Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Sewage Treatment
Sewage Treatment
Uploaded by
nehashivani2003Copyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Water-Purification 7471604 PowerpointDocument24 pagesWater-Purification 7471604 Powerpointramniwas mahoreNo ratings yet
- ItemDocument13 pagesItemRedw AnNo ratings yet
- Subject: Public Health EngineeringDocument16 pagesSubject: Public Health EngineeringBhavesh ShelawaleNo ratings yet
- Sewage-Treatment 2Document32 pagesSewage-Treatment 2muyisco EmmaNo ratings yet
- SewageDocument34 pagesSewageMongolian MutuNo ratings yet
- Treatment of Waste WaterDocument4 pagesTreatment of Waste WaterDibyakNo ratings yet
- Air Water PollutionDocument79 pagesAir Water PollutionÅyìshą RəəmNo ratings yet
- Sewage-Fed AquacultureDocument15 pagesSewage-Fed Aquacultureapi-3803371100% (2)
- Sewagetreatment1 130927055820 Phpapp01Document56 pagesSewagetreatment1 130927055820 Phpapp01Divakar MauryaNo ratings yet
- Water Treatment PlantDocument4 pagesWater Treatment PlantVaishali SinghNo ratings yet
- Modern Sewage TreatmentDocument2 pagesModern Sewage TreatmentZothan Puia100% (1)
- Sewae Purification and DisposalDocument26 pagesSewae Purification and DisposaldhruvNo ratings yet
- Main UASB ReactorDocument23 pagesMain UASB ReactorsasisNo ratings yet
- Sanitaire Filtration and SterilazitionDocument3 pagesSanitaire Filtration and Sterilazitiondeath armyNo ratings yet
- Lecture 6 - Waste Water Treatment MethodsDocument45 pagesLecture 6 - Waste Water Treatment MethodsHamza RiazNo ratings yet
- Sewage TreatmentDocument38 pagesSewage TreatmentBernard Ting Yiew Sing100% (1)
- Lesson 5 ReviewerDocument5 pagesLesson 5 ReviewerAlison Ace AbantasNo ratings yet
- Sewage Treatment PlantDocument34 pagesSewage Treatment PlantAthi MNo ratings yet
- Sewage TreatmentDocument13 pagesSewage Treatmentshazeen shoaibNo ratings yet
- MCB 403 Group 13Document10 pagesMCB 403 Group 13ejohn8340No ratings yet
- Environmental LectureDocument56 pagesEnvironmental LectureDean Joyce AlborotoNo ratings yet
- Field Visit To Water Treatment Plant, NashikDocument6 pagesField Visit To Water Treatment Plant, NashikMarmik Javare100% (1)
- Ipal UmumDocument17 pagesIpal UmumDannysArifKusumaNo ratings yet
- Ene Report Ni KeiDocument34 pagesEne Report Ni KeiKaulayaw PormentoNo ratings yet
- Disposal of WastesDocument53 pagesDisposal of WastesPriya Sharma100% (1)
- Water PPT - Copy-1Document43 pagesWater PPT - Copy-1SAQIBPASHANo ratings yet
- Field Visit To Water Treatment Plant, AluvaDocument6 pagesField Visit To Water Treatment Plant, AluvaAdinathNo ratings yet
- Purification of WaterDocument38 pagesPurification of WaterSilver ShadowNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Dab 30102Document75 pagesChapter 3 Dab 30102Muhammad Fazlan AliffNo ratings yet
- Lecture 12 - Waste Water Treatment MethodsDocument41 pagesLecture 12 - Waste Water Treatment MethodsUsman KhalidNo ratings yet
- Overview of Wastewater TreatmentDocument34 pagesOverview of Wastewater TreatmentFitriaSukmawati100% (1)
- Sewage Treatment Plant: By: Abhishek Jat Aditi Singh Parihar Aishwarya & Akshay ShahDocument27 pagesSewage Treatment Plant: By: Abhishek Jat Aditi Singh Parihar Aishwarya & Akshay Shahbhobho100% (1)
- OXIDATION POND PresentationDocument15 pagesOXIDATION POND PresentationarinamahirahNo ratings yet
- Wastewater TreatmentDocument9 pagesWastewater TreatmentreymoreNo ratings yet
- IGNTU EContent 673390684976 B.SC EnvironmentalSciences 2 PallaviDas EnvironmentalPollutionandHumanHealth 3Document34 pagesIGNTU EContent 673390684976 B.SC EnvironmentalSciences 2 PallaviDas EnvironmentalPollutionandHumanHealth 3Riyasath ahamedNo ratings yet
