Professional Documents
Culture Documents
ScheSyll
ScheSyll
Uploaded by
anuragbhattacharjee56Copyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Saris-Tradition and BeyondDocument257 pagesSaris-Tradition and BeyondSwathi G. Salem60% (5)
- Advanced Engineering Mathematics 8th Edition Oneil Solutions ManualDocument21 pagesAdvanced Engineering Mathematics 8th Edition Oneil Solutions Manuallanguor.shete0wkzrt100% (30)
- Weaving Preparatory ProcessDocument5 pagesWeaving Preparatory ProcessKhubab Shaker100% (10)
- Application Handbook USTER Statistics 2013Document38 pagesApplication Handbook USTER Statistics 2013Kaushik Mukherjee100% (2)
- GATE SyllabusDocument3 pagesGATE Syllabusgotita shuklaNo ratings yet
- TF - Gate 2021Document3 pagesTF - Gate 2021ARIHARASUDHAN sNo ratings yet
- 116102005Document4 pages116102005mohan smrNo ratings yet
- Textile Engineering mtqp12Document4 pagesTextile Engineering mtqp12Ankit SinghNo ratings yet
- Common For The Subjects/Streams Mentioned Below: Textile Engineering and Fibre Science (Max. Marks: 70)Document4 pagesCommon For The Subjects/Streams Mentioned Below: Textile Engineering and Fibre Science (Max. Marks: 70)Ambika RajawatNo ratings yet
- GateDocument3 pagesGatesandeepNo ratings yet
- Textile Engineering and Fibre ScienceDocument3 pagesTextile Engineering and Fibre ScienceNikhil TakbhateNo ratings yet
- GATE Syllabus For Textile Engineering and Fiber ScienceDocument4 pagesGATE Syllabus For Textile Engineering and Fiber ScienceVinay Prajapati100% (1)
- How To Find Yarn Count From GSM - Textile Learner PDFDocument1 pageHow To Find Yarn Count From GSM - Textile Learner PDFKM NAZRUL IslamNo ratings yet
- Syllabus For Textile Engineering and Fibre Science (TF) : Linear AlgebraDocument4 pagesSyllabus For Textile Engineering and Fibre Science (TF) : Linear AlgebrakamalkantmbbsNo ratings yet
- Diploma Lect Textile Technology PDFDocument2 pagesDiploma Lect Textile Technology PDFRevappa YeddeNo ratings yet
- Gate 2014 Syllabus Textile Engineering and Fibre Science TFDocument3 pagesGate 2014 Syllabus Textile Engineering and Fibre Science TFapi-287058159No ratings yet
- Gate Syllabus For TextileDocument2 pagesGate Syllabus For Textileshubham_yadav51710% (1)
- Module 114 Basic Textile - 001-KnittingDocument60 pagesModule 114 Basic Textile - 001-KnittingTran Quoc VietNo ratings yet
- Full Book TPSPDocument120 pagesFull Book TPSPDeenaNo ratings yet
- GATE SyllabusDocument3 pagesGATE SyllabusMahesh PurbiaNo ratings yet
- Exp 01 CorrectedDocument14 pagesExp 01 CorrectedIstiak Ahmed TussharNo ratings yet
- SLV 3Document1 pageSLV 3mohsinNo ratings yet
- Sizing Draw inDocument23 pagesSizing Draw inteegalajyothiNo ratings yet
- Six SigmaDocument6 pagesSix Sigmasayeef khanNo ratings yet
- Sizing Draw inDocument23 pagesSizing Draw inNikita JainNo ratings yet
- Effect of Machine Parameters On Knit FabDocument5 pagesEffect of Machine Parameters On Knit FablfomlfomNo ratings yet
- Knitting: Ms. Nasrin AkterDocument24 pagesKnitting: Ms. Nasrin AkterCimaNo ratings yet
- Explaining TextilesDocument109 pagesExplaining TextilesGOWTHAM CHANDRUNo ratings yet
- TEX-2202.Fabric Preparatory Process (Lab) : IDocument18 pagesTEX-2202.Fabric Preparatory Process (Lab) : IRatul HasanNo ratings yet
- Fabric Manufacturing - I Unit 1Document28 pagesFabric Manufacturing - I Unit 1nikitaNo ratings yet
- Course Outline 1Document2 pagesCourse Outline 1kkkgn007No ratings yet
