Professional Documents
Culture Documents
6582e741d388fa0018c74962_##_Kinetic Theory of Gases Mind Maps
6582e741d388fa0018c74962_##_Kinetic Theory of Gases Mind Maps
Uploaded by
n9134152Copyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Homework 3Document2 pagesHomework 3apple832100No ratings yet
- Amath Binomial TheoremDocument10 pagesAmath Binomial TheoremshannonNo ratings yet
- 65601a476c0a0100185f2bbc ## Dual Nature of Radiation & Matter MindDocument1 page65601a476c0a0100185f2bbc ## Dual Nature of Radiation & Matter MindprincipaltamannaNo ratings yet
- Dual Nature of Matter & Radiation - Mind Maps - Lakshya JEE 2024Document1 pageDual Nature of Matter & Radiation - Mind Maps - Lakshya JEE 2024xoranek474No ratings yet
- Assignment 2Document3 pagesAssignment 2forgamesforgames7No ratings yet
- Kinetic Theory of GasesDocument1 pageKinetic Theory of GasesJawad AzizNo ratings yet
- Untitled NotebookDocument1 pageUntitled Notebookapareshbera725No ratings yet
- Ce226 Q6 Corpuz J 3cegDocument12 pagesCe226 Q6 Corpuz J 3cegJermaine CorpuzNo ratings yet
- 05 - 15 Note - DA, CordicDocument2 pages05 - 15 Note - DA, Cordic洪恩欽No ratings yet
- Bonus Assignment 3Document1 pageBonus Assignment 3Arundhati GuptaNo ratings yet
- Álgebra 6Document1 pageÁlgebra 6PaulaNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding and Molecular StructureDocument10 pagesChemical Bonding and Molecular Structureshivammalik467xNo ratings yet
- 11ไฟฟ้าสถิตDocument10 pages11ไฟฟ้าสถิตtim846gNo ratings yet
- Physics Constants and CoefficientsDocument1 pagePhysics Constants and Coefficientslakshya singhalNo ratings yet
- Physics Constants and Coefficients 2Document1 pagePhysics Constants and Coefficients 2prvmahurkarNo ratings yet
- Física 3Document11 pagesFísica 3isadorabettiNo ratings yet
- Tutoring Termo Ujian 5Document3 pagesTutoring Termo Ujian 5hilmi abyanNo ratings yet
- Tarea 3.1Document3 pagesTarea 3.1maria pazNo ratings yet
- Vectors DTS 7Document2 pagesVectors DTS 7every1 calls me meera DcNo ratings yet
- Physical Chemistry Formula (2) 3Document6 pagesPhysical Chemistry Formula (2) 3Anand RockyNo ratings yet
- Problemes Contingut 3Document1 pageProblemes Contingut 3enricguiotcosta04No ratings yet
- Đề Thi HK1 Ams 2022-2023Document4 pagesĐề Thi HK1 Ams 2022-2023AlaskaNo ratings yet
- Dynamics of A Particle DTS-7Document2 pagesDynamics of A Particle DTS-7Privacy 01No ratings yet
- CH 2Document9 pagesCH 2jamalyyy111No ratings yet
- Sp2019-MAS-I Super Messy Preliminary HandWritten Solutions 2019-08-09 PDFDocument45 pagesSp2019-MAS-I Super Messy Preliminary HandWritten Solutions 2019-08-09 PDFUngoliant101No ratings yet
- Chapter 22Document19 pagesChapter 22Ali AlhammadiNo ratings yet
- Dimensi Tiga JugaDocument8 pagesDimensi Tiga JugaDavina AlmaNo ratings yet
- Emanating: BroglieDocument5 pagesEmanating: BroglieGourav SinghNo ratings yet
- Mai Nhat Thong - BTVN 03Document5 pagesMai Nhat Thong - BTVN 03THÔNG MAI NHẬTNo ratings yet
- Wind Power Part 4Document10 pagesWind Power Part 4ttNo ratings yet
- EllipsesDocument1 pageEllipsesMastermsyNo ratings yet
- PC SB 7.4 (F) The Tangent Function (pp.40-42) 2Document7 pagesPC SB 7.4 (F) The Tangent Function (pp.40-42) 2failuremanagement.hku.hkNo ratings yet
- B1 ElectrostaticsDocument1 pageB1 Electrostaticsdarkgaemer47No ratings yet
- ASEN 4013 - Exam 1: Section 3: Compressible FlowDocument2 pagesASEN 4013 - Exam 1: Section 3: Compressible FlowJacob WeinerNo ratings yet