- Assignment of Applied Chemistry-I: Topic: Sewage TreatmentDocument8 pagesAssignment of Applied Chemistry-I: Topic: Sewage TreatmentTAHIR SRKNo ratings yet
- Lect 2Document64 pagesLect 2Patricia Jayshree Samuel JacobNo ratings yet
- Water Purification Written ReportDocument10 pagesWater Purification Written ReportMenric LunarNo ratings yet
- Water Pollution For Environmental ScienceDocument21 pagesWater Pollution For Environmental Scienceobaid kuraishyNo ratings yet
- Wastewater Primary Treatment PDFDocument4 pagesWastewater Primary Treatment PDFEnrique MartinezNo ratings yet
- BNR Process BendigoDocument6 pagesBNR Process Bendigobansa79No ratings yet
- Sewage Water TreatmentDocument8 pagesSewage Water Treatmentsivani rayavarapuNo ratings yet
- Aquaculture (Chapter 5 Lesson 2)Document27 pagesAquaculture (Chapter 5 Lesson 2)Juramae SuanNo ratings yet
- Sanitary Water ReportDocument9 pagesSanitary Water ReportSushil AchhamiNo ratings yet
- STP ReportDocument11 pagesSTP ReportNasrul100% (1)
- Pe Project Class 11Document19 pagesPe Project Class 11Kalp patniNo ratings yet
- Astewater Reatment Lant DesignDocument2 pagesAstewater Reatment Lant Designas3ateNo ratings yet
- Asifa P.A Lanscape PPT 2Document31 pagesAsifa P.A Lanscape PPT 2Asifa AseezNo ratings yet
- Technology Details (Description / Functions) Better Still If Photos, Visuals IncludedDocument12 pagesTechnology Details (Description / Functions) Better Still If Photos, Visuals IncludedShavin ChandNo ratings yet
- Waste Water TreatmentDocument28 pagesWaste Water TreatmentRoseNavyaNo ratings yet
- Microproject in CssDocument6 pagesMicroproject in CsssalapeshivaniNo ratings yet
- Excreta DisposalDocument20 pagesExcreta DisposalRahul Netragaonkar75% (4)
- Field Visit To Water Treatment Plant, AluvaDocument6 pagesField Visit To Water Treatment Plant, Aluvanaimdangre869No ratings yet
- Environmental Science and EngineeringDocument4 pagesEnvironmental Science and Engineeringmenma JintanNo ratings yet
- Lecture - 3 - Wastewater Treatment - Aerobic and Anaerobic-1Document11 pagesLecture - 3 - Wastewater Treatment - Aerobic and Anaerobic-1negaathanipalanisamyNo ratings yet
- Metode Pengelolaan Air LimbahDocument3 pagesMetode Pengelolaan Air LimbahMuhammad AkbarNo ratings yet
- L-1 Natural Method of Sewage DisposalDocument62 pagesL-1 Natural Method of Sewage Disposalzubair k peerzadeNo ratings yet
- Presentation 1Document14 pagesPresentation 1HP2266No ratings yet
- Waste Water TreatmentDocument44 pagesWaste Water TreatmentSangeethika Madubashini T. Hettige100% (1)
- Water Pollution ControlFrom EverandWater Pollution ControlSuresh T. NesaratnamNo ratings yet
- Department of Civil Engineering: Don Honorio Ventura State UniversityDocument8 pagesDepartment of Civil Engineering: Don Honorio Ventura State Universityoblix.gaming12No ratings yet
- De Oliveira e Silva - Hendrick - 2016 - Pumped Hydro Energy Storage in BuildingsDocument9 pagesDe Oliveira e Silva - Hendrick - 2016 - Pumped Hydro Energy Storage in BuildingsJalcamNo ratings yet
- WaterDocument124 pagesWaterJessa Mae Manalo DavidNo ratings yet
- CEB601 Lab Report 6Document9 pagesCEB601 Lab Report 6divikesh kumarNo ratings yet
- Airport DrainageDocument68 pagesAirport DrainageAngelo Ros100% (1)
- Adisu SeminarDocument18 pagesAdisu SeminartmariamyididiyaNo ratings yet
- 6.water RecyclingDocument8 pages6.water RecyclingmariyaNo ratings yet
- Chapter FourDocument15 pagesChapter FourEphrem GizachewNo ratings yet
- Canal & Related StructuresDocument376 pagesCanal & Related StructuresEE MI NandyalNo ratings yet
- Sanjeev BaralDocument30 pagesSanjeev BaralPujan Bajracharya33% (3)
- Specifications of Ductile Iron Pipes and Carbon Steel Pipes-EnDocument3 pagesSpecifications of Ductile Iron Pipes and Carbon Steel Pipes-Endjrote4No ratings yet
- FSX-A Deluge Valve (Jan 2021)Document12 pagesFSX-A Deluge Valve (Jan 2021)Mohammed ElmakNo ratings yet
- Reverse Engineering and Automization of Atomized Nozzle For Water ConservationDocument100 pagesReverse Engineering and Automization of Atomized Nozzle For Water ConservationSaif UllahNo ratings yet
- Open Channel Flowmeter - UVH-2000Document4 pagesOpen Channel Flowmeter - UVH-2000Ferry YusufNo ratings yet
- Automatic Backwash Filter CatalogueDocument2 pagesAutomatic Backwash Filter CatalogueCarlos BarriosNo ratings yet
- cw822nj R1-SpecDocument1 pagecw822nj R1-Specswathisubramaniyan77No ratings yet
- Faecal Sludge Treatment Plant (FSTP) - LehDocument15 pagesFaecal Sludge Treatment Plant (FSTP) - LehShaun GeorgeNo ratings yet
- Kala Amb ValleyDocument3 pagesKala Amb ValleyShivani SoniNo ratings yet
- Boletin 161Document43 pagesBoletin 161jhonatanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 - Hydroelectric PowerDocument50 pagesChapter 4 - Hydroelectric PowerAdreana AmirahNo ratings yet
- Water ResourcesDocument21 pagesWater ResourcesJessalyn Joy ReforsadoNo ratings yet
- Nora LR Plots BrochureDocument26 pagesNora LR Plots Brochureapriliahasna20No ratings yet
- Erosion Control Plan Legend: Gabion Check Dam: Top of DitchDocument1 pageErosion Control Plan Legend: Gabion Check Dam: Top of Ditchshafiullah NaseriNo ratings yet
- Bye-Laws of SikkimDocument13 pagesBye-Laws of SikkimNelima Joshi100% (1)
- Class Project: Kothagudem Municipal Council Bhadradi DistrictDocument22 pagesClass Project: Kothagudem Municipal Council Bhadradi Districtabdul khaliqNo ratings yet
- Limnology (2+1)Document87 pagesLimnology (2+1)Haha HahaNo ratings yet
- CE Course DescriptionDocument13 pagesCE Course DescriptionAngelito AngelesNo ratings yet
- BIDAR Brochure 2012Document35 pagesBIDAR Brochure 2012maheshanischithaNo ratings yet
- HVAC CalcDocument16 pagesHVAC CalcHashimi JuniNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3 Water PollutionDocument4 pagesLesson 3 Water Pollutionjisas criesNo ratings yet
Sewage Treatment
Sewage Treatment
Uploaded by
nehashivani2003Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Sewage Treatment
Sewage Treatment
Uploaded by
nehashivani2003Copyright:
Available Formats
REPORT: VISIT TO SEWAGE TREATMENT PLANT
DATE OF VISIT: 24.02.24
LOCATION: SRINIVAS INSTITUTE OF MEDICAL SCIENCES
OBJECTIVE: To study the various units of sewage treatment plant and to know the processes
used to for the treatment.
INTRODUCTION:
Sewage is waste water from community containing solid and liquid excreta derived from
houses, street etc. Sewage contains 99.9% of water. The solid comprises of organic and
inorganic materials.
It includes physical, biological and chemical processes.
• PHYSICAL PROCESS: -
1. Preliminary physical process
2. Primary physical process
• BIOLOGICAL PROCESS: -
1. Anaerobic process
2. Aerobic process
3. Facultative process
• CHEMICAL PROCESS: -
Chlorination is done
UNITS IN SEWAGE TREATMENT PLANT:
1. INLET CHAMBER: includes the waste water from different areas
2. GRIT CHAMBER: contains organic and inorganic materials is removed
3. UPFLOW ANAEROBIC SLUDGE BLANKET (USAB) REACTOR: the collected water is then
distributed in the USAB Reactor.
4. AERATION TANK: Aims at bringing water in intimate contact with air. In this process of
aeration, oxygen is absorbed by water and carbon dioxide is liberated. It removes
hydrogen sulphide which removes the odour.
5. DRYING BED SLUDGE: Sludge is dried by spreading over the land. It is composed of 4
layers consisting of coarse gravel, fine gravel, sand.
AIM OF SEWAGE PURIFICATION:
1. Untreated sewage should not be discharged into rivers, sea etc.
2. The oxygen in water supply is used by aerobic bacteria found in the sewage,
which leads to the depletion of oxygen in water which leads to death of
animals and plants.
3. Stabilizes the organic matter.
MODERN SEWAGE TREATMENT:
• PRIMARY TREATMENT
1. SCREENING: First its passed through an metal screen, which interprets large
floating objects.
2. GRIT CHAMBER: Sewage is passed through grit chamber. Chamber allows the
settlement of heavier solids such as sand gravels.
3. PRIMARY SEDIMENTATION: It’s admitted to primary sedimentation tank.
Sewage is made to flow very slowly across the tank at a velocity of 1-2ft/min.
The sewage spends about 6-8 hours in the tank.
• SECONDARY TREATMENT
1. TRICKLING METHOD: It’s a bed of crushed stones. The effluent is sprinkled on
the surface of the bed. Effluent gets oxidized by zoological layer.
2. ACTIVATED SLUDGE PROCESS: Effluent is mixed with activated sludge. This
mixture is subjected to aeration in the aeration chamber for about 6-8 hours.
Organic matter oxidised co2, nitrates and water.
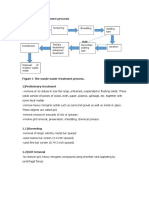
FLOW DIAGRAM OF VARIOUS TREATMENT UNITS IN STP:
CONCLUSION: From this we came to know more about the sewage treatment plant. The
principle behind it, design, parts and the processes.
You might also like
- Water-Purification 7471604 PowerpointDocument24 pagesWater-Purification 7471604 Powerpointramniwas mahoreNo ratings yet
- ItemDocument13 pagesItemRedw AnNo ratings yet
- Subject: Public Health EngineeringDocument16 pagesSubject: Public Health EngineeringBhavesh ShelawaleNo ratings yet
- Sewage-Treatment 2Document32 pagesSewage-Treatment 2muyisco EmmaNo ratings yet
- SewageDocument34 pagesSewageMongolian MutuNo ratings yet
- Treatment of Waste WaterDocument4 pagesTreatment of Waste WaterDibyakNo ratings yet
- Air Water PollutionDocument79 pagesAir Water PollutionÅyìshą RəəmNo ratings yet
- Sewage-Fed AquacultureDocument15 pagesSewage-Fed Aquacultureapi-3803371100% (2)
- Sewagetreatment1 130927055820 Phpapp01Document56 pagesSewagetreatment1 130927055820 Phpapp01Divakar MauryaNo ratings yet
- Water Treatment PlantDocument4 pagesWater Treatment PlantVaishali SinghNo ratings yet
- Modern Sewage TreatmentDocument2 pagesModern Sewage TreatmentZothan Puia100% (1)
- Sewae Purification and DisposalDocument26 pagesSewae Purification and DisposaldhruvNo ratings yet
- Main UASB ReactorDocument23 pagesMain UASB ReactorsasisNo ratings yet
- Sanitaire Filtration and SterilazitionDocument3 pagesSanitaire Filtration and Sterilazitiondeath armyNo ratings yet
- Lecture 6 - Waste Water Treatment MethodsDocument45 pagesLecture 6 - Waste Water Treatment MethodsHamza RiazNo ratings yet
- Sewage TreatmentDocument38 pagesSewage TreatmentBernard Ting Yiew Sing100% (1)
- Lesson 5 ReviewerDocument5 pagesLesson 5 ReviewerAlison Ace AbantasNo ratings yet
- Sewage Treatment PlantDocument34 pagesSewage Treatment PlantAthi MNo ratings yet
- Sewage TreatmentDocument13 pagesSewage Treatmentshazeen shoaibNo ratings yet
- MCB 403 Group 13Document10 pagesMCB 403 Group 13ejohn8340No ratings yet
- Environmental LectureDocument56 pagesEnvironmental LectureDean Joyce AlborotoNo ratings yet
- Field Visit To Water Treatment Plant, NashikDocument6 pagesField Visit To Water Treatment Plant, NashikMarmik Javare100% (1)
- Ipal UmumDocument17 pagesIpal UmumDannysArifKusumaNo ratings yet
- Ene Report Ni KeiDocument34 pagesEne Report Ni KeiKaulayaw PormentoNo ratings yet
- Disposal of WastesDocument53 pagesDisposal of WastesPriya Sharma100% (1)
- Water PPT - Copy-1Document43 pagesWater PPT - Copy-1SAQIBPASHANo ratings yet
- Field Visit To Water Treatment Plant, AluvaDocument6 pagesField Visit To Water Treatment Plant, AluvaAdinathNo ratings yet
- Purification of WaterDocument38 pagesPurification of WaterSilver ShadowNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Dab 30102Document75 pagesChapter 3 Dab 30102Muhammad Fazlan AliffNo ratings yet
- Lecture 12 - Waste Water Treatment MethodsDocument41 pagesLecture 12 - Waste Water Treatment MethodsUsman KhalidNo ratings yet
- Overview of Wastewater TreatmentDocument34 pagesOverview of Wastewater TreatmentFitriaSukmawati100% (1)
- Sewage Treatment Plant: By: Abhishek Jat Aditi Singh Parihar Aishwarya & Akshay ShahDocument27 pagesSewage Treatment Plant: By: Abhishek Jat Aditi Singh Parihar Aishwarya & Akshay Shahbhobho100% (1)
- OXIDATION POND PresentationDocument15 pagesOXIDATION POND PresentationarinamahirahNo ratings yet
- Wastewater TreatmentDocument9 pagesWastewater TreatmentreymoreNo ratings yet
- IGNTU EContent 673390684976 B.SC EnvironmentalSciences 2 PallaviDas EnvironmentalPollutionandHumanHealth 3Document34 pagesIGNTU EContent 673390684976 B.SC EnvironmentalSciences 2 PallaviDas EnvironmentalPollutionandHumanHealth 3Riyasath ahamedNo ratings yet
- Assignment of Applied Chemistry-I: Topic: Sewage TreatmentDocument8 pagesAssignment of Applied Chemistry-I: Topic: Sewage TreatmentTAHIR SRKNo ratings yet
- Lect 2Document64 pagesLect 2Patricia Jayshree Samuel JacobNo ratings yet
- Water Purification Written ReportDocument10 pagesWater Purification Written ReportMenric LunarNo ratings yet
- Water Pollution For Environmental ScienceDocument21 pagesWater Pollution For Environmental Scienceobaid kuraishyNo ratings yet
- Wastewater Primary Treatment PDFDocument4 pagesWastewater Primary Treatment PDFEnrique MartinezNo ratings yet
- BNR Process BendigoDocument6 pagesBNR Process Bendigobansa79No ratings yet
- Sewage Water TreatmentDocument8 pagesSewage Water Treatmentsivani rayavarapuNo ratings yet
- Aquaculture (Chapter 5 Lesson 2)Document27 pagesAquaculture (Chapter 5 Lesson 2)Juramae SuanNo ratings yet
- Sanitary Water ReportDocument9 pagesSanitary Water ReportSushil AchhamiNo ratings yet
- STP ReportDocument11 pagesSTP ReportNasrul100% (1)
- Pe Project Class 11Document19 pagesPe Project Class 11Kalp patniNo ratings yet
- Astewater Reatment Lant DesignDocument2 pagesAstewater Reatment Lant Designas3ateNo ratings yet
- Asifa P.A Lanscape PPT 2Document31 pagesAsifa P.A Lanscape PPT 2Asifa AseezNo ratings yet
- Technology Details (Description / Functions) Better Still If Photos, Visuals IncludedDocument12 pagesTechnology Details (Description / Functions) Better Still If Photos, Visuals IncludedShavin ChandNo ratings yet
- Waste Water TreatmentDocument28 pagesWaste Water TreatmentRoseNavyaNo ratings yet
- Microproject in CssDocument6 pagesMicroproject in CsssalapeshivaniNo ratings yet
- Excreta DisposalDocument20 pagesExcreta DisposalRahul Netragaonkar75% (4)
- Field Visit To Water Treatment Plant, AluvaDocument6 pagesField Visit To Water Treatment Plant, Aluvanaimdangre869No ratings yet
- Environmental Science and EngineeringDocument4 pagesEnvironmental Science and Engineeringmenma JintanNo ratings yet
- Lecture - 3 - Wastewater Treatment - Aerobic and Anaerobic-1Document11 pagesLecture - 3 - Wastewater Treatment - Aerobic and Anaerobic-1negaathanipalanisamyNo ratings yet
- Metode Pengelolaan Air LimbahDocument3 pagesMetode Pengelolaan Air LimbahMuhammad AkbarNo ratings yet
- L-1 Natural Method of Sewage DisposalDocument62 pagesL-1 Natural Method of Sewage Disposalzubair k peerzadeNo ratings yet
- Presentation 1Document14 pagesPresentation 1HP2266No ratings yet
- Waste Water TreatmentDocument44 pagesWaste Water TreatmentSangeethika Madubashini T. Hettige100% (1)
- Water Pollution ControlFrom EverandWater Pollution ControlSuresh T. NesaratnamNo ratings yet
- Department of Civil Engineering: Don Honorio Ventura State UniversityDocument8 pagesDepartment of Civil Engineering: Don Honorio Ventura State Universityoblix.gaming12No ratings yet
- De Oliveira e Silva - Hendrick - 2016 - Pumped Hydro Energy Storage in BuildingsDocument9 pagesDe Oliveira e Silva - Hendrick - 2016 - Pumped Hydro Energy Storage in BuildingsJalcamNo ratings yet
- WaterDocument124 pagesWaterJessa Mae Manalo DavidNo ratings yet
- CEB601 Lab Report 6Document9 pagesCEB601 Lab Report 6divikesh kumarNo ratings yet
- Airport DrainageDocument68 pagesAirport DrainageAngelo Ros100% (1)
- Adisu SeminarDocument18 pagesAdisu SeminartmariamyididiyaNo ratings yet
- 6.water RecyclingDocument8 pages6.water RecyclingmariyaNo ratings yet
- Chapter FourDocument15 pagesChapter FourEphrem GizachewNo ratings yet
- Canal & Related StructuresDocument376 pagesCanal & Related StructuresEE MI NandyalNo ratings yet
- Sanjeev BaralDocument30 pagesSanjeev BaralPujan Bajracharya33% (3)
- Specifications of Ductile Iron Pipes and Carbon Steel Pipes-EnDocument3 pagesSpecifications of Ductile Iron Pipes and Carbon Steel Pipes-Endjrote4No ratings yet
- FSX-A Deluge Valve (Jan 2021)Document12 pagesFSX-A Deluge Valve (Jan 2021)Mohammed ElmakNo ratings yet
- Reverse Engineering and Automization of Atomized Nozzle For Water ConservationDocument100 pagesReverse Engineering and Automization of Atomized Nozzle For Water ConservationSaif UllahNo ratings yet
- Open Channel Flowmeter - UVH-2000Document4 pagesOpen Channel Flowmeter - UVH-2000Ferry YusufNo ratings yet
- Automatic Backwash Filter CatalogueDocument2 pagesAutomatic Backwash Filter CatalogueCarlos BarriosNo ratings yet
- cw822nj R1-SpecDocument1 pagecw822nj R1-Specswathisubramaniyan77No ratings yet
- Faecal Sludge Treatment Plant (FSTP) - LehDocument15 pagesFaecal Sludge Treatment Plant (FSTP) - LehShaun GeorgeNo ratings yet
- Kala Amb ValleyDocument3 pagesKala Amb ValleyShivani SoniNo ratings yet
- Boletin 161Document43 pagesBoletin 161jhonatanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 - Hydroelectric PowerDocument50 pagesChapter 4 - Hydroelectric PowerAdreana AmirahNo ratings yet
- Water ResourcesDocument21 pagesWater ResourcesJessalyn Joy ReforsadoNo ratings yet
- Nora LR Plots BrochureDocument26 pagesNora LR Plots Brochureapriliahasna20No ratings yet
- Erosion Control Plan Legend: Gabion Check Dam: Top of DitchDocument1 pageErosion Control Plan Legend: Gabion Check Dam: Top of Ditchshafiullah NaseriNo ratings yet
- Bye-Laws of SikkimDocument13 pagesBye-Laws of SikkimNelima Joshi100% (1)
- Class Project: Kothagudem Municipal Council Bhadradi DistrictDocument22 pagesClass Project: Kothagudem Municipal Council Bhadradi Districtabdul khaliqNo ratings yet
- Limnology (2+1)Document87 pagesLimnology (2+1)Haha HahaNo ratings yet
- CE Course DescriptionDocument13 pagesCE Course DescriptionAngelito AngelesNo ratings yet
- BIDAR Brochure 2012Document35 pagesBIDAR Brochure 2012maheshanischithaNo ratings yet
- HVAC CalcDocument16 pagesHVAC CalcHashimi JuniNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3 Water PollutionDocument4 pagesLesson 3 Water Pollutionjisas criesNo ratings yet