- Lie Groups and Lie Algebras For PhysicistsDocument50 pagesLie Groups and Lie Algebras For PhysicistsJoel CurtisNo ratings yet
- Differential EquationDocument134 pagesDifferential EquationHalzinashein Abella100% (1)
- Lesson 2 3 Solving Quadratic Equation by Completing The SquareDocument9 pagesLesson 2 3 Solving Quadratic Equation by Completing The SquareflyleafNo ratings yet
- Test 1 Review W2022Document4 pagesTest 1 Review W2022pissyonchrissyNo ratings yet
- Notes 2 Quadratic Equation by Extracting The RootsDocument2 pagesNotes 2 Quadratic Equation by Extracting The RootsKenneth AcostaNo ratings yet
- WEEK 1 - 2math 8Document8 pagesWEEK 1 - 2math 8Gerald TorresNo ratings yet
- V1663930820koswaal CBSE Class-9 Mathematics - Self Assessment Paper-3Document6 pagesV1663930820koswaal CBSE Class-9 Mathematics - Self Assessment Paper-3Ryan TakkarNo ratings yet
- SDLP - Completing The SquareDocument5 pagesSDLP - Completing The Squarekylene.abante.sNo ratings yet
- Algebra 101 DDocument7 pagesAlgebra 101 DjohannyNo ratings yet
- Gr9math Q1W1 - LasDocument22 pagesGr9math Q1W1 - LasIvanhoe BalaroteNo ratings yet
- Rational ExpressionsDocument9 pagesRational ExpressionsShineNo ratings yet
- Module in Mathematics 9: Department of Education-National Capital Region Schools Division of Pasay CityDocument5 pagesModule in Mathematics 9: Department of Education-National Capital Region Schools Division of Pasay CityShein SheilaNo ratings yet
- Juancho PDFDocument1 pageJuancho PDFJacinto Huamani SulcaNo ratings yet
- Maths MSDocument20 pagesMaths MSsavoupNo ratings yet
- Mathematics Notes Gr.11Document59 pagesMathematics Notes Gr.11iyermagsNo ratings yet
- Week 2Document10 pagesWeek 2lalaineNo ratings yet
- Edexcel IAL P2 Exercise 5C (Solution)Document3 pagesEdexcel IAL P2 Exercise 5C (Solution)Kaif HasanNo ratings yet
- Ial Maths Pure 2 Ex5cDocument3 pagesIal Maths Pure 2 Ex5cAhmadNo ratings yet
- Quadratic Equations: Solving A Quadratic Equation Completing The Square The Quadratic FormulaDocument24 pagesQuadratic Equations: Solving A Quadratic Equation Completing The Square The Quadratic FormulaJerard BalalaNo ratings yet
- Quadratic Formula ProjectDocument6 pagesQuadratic Formula ProjectCameron TomNo ratings yet
- Y8 Linear Equations 2Document18 pagesY8 Linear Equations 2Jackie TsoiNo ratings yet
- Math 99 Short SetsDocument3 pagesMath 99 Short SetscmcavoyNo ratings yet
- Mathematics: Quarter 2 - Module 9: Solve Equations Involving Radical ExpressionsDocument24 pagesMathematics: Quarter 2 - Module 9: Solve Equations Involving Radical ExpressionsKitkattyNo ratings yet
- Csec Add Maths June 2015Document24 pagesCsec Add Maths June 2015ValNo ratings yet
- Y10 Maths - Algebra - I Can ListDocument2 pagesY10 Maths - Algebra - I Can ListMicah SharpNo ratings yet
- Quadratic FunctionsDocument37 pagesQuadratic FunctionsHadi Alnaher100% (3)
- Instant Download PDF College Algebra An Early Functions Approach 1st Edition Blitzer Solutions Manual Full ChapterDocument144 pagesInstant Download PDF College Algebra An Early Functions Approach 1st Edition Blitzer Solutions Manual Full Chaptermickeykepple100% (5)
- Factoring Polynomials Perfect Square TrinomialsDocument3 pagesFactoring Polynomials Perfect Square TrinomialsCARYL FAITH ROSALLO GADIANNo ratings yet
- Math Solving EquationDocument12 pagesMath Solving EquationgeloloNo ratings yet
- Project in Math: Fourth QuarterDocument2 pagesProject in Math: Fourth QuarterJiyahnBayNo ratings yet
- Hand-Outs in MATH 9Document9 pagesHand-Outs in MATH 9Lee EspeletaNo ratings yet