- Unit Test 1Document2 pagesUnit Test 1Ykhay ElfanteNo ratings yet
- Linear Equations9Document21 pagesLinear Equations9Aaryan AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Assignment 5 FM Intan Nur Haslinda 18001912Document14 pagesAssignment 5 FM Intan Nur Haslinda 18001912Intan NurhaslindaNo ratings yet
- Correl 2 Hge NotesDocument21 pagesCorrel 2 Hge Notesromelio salumbidesNo ratings yet
- Ex - 7-3 Front 6230407121Document1 pageEx - 7-3 Front 6230407121pao14082543No ratings yet
- Go ThroughDocument3 pagesGo ThroughlavanyaNo ratings yet
- SYDE 113 Lecture 3Document6 pagesSYDE 113 Lecture 3bobpatel1379No ratings yet
- Gericke 2002Document4 pagesGericke 2002LuisggscNo ratings yet
- Pretestare 2024Document6 pagesPretestare 2024mihailzghibarta74No ratings yet
- TD 4 Experimental Base of Quantum TheoryDocument15 pagesTD 4 Experimental Base of Quantum TheoryusaroufNo ratings yet
- Problemario Primera Ley de Sistemas Abiertos de Flujo No EstacionarioDocument2 pagesProblemario Primera Ley de Sistemas Abiertos de Flujo No EstacionarioRulis DCNo ratings yet
- 學會學數學hw8Document1 page學會學數學hw8janechangymcaNo ratings yet
- Ass KeysDocument3 pagesAss KeysSuDheer KumarNo ratings yet
- Meditatii 10 Iunie 2024Document18 pagesMeditatii 10 Iunie 2024Claudia ArdeleanNo ratings yet
- S ALjg T0 CH 9 H32 QM HPJ KCDocument2 pagesS ALjg T0 CH 9 H32 QM HPJ KCYash KapoorNo ratings yet
- Incidence Map 102221Document1 pageIncidence Map 102221Debbie HarbsmeierNo ratings yet
- Periodic Properties - UADocument4 pagesPeriodic Properties - UAtechnicalfacts31No ratings yet
- Question Paper of July MonthDocument19 pagesQuestion Paper of July MonthAvijeet kumar MishraNo ratings yet
- Formula + MockDocument2 pagesFormula + MockaspectrektyouNo ratings yet
- Trigo Question VT Sir 1 (@HeyitsyashXD)Document11 pagesTrigo Question VT Sir 1 (@HeyitsyashXD)PiyushNo ratings yet
- Heat ConductionDocument12 pagesHeat ConductionNuttibase CharupengNo ratings yet
- 2020 2Document41 pages2020 2Amanda PerinNo ratings yet
- Trigonometry NotesDocument4 pagesTrigonometry NoteschexNo ratings yet
- Incidence Map 07082021Document1 pageIncidence Map 07082021Debbie HarbsmeierNo ratings yet
- Red Zone Map 10/19/21Document1 pageRed Zone Map 10/19/21Bryce ShreveNo ratings yet
- 2 Puc 18 TH Group Elements QPDocument3 pages2 Puc 18 TH Group Elements QPGowri ShankarNo ratings yet
- 1 Type of Flow: 1.1 Wider SectionDocument3 pages1 Type of Flow: 1.1 Wider SectionBrendan LimNo ratings yet
- Che2060 Vsepr Geometry Ws KeyDocument5 pagesChe2060 Vsepr Geometry Ws Keyqvcws4h5spNo ratings yet
- 9002-0057-01 - Process P&ID Unit A-ModelDocument1 page9002-0057-01 - Process P&ID Unit A-ModelLavinia DamianNo ratings yet
- MT Ii - HW 1Document1 pageMT Ii - HW 1Omkar RoyNo ratings yet
- Translate 2.6.3 - Determination of Z-FactorDocument2 pagesTranslate 2.6.3 - Determination of Z-FactorelaNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics - IDocument50 pagesFluid Mechanics - ISWAGATAM BAZNo ratings yet
- Gas CylinderDocument5 pagesGas CylinderAnonymous du4yYem5No ratings yet
- Properties of FluidDocument71 pagesProperties of FluidNur Syatiera Alisha Binti SaffrizanNo ratings yet
- Solution Manual Gas Dynamics 3rd Edition James E.A. John Theo G. KeithDocument10 pagesSolution Manual Gas Dynamics 3rd Edition James E.A. John Theo G. KeithPatnala Susmitha ae17b012No ratings yet
- Omega Air - O-GenDocument2 pagesOmega Air - O-GenLinh TrọngNo ratings yet