- Introduction To WeavingDocument17 pagesIntroduction To WeavingJahaziNo ratings yet
- Knitted Fabric StructureDocument2 pagesKnitted Fabric Structuremobarok2613No ratings yet
- Denim - ProcessDocument28 pagesDenim - ProcessSajjad Ashraf100% (1)
- Textile Internship Report AlokDocument39 pagesTextile Internship Report AlokRahul TelangNo ratings yet
- Recent Development in Denim ManufacturingDocument24 pagesRecent Development in Denim ManufacturingMichael LiuNo ratings yet
- Student NOTESDocument53 pagesStudent NOTESRohan YadavNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Textile TechnologyDocument2 pagesIntroduction To Textile Technologyabhijeet9solankiNo ratings yet
- Seam Performance Evaluation of Plain Fabric UsingDocument9 pagesSeam Performance Evaluation of Plain Fabric UsingMd NurunnabiNo ratings yet
- Circular Knitting MachineDocument24 pagesCircular Knitting MachinemohsinNo ratings yet
- Textilelearner Blogspot Com 2012 07 Fabric Spreading Types of Fabric HTMLDocument6 pagesTextilelearner Blogspot Com 2012 07 Fabric Spreading Types of Fabric HTMLDeepthi SonuNo ratings yet
- Es2 KTDocument3 pagesEs2 KTPalash BaruaNo ratings yet
- Weft Knitting: MD - Azmeri Latif Beg M. SC in Textile Engineering Department of Textile Engineering, DIUDocument16 pagesWeft Knitting: MD - Azmeri Latif Beg M. SC in Textile Engineering Department of Textile Engineering, DIUaqsa imranNo ratings yet
- Slidw Group 009 Yarn Structure AnalysisDocument59 pagesSlidw Group 009 Yarn Structure AnalysisAliAhmadNo ratings yet
- Knitting Faults Causes and Remedies of Knit FabricsDocument14 pagesKnitting Faults Causes and Remedies of Knit FabricsRavi KumarNo ratings yet
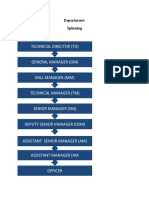
- Technical Director (TD) : Department: Spinning HierarchyDocument14 pagesTechnical Director (TD) : Department: Spinning HierarchyWaqas AkramNo ratings yet
- BGMEA University of Fashion & Technology (BUFT) : Assignment. (k-3)Document19 pagesBGMEA University of Fashion & Technology (BUFT) : Assignment. (k-3)NeFariOus ArYan AraFat AnikNo ratings yet
- WEAVING ParameterDocument5 pagesWEAVING ParameterAshraful Himel33% (3)
- Warp KnittingDocument44 pagesWarp KnittingEngineer WaleedNo ratings yet
- M.SC Fashion DesigningDocument27 pagesM.SC Fashion DesigningAIM INSTITUTENo ratings yet
- FM-III Unit 3Document72 pagesFM-III Unit 3Jjeerryyy NikharNo ratings yet
- Effect of Gauge Variation of Circular KNDocument6 pagesEffect of Gauge Variation of Circular KNSukram HembromNo ratings yet
- KnittingDocument38 pagesKnittingmahes_texNo ratings yet
- Course Title: Cut & Sew Knitwear: Lecture PlanDocument1 pageCourse Title: Cut & Sew Knitwear: Lecture PlanRiponPrasadNo ratings yet
- Weaving: Weaving Department Standard Operating Manual Process DefinitionDocument20 pagesWeaving: Weaving Department Standard Operating Manual Process DefinitionSabeeh Ul HassanNo ratings yet
- Effects of Combed and Carded Yarn On Weft Knitted Finished Quality-MinDocument5 pagesEffects of Combed and Carded Yarn On Weft Knitted Finished Quality-MinNasrin AkterNo ratings yet
- Textile Warping NotesDocument2 pagesTextile Warping NotesKali MuthuNo ratings yet
- Fabric Terms and Woven Prepartory Process - Lecture 2Document24 pagesFabric Terms and Woven Prepartory Process - Lecture 2Shresha DasNo ratings yet
- Lab Manual: Fabric Structure and DesignDocument19 pagesLab Manual: Fabric Structure and DesignZillur Rahman SaykatNo ratings yet
- Weft Knitting .1Document16 pagesWeft Knitting .1Mina Samy abd el zaherNo ratings yet
- Complete Book of Sewing Techniques, New 2nd Edition: More Than 30 Essential Sewing Techniques for You to MasterFrom EverandComplete Book of Sewing Techniques, New 2nd Edition: More Than 30 Essential Sewing Techniques for You to MasterRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (3)
- BSL PrintDocument62 pagesBSL Printrishi100% (1)
- 1 Complete Weaving MillDocument6 pages1 Complete Weaving MillKomol KabirNo ratings yet
- Bài Tập Tiếng Anh 9 Mới Theo Unit - giasuvina.com.VnDocument81 pagesBài Tập Tiếng Anh 9 Mới Theo Unit - giasuvina.com.VnNguyễn Thị Lệ ThiNo ratings yet
- Lab 1Document4 pagesLab 1Mujahid MehdiNo ratings yet
- The Cultural Economy: Globalization and Crafts in South AsiaDocument7 pagesThe Cultural Economy: Globalization and Crafts in South AsiaQuan DoanNo ratings yet
- q3 Lc2 Visual ArtsDocument13 pagesq3 Lc2 Visual ArtsGEMINO JIM MONTERONANo ratings yet
- Stash Buster - CaterpillarDocument1 pageStash Buster - CaterpillarSuzanne Yates Byford100% (1)
- wvg5 PDFDocument28 pageswvg5 PDFKing KishanNo ratings yet
- Tuần 13 - Anh 9Document15 pagesTuần 13 - Anh 9Đức MinhNo ratings yet
- Harpar Group Profile New IntDocument38 pagesHarpar Group Profile New IntKrishnaRajaNo ratings yet
- Mapeh 7 q1 - Week 3 (Arts)Document7 pagesMapeh 7 q1 - Week 3 (Arts)joel cagaananNo ratings yet
- Picanol: Industrial Machinery and Heavy EquipmentDocument5 pagesPicanol: Industrial Machinery and Heavy EquipmentbrufpotNo ratings yet
- First Grading Period Lesson 1: Fabric/Fabric Design ThailandDocument11 pagesFirst Grading Period Lesson 1: Fabric/Fabric Design ThailandShane HernandezNo ratings yet
- Silk Weaving - KanchipuramDocument31 pagesSilk Weaving - KanchipuramananyaNo ratings yet
- Almohada Harry PotterDocument11 pagesAlmohada Harry PotterMaría Montilla100% (1)
- Lesson Plan Grade 8 Arts June 7, 13, and 20Document3 pagesLesson Plan Grade 8 Arts June 7, 13, and 20Glaisa D. LanoNo ratings yet
- Basic WeaveDocument34 pagesBasic Weavejennygraceshalini100% (4)
- Shop Tangaliya & PatolaDocument4 pagesShop Tangaliya & PatolaEkta AroraNo ratings yet
- Kanchipuram Product TrainingDocument38 pagesKanchipuram Product TrainingApoorva NatrajNo ratings yet
- Siyarams RoughDocument38 pagesSiyarams RoughASHISH BHUWANIANo ratings yet
- AlvinT Price List 2016 - IDR - Okt2016 PDFDocument5 pagesAlvinT Price List 2016 - IDR - Okt2016 PDFDavid Epson Mayer0% (1)
- Chapter OneDocument35 pagesChapter OneHamzaNo ratings yet
- Impact On Indian Econmy - Ignou NotesDocument13 pagesImpact On Indian Econmy - Ignou NotesVANSHIKA CHAUDHARYNo ratings yet
- Case Summary KhawajaDocument2 pagesCase Summary KhawajakhawajaNo ratings yet
- 'BEBE CON GORRO' ContigoDocument26 pages'BEBE CON GORRO' ContigoGi Torres67% (6)
- Lesson Plan CH 4 Class 8Document11 pagesLesson Plan CH 4 Class 8preetichughduNo ratings yet
- HRP AssignmentDocument11 pagesHRP AssignmentSreeram BaddilaNo ratings yet
ScheSyll
ScheSyll
Uploaded by
anuragbhattacharjee56Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
ScheSyll
ScheSyll
Uploaded by
anuragbhattacharjee56Copyright:
Available Formats
Scheme for Screening Test for recruitment to the posts
Technical Assistant-III in the Directorate of Textiles (Handloom
etc Div.) under the Department of M.S.M.E & Textiles, Govt. of
W.B. [Advt. No. 15/2023]
Screening Test will be objective type (MCQ) in 4 different series,
viz., A, B, C & D.
Number of questions: 100, each carrying 1 mark.
Full marks: 100.
Duration: 1 hour 30 minutes.
N.B.: There will be negative marking for each wrong answer as per
norms (1/4th of the marks for each wrong answer).
Multiple choice objective type questions on:-
(i) Textile Technology & Handloom – 70 marks
Technology and Textile Chemistry[Diploma Standard]
(ii) English [Basic Grammar- Madhyamik standard] – 15 marks
(iii) General Awareness & Arithmetic – 15 marks
[Arithmetic - Madhyamik standard]
Syllabus for Screening Test for rectt. to the post of
Technical Assistant Grade-IIIin the Directorate of Textiles
(Handloom etc Div.) under the Department of M.S.M.E &
Textiles, Govt. of W.B.[Advt. No. 15/2023]
Topic Sub-Topic
Fibre Science Characteristics of textile fibre
Classification of textile fibre on basis of its source/origin
NATURAL FIBRE
Cotton Fibre
Commercial varieties of cotton; Physical properties of cotton; Chemical Properties
of cotton,
Brief study of uses of cotton
Bast Fibre (extraction process and different uses)
Jute; Flax, Ramie; Hemp
Silk
Rearing; Reeling and Throwing of silk fibre; Degumming of silk fibre; Physical
And chemical properties of silk fibre; Different uses of wool fibre
MANMADE FIBRE
Viscose, Polyester, Nylon and acrylic
Raw materials ' Physical and chemical properties' Uses
Outline of weaving process
Weaving Definition of weaving, common weaving terms; Classification of looms
Primary, secondary & auxiliary motions of weaving; Functions & uses of
various important loom parts & accessories
Handloom
Type of handloom;
Fly shuttle frame loom; Semiautomatic looms; Tie up of healds
Yarn for weaving
Varieties of yarn; Various forms yarn packages; Outline of the process for
conversion of yarn into fabric
Winding
Object of warp & weft winding; Cone winding machine-mechanism & working
Principle;
Pirn winding machine-mechanism & working principle
Warping
Object of warping; Beam warping machine-mechanism & working principles;
Sectional warping machine-mechanism & working principles; Defects of beam and
their remedies.
Picking Mechanism
Type of picking mechanism & working principles
Beating up mechanism
The motion of the sley; Eccentricity of sleys motion & its effect
Secondary motion
Take up motion & its type; Seven wheel take up motion; Let off motion & its type;
Negative & positive let off mechanism.
Sizing
Object of sizing; Study of sizing ingredients & their function; Preparation of
sizing paste; Sizing machine-mechanism & working principles
Dobby Loom
Principles of dobby shedding; Types of dobby: Timing & setting of dobby;
Common defects of dobby-causes & remedies
Jacquard Loom
Objects & principles of jacquard shedding; Types of jacquard; Timing and
setting of jacquard loom; Study of different system of harness mounting and
harness ties; Study of working of piano card cutting machine card lacing and
their mounting
Fabric Defects
Common fabric defects, causes and their remedies
Calculation related to cost of fabrics
Plain weave & its derivatives
Fabric Plain weave; rib weaves; Weft rib weaves; Mat weaves
Structure Twill weave of & its derivatives
Characteristics of twill weave; Construction of twill weave; Rearranged twill
Combined twill; Broken twill; Diamond design; Influence of twist direction &
angle of twill on appearance to twill; Satin weavers
Simple toweling & curtain fabrics
Ordinary honey comp design; Double stitched ordinary honey comp; Straight
draft honey comp; Brighten honey comp
Yarn numbering system
Indirect system of numbering of yarn; Direct system of numbering of yarn
Resultant count of folded yarn; Conversion of count of yarn
Heald count & reed count
Different system of heald count; Different system of reed count
Bedford cord & Pique design
Plain faced Bedford cord design produced by of picks; Plain faced
Bedford cord design produced by alternative picks; Twill face Bedford cord;
Extra warp and extra weft figuring; Cross over the spot figures; Loose back and
fast back pique
Warp pile fabric
Construction of different types of terry pile fabrics-3 pick, 4 pick, 5 pick & 6 pick
terry pile;
Weaving mechanism for producing terry pile structure
Weft pile fabric
Velveteen; Plain back velveteen; Twill back velveteen; Length of pile; Density of
pile; Fast pile structure
Back cloth design
Principle of tying & stitching back cloth; Types of back cloth; Warp back; Weft
back; Reversible back cloth; Warp wadded weft back cloth; Weft wadded warp
back cloth
Double cloth
Classification of double cloth; Self stitched double cloth; Centre stitched double
cloth; Thread interchange double cloth; Cloth interchange double cloth; One side
binding double cloth; Both side binding double cloth
Gauze & Leno weaving
Introduction of gauze & leno structure; Construction of doup healds & its uses
Gauze & leno design; drafting plan, lifting plan & types of sheds
Yarn & cloth calculation
Influence of yarn diameter on cloth setting rules; Determination of cover factor &
cloth particulars
Jacquard design
Construction of jacquard design for side border & all over effect e.g.
Bisymmetrical & multi symmetrical design; Different stages for transferring a
small motif to the fabric; Arrangement of figured in jacquard design like-unit
repeat drop principle satin
Analysis of woven fabrics
Identification of warp and weft, Brief discussion about the analysing procedures
Calculation of weight of warp & weft
Extra Warp and Extra Weft Designs
Textile Dyeing
Chemistry Classification of dyestuff according to methods of application; Determination
of water hardness; Scouring of cotton yarn; Bleaching of cotton yarn; Mercerizing;
Dyeing with direct dyes of cotton; After treatment of direct colours on cotton;
Basic & Acid dye-general characteristics and methods of application; Reactive
Vat and Sulphur dye-general characteristics and methods of application;
Combined scouring and bleaching of jute; jute bleach for white and use; Dyeing of
jute materials; Dyeing of Silk; A brief study of some vegetable colour and their
methods of application; Azo Free Dyes, Colour Fastness-washing; light; rubbing;
hot ironing
Printing
Preparation of cotton tor printing, Thickening agents and assistance used in
textiles printing) Methods of printing-Hand Block, Stencil Screen; Various styles of
printing-direct, discharge, Preparation of printing pastes with different dyestuff;
Some common faults in printing and their rectifications
Textile Moisture and Textiles
Testing Effect of moisture on textiles and textile processing and testing, Definition of
absolute and relative humidity, moisture content moisture regain and their
relationship; Study of the methods for the determination of-relative humidity by
wet & bulb hygrometer and Moisture content moisture regain by conditioning
oven & Shirley moisture meter
Yarn Number
Principle involved in determination of yarn number, Determination of yarn
number from yarn cloth; Use of instruments for determination of yarn number-
knowledge balance; Quadrant balance and Beasley balance
Yarn Twist
Effect of twist on the quality of yarn and fabrics; Optimum twist and its
essentiality;
Determination of twist of single and ply yarn
Yarn Strength Testing
Principle of different methods; Study of yarn strength testing instruments-
LeaTester, Singie thread tester, Ballistic tester
Yarn evenness
Meaning of random variation; periodic variation; short, medium and long term
variation;
Index of irregularity in evenness determination: Measurement of yarn evenness
by-Black Board Test, Fielden Walker Test
Fabric Testing
Determination of fabric testing related to Thickness; Weight; Crimp; Study of tear,
tensile, bursting, and abrasion properties of fabric; Air and water permeability
test
Crease Resistance and Crease Recovery
Determination of crease resistance and crease recovery properties
Environment General concept
and Nature and scope of environmental problems
Pollution Environmental Pollution
Management Water pollution-types, sources and their effects; Occupational health-hazards
related handloom industry processes; various sources of water in wet processing;
characteristics of waste water, water conservation
Pollution Monitoring and control
Principles and methods of waste water treatments; design of effluent treatment
plant and disposal of waste
English Basic Grammar [Madhyamik Standard]
Arithmetic & General Awareness,
General Arithmetic – Madhyamik Standard
Awareness
N.B.:-
The Syllabus is indicative only, candidates should be prepared to answer any
question from essential qualification/degree mentioned in the advertisement for the
relevant post.
You might also like
- Saris-Tradition and BeyondDocument257 pagesSaris-Tradition and BeyondSwathi G. Salem60% (5)
- Advanced Engineering Mathematics 8th Edition Oneil Solutions ManualDocument21 pagesAdvanced Engineering Mathematics 8th Edition Oneil Solutions Manuallanguor.shete0wkzrt100% (30)
- Weaving Preparatory ProcessDocument5 pagesWeaving Preparatory ProcessKhubab Shaker100% (10)
- Application Handbook USTER Statistics 2013Document38 pagesApplication Handbook USTER Statistics 2013Kaushik Mukherjee100% (2)
- GATE SyllabusDocument3 pagesGATE Syllabusgotita shuklaNo ratings yet
- TF - Gate 2021Document3 pagesTF - Gate 2021ARIHARASUDHAN sNo ratings yet
- 116102005Document4 pages116102005mohan smrNo ratings yet
- Textile Engineering mtqp12Document4 pagesTextile Engineering mtqp12Ankit SinghNo ratings yet
- Common For The Subjects/Streams Mentioned Below: Textile Engineering and Fibre Science (Max. Marks: 70)Document4 pagesCommon For The Subjects/Streams Mentioned Below: Textile Engineering and Fibre Science (Max. Marks: 70)Ambika RajawatNo ratings yet
- GateDocument3 pagesGatesandeepNo ratings yet
- Textile Engineering and Fibre ScienceDocument3 pagesTextile Engineering and Fibre ScienceNikhil TakbhateNo ratings yet
- GATE Syllabus For Textile Engineering and Fiber ScienceDocument4 pagesGATE Syllabus For Textile Engineering and Fiber ScienceVinay Prajapati100% (1)
- How To Find Yarn Count From GSM - Textile Learner PDFDocument1 pageHow To Find Yarn Count From GSM - Textile Learner PDFKM NAZRUL IslamNo ratings yet
- Syllabus For Textile Engineering and Fibre Science (TF) : Linear AlgebraDocument4 pagesSyllabus For Textile Engineering and Fibre Science (TF) : Linear AlgebrakamalkantmbbsNo ratings yet
- Diploma Lect Textile Technology PDFDocument2 pagesDiploma Lect Textile Technology PDFRevappa YeddeNo ratings yet
- Gate 2014 Syllabus Textile Engineering and Fibre Science TFDocument3 pagesGate 2014 Syllabus Textile Engineering and Fibre Science TFapi-287058159No ratings yet
- Gate Syllabus For TextileDocument2 pagesGate Syllabus For Textileshubham_yadav51710% (1)
- Module 114 Basic Textile - 001-KnittingDocument60 pagesModule 114 Basic Textile - 001-KnittingTran Quoc VietNo ratings yet
- Full Book TPSPDocument120 pagesFull Book TPSPDeenaNo ratings yet
- GATE SyllabusDocument3 pagesGATE SyllabusMahesh PurbiaNo ratings yet
- Exp 01 CorrectedDocument14 pagesExp 01 CorrectedIstiak Ahmed TussharNo ratings yet
- SLV 3Document1 pageSLV 3mohsinNo ratings yet
- Sizing Draw inDocument23 pagesSizing Draw inteegalajyothiNo ratings yet
- Six SigmaDocument6 pagesSix Sigmasayeef khanNo ratings yet
- Sizing Draw inDocument23 pagesSizing Draw inNikita JainNo ratings yet
- Effect of Machine Parameters On Knit FabDocument5 pagesEffect of Machine Parameters On Knit FablfomlfomNo ratings yet
- Knitting: Ms. Nasrin AkterDocument24 pagesKnitting: Ms. Nasrin AkterCimaNo ratings yet
- Explaining TextilesDocument109 pagesExplaining TextilesGOWTHAM CHANDRUNo ratings yet
- TEX-2202.Fabric Preparatory Process (Lab) : IDocument18 pagesTEX-2202.Fabric Preparatory Process (Lab) : IRatul HasanNo ratings yet
- Fabric Manufacturing - I Unit 1Document28 pagesFabric Manufacturing - I Unit 1nikitaNo ratings yet
- Course Outline 1Document2 pagesCourse Outline 1kkkgn007No ratings yet
- Introduction To WeavingDocument17 pagesIntroduction To WeavingJahaziNo ratings yet
- Knitted Fabric StructureDocument2 pagesKnitted Fabric Structuremobarok2613No ratings yet
- Denim - ProcessDocument28 pagesDenim - ProcessSajjad Ashraf100% (1)
- Textile Internship Report AlokDocument39 pagesTextile Internship Report AlokRahul TelangNo ratings yet
- Recent Development in Denim ManufacturingDocument24 pagesRecent Development in Denim ManufacturingMichael LiuNo ratings yet
- Student NOTESDocument53 pagesStudent NOTESRohan YadavNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Textile TechnologyDocument2 pagesIntroduction To Textile Technologyabhijeet9solankiNo ratings yet
- Seam Performance Evaluation of Plain Fabric UsingDocument9 pagesSeam Performance Evaluation of Plain Fabric UsingMd NurunnabiNo ratings yet
- Circular Knitting MachineDocument24 pagesCircular Knitting MachinemohsinNo ratings yet
- Textilelearner Blogspot Com 2012 07 Fabric Spreading Types of Fabric HTMLDocument6 pagesTextilelearner Blogspot Com 2012 07 Fabric Spreading Types of Fabric HTMLDeepthi SonuNo ratings yet
- Es2 KTDocument3 pagesEs2 KTPalash BaruaNo ratings yet
- Weft Knitting: MD - Azmeri Latif Beg M. SC in Textile Engineering Department of Textile Engineering, DIUDocument16 pagesWeft Knitting: MD - Azmeri Latif Beg M. SC in Textile Engineering Department of Textile Engineering, DIUaqsa imranNo ratings yet
- Slidw Group 009 Yarn Structure AnalysisDocument59 pagesSlidw Group 009 Yarn Structure AnalysisAliAhmadNo ratings yet
- Knitting Faults Causes and Remedies of Knit FabricsDocument14 pagesKnitting Faults Causes and Remedies of Knit FabricsRavi KumarNo ratings yet
- Technical Director (TD) : Department: Spinning HierarchyDocument14 pagesTechnical Director (TD) : Department: Spinning HierarchyWaqas AkramNo ratings yet
- BGMEA University of Fashion & Technology (BUFT) : Assignment. (k-3)Document19 pagesBGMEA University of Fashion & Technology (BUFT) : Assignment. (k-3)NeFariOus ArYan AraFat AnikNo ratings yet
- WEAVING ParameterDocument5 pagesWEAVING ParameterAshraful Himel33% (3)
- Warp KnittingDocument44 pagesWarp KnittingEngineer WaleedNo ratings yet
- M.SC Fashion DesigningDocument27 pagesM.SC Fashion DesigningAIM INSTITUTENo ratings yet
- FM-III Unit 3Document72 pagesFM-III Unit 3Jjeerryyy NikharNo ratings yet
- Effect of Gauge Variation of Circular KNDocument6 pagesEffect of Gauge Variation of Circular KNSukram HembromNo ratings yet
- KnittingDocument38 pagesKnittingmahes_texNo ratings yet
- Course Title: Cut & Sew Knitwear: Lecture PlanDocument1 pageCourse Title: Cut & Sew Knitwear: Lecture PlanRiponPrasadNo ratings yet
- Weaving: Weaving Department Standard Operating Manual Process DefinitionDocument20 pagesWeaving: Weaving Department Standard Operating Manual Process DefinitionSabeeh Ul HassanNo ratings yet
- Effects of Combed and Carded Yarn On Weft Knitted Finished Quality-MinDocument5 pagesEffects of Combed and Carded Yarn On Weft Knitted Finished Quality-MinNasrin AkterNo ratings yet
- Textile Warping NotesDocument2 pagesTextile Warping NotesKali MuthuNo ratings yet
- Fabric Terms and Woven Prepartory Process - Lecture 2Document24 pagesFabric Terms and Woven Prepartory Process - Lecture 2Shresha DasNo ratings yet
- Lab Manual: Fabric Structure and DesignDocument19 pagesLab Manual: Fabric Structure and DesignZillur Rahman SaykatNo ratings yet
- Weft Knitting .1Document16 pagesWeft Knitting .1Mina Samy abd el zaherNo ratings yet
- Complete Book of Sewing Techniques, New 2nd Edition: More Than 30 Essential Sewing Techniques for You to MasterFrom EverandComplete Book of Sewing Techniques, New 2nd Edition: More Than 30 Essential Sewing Techniques for You to MasterRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (3)
- BSL PrintDocument62 pagesBSL Printrishi100% (1)
- 1 Complete Weaving MillDocument6 pages1 Complete Weaving MillKomol KabirNo ratings yet
- Bài Tập Tiếng Anh 9 Mới Theo Unit - giasuvina.com.VnDocument81 pagesBài Tập Tiếng Anh 9 Mới Theo Unit - giasuvina.com.VnNguyễn Thị Lệ ThiNo ratings yet
- Lab 1Document4 pagesLab 1Mujahid MehdiNo ratings yet
- The Cultural Economy: Globalization and Crafts in South AsiaDocument7 pagesThe Cultural Economy: Globalization and Crafts in South AsiaQuan DoanNo ratings yet
- q3 Lc2 Visual ArtsDocument13 pagesq3 Lc2 Visual ArtsGEMINO JIM MONTERONANo ratings yet
- Stash Buster - CaterpillarDocument1 pageStash Buster - CaterpillarSuzanne Yates Byford100% (1)
- wvg5 PDFDocument28 pageswvg5 PDFKing KishanNo ratings yet
- Tuần 13 - Anh 9Document15 pagesTuần 13 - Anh 9Đức MinhNo ratings yet
- Harpar Group Profile New IntDocument38 pagesHarpar Group Profile New IntKrishnaRajaNo ratings yet
- Mapeh 7 q1 - Week 3 (Arts)Document7 pagesMapeh 7 q1 - Week 3 (Arts)joel cagaananNo ratings yet
- Picanol: Industrial Machinery and Heavy EquipmentDocument5 pagesPicanol: Industrial Machinery and Heavy EquipmentbrufpotNo ratings yet
- First Grading Period Lesson 1: Fabric/Fabric Design ThailandDocument11 pagesFirst Grading Period Lesson 1: Fabric/Fabric Design ThailandShane HernandezNo ratings yet
- Silk Weaving - KanchipuramDocument31 pagesSilk Weaving - KanchipuramananyaNo ratings yet
- Almohada Harry PotterDocument11 pagesAlmohada Harry PotterMaría Montilla100% (1)
- Lesson Plan Grade 8 Arts June 7, 13, and 20Document3 pagesLesson Plan Grade 8 Arts June 7, 13, and 20Glaisa D. LanoNo ratings yet
- Basic WeaveDocument34 pagesBasic Weavejennygraceshalini100% (4)
- Shop Tangaliya & PatolaDocument4 pagesShop Tangaliya & PatolaEkta AroraNo ratings yet
- Kanchipuram Product TrainingDocument38 pagesKanchipuram Product TrainingApoorva NatrajNo ratings yet
- Siyarams RoughDocument38 pagesSiyarams RoughASHISH BHUWANIANo ratings yet
- AlvinT Price List 2016 - IDR - Okt2016 PDFDocument5 pagesAlvinT Price List 2016 - IDR - Okt2016 PDFDavid Epson Mayer0% (1)
- Chapter OneDocument35 pagesChapter OneHamzaNo ratings yet
- Impact On Indian Econmy - Ignou NotesDocument13 pagesImpact On Indian Econmy - Ignou NotesVANSHIKA CHAUDHARYNo ratings yet
- Case Summary KhawajaDocument2 pagesCase Summary KhawajakhawajaNo ratings yet
- 'BEBE CON GORRO' ContigoDocument26 pages'BEBE CON GORRO' ContigoGi Torres67% (6)
- Lesson Plan CH 4 Class 8Document11 pagesLesson Plan CH 4 Class 8preetichughduNo ratings yet
- HRP AssignmentDocument11 pagesHRP AssignmentSreeram BaddilaNo ratings yet