- Grade 9 Solving Quadratic Equations by Using The Quadratic FormulaDocument2 pagesGrade 9 Solving Quadratic Equations by Using The Quadratic FormulaJowelyn MaderalNo ratings yet
- Solving Quadratic Equations by Completing The Square: ObjectivesDocument6 pagesSolving Quadratic Equations by Completing The Square: ObjectivesBaems AmborNo ratings yet
- Equation of Quadratic FunctionsDocument5 pagesEquation of Quadratic FunctionsJerson YhuwelNo ratings yet
- Rational Functions : X 2 X 4 X 2 X 4Document1 pageRational Functions : X 2 X 4 X 2 X 4Angel CariñoNo ratings yet
- 2014 EFsolnsDocument3 pages2014 EFsolnsBo WangNo ratings yet
- Q1 Math9Module1 Module2 PrintDocument9 pagesQ1 Math9Module1 Module2 PrintBrigida MaglalangNo ratings yet
- LESSON 7 Part 1Document12 pagesLESSON 7 Part 1phython 1109No ratings yet
- Math Reviewer - Sa1q1Document3 pagesMath Reviewer - Sa1q1AudreyNo ratings yet
- Factoring Brochure 2022-2023Document4 pagesFactoring Brochure 2022-2023Louela OrozcoNo ratings yet
- Any Trinomial of The Form Ax Factored To Be A (BINOMIAL Factor) SquaredDocument12 pagesAny Trinomial of The Form Ax Factored To Be A (BINOMIAL Factor) SquaredAml AmlNo ratings yet
- Pre-Cal Final ExamDocument8 pagesPre-Cal Final ExamJasmina Angelevska KostadinoskaNo ratings yet
- College and Advance Algebra MODULE 4Document6 pagesCollege and Advance Algebra MODULE 4Jefferson SociasNo ratings yet
- Year 9 Maths Test - Yearly Exam - AnswersDocument9 pagesYear 9 Maths Test - Yearly Exam - Answershannah20400oNo ratings yet
- Instant Download PDF College Algebra Essentials 2nd Edition Blitzer Solutions Manual Full ChapterDocument131 pagesInstant Download PDF College Algebra Essentials 2nd Edition Blitzer Solutions Manual Full Chaptermickeykepple100% (4)
- Algebra 1 Test and SolutionDocument11 pagesAlgebra 1 Test and SolutionZulfan AhmadiNo ratings yet
- MST129 - Applied Calculus 2021-2022 / Spring 1Document13 pagesMST129 - Applied Calculus 2021-2022 / Spring 1Hatem AlsofiNo ratings yet
- Delhi Public School Bangalore - East Mathematics Rational Numbers (Answer Key) NAME: - CLASS: VIII SEC: - DATEDocument26 pagesDelhi Public School Bangalore - East Mathematics Rational Numbers (Answer Key) NAME: - CLASS: VIII SEC: - DATESaket TNo ratings yet
- 9.3 Complete The Square PDFDocument9 pages9.3 Complete The Square PDFJoby ChenNo ratings yet
- EMT 1101 End of Semester Supplementary Exam December 2015Document6 pagesEMT 1101 End of Semester Supplementary Exam December 2015jonathane nhlaneNo ratings yet
- 12333Document144 pages12333jubaerkuroe5No ratings yet
- Algebra Task 2 - SolutionsDocument5 pagesAlgebra Task 2 - SolutionsJames BangNo ratings yet
- S22 FinalDocument11 pagesS22 FinalGathai MundiaNo ratings yet
- 02 Algebraic Fractional EquationsDocument9 pages02 Algebraic Fractional EquationsDivyaNo ratings yet
- The Graph of A Quadratic FunctionDocument30 pagesThe Graph of A Quadratic FunctionIr HeriawanNo ratings yet
- Determining Roots Using The Methods of Soving Quadratic EquationDocument6 pagesDetermining Roots Using The Methods of Soving Quadratic EquationBaems Ambor0% (1)
- Notre Dame of Jaro, Inc.: Motivation/DrillDocument5 pagesNotre Dame of Jaro, Inc.: Motivation/DrillVia Terrado CañedaNo ratings yet
- Inbound 580570974400447793Document3 pagesInbound 580570974400447793Jomaili A. JamalolNo ratings yet
- Math 10 Module 2Document27 pagesMath 10 Module 2regilynNo ratings yet
- A-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandA-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (8)
- MATH9-CVIF-DLP-MODULE 7Document1 pageMATH9-CVIF-DLP-MODULE 7Marvin FloresNo ratings yet
- 3RD Q Summative Test 1 Math 9Document2 pages3RD Q Summative Test 1 Math 9Marvin FloresNo ratings yet
- 3RD Q Summative Test 2 Math 9Document3 pages3RD Q Summative Test 2 Math 9Marvin Flores100% (1)
- 3rd and 4th Summative Test Math 9 2nd QDocument2 pages3rd and 4th Summative Test Math 9 2nd QMarvin FloresNo ratings yet
- 8th Maths Chapter 14 PDFDocument27 pages8th Maths Chapter 14 PDFRaj dhareNo ratings yet
- Notes For Finding The Inverse Laplace TransformDocument6 pagesNotes For Finding The Inverse Laplace TransformMukesh Kumar MeherNo ratings yet
- Soal Tugas 3Document4 pagesSoal Tugas 3Auliya Nusyura Al IslamiNo ratings yet
- SolutionDocument9 pagesSolutionParkVegasNo ratings yet
- Q1 - W8 - MATH6 - D1 - Dividing Decimals Up To 4 Decimal Places by 0.1, 0.01, and 0.001Document11 pagesQ1 - W8 - MATH6 - D1 - Dividing Decimals Up To 4 Decimal Places by 0.1, 0.01, and 0.001jigs michelle pasamonteNo ratings yet
- Lecture 16 - Matrix Method of Analysis of TrussesDocument16 pagesLecture 16 - Matrix Method of Analysis of TrussesAkshayNo ratings yet
- Write A Program To Store and Calculate The Sum of 5 Numbers Entered by The User Using ArraysDocument5 pagesWrite A Program To Store and Calculate The Sum of 5 Numbers Entered by The User Using Arraystarek mahmoudNo ratings yet
- Discrete Time Markov ChainsDocument59 pagesDiscrete Time Markov ChainsIsabella AlvarengaNo ratings yet
- 2 - Matrix Displacement Method For Plane TrussesDocument8 pages2 - Matrix Displacement Method For Plane TrussestrixiaNo ratings yet
- Applications Involving Fourier TransformsDocument60 pagesApplications Involving Fourier TransformsHimanshu MeenaNo ratings yet
- F3a 1Document126 pagesF3a 1Ng Kwan YinNo ratings yet
- Fractional Fourier TransformDocument12 pagesFractional Fourier Transformvolly666No ratings yet
- 5131 Week 2Document5 pages5131 Week 2Jeanneth Tatiana GuamanNo ratings yet
- Integral Calculus and Differential Equations Using MathematicaDocument223 pagesIntegral Calculus and Differential Equations Using MathematicaAlexander P. BelkaNo ratings yet
- Linear Algebra For Machine Learning: Sargur N. Srihari Srihari@cedar - Buffalo.eduDocument62 pagesLinear Algebra For Machine Learning: Sargur N. Srihari Srihari@cedar - Buffalo.eduHost Van BraundNo ratings yet
- W s-5 Vectors Vector CoordinatesDocument3 pagesW s-5 Vectors Vector Coordinatesapi-253679034No ratings yet
- Worksheet 7: Math3 (814013) - Group F31 - Fall 2006Document2 pagesWorksheet 7: Math3 (814013) - Group F31 - Fall 2006dennieboyNo ratings yet
- Calc05 4Document13 pagesCalc05 4Noli NogaNo ratings yet
- 10th Preboard (C) SchoolDocument7 pages10th Preboard (C) Schooljm2ccmukul35No ratings yet
- Gauss ExamplesDocument5 pagesGauss ExamplesHerath Mudiyanselage Indika HerathNo ratings yet
- An Integer-Arithmetic Algorithm For Observability Analysis of Systems With SCADA and PMU MeasurementsDocument15 pagesAn Integer-Arithmetic Algorithm For Observability Analysis of Systems With SCADA and PMU Measurementswvargas926No ratings yet
- RBHS GR 12 June P1 MEMO 2017Document12 pagesRBHS GR 12 June P1 MEMO 2017Chey1242No ratings yet
- Aops Community 1960 Amc 12/ahsmeDocument7 pagesAops Community 1960 Amc 12/ahsmeQFDqNo ratings yet
- C2 Exponentials & Logs - Laws of Logs PDFDocument16 pagesC2 Exponentials & Logs - Laws of Logs PDFtechang1No ratings yet
- Consolidated Test-1Document26 pagesConsolidated Test-1UnknownNo ratings yet