- Viscometer and Oil Standard BrochureDocument2 pagesViscometer and Oil Standard BrochureNam NguyenNo ratings yet
- AP Physics 2 Solid and FluidDocument1 pageAP Physics 2 Solid and FluidChoy DanNo ratings yet
- Sahara Air Products - Sahara-Pak Model HC Theory of Operation and SpecificationsDocument2 pagesSahara Air Products - Sahara-Pak Model HC Theory of Operation and SpecificationsAdriano CostaNo ratings yet
- Lab ManualDocument46 pagesLab ManualAizaz HabibNo ratings yet
- RayLeigh NumberDocument3 pagesRayLeigh Numberaleksandar_djordjicNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 DryingDocument71 pagesUnit 3 Dryingpooja wawareNo ratings yet
- Power Productions Quiz - 2 Steam TableDocument4 pagesPower Productions Quiz - 2 Steam TableDar QuetzalNo ratings yet
- PIMS BlendingDocument47 pagesPIMS BlendingOwais HussainNo ratings yet
- Fci Tuv Nel v3Document17 pagesFci Tuv Nel v3Reza GhanavatiNo ratings yet
- Flat Plate: Convective Mass Transfer CorrelationDocument83 pagesFlat Plate: Convective Mass Transfer CorrelationMriganabh SarmaNo ratings yet
- Design Manual SPD0005EIE: Samsung Engineering Co., LTDDocument10 pagesDesign Manual SPD0005EIE: Samsung Engineering Co., LTDchuntao fengNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1Document45 pagesLesson 1Bethwaine VicenteNo ratings yet
- Lesson Objective Lesson PlanDocument8 pagesLesson Objective Lesson PlanJennielyn de VeraNo ratings yet
- Chlorodifluoromethane (R22), CHClF2, Physical Properties, Safety, MSDS, Enthalpy, Material Compatibility, Gas Liquid Equilibrium, Density, Viscosity, Flammability, Transport PropertiesDocument4 pagesChlorodifluoromethane (R22), CHClF2, Physical Properties, Safety, MSDS, Enthalpy, Material Compatibility, Gas Liquid Equilibrium, Density, Viscosity, Flammability, Transport PropertiesRavi VikneshNo ratings yet
- BET TheoryDocument4 pagesBET TheoryUmar SyaidNo ratings yet
- Procedure For Condenser Vacuum PullingDocument4 pagesProcedure For Condenser Vacuum PullingPulkit Agarwal100% (1)
- Perrys Chemical Engineering Handbook-Halaman-132-134 PDFDocument3 pagesPerrys Chemical Engineering Handbook-Halaman-132-134 PDFJuana HizkiaNo ratings yet
- Boiling and Condensation ProblemsDocument24 pagesBoiling and Condensation Problemskeerthi srijithNo ratings yet
- Training Papers Distillation With A Rotary Evaporator: Imlab Oude Vijvers 1 B-3370 BoutersemDocument16 pagesTraining Papers Distillation With A Rotary Evaporator: Imlab Oude Vijvers 1 B-3370 BoutersemBogdan NechitaNo ratings yet
6582e741d388fa0018c74962_##_Kinetic Theory of Gases Mind Maps
6582e741d388fa0018c74962_##_Kinetic Theory of Gases Mind Maps
Uploaded by
n9134152Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
6582e741d388fa0018c74962_##_Kinetic Theory of Gases Mind Maps
6582e741d388fa0018c74962_##_Kinetic Theory of Gases Mind Maps
Uploaded by
n9134152Copyright:
Available Formats
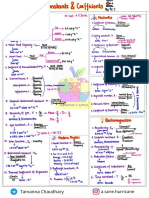
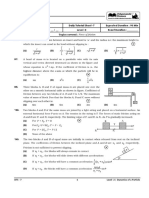
01 02 03 LAW OF EQUIPARTITION OF ENERGY
DEGREES OF FREEDOM SPECIFIC HEAT CAPACITY MIXING OF GASES 1 K T
Energy for each molecule per f =-
2 B
CP − C V = R n1cv + n2cv +...... f
a) Total energy for molecule = -KB T
. For monoatomic gas, f =3 CVmix = 1 2 2
. For diatomic gas, CP − C V = R n 1+ n 2 3
KINETIC THEORY OF GASES
b)
- Mono- = -
5 +...... Monoatomic Molecule = -KB T
M
(specific heat 3 2
(a) at room temperature, f = 5 per unit mask)
n1cP + n2cP +......
f
Total energy for a mole= -R T
7 2
(b) at high temperature, R f Dia- = -
5
CPmix = 1 2
f = 7 c) C =- =- R
n1+ n2 +...... Total energy for n moles=nfRT
V -1 2 4 2
Tri- = - 3
For triatomic gas, 3 Monoatomic=-R T
(a) Linear f= 5 d) C
R
=- = 1+ -
f R
( 2) CP mix (1 mole) 2
-1
= 5
P
mix Diatomic= -R T
(b) Non-linear f= 6
e) =
CP
= 1 +-
2 CV mix (1 mole) 2
For each vibrational mode, f = 2 Cv Translatory Kinetic energy=-R T
3
f
(1 mole, f= 3)
2
Q3
Ideal gas is composed of polyatomic If CP and Cv denote the specific heats
Q1 Q2
Consider a mixture of n moles of helium gas and
Q4
A gas mixture consists of 2 moles of 02 and 4 moles
molecule that has 4 vibrational modes. of unit mass of nitrogen at constant pressure 2n moles of oxygen gas (molecules taken to be rigid) of Ar at temperature T. Neglecting all vibrational
and volume respectively, then as an ideal gas. It‛s Cp/CV value will be: modes, the total internal energy of the system is
Total degrees of freedom is
R R R
a) 12 b) 14 c) 8 d) 6 a) CP-CV= b) CP-CV= c) CP-CV= d) C -CV= R a) 19/13 b) 67/45 c) 40/27 d) 23/15 a) 4RT b) 15RT c) 9RT d) 11RT
28 14 7 P
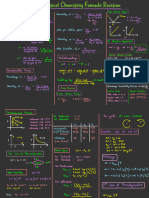
VELOCITY OF GAS
06 05
Root Mean Average Speed: Most probable FIRST LAW OF
square speed: speed: Vmp :Vavg:Vrms = 1 : 1.13 : 1.225 THERMODYNAMICS
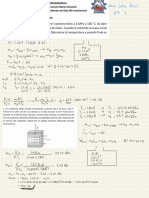
Arithmetic mean of speed of QP= U + W
07
U= ncv T
Square root of mean of square Speed possessed by maximum
molecules of gas at given
of speeds of different molecules, number of molecules of gas.
temperature.
vrms = v1 + v2 +............... + vn
W = Pdv
2 2 2
2RT 2P 2 kBT
n
v avg = I v1 I + I v2 I + ....... + I vnI vmp = =
ρ =
n M m
U
vrms =
3RT
=
3P
=
3kBT
v avg = 8RT = 8P MEAN FREE PATH = 1
M ρ m
πM πρ QP
Average distance travelled by
W
molecules between two
successive collisions
1 = 1- 1
1
d2 QP
λ mean = 1
2 πd n
2
Consider a gas of triatomic molecules. The molecules
are assumed to be triangular, made up of massless rigid
The rms speeds of the molecules of Hydrogen,
The mean free path of molecules of gas, r2
Oxygen & Carbon dioxide at the same temparature
Q5 Q6
rods whose vertices are occupied by atoms.The internal are VH, VO and Vc respectively, then: (radius r) is inversely proportional to d = diameter of molecules. T
energy of a mole of the gas at temperature T is:
a) r3 b) r2 n = no. of molecules per P
a) VH >VO>VC b) VC >VO>VH
a)
5
RT b)
3
RT c)
9
RT d) 3RT unit volume
2 2 2
c) VH =VO>VC d) VH =VO=VC c) r d) r
1 -
IDEAL PV=nRT
GAY PV
2
mn Vrms mn v 2 GAS
PRESSURE R=8.314 JK-1mol-1
BOYLE’S CHARLE’S LUSSAC’S P P/T
OF GAS 3 LAW
LAW
PV V V/T
LAW LAW
V
T V
T P
ρ
Relation between pressure
P
. PV = constant, if T =Constant . V α T; v = constant; P = constant.
. P α T; = constant; V = constant. and Kinetic Energy.
T T
3
. P 1V1 = P2V2 ,when gas changes it‛s . v 1 = v 2 ,when gas change its state . P1 =
P2 , when gas changes its state E = PV
state under constant T1 T2 under constant pressure. T1 T2 under constant Volume. 2
temperature.
Specific heat of Solids = 3R
WATER = 9R
You might also like
- Homework 3Document2 pagesHomework 3apple832100No ratings yet
- Amath Binomial TheoremDocument10 pagesAmath Binomial TheoremshannonNo ratings yet
- 65601a476c0a0100185f2bbc ## Dual Nature of Radiation & Matter MindDocument1 page65601a476c0a0100185f2bbc ## Dual Nature of Radiation & Matter MindprincipaltamannaNo ratings yet
- Dual Nature of Matter & Radiation - Mind Maps - Lakshya JEE 2024Document1 pageDual Nature of Matter & Radiation - Mind Maps - Lakshya JEE 2024xoranek474No ratings yet
- Assignment 2Document3 pagesAssignment 2forgamesforgames7No ratings yet
- Kinetic Theory of GasesDocument1 pageKinetic Theory of GasesJawad AzizNo ratings yet
- Untitled NotebookDocument1 pageUntitled Notebookapareshbera725No ratings yet
- Ce226 Q6 Corpuz J 3cegDocument12 pagesCe226 Q6 Corpuz J 3cegJermaine CorpuzNo ratings yet
- 05 - 15 Note - DA, CordicDocument2 pages05 - 15 Note - DA, Cordic洪恩欽No ratings yet
- Bonus Assignment 3Document1 pageBonus Assignment 3Arundhati GuptaNo ratings yet
- Álgebra 6Document1 pageÁlgebra 6PaulaNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding and Molecular StructureDocument10 pagesChemical Bonding and Molecular Structureshivammalik467xNo ratings yet
- 11ไฟฟ้าสถิตDocument10 pages11ไฟฟ้าสถิตtim846gNo ratings yet
- Physics Constants and CoefficientsDocument1 pagePhysics Constants and Coefficientslakshya singhalNo ratings yet
- Physics Constants and Coefficients 2Document1 pagePhysics Constants and Coefficients 2prvmahurkarNo ratings yet
- Física 3Document11 pagesFísica 3isadorabettiNo ratings yet
- Tutoring Termo Ujian 5Document3 pagesTutoring Termo Ujian 5hilmi abyanNo ratings yet
- Tarea 3.1Document3 pagesTarea 3.1maria pazNo ratings yet
- Vectors DTS 7Document2 pagesVectors DTS 7every1 calls me meera DcNo ratings yet
- Physical Chemistry Formula (2) 3Document6 pagesPhysical Chemistry Formula (2) 3Anand RockyNo ratings yet
- Problemes Contingut 3Document1 pageProblemes Contingut 3enricguiotcosta04No ratings yet
- Đề Thi HK1 Ams 2022-2023Document4 pagesĐề Thi HK1 Ams 2022-2023AlaskaNo ratings yet
- Dynamics of A Particle DTS-7Document2 pagesDynamics of A Particle DTS-7Privacy 01No ratings yet
- CH 2Document9 pagesCH 2jamalyyy111No ratings yet
- Sp2019-MAS-I Super Messy Preliminary HandWritten Solutions 2019-08-09 PDFDocument45 pagesSp2019-MAS-I Super Messy Preliminary HandWritten Solutions 2019-08-09 PDFUngoliant101No ratings yet
- Chapter 22Document19 pagesChapter 22Ali AlhammadiNo ratings yet
- Dimensi Tiga JugaDocument8 pagesDimensi Tiga JugaDavina AlmaNo ratings yet
- Emanating: BroglieDocument5 pagesEmanating: BroglieGourav SinghNo ratings yet
- Mai Nhat Thong - BTVN 03Document5 pagesMai Nhat Thong - BTVN 03THÔNG MAI NHẬTNo ratings yet
- Wind Power Part 4Document10 pagesWind Power Part 4ttNo ratings yet
- EllipsesDocument1 pageEllipsesMastermsyNo ratings yet
- PC SB 7.4 (F) The Tangent Function (pp.40-42) 2Document7 pagesPC SB 7.4 (F) The Tangent Function (pp.40-42) 2failuremanagement.hku.hkNo ratings yet
- B1 ElectrostaticsDocument1 pageB1 Electrostaticsdarkgaemer47No ratings yet
- ASEN 4013 - Exam 1: Section 3: Compressible FlowDocument2 pagesASEN 4013 - Exam 1: Section 3: Compressible FlowJacob WeinerNo ratings yet
- Unit Test 1Document2 pagesUnit Test 1Ykhay ElfanteNo ratings yet
- Linear Equations9Document21 pagesLinear Equations9Aaryan AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Assignment 5 FM Intan Nur Haslinda 18001912Document14 pagesAssignment 5 FM Intan Nur Haslinda 18001912Intan NurhaslindaNo ratings yet
- Correl 2 Hge NotesDocument21 pagesCorrel 2 Hge Notesromelio salumbidesNo ratings yet
- Ex - 7-3 Front 6230407121Document1 pageEx - 7-3 Front 6230407121pao14082543No ratings yet
- Go ThroughDocument3 pagesGo ThroughlavanyaNo ratings yet
- SYDE 113 Lecture 3Document6 pagesSYDE 113 Lecture 3bobpatel1379No ratings yet
- Gericke 2002Document4 pagesGericke 2002LuisggscNo ratings yet
- Pretestare 2024Document6 pagesPretestare 2024mihailzghibarta74No ratings yet
- TD 4 Experimental Base of Quantum TheoryDocument15 pagesTD 4 Experimental Base of Quantum TheoryusaroufNo ratings yet
- Problemario Primera Ley de Sistemas Abiertos de Flujo No EstacionarioDocument2 pagesProblemario Primera Ley de Sistemas Abiertos de Flujo No EstacionarioRulis DCNo ratings yet
- 學會學數學hw8Document1 page學會學數學hw8janechangymcaNo ratings yet
- Ass KeysDocument3 pagesAss KeysSuDheer KumarNo ratings yet
- Meditatii 10 Iunie 2024Document18 pagesMeditatii 10 Iunie 2024Claudia ArdeleanNo ratings yet
- S ALjg T0 CH 9 H32 QM HPJ KCDocument2 pagesS ALjg T0 CH 9 H32 QM HPJ KCYash KapoorNo ratings yet
- Incidence Map 102221Document1 pageIncidence Map 102221Debbie HarbsmeierNo ratings yet
- Periodic Properties - UADocument4 pagesPeriodic Properties - UAtechnicalfacts31No ratings yet
- Question Paper of July MonthDocument19 pagesQuestion Paper of July MonthAvijeet kumar MishraNo ratings yet
- Formula + MockDocument2 pagesFormula + MockaspectrektyouNo ratings yet
- Trigo Question VT Sir 1 (@HeyitsyashXD)Document11 pagesTrigo Question VT Sir 1 (@HeyitsyashXD)PiyushNo ratings yet
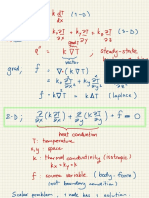
- Heat ConductionDocument12 pagesHeat ConductionNuttibase CharupengNo ratings yet
- 2020 2Document41 pages2020 2Amanda PerinNo ratings yet
- Trigonometry NotesDocument4 pagesTrigonometry NoteschexNo ratings yet
- Incidence Map 07082021Document1 pageIncidence Map 07082021Debbie HarbsmeierNo ratings yet
- Red Zone Map 10/19/21Document1 pageRed Zone Map 10/19/21Bryce ShreveNo ratings yet
- 2 Puc 18 TH Group Elements QPDocument3 pages2 Puc 18 TH Group Elements QPGowri ShankarNo ratings yet
- 1 Type of Flow: 1.1 Wider SectionDocument3 pages1 Type of Flow: 1.1 Wider SectionBrendan LimNo ratings yet
- Che2060 Vsepr Geometry Ws KeyDocument5 pagesChe2060 Vsepr Geometry Ws Keyqvcws4h5spNo ratings yet
- 9002-0057-01 - Process P&ID Unit A-ModelDocument1 page9002-0057-01 - Process P&ID Unit A-ModelLavinia DamianNo ratings yet
- MT Ii - HW 1Document1 pageMT Ii - HW 1Omkar RoyNo ratings yet
- Translate 2.6.3 - Determination of Z-FactorDocument2 pagesTranslate 2.6.3 - Determination of Z-FactorelaNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics - IDocument50 pagesFluid Mechanics - ISWAGATAM BAZNo ratings yet
- Gas CylinderDocument5 pagesGas CylinderAnonymous du4yYem5No ratings yet
- Properties of FluidDocument71 pagesProperties of FluidNur Syatiera Alisha Binti SaffrizanNo ratings yet
- Solution Manual Gas Dynamics 3rd Edition James E.A. John Theo G. KeithDocument10 pagesSolution Manual Gas Dynamics 3rd Edition James E.A. John Theo G. KeithPatnala Susmitha ae17b012No ratings yet
- Omega Air - O-GenDocument2 pagesOmega Air - O-GenLinh TrọngNo ratings yet
- Viscometer and Oil Standard BrochureDocument2 pagesViscometer and Oil Standard BrochureNam NguyenNo ratings yet
- AP Physics 2 Solid and FluidDocument1 pageAP Physics 2 Solid and FluidChoy DanNo ratings yet
- Sahara Air Products - Sahara-Pak Model HC Theory of Operation and SpecificationsDocument2 pagesSahara Air Products - Sahara-Pak Model HC Theory of Operation and SpecificationsAdriano CostaNo ratings yet
- Lab ManualDocument46 pagesLab ManualAizaz HabibNo ratings yet
- RayLeigh NumberDocument3 pagesRayLeigh Numberaleksandar_djordjicNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 DryingDocument71 pagesUnit 3 Dryingpooja wawareNo ratings yet
- Power Productions Quiz - 2 Steam TableDocument4 pagesPower Productions Quiz - 2 Steam TableDar QuetzalNo ratings yet
- PIMS BlendingDocument47 pagesPIMS BlendingOwais HussainNo ratings yet
- Fci Tuv Nel v3Document17 pagesFci Tuv Nel v3Reza GhanavatiNo ratings yet
- Flat Plate: Convective Mass Transfer CorrelationDocument83 pagesFlat Plate: Convective Mass Transfer CorrelationMriganabh SarmaNo ratings yet
- Design Manual SPD0005EIE: Samsung Engineering Co., LTDDocument10 pagesDesign Manual SPD0005EIE: Samsung Engineering Co., LTDchuntao fengNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1Document45 pagesLesson 1Bethwaine VicenteNo ratings yet
- Lesson Objective Lesson PlanDocument8 pagesLesson Objective Lesson PlanJennielyn de VeraNo ratings yet
- Chlorodifluoromethane (R22), CHClF2, Physical Properties, Safety, MSDS, Enthalpy, Material Compatibility, Gas Liquid Equilibrium, Density, Viscosity, Flammability, Transport PropertiesDocument4 pagesChlorodifluoromethane (R22), CHClF2, Physical Properties, Safety, MSDS, Enthalpy, Material Compatibility, Gas Liquid Equilibrium, Density, Viscosity, Flammability, Transport PropertiesRavi VikneshNo ratings yet
- BET TheoryDocument4 pagesBET TheoryUmar SyaidNo ratings yet
- Procedure For Condenser Vacuum PullingDocument4 pagesProcedure For Condenser Vacuum PullingPulkit Agarwal100% (1)
- Perrys Chemical Engineering Handbook-Halaman-132-134 PDFDocument3 pagesPerrys Chemical Engineering Handbook-Halaman-132-134 PDFJuana HizkiaNo ratings yet
- Boiling and Condensation ProblemsDocument24 pagesBoiling and Condensation Problemskeerthi srijithNo ratings yet
- Training Papers Distillation With A Rotary Evaporator: Imlab Oude Vijvers 1 B-3370 BoutersemDocument16 pagesTraining Papers Distillation With A Rotary Evaporator: Imlab Oude Vijvers 1 B-3370 BoutersemBogdan NechitaNo ratings